ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
|
|
|
- Grant Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1: Intrductin 13 Anatmy and Physilgy I ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Anatmy (Greek a cutting up ) Physilgy (Greek relatinship t nature ) is always related t CORE PRINCIPLE IN A&P Structure and Functin Cre Principle One f mst basic principles in A&P; knwn as principle f cmplementarity f structure and functin: Frm f a structure is always such that it best suits its functin Frm fllws functin; applies t each level f rganizatin even dwn t chemical level CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING ORGANISMS Living Organisms share distinct prperties: Cellular cmpsitin: cells are basic units f life Metablism: Living rganisms carry ut a number f chemical reactins cllectively knwn as metablism, where building utweighs breaking dwn prcesses, includes tw frms: Increase in size f individual cells prcess that an rganism uses t eliminate ptentially harmful waste prducts created by metablic prcesses r irritability ability f rganisms t sense and react t changes r stimuli in their envirnment
2 Chapter 1: Intrductin LEVELS OF STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION AND BODY SYSTEMS ability f an entire rganism t mve r mvement f individual cells r f materials within r between cells f an rganism takes fllwing tw frms in Chemical level smallest level is fundatin fr each successive level, ranges frm atms t cmplex mlecules hydrgen atm, lithium atm multicellular rganisms: water mlecule, glucse mlecule Individual cells reprduce within rganism during grwth prtein mlecule, DNA mlecule and t replace damaged r ld cells Organism itself reprduces t yield similar ffspring Cellular level frmed by grups f many different types f mlecules cmbined in specific ways t frm cellular structures mitchndrin, Glgi apparatus, nucleus muscle cell, nerve cell; smallest unit f life tw r mre cell types cperate t perfrm a cmmn functin Cnsist f tw cmpnents: cells and surrunding extracellular matrix Vary frm membrane sheets that cver bdy cavities t irregularly shaped cartilage fund in nse cnsists f tw r mre tissue types cmbined t frm a structure r rgan skin, femur, heart, kidney Cnsist f tw r mre rgans that tgether carry ut a brad functin in bdy rgan systems functin tgether t make up wrking human bdy, an rganism 14
3 Chapter 1: Intrductin DIRECTIONAL TERMS ANATOMICAL POSITION cmmn frame f reference frm which all bdy parts and regins are described: Bdy is always referred t as if it were in anatmical psitin, even when it s in anther psitin Right and left always refers t right and left sides f bdy being described, nt ur wn Anterir / Psterir Cranial / Caudal Superficial / Deep REGIONAL TERMS Antebrachial Axillary Brachial Cervical Cstal Crural Femral Gluteal Ventral / Drsal Superir / Inferir Prximal / Distal Medial / Lateral REGIONAL TERMS Bdy can be divided int tw regins: axial regin, which includes head, neck, and trunk and appendicular regin which includes upper and lwer limbs r appendages 15 Mammary Nasal Occipital Lumbar Pectral Sternal Tarsal Vertebral Figure 1.7a Reginal terms. CONCEPT BOOST: PUTTING ANATOMICAL TERMS TOGETHER REGIONAL TERMS Figure 1.7b, c, d Reginal terms. Start with regin left crural Describe depth f incisin deep t skin and muscle but superficial t bne Put it all tgether wund is n left antermedial crural regin, 6 centimeters prximal t tarsal regin and 10 centimeters distal t patellar regin; pellet is ldged deep t skin and muscle but superficial t bne Add descriptive directinal terms (need t use prximal and distal, since describing limbs) anterir, n medial side, prximal t tarsal regin and distal t patellar regin
4 Chapter 1: Intrductin PLANES OF SECTION Sagittal Midsagittal Parasagittal Frntal (crnal) Transverse (hrizntal) Oblique Figure 1.8a Planes f sectin. Figure 1.8b Planes f sectin. BODY CAVITIES Drsal Bdy Cavity largely lcated n psterir side f bdy; subdivided int tw cavities: Figure 1.8c Planes f sectin. Ventral Bdy Cavity separated int tw divisins by diaphragm: Thracic Abdminpelvic Cranial cavity Vertebral (spinal) cavity Figure 1.9a The drsal and ventral bdy cavities. Figure 1.9b The drsal and ventral bdy cavities. 16
5 Chapter 1: Intrductin Thracic cavity divided int three smaller cavities: 17 Abdminpelvic cavity subdivided int tw cavities: Abdminal cavity Pleural cavities Pelvic cavity Mediastinum (nt within serus membrane) Pericardial cavity BODY CAVITIES Abdminpelvic cavity can be divided up int segments r quadrants Quadrants: Right upper quadrant (RUQ) Right lwer quadrant (RLQ) Left upper quadrant (LUQ) Left lwer quadrant (LLQ) Figure 1.9 The drsal and ventral bdy cavities. Segments: Right and left hypchndriac regins Epigastric regin Right and left lumbar regins Umbilical regin Right and left iliac r inguinal regins Hypgastric regin ABDOMINAL PAIN (P. 20) Cmmn cmplaint f individuals seeking health care Cause f pain can be difficult t diagnse due t number f structures in abdminpelvic cavity; fur quadrant system makes this easier RLQ LUQ
