Psychology, 8 th Edition Myers. Chapter 13 Emotion. Where do emotions come from? Why do we have them? What are they made of?
|
|
|
- Theodore Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Psychology, 8 th Edition Myers Chapter 13 Emotion Where do emotions come from? Why do we have them? What are they made of? Emotions are adaptive they enhance our survival. Theories of Emotion Emotion a response of the whole organism, involving 1) physiological arousal, 2) expressive behaviors, and 3) conscious experience. Ex: Myers explains a situation in which he thought his son was kidnapped at a store. o Physiological arousal heartbeat quickening o Expressive behaviors quickened pace o Conscious experience thoughts (is this a kidnapping?) and feelings (fear, later joy) 2 chicken-or-the-egg debates surrounding emotions: Does your physiological arousal precede or follow your emotional experience? Does cognition always follow emotion does thinking precede or follow feeling? o Experience tells us that conscious awareness precedes physiological actions (sad crying; angry lashing out; afraid trembling) James-Lange Theory the theory that our experience of emotion is our awareness of our physiological responses to emotion-arousing stimuli (feeling of emotions follow physical manifestations of emotions) Combination of William James and Carl Lange Ex: your car skids and your fishtail into another lane once you realize you are ok, you realize you are trembling and your heart is pounding THEN you feel the emotional wave of feelings about the gravity of what could have happened. Cannon-Bard Theory the theory that an emotion-arousing stimulus simultaneously triggers 1) physiological responses and 2) the subjective experience of emotion Walter Cannon, and later Phillip Bard o The body s physiological responses are not distinct enough to trigger different emotions (ex: does a racing heart beat = fear? Love?; does crying = sadness? Happiness?) o Changes in the body s state are too slow to trigger sudden emotions The emotion-triggering stimulus is routed simultaneously to the brain s cortex awareness of emotion WHILE SIMULTANEOUSLY the emotion-triggering stimulus is routed to the sympathetic nervous system arousal in the body.
2 Ex: you heart beats AS you experience fear; one does not cause the other. Schachter-Singer Two-Factory Theory the theory that to experience emotion one must 1) be physically aroused and 2) cognitively label the arousal. Physiology and cognition (memory, perception, and interpretations) together create emotions To experience emotion, you must cognitive interpret and label the cause of the arousal.
3
4 Embodied Emotion Emotions are not only felt by the mind, but by the entire body. Emotions and the Autonomic Nervous System The autonomic nervous system mobilizes your body for action Parasympathetic nervous system calms body Sympathetic nervous system arouses body Sympathetic (arousing) Parasympathetic (calming) Pupils dilate Eyes Pupils contract Decreases Salivation Increases Perspires Skin Dries Increases Respiration Decreases Accelerates Heart Slows Inhibits Digestion Activates Secrete stress hormones Adrenal glands Decrease secretion of stress hormones Arousal and Performance Arousal is adaptive too much or too little can be disruptive Level of optimum arousal varies with task o Difficult tasks lower level of optimal arousal o Easy tasks higher level of optimal arousal Physiological Similarities Among Specific Emotions Some emotions present similarly physiologically fear, anger, and sexual arousal even though they look and feel different Physiological Differences Among Specific Emotions Fear and joy can produce similar heart rates, but activate different muscles tension in the brow (fear) or movement in the cheeks and under the eyes (joy, smiling) Amygdala fear and aggression (activity noticed during observing or experiencing these emotions) Emotions activate different parts of the brain s cortex o Right frontal lobe disgust, negative emotions, depression o Left frontal lobe positive emotions and moods, enthusiasm, people with positive personalities More dopamine (rewarding) Cognition and Emotion Which comes first: Thinking or feeling? Cognition Can Define Emotion Spillover effect sometimes our arousal response to one event influences our response to the next event. Schachter and Singer s experiment injected college males with the hormone epinephrine half were told of the side effects (flushed face, increased heart and breathing rates) and when they started to experience the effects, they attributed it to the injection. The other half was not told about the side effects and was placed in a waiting room with a man acting either euphoric or irritated. The participants in the second group caught the emotion that the man was feeling and attributed the side effects of the injection to feeling either happy or irritated. emotion felt was based on how it was labeled (cognition) Arousal fuels emotion; cognition channels it.
5 Cognition Does Not Always Precede Emotion What happen when we feel an unlabeled emotion? o Ex: a bad feeling that cannot be labeled; you know there s a reason for it but you can t put your finger on it. Robert Zajonc we feel emotional reactions apart from, or before, our interpretations of the situation. o Ex: people subliminally flashed a picture of a happy looking face drank 50% more fruit flavored drink than those flashed a neutral face while the group flashed a angry looking face drank substantially less than both groups. emotions can precede cognitive awareness of them o Demonstrates the speedy/immediate low road (sensory input goes directly to the thalamus then the amygdala to trigger a rapid reaction that is often out of our conscious awareness) Richard Lazarus some emotional responses do not require conscious thinking but can be unconsciously appraised and labeled. o Demonstrates the thinking high road (sensory input goes from the thalamus to the sensory cortex, then prefrontal cortex to be appraised, then to the amygdale to trigger a reaction that can be out of conscious awareness but still appraised) o Feelings like guilt, happiness, and love complex emotions
6 Lie Detection Polygraph a machine, commonly used in attempts to detect lies, that measures several of the physiological responses accompanying emotion (such as perspiration and cardiovascular and breathing changes) Attempts to use physical indicators to indicate emotions Seen as increasingly questionable as our understanding of emotions has broadened Problems o Our physiological arousal is much the same from one emotion to the other o These tests err about 1/3 of the time, especially when innocent people respond with heightened tension to the accusations implied by the questions More than 9 in 10 psychophysiologists and psychologists agreed that savvy criminals and spies could beat the test by augmenting their arousal to questions More appropriate way to use a polygraph is with the guilty knowledge test assesses a suspect s physiological responses to crime-scene details known only to the police and the criminal Expressed Emotion People s expressive behaviors (expressions) can reveal their emotions. Does this nonverbal language vary with culture or is it universal? Do our expressions influence our experienced emotions? Nonverbal Communication Most people can detect nonverbal cues, especially those that indicate a threat (angry faces). o Can understand movies and TV on mute or in a different language We read fear and anger mostly in the eyes and happiness in the mouth Experience can sensitize us to recognizing certain emotions physically abused children are much quicker to recognize anger in a face; also more likely to perceive a face as angry if it is 40% anger and 60% fear. Gender, Emotion, and Nonverbal Behavior Women generally surpass men at reading nonverbal emotional cues and at detecting lies greater emotional literacy Women have a greater emotional responsiveness in both positive and negative situations; more likely to open up Women, far more than men, describe themselves as empathic (the ability to identify with others); also more likely to express empathy than men (cry or report distress when observing someone in distress) Women express emotion physically more than men. Detecting and Computing Emotion Some facial muscles are hard to manipulate consciously to display emotion o Worry/distress lifting just the inner part of your eyebrows o Fear eyebrows pulled together o Natural smile activated muscles under the eyes and raised cheeks Authentic expressions are quick, unlike fake smiles which can last 4-5 seconds The untrained eye can detect lying about 50% of the time random/chance
