6. Which division of the nervous system calms the body after an emergency passes? A) somatic B) central C) sympathetic D) parasympathetic
|
|
|
- Kristian Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bryant-Taneda: AP Psychology Test Bank Emotions (Chapter 13) 1. Several studies have shown that physical arousal can intensify just about any emotion. For example, when people who have been physically aroused by exercise are insulted, they often misattribute their arousal to the insult. This finding illustrates the importance of: A) cognitive labels of arousal in the conscious experience of emotions. B) a minimum level of arousal in triggering emotional experiences. C) the simultaneous occurrence of physical arousal and cognitive labeling in emotional experience. D) all of the above. 2. Most human fears are: A) universal. B) biologically determined. C) present at birth. D) learned. 3. Jane was so mad at her brother that she exploded at him when he entered her room. That she felt less angry afterward is best explained by the principle of: A) adaptation level. B) opponent processes. C) relative deprivation. D) catharsis. 4. Which of these factors have researchers not found to correlate with happiness? A) a satisfying marriage or close friendship B) high self-esteem C) religious faith D) intelligence 5. Alessandra's mother told her, "You know you are in love when your heart beats fast and you experience that unique trembling feeling inside." This remark best illustrates the theory of emotion. A) Cannon-Bard B) two-factor C) opponent-process D) James-Lange 6. Which division of the nervous system calms the body after an emergency passes? A) somatic B) central C) sympathetic D) parasympathetic 7. Jim, a 42-year-old engineer, is unhappy about his yearly salary although it is the highest salary he has ever earned. His wife, Carla, suggests that he vividly recall how little he earned at the age of 32. She also recommends that he watch a TV program about famine victims in Africa. Use your understanding of psychological principles to explain why Carla's suggestions might help to increase Jim's feelings of economic satisfaction. 8. When her son fails to arrive home as expected, Elena fears he has been in an accident. Both her heart and respiration rate remain elevated until she sees him come safely through the door. Her body soon
2 returns to normal due to the action of her nervous system. A) parasympathetic B) sympathetic C) central D) somatic 9. Research suggests that people generally experience the greatest well-being when they strive for: A) wealth. B) modest income increases from year to year. C) slightly higher status than their friends, neighbors, and co-workers. D) intimacy and personal growth. 10. The adaptation-level phenomenon refers to the: A) perception that one is worse off than those with whom one compares oneself. B) tendency for standards of judgment to be heavily influenced by previous experiences. C) tendency for emotional release to reduce levels of physiological arousal. D) tendency for evolution to favor organisms that adapt best to the environment. 11. Who is the least likely to display negative emotions openly? A) Paul, a game warden in Australia B) Niles, a stockbroker in Belgium C) Deborah, a physicist in Toronto D) Yoko, a dentist in Japan 12. After learning to associate a blue slide with a blaring horn, people who have suffered damage to the hippocampus show a fear reaction to the blue slide, and they be able to remember why they are fearful of the blue slide. A) will; will B) will not; will not C) will; will not D) will not; will 13. Which of the following best explains why million-dollar lottery winners and paraplegics report similar levels of happiness? A) James-Lange theory B) opponent-process theory C) relative deprivation principle D) two-factor theory E) adaptation-level phenomenon. 14. The James-Lange theory of emotion states that: A) to experience emotion is to be aware of one's physiological responses to an emotion-arousing event. B) the expression of emotion reduces one's level of physiological arousal. C) an emotion-arousing stimulus simultaneously triggers both physiological arousal and the subjective experience of emotion. D) to experience emotion one must be physically aroused and able to cognitively label the emotion. 15. The opponent-process theory would predict that with repeated use of an addictive euphoria-producing drug, the drug user would begin to experience pleasant highs and unpleasant withdrawal reactions. A) more intensely; more intensely
3 B) less intensely; less intensely C) more intensely; less intensely D) less intensely; more intensely 16. Anger is to rage as fear is to: A) guilt. B) shame. C) pain. D) disgust. E) terror. 17. Which of the following was not presented in the text as evidence that some emotional reactions involve no deliberate, rational thinking? A) Some of the neural pathways involved in emotion are separate from those involved in thinking and memory. B) Emotional reactions are sometimes quicker than our interpretations of a situation. C) People can develop an emotional preference for visual stimuli to which they have been unknowingly exposed. D) Arousal of the sympathetic nervous system will trigger an emotional reaction even when artificially induced by an injection of epinephrine. 18. The universally understandable language of human emotion consists of: A) hand gestures. B) body postures. C) facial expressions. D) tone of voice. E) music and dance. 19. In the Schachter-Singer experiment, which subjects reported feeling an emotional change in the presence of the experimenter's highly emotional confederate? A) those receiving epinephrine and expecting to feel physical arousal B) those receiving a placebo and expecting to feel physical arousal C) those receiving epinephrine but not expecting to feel physical arousal D) those receiving a placebo and not expecting to feel physical arousal 20. Research on the accuracy of lie detector tests suggests that they: A) pose no threat to the innocent. B) are accurate only 50 percent of the time, even when administered by experts. C) are more likely to declare the innocent guilty than to declare the guilty innocent. D) are more likely to declare the guilty innocent than to declare the innocent guilty. 21. Our most rapid and automatic emotional responses may result from the routing of sensory input from the thalamus directly to the: A) hippocampus. B) hypothalamus. C) cerebellum. D) brainstem. E) amygdala. 22. Averill found that most people become angry: A) once a day.
4 B) once a week. C) several times a week. D) several times a month. E) There is no common pattern to anger. 23. Margaret is a finalist in the U.S. Ice Skating Championship. She is very excited about the competition and is feeling energized. More than likely, the two dimensions of her current emotion would be a and. A) positive valence; low arousal B) negative valence; low arousal C) positive valence; high arousal D) negative valence; high arousal 24. Women are especially likely to surpass men in their ability to convey nonverbal expressions of: A) happiness. B) sadness. C) surprise. D) anger. 25. Expressing anger can be adaptive when you: A) retaliate immediately. B) have mentally rehearsed all the reasons for your anger. C) count to ten, then blow off steam. D) first wait until the anger subsides, then deal with the situation in a civil manner. 26. A general sense of happiness or life satisfaction is most unrelated to whether or not people: A) exercise regularly. B) sleep well. C) are well educated. D) have a happy marriage. E) have a meaningful religious faith. 27. After Brenda scolded her brother for forgetting to pick her up from school, the physical arousal that had accompanied her anger diminished. Which division of her nervous system mediated her physical relaxation? A) sympathetic division B) parasympathetic division C) skeletal division D) peripheral nervous system 28. Rabbits fail to react with fear to a signal of impending shock if they have suffered damage to the: A) hippocampus. B) amygdala. C) thalamus. D) hypothalamus. E) corpus callosum. 29. Sylvia is upset with her husband for not putting his dirty clothes in the laundry basket. Anger experts would most likely recommend that she deal with her frustration by saying to him: A) "Why do you expect me to do all the work around here?" B) "I'm not your mother like you think. Take some responsibility."
