Nephrology - Tubular disorders (not including RTA or stones) David Metz Paediatric Nephrology
|
|
|
- Avis Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nephrology - Tubular disorders (not including RTA or stones) David Metz Paediatric Nephrology
2 Bowman s capsule containing glomerular filtrate ACTION Uptake++ Fine tune Ca Mg Na Proximal convoluted tubule Distal convoluted tubule Create concentrated interstitium Mg and Ca uptake Collecting duct Water balance K secretion H secretion Loop of Henle (ascending and descending limbs, thick and thin)
3 "Renal Diuretics" by Haisook at en.wikipedia - Own workoriginally from en.wikipedia; description page is/was here.. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike via Wikimedia Commons - al_diuretics.gif#mediaviewer/file:renal_di uretics.gif "Renal Diuretics" by Haisook at en.wikipedia - Own work
4 Transport mechanisms Transcellular Passive or active transporters Uniporter, cotransporter/symporter, exhanger/antiporter Facilitated diffusion (passive) along electrochemical gradients ATPases active transporters Secondary active favorable (chemical or electrochemical) gradient of 1 solute drives another (against unfavorable)
5 Transport mechanisms Channels Ion selective or non-selective Regulated by number of functional channels, and whether open or closed When open can see high rate of ion passage Paracellular route (through tight junctions, with segment specific ion selectivity) Endocytic receptors Substrates (or substrates bound to carrier proteins) endocytosed
6 Review of normal processes Glomerular filtrate (in Bowman s capsule) undergoes extensive reabsorption and exchange before final urine 99% of volume reabsorbed >99% of Na and Cl 85-95% K 95% Ca, 97% Mg, 80-95% Pi Reabsorption largely driven by Na reabsorption
7 Percentage Na reabsorption 8% Site of thiazide action 65% 25% Site of frusemide action 1.5% 0.5% left
8 PCT
9 Proximal tubule Lion s share of reabsorption (60% of glomerular filtrate) Most reabsorption is coupled to Na reclamation (applies to many segments of nephron) (low intracellular Na maintained by basolateral NaKATPase and Na-HCO3- cotransporter) All major solutes reabsorbed to some degree in PCT
10
11 Fanconi syndrome Generalized PCT defect Key = glucosuria, aminoaciduria, tubular proteinuria, hypophosphatemia, prta Also can see Na and K losses Na losses = hyponatremia, hypotension, dehydration, and secondary hypokalemia (RAAS activation) FTT (hypok, acidosis, hypopi) Polyuria/polydipsia/dehydration Osmotic diuresis from urinary solute losses, CD concentrating defect 2 hypokalemia Treat = treat cause, replace what s being lost
12 Causes Fanconi syndrome Genetic Cystinosis, Lowe s, galactosemia, tyrosinemia, Wilson s, HFI Toxin heavy metals, aminoglycosides, ifosfamide, mercaptopurine, multiple myeloma
13 Dent s disease X-linked PT dysfunction with LWM proteinuria, hypercalciuria, nephrolithiasis, nephrocalcinosis, progressive renal failure Concentrating defect (thus polyuria) Hematuria (likely from hypercalciuria/nc/stones) Can have broader PT dysfunction (renal fanconi) Aminoaciduria, phosphaturia (and rickets), glycosuria, uricosuria, kaliuresis, proximal RTA Orphanet Dx: LWMP, hypercalciuria, and at least one of NC, stones, hematuria, hypophosphatemia, progressive renal failure
14 Dent s: genetics 60% = Xp11.22 CLC-5 channel inactivation (voltage gated chloride channel) CLC-5 facilitates maximal acidification of endosomes 15% = OCRL1 gene also mutated in Lowe Syndrome (which includes cataracts, mental developmental delay, renal tubular acidosis)
15
16 Mechanism of abnormalities Proteinuria Proteins endocytosed in PCT Impaired endosomal acidification = impaired processing of proteins, and decreased recycling of endosomal membrane Hypercalciuria Related to hyperabsorption Ca at gut level Hyperphosphaturia / increased 1,25 D? Due to increased PTH at distal PCT (not endocytosed earlier)