7 o Those trained to detect liars can detect lies with greater accuracy, while searching for cues for guilt, despair, and fear It is easier for us to detect emotions when we are not being deceived; but we need to be aware that body language cues can mean multiple things (ex: crossed arms can reveal irritation or relaxation) Nonverbal cues from facial expressions and body language are absent in computer-based communication (unless containing emoticons), and it can be easy to misread emotions and meanings in s or texts. Culture and Emotional Expression The meaning of gestures varies with cultures o Thumbs up, while a gesture of praise and positivity in North America, can be an insult in other cultures. Also, raising the middle finger (derogatory in North America) may not carry the same meaning in other cultures. Facial expressions carry basically the meaning in all cultures. o A smile conveys happiness; anger and fear are universal. o This similarity has nothing to do with shared experiences such as American movies, European news channels, etc. However, people of the same culture can more easily identify facial expressions of people of their own culture. Blind people, who have never seen facial expressions, also demonstrate the same facial expressions for certain emotions as seeing people. Universally, infants cry when distressed, smile when happy, and shake their heads when defiant. Evolutionary perspective o We share the same facial expressions because it was a common language that allowed our ancestors to communicate or detect threats. o Emotional expressions can enhance survival Surprise raises the eyebrows and widens the eyes to take in more information Disgust wrinkles the nose to close off the airway to foul smelling or dangerous odors The expression of emotions in public and their intensity changes between cultures o People of Western cultures tend to display more emotion than people from Japan. The Effects of Facial Expressions Expressions not only communicate emotion, but amplify and regulate it. o Facial feedback hypothesis - making certain facial expressions can make you feel the effects of the conveyed emotion. Smiling can make you happier. o Behavior feedback hypothesis - going through the motions awakens the emotions If we move our body as if we were experiencing an emotion, we are likely to feel that emotion to some degree. Emotion Biological Psychological Socio-cultural Physiological arousal Cognitive labeling Expressiveness Evolutionary adaptiveness Gender differences Presence of others Response pathways in the brain Cultural expectations Spillover effect
8 Experienced Emotion How many emotions are there? o Carroll Izard 10 basic emotions (joy, interest-excitement, surprise, sadness, anger, disgust, contempt, fear, shame, and guilt) o Some psychologists believe pride and love are also basic emotions Two dimensions of emotions o Arousal (high or low) o Valence (pleasant or unpleasant) Fear Fear can be poisonous, contagious, and fatal. o 1903 fire in Chicago s Iroquois theater a small fire caused more than 500 people to die, not from the fire but from being trampled by others due to fear. Fear is adaptive the body s alarm system that prepares us to flee from danger (real or imagined) Learning Fear Learning fear through conditioning o Little Albert o Crawling leads infants to gradually fear heights through falls and near-falls o Any experience can lead to a conditioned fear Learning fear through observation o Wild monkeys fear snakes while lab monkeys do not lab monkeys observed wild monkeys fearful behavior around snakes and learned to fear snakes from this observation. o 9/11 produced a fear of flying from the observation of such a traumatic event. o Sandy Hook students scared of school after observing shooting. (NPR Shootings Leave Sandy Hook Survivors Rethinking the Odds fear could be explained by conditioned or observationally learning). The Biology of Fear We may be biologically prepared to learn certain fears more quickly than others. o Snakes, spiders, cliffs, etc fears that probably helped our ancestors survive o Unprepared for new-age dangers like cars, electricity, bombs, global warming all of which are now far more dangerous Amygdala in the limbic system (emotion), deals with fear and aggression o Associates fears with specific situations o Receives input from cortical areas that process emotion and sends output information to other areas that produce the bodily symptoms of fear Phobia an intense fear of objects or situations that disrupts the ability to cope Fear may be genetically influenced o Scientists have found a gene, that when shorter in some people, experience more fear due to decreased serotonin absorption.
9 Anger Anger usually stems from a reaction to something someone has done, especially when the act is seen as having ill intentions. Anger can also stem from blameless annoyances like foul smells, traffic, high temperatures, etc. Boys report resolving anger with exercise while girls resolve anger by talking with a friend, listening to music, or writing. Anger can lead to aggression, prejudice, and illness. Western cultures encourage anger venting, while not encouraged in collectivist cultures. Catharsis emotional release; can be achieved through venting anger an aggressive way or fantasy o Expressing anger towards the cause/blame for the anger can be helpful if it does not leave us feeling guilty or anxious. o However, catharsis can lead to more anger by provoking more retaliation, magnifying anger (expressing anger makes you feel the anger behavior feedback hypothesis) Venting to reduce anger is like using gasoline to put out a fire. Brad Bushman, studied anger What is the best way to handle anger? o Wait and let the emotion simmer. o Find appropriate outlets for anger instead of ruminating on it (exercise, talking with a friend, etc) o Form nonaccusatory statements to discuss anger (I get irritated when dirty dishes are left in the sink.) Happiness People who are happy perceive the world as safer, make decisions more easily, rate job applicants more favorably, are more cooperative, and live healthier, more energized and satisfied lives. When your mood is gloomy, life as a whole seems more depressing (remember state-dependent memories?) When we feel happy we are more likely to help others. o Feel-good-do-good phenomenon people s tendency to be helpful when already in a good mood. Subjective well-being self-perceived happiness or satisfaction with life; used along with objective well-being which focuses on physical and economic indicators. The Short Life of Emotional Ups and Downs Positive emotions rise over the early to middle part of the day, while negative emotions are common just after waking and just before falling asleep. Moods triggered by good or bad events seldom last beyond that day. People tend to rebound from bad days with better-than-usual good days. Significant bad events can cause prolonged sadness, but we adapt and can return to average levels of day-to-day happiness. Wealth and Well-Being Wealth can increase short-term happiness, but has not been seen to increase long-term happiness. Two Psychological Phenomena: Adaptation and Comparison Adaptation-level phenomenon our tendency to form judgments relative to a neutral level defined by our prior experience. o The neutral point fluctuates depending on events in one s life. Relative deprivation the perception that one is worse off relative to those with whom one compares oneself. o Sports stars or celebrities that complain that they aren t paid enough.
