S Alandete, M Meseguer, CR Poyatos, D Uceda, E de la Via, J Sales, J Vilar. H.U. Dr Peset, Valencia (Spain)
|
|
|
- Claude Mosley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S Alandete, M Meseguer, CR Poyatos, D Uceda, E de la Via, J Sales, J Vilar. H.U. Dr Peset, Valencia (Spain)
2 Introduction Cystic lesions are usually a common finding in clinical practice and you can find in any diagnostic technique (ultrasound, CT and MRI) Understand and identify the different benign and malignant intracranial cystic lesions and review the radiologic appearance is important to make a correct differential diagnosis.
3 Normal variations: Cavum septi pellucidi and Cavum veli interpositi Cavum septi pellucidi: The septum pellucidum consists of two thin leaves of white matter surrounded by gray matter. The persistence of this septum after birth is called cavum septi pellucidi. It is between frontal horns and lateral ventricles. Cavum veli interpositi: Or cyst of the veli interpositi is localized between the lateral ventricles over talami, the internal cerebral veins flows inferiorly.
4 Normal variations: Cavum vergae and Megacisterna magna Cavum vergae: It is the persistence of the embryological fluid-filled space between the leaflets of the septum pellucidum. Mega cisterna magna: It is considered megacisterna magna when measured in the sagittal plane exceeds 10mm without involvement of the cerebellar hemispheres.
5 Normal variations: Dandy-Walker malformation This is a congenital anomaly characterized by the classic triad of hydrocephalus, absence or agenesis of the cerebellar vermis and posterior fossa cyst communicated with the fourth ventricle. Secondarily can cause hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension.
6 Cystic lesions of development: Periventricular leukomalacia Periventricular leukomalacia is the necrosis of white matter with a characteristic distribution, external to the lateral ventricles involving the centrum semiovale that occurs in preterm infants less than 32 weeks. Ultrasound is the most sensitive technique to ischemia and shows hyperechoic areas. The control ultrasound reveals the formation of cystic lesions.
7 Cystic lesions of development: Periventricular cyst It is the result of incomplete formation of the lateral ventricle. It is always located adjacent the frontal horn. They may regress spontaneously.
8 Cystic lesions of development: Ventriculomegalia It consists in dilation of the ventricles due to hydrocephalus, it may mimic cystic structures. Linear ultrasound imaging transducer may be useful in identifying the thinned cortical hydrocephalus present and absent in the hydrancephaly.
9 Benign lesion: Arachnoid cyst They are CSF filled lesions, therefore they have the same intensity in MRI, which do not communicate with the ventricular system. It is the most common congenital intracranial cyst. It is the most frequent supratentorial cyst in the middle cranial fossa. It is a well-defined extraaxial cyst isointense attenuation with CSF. Scalloping of adjacent bone is a common finding is observed.
10 Benign lesion: Epidermoid cyst A common location is in the cerebellopontine angle. The radiographic appearance is similar to arachnoid cysts. Distinguishable characteristics are slightly hyperintense on FLAIR and diffusion-restricted.
11 Benign lesion: Dermoid cyst They represent 0.5% of all intracranial tumors. The majority are asymptomatic, symptoms only appear if mass effect and breakage. Locations vary according to the publications. The characteristics that differentiate it from the rest is its fat content observed as hypodense (fat density) on CT. On RM shows hyperintense on both T1 and T2 by the fat content.
12 Benign lesion: Neuroglial cyst Nonenhancing intraaxial CSF-like parenchymal cyst with no sorrounding signal intensity. May occur anywhere. The most characteristic finding is a cyst that follow CSF signal. The differential diagnosis must be made with arachnoid cysts and dilated Virchow-Robin spaces.
13 Benign lesion: Dilated Virchow-Robin spaces They follow CSF signal on all sequences. They have no enhancement or restricted diffusion. The differential diagnosis must be done with lacunar infarcts. They are pial lined interstitial fluid filled spaces that surround perforating vessels. They are common incidental findings. Their common sites are the basal ganglia (type 1), cortical gray matter (type 2) and midbrain (type 3).