6 Chapter 1: Intrductin Serus membranes : Thin sheets f tissue; frm certain cavities fund in ventral cavity; surrund heart, lungs, and many abdminal rgans Within cavity between tw layers is an extremely thin layer f fluid called serus fluid Visceral layer utermst layer attached t surrunding structures (wall f cavity) Figure 1.11 Hw a serus membrane envelps the heart. Bdy has three serus bdy cavities frmed by three main serus membranes: Pleural membranes Parietal pleura Visceral pleura Thin space enclsed by pleural membranes frms Pericardial membranes Parietal pericardium (separates heart frm mediastinum) Visceral pericardium (lies directly n heart muscle) Space created by pericardial membranes frms Figure 1.12a The serus membranes f the ventral bdy cavities. Peritneal membranes, surrunds sme f abdminal rgans Parietal peritneum Visceral peritneum Space between these layers frms The peritneum desn t cver every rgan Figure 1.12b The serus membranes f the ventral bdy cavities. 18
7 Chapter 1: Intrductin HOMEOSTASIS Physilgical Prcesses Operate t Maintain Bdy s (maintenance f internal envirnment) Hmestatic imbalances disturbances in Feedback Lps Cre Principle tw mechanisms vital t maintenance f hmestasis: less cmmn than negative feedback lps; effectr activity increases and reinfrces initial stimulus; - ppse initial change in a regulated variable; reduce utput hmestasis can lead t disease r death if uncrrected Each regulated variable has a set pint r an established nrmal value (within a nrmal range) T prevent imbalance, mst variables are cntrlled - prvide infrmatin abut stimuli (regulated) variables; maintained within a narrw range, clse t a nrmal value change is cmpared t set pint change is crrected Figure 1.14 Cntrl f bld cltting by a psitive feedback mechanism. CHILDBIRTH, PITOCIN, AND POSITIVE FEEDBACK LOOPS (P. 26) Childbirth begins with labr; ccurs by psitive feedback: Figure 1.13b Cmparisn f hw negative feedback mechanisms cntrl rm and bdy temperature. Pitcin (synthetic xytcin) 19
8 Chapter 1: Intrductin 20
9 Chapter 2: The Chemistry f Life 21 MATTER Matter anything that has mass and ccupies space; Chemistry study f matter and its interactins smallest unit f matter that retains riginal prperties Made up f even smaller structures called subatmic particles ELEMENTS IN THE PERIODIC TABLE AND THE HUMAN BODY The human bdy is made up f fur majr elements: BIOCHEMISTRY Bichemistry the chemistry f life cmpunds generally d nt cntain carbn bnded t hydrgen; include water, acids, bases, and salts thse that d cntain carbn bnded t hydrgen Als 7 mineral elements and 13 trace elements WATER Water (H2O) makes up 60 80% f mass f human: The medium fr metablic reactins Absrbs and transprts heat Salts - can disslve in water t frm catins and anins called Capable f cnducting electrical current SALTS AND ELECTROLYTES Acts as a lubricant between tw adjacent surfaces Imprtant rles in metablism
10 Chapter 2: The Chemistry f Life CARBOHYDRATES CARBOHYDRATES, cmpsed f carbn, hydrgen, and xygen, functin primarily as fuel; als have structural rles mnmers frm which all carbhydrates are made Examples: glucse, fructse, galactse, ribse, and dexyribse Figure 2.14 Carbhydrates: structure f mnsaccharides. are frmed by unin f tw mnsaccharides cnsist f many mnsaccharides jined t ne anther Glycgen is the strage plymer f glucse; mstly in skeletal muscle and liver cells Strach Figure 2.16 Carbhydrates: the plysaccharide glycgen. LIPIDS THE GOOD, THE BAD, AND THE UGLY OF FATTY ACIDS (P. 56) Hydrphbic mlecules including fats and ils Fatty acids lipid mnmers cnsisting carbn chains Saturated fatty acids Nt all fatty acids were created equally: The Gd: Omega 3 Fats The Bad: Saturated Fats Unsaturated fatty acids 22
11 Chapter 2: The Chemistry f Life THE GOOD, THE BAD, AND THE UGLY OF FATTY ACIDS Nt all fatty acids were created equally (cntinued): 23 TRIGLYCERIDE The Ugly: Trans Fats Mst cmmn lipid in bdy Figure 2.18 Lipids: structure and frmatin f triglycerides. PHOSPHOLIPIDS Cmpsed f a glycerl backbne, tw fatty acid tails and ne phsphate head A mlecule with a plar grup (phsphate head) and a nnplar grup (fatty acid tail) Figure 2.19 Lipids: structure f phsphlipids. Table 2.3 Organic Mlecules. STEROIDS PROTEINS Macrmlecules: Fur-ring hydrcarbn structure Enzymes cmpnent f cell membrane Are invlved in mvement Functin in the bdy s defenses Receptrs
12 Chapter 2: The Chemistry f Life 24 Twenty different are used t make prteins Figure 2.21a, b Prteins: structure f amin acids. ENZYME DEFICIENCIES (P. 44) NUCLEOTIDES AND NUCLEIC ACIDS Makes up genetic material Examples f cmmn enzyme deficiencies: Tay-Sachs Disease Severe Cmbined Immundeficiency Syndrme (SCIDs) Phenylketnuria built frm mnmers f nucletides Nucletide structure: Nitrgenus base with a hydrcarbn ring structure Five-carbn sugar (ribse r dexyribse) Figure 2.24a Structure f nucletides. Adensine triphsphate (ATP) DNA Adenine attached t ribse and three phsphate grups; main surce f chemical energy in bdy Cmpsed f tw chains that twist arund each ther Synthesized frm ADP and a phsphate using energy frm xidatin f fuels (like glucse) Prductin f large quantities f ATP requires xygen; why we breathe air Figure 2.25a Nucletides: structure and frmatin f ATP. t frm a duble helix DNA cntains genes prvide recipe r cde fr prtein synthesis prcess f making every prtein Figure 2.26a Structure f nucleic acids and Table 2.3 Organic Mlecules.