5 C) "From now on I'm going to leave my dirty clothes around for you to pick up." D) "I get annoyed when you leave your dirty clothes for me to pick up." E) "I refuse to make dinner until you do the laundry." 30. Research suggests that monkeys reared in the wild fear snakes because they: A) are biologically predisposed to fear nearly all primitive forms of life. B) have a particularly strong nervous system reaction to snake bites. C) have encountered snakes near dead monkeys. D) have observed other monkeys' fearful reactions to snakes. E) frequently compete with snakes for control of territory and natural resources. 31. As elderly Mr. Hooper crosses the busy intersection, he stumbles and drops the packages he is carrying. Which passerby is most likely to help Mr. Hooper? A) Drew, who has been laid off from work for three months B) Leon, who is on his way to work C) Bonnie, who graduated from college the day before D) Nancy, whose father recently passed away 32. Activation of the sympathetic nervous system respiration and salivation. A) increases; increases B) increases; decreases C) decreases; decreases D) decreases; increases 33. Most young children are fearful of bees, even though they have never been stung by one. This best illustrates that fear: A) is a maladaptive response. B) can be learned through observation. C) is genetically determined. D) results from relative deprivation. 34. As people experience negative emotions, the hemisphere of the brain becomes electrically active. A) right; more B) right; less C) left; more D) left; less 35. People from different cultures are most likely to differ with respect to: A) the way they categorize basic emotions such as fear and anger. B) their facial expressions of different emotions such as sadness or surprise. C) the specific states of physiological arousal associated with their feelings of happiness or disgust. D) how they interpret hand gestures such as the "thumbs up" signal. 36. The term "catharsis" refers to emotional: A) disturbance. B) inhibition. C) release. D) adaptation.
6 37. After hitting a grand-slam home run, Mike noticed that his heart was pounding. Later that evening, after nearly having a collision while driving on the freeway, Mike again noticed that his heart was pounding. That he interpreted this reaction as fear, rather than as ecstasy, can best be explained by the: A) James-Lange theory. B) Cannon-Bard theory. C) opponent-process theory. D) two-factor theory. E) adaptation-level theory. 38. The parasympathetic nervous system is to the sympathetic nervous system as is to. A) raising of blood sugar; lowering of blood sugar B) inhibition of digestion; activation of digestion C) contraction of pupils; dilation of pupils D) increasing blood pressure; decreasing blood pressure 39. Repeatedly saying the word "me" puts people in a better mood than repeatedly saying "you." This best illustrates the: A) opponent-process theory. B) feel good, do good phenomenon. C) adaptation-level phenomenon. D) facial feedback effect. E) relative deprivation principle. 40. A polygraph examination of a suspected murderer included an assessment of his reaction to a detailed description of the victim's clothing and death wounds details that would be known only to a person at the scene of the crime. The investigators were using: A) catharsis. B) the opponent-process effect. C) the guilty knowledge test. D) the adaptation-level phenomenon. E) the relative deprivation principle. 41. The fact that people from widely different cultures display and interpret facial expressions of emotion in a similar manner best illustrates the impact of: A) human genetic similarities. B) the adaptation-level phenomenon. C) cognition on emotion. D) opponent-processes. E) the worldwide distribution of American television programming. 42. Two years ago Maria was in an automobile accident in which her spinal cord was severed, leaving her paralyzed from her neck down. Today, Maria finds that she experiences emotions less intensely than she did before her accident. This tends to support which theory of emotion? A) James-Lange theory B) Cannon-Bard theory C) opponent-process theory D) adaptation-level theory E) relative deprivation theory 43. The Cannon-Bard theory of emotion states that:
7 A) emotions have two ingredients: physical arousal and a cognitive label. B) the conscious experience of an emotion occurs at the same time as the body's physical reaction. C) emotional experiences are based on an awareness of the body's responses to an emotion-arousing stimulus. D) emotional ups and downs tend to balance in the long run. 44. Schachter's two-factor theory emphasizes that emotion involves both: A) the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the nervous system. B) verbal and nonverbal expression. C) physical arousal and a cognitive label. D) universal and culture-specific aspects. 45. During World War II, promotion rates in the U.S. Air Corps were high, yet soldiers in this military branch were unhappy about the speed at which they were promoted. Their unhappiness is best explained in terms of the: A) James-Lange theory. B) adaptation-level phenomenon. C) relative deprivation principle. D) two-factor theory. E) opponent-process theory. 46. Emotions are: A) physiological reactions. B) behavioral expressions. C) conscious feelings. D) all of the above. 47. In terms of ability to recognize others' facial expressions of emotion, introverts do than extraverts and women do than men. A) better; better B) worse; better C) better; worse D) worse; worse 48. The emotion of anger is characterized by negative valence and arousal. A) high B) positive C) low D) negative 49. You would still be able to experience emotion in the absence of any sympathetic nervous system arousal according to the: A) Cannon-Bard theory. B) James-Lange theory. C) two-factor theory. D) catharsis hypothesis. E) opponent-process theory. 50. When the scientist electrically stimulated one area of a monkey's brain, the monkey became enraged. When another electrode was activated, the monkey cowered in fear. The electrodes were most likely implanted in the:
8 A) pituitary gland. B) adrenal glands. C) limbic system. D) right hemisphere. 51. While completing a final exam, Karen labels her arousal as energizing, whereas Mike labels his arousal as threatening. The emotional experiences of the two test takers are likely to differ the most with respect to: A) duration. B) intensity. C) adaptation level. D) valence. 52. Rannilt was euphoric after learning of her acceptance into the medical school of her choice. After a few weeks, however, she feels no emotional excitement when she thinks about her admission to medical school. This change in her feelings can best be explained in terms of the: A) catharsis hypothesis. B) relative deprivation principle. C) opponent-process theory. D) Cannon-Bard theory. E) adaptation-level phenomenon. 53. According to the Cannon-Bard theory, body arousal is to the sympathetic nervous system as subjective awareness of emotion is to the: A) cortex. B) hypothalamus. C) thalamus. D) parasympathetic nervous system. 54. Evidence that neck-level spinal cord injuries reduce the intensity with which people experience certain emotions most directly supports the: A) Cannon-Bard theory. B) adaptation-level principle. C) James-Lange theory. D) catharsis hypothesis. E) opponent-process theory. 55. Jason is an unsuccessful businessman who feels depressed. In order to increase his satisfaction and happiness with life, Jason should: A) imagine what his own life might be like if he became rich and famous. B) compare himself with friends who became rich and successful. C) identify how his own foolish decisions and lack of foresight have contributed to his unhappiness. D) recall past moments when his life was much more pleasant than it is now. E) imagine what his life might be like if he were suffering from a fatal disease. 56. Which of the following children is most likely to calm down emotionally shortly after venting his anger? A) Jack, who attacks his older brother for spitting at him B) Jeremiah, who attacks his younger brother for spitting at him C) Jed, who attacks his older brother for no good reason at all D) Jason, who attacks his younger brother for no good reason at all
9 57. Relatively high levels of physiological arousal would most likely interfere with effectively: A) solving a crossword puzzle. B) repeating the alphabet. C) riding a bicycle. D) washing dishes. E) enjoying a televised football game. 58. Nine-month-old Nicole's left frontal lobe is more active than her right frontal lobe. We can expect that, all other things being equal, Nicole: A) may suffer from mild depression for most of her life. B) may have trouble "turning off" upsetting feelings later in her life. C) may be more cheerful than those with more active right frontal lobes. D) may have trouble expressing feelings later in her life. 59. During an emergency, increasing levels of emotional arousal are likely to be accompanied by: A) decreases in blood sugar levels. B) slowing of digestion. C) increases in salivation. D) constriction of pupils to increase visual acuity. E) decreases in respiration rate. 60. A hormone that increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels in times of emergency is: A) acetylcholine. B) epinephrine. C) testosterone. D) insulin. E) glycogen. 61. Children in New York, Nigeria, and New Zealand smile when they are happy and frown when they are sad. This suggests that: A) the Cannon-Bard theory is correct. B) some emotional expressions are learned at a very early age. C) the two-factor theory is correct. D) facial expressions of emotion are universal and biologically determined. 62. The two-factor theory of emotion was proposed by: A) Walter Cannon. B) Carl Lange. C) William James. D) Stanley Schachter. E) Richard Solomon. 63. Jed wants his roommate Meron to help him study for a physics test. Meron is most likely to want to help after he has: A) helped some friends repair a flat tire on their car. B) received an unexpected "A" on his psychology test. C) heard that a friend was involved in an automobile accident. D) been caught cheating on a math test. 64. Electrical stimulation of which brain region can produce terror or rage in cats?