17 Treatment DENT s For hypercalciuria Low NaCl diet Thiazides For bone disease Oral PO4 Vitamin D (watch U.Ca) Replacement of Na/K/H20 in more general PT dysfunction Progression to ESKD between 3 rd and 5 th decade in 30-80%
18 LOH
19 Loop of Henle Differential permeability to water, Na, Urea Generates hyperosmolar interstitium (and hypoosmolar filtrate) Ability of ascending limbs ability to reabsorb NaCl in excess of water (TAL selectively reabsorbs 25-35% of filtered NaCl without water)
20 Loop of Henle Countercurrent mechanism in LOH creates hypertonic medullary interstitium In TAL of LOH, NaCl driven into interstitium without H20 concentrated Allows for H20 reabsorption in collecting duct via aquaporin channels (into high concentration interstitium)
21 Salt-losing tubulopathies Frusemide = Bartter syndrome Thiazide = Gitelman syndrome Other diureticopathies Spironalactone = pseudohypoaldosteronis m 1 Amiloride Liddle
22 Bartter s 1:1,000,000 AR; four genetic variants Direct or indirect compromise of Na-K-2Cl co-transporter in TAL of LOH Defect of luminal NKCC2 Defect of luminal ROMK Defect of basolateral Cl channel ClC-ka or kb (or Barttin subunit)
23 Seyberth H et al, Bartter- and Gitelman-like syndromes: salt losing tubulopathies with loop or DCT defects, April 2011
24 Creates intracellular low Na, electronegative
25 Drives this Creates intracellular low Na, electronegative
26 K is recycled
27 Creates lumen positivity (K + Cl)
28 Creates lumen Positivity (K + Cl) Drives this Hence in some phenotypes also get Mg and Ca loss in urine hypomagnesemia, hypercalciuria + nephrocalcinosis
29 LOH Ca & Mg Ca and Mg transport = passive paracellular process driven by positive lumen potential Mediated by tight junctional permselectivity proteins claudin 16 (CLDN16) and claudin 19 (CLDN19) Also - basolateral CaSR activation of which inhibits Na transport (inhibits NKCC and ROMK) Thus decreased TTPG driving Ca and Mg reabsorption
30 Brenner: Brenner and Rector's The Kidney; 8th Edition
31 Bartter syndrome Defective NaCl uptake in LOH massive salt losses Wash out medullary concentration gradient Large increase in NaCl delivery to distal nephron (severe volume contraction if no compenstory mechanism seen in severe AN Bartter s) Compensation by RAAS activity Hyperplasia of JG apparatus and PG secretion Increased Na reabsorption in exchange for K/H-Cl excretion (hence hypokalemia) Ca/Mg losses (and nephrocalcinosis) in some phenotypes
32 Findings Hypokalemia, hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis Polyuria and isothenuria Hypercalciuria, hypomagnesemia (in some) High levels of some urinary prostaglandins (Hyper PG syndrome) High PRA and aldosterone
33 2 phenotypes Classic Bartter insidious onset early life FTT / longitudinal retardation Impaired ability to concentrate / dilute urine Polyuria, polydipsia, salt craving Prone to hypernatremic dehydration Constipation Severe antenatal / hyper PGE syndrome Severe AN salt wasting - polyhydramnios (with high chloride) +/- premature delivery Life threatening volume depletion (NaCl loss and polyuria) for a number of weeks (may not be hypokalemic initially - ROMK) After which classical Bartter constellation becomes evident
34 Calcium-sensing Receptor Mutation Potent gain of function CaSR mutation ( L125P) leading to autosomal dominant hypocalcaemia. Case described of this associated with Bartter-like syndrome (Vargas-Poussou et al, JASN 2002). Thakker 1999 NEJM p1177
35 DCT
36 Gitelman (DCT thiazide) DCT - minor capacity of salt reabsorption (8% cf 25%) Crucial role in fine-tuning of urinary calcium and magnesium excretion In Gitelman, more chronic solute imbalances similar to the effects of chronic treatment with thiazides. Increased apical Ca reabsorption and Mg loss (not well defined)
37 Percentage Na reabsorption 8% Site of thiazide action, Gitelman syndrome 65% 25% Site of frusemide action, Bartter syndrome 1.5% 0.5% left
