Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
|
|
|
- Kristopher Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2 : please go back and see the pictures because i didn't include them. #3: doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions. Good luck
2 Slides are in Bold before we start, in the last lecture when we talked about Spinal shock : 1- all the reflexes will be shutdown 2- upper motor neuron lesion will appear directly after chronic injury to the spine Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia include the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus and number of closely related nuclei.. there is other nuclei we will take them. They influence motor system primarily through projections to upper motor neurons Motor deficits depend on the specific nucleus damaged Understanding the neurochemistry of basal ganglia drives the development of clinical treatment Remember the hierarchy in the last lecture the beginning of motor system was in cerebellum and basal ganglia. The basal ganglia act as Brake against involuntary movement Switch to turn on a fixed action pattern Their major output is to the VA of the thalamus Projects primarily to area 6 (premotor & supplementary motor areas).. there is other functions but we will focus on motor. Important in smoothness of movement, so if it is disrupted, there will be movement but it will not be smooth and it will be hard یعني مثال بدك تمسك كا س, بدایة الحركة من basal ganglia یعني لو انضربت رح یكون في تردد في البدایة Basal Ganglia Terminology they are all close to each other Striatum (neostriatum) = caudate + putamen Lentiform nucleus = putamen + globus pallidus Corpus striatum = caudate + lentiform Basal ganglia = corpus striatum + amygdala Globus pallidus = pallidum = paleostriatum Claustrum is some times included with the basal ganglia Basal ganglia is included by the extrapyramidal system Basal Ganglia: Gross Anatomy Caudate nucleus Parts.. 1- head of caudate nucleus, largest part, and 2- ends with tail. As you go to tail the caudate will decrease in size. Location Relations Lateral ventricle.. part of lateral wall of lateral ventricle. Amygdaloid nucleus.. found near the end of the caudate nucleus (tail).
3 Lentiform nucleus Parts Putamen Globus pallidus.. medial to putamen Internal (GPi).. medial to external one External (GPe) Shape Location Relations External & internal capsules.. external capsule is association fibers whereas internal capsule is projection fibers Claustrum.. found after external capsule, close to Insula Amygdaloid nucleus Subthalamic nucleus.. found inferior to thalamus, superior to midbrain, posterior to hypothalamus Substantia nigra Pars reticulata (SNr) Pars compacta (SNc) Claustrum Caudate with putamen it is straitum, the most anterior part of this straitum called ventral striatum, it is the same "nucleus accumbens" Basal Ganglia Circuitry.. we will take function quickly and more info will be taken in physiology Inputs Most inputs enter the striatum From cerebral cortex & thalamus These inputs are excitatory Outputs Most leave from Gpi & SNr.. globus pallidus internal &substantia nigra reticulata Most go to VA nucleus of the thalamus, which projects to motor cortex The outputs are GABAergic and inhibitory VA excites motor cortex, leading to movements Increase basal ganglia output will inhibit the VA and reduce overall movements Basal Ganglia Circuitry Intrinsic Circuits Large number of connections between components of the basal ganglia Can be grouped into
4 Direct pathway Indirect pathway These pathways affect the VA activity and thus the motor cortex Activity The Direct Pathway From striatum to Gpi.. input to striatum is excitatory Uses GABA, which inhibits another GABAergic projection (Gpi to VA) Disinhibition Cortical activity direct pathway Gpi activity VA activity Activity in the direct pathway leads to increased motor cortex activity and increased movements As we said the output of basal ganglia to Ventral anterior is inhibitory, so, if we inhibit this process (inhibition of inhibition) that s mean excitation so the ventral anterior nucleus activity will increased. بالعربي اذا ما وصلت الفكرة, طبیعة المسار العصبي ھو تثبیطي, احنا عملنا تثبیط لھذا المسار ) يعني تثبیط للمسار الي اصلا ھو تثبیطي) بالتالي بشكل عام بكون تحفیزي The Indirect Pathway Goes from striatum to GPe (GABA) to the subthalamic nucleus (GABA) Subthalamic nucleus to Gpi (Glu) activity in the cortex activity of subthalamic nu. GPi VA activity motor cortex activity Here in indirect the opposite, again we said the output is inhibitory, but here we didn't inhibit the output, here we increase it! so we increase the inhibiton, so the ventral anterior nucleus activity will decrease so the movements will decrease. so in the end direct pathway --> increase movements indirect pathway --> decrease movements
5 Basal Ganglia Circuitry The direct pathway increase movements The indirect pathway decrease movements Normal behavior requires a balance between the direct and indirect pathways All pathways are uncrossed Right basal ganglia modulate right cortex and affect movements on the left side of the body Acetylcholine is used by the interneurons in the striatum It affect the output of the direct and indirect pathways It s a target for drug therapy Nigrostriatal Pathway In the striatum different cell types give rise to the direct and indirect pathways Both cell types receive dopaminergic input from SN pars compacta These cells have different receptors for DA For direct pathway, DA excites the striatal cells For indirect pathway, DA inhibits the striatal cells Thus the nigrostriatal pathway the activity of the VA and motor cortex PD leads to.. direct pathway activity indirect pathway activity activity of VA and motor cortex Here we are talking about substantia nigra compacta NOT reticulata this reticulata affect both direct and indirect pathway Overall this Nigrostriatal pathway INCREASE the VA and movements How?? it excites the direct pathway وھو اصلا تحفیزي يعني رح يزداد نشاطه it inhibit the indirect pathway وھو اصلا تثبیطي, فاحنا ثبطناه (تثبیط التثبیط) فطلع بالنھاية تحفیزي so in the end it will excite VA and the movements all these processes are on Dopamine receptor In parkinson disease the opposite occur!!