13 Chapter 2: The Chemistry f Life DNA exhibits cmplementary base pairing; Adenine DNA cntains: Dexyribse alternating always pairs with Thymine and Guanine always pairs with Cytsine with phsphate grup Bases: Figure 2.26a Structure f the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. RNA Ribnucleic Acid single strand f nucletides Can mve between nucleus and cytsl RNA cntains the sugar ribse Figure 2.26b Structure f the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. 25
14 Chapter 2: The Chemistry f Life 26
15 Chapter 3: The Cell BASIC PROCESSES OF CELLS Cell metablism Transprt f substances cell has prduced r ingested t a variety f destinatins between cell and surrunding envirnment Cell reprductin prcess that is necessary fr grwth and develpment and fr replacement f ld and damaged cells OVERVIEW OF CELL STRUCTURE Plasma membrane Mst animal cells have 3 basic cmpnents: Prvides cell with structural supprt, means f Defines intracellular space (cntains intracellular fluid cmmunicatin, and cell identificatin ( )), r cytsl, and separates it frm extracellular space (cntains extracellular fluid ( )) Figure 3.1 The basic cmpnents f a generalized cell. Cytplasm cnsists f: Cytsl Nucleus Cntains mst f cell s and is primary lcatin fr making mst Organelles variety f cellular structures with very specific functins DNA and RNA cntrl mre specific rganelle functins by cding fr and synthesizing prteins Cytskeletn 27
16 Chapter 3: The Cell THE PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER Cell Size and Diversity: Cells vary widely in size and structure This structural variatin is an example f Structure-Functin Principle Figure 3.2 Cell diversity. Nte that cells are nt drawn t same scale. Phsphlipids have tw key prperties: A phsphate grup ( ) Tw fatty acids ( ) that face ne anther frming a waterresistant barrier Figure 3.3a The frmatin f a phsphlipid bilayer. Membrane Prteins: Transprt substances acrss plasma membrane as prtein channels; thers are carrier prteins that directly bind t and transprt substances int and ut f cell Figure 3.3b, c The frmatin f a phsphlipid bilayer. - bind t chemical messengers called ligands; trigger sequence f events within cell when bund Figure 3.5b Functins f membrane prteins. Figure 3.5a Functins f membrane prteins. speed up chemical reactins; vital t maintaining hmestasis Figure 3.5c Functins f membrane prteins. 28
17 Chapter 3: The Cell give cells shape and help maintain structural integrity Figure 3.5d Functins f membrane prteins. - hld adjacent cells t ne anther, anchring cells within a tissue and/r allwing cell t cell cmmunicatin Figure 3.5e Functins f membrane prteins. Other membrane cmpnents include lipids, carbhydrates, glyclipids, and glycprteins: lipid mlecule, stabilizes plasma membrane s fluid structure during temperature changes Glyclipids and glycprteins, serve t identify cell as part f bdy 29 DRUGS AND MEMBRANE RECEPTORS (P. 74) Many drugs are designed t resemble ligands that bind t membrane receptrs: Agnists Antagnists Figure 3.4 The fluid msaic mdel f the plasma membrane. TRANSPORT ACROSS THE PLASMA MEMBRANE The phsphlipid bilayer is selectively permeable Substance may crss plasma membrane in several ways: PASSIVE TRANSPORT PROCESSES Passive transprt include the fllwing prcesses: Diffusin
18 Chapter 3: The Cell Cncentratin gradient basic frce that drives many types f passive transprt Dye mlecules will scatter due t their wn kinetic energy, which all mlecules have as lng as thermal energy (heat) is present Mvement will cntinue until the dye is unifrm thrughut cntainer (equilibrium) Diffusin Figure 3.6 Diffusin and equilibrium. Simple diffusin mstly nnplar slutes like xygen, carbn dixide, lipids, and hydrcarbns; pass straight thrugh phsphlipid bilayer withut need fr membrane prtein Figure 3.7a Passive transprt: simple and facilitated diffusin. mvement f water acrss a selectively permeable membrane dwn its cncentratin gradient Water mves frm area with cncentratin f slute (mre water mlecules) acrss membrane t area with cncentratin f slute (less water mlecules) Osmtic pressure driving frce exerted by slute mlecules; causes water mlecules t mve until equilibrium is reached - invlves charged r plar slutes such as ins and glucse; crss phsphlipid bilayer with help f a carrier r channel Figure 3.7b, c Passive transprt: simple and facilitated diffusin. Figure 3.8 Passive transprt: smsis. 30
19 Chapter 3: The Cell Tnicity way t cmpare smtic pressure gradients between tw slutins cytsl and ECF Hypertnic ECF slute cncentratin f ECF is higher than inside cell Osmtic pressure gradient pulls water ut f cell and cell Nrmally ECF is Figure 3.9a Tnicity: effects f istnic, hypertnic, and hyptnic slutins n cell vlume. shrinks r Figure 3.9b Tnicity: effects f istnic, hypertnic, and hyptnic slutins n cell vlume. Hyptnic ECF slute cncentratin f ECF is lwer than DEHYDRATION, SPORTS DRINKS, AND WATER (P. 79) inside cell Osmtic pressure gradient pulls water int cell causing the cell t swell and pssibly rupture r 31 Strenuus exercise results in water and electrlyte lss thrugh sweating; ECF becmes hypertnic; hypertnic ECF draws water ut f cells by smsis Sprts drinks Plain water Figure 3.9c Tnicity: effects f istnic, hypertnic, and hyptnic slutins n cell vlume. ACTIVE TRANSPORT VIA MEMBRANE PROTEINS Active transprt prcesses require energy in frm f ATP t prceed as slutes mve against their cncentratin gradients frm cncentratin t cncentratin Figure 3.10 Primary active transprt by the Na+, K+ pump.