38 Gitelman syndrome Present childhood or adolescence Less severe; usually N growth; salt craving, nocturia and paraesthesia Muscle cramps and tetany common; dizziness, jt pains, nocturia Biochemical: Mild hypokalemia & alkalosis Low serum Mg, low urine Ca Elevated PRA, normal aldosterone
39 Gitelman cf Bartter Very low U Ca calcium (cf. often elevated in BS) S Mg low, U Mg elevated Renin and aldosterone usually normal
40
41 Transporter / Pharm based (shows confusion)* Loop disorders (polyhydramnios; most = NC) L1 = (Type 1 Bartter) - NKCC2 (TAL) - frusemide L2 = (Type 2 Bartter) - ROMK (TAL/CCD) - frusemide/amiloride Combined (polyhydramnios) L-DC1 - ClC-Ka+b - TAL/DCT - frusemide-thiazide L-DC2 - (Type 4 Bartter) - Barttin (TAL/DCT) - frusemide/thiazide Sensorineural HL (Barttin subunit also on K-secreting cells of stria vascularis of inner ear) *Seyberth H et al, Bartter- and Gitelman-like syndromes: salt losing tubulopathies with loop or DCT defects, April 2011
42 DCT DC2 - (Gitelman Sx, 16q13) NCCT (NaCl cotransporter) - thiazide DC2 - (Type 3 Bartter, cbs) - ClC-Kb (Cl channel; DCT/TAL) - thiazide/frusemide Though can have polyhydramnios Only 20% have nephrocalcinosis
43 Seyberth H et al, Bartter- and Gitelman-like syndromes: salt losing tubulopathies with loop or DCT defects, April 2011
44
45 MANAGEMENT OF BARTTER SYNDROME NaCl, KCl, and water supplementation (titrated to response). NSAID (reduce hyperprostaglandin effeect) Indomethacin COX2 (eg celecoxib) Nutrition and fluids- Tube Care during illness/ surgery MANAGEMENT OF GITELMAN SYNDROME Normal diet. KCl supplementation +/- Mg as necessary. Rarely, Spironolactone.
46 DCT
47 Distal convoluted tubule Water impermeable furthers process of Na reabsorption and dilution of tubular urine Thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC) NCC activity regulated by: distal Na delivery, aldosterone, WNK1 and WNK4 WNK1 and WNK4 mutations that upregulate NCC activity cause pseudohypoaldosteronism type 2 (familial hyperkalemic hypertension Gordon s) Less distal Na to aldosterone sensitive channels, intravascular NaCl excess K NCC defect (or basolateral Cl channel) Gitelman s, prior slides
48 DCT major distal site Ca/Mg reabsorption Calcium Luminal Ca entry (Ca selective TRPV5 channel) Basolateral Ca efflux through Ca-ATPases and Na-Ca exchangers Ca reabsorption regulated by PTH, calcitriol, ph, dietary Na intake and urinary excretion, thiazides (enhance Ca reabsorption by uncertain mechanism)
49 DCT major distal site Ca/Mg reabsorption Magnesium Main site of active regulated transcellular Mg reabsorption (10-15% of filtered load vs 70% in TAL) Luminal TRPM6/TRPM7 cation channel; regulated by luminal ph (acidosis = increased excretion) Unknown basolateral pathway (? Na-Mg exchange) Magnesium disorders discussed later
50 Luminal Ca channel Thiazidesensitive NaCl channel Luminal Mg channel Christov 2010, Am J Kidney Dis
51 Principal cells of collecting tubule ENaC Provides energy for ENaC Creates ve TEP for ROMK K + Na + ROMK Aldosterone increases number of open ENaC and number of Na-K- ATPase pumps ANP closes ENaC K-sparing diuretics close Na channels (amiloride, triamterene, spironalactone (competes with aldosterone))
52 CD
53 Connecting segment + collecting duct Completion of NaCl reabsorption Secrete K and H as required Concentrate urine (by reabsorption of H20)
54 Na reabsorption Connecting segment and CCD Luminal ENaC (epithelial Na channels) Regulated by aldosterone, inhibited by ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) Activating mutations in ENaC Liddle Syndrome (monogenic HT) Inactivating mutation ENaC / aldosterone receptor Pseudohypoaldosteronism type 1 (salt wasting, hypotensive, hyperkalemia) ENaC Na transport leads to lumen-negative TEP Drives paracellular Cl reabsorption, K secretion (principal cells eg ROMK channel), H secretion (intercalated cells)