10 Predictors of Happiness Happiness (and all emotions) is a biopsychosocial phenomenon. o Biological genetics, brain activity o Psychological outlooks, interpretation of experiences o Cultural emotional expression (how much or little) varies with cultures How to be Happier Realize happiness does not stem from money or wealth. Take control of your time (set goals, short and long term) Act happy Seek work and leisure that engage your skills. Exercise. Sleep enough. Form and value close relationships Do good feel good Be grateful Nurture your spiritual self.
Where do emotions come from? What are they made of? Why do we have them? ADAPTIVE - Survival. Emotion. AP Psych Myers Ch. 13
 Where do emotions come from? What are they made of? Why do we have them? ADAPTIVE - Survival Emotion AP Psych Myers Ch. 13 Emotion A response of the whole organism, involving physiological arousal expressive
Where do emotions come from? What are they made of? Why do we have them? ADAPTIVE - Survival Emotion AP Psych Myers Ch. 13 Emotion A response of the whole organism, involving physiological arousal expressive
Theories and Physiology of Emotion. AP Psychology Module 41
 Theories and Physiology of Emotion AP Psychology Module 41 Theories of Emotion Use your textbook to research the 5 theories of emotion and examples of each. Note the time difference in the research our
Theories and Physiology of Emotion AP Psychology Module 41 Theories of Emotion Use your textbook to research the 5 theories of emotion and examples of each. Note the time difference in the research our
Emotion. Emotion. Theories of Emotion. Chapter 13. Emotion. James-Lange Theory of Emotion
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 13 James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Theories
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 13 James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Theories
MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION
 MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION EMOTION: a response of the whole organism, involving 1. physiological arousal 2. expressive behaviors, and 3. conscious experience A mix of bodily arousal
MODULE 41: THEORIES AND PHYSIOLOGY OF EMOTION EMOTION: a response of the whole organism, involving 1. physiological arousal 2. expressive behaviors, and 3. conscious experience A mix of bodily arousal
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 12: Emotions, Stress, & Health pp
 Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 12: Emotions, Stress, & Health pp. 497-549 A QUESTION to consider BEFORE you read pp. 497-499: What are the components of emotion? READ Emotions, Stress & Heath and
Name: Period: Reading Guide Chapter 12: Emotions, Stress, & Health pp. 497-549 A QUESTION to consider BEFORE you read pp. 497-499: What are the components of emotion? READ Emotions, Stress & Heath and
Scientists have identified subtle differences in the brain circuits and hormones associated with different emotions. 2
 1 Scientists have identified subtle differences in the brain circuits and hormones associated with different emotions. 2 The polygraph has proved to be extremely effective in detecting lies. 3 Some emotional
1 Scientists have identified subtle differences in the brain circuits and hormones associated with different emotions. 2 The polygraph has proved to be extremely effective in detecting lies. 3 Some emotional
Characteris$cs of Emo$ons
 Emo$on Characteris$cs of Emo$ons Emo$ons are a mix of Physiological ac$va$on Expressive behaviors Conscious experience Theories of Emo$on James- Lange Emo$onal s$mulus causes physiological reac$on Physiological
Emo$on Characteris$cs of Emo$ons Emo$ons are a mix of Physiological ac$va$on Expressive behaviors Conscious experience Theories of Emo$on James- Lange Emo$onal s$mulus causes physiological reac$on Physiological
AP Psychology Guided Reading Unit 8B Emotions, Stress, and Health
 Unit 8B - 1 3Name: Period: SECTION 1 THEORIES OF EMOTION 1. What are emotions? AP Psychology Guided Reading Unit 8B Emotions, Stress, and Health 2. What are the two controversies over the interplay of
Unit 8B - 1 3Name: Period: SECTION 1 THEORIES OF EMOTION 1. What are emotions? AP Psychology Guided Reading Unit 8B Emotions, Stress, and Health 2. What are the two controversies over the interplay of
EMOTION. Joy, Sorrow, Anger, Fear, Love, Hate, Happiness
 EMOTION Joy, Sorrow, Anger, Fear, Love, Hate, Happiness Defining Characteristics Most psychologists see emotion as psychological and physiological reactions to changes in our relationship with the world.
EMOTION Joy, Sorrow, Anger, Fear, Love, Hate, Happiness Defining Characteristics Most psychologists see emotion as psychological and physiological reactions to changes in our relationship with the world.
Chapter 11 Emotion. Emotion. The Nature of Emotion
 Chapter 11 Emotion Emotion Emotions are temporary experiences with either positive, negative, or mixed qualities. People experience emotion with varying intensity as happening to them, as generated in
Chapter 11 Emotion Emotion Emotions are temporary experiences with either positive, negative, or mixed qualities. People experience emotion with varying intensity as happening to them, as generated in
Chapter 7 Motivation and Emotion
 Chapter 7 Motivation and Emotion Emotion Emotion a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Eight Basic Emotions Fear Surprise Disgust Anger Sadness
Chapter 7 Motivation and Emotion Emotion Emotion a response of the whole organism physiological arousal expressive behaviors conscious experience Eight Basic Emotions Fear Surprise Disgust Anger Sadness
EMOTIONS S E N I O R S P E C I A L I S T I N P S Y C H I A T R Y A N D S E X T H E R A P Y
 EMOTIONS C O L. S A E D S H U N N A Q S E N I O R S P E C I A L I S T I N P S Y C H I A T R Y A N D S E X T H E R A P Y EMOTIONS Emotion is any conscious experience characterized by intense mental activity
EMOTIONS C O L. S A E D S H U N N A Q S E N I O R S P E C I A L I S T I N P S Y C H I A T R Y A N D S E X T H E R A P Y EMOTIONS Emotion is any conscious experience characterized by intense mental activity
Emotion Theory. Dr. Vijay Kumar
 Emotion Theory Dr. Vijay Kumar Emotions Just how many emotions are there? Basic Emotions Some have criticized Plutchik s model as applying only to English-speakers Revised model of basic emotions includes:
Emotion Theory Dr. Vijay Kumar Emotions Just how many emotions are there? Basic Emotions Some have criticized Plutchik s model as applying only to English-speakers Revised model of basic emotions includes:
Introduction to Psychology. Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS
 Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS o Derived from the Latin word Emovere emotion means to excite, stir up or agitate. o A response that includes feelings such as happiness, fear, sadness, grief, sorrow etc: it is
Lecture no: 27 EMOTIONS o Derived from the Latin word Emovere emotion means to excite, stir up or agitate. o A response that includes feelings such as happiness, fear, sadness, grief, sorrow etc: it is
Emotion. Chapter 13. Emotion. Emotion. Emotion. Myers PSYCHOLOGY. Theories of Emotion. Outline. Theory of Emotion. Theory of.