10 A) limbic system B) hypothalamus C) cortex D) cerebellum 65. Catharsis will be most effective in reducing anger toward another person if: A) you wait until you are no longer angry before confronting the person. B) the target of your anger is someone you feel has power over you. C) your anger is directed specifically toward the person who angered you. D) the other person is able to retaliate by also expressing anger. 66. Which of the following factors has been found to be clearly related to feelings of general happiness or life satisfaction? A) being well educated B) having children C) being over 50 years old D) having a meaningful religious faith E) being physically attractive 67. Subjective well-being among college students is with the extent to which love is valued and with the extent to which money is valued. A) positively correlated; positively correlated B) positively correlated; uncorrelated C) uncorrelated; positively correlated D) uncorrelated; uncorrelated E) positively correlated; negatively correlated 68. In the Schachter and Singer experiment, subjects were injected with epinephrine prior to spending time with a person who acted either euphoric or irritated. Which individuals in this experiment were least likely to experience the emotion demonstrated by the experimenter's accomplice? A) those who were led to think the injection would produce no physiological arousal B) those who were promised a large sum of money for participating in the experiment C) those who were told that the injection would cause them to become physiologically aroused D) those who were asked to run in place after receiving the injection 69. The loss of an arm in an automobile accident is likely to a person's long-term feelings of life satisfaction. Winning first place in a national tennis tournament is likely to a person's long-term feelings of life satisfaction. A) decrease; have little effect on B) decrease; increase C) have little effect on; increase D) have little effect on; have little effect on 70. In which country are people most likely to convey obvious facial expressions of their inner feelings? A) China B) Australia C) Japan D) India E) Soviet Union 71. Idaliza is furious because her steady boyfriend spent half an hour talking with his former girlfriend at
11 last night's school dance. A friend suggests that Idaliza ought to get the anger out of her system by repeatedly pounding her pillow while she imagines that she is hitting her boyfriend. Explain why this might be an ineffective way for Idaliza to reduce her anger. Suggest better ways. 72. Researchers have found that people experience cartoons as more amusing while holding a pen with their teeth than while holding it with their lips. This finding best serves to support the: A) opponent-process theory. B) Cannon-Bard theory. C) adaptation-level principle. D) James-Lange theory. E) catharsis hypothesis. 73. People are especially good at quickly detecting facial expressions of: A) love. B) anger. C) surprise. D) happiness. E) boredom. 74. The level of arousal typically associated with optimal performance tends to be on tasks that are. A) lower; frequently practiced B) higher; relatively difficult C) lower; relatively easy D) lower; relatively difficult 75. In an experiment on emotional arousal, Professor Davis notes a marked increase in heart rate, blood pressure, and perspiration in one subject. The professor could reasonably infer, on the basis of these physiological responses, that the subject is experiencing: A) anger. B) fear. C) sexual arousal. D) any of the above. 76. Lee was momentarily terrified as a passing automobile nearly side-swiped his car. When one of his passengers joked that he almost had a two-color car, Lee laughed uncontrollably. Lee's emotional volatility is best explained in terms of the: A) opponent-process theory. B) relative deprivation principle. C) James-Lange theory. D) catharsis hypothesis. E) two-factor theory. 77. Tranquilizing drugs that inhibit sympathetic nervous system activity often effectively reduce people's subjective experience of intense fear and anxiety. Which theory of emotion would have the greatest difficulty explaining this effect? A) James-Lange B) Cannon-Bard C) two-factor D) All the above would have equal difficulty explaining this effect.
12 78. Employees who have just been laid off are asked questions that encourage them to express hostility toward their employer. Research suggests that this opportunity to vent anger will: A) calm their emotions and reduce their anger. B) improve their relationships with management by allowing an open airing of differences. C) rechannel their anger into constructive motivation. D) increase their hostility. 79. According to the opponent-process theory, as an emotion is repeatedly experienced: A) the primary emotional experience becomes stronger. B) the opposing emotional experience becomes weaker. C) both a. and b. occur. D) the primary emotional experience becomes weaker; the opposing emotional experience becomes stronger. 80. Specific interpretations of the emotional significance of nonverbal behaviors are risky because: A) there is very little relationship between cognition and emotion. B) specific nonverbal responses may be associated with a variety of different emotions. C) people typically attempt to conceal their true feelings. D) there is very little relationship between specific emotions and specific facial expressions. 81. A psychotherapist suggests that Theresa can effectively reduce the anger she feels toward her exboyfriend by tearing pictures of him into little pieces. This suggestion illustrates the therapist's acceptance of the: A) catharsis hypothesis. B) adaptation-level principle. C) James-Lange theory. D) two-factor theory. E) relative deprivation principle. 82. As her professor distributed the mathematics test to the class, Alice's heart started to pound and her palms began sweating. These physiological reactions were activated by her nervous system. A) sympathetic B) central C) somatic D) parasympathetic 83. During the last four decades, the spendable income of Americans (adjusting for inflation) has and their self-reported personal happiness has. A) remained almost unchanged; decreased B) increased; remained almost unchanged C) remained almost unchanged; increased D) remained almost unchanged; remained almost unchanged 84. George, a suspect in a criminal investigation, has agreed to take a lie detector test. The machine used in this test is most likely to measure his: A) blood sugar levels. B) pupil dilation. C) hormone secretions. D) perspiration levels. E) facial expressions of emotions.
13 85. The guilty knowledge test is typically used to: A) provide emotionally troubled individuals with a way to safely release their aggressive urges. B) assess a suspect's responses to details of a crime. C) screen potential employees for possible past misdeeds. D) assure people that they are no worse than others with whom they compare themselves. 86. Which theory of emotion implies that every emotion is associated with a unique physiological reaction? A) James-Lange theory B) Cannon-Bard theory C) two-factor theory D) opponent-process theory 87. According to the opponent-process theory of emotion, repetitions of an emotion-arousing event tend to: A) weaken the experience of both the primary and the opposing emotion. B) weaken the experience of only the opposing emotion. C) strengthen the experience of both the primary and the opposing emotion. D) strengthen the experience of only the opposing emotion. 88. Julio was extremely angry when he came in for a routine EEG of his brain activity. When he later told this to the doctor, she was no longer concerned about the: A) increased electrical activity in Julio's right hemisphere. B) increased electrical activity in Julio's left hemisphere. C) decreased electrical activity in Julio's amygdala. D) increased electrical activity in Julio's amygdala. 89. Research on nonverbal communication indicates that: A) very young children's facial expressions of emotion are very difficult to interpret. B) children learn the facial expressions associated with emotion by observing adults. C) blind children who have never observed others demonstrate normal facial expressions of emotion. D) boys are better than girls at recognizing nonverbal expressions of emotion. E) children are unable to interpret facial expressions until they reach adolescence. 90. Which division of the nervous system is especially involved in bringing about emotional arousal? A) skeletal nervous system B) peripheral nervous system C) sympathetic nervous system D) parasympathetic nervous system E) central nervous system 91. The two-factor theory of emotion would have the greatest difficulty explaining why a: A) person comes to fear snakes after he sees someone else bitten by one. B) person's fear of snakes is reduced after she receives a calming tranquilizer. C) person automatically fears snakes even though he thinks they are attractive and harmless. D) person's fear of snakes is reduced after she learns that most snakes are harmless. 92. Research supporting the opponent-process theory of emotion suggests that: A) the price of pleasure is pain. B) with repetition a task that arouses fear will become more tolerable.