14 Benign lesion: Colloid cyst They are cysts filled with mucin which gives a typical image. Almost 100% are in the foramen of Monro. The radiographic appearance is pathognomonic. On CT it is a well-defined hyperdense lesion. On MR it is hyperintense on T1 and isointense on T2 to the brain parenchyma.
15 Benign lesion: Choroid plexus cyst These cysts appears in the choroid plexus epithelium. The majority are asymptomatic and they are incidental findings. Most common in the atria of lateral ventricles. On unenhanced CT images is isointense to CSF and can show contrast enhancement, a finding that should not be confused with mass lesions in this location. On RM are hyperintense on T2 and 2/3 shows restricted diffusion.
16 Benign lesion: Miscellany Porencephalic cyst: These are cavities caused after infection, ischemic stroke, or surgery in the brain parenchyma. It follows CSF on MR sequences. Subependymal cyst: These are rare, benign cyst. More frequent intraventicular in the lateral ventricles. Most are incidental, if symptoms can appear, headache, seizures or obstructive hydrocephalus. The diagnostic clue is a cyst containing CSF with thin wall without enhancement.
17 Benign lesion: Miscellany Cyst of the anterior commisure: Receive their name to appear in this location. The anterior commissure is a fiber tract connecting the two frontal lobes in its basal part. On RM follows the same CSF signal. Choroid fissure cyst: This is well-defined nodular lesions typically located on the choroid fissure (between the fimbria of the hippocampus and diencephalon) On RM follows the same CSF signal, without restriction or enhancement.
18 Benign lesion: Miscellany Pineal cyst: Unilocular cyst located in the pineal gland which attenuation varies according to content. On MR it is slightly hyperintense to CSF and does not suppress on FLAIR. After contrast administration may show nodular or ring enhancement. The differential diagnosis is made with pineocytoma, imaging may be indistinguishable. Cyst of Rathke's pouch: These cysts arise from embryonic remnants of Rathke's cleft. The best imaging clue is a suprasellar cyst with a small intracystic nodule. MRI features are variable on T1 and hyperintense on T2.
19 Benign lesion: Miscellany Meningocele of the petrous apex: It is a rare lesion, corresponds to a herniation of the subarachnoid space from the posterolateral portion of Meckel's cave to the petrous apex. It is well defined hypodense lesions on CT and hyperintense on T2. Subdural hygroma: It is a CSF lesion that appears secondary to a subdural hematoma. The knowledge of the previous history gives us the diagnosis.
20 Infectious lesion: Neurocysticercosis Most neurocysticercosis cysts are in the subarachnoid space. Radiographic findings vary chronologically: Early vesicular stage: Smooth thin-walled cyst that is CSF-like on CT and MR images. A mural nodule is often present that represents the viable larval scolex, the cyst with a dot appearance. Colloidal-vesicular stage: Cyst fluid is hyperintense to CSF on MR images. Healing or granular nodular stage: nonenhanced CT scans show an isoattenuated cyst with a hyperattenuated calcified scolex. Quiescent or residual stage: Small calcified nodules. Multifocal lesions and lesions in different stages of development are common. Image courtesy of [1]
21 Infectious lesion: Hydatid cyst Cerebral hydatid cysts are rare. The most common location for intracranial hydatid cysts is the hemispheric parenchyma It is a single, large, thinwalled, spherical, nonenhancing CSFattenuation cyst in the parietal region of the brain Perilesional edema is usually absent. Image courtesy of [1]
22 Infectious lesion: Abcess Clinical patient is especially useful for diagnosis. Abscesses are characterized by low signal intensity on T1 and hyperintense on T2 and FLAIR with peripheral ring enhancement and restricted diffusion. The differential diagnosis is with primary tumor.
23 Tumoral lesions: Hemangioblastoma It is a vascular tumor that occurs in patients with syndrome of Von- Hippel-Lindau. Typically occurs in young patients in posterior fossa (95%). CT and MRI shows a cystic lesion with a mural nodule that enhances after contrast.