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 13 C13:1 Response of whole organism to pleasant and aversive events of different types Happiness, Sadness, Fear, Anger, Three elements Physiological arousal Expressive behaviors
Myers PSYCHOLOGY Chapter 13 C13:1 Response of whole organism to pleasant and aversive events of different types Happiness, Sadness, Fear, Anger, Three elements Physiological arousal Expressive behaviors
Introduction to Emotion
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Introduction to Emotion Module 38 2 Emotion Theories of Emotion Embodied
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Introduction to Emotion Module 38 2 Emotion Theories of Emotion Embodied
Practice Question MOTIVATION AND EMOTION. Motivation as Drives. Motivation 10/22/2012
 Practice Question Gabriela s mother practices the authoritative style of parenting. This suggests that Gabriela s mother. MOTIVATION AND EMOTION Motivation Motivation as Drives Purpose or cause of an action
Practice Question Gabriela s mother practices the authoritative style of parenting. This suggests that Gabriela s mother. MOTIVATION AND EMOTION Motivation Motivation as Drives Purpose or cause of an action
Unit 8 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. Ten-year-old Vito tells his friend, When you notice that your knees knock, your hands sweat, and your stomach is in knots, then you really get scared. This statement best illustrates the
Name: Date: 1. Ten-year-old Vito tells his friend, When you notice that your knees knock, your hands sweat, and your stomach is in knots, then you really get scared. This statement best illustrates the
Chapter Eight: Emotion and Motivation
 Chapter Eight: Emotion and Motivation Emotions Four Part Process of Emotion 1. Physiological arousal of the body 2. Cognitive Interpretation of events and feelings conscious and unconscious 3. Subjective
Chapter Eight: Emotion and Motivation Emotions Four Part Process of Emotion 1. Physiological arousal of the body 2. Cognitive Interpretation of events and feelings conscious and unconscious 3. Subjective
Emotions and Motivation
 Emotions and Motivation LP 8A emotions, theories of emotions 1 10.1 What Are Emotions? Emotions Vary in Valence and Arousal Emotions Have a Physiological Component What to Believe? Using Psychological
Emotions and Motivation LP 8A emotions, theories of emotions 1 10.1 What Are Emotions? Emotions Vary in Valence and Arousal Emotions Have a Physiological Component What to Believe? Using Psychological
A musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately at peace with himself.
 A musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately at peace with himself. What a man can be, he must be. -Abraham Maslow Can you tell me what Maslow is describing?
A musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately at peace with himself. What a man can be, he must be. -Abraham Maslow Can you tell me what Maslow is describing?
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 9 Motivation and Emotion 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 9.1 What Motivates Our Behavior? The words emotion
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 9 Motivation and Emotion 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 9.1 What Motivates Our Behavior? The words emotion
General Psych Thinking & Feeling
 General Psych Thinking & Feeling Piaget s Theory Challenged Infants have more than reactive sensing Have some form of discrimination (reasoning) 1-month-old babies given a pacifier; never see it Babies
General Psych Thinking & Feeling Piaget s Theory Challenged Infants have more than reactive sensing Have some form of discrimination (reasoning) 1-month-old babies given a pacifier; never see it Babies
Psychology Chapter 12 Study Guide
 Psychology Chapter 12 Study Guide Emotion is a full body/mind/behavior response to a situation Theories of emotion James-Lange theory body before thoughts Cannon-Bard theory body with thoughts Singer-Shater
Psychology Chapter 12 Study Guide Emotion is a full body/mind/behavior response to a situation Theories of emotion James-Lange theory body before thoughts Cannon-Bard theory body with thoughts Singer-Shater
Motivation. Notes by E & V 2015 Unit 10: Motivation & Emotion
 Notes by E & V 2015 Unit 10: Motivation & Emotion Motivation What is Motivation? Motivation: the factors that energize and direct the behavior of organisms (includes day-to-day things); a need or desire
Notes by E & V 2015 Unit 10: Motivation & Emotion Motivation What is Motivation? Motivation: the factors that energize and direct the behavior of organisms (includes day-to-day things); a need or desire
Emotions, Stress, and Health
 Emotion Emotions are our body's adaptive response. Emotions, Stress, and Health Chapter 12 Theories of Emotion Emotions are a mix of 1) physiological activation, 2) expressive behaviors, and 3) conscious
Emotion Emotions are our body's adaptive response. Emotions, Stress, and Health Chapter 12 Theories of Emotion Emotions are a mix of 1) physiological activation, 2) expressive behaviors, and 3) conscious
drive-reduction theory
 motivation hierarchy of neds instinct glucose drive-reduction theory set point homeostasis basal metabolic rate incentive anorexia nervosa 1a Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with
motivation hierarchy of neds instinct glucose drive-reduction theory set point homeostasis basal metabolic rate incentive anorexia nervosa 1a Maslow's pyramid of human needs, beginning at the base with
Name: Period: Chapter 11 & 12 Reading Guide Motivation, Emotion, & Stress
 Name: Period: Chapter 11 & 12 Reading Guide Motivation, Emotion, & Stress Introduction & Motivational Concepts (pg. 443-447) 1. Motivation: Theories of Motivation 2. Instinct: 3. What is the underlying
Name: Period: Chapter 11 & 12 Reading Guide Motivation, Emotion, & Stress Introduction & Motivational Concepts (pg. 443-447) 1. Motivation: Theories of Motivation 2. Instinct: 3. What is the underlying
Emotion. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers. Emotion. Chapter 13. Theories of Emotion. Embodied Emotion
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Emotion Chapter 13 2 Emotion Theories of Emotion Embodied Emotion Emotions and The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2006 1 Emotion Chapter 13 2 Emotion Theories of Emotion Embodied Emotion Emotions and The
Psychology for Nurses EMOTION. By Dr. Hayder Al-hadrawi University of Babylon, College of Nursing
 Psychology for Nurses EMOTION By Dr. Hayder Al-hadrawi University of Babylon, College of Nursing 2016-2017 4 Aristotle s meaning of emotion Any body can become ANGRY that is easy, but to be angry with
Psychology for Nurses EMOTION By Dr. Hayder Al-hadrawi University of Babylon, College of Nursing 2016-2017 4 Aristotle s meaning of emotion Any body can become ANGRY that is easy, but to be angry with
Chapter 12,13 &14. Motivation, Emotion, Stress & Health
 Chapter 12,13 &14 Motivation, Emotion, Stress & Health Motivation Motivation a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior Instinct complex behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species
Chapter 12,13 &14 Motivation, Emotion, Stress & Health Motivation Motivation a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior Instinct complex behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species
PSYC 222 Motivation and Emotions
 PSYC 222 Motivation and Emotions Session 6 The Concept of Emotion Lecturer: Dr. Annabella Osei-Tutu, Psychology Department Contact Information: aopare-henaku@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
PSYC 222 Motivation and Emotions Session 6 The Concept of Emotion Lecturer: Dr. Annabella Osei-Tutu, Psychology Department Contact Information: aopare-henaku@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing
Motivation and Emotion deals with the drives and incentives behind everyday thoughts and actions.