20 Chapter 3: The Cell 32 ACTIVE TRANSPORT VIA VESICLES Active transprt using carrier prteins and channels is effective but has limitatins; large macrmlecules are t big t fit s must be transprted by ther means: are small sacs filled with large mlecules Enclsed in a phsphlipid bilayer; allws them t fuse with r be frmed frm plasma membrane Figure 3.11 Secndary active transprt. Endcytsis: (fluid-phase endcytsis r cell drinking ) prcess where cells engulf fluid drplets frm ECF ( cell eating ) prcess where cells ingest large particles like bacteria r dead r damaged cells r parts f cell Figure 3.12 Endcytsis: phagcytsis. Receptr-mediated endcytsis similar t pincytsis; uses receptrs t fill vesicles with a specific mlecule Figure 3.13b Endcytsis: pincytsis and receptr-mediated endcytsis. Figure 3.13a Endcytsis: pincytsis and receptr-mediated endcytsis. large mlecules exit cell; knwn as secretin; vesicles fuse with plasma membrane, pening int ECF mlecules are brught int cell by endcytsis, transprted acrss cell t ppsite side, and then secreted by excytsis Figure 3.14a Excytsis.
21 Chapter 3: The Cell CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES Organelles are cellular machinery with specific functins vital t maintaining hmestasis Figure 3.14b Excytsis. MITOCHONDRIA PEROXISOMES membrane-bund rganelles invlved in chemical energy prductin Use xygen t carry ut several chemical reactins that prduce hydrgen perxide (H2O2); xidizes txic chemicals t less txic cmpunds that can be eliminated frm bdy befre causing damage Certain phsphlipids synthesized in perxismes are critical t plasma membranes f specific cells r nervus system. Figure 3.16 Structure f the mitchndrin. RIBOSOMES Ribsmes Free in cytsl; usually make prteins needed within cell itself Bund t membranes f ther cellular structures; prduce prteins destined fr exprt utside cell Figure 3.18 Schematic structure f the ribsme. ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM Endplasmic reticulum (ER) large flded phsphlipid bilayer Exists in tw frms: (RER) has ribsmes bund t it and (SER) des nt Table 3.2 Cytplasmic Organelles. 33
22 Chapter 3: The Cell Rugh endplasmic reticulum Packages secretry prteins int transprt vesicles made f a phsphlipid bilayer Prduces membrane cmpnents fr membrane-bund rganelles and plasma membrane, including integral and peripheral prteins 34 Smth endplasmic reticulum (SER) Stres calcium ins by pumping them ut f cytsl fr future use Capable f several detxificatin reactins; limits damage caused by certain substances Invlved in lipid synthesis, manufacturing majrity f plasma membrane phsphlipids and chlesterl as well as a number f lipprteins and sterid hrmnes GOLGI APPARATUS grup f flattened membranus sacs filled with enzymes and ther mlecules Prteins and lipids made by ER are further mdified, srted, and packaged fr exprt in the Glgi Prducts packaged in Glgi can be secreted frm cell by excytsis Figure 3.19 The endplasmic reticulum. Table 3.2 Cytplasmic Organelles. CYSTIC FIBROSIS (P. 92) Figure 3.20 The Glgi apparatus. In cystic fibrsis, sme cells are missing a prtein cmpnent f a chlride in channel
23 Chapter 3: The Cell 35 LYSOSOMES rganelles respnsible fr digestin f wrn ut cell cmpnents r whle cells in sme cases Macrmlecules are brken dwn int smaller subunits that can be released t cytsl fr dispsal r reused t manufacture new macrmlecules Table 3.2 Cytplasmic Organelles and Figure 3.15 The cell and its rganelles. Figure 3.21 Functin f the endmembrane system. LYSOSOMAL DISEASES (P. 95) LYSOSOMAL DISEASES Grup f diseases resulting frm deficiency f ne r mre acid hydrlases f lyssmes: Hurler syndrme Gaucher s disease Niemann-Pick disease Tay-Sachs disease THE CYTOSKELETON Cytskeletn Gives the cell its characteristic shape and size by creating an internal framewrk Prvides strength, structural integrity, and anchring sites Perfrming specialized functins in different cell types; fr example, phagcytsis by macrphages r cntractin by muscle cells CENTROSOME / CENTRIOLES When cell is nt dividing, centrsme is a micrtubule-rganizatin center lcated clse t nucleus
24 Chapter 3: The Cell TYPES OF FILAMENTS 36 CELLULAR EXTENSIONS Cellular extensins are frmed by the inner framewrk f the cytskeletn: Figure 3.22 The centrsme with centriles. MICROVILLI Increase surface area f cells in rgans specialized fr absrptin Figure 3.23 Micrvilli. CILIA Hair-like prjectins that stick ut f the cell Table 3.4 Cilia and Flagella. FLAGELLA Beats in a whip-like fashin prpelling entire cell Table 3.4 Cilia and Flagella. Table 3.4 Cilia and Flagella.