14 C) suffering can pay emotional dividends. D) all of the above are true. 93. Tranquilizing drugs that inhibit sympathetic nervous system activity often effectively reduce people's subjective experience of intense fear and anxiety. Use one of the major theories of emotion to account for the emotion-reducing effects of such tranquilizers. Which theory of emotion would have the greatest difficulty explaining these effects? Why? 94. Darwin believed that: A) the expression of emotions helped our ancestors to survive. B) all humans express basic emotions using similar facial expressions. C) human facial expressions of emotion retain elements of animals' emotional displays. D) all of the above are true. 95. Noticing that his heart was pounding and that his palms were sweaty while he was taking a difficult test, Pedro concluded that he was "anxious." Noticing that his heart was pounding and that his palms were sweaty when an attractive lady asked him to dance, Dmitri concluded that he was "falling in love." The differing emotions experienced by Pedro and Dmitri can best be explained by the: A) relative deprivation principle. B) James-Lange theory. C) two-factor theory. D) opponent-process theory. E) adaptation-level principle. 96. Which of the following was not raised as a criticism of the James-Lange theory of emotion? A) The body's responses are too similar to trigger the various emotions. B) Emotional reactions occur before the body's responses can take place. C) The cognitive activity of the cortex plays a role in the emotions we experience. D) People with spinal cord injuries at the neck typically experience less emotion. 97. A relatively high level of arousal would be most likely to facilitate: A) remembering the lines of a play. B) shooting free throws in basketball. C) sprinting 100 meters. D) taking a final exam in introductory psychology. 98. Performance of a task is typically when arousal is. A) best; moderate B) worst; moderate C) best; low D) best; high E) mediocre; moderate 99. Charles Darwin's suggestion that violent gestures increase one's anger is most inconsistent with the: A) James-Lange theory. B) adaptation-level principle. C) opponent process theory. D) catharsis hypothesis. E) relative deprivation principle.
15 100. Cheryl's boyfriend says he loves her, but she wants proof. In order to obtain the most trustworthy nonverbal signals of how he really feels, Cheryl should carefully observe: A) his general body posture when he stands near her. B) the way he holds her hand when they walk together. C) how close he stands to her when they are talking. D) his facial expressions when they spend time together. E) the way he positions his legs when he sits near her. Answer Key Ch.13:Untitled Exam-2 1. A 2. D 3. D 4. D 5. D 6. D A 9. D 10. B 11. D 12. C 13. E 14. A 15. D 16. E 17. D 18. C 19. C 20. C 21. E 22. C 23. C 24. A 25. D 26. C 27. B 28. B 29. D 30. D 31. C 32. B 33. B 34. A 35. D 36. C 37. D 38. C 39. D 40. C 41. A 42. A 43. B 44. C 45. C 46. D 47. A
16 48. A 49. A 50. C 51. D 52. E 53. A 54. C 55. E 56. B 57. A 58. C 59. B 60. B 61. D 62. D 63. B 64. A 65. C 66. D 67. E 68. C 69. D 70. B D 73. B 74. D 75. D 76. E 77. B 78. D 79. D 80. B 81. A 82. A 83. B 84. D 85. B 86. A 87. D 88. A 89. C 90. C 91. C 92. D D 95. C 96. D 97. C 98. A 99. D 100. D
Emotion. Emotion. Theories of Emotion. Chapter 13. Emotion. James-Lange Theory of Emotion
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 13 James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Theories
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 13 James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Theories
Emotion 1. Cognition and Emotion
 Emotion 1 Cognition and Emotion Objective 12-1: Describe how arousal and expressive behaviors interact in emotion. 1. Emotions have three components:,, and 2. According to the James-Lange theory, emotional
Emotion 1 Cognition and Emotion Objective 12-1: Describe how arousal and expressive behaviors interact in emotion. 1. Emotions have three components:,, and 2. According to the James-Lange theory, emotional
Where do emotions come from? What are they made of? Why do we have them? ADAPTIVE - Survival. Emotion. AP Psych Myers Ch. 13
 Where do emotions come from? What are they made of? Why do we have them? ADAPTIVE - Survival Emotion AP Psych Myers Ch. 13 Emotion A response of the whole organism, involving physiological arousal expressive
Where do emotions come from? What are they made of? Why do we have them? ADAPTIVE - Survival Emotion AP Psych Myers Ch. 13 Emotion A response of the whole organism, involving physiological arousal expressive
Theories and Physiology of Emotion. AP Psychology Module 41
 Theories and Physiology of Emotion AP Psychology Module 41 Theories of Emotion Use your textbook to research the 5 theories of emotion and examples of each. Note the time difference in the research our
Theories and Physiology of Emotion AP Psychology Module 41 Theories of Emotion Use your textbook to research the 5 theories of emotion and examples of each. Note the time difference in the research our
MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION
 MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION EMOTION: a response of the whole organism, involving 1. physiological arousal 2. expressive behaviors, and 3. conscious experience A mix of bodily arousal
MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION EMOTION: a response of the whole organism, involving 1. physiological arousal 2. expressive behaviors, and 3. conscious experience A mix of bodily arousal
24. People are especially good at quickly detecting facial expressions of: A) love. B) anger. C) surprise. D) happiness. E) boredom.
 Name: Date: 1. Psychologists have used four perspectives in their efforts to explain motivation. These include an emphasis on instincts, optimum arousal, a hierarchy of motives, and: A) drive reduction.
Name: Date: 1. Psychologists have used four perspectives in their efforts to explain motivation. These include an emphasis on instincts, optimum arousal, a hierarchy of motives, and: A) drive reduction.
Scientists have identified subtle differences in the brain circuits and hormones associated with different emotions. 2
 1 Scientists have identified subtle differences in the brain circuits and hormones associated with different emotions. 2 The polygraph has proved to be extremely effective in detecting lies. 3 Some emotional
1 Scientists have identified subtle differences in the brain circuits and hormones associated with different emotions. 2 The polygraph has proved to be extremely effective in detecting lies. 3 Some emotional
Unit 8 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. Ten-year-old Vito tells his friend, When you notice that your knees knock, your hands sweat, and your stomach is in knots, then you really get scared. This statement best illustrates the
Name: Date: 1. Ten-year-old Vito tells his friend, When you notice that your knees knock, your hands sweat, and your stomach is in knots, then you really get scared. This statement best illustrates the
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 12: Emotions, Stress, & Health pp
 Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 12: Emotions, Stress, & Health pp. 497-549 A QUESTION to consider BEFORE you read pp. 497-499: What are the components of emotion? READ Emotions, Stress & Heath and
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 12: Emotions, Stress, & Health pp. 497-549 A QUESTION to consider BEFORE you read pp. 497-499: What are the components of emotion? READ Emotions, Stress & Heath and
Emotions and Motivation
 Emotions and Motivation LP 8A emotions, theories of emotions 1 10.1 What Are Emotions? Emotions Vary in Valence and Arousal Emotions Have a Physiological Component What to Believe? Using Psychological
Emotions and Motivation LP 8A emotions, theories of emotions 1 10.1 What Are Emotions? Emotions Vary in Valence and Arousal Emotions Have a Physiological Component What to Believe? Using Psychological
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
A musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately at peace with himself.