55 Chloride reabsorption Also two Cl transporters in CCD (B intercalated cells) Luminal exchange of HCO3 for Cl, in setting HCO3 load
56 K secretion / uptake Principal cell ROMK, K secretion (cortical and medullary collecting duct) ROMK affected by dietary K load, aldosterone, degree of lumen-negative electrical potential from ENaC mediated reabsorption, WNK1/4 Also K secretion by Ca-activated K channels of intercalated cell luminal membrane K reabsorption by H-K-ATPase of intercalated cell luminal membrane
57 Principal cells of collecting tubule ENaC Provides energy for ENaC Creates ve TEP for ROMK ROMK Aldosterone increases number of open ENaC and number of Na-K- ATPase pumps ANP closes ENaC K-sparing diuretics close Na channels (amiloride, triamterene, spironalactone (competes with aldosterone))
58 Principal cells of collecting tubule ENaC Provides energy for ENaC Creates ve TEP for ROMK K + Na + ROMK Aldosterone increases number of open ENaC and number of Na-K- ATPase pumps ANP closes ENaC K-sparing diuretics close Na channels (amiloride, triamterene, spironalactone (competes with aldosterone))
59 Distal RTA H+ secretion Another lecture
60 Water reabsorption Principal cells of cortical and medullary collecting ducts, inner medullary collecting duct cells ADH(vasopressin)-dependant water permeability, activated by luminal insertion of AQP2 water channels (aquaporin 2) ADH binds to vasopressin receptor V2R increases camp fusion of subluminal AQP2-bearing vesicles with the luminal membrane Water is then reabsorbed into hyper-osmolar medullary interstitium (created by LOH)
61 Tubular lumen Concentrated interstitium (hyperosmolar) AQP2 V2R ADH
62 Tubular lumen Concentrated interstitium (hyperosmolar) AQP2 Activates ADH V2R
63 Tubular lumen AQP2 Concentrated interstitium (hyperosmolar) ADH V2R
64 Tubular lumen H2O can now diffuse out following concentration gradient AQP2 ADH V2R Concentrated interstitium (hyperosmolar)
65 Nephrogenic DI Congenital rare XLR neph DI loss-of-function V2R mutations 90% of cases AR DI loss-of-function AQP2 mutations Acquired / secondary CKD, Obstructive uropathy, renal dysplasia, chronic pyelonephritis High Ca, low K Drugs lithium, tetracyclines
66 Congenital NDI From birth; breastfeeding may delay presentation (low solute) Dehydration, seizures, constipation, fever. Enuresis, nocturia. Mild FTT (? LOA due to fluid volumes required) Cognitive impairment (late presentation) Dx polyuria, Na, U. osm <200 (N>800)
67 Diagnosis of Polyuria Cause Onset P Na Max. Uosm with dehydration Central DI Usu Sudden Usu >143 Uosm after ADH % Uosm after ADH <300 >300 >50 Partial central DI Usu Sudden Usu >143 <600 > Nephrogenic DI Usu gradual Usu >143 <300 < Primary polydipsia Usu Gradual Usu < <9 Normal >800 >800 <9 Josh Kausman
68 Other tubular issues Calcium (covered in Endo talk) Magnesium Phosphate Acid handling (covered in acid-base talk)
69 Magnesium reabsorption 5-10% 15-20% Luminal Mg channel 65-75% Passive, paracellular, Claudin 16 (tight junction protein) 3-5%
70 TAL Ca&Mg paracellular diffusion driven by positive lumen potential (from K / Cl mvmt) Basolateral CaSR activation of which inhibits Na transport (inhibits NKCC and ROMK) Thus decreased TTPG driving Ca and Mg reabsorption
71 Mg channel in DCT
72 Claudin, loop of Henle Gut absorption Calcium sensing receptor abnormality HypoMg with abn NaCl transport
73
74 Symptoms of low Mg (general) Weakness, anorexia, tetany, +ve Trousseau and Chvostek, hypokalemia (needing Mg Rx to correct), hypocalcemia Apathy, delerium, coma Hypocalcemia and hypoparathyroidism (in severe Mg depletion) ECG changes ventricular arrythmias particularly during AMI / bypass