6 Cerebellum.. important in movements, mostly close in function to basal ganglia Cerebellum The cerebellum is essential for normal movements It affects motor behavior by affecting UMNs The cerebellum acts as a comparator Compares intended movements (data from cerebral cortex) to the actual movements (sensory data) Sends corrective signals into the descending motor Pathways Remember basal ganglia was initiator for movements but cerebellum for modification of movements یعني تدارك الحركات الي اصلا موجودة نرجع لمثال الكا س, بعد ما مسكتھ حسیت انھ بده یقع فالحركة الي عملتھا حتى ما cerebellum یقع وتداركت الموقف ھاي جایة من ال Cerebellar Function.. it has close association with vestibular nuclei for balance during movements It affects all movements, it is important in: Balance Locomotion Simple & complex movements Eye movements, etc. Site of motor learning Important for learning new motor skills and adjusting movements to changing sensory inputs Cerebellar Anatomy Gross Anatomy Location. Relations.. doctor said we already know the location and relations in previous lectures. The cerebellum consists of two hemispheres The hemispheres are connected by vermis Cerebellum composed of cerebellar cortex on the periphery, inside there is white matter, and within the white matter there is also islands of grey matter. Similar to cerebrum, but here the fissure between the two hemisphers is narrow,, what is this fissure?? the falx cerebelli.
7 Three main lobes Anterior lobe Primary fissure.. between anterior and posterior lobe Posterior lobe (middle lobe).. the largest lobe Cerebellar tonsils Posterolateral fissure (uvulonodular fissure).. between posterior and flocculonodular lobe Flocculonodular lobe.. folliculus with nodular (nodular is the most inferior anterior part of vermis ) Cerebellum: Internal Structure Content Cerebellar cortex (folia) & central nuclei are grey matter Arbor vitae = tree of life = white matter The white matter also called arbor vitae or tree of life. Cerebellar Anatomy Cerebellum includes a cortex & deep nuclei The deep nuclei are the major source of output from the cerebellum Four nuclei from medial to lateral Fastigial Globose Emboliform Dentate These nuclei, mostly the efferent will exit from them. The white matter contains 4 nuclei, the fastigial which is the most medial one, Globose and Emboliform called interposed nuclei because they have the same function, and the most lateral one which is Dentate nucleus " Not dentate gyrus!!" Cerebellar Cortex Cerebellar cortex includes 5 cell types in 3 layers Five cell types Inhibitory cells Purkinje, basket, Golgi, and stellate cells
8 Excitatory cells Granule cells Three layers Molecular layer Purkinje cell layer Granule cell layer Cerebellar cortex efferent is the purkinje, the other layers affect the purkinje. Purkinje cells " which is the output (efferent)" it is inhibitory so if you inhibit it, overall you are exciting. Cerebellar Inputs Inputs to the cerebellum Climbing fibers.. climbing fibers directly affect purkinje From inferior olivary complex (olivocerebellar fibers) Decussate Inferior cerebellar peduncle.. climbing fibers enter cerebellum through inferior cerebellar peduncle Mossy fibers.. entrance is different from climbing fibers, mossy fibers affect other cells, where these other cells affect purkinje as we said. All remaining inputs: spinal cord, vestibular n. & nuclei, & pontine nuclei Each type of input fibers branches Branch to deep nuclei Branch to cerebellar cortex Cerebellar Circuit The basic cerebellar circuit includes Main excitatory loop Inhibitory cortical side loop The Main Excitatory Loop Includes the input and the deep cerebellar nuclei Both the inputs & the cells of the deep nuclei are excitatory The Inhibitory Cortical Side Loop Serves to modulate the activity in the deep cerebellar nuclei
9 Mossy & climbing fibers are inputs to cerebellar cortex Climbing fibers contact Purkinje cells directly Mossy fibers contact granule cells Granule cells contact Purkinje cells Output of cerebellar cortex (Purkinje fibers) depend on the mossy & climbing fibers Remaining cells (Golgi, basket & stellate) are inhibitory interneurons Alter granule & Purkinje cells Purkinje cells (cerebellar cortex output) are inhibitory Purkinje cells targets deep cerebellar nuclei & vestibular nuclei Thus cerebellar output is driven by the main excitatory loop and limited by the inhibitory cortical side loop Cerebellar Functional Divisions 1. Vestibulocerebellum Flocculonodular lobe & fastigial nu. Balance, eye movements from vestibular nuclei to cerebellum composed of flocculonodular lobe & fastifial nucleimain function is balance and eye movements. 2. Spinocerebellum Vermis & paravermal parts of hemispheres & interposed nuclei (emboliform & globose) Motor execution from spine, composed of vermis and paravermal parts of hemispheres and interposed nuclei function is motor execution. 3. Cerebrocerebellum.. from two hemispheres Lateral hemispheres & dentate
10 nu. Motor planning Vestibulocerebellum Function Balance & eye movements Inputs Vestibular n. fibers Vestibular nuclei Inferior olive Deep nucleus Fastigial nucleus Outputs (From fastigial nu. & Purkinje cells).. this is the only exception in the 3 functional divisions that the purkinje fibers are present here, as we they are efferents. Vestibular nuclei Reticular formation VL of thalamus Part of motor system targeted UMNs of medial pathway Major signs of damage Staggering or falling, nystagmus Spinocerebellum Function Execution of movement Compensates for changes in load, regulates muscle tone, guides limb movement, helps maintain posture Organized somatotopically Head & trunk vermis Limbs paravermal areas Inputs Spinal & trigeminal inputs Inferior olive Deep nucleus Fastigial & interposed nuclei Outputs Vermis Reticular formation & Vestibular nu. Paravermal Red nucleus, VL of thalamus & Inferior olive Part of motor system targeted UMNs of medial & lateral pathways Major signs of damage