 A musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately at peace with himself. What a man can be, he must be. -Abraham Maslow Can you tell me what Maslow is describing?
A musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately at peace with himself. What a man can be, he must be. -Abraham Maslow Can you tell me what Maslow is describing?
Chapter 7 Motivation and Emotion
 Chapter 7 Motivation and Emotion Emotion Emotion a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Eight Basic Emotions Fear Surprise Disgust Anger Sadness
Chapter 7 Motivation and Emotion Emotion Emotion a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Eight Basic Emotions Fear Surprise Disgust Anger Sadness
Introduction to Psychology. Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS
 Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS o Derived from the Latin word Emovere emotion means to excite, stir up or agitate. o A response that includes feelings such as happiness, fear, sadness, grief, sorrow etc: it is
Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS o Derived from the Latin word Emovere emotion means to excite, stir up or agitate. o A response that includes feelings such as happiness, fear, sadness, grief, sorrow etc: it is
Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition. Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AK
 Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AK The wheel allows him to show how he thinks these emotions blend with each other to form more complicated ones.
Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AK The wheel allows him to show how he thinks these emotions blend with each other to form more complicated ones.
EMOTIONS S E N I O R S P E C I A L I S T I N P S Y C H I A T R Y A N D S E X T H E R A P Y
 EMOTIONS C O L. S A E D S H U N N A Q S E N I O R S P E C I A L I S T I N P S Y C H I A T R Y A N D S E X T H E R A P Y EMOTIONS Emotion is any conscious experience characterized by intense mental activity
EMOTIONS C O L. S A E D S H U N N A Q S E N I O R S P E C I A L I S T I N P S Y C H I A T R Y A N D S E X T H E R A P Y EMOTIONS Emotion is any conscious experience characterized by intense mental activity
Chapter 11 Emotion. Emotion. The Nature of Emotion
 Chapter 11 Emotion Emotion Emotions are temporary experiences with either positive, negative, or mixed qualities. People experience emotion with varying intensity as happening to them, as generated in
Chapter 11 Emotion Emotion Emotions are temporary experiences with either positive, negative, or mixed qualities. People experience emotion with varying intensity as happening to them, as generated in
Emotion Theory. Dr. Vijay Kumar
 Emotion Theory Dr. Vijay Kumar Emotions Just how many emotions are there? Basic Emotions Some have criticized Plutchik s model as applying only to English-speakers Revised model of basic emotions includes:
Emotion Theory Dr. Vijay Kumar Emotions Just how many emotions are there? Basic Emotions Some have criticized Plutchik s model as applying only to English-speakers Revised model of basic emotions includes:
EMOTION. Joy, Sorrow, Anger, Fear, Love, Hate, Happiness
 EMOTION Joy, Sorrow, Anger, Fear, Love, Hate, Happiness Defining Characteristics Most psychologists see emotion as psychological and physiological reactions to changes in our relationship with the world.
EMOTION Joy, Sorrow, Anger, Fear, Love, Hate, Happiness Defining Characteristics Most psychologists see emotion as psychological and physiological reactions to changes in our relationship with the world.
AP Psychology Guided Reading Unit 8B Emotions, Stress, and Health
 Unit 8B - 1 3Name: Period: SECTION 1 THEORIES OF EMOTION 1. What are emotions? AP Psychology Guided Reading Unit 8B Emotions, Stress, and Health 2. What are the two controversies over the interplay of
Unit 8B - 1 3Name: Period: SECTION 1 THEORIES OF EMOTION 1. What are emotions? AP Psychology Guided Reading Unit 8B Emotions, Stress, and Health 2. What are the two controversies over the interplay of
Characteris$cs of Emo$ons
 Emo$on Characteris$cs of Emo$ons Emo$ons are a mix of Physiological ac$va$on Expressive behaviors Conscious experience Theories of Emo$on James- Lange Emo$onal s$mulus causes physiological reac$on Physiological
Emo$on Characteris$cs of Emo$ons Emo$ons are a mix of Physiological ac$va$on Expressive behaviors Conscious experience Theories of Emo$on James- Lange Emo$onal s$mulus causes physiological reac$on Physiological
DEFINING EMOTION 11/19/2009 THE BIOLOGY OF EMOTION & STRESS. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense.
 DEFINING EMOTION Emotion A feeling that differs from a person s normal affective state; a biological function of the nervous system. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense. An
DEFINING EMOTION Emotion A feeling that differs from a person s normal affective state; a biological function of the nervous system. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense. An
Practice Question MOTIVATION AND EMOTION. Motivation as Drives. Motivation 10/22/2012
 Practice Question Gabriela s mother practices the authoritative style of parenting. This suggests that Gabriela s mother. MOTIVATION AND EMOTION Motivation Motivation as Drives Purpose or cause of an action
Practice Question Gabriela s mother practices the authoritative style of parenting. This suggests that Gabriela s mother. MOTIVATION AND EMOTION Motivation Motivation as Drives Purpose or cause of an action
Psychology for Nurses EMOTION. By Dr. Hayder Al-hadrawi University of Babylon, College of Nursing
 Psychology for Nurses EMOTION By Dr. Hayder Al-hadrawi University of Babylon, College of Nursing 2016-2017 4 Aristotle s meaning of emotion Any body can become ANGRY that is easy, but to be angry with
Psychology for Nurses EMOTION By Dr. Hayder Al-hadrawi University of Babylon, College of Nursing 2016-2017 4 Aristotle s meaning of emotion Any body can become ANGRY that is easy, but to be angry with
Psychology, 8 th Edition Myers. Chapter 13 Emotion. Where do emotions come from? Why do we have them? What are they made of?
 Psychology, 8 th Edition Myers Chapter 13 Emotion Where do emotions come from? Why do we have them? What are they made of? Emotions are adaptive they enhance our survival. Theories of Emotion Emotion a
Psychology, 8 th Edition Myers Chapter 13 Emotion Where do emotions come from? Why do we have them? What are they made of? Emotions are adaptive they enhance our survival. Theories of Emotion Emotion a
Chapter Eight: Emotion and Motivation
 Chapter Eight: Emotion and Motivation Emotions Four Part Process of Emotion 1. Physiological arousal of the body 2. Cognitive Interpretation of events and feelings conscious and unconscious 3. Subjective
Chapter Eight: Emotion and Motivation Emotions Four Part Process of Emotion 1. Physiological arousal of the body 2. Cognitive Interpretation of events and feelings conscious and unconscious 3. Subjective
drive-reduction theory
 motivation hierarchy of neds instinct glucose drive-reduction theory set point homeostasis basal metabolic rate incentive anorexia nervosa 1a Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with
motivation hierarchy of neds instinct glucose drive-reduction theory set point homeostasis basal metabolic rate incentive anorexia nervosa 1a Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with
Chapter 12,13 &14. Motivation, Emotion, Stress & Health
 Chapter 12,13 &14 Motivation, Emotion, Stress & Health Motivation Motivation a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior Instinct complex behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species
Chapter 12,13 &14 Motivation, Emotion, Stress & Health Motivation Motivation a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior Instinct complex behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species
Emotion. Chapter 13. Emotion. Emotion. Emotion. Myers PSYCHOLOGY. Theories of Emotion. Outline. Theory of Emotion. Theory of.