75 Symptoms Hypomagnesemia w/ 2 hypocalcemia <6m age with tetany, muscle spasms, sz Older: Clouded sensorium, disturbed speech, choreoathetoid mvmts Infantile isolated renal Mg wasting (dominant) Chondrocalcinosis Hypomagnesemia with hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis Rec UTI, polyuria/polydipsia, isosthenuria, renal stones FTT, vomiting, abdo pain, tetanic episodes, sz Hearing impairment, chondrocalcinosis, rickets, partial drta Ocular abnormalities
76 Calcium homeostasis Renal tubular Ca reabsorption: PCT-65%, TALH-20%, DCT-10%, CD-1.5% Ca reciprocal relationship with: Phosphate ph Symptoms common with or Ca levels
77 MJA 2004 p354
78 Phosphate homeostasis Level decreases with age When PTH and PO4 intake normal in N kidney 85-90% filtered PO4 reabsorbed 10-15% fractional excretion PO4 Measure TRP, TmP/GFR Derangements rarely cause clinical symptoms Chronic hypophosphatemia rickets
79 Rickets Calcipenic or Phosphopenic Calcipenic Vit D or Ca deficiency including poor absorption (antacids, PHT/PB, CF, hepatic insuff) Defective 1a-hydroxylase activity (VDDR type 1, or pseudovitamin D deficiency; AR) Normal 25 D, low 1,25 D 1,25-OH2 Vit D resistance (receptor defect, VDDR type 2; AR) Normal 25 D, very high 1,25 D
80 Phosphopenic rickets Renal phosphate wasting in PCT: Isolated renal PO4 wasting X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets AD hypophosphatemic rickets Oncogenic osteomalacia (tumour induced) Hypophosphatemic rickets with hypercalciuria High calcitriol, high U Ca excretion (cf above) Renal Fanconi (PO4 wasting plus aa, glucose, HCO3, Ca)
81 Renal PO4 wasting Reabsorption primarily in PCT Na-Phosphate co-transporters NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c (on luminal membrane) Major regulators of NaPi-2a and -2c PTH, dietary PO4 intake, FGF-23 (phosphatonin) (and to a lesser extent calcitriol) High FGF-23 or PTH leads to reduced PO4 reabsorption in PCT increased PO4 wasting into urine
82 Alizadeh Naderi A, Nature Reviews Nephrology 2010
83 Clinical In eg. XLH (most common) Progressive growth failure and bony deformities beginning first year of life (if untreated) Rachitic changes bowed legs, short stature, other (genu varum/valgum, metaphyseal widening, rachitic rosary, frontal prominence.
84 Oral phosphate and calcitriol Treatment (XLH) Phosphate in 4-5 spaced doses Increase as needed to see improved growth velocity (do NOT need to normalize s PO4) Rate limiter diarrhoea major issue Calcitriol required as Endogenous 1,25 (OH) Vit D suppressed by FGF-23 Needed for Absorption of PO4 Prevent secondary hyperparathyroidism (stimulated by episodes of low ionized Ca, from Ca-Pi complexing)
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED. Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics
 Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Functions of Proximal Convoluted Tubules
 1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
11/05/1431. Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
MS1 Physiology Review of Na+, K+, H + /HCO 3. /Acid-base, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology
 MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
Renal Tubular Acidosis
 1 Renal Tubular Acidosis Mohammad Tariq Ibrahim 6 th Grade Diyala College Of Medicine supervisor DR. Sabah Almaamoory 2 *Renal Tubular Acidosis:- RTA:- is a disease state characterized by a normal anion
1 Renal Tubular Acidosis Mohammad Tariq Ibrahim 6 th Grade Diyala College Of Medicine supervisor DR. Sabah Almaamoory 2 *Renal Tubular Acidosis:- RTA:- is a disease state characterized by a normal anion
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions
 Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Sodium and chlorine transport
 Kidney physiology 2 Sodium and chlorine transport The kidneys help to maintain the body's extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by regulating the amount of Na+ in the urine. Sodium salts (predominantly NaCl)
Kidney physiology 2 Sodium and chlorine transport The kidneys help to maintain the body's extracellular fluid (ECF) volume by regulating the amount of Na+ in the urine. Sodium salts (predominantly NaCl)