11 Staggering gait, intention tremor Cerebrocerebellum Function Coordination, planning of voluntary movements Inputs Pontine nuclei (relaying information from sensory & motor cerebral cortex) Inferior olive Deep nucleus Dentate nucleus Outputs Red nucleus (to inferior olive, back to cerebellum) VL of thalamus Part of motor system targeted Motor cortex (via VL) Major signs of damage Decomposition of movements
12 Blood Supply of Cerebellum SCA Superior cerebellar hemispheres Superior vermis Dentate nucleus Most of white matter Superior cerebellar peduncle AICA Middle cerebellar peduncle Flocculus Anteroinferior surface of the cerebellum PICA Posteroinferior cerebellar hemispheres Inferior portion of the vermis Inferior cerebellar peduncle
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
Medial View of Cerebellum
 Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
The Cerebellum. The Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
The Cerebellum. Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Abdullah AlZibdeh. Dr. Maha ElBeltagy. Maha ElBeltagy
 19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
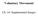 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
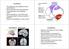 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
The Cerebellum. Outline. Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
Connection of the cerebellum
 CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Cerebellum. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
Organization of Motor Functions 4.
 Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
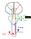 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
THE CEREBELLUM. - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum
 CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Connections of basal ganglia
 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas. MBChB, MSc, PhD
 Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
Dr. Farah Nabil Abbas MBChB, MSc, PhD The Basal Ganglia *Functions in association with motor cortex and corticospinal pathways. *Regarded as accessory motor system besides cerebellum. *Receive most of
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia
 Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Basal Ganglia The Wonders of the Basal Ganglia by Mackenzie Breton and Laura Strong /// https://kin450- neurophysiology.wikispaces.com/basal+ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei
Cerebellum 1/20/2016. Outcomes you need to be able to demonstrate. MHD Neuroanatomy Module
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
THE CEREBELLUM SUDIVISIONS, STRUCTURE AND CONNECTIONS
 THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo
 Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
FUNCTION: It COORDINATES movement HOW IT WORKS
 CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy
 Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
skilled pathways: distal somatic muscles (fingers, hands) (brainstem, cortex) are giving excitatory signals to the descending pathway
 L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
CNS MCQ 2 nd term. Select the best answer:
 Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves
 CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves 1 As with sensory input, motor output is organized in central nervous system Peripheral Nervous system divides efferent signals somatotopically
CNS consists of brain and spinal cord PNS consists of nerves 1 As with sensory input, motor output is organized in central nervous system Peripheral Nervous system divides efferent signals somatotopically
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal
 I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
PSY 315 Lecture 11 (2/23/2011) (Motor Control) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 11 Topic: Motor System Chapter 8, pages
 Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
Corrections: No Corrections Announcements: Exam #2 next Wednesday, March 2, 2011 Monday February 28, 2011 we will be going over the somatosensory system, and there will be time left in class to review
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
Brainstem: Midbrain. 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain:
 Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum
 The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
Functions. Traditional view: Motor system. Co-ordination of movements Motor learning Eye movements. Modern view: Cognition
 The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Gross Morphology of the Brain
 Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
Gross Morphology of the Brain Done by : Marah Marahleh & Razan Krishan *slides in bold Principal Parts of the Brain Cerebrum : largest part of the brain Diencephalon Thalamus & hypothalamus Cerebellum
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29:
 The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
-Zeina Assaf. -Omar Odeh. - Maha Beltagy
 -3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
-3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU)
 Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? 1 Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU) Cerebellum The Little Brain 2 The Cerebellum takes ~10% of the Brain in Volume Small but Hefty
Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? 1 Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU) Cerebellum The Little Brain 2 The Cerebellum takes ~10% of the Brain in Volume Small but Hefty
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