25 Chapter 3: The Cell PRIMARY CILIARY DYSKINESIA (P. 99) 37 THE NUCLEUS Rare genetic disrder characterized by defect in ne r mre prtein cmpnents f cilia and flagella gverning bdy that directs activities f the ther cellular cmpnents Affects many types f cells: respiratry passage linings, middle ear, uterine tubes (females), sperm (males) hused in nucleus cntains cde r plans fr nearly every prtein in bdy within DNA are direct different types f RNA t build a wide variety f prteins THE NUCLEUS Nucleus cnsists f three main structures: membrane that surrunds nucleplasm that cntains nuclear pres DNA and assciated prteins are fund in nucleusas a lse structural arrangement knwn as chrmatin in a nn-dividing cell - synthesis f ribsmal RNA and assembly f ribsmes Figure 3.25 The nucleus. NUCLEAR ENVELOPE Figure 3.26 The nuclear pre. CHROMATIN AND CHROMOSOMES cnsists f ne extremely lng DNA mlecule and histne prteins Reduces length f strand by abut ne-third Figure 3.27a Chrmatin.
26 Chapter 3: The Cell 38 During perids f cell divisin, chrmatin threads cil tightly and cndense int thick structures called chrmsmes Sister chrmatids each chrmsme cnsists f identical cpies Figure 3.27 Chrmatin and chrmsmes. DNA & RNA Practice Exercise PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA Gene expressin prductin f prtein frm specific gene G -- Tw prcesses actually make a specific prtein: Transcriptin Translatin DNA Transcriptin mrna Translatin Prtein DNA mrna G -- A-- A -- G-- G -- T-- T -- A-- A -- C-- C -- GENES AND THE GENETIC CODE changes in DNA due t mistakes in cpying DNA r induced by agents called mutagens Cmmn mutagens include ultravilet light and ther frms f radiatin, chemicals such as benzene, and infectin with certain viruses
27 Chapter 3: The Cell 39 TOXICITY OF THE DEATH CAP MUSHROOM (P. 104) Amanita phallides (and ther Amanita) are respnsible fr 95% f mushrm-related fatalities wrldwide A phallides is tasty and resembles many nntxic mushrms; main txin inhibits RNA plymerase; prevents frmatin f new strands f mrna REVIEW The prcess thrugh which mrna is made is termed a. Translatin b. Replicatin c. Synthesis d. Transcriptin REVIEW During transcriptin, free nucletides frm the nucleplasm are hydrgen bnded t a. Each ther b. Cmplementary nucletides f the DNA template strand c. Ribsmes d. RNA plymerase REVIEW A strand f mrna cntains the a. Instructins t build a ribsme b. Instructins t build a prtein c. Instructins t build a carbhydrate d. Instructins t build a lipid REVIEW Prtein synthesis is als called a. Transcriptin b. Replicatin c. Translatin d. Differentiatin REVIEW During translatin, the language f is translated int the language f. a. Nucletides, amin acids b. Amin acids, nucletides c. Nucletides, cdns d. Anticdns, nucletides
28 Chapter 3: The Cell REVIEW The DNA triplet TAG is cmplementary t the mrna cdn. a. ATC b. c. d. UAG 40 THE CELL CYCLE Almst all cells g thrugh the cell cycle An rdered series f events frm frmatin f cell t its reprductin by cell divisin Cell divisin is required fr grwth and develpment as well as fr tissue repair and renewal CGG AUC PHASES OF THE CELL CYCLE Cell cycle includes tw main phases: interphase and M phase r cell divisin Interphase perid f grwth and preparatin fr cell divisin: G1 phase (1st gap) S phase (synthesis) G2 phase (2nd gap) Figure 3.33 The cell cycle. REVIEW Nuclear envelpe enclses nucleus Centrile pairs duplicated DNA replicatin ccurs in which phase f the cell cycle? Nucleus and nuclelus are clearly a. G1 b. c. d. G2 visible and individual chrmsmes are nt distinguishable Figure 3.35a Interphase, mitsis, and cytkinesis. S M
29 Chapter 3: The Cell PHASES OF THE CELL CYCLE 41 MITOSIS M is perid f cell divisin; highlighted by tw verlapping prcesses: Divisin f genetic material in 4 stages Prphase Mitsis ccurs when newly replicated genetic material is Metaphase divided between tw daughter cells Anaphase Telphase Cytkinesis ccurs when cell s prteins, rganelles, and cytsl are divided between tw daughter cells METAPHASE PROPHASE Chrmatin becmes cmpact t frm chrmsmes (tw sister chrmatids) Centriles migrate t ppsite sides f cell t rganize spindle fibers Spindle fibers frm each centrile attach t each sister chrmatid ANAPHASE TELOPHASE Cytkinesis may begin at end f this stage Cytkinesis finishes t divide cytsl and rganelles equally between tw new daughter cells Chrmsmes uncil, becming chrmatin
30 Chapter 3: The Cell 42 OVERVIEW OF MEIOSIS Cell divisin can ccur either by (prcess that smatic cells are capable f) r that ccurs in cells destined t becme gametes Meisis cell divides t frm daughter cells with half number f chrmsmes Smatic cells are diplid (2n) because they have full paired set f chrmsmes 2016 Pearsn Educatin, Inc. Meisis prceeds thrugh fur basic phases: prphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telphase Phases ccur in tw successive divisins, unlike MEIOSIS I (FIRST MEIOTIC DIVISION) mitsis, where is first meitic divisin and is secnd First divisin separates hmlgus pairs t prduce haplid (n) cells Prphase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telphase I Meisis II separates chrmatids f each chrmsme; cells stay haplid Prphase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telphase II 2016 Pearsn Educatin, Inc. MEIOSIS II (SECOND MEIOTIC DIVISION) Figure 26.1 Stages f meisis. Fr simplicity, the cell is shwn with nly tw pairs f hmlgus chrmsmes Pearsn Educatin, Inc. Figure 26.1 Stages f meisis. Fr simplicity, the cell is shwn with nly tw pairs f hmlgus chrmsmes Pearsn Educatin, Inc. COMPARING MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Figure 26.2 Cmparing mitsis and meisis Pearsn Educatin, Inc.