 Motivation and Emotion deals with the drives and incentives behind everyday thoughts and actions. Motivation- A need or desire that energizes and directs behavior primarily based on our instincts that
Motivation and Emotion deals with the drives and incentives behind everyday thoughts and actions. Motivation- A need or desire that energizes and directs behavior primarily based on our instincts that
The innate hypothesis
 The innate hypothesis DARWIN (1872) proposed that the facial expression of emotion evolved as part of the actions necessary for life: Anger: Frowning (to protect eyes in anticipation of attack) Surprise:
The innate hypothesis DARWIN (1872) proposed that the facial expression of emotion evolved as part of the actions necessary for life: Anger: Frowning (to protect eyes in anticipation of attack) Surprise:
Emotions. These aspects are generally stronger in emotional responses than with moods. The duration of emotions tend to be shorter than moods.
 LP 8D emotions & James/Lange 1 Emotions An emotion is a complex psychological state that involves subjective experience, physiological response, and behavioral or expressive responses. These aspects are
LP 8D emotions & James/Lange 1 Emotions An emotion is a complex psychological state that involves subjective experience, physiological response, and behavioral or expressive responses. These aspects are
Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Typically, this unit is described as a goal
 Motivation What is motivation? Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Reasons here implies some sort of desired end state Typically, this unit is described as a goal
Motivation What is motivation? Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Reasons here implies some sort of desired end state Typically, this unit is described as a goal
Emotion. Emotion. Theories of Emotion. Controversy. James-Lange Theory. Commonsense View. Chapter 13 Psy Spring, 2009
 Emotion Emotions are our body s adaptive response. They help energize, they communicate, they give us and others warnings. Emotion Chapter 13 Psy12000.003 Spring, 2009 1 Theories of Emotion 2 Controversy
Emotion Emotions are our body s adaptive response. They help energize, they communicate, they give us and others warnings. Emotion Chapter 13 Psy12000.003 Spring, 2009 1 Theories of Emotion 2 Controversy
Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition. Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AK
 Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AK The wheel allows him to show how he thinks these emotions blend with each other to form more complicated ones.
Unit Three: Behavior and Cognition Marshall High School Mr. Cline Psychology Unit Three AK The wheel allows him to show how he thinks these emotions blend with each other to form more complicated ones.
Overview. Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions
 Emotion Overview Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions Definition of Emotion Emotions are biologically-based responses
Emotion Overview Basic concepts Theories of emotion Universality of emotions Brain basis of emotions Applied research: microexpressions Definition of Emotion Emotions are biologically-based responses
Motivation an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal
 Chapter 12 Motivation and Emotion Sec 1: Theories of Motivation Motivation an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal 1. Instinct Theory a. Instincts innate tendencies that
Chapter 12 Motivation and Emotion Sec 1: Theories of Motivation Motivation an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal 1. Instinct Theory a. Instincts innate tendencies that
Emotion. Emotion. Theories of Emotion. Controversy. Commonsense View. James-Lange Theory. Chapter 12 Psy Spring, 2010
 Emotion Emotions are our body s adaptive response. They help energize, they communicate, they give us and others warnings. Emotion Chapter 12 Psy12000.003 Spring, 2010 1 Theories of Emotion 2 Controversy
Emotion Emotions are our body s adaptive response. They help energize, they communicate, they give us and others warnings. Emotion Chapter 12 Psy12000.003 Spring, 2010 1 Theories of Emotion 2 Controversy
Biological Psych Emotions. Limbic System Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Gland Amygdala
 Biological Psych Emotions Limbic System Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Gland Amygdala Amygdala Also called nucleus amygdalæ Almond-shaped groups of nuclei Medial temporal lobes Part of basal ganglia?
Biological Psych Emotions Limbic System Thalamus Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Gland Amygdala Amygdala Also called nucleus amygdalæ Almond-shaped groups of nuclei Medial temporal lobes Part of basal ganglia?
Chapter 8. What Is Emotion? What Do Our Emotions Do For Us? Emotion and Motivation
 Chapter 8 Emotion and Motivation This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission
Chapter 8 Emotion and Motivation This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission
Emotion. I. Mood vs. Affect/emotion
 I. Mood vs. Affect/emotion Emotion A. Mood: enduring disposition B. Affect/emotion: transient, reaction to stimuli. Components: 1. Subjective experience 2. Internal physiological responses 3. Belief or
I. Mood vs. Affect/emotion Emotion A. Mood: enduring disposition B. Affect/emotion: transient, reaction to stimuli. Components: 1. Subjective experience 2. Internal physiological responses 3. Belief or
The Importance of the Mind for Understanding How Emotions Are
 11.3 The Importance of the Mind for Understanding How Emotions Are Embodied Naomi I. Eisenberger For centuries, philosophers and psychologists alike have struggled with the question of how emotions seem
11.3 The Importance of the Mind for Understanding How Emotions Are Embodied Naomi I. Eisenberger For centuries, philosophers and psychologists alike have struggled with the question of how emotions seem
Motivation and Emotion
 Motivation and Emotion Definitions Motivation: what drives us to seek a specific goal Emotion: a state of body that causes feelings. Both involve physiological and psychological factors. Physiological
Motivation and Emotion Definitions Motivation: what drives us to seek a specific goal Emotion: a state of body that causes feelings. Both involve physiological and psychological factors. Physiological
Myers Psychology for AP, 2e
 Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014 AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP, 2e David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2014 AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Biological Psychology Unit Two AB Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology What happens in your nervous system when you react to stimuli? Did you know that the brain is sometimes uninvolved with reflexes?