24 Tumoral lesions: Pilocytic astrocytoma It most often occurs in young patients and located in the cerebellum. It has a strong association with neurofibromatosis type 1. Radiologically large cyst with a mural nodule that enhances after contrast administration. On MRI it is iso-hypointense to brain parenchyma on T1 and hyperintense on T2.
25 Tumoral lesions: Central neurocytoma Rare tumour, less than 1%. Typically seen in young patients. A high percentage of these tumors are intraventricular located mostly in the lateral ventricles. On CT are usually hyperattenuating compared to white matter. Calcification and cystic regions are frequently present. On MR the main feature is cystic regions which are hypointense on FLAIR.
26 Tumoral lesions: Craniopharyngioma Typically arise in the sellar/suprasellar region. It is a cystic lesion with a solid minor component that enhance vividly on both CT and MRI. Calcification is very common
27 Tumoral lesions: Cystic meningioma About 10-20% of meningioma undergo cystic degeneration. The tumor has the same radiological features as meningioma, slightly hyperdense calcifications with intense and homogeneous enhancement after contrast administration with dural tail. On RM the cystic component is hyperintense on T2.
28 Conclusion Intra o extraaxial? Extraaxial Infratentorial Supratentorial Midline Off-midline Midline Off-midline Arachnoid cyst Epidermoid cyst Arachnoid cyst Pineal cyst Dermoid cyst Rathke cleft cyst Arachnoid cyst (convexity) Epidermoid cyst Arachnoid cyst (suprasellar)
29 Conclusion Intra o extraaxial? Intraaxial? Infratentorial Supratentorial Intraventricular Parenchymal Intraventricular Parenchymal Epidermoid cyst Enlarged perivascular spaces Choroid plexus cyst Ependymal cyst Colloid cyst Enlarged perivascular spaces Neural cyst Porencephalic cyst Connatal cyst
30 Conclusion There is a wide spectrum of organizations, knowledge of the radiologic features and its location allows us to narrow the list of differential diagnosis.
31 References 1. Intracranial Cysts: RadiologicPathologic Correlation and Imaging Approach Anne G. Osborn, MD Michael T. Preece, MD Radiology: Volume 239: Number 3 June Differential Diagnosis of Intracranial Cystic Lesions at Head US: Correlation with CT and MR Imaging Monica Epelman, MD Alan Daneman RadioGraphics 2006; 26: Posterior Fossa Malformations Karuna Shekdar, MD Semin Ultrasound CT MRI 32: Truex RC, Carpenter MB. Human neuroanatomy.6th ed. Baltimore, Md: Williams & Wilkins, 1969; Pauling KJ, Bodensteiner JB, Hogg JP, Schaefer GB. Does selection bias determine the prevalence of the cavum septi pellucidi? Pediatr Neurol 1998; 19: Born CM, Meisenzahl EM, Frodl T, et al. The septum pellucidum and its variants: an MRI study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2004;254: Kwon JS, Shenton ME, Hirayasu Y, et al. MRI study of cavum septi pellucidi in schizophrenia, affective disorder, and schizotypal personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry 1998;155: Filipovic B, Prostran M, Ilankovic N, Filipovic B.Predictive potential of cavum septi pellucidi (CSP) in schizophrenics, alcoholics and persons with past head trauma: a post-mortem study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2004;254: Bodensteiner JB, Schaefer GB, Craft JM. Cavum septi pellucidi and cavum vergae in normal and developmentally delayed populations. J Child Neurol 1998;13: Correspondence: Dr. Alandete salaiger@gmail.com
Differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions.
 Differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0215 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. G. Alandete, M. A. Meseguer, E. De la Via, D. Uceda, C. Poyatos; Valencia/ES
Differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0215 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. G. Alandete, M. A. Meseguer, E. De la Via, D. Uceda, C. Poyatos; Valencia/ES
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings
 Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings Robert J Sevick, MD, FRCPC, FACR Professor, Radiology and Clinical Neurosciences Cumming School of Medicine University of Calgary Learning objectives:
Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings Robert J Sevick, MD, FRCPC, FACR Professor, Radiology and Clinical Neurosciences Cumming School of Medicine University of Calgary Learning objectives:
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN. Scalp, Skull. Anatomically Based Differentials. Skull Normal Variants. Scalp Mass, Child.
 Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
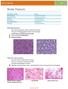 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
MRI Evaluation of Intracranial Cystic Lesions
 Original Research Article. MRI Evaluation of Intracranial Cystic Lesions Naveen Kumar. S 1, Vidyadhara Rani. P 2 1Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology, 2Associate Professor, Department of Pathology,
Original Research Article. MRI Evaluation of Intracranial Cystic Lesions Naveen Kumar. S 1, Vidyadhara Rani. P 2 1Assistant Professor, Department of Radiology, 2Associate Professor, Department of Pathology,
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated.
 Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated. Poster No.: C-1092 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Ospina Moreno, I. Montejo
Intracranial arachnoid cysts: radiological study of the incidental, the symptomatic and the complicated. Poster No.: C-1092 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Ospina Moreno, I. Montejo
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
 EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region. Child thirsty, increased urination. Imaging. Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) No Disclosures
 Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity
 Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Cysts Arachnoid Cyst (also called Leptomeningeal Cyst)
 Cysts This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Co-Director of the Neuro-Oncology Center and Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
Cysts This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Co-Director of the Neuro-Oncology Center and Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool.
 Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 5 Masses and tumors K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL part
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Disclosures. Posterior Fossa Masses. I m from the Government. and I here to help! Differential Diagnosis
 Posterior Fossa Masses Differential Diagnosis James G. Smirniotopoulos, M.D. Radiology, Neurology, Biomedical Informatics Uniformed Services University Bethesda, Maryland http://rad.usuhs.edu http://medpix.usuhs.edu
Posterior Fossa Masses Differential Diagnosis James G. Smirniotopoulos, M.D. Radiology, Neurology, Biomedical Informatics Uniformed Services University Bethesda, Maryland http://rad.usuhs.edu http://medpix.usuhs.edu
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Cavum velum interpositum cyst causing symptomatic trapped ventricle: A case report
 Cavum velum interpositum cyst causing symptomatic trapped ventricle: A case report Poster No: R-0286 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T Singh, S Dupre; NAMBOUR/AU Keywords: CNS, Neuroradiology
Cavum velum interpositum cyst causing symptomatic trapped ventricle: A case report Poster No: R-0286 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T Singh, S Dupre; NAMBOUR/AU Keywords: CNS, Neuroradiology
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess,
MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case
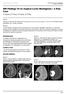 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 14 Number 1 MRI Findings Of An Atypical Cystic Meningioma A Rare Case D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip Citation D Saxena, P Rout, K Pavan, B Philip.
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Skull & Brain Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 4 & 5 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS. Kim Learned, MD
 PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
Metastasis. 57 year old with progressive Headache and Right Sided Visual Loss
 Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review
 Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI
 Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
A case of posterior fossa dermoid
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 4 2016 A case of posterior fossa dermoid SURESH BABU THANGAVEL Department of Neuro Surgery, MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 4 2016 A case of posterior fossa dermoid SURESH BABU THANGAVEL Department of Neuro Surgery, MADRAS MEDICAL COLLEGE AND
Spectrum of benign intracranial cystic lesions
 Spectrum of benign intracranial cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1945 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Alami, A. L. M. Youssef, O. Addou, M. Jaffal, N. Sqali, M. Boubou, M. Mustapha,
Spectrum of benign intracranial cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1945 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Alami, A. L. M. Youssef, O. Addou, M. Jaffal, N. Sqali, M. Boubou, M. Mustapha,
Imaging in Epilepsy. Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015
 Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
Central nervous system
 Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
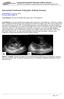 Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
What Are We Going to Do? Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy. Hydrocephalus and Effects of Interruption of CSF Flow. Tube Blockage Doctrine
 Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Peter Canoll MD. PhD.
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they ypresent? What do they look like? How do they behave?