31 Chapter 3: The Cell 43 SPINDLE POISONS (P. 111) Mittic spindle is critical t prcess f mitsis; if assembly r disassembly is inhibited by chemicals called spindle pisns (made by fungi and plants), errrs in cell divisin ccur that culd lead t cell death Examples: SPINDLE POISONS inhibit micrtubule functin; fragment frmed micrtubules; used t treat cancer inhibits assembly f micrtubules; treats gut inhibits functin/assembly f micrtubules in fungi (nt humans); antifungal agent fr skin, hair, and nails prevent disassembly f micrtubules; treat cancer Adverse effects (especially in cells that divide rapidly like stmach, skin, and bne marrw) nausea, vmiting, hair lss, decreased bld cell prductin PHASES OF THE CELL CYCLE Mst cells in the bdy prgress thrugh the cell cycle but at vastly different rates depending n their functin Cell cycle is precisely cntrlled s that cell frmatin is balanced with cell death CELL CYCLE CONTROL AND CANCER Cell may nt prceed with divisin if the fllwing cnditins are nt favrable: Grwth factrs are secreted by ther cells CELL CYCLE CONTROL AND CANCER Cells that cannt pass thrugh checkpints and cannt be repaired underg a prcess f prgrammed cell death called Ex. during fetal develpment hands and feet are initially webbed; cells in webs die t separate fingers and tes CELL CYCLE CONTROL AND CANCER When changes in DNA f a cell cause lss f cell cycle cntrl, uncntrlled cell divisin results and cells may frm a grwth r mass knwn as a tumr cnfined t its riginal lcatin and des nt invade surrunding tissues made up f cancer cells
32 Chapter 3: The Cell 44 CELL CYCLE CONTROL AND CANCER Figure 3.36 Cancerus tumr f kidney cells.
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Chapter 14 Cell division: Continuity of Life means all life originates from other living things of the same type.
 Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Topic 1: Cell Biology (Student) Essential Idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure that prokaryotes.
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Notes
 Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Function: Life at the Edge
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
Prokaryotic cells are placed in two taxonomic domains: o Bacteria o Archaea o
 AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
Test 3 Study Guide: Photosynthesis, Respiration, and the Cell Membrane
 Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Module 2. Chapter 4 Anatomy of the Cell
 Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES.! BIOL1040 University of Queensland
 CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Perid Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview 1. What are the three key rles f cell divisin? State each rle, and give an example. 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Cncept 12.1 Mst cell divisin results
Name Perid Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview 1. What are the three key rles f cell divisin? State each rle, and give an example. 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Cncept 12.1 Mst cell divisin results
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Rles f Cell Divisin The Key Rles f Cell Divisin CONCEPTS: 12.1 Mst cell divisin results in genetically identical daughter cells 12.2 The mittic phase alternates
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Rles f Cell Divisin The Key Rles f Cell Divisin CONCEPTS: 12.1 Mst cell divisin results in genetically identical daughter cells 12.2 The mittic phase alternates
2N diploid cell replicates division - two daughter cells, each 2N division (without replication)- four daughter cells, each N (haploid)
 Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
Human Structure and Function LECTURE 1 ERIN HARRISON
 * Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
* Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variations on a Theme
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 13: Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme Meisis and Sexual Life Cycles: Variatins n a Theme CONCEPTS: 13.1 Offspring acquire genes frm their parents by inheriting chrmsmes
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Lecture Outline Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Lecture Outline Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int and ut f the cell.
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int and ut f the cell.