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 13 C13:1 Response of whole organism to pleasant and aversive events of different types Happiness, Sadness, Fear, Anger, Three elements Physiological arousal Expressive behaviors
Myers PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 13 C13:1 Response of whole organism to pleasant and aversive events of different types Happiness, Sadness, Fear, Anger, Three elements Physiological arousal Expressive behaviors
autonomic ne rvous system The autonomic ne rvous system The autonomic ne rvous system Pa rasympathetic Sympathetic
 Chapter 5: Bodily Changes and Emotion William James contended that an emotionally exciting fact provokes bodily responses, which in turn lead to the experience of emotion My thesis is that the bodily changes
Chapter 5: Bodily Changes and Emotion William James contended that an emotionally exciting fact provokes bodily responses, which in turn lead to the experience of emotion My thesis is that the bodily changes
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
General Psychology 2/23/2010. What Is Motivation? Theories of Motivation. Lawrence D. Wright Ph.D. Professor. Chapter 6 Motivation and Emotion
 General Psychology Lawrence D. Wright Ph.D. Professor Chapter 6 Motivation and Emotion 6-1 What Is Motivation? Motivation: The aspects of motivation are a) b) c) Instincts: 6-2 Biological theories of motivation:
General Psychology Lawrence D. Wright Ph.D. Professor Chapter 6 Motivation and Emotion 6-1 What Is Motivation? Motivation: The aspects of motivation are a) b) c) Instincts: 6-2 Biological theories of motivation:
Emotions. These aspects are generally stronger in emotional responses than with moods. The duration of emotions tend to be shorter than moods.
 LP 8D emotions & James/Lange 1 Emotions An emotion is a complex psychological state that involves subjective experience, physiological response, and behavioral or expressive responses. These aspects are
LP 8D emotions & James/Lange 1 Emotions An emotion is a complex psychological state that involves subjective experience, physiological response, and behavioral or expressive responses. These aspects are
Emotion and Motivation. Chapter 8
 Emotion and Motivation Chapter 8 Motivation & Emotion in Historical Perspective Motivation and emotion are relatively new concepts: Motivation was a collection of other concepts, such as pleasure, lust,
Emotion and Motivation Chapter 8 Motivation & Emotion in Historical Perspective Motivation and emotion are relatively new concepts: Motivation was a collection of other concepts, such as pleasure, lust,
Overview. Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions
 Emotion Overview Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions Definition of Emotion Emotions are biologically-based responses
Emotion Overview Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions Definition of Emotion Emotions are biologically-based responses
AP Psychology. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The subfield of psychology that provides psychology's contribution to the prevention and treatment of illness is known as A) medical psychology. B) health psychology. C) behavioral psychology.
Name: Date: 1. The subfield of psychology that provides psychology's contribution to the prevention and treatment of illness is known as A) medical psychology. B) health psychology. C) behavioral psychology.
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
The Emotional Nervous System
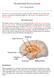 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Typically, this unit is described as a goal
 Motivation What is motivation? Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Reasons here implies some sort of desired end state Typically, this unit is described as a goal
Motivation What is motivation? Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Reasons here implies some sort of desired end state Typically, this unit is described as a goal
Chapter Introduction Section 1: Theories of Motivation Section 2: Biological and Social Motives Section 3: Emotions. Chapter Menu
 Chapter Introduction Section 1: Theories of Motivation Section 2: Biological and Social Motives Section 3: Emotions Chapter Menu Chapter Objectives Section 1 Theories of Motivation Explain motivation and
Chapter Introduction Section 1: Theories of Motivation Section 2: Biological and Social Motives Section 3: Emotions Chapter Menu Chapter Objectives Section 1 Theories of Motivation Explain motivation and
Motivation an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal
 Chapter 12 Motivation and Emotion Sec 1: Theories of Motivation Motivation an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal 1. Instinct Theory a. Instincts innate tendencies that
Chapter 12 Motivation and Emotion Sec 1: Theories of Motivation Motivation an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal 1. Instinct Theory a. Instincts innate tendencies that
ADHD Explanation 2: Oppositional defiant disorder and MERIM
 ADHD Explanation 2: Oppositional Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) ODD is very frequently associated with ADHD. People with ODD typically overreact with anger in response to minor frustration. The lack
ADHD Explanation 2: Oppositional Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD) ODD is very frequently associated with ADHD. People with ODD typically overreact with anger in response to minor frustration. The lack
did you feel sad or depressed? did you feel sad or depressed for most of the day, nearly every day?
 Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
Name: Age: Date: PDSQ This form asks you about emotions, moods, thoughts, and behaviors. For each question, circle YES in the column next to that question, if it describes how you have been acting, feeling,
PSYC 222 Motivation and Emotions
 PSYC 222 Motivation and Emotions Session 6 The Concept of Emotion Lecturer: Dr. Annabella Osei-Tutu, Psychology Department Contact Information: aopare-henaku@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
PSYC 222 Motivation and Emotions Session 6 The Concept of Emotion Lecturer: Dr. Annabella Osei-Tutu, Psychology Department Contact Information: aopare-henaku@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
Motivation and Emotion
 Motivation and Emotion Definitions Motivation: what drives us to seek a specific goal Emotion: a state of body that causes feelings. Both involve physiological and psychological factors. Physiological
Motivation and Emotion Definitions Motivation: what drives us to seek a specific goal Emotion: a state of body that causes feelings. Both involve physiological and psychological factors. Physiological
For example, the two-factor theory of emotion argues that when people become aroused they look for cues as to why they feel the way they do.
 COGNITIVE, SOCIAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS OF EMOTIONAL STATE STANLEY SCHACHTER & JEROME E. SINGER (1962) HISTORY Schachter and Singer developed the two-factor theory of emotion. The two-factor theory
COGNITIVE, SOCIAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL DETERMINANTS OF EMOTIONAL STATE STANLEY SCHACHTER & JEROME E. SINGER (1962) HISTORY Schachter and Singer developed the two-factor theory of emotion. The two-factor theory
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Motivation and Emotion
 Motivation and Emotion Motivation Vocabulary Terms MOTIVATION an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal INSTINCTS innate tendencies that determine behavior NEED a biological
Motivation and Emotion Motivation Vocabulary Terms MOTIVATION an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal INSTINCTS innate tendencies that determine behavior NEED a biological
Learning Outcome: To what extent do cognitive and biological factors interact in emotion?