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE
 NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
BLOCK REVIEW Renal Physiology. May 9, 2011 Koeppen & Stanton. EXAM May 12, Tubular Epithelium
 BLOCK REVIEW Renal Physiology Lisa M. HarrisonBernard, Ph.D. May 9, 2011 Koeppen & Stanton EXAM May 12, 2011 Tubular Epithelium Reabsorption Secretion 1 1. 20, 40, 60 rule for body fluid volumes 2. ECF
BLOCK REVIEW Renal Physiology Lisa M. HarrisonBernard, Ph.D. May 9, 2011 Koeppen & Stanton EXAM May 12, 2011 Tubular Epithelium Reabsorption Secretion 1 1. 20, 40, 60 rule for body fluid volumes 2. ECF
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
ACID-BASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR
 ACIDBASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR H 2 PO 4 NH 4 HCO 3 KIDNEY H H HCO 3 CELLS Hb H LUNG H 2 CO 3 HHb CO 2 H 2 O ph = 7.4 [HCO 3 ] = 24 meq/l PCO 2 = 40 mm Hg CO 2 PRIMARY RENAL MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ACIDBASE
ACIDBASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR H 2 PO 4 NH 4 HCO 3 KIDNEY H H HCO 3 CELLS Hb H LUNG H 2 CO 3 HHb CO 2 H 2 O ph = 7.4 [HCO 3 ] = 24 meq/l PCO 2 = 40 mm Hg CO 2 PRIMARY RENAL MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ACIDBASE
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine. Amal Alamri
 Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Normal Renal Function
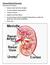 Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
TUBULOPATHY Intensive Care Unit Sina Hospital
 TUBULOPATHY Intensive Care Unit Sina Hospital A 13 years old female who is known case of Scoliosis. She was operated 2 months ago for spinal curve repair. PMH:EMG-MCV In 2 years old =>No Motoneuron Disease
TUBULOPATHY Intensive Care Unit Sina Hospital A 13 years old female who is known case of Scoliosis. She was operated 2 months ago for spinal curve repair. PMH:EMG-MCV In 2 years old =>No Motoneuron Disease
DIURETICS-2. Dr. Shariq Syed. Shariq AIKC/TYB/2014
 DIURETICS-2 Dr. Syed Structure of Kidney Blood filtered by functional unit: Nephron Except for cells, proteins, other large molecules, rest gets filtered Structure of Kidney 3 major regions of nephron
DIURETICS-2 Dr. Syed Structure of Kidney Blood filtered by functional unit: Nephron Except for cells, proteins, other large molecules, rest gets filtered Structure of Kidney 3 major regions of nephron
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Kidney and urine formation
 Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys
 Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Hill et al. 2004, Fig. 27.6
 Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys
 Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
DIURETICS-3 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-3 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Diuretics primarily prevent the reabsorption of K Na Cl I Don t know, Too busy with periodic exams! AIKTC - Knowledge
DIURETICS-3 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Diuretics primarily prevent the reabsorption of K Na Cl I Don t know, Too busy with periodic exams! AIKTC - Knowledge
Therapeutics of Diuretics
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/80/80449526.jpg) 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Diuretic Agents Part-1. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-1 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Kidneys eliminates waste products and regulates the volume, electrolyte and ph of
Diuretic Agents Part-1 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Kidneys eliminates waste products and regulates the volume, electrolyte and ph of
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
Martin Konrad has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve.