Chapter 3. Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance
 Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports
 Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
Imaging The Turkish Saddle. Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Posterior Fossa Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Posterior Fossa Lesions Gupta MK 1, Rauniyar RK 1, Bhatta N 2, Raja S 3, Ahmad K 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis & Imaging, 2 Department of Internal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomographic Evaluation of Posterior Fossa Lesions Gupta MK 1, Rauniyar RK 1, Bhatta N 2, Raja S 3, Ahmad K 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis & Imaging, 2 Department of Internal
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma in the Cerebellum: Case Report
 Case Report Neuroimaging and Head and Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.151 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):151-155 Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma
Case Report Neuroimaging and Head and Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.151 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):151-155 Infratentorial and Intraparenchymal Subependymoma
CT of Pineal Region Tumors
 97 CT of Pineal Region Tumors S. Ramaiah Ganti1 S. K. Hilal 1. M. Stein 2. John Silver 1 M. Mawad 1 P. Sane 1 The computed tomographic (CT) features of pineal region tumors were analyzed in 60 histologically
97 CT of Pineal Region Tumors S. Ramaiah Ganti1 S. K. Hilal 1. M. Stein 2. John Silver 1 M. Mawad 1 P. Sane 1 The computed tomographic (CT) features of pineal region tumors were analyzed in 60 histologically
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, et al. Incidental findings
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, et al. Incidental findings
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound. trimester on
 Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
What the pediatric lateral ventricles tell us.
 What the pediatric lateral ventricles tell us. Poster No.: C-2069 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Dominguez Piedra, M. I. Martinez-Leon, V. Romero Laguna, 1 1 2 1 1 2 M. Sánchez-Porro
What the pediatric lateral ventricles tell us. Poster No.: C-2069 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Dominguez Piedra, M. I. Martinez-Leon, V. Romero Laguna, 1 1 2 1 1 2 M. Sánchez-Porro
A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
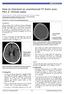 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales
 28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain
 The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
The view from the mastoid fontanel of the neonatal brain Poster No.: C-0974 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Pekcevik, F. C. Sarioglu, H. Sahin ; Karabaglar/Izmir/TR, 1 2 2 1 2
Lesions of the Pineal Region: A Practical Approach
 Lesions of the Pineal Region: A Practical Approach Poster No.: C-0937 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Calles Blanco, J. A. Guzman de Villoria ; Madrid/ES, Madrid, Ma/ES Keywords:
Lesions of the Pineal Region: A Practical Approach Poster No.: C-0937 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Calles Blanco, J. A. Guzman de Villoria ; Madrid/ES, Madrid, Ma/ES Keywords:
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn
 Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
DISCLOSURES LEARNING OBJECTIVES WE WILL NOT DISCUSS. CSB: Birdseye View MESSAGE NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE
 NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE Christopher P. Hess, M.D., Ph.D. DISCLOSURES Research Support, General Electric SLIDES: http://www.radiology.ucsf.edu/research/meetings/rsna LEARNING OBJECTIVES
NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE Christopher P. Hess, M.D., Ph.D. DISCLOSURES Research Support, General Electric SLIDES: http://www.radiology.ucsf.edu/research/meetings/rsna LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Acute Ischaemic Stroke
 Acute Ischaemic Stroke CT or MR SCA READIG FORM SCA ID: DATE OF READIG: SCA QUALIT: Good Moderate Poor Comment: READER ID: TPE OF SCA: CT: Without contrast: With contrast: MR: Diffusion: Perfusion ote
Acute Ischaemic Stroke CT or MR SCA READIG FORM SCA ID: DATE OF READIG: SCA QUALIT: Good Moderate Poor Comment: READER ID: TPE OF SCA: CT: Without contrast: With contrast: MR: Diffusion: Perfusion ote
Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Common Liver Diseases Hemangioma Cyst FNH Focal Fat/Sparing THID Non-Cirrhotic
Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Common Liver Diseases Hemangioma Cyst FNH Focal Fat/Sparing THID Non-Cirrhotic
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