 Learning Outcome: To what extent do cognitive and biological factors interact in emotion? Schachter & Singer 1962: Two Factor Theory Aim: to challenge several theories of emotion and test the two factor
Learning Outcome: To what extent do cognitive and biological factors interact in emotion? Schachter & Singer 1962: Two Factor Theory Aim: to challenge several theories of emotion and test the two factor
Psychology Chapter 12 Study Guide
 Psychology Chapter 12 Study Guide Emotion is a full body/mind/behavior response to a situation Theories of emotion James-Lange theory body before thoughts Cannon-Bard theory body with thoughts Singer-Shater
Psychology Chapter 12 Study Guide Emotion is a full body/mind/behavior response to a situation Theories of emotion James-Lange theory body before thoughts Cannon-Bard theory body with thoughts Singer-Shater
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Motivation. Notes by E & V 2015 Unit 10: Motivation & Emotion
 Notes by E & V 2015 Unit 10: Motivation & Emotion Motivation What is Motivation? Motivation: the factors that energize and direct the behavior of organisms (includes day-to-day things); a need or desire
Notes by E & V 2015 Unit 10: Motivation & Emotion Motivation What is Motivation? Motivation: the factors that energize and direct the behavior of organisms (includes day-to-day things); a need or desire
Three Minute Review: Motivation 1. Test Yourself Sex. Dimensions of Emotion
 Three Minute Review: Motivation 1 what drives people to behave the way they do? regulatory drives non-regulatory drives hypothalamus Hunger homeostasis thermostat analogy tiny area, important functions,
Three Minute Review: Motivation 1 what drives people to behave the way they do? regulatory drives non-regulatory drives hypothalamus Hunger homeostasis thermostat analogy tiny area, important functions,
EMOTIONS MODULE-II OBJECTIVES 10.1 NATURE OF EMOTION. Emotions. Key Psychological Processes. Notes
 Emotions MODULE-II 10 EMOTIONS When we meet our friend after a long time we feel happy; when a baby clings to her mother she displays love, when we are praised by our parents or teachers we feel proud
Emotions MODULE-II 10 EMOTIONS When we meet our friend after a long time we feel happy; when a baby clings to her mother she displays love, when we are praised by our parents or teachers we feel proud
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Emotion October 16th, 2009 : Lecture 11
 Lecture Overview October 16th, 2009 : Lecture 11 Finishing up Groups s Jury Decision Making Jury Decision Making Group Polarization and Group Think Group Decision Making and Juries Value of Unanimity 12
Lecture Overview October 16th, 2009 : Lecture 11 Finishing up Groups s Jury Decision Making Jury Decision Making Group Polarization and Group Think Group Decision Making and Juries Value of Unanimity 12
Dealing with Depression Feature Article July 2008
 Dealing with Depression Feature Article July 2008 Marjorie and Ann were housemates for about three years. Everyone thought that they did not like each other very much. Direct support staff said that they
Dealing with Depression Feature Article July 2008 Marjorie and Ann were housemates for about three years. Everyone thought that they did not like each other very much. Direct support staff said that they
The Thinking-Feeling Connection Contents
 The Thinking-Feeling Connection Contents Page The Thinking-Feeling Connection 2 Making Connection 4 Module Summary 6 Page 1 The Thinking-Feeling Connection People often believe that feelings and emotions
The Thinking-Feeling Connection Contents Page The Thinking-Feeling Connection 2 Making Connection 4 Module Summary 6 Page 1 The Thinking-Feeling Connection People often believe that feelings and emotions
Elements of Communication
 Elements of Communication Elements of Communication 6 Elements of Communication 1. Verbal messages 2. Nonverbal messages 3. Perception 4. Channel 5. Feedback 6. Context Elements of Communication 1. Verbal
Elements of Communication Elements of Communication 6 Elements of Communication 1. Verbal messages 2. Nonverbal messages 3. Perception 4. Channel 5. Feedback 6. Context Elements of Communication 1. Verbal
Managing Stress. pressure, fear, confusion, anger and sweating.
 Managing Stress Introduction Stress is a physical and emotional reaction that everyone experiences as they encounter changes in life. These reactions can have positive or negative effects. Stress has positive
Managing Stress Introduction Stress is a physical and emotional reaction that everyone experiences as they encounter changes in life. These reactions can have positive or negative effects. Stress has positive
GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Never or Sometimes Often Very Often
 GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Here are some questions about behaviors that occur in the general population. Think about how often they occur for you. Using the scale below, select the
GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Here are some questions about behaviors that occur in the general population. Think about how often they occur for you. Using the scale below, select the
Introduction to Emotion
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Introduction to Emotion Module 38 2 Emotion Theories of Emotion Embodied
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Introduction to Emotion Module 38 2 Emotion Theories of Emotion Embodied
Emotion Lecture 26 1
 Emotion Lecture 26 1 The Trilogy of Mind Immanuel Kant (1791); Hilgard (1980) There are three absolutely irreducible faculties of mind: knowledge, feeling, and desire. Cognition Knowledge and Beliefs Emotion
Emotion Lecture 26 1 The Trilogy of Mind Immanuel Kant (1791); Hilgard (1980) There are three absolutely irreducible faculties of mind: knowledge, feeling, and desire. Cognition Knowledge and Beliefs Emotion
Basic Nervous System anatomy. Neurobiology of Happiness
 Basic Nervous System anatomy Neurobiology of Happiness The components Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral" Nervous System (PNS) Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Basic Nervous System anatomy Neurobiology of Happiness The components Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral" Nervous System (PNS) Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Coach on Call. Letting Go of Stress. A healthier life is on the line for you! How Does Stress Affect Me?
 Coach on Call How Does Stress Affect Me? Over time, stress can affect the way you feel, think, and act. You need some time when you are free of stress. You need ways to get relief from stress. Without
Coach on Call How Does Stress Affect Me? Over time, stress can affect the way you feel, think, and act. You need some time when you are free of stress. You need ways to get relief from stress. Without
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE The key to harmonious relationships Lisa Tenzin-Dolma
 Emotional Intelligence This hand out is for your personal use only. All content and photos are copyright to Lisa Tenzin- Dolma, (unless credited to a third party). You may not share, copy, or use the content
Emotional Intelligence This hand out is for your personal use only. All content and photos are copyright to Lisa Tenzin- Dolma, (unless credited to a third party). You may not share, copy, or use the content
Motivation, Conflict, Emotion. Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry
 Motivation, Conflict, Emotion Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Motivation Motivation is the psychological feature that arouses an organism to action toward a desired goal and
Motivation, Conflict, Emotion Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Motivation Motivation is the psychological feature that arouses an organism to action toward a desired goal and
Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews
 Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews Presenter: Martin TAYLOR Position: Senior Legal Specialist Australian Criminal Intelligence
Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews Presenter: Martin TAYLOR Position: Senior Legal Specialist Australian Criminal Intelligence
Emotions. What makes you ick? What makes you love?