Dikran J. Martin. Psychology 110. Name: Date: Principal Features. Question: What is drive theory of motivation? (373)
 Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 10 Motivation and Emotion Pages: 21 TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition). Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon. Principal
Dikran J. Martin Psychology 110 Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 10 Motivation and Emotion Pages: 21 TEXT: Baron, Robert A. (2001). Psychology (Fifth Edition). Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon. Principal
autonomic ne rvous system The autonomic ne rvous system The autonomic ne rvous system Pa rasympathetic Sympathetic
 Chapter 5: Bodily Changes and Emotion William James contended that an emotionally exciting fact provokes bodily responses, which in turn lead to the experience of emotion My thesis is that the bodily changes
Chapter 5: Bodily Changes and Emotion William James contended that an emotionally exciting fact provokes bodily responses, which in turn lead to the experience of emotion My thesis is that the bodily changes
Motivation and Emotion
 Motivation and Emotion Motivation Vocabulary Terms MOTIVATION an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal INSTINCTS innate tendencies that determine behavior NEED a biological
Motivation and Emotion Motivation Vocabulary Terms MOTIVATION an internal state that activates behavior and directs it toward a goal INSTINCTS innate tendencies that determine behavior NEED a biological
Drive-reducing behaviors (eating, drinking) Drive (hunger, thirst) Need (food, water)
 Instinct Theory: we are motivated by our inborn automated behaviors that generally lead to survival. But instincts only explain why we do a small fraction of our behaviors. Does this behavior adequately
Instinct Theory: we are motivated by our inborn automated behaviors that generally lead to survival. But instincts only explain why we do a small fraction of our behaviors. Does this behavior adequately
Chapter 11 Motivation and Emotion
 Chapter 11 Motivation and Emotion Copyright 2001 by McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Motivation! What is motivation?! Motivation involves the question of why people behave, think, and feel the way they do!
Chapter 11 Motivation and Emotion Copyright 2001 by McGraw-Hill Ryerson Limited Motivation! What is motivation?! Motivation involves the question of why people behave, think, and feel the way they do!
Emotions. What makes you ick? What makes you love?
 Emotions What makes you ick? What makes you love? Where we are headed: What are four theories of emotion? common sense theory - Cannon-Bard theory James-Lange theory - Two-factor theory ALL DEAL WITH
Emotions What makes you ick? What makes you love? Where we are headed: What are four theories of emotion? common sense theory - Cannon-Bard theory James-Lange theory - Two-factor theory ALL DEAL WITH
Emotion 1. Cognition and Emotion
 Emotion 1 Cognition and Emotion Objective 12-1: Describe how arousal and expressive behaviors interact in emotion. 1. Emotions have three components:,, and 2. According to the James-Lange theory, emotional
Emotion 1 Cognition and Emotion Objective 12-1: Describe how arousal and expressive behaviors interact in emotion. 1. Emotions have three components:,, and 2. According to the James-Lange theory, emotional
DEFINING EMOTION 11/19/2009 THE BIOLOGY OF EMOTION & STRESS. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense.
 DEFINING EMOTION Emotion A feeling that differs from a person s normal affective state; a biological function of the nervous system. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense. An
DEFINING EMOTION Emotion A feeling that differs from a person s normal affective state; a biological function of the nervous system. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense. An
Motivation, Conflict, Emotion. Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry
 Motivation, Conflict, Emotion Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Motivation Motivation is the psychological feature that arouses an organism to action toward a desired goal and
Motivation, Conflict, Emotion Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Motivation Motivation is the psychological feature that arouses an organism to action toward a desired goal and
Nature of emotion: Five perennial questions. Motivation & Emotion Nature of emotion. Five questions. Outline Nature of emotion. Remaining chapters
 Motivation & Emotion Nature of emotion 1. What is an emotion? Five questions 2. What causes an emotion? 3. How many emotions are there? 4. What good are the emotions? Dr James Neill Centre for Applied
Motivation & Emotion Nature of emotion 1. What is an emotion? Five questions 2. What causes an emotion? 3. How many emotions are there? 4. What good are the emotions? Dr James Neill Centre for Applied
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 9 Motivation and Emotion 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 9.1 What Motivates Our Behavior? 9.1 What
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life FIRST EDITION Chapter 9 Motivation and Emotion 2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Section 9.1 What Motivates Our Behavior? 9.1 What
MODULE 43 & 44: STRESS AND HEALTH; STRESS AND ILLNESS
 MODULE 43 & 44: STRESS AND HEALTH; STRESS AND ILLNESS WHAT IS STRESS? the process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors. depends on how environmental events are appraised
MODULE 43 & 44: STRESS AND HEALTH; STRESS AND ILLNESS WHAT IS STRESS? the process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors. depends on how environmental events are appraised
MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI
 MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI August 7, 2017 Anxiety Anxiety is a normal human experience Anxiety which interferes with functionality is the definition of dysfunction What
MAXIMIZING PERFORMANCE BY MINIMIZING ANXIETY RICHARD BOGIELSKI August 7, 2017 Anxiety Anxiety is a normal human experience Anxiety which interferes with functionality is the definition of dysfunction What
Chapter 13: From Social Cognition to Affect
 Chapter 13: From Social Cognition to Affect 1. Which of the following refers to relatively mild subjective reactions that are essentially either pleasant or unpleasant? a. Bivalence. b. Moods. c. Preferences.
Chapter 13: From Social Cognition to Affect 1. Which of the following refers to relatively mild subjective reactions that are essentially either pleasant or unpleasant? a. Bivalence. b. Moods. c. Preferences.
References. Note: Image credits are in the slide notes
 References Reeve, J. (2009). Understanding motivation and (5th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. Tomkins, S. S. (1970) Affect as the primary motivational system. In M. B. Arnold (ed.), Feelings and s (pp. 101-110).
References Reeve, J. (2009). Understanding motivation and (5th ed.). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley. Tomkins, S. S. (1970) Affect as the primary motivational system. In M. B. Arnold (ed.), Feelings and s (pp. 101-110).