 Martin Konrad has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Nephrocalcinosis Clinical / Genetic Work-up and Outcome Martin Konrad University
Martin Konrad has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Nephrocalcinosis Clinical / Genetic Work-up and Outcome Martin Konrad University
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation
 Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College BIOL 2402 Fluid/Electrolyte Regulation 1 Body Water Content On average, we are 50-60 % water For a 70 kg male = 40 liters water This water is divided into
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview
 RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Chapter 21. Diuretic Agents. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Urinary System. Dr. ZHANG Xiong. Dept. of Physiology. ZJU School of Medicine. QUESTION 6
 Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine http://10.71.121.158 Copyright@ Xiong Zhang QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed in tubular system? Copyright@ Xiong Zhang
Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine http://10.71.121.158 Copyright@ Xiong Zhang QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed in tubular system? Copyright@ Xiong Zhang
PRINCIPLES OF DIURETIC ACTIONS:
 DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
Disclosures. Familial Hypomagnesemia with Hypercalciuria and Nephrocalcinosis 05/06/2018
 Familial Hypomagnesemia with Hypercalciuria and Nephrocalcinosis Gema Ariceta PediatricNephrology, University Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona, Spain 05.06.2018 Tubulopathies Nothing to declare Disclosures
Familial Hypomagnesemia with Hypercalciuria and Nephrocalcinosis Gema Ariceta PediatricNephrology, University Hospital Vall d Hebron Barcelona, Spain 05.06.2018 Tubulopathies Nothing to declare Disclosures
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
3/19/2009. The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load. Buffering of an acid load. A o B - + H + B - A o +OH - C +
 The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
Identify and describe. mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption
 Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES
 THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
Chapter 15 Diuretic Agents
 Chapter 15 Diuretic Agents Diuretics Diuretics are agents that increase the rate of urine formation and salt excretion. Diuresis = increased water formation, but the term is also used to indicate increased
Chapter 15 Diuretic Agents Diuretics Diuretics are agents that increase the rate of urine formation and salt excretion. Diuresis = increased water formation, but the term is also used to indicate increased
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Michael Heung, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (4) Dr. Attila Nagy 2018
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (4) Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Intercalated cells Intercalated cells secrete either H + (Typ A) or HCO 3- (Typ B). In intercalated cells Typ A can be observed
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (4) Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Intercalated cells Intercalated cells secrete either H + (Typ A) or HCO 3- (Typ B). In intercalated cells Typ A can be observed
Early Filtrate Processing Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.
 Early Filtrate Processing Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Once the filtrate is formed, the early
Early Filtrate Processing Graphics are used with permission of: Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings (http://www.aw-bc.com) Page 1. Introduction Once the filtrate is formed, the early
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140
 هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
هللامسب Na regulation: Na concentration in the extracellular compartment is 140 meq\l. Na is important because: -It determines the volume of extracellular fluid : the more Na intake will expand extracellular
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
DIURETICS. Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut
 DIURETICS Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Classification of Diuretics The best way to classify diuretics is to look for their Site of action in the nephron A. Diuretics that inhibit transport in the Proximal
DIURETICS Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Classification of Diuretics The best way to classify diuretics is to look for their Site of action in the nephron A. Diuretics that inhibit transport in the Proximal
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Faculty version with model answers
 Faculty version with model answers Urinary Dilution & Concentration Bruce M. Koeppen, M.D., Ph.D. University of Connecticut Health Center 1. Increased urine output (polyuria) can result in a number of
Faculty version with model answers Urinary Dilution & Concentration Bruce M. Koeppen, M.D., Ph.D. University of Connecticut Health Center 1. Increased urine output (polyuria) can result in a number of
Lithium-induced Tubular Dysfunction. Jun Ki Park 11/30/10
 Lithium-induced Tubular Dysfunction Jun Ki Park 11/30/10 Use of Lithium Mid 19 th century: treatment of gout Late 19 th century: used for psychiatric disorders Early 20 th century: sodium substitute to
Lithium-induced Tubular Dysfunction Jun Ki Park 11/30/10 Use of Lithium Mid 19 th century: treatment of gout Late 19 th century: used for psychiatric disorders Early 20 th century: sodium substitute to
CALCIUM BALANCE. James T. McCarthy & Rajiv Kumar
 CALCIUM BALANCE James T. McCarthy & Rajiv Kumar CALCIUM BALANCE TOTAL BODY CALCIUM (~ 1000g in a normal 60 kg adult) - > 99% in bones - ~ 0.6% in the intracellular space - ~ 0.1% in the extracellular space
CALCIUM BALANCE James T. McCarthy & Rajiv Kumar CALCIUM BALANCE TOTAL BODY CALCIUM (~ 1000g in a normal 60 kg adult) - > 99% in bones - ~ 0.6% in the intracellular space - ~ 0.1% in the extracellular space
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Kidney Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 November 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Kidney Int. 2013 May ; 83(5): 779 782. doi:10.1038/ki.2012.468. Need to quickly excrete K +? Turn off NCC Alicia A. McDonough 1 and
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Dept. of Physiology. ZJU School of Medicine.
 Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151/Able.Acc2.Web/Template/View.aspx?action =view&coursetype=0&courseid=26519 QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed
Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine Http://10.10.10.151/Able.Acc2.Web/Template/View.aspx?action =view&coursetype=0&courseid=26519 QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed
Diuretics are drugs that increase the volume of urine excreted. Most diuretic agents are inhibitors of renal ion transporters that decrease the
 Diuretics Diuretics are drugs that increase the volume of urine excreted. Most diuretic agents are inhibitors of renal ion transporters that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at different sites in the nephron.
Diuretics Diuretics are drugs that increase the volume of urine excreted. Most diuretic agents are inhibitors of renal ion transporters that decrease the reabsorption of Na+ at different sites in the nephron.
Kidneycentric. Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Gitelman syndrome David Steflik Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional works
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Gitelman syndrome David Steflik Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional works
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Inherited Calcium and Magnesium Disorders
 Inherited Calcium and Magnesium Disorders Martin Konrad University Children s Hospital Münster, Germany IPNA / ESPN Master Class, Leuven, Sep 2nd 2015 Outline Hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia Outline Hypercalcemia
Inherited Calcium and Magnesium Disorders Martin Konrad University Children s Hospital Münster, Germany IPNA / ESPN Master Class, Leuven, Sep 2nd 2015 Outline Hypercalcemia Hypomagnesemia Outline Hypercalcemia
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018. Rahmeh Alsukkar
 Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).
![Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside). Potassium secretion. E k = -61 log ([k] inside / [k] outside).](/thumbs/80/80478709.jpg) 1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
1 Potassium secretion In this sheet, we will continue talking about ultrafiltration in kidney but with different substance which is K+. Here are some informations that you should know about potassium;
Renal physiology II. Basic renal processes. Dr Alida Koorts BMS
 Renal physiology II Basic renal processes Dr Alida Koorts BMS 7-12 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Basic renal processes 1. filtration 2. reabsorption 3. secretion Glomerular filtration The filtration
Renal physiology II Basic renal processes Dr Alida Koorts BMS 7-12 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Basic renal processes 1. filtration 2. reabsorption 3. secretion Glomerular filtration The filtration
Renal Control of Calcium, Phosphate, and Magnesium Homeostasis
 Renal Physiology Renal Control of Calcium, Phosphate, and Magnesium Homeostasis Judith Blaine, Michel Chonchol, and Moshe Levi Abstract Calcium, phosphate, and magnesium are multivalent cations that are
Renal Physiology Renal Control of Calcium, Phosphate, and Magnesium Homeostasis Judith Blaine, Michel Chonchol, and Moshe Levi Abstract Calcium, phosphate, and magnesium are multivalent cations that are
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Diagram of the inner portions of the kidney
 Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi
 Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: The loop of Henle is referred to as countercurrent
Done By: Lulu Al-Obaid - Abdulrahman Al-Rashed Reviewed By: Mohammed Jameel Khulood Al-Raddadi At the end of this lecture student should be able to describe: The loop of Henle is referred to as countercurrent
Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Lecture 5, 6. Objectives: Editing file. by the end of this lecture you will be able to:
 Index: Important Extra information Doctor s notes Only in female slides Only in male slides Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Lecture 5, 6 Editing file Objectives: by the end of this lecture you will be
Index: Important Extra information Doctor s notes Only in female slides Only in male slides Tubular Reabsorption & Secretion Lecture 5, 6 Editing file Objectives: by the end of this lecture you will be
Chapter 26 The Urinary System. Overview of Kidney Functions. External Anatomy of Kidney. External Anatomy of Kidney
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
mid ihsan (Physiology ) GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B **
 (Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
(Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