 Emotions What makes you ick? What makes you love? Where we are headed: What are four theories of emotion? common sense theory - Cannon-Bard theory James-Lange theory - Two-factor theory ALL DEAL WITH
Emotions What makes you ick? What makes you love? Where we are headed: What are four theories of emotion? common sense theory - Cannon-Bard theory James-Lange theory - Two-factor theory ALL DEAL WITH
ANGER MANAGEMENT. So What is Anger? What causes you to be angry? Understanding and Identifying the Cause of your Anger
 ANGER MANAGEMENT Georgia Association of Code Enforcement So What is Anger? Anger is "an emotional state that varies in intensity from mild irritation to intense fury and rage. An EMOTIONAL State What causes
ANGER MANAGEMENT Georgia Association of Code Enforcement So What is Anger? Anger is "an emotional state that varies in intensity from mild irritation to intense fury and rage. An EMOTIONAL State What causes
Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski
 Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski With additions by: Lee Jamison When most people think about alcoholism or drug addiction they think only of the alcohol/drug-based symptoms and forget
Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski With additions by: Lee Jamison When most people think about alcoholism or drug addiction they think only of the alcohol/drug-based symptoms and forget
Emotional Expression
 FEELING AND EMOTIOS FEELING Feeling is attitudes towards certain topics. It is both sensory and motor. On the sensory side, it is the sensation mass unanalysed and not utilized to indicate facts. On the
FEELING AND EMOTIOS FEELING Feeling is attitudes towards certain topics. It is both sensory and motor. On the sensory side, it is the sensation mass unanalysed and not utilized to indicate facts. On the
PREVENTING WORKPLACE VIOLENCE PRESENTED BY THE SOLUTIONS GROUP
 PREVENTING WORKPLACE VIOLENCE PRESENTED BY THE SOLUTIONS GROUP 20 WORKERS MURDERED EACH WEEK IN U.S. - SOURCE = NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH HOW MANY NONFATAL WORKPLACE ASSAULTS?
PREVENTING WORKPLACE VIOLENCE PRESENTED BY THE SOLUTIONS GROUP 20 WORKERS MURDERED EACH WEEK IN U.S. - SOURCE = NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH HOW MANY NONFATAL WORKPLACE ASSAULTS?
Chapter 13: From Social Cognition to Affect
 Chapter 13: From Social Cognition to Affect 1. Which of the following refers to relatively mild subjective reactions that are essentially either pleasant or unpleasant? a. Bivalence. b. Moods. c. Preferences.
Chapter 13: From Social Cognition to Affect 1. Which of the following refers to relatively mild subjective reactions that are essentially either pleasant or unpleasant? a. Bivalence. b. Moods. c. Preferences.
Chapter 13 and 16. Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text
 Chapter 13 and 16 Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text Key Concepts Identify causes and symptoms of stress Determine how people can manage stress. Section 13.2 Stress Management Stress
Chapter 13 and 16 Combined by Mrs. Parker Taken from Families Today Text Key Concepts Identify causes and symptoms of stress Determine how people can manage stress. Section 13.2 Stress Management Stress
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Teena Jain 2017 Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder What is post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD? PTSD is a disorder that some people develop after experiencing a shocking,
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Chapter 8. The Nervous System
 Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
EMOTION CARDS. Introduction and Ideas. How Do You Use These Cards?
 Introduction and Ideas A significant part of helping kids to deal with their emotions (Jump In! Stand Strong! Rise Up!) is helping them to develop a robust feelings vocabulary. That is why we are excited
Introduction and Ideas A significant part of helping kids to deal with their emotions (Jump In! Stand Strong! Rise Up!) is helping them to develop a robust feelings vocabulary. That is why we are excited
Motivation and Emotion. Unit 2: Biopsychology
 Motivation and Emotion Unit 2: Biopsychology Theories of Motivation Motivation: an internal state that activates behaviour and directs it towards a goal. Motivation cannot be observed directly so psychologists
Motivation and Emotion Unit 2: Biopsychology Theories of Motivation Motivation: an internal state that activates behaviour and directs it towards a goal. Motivation cannot be observed directly so psychologists
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Review Sheet: Emotion/Stress and Health (2-4%)
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Emotion/Stress and Health (2-4%) Theories of Emotion 1) emotion 2) James-Lange theory 3) Cannon-Bard theory 4) two-factor theory 5)
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Emotion/Stress and Health (2-4%) Theories of Emotion 1) emotion 2) James-Lange theory 3) Cannon-Bard theory 4) two-factor theory 5)
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Emotional State Recognition via Physiological Measurement and Processing
 APPLICATION NOTE 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 Tel (805) 685-0066 Fax (805) 685-0067 info@biopac.com www.biopac.com Application Note 276: Emotional State Recognition via Physiological Measurement and
APPLICATION NOTE 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 Tel (805) 685-0066 Fax (805) 685-0067 info@biopac.com www.biopac.com Application Note 276: Emotional State Recognition via Physiological Measurement and
Henry VIII and his Six Wives. By Janet Hardy-Gould
 Henry VIII and his Six Wives By Janet Hardy-Gould 1 King Henry is dead 1 A month ago I was the Queen of, the of King Henry the Eighth. 2 Who was buried in St. George s Church? 3 Two days ago, on 16 th
Henry VIII and his Six Wives By Janet Hardy-Gould 1 King Henry is dead 1 A month ago I was the Queen of, the of King Henry the Eighth. 2 Who was buried in St. George s Church? 3 Two days ago, on 16 th
Ch. 12, 13, 14 Test Review
 Name: Date: Period: Score: + Ch. 12, 13, 14 Test Review In order to minimize paper waste and get the review to fit in the format it is in below, please adjust your margins to 0.3 before you print. Please
Name: Date: Period: Score: + Ch. 12, 13, 14 Test Review In order to minimize paper waste and get the review to fit in the format it is in below, please adjust your margins to 0.3 before you print. Please
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Connecting to the Guest. Dr. John L. Avella Ed.D Cal State Monterey Bay
 Connecting to the Guest Dr. John L. Avella Ed.D Cal State Monterey Bay Connecting to Guest Developing Relationships Create Loyal Guests Role of Guest Service Provider To create a unique emotional experience
Connecting to the Guest Dr. John L. Avella Ed.D Cal State Monterey Bay Connecting to Guest Developing Relationships Create Loyal Guests Role of Guest Service Provider To create a unique emotional experience
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 9 Motivation and Emotion 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 9.1 What Motivates Our Behavior? The words emotion
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 9 Motivation and Emotion 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 9.1 What Motivates Our Behavior? The words emotion
ANGER MANAGEMENT CHOICES. by Sherwood Stauffer
 ANGER MANAGEMENT CHOICES by Sherwood Stauffer Anger shows us many faces in our day-to-day interactions. This article talks about five common ways in which people express or handle their anger. These are
ANGER MANAGEMENT CHOICES by Sherwood Stauffer Anger shows us many faces in our day-to-day interactions. This article talks about five common ways in which people express or handle their anger. These are
PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS
 START TIME : PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS Statement I.1: These next questions are about difficult or stressful things that can happen to people. It may be hard to remember everything about these
START TIME : PRISM SECTION 15 - STRESSFUL EVENTS Statement I.1: These next questions are about difficult or stressful things that can happen to people. It may be hard to remember everything about these
FOREVER FREE STOP SMOKING FOR GOOD. Stop Smoking. For Good. Smoking, Stress, & Mood
 B O O K L E T 6 Stop Smoking For Good Smoking, Stress, & Mood Contents What Causes Stress? 2 What is Stress? 4 How is Stress Related to Smoking? 4 So, Why Not Smoke When Stressed? 6 Better Ways to Deal
B O O K L E T 6 Stop Smoking For Good Smoking, Stress, & Mood Contents What Causes Stress? 2 What is Stress? 4 How is Stress Related to Smoking? 4 So, Why Not Smoke When Stressed? 6 Better Ways to Deal
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Emotional Changes After a Traumatic Brain Injury
 Emotional Changes After a Traumatic Brain Injury EMOTIONAL LABILITY Emotional lability can be caused by damage to the parts of the brain that control emotion. Some people with Traumatic Brain Injury or
Emotional Changes After a Traumatic Brain Injury EMOTIONAL LABILITY Emotional lability can be caused by damage to the parts of the brain that control emotion. Some people with Traumatic Brain Injury or