General Psychology 2/23/2010. What Is Motivation? Theories of Motivation. Lawrence D. Wright Ph.D. Professor. Chapter 6 Motivation and Emotion
 General Psychology Lawrence D. Wright Ph.D. Professor Chapter 6 Motivation and Emotion 6-1 What Is Motivation? Motivation: The aspects of motivation are a) b) c) Instincts: 6-2 Biological theories of motivation:
General Psychology Lawrence D. Wright Ph.D. Professor Chapter 6 Motivation and Emotion 6-1 What Is Motivation? Motivation: The aspects of motivation are a) b) c) Instincts: 6-2 Biological theories of motivation:
Emotion and Motivation. Chapter 8
 Emotion and Motivation Chapter 8 Motivation & Emotion in Historical Perspective Motivation and emotion are relatively new concepts: Motivation was a collection of other concepts, such as pleasure, lust,
Emotion and Motivation Chapter 8 Motivation & Emotion in Historical Perspective Motivation and emotion are relatively new concepts: Motivation was a collection of other concepts, such as pleasure, lust,
Elements of Communication
 Elements of Communication Elements of Communication 6 Elements of Communication 1. Verbal messages 2. Nonverbal messages 3. Perception 4. Channel 5. Feedback 6. Context Elements of Communication 1. Verbal
Elements of Communication Elements of Communication 6 Elements of Communication 1. Verbal messages 2. Nonverbal messages 3. Perception 4. Channel 5. Feedback 6. Context Elements of Communication 1. Verbal
Culture and Emotion THE EVOLUTION OF HUMAN EMOTION. Outline
 Outline Culture and Emotion The Evolution of Human Emotion Universality in Emotion- The Basic Emotions Perspective Cultural Differences in Emotion Conclusion Chapter 8 THE EVOLUTION OF HUMAN EMOTION Emotion:
Outline Culture and Emotion The Evolution of Human Emotion Universality in Emotion- The Basic Emotions Perspective Cultural Differences in Emotion Conclusion Chapter 8 THE EVOLUTION OF HUMAN EMOTION Emotion:
Outline. Emotion. Emotions According to Darwin. Emotions: Information Processing 10/8/2012
 Outline Emotion What are emotions? Why do we have emotions? How do we express emotions? Cultural regulation of emotion Eliciting events Cultural display rules Social Emotions Behavioral component Characteristic
Outline Emotion What are emotions? Why do we have emotions? How do we express emotions? Cultural regulation of emotion Eliciting events Cultural display rules Social Emotions Behavioral component Characteristic
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE QUESTIONNAIRE
 EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Report JOHN SMITH 2017 MySkillsProfile. All rights reserved. Introduction The EIQ16 measures aspects of your emotional intelligence by asking you questions
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Report JOHN SMITH 2017 MySkillsProfile. All rights reserved. Introduction The EIQ16 measures aspects of your emotional intelligence by asking you questions
Motivation and Emotion
 Motivation and Emotion Chapter 8 Motivation and Emotion I. What is Motivation II. III. How Does Motivation Affect Behavior? What is Emotion? IV. How Does Emotion Affect Behavior? What is Motivation? A
Motivation and Emotion Chapter 8 Motivation and Emotion I. What is Motivation II. III. How Does Motivation Affect Behavior? What is Emotion? IV. How Does Emotion Affect Behavior? What is Motivation? A
AP PSYCH Unit 8B.3 Happiness & Stress
 AP PSYCH Unit 8B.3 Happiness & Stress 1. What are the causes and consequences of happiness? 2. Is happiness healthy? 3. Are there levels of happiness that we can measure? 4. Why are countries like Denmark
AP PSYCH Unit 8B.3 Happiness & Stress 1. What are the causes and consequences of happiness? 2. Is happiness healthy? 3. Are there levels of happiness that we can measure? 4. Why are countries like Denmark
EMOTIONS MODULE-II OBJECTIVES 10.1 NATURE OF EMOTION. Emotions. Key Psychological Processes. Notes
 Emotions MODULE-II 10 EMOTIONS When we meet our friend after a long time we feel happy; when a baby clings to her mother she displays love, when we are praised by our parents or teachers we feel proud
Emotions MODULE-II 10 EMOTIONS When we meet our friend after a long time we feel happy; when a baby clings to her mother she displays love, when we are praised by our parents or teachers we feel proud
Emotion October 16th, 2009 : Lecture 11
 Lecture Overview October 16th, 2009 : Lecture 11 Finishing up Groups s Jury Decision Making Jury Decision Making Group Polarization and Group Think Group Decision Making and Juries Value of Unanimity 12
Lecture Overview October 16th, 2009 : Lecture 11 Finishing up Groups s Jury Decision Making Jury Decision Making Group Polarization and Group Think Group Decision Making and Juries Value of Unanimity 12
Basic Nervous System anatomy. Neurobiology of Happiness
 Basic Nervous System anatomy Neurobiology of Happiness The components Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral" Nervous System (PNS) Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Basic Nervous System anatomy Neurobiology of Happiness The components Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral" Nervous System (PNS) Somatic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The Emotional Nervous System
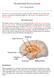 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
Learning Outcome: To what extent do cognitive and biological factors interact in emotion?
 Learning Outcome: To what extent do cognitive and biological factors interact in emotion? Schachter & Singer 1962: Two Factor Theory Aim: to challenge several theories of emotion and test the two factor
Learning Outcome: To what extent do cognitive and biological factors interact in emotion? Schachter & Singer 1962: Two Factor Theory Aim: to challenge several theories of emotion and test the two factor
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom //
 Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
Cognitive Level of Analysis - Cognition and Emotions
 Camden E. Gaultney Year 12 IB Higher Level Psychology Ms. Cruz The 16th of April, 2012 Cognitive Level of Analysis - Cognition and Emotions The Learning Outcome #30: To what extent do cognitive and biological
Camden E. Gaultney Year 12 IB Higher Level Psychology Ms. Cruz The 16th of April, 2012 Cognitive Level of Analysis - Cognition and Emotions The Learning Outcome #30: To what extent do cognitive and biological
Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews
 Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews Presenter: Martin TAYLOR Position: Senior Legal Specialist Australian Criminal Intelligence
Behavioural Indicators That Could Be Used To Detect Interviewee Deception In The Conduct Of Investigative Interviews Presenter: Martin TAYLOR Position: Senior Legal Specialist Australian Criminal Intelligence
Eating Disorder information:
 Eating Disorder information: The most common behavior that will lead to an eating disorder is dieting. Body shape and weight overly influence self-image It is estimated that currently 11% of high school
Eating Disorder information: The most common behavior that will lead to an eating disorder is dieting. Body shape and weight overly influence self-image It is estimated that currently 11% of high school
Healthier, greater sense of well being Less stress, more inner peace More focused, more easily access a flow state. Theta waves, 4 and 8 Hz
 SL #6 Wow. It s been 12 weeks since you started using Holosync. That s 3 months. What are you noticing? Please call us and have a chat with a support coach about what s happening. A month from the minimum
SL #6 Wow. It s been 12 weeks since you started using Holosync. That s 3 months. What are you noticing? Please call us and have a chat with a support coach about what s happening. A month from the minimum
Chapter 11. Motivation and Emotion
 Motivation and Emotion Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Motivation and Emotion Activating Behavior Meeting Biological Needs Hunger and Eating Sexual Behavior Expressing and Experiencing
Motivation and Emotion Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Motivation and Emotion Activating Behavior Meeting Biological Needs Hunger and Eating Sexual Behavior Expressing and Experiencing
Principles of Emotional Intervention 1 (Part2)
 Principles of Emotional Intervention 1 (Part2) Leslie S Greenberg, York University, Toronto. Manuscript MOOC Leuven University. Abstract: From the EFT perspective change occurs by helping people make sense
Principles of Emotional Intervention 1 (Part2) Leslie S Greenberg, York University, Toronto. Manuscript MOOC Leuven University. Abstract: From the EFT perspective change occurs by helping people make sense
1/12/2012. How can you tell if someone is experiencing an emotion? Emotion. Dr.