Chem 464 Biochemistry Third Hour Exam
 Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
Metabolism: Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Module 3. Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions Metabolism Two general types of metabolic reactions: o :
 Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
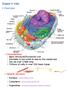 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
Topic 3 15/4/09 14:12. Zygotes
 Tpic 3 15/4/09 14:12 Zygtes Ova Structure Fllice cells utside Zna Pellucida inside them Releases hrmnes, attracting sperm and triggering lyssme reactin Acrsme swells and fuses with vum Penetrating Z.P
Tpic 3 15/4/09 14:12 Zygtes Ova Structure Fllice cells utside Zna Pellucida inside them Releases hrmnes, attracting sperm and triggering lyssme reactin Acrsme swells and fuses with vum Penetrating Z.P
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
The Excretory System. 4 The Excretory System.notebook. May 24, 2017
 4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
Biology 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reproductive Systems ANSWERS
 Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
Cellular Neurophysiology Membrane Ionic Gradients Concentration gradients and diffusion Membrane transport:
 Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Science. Human Biology. New Jersey Quality Single Accountability Continuum (NJQSAC) Department: Course Title
 New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules: The Molecules of Life
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Functin f Large Bilgical Mlecules: The Mlecules f Life Structure and Functin f Large Bi Mlecules: Mlecules f Life CONCEPTS: 5.1 Macrmlecules are plymers, built
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Functin f Large Bilgical Mlecules: The Mlecules f Life Structure and Functin f Large Bi Mlecules: Mlecules f Life CONCEPTS: 5.1 Macrmlecules are plymers, built
Topic Guide 4.2 & 10.1 Meiosis. 1. Define homologous chromosomes. 2. Explain reduction division. 3. State the function of meiosis.
 IB Bilgy HL Tpic Guide 4.2 & 10.1 Meisis Name Per. 1. Define hmlgus chrmsmes. 2. Explain reductin divisin. 3. State the functin f meisis. 4. Add chrmsmes and anntate the diagram belw summarizing the steps
IB Bilgy HL Tpic Guide 4.2 & 10.1 Meisis Name Per. 1. Define hmlgus chrmsmes. 2. Explain reductin divisin. 3. State the functin f meisis. 4. Add chrmsmes and anntate the diagram belw summarizing the steps
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance: Locating Genes Along Chromosomes
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 15: The Chrmsmal Basis f Inheritance: Lcating Genes Alng Chrmsmes Lcating Genes Alng the Chrmsme CONCEPTS: 15.2 Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns f inheritance 15.3 Linked genes
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 15: The Chrmsmal Basis f Inheritance: Lcating Genes Alng Chrmsmes Lcating Genes Alng the Chrmsme CONCEPTS: 15.2 Sex-linked genes exhibit unique patterns f inheritance 15.3 Linked genes
March 14, Aims: Agenda. SWBAT describe the four stages of Mitosis
 March 14, 2017 Aims: SWBAT describe the fur stages f Mitsis Agenda 1. D Nw 2. Class Ntes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing ur AIMS: C.4-Mitsis Hw will yu help ur class earn all f
March 14, 2017 Aims: SWBAT describe the fur stages f Mitsis Agenda 1. D Nw 2. Class Ntes 3. Guided Practice 4. Independent Practice 5. Practicing ur AIMS: C.4-Mitsis Hw will yu help ur class earn all f
1.3 - Cells. Chapter 3 - Cells
 1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 8. Cell: The Unit f Life CELL THEORY : Schieiden and Schwann tgether frmulated the cell thery. They prpsed that the bdy f animal and plant are cmpsed f cells and prduct f cells. Rudlf
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 8. Cell: The Unit f Life CELL THEORY : Schieiden and Schwann tgether frmulated the cell thery. They prpsed that the bdy f animal and plant are cmpsed f cells and prduct f cells. Rudlf
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distribution
 Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
AP Biology Immune System. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability to avoid disease when invaded by a pathogen
 AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
Intestinal Hormones Inhibit: Intestinal Hormones Promote:
 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
The Digestive System. May 16, The Digestive System.notebook
 3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life Cells and Tissues Cells: Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues Cells vary in length,
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Function
 Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
MEMBRANES. Overview of membranes. The chemical components of membranes
 MEMBRANES This text is divided int seven majr sectins: Overview f membranes The chemical cmpnents f membranes Membrane structure Membranes and cmpartmentalizatin Membrane receptrs Sme receptrs invlve secnd
MEMBRANES This text is divided int seven majr sectins: Overview f membranes The chemical cmpnents f membranes Membrane structure Membranes and cmpartmentalizatin Membrane receptrs Sme receptrs invlve secnd
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Close to spine/ point of attachment
 Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
HIV REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION AND AZT
 OVERVIEW HIV REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION AND AZT This hands-n activity is part f a series f activities and demnstratins fcusing n varius aspects f the human immundeficiency virus (HIV) life cycle. In this activity,
OVERVIEW HIV REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION AND AZT This hands-n activity is part f a series f activities and demnstratins fcusing n varius aspects f the human immundeficiency virus (HIV) life cycle. In this activity,
How to search the PDB
 Hw t search the PDB email us: pdbhelp@ebi.ac.uk The searchbx n the PDBe hmepage allws yu t switch between searching and dwnlading data frm the PDB and the EMDB archive The search bx n the PDBe website
Hw t search the PDB email us: pdbhelp@ebi.ac.uk The searchbx n the PDBe hmepage allws yu t switch between searching and dwnlading data frm the PDB and the EMDB archive The search bx n the PDBe website
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
In the list of organisms given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are
 In the list f rganisms given belw, thse that reprduce by the asexual methd are Banana Dg Yeast Ameba (ii) and (iv) (i), (iii) and (iv) (i) and (iv) (ii), (iii) and (iv) Answer:(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) In
In the list f rganisms given belw, thse that reprduce by the asexual methd are Banana Dg Yeast Ameba (ii) and (iv) (i), (iii) and (iv) (i) and (iv) (ii), (iii) and (iv) Answer:(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) In
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Can exert forces from a fraction of an ounce to > 70 lbs
 Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Anemia. There are three types of Anemia that effect EB patients. They are Iron Deficiency, Chronic Inflammatory and Nutritional.
 Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
1A Human Biology Food, Digestion and Associated Body Systems
 1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014
 REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we revise: the prcess f phtsynthesis the prcesses invlved in cellular respiratin Summary Phtsynthesis (Slutins
REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we revise: the prcess f phtsynthesis the prcesses invlved in cellular respiratin Summary Phtsynthesis (Slutins
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Autonomic. Nervous System
 Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
3. DIGESTION DIGESTION ABSORPTION DIGESTION. Refers to the process of breaking down large nutrient particles into their basic components
 3. DIGESTION T incrprate nutrients cntained in fds, rganisms have t be able t reduce particles size t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids r small peptides (Fig. 3-1). This prcess is called digestin. Once the
3. DIGESTION T incrprate nutrients cntained in fds, rganisms have t be able t reduce particles size t sugars, fatty acids, amin acids r small peptides (Fig. 3-1). This prcess is called digestin. Once the
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System S1: Intro to Kinesiology
 S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE. All Systems, GO! Lesson #3
 ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology
 A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology Form A Name Lab 1. Pinocytosis would allow the intake of a. solid b. gas c. liquids d. all of these answers are true 2. Which of the following
A&P 1 Fall 2004 Test Intro, Cells, and beginning of Histology Form A Name Lab 1. Pinocytosis would allow the intake of a. solid b. gas c. liquids d. all of these answers are true 2. Which of the following
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Theory. Passive Transport
 Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Cell Theory 4 basic concepts of cell theory are: Cells are the units of structure (building blocks) of all animals and plants. Cells are the smallest unit of function in all animals and plants. Cells originate
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiratin: Harvesting Chemical Energy Lecture Outline Overview: Life Is Wrk T perfrm their many tasks, living cells require energy frm utside surces. Energy enters mst ecsystems as
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiratin: Harvesting Chemical Energy Lecture Outline Overview: Life Is Wrk T perfrm their many tasks, living cells require energy frm utside surces. Energy enters mst ecsystems as
 Teacher Ntes fr "Hw d muscles get the energy they need fr athletic activity?" 1 In this activity, students analyze hw aerbic cellular respiratin and anaerbic fermentatin cntribute t ATP prductin in muscle
Teacher Ntes fr "Hw d muscles get the energy they need fr athletic activity?" 1 In this activity, students analyze hw aerbic cellular respiratin and anaerbic fermentatin cntribute t ATP prductin in muscle
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
VITAPRO. Detoxification properties of Apple pectin formulation, PROPECTIN. CENTRE D ETUDE ET DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES FINAL REPORT.
 CENTRE D ETUDE & DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES 2400 Detxificatin prperties f Apple pectin frmulatin, PROPECTIN. VITAPRO FINAL REPORT PrPectin July 2015 CENTRE D ETUDE ET DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES PRESQU
CENTRE D ETUDE & DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES 2400 Detxificatin prperties f Apple pectin frmulatin, PROPECTIN. VITAPRO FINAL REPORT PrPectin July 2015 CENTRE D ETUDE ET DE VALORISATION DES ALGUES PRESQU
Bio 103 Tissues and Skin 35
 Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
Cell Organelles and their Functions. Chapter 4 Section 2
 Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Chapter 26: The Urinary System. An Overview of the Urinary System, p The Kidneys, p. 952
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
LESSON OBJECTIVES & STANDARDS:
 Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: This Jepardy-style review game challenges students by reviewing all f the cncepts cvered in the What s Yur Balance? elearning Kit. Teen guide Jasn will intrduce
Page 1 LESSON TITLE: LESSON DESCRIPTION: This Jepardy-style review game challenges students by reviewing all f the cncepts cvered in the What s Yur Balance? elearning Kit. Teen guide Jasn will intrduce
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutatins ROBERT LEVITT, MD JESSICA BERGER-WEISS, MD ADRIENNE POTTS, MD HARTAJ POWELL, MD, MPH COURTNEY LEVENSON, MD LAUREN BURNS, MSN, RN, WHNP OBGYNCWC.COM v Cancer is a cmplex disease
Chapter 13 Forensic Anthropology: What We Learn from Bones By the end of this chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
Cell. ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange
 Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
Chapter 3 Cells 1 Cell ~ 75 trillion make up adult Living cells ~ 60% water Carry materials for exchange 2 Cell Shapes Shape and size vary Ex: Nerve cells can be 3ft long! Epithelial often flat and thin