 http://www.bitrebels.com/design/76-unbelievable-street-and-wall-art-illusions/ 1/12/2012 Psychology 456 Emotion Dr. Jamie Nekich A Little About Me Ph.D. Counseling Psychology Stanford University Dissertation:
http://www.bitrebels.com/design/76-unbelievable-street-and-wall-art-illusions/ 1/12/2012 Psychology 456 Emotion Dr. Jamie Nekich A Little About Me Ph.D. Counseling Psychology Stanford University Dissertation:
Nineteen Relational Brain-Skills That Must Be Learned
 Nineteen Relational Brain-Skills That Must Be Learned Skill 1 Share Joy Mutual amplification of joy through nonverbal facial expressions and voice tone that conveys, We are glad to be together. This capacity
Nineteen Relational Brain-Skills That Must Be Learned Skill 1 Share Joy Mutual amplification of joy through nonverbal facial expressions and voice tone that conveys, We are glad to be together. This capacity
Signs of Acute Stress Disorder Symptom Behavioral Signs Support Needed
 APPENDIX G: A GUIDE TO RECOGNIZING ACUTE STRESS DISORDER IN POSTPARTUM WOMEN IN THE HOSPITAL SETTING Michelle Flaum Hall, EdD, LPCC-S, Xavier University INTRODUCTION The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual
APPENDIX G: A GUIDE TO RECOGNIZING ACUTE STRESS DISORDER IN POSTPARTUM WOMEN IN THE HOSPITAL SETTING Michelle Flaum Hall, EdD, LPCC-S, Xavier University INTRODUCTION The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual
Chapter 12 Emotions, Stress, and Health
 Chapter 12 Emotions, Stress, and Health PowerPoint Presentation by Jim Foley 2013 Worth Publishers Chapter Overview Emotions How emotions are related to cognition, and yet sometimes seem to bypass cognition
Chapter 12 Emotions, Stress, and Health PowerPoint Presentation by Jim Foley 2013 Worth Publishers Chapter Overview Emotions How emotions are related to cognition, and yet sometimes seem to bypass cognition
AP Psychology. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The subfield of psychology that provides psychology's contribution to the prevention and treatment of illness is known as A) medical psychology. B) health psychology. C) behavioral psychology.
Name: Date: 1. The subfield of psychology that provides psychology's contribution to the prevention and treatment of illness is known as A) medical psychology. B) health psychology. C) behavioral psychology.
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Psych 260
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Psych 260 Kim Sweeney ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260eve.html What is an emotion? appraisal experience physiological response behavior
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Psych 260 Kim Sweeney ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260eve.html What is an emotion? appraisal experience physiological response behavior
R E L A X. Y O U L L L I V E L O N G E R
 Stress and Health R E L A X. Y O U L L L I V E L O N G E R 15.1 What is stress? Event Response Perception Stress = anxious / threatening feeling resulting from appraisal of a situation and the reaction
Stress and Health R E L A X. Y O U L L L I V E L O N G E R 15.1 What is stress? Event Response Perception Stress = anxious / threatening feeling resulting from appraisal of a situation and the reaction
Timothy W. Pedigo, Ph.D. Psychology and Counseling Governors State University
 Timothy W. Pedigo, Ph.D. Psychology and Counseling Governors State University What is Mindfulness? What is Stress? And How Does Mindfulness Help with Stress? Mindfulness is a non-judgmental awareness of
Timothy W. Pedigo, Ph.D. Psychology and Counseling Governors State University What is Mindfulness? What is Stress? And How Does Mindfulness Help with Stress? Mindfulness is a non-judgmental awareness of
Expanding Mindfulness as a Core Treatment Skill for Men and Women With Cognitive Deficits Thomas G. Beckers BS, LADC Vinland Center
 Expanding Mindfulness as a Core Treatment Skill for Men and Women With Cognitive Deficits Thomas G. Beckers BS, LADC Vinland Center What Are We Going to Cover? To gain understanding of the nature of addiction
Expanding Mindfulness as a Core Treatment Skill for Men and Women With Cognitive Deficits Thomas G. Beckers BS, LADC Vinland Center What Are We Going to Cover? To gain understanding of the nature of addiction
Emotion Lecture 26 1
 Emotion Lecture 26 1 The Trilogy of Mind Immanuel Kant (1791); Hilgard (1980) There are three absolutely irreducible faculties of mind: knowledge, feeling, and desire. Cognition Knowledge and Beliefs Emotion
Emotion Lecture 26 1 The Trilogy of Mind Immanuel Kant (1791); Hilgard (1980) There are three absolutely irreducible faculties of mind: knowledge, feeling, and desire. Cognition Knowledge and Beliefs Emotion
Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (EIQ16)
 MSP Feedback Guide 2009 Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (EIQ16) Feedback to Test Takers Introduction (page 2 of the report) The Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (EIQ16) measures aspects of your
MSP Feedback Guide 2009 Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (EIQ16) Feedback to Test Takers Introduction (page 2 of the report) The Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire (EIQ16) measures aspects of your
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School
 Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
Mr. Stanley Kuna High School Stress What is Stress? Stress is - The mental, emotional, and physiological response of the body to any situation that is new, threatening, frightening, or exciting. Stress
Psychological. Psychological First Aid: MN Community Support Model Teen version. April 3, Teen Version
 Psychological First Teen Version Aid A Minnesota Community Support Model Why Should You Learn Psychological First Aid? Helps you to understand stress, and what it does to your mind and body Gives you simple
Psychological First Teen Version Aid A Minnesota Community Support Model Why Should You Learn Psychological First Aid? Helps you to understand stress, and what it does to your mind and body Gives you simple
Chapter 3 Self-Esteem and Mental Health
 Self-Esteem and Mental Health How frequently do you engage in the following behaviors? SCORING: 1 = never 2 = occasionally 3 = most of the time 4 = all of the time 1. I praise myself when I do a good job.
Self-Esteem and Mental Health How frequently do you engage in the following behaviors? SCORING: 1 = never 2 = occasionally 3 = most of the time 4 = all of the time 1. I praise myself when I do a good job.
Emotional State Recognition via Physiological Measurement and Processing
 APPLICATION NOTE 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 Tel (805) 685-0066 Fax (805) 685-0067 info@biopac.com www.biopac.com Application Note 276: Emotional State Recognition via Physiological Measurement and
APPLICATION NOTE 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 Tel (805) 685-0066 Fax (805) 685-0067 info@biopac.com www.biopac.com Application Note 276: Emotional State Recognition via Physiological Measurement and
Emotion, Stress, and Health
 CHAPTER 12 Emotion, Stress, and Health Preview Emotions are psychological responses that involve an interplay among (1) physiological arousal, (2) expressive behavior, and (3) conscious experience. James
CHAPTER 12 Emotion, Stress, and Health Preview Emotions are psychological responses that involve an interplay among (1) physiological arousal, (2) expressive behavior, and (3) conscious experience. James
