Review for Midyear Exam ( )
|
|
|
- Tracy Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Cells and Genetics Review for Midyear Exam ( ) 1. Which cells in the human body normally have a diploid number of chromosomes in their nuclei? a) all cells b) only cells produced by mitosis c) only cells produced by meiosis d) only reproductive cells 2. The diploid chromosome number in humans is a) 23 b) 46 b) 48 d) The following is a portion of a DNA strand: CCG ATT TGC ACG. The complimentary DNA strand would be : a) CCG ATT TGC ACG b) GGC TAA ACG TGC c) GGC UAA UCG UGC d) CCG TAU UCG UGC 4. Crossing over of chromosomes is most likely to occur during: a) meiosis b) mitosis c) cell death d) fertilization 5. DNA is made up of types of nucleotides a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 6. Why do cells divide? Give 3 differences between the processes of Mitosis and Meiosis. a. b. c.
2 8. Identify the processes as Meiosis or Mitosis a) Produces identical cells b) Used for sexual reproduction c) Has 2 cell divisions d) Contains 46 chromosomes (human cell) e) Produces gametes f) Produces 4 daughter cells g) Contains half the genetic material of parent cell h) Used for growth and repair of cells and tissues 9. What do the letters GMO mean? 10. Give 2 methods to create a GMO: 1-2- Reproduction and Puberty 1. Gametes are a) Sex cells c) n b) Haploid d) A, B and C are all correct 2. Fertilization occurs. a) When ovulation happens b) When the sperm fuses with the ovum c) When a female has her period d) When a male and female have intercourse 3. What is a Zygote? a) A fertilized ovum c) An immature ovum b) A follicle d) A gland which secretes hormones
3 4. The 1 gland is found in both males and females it secretes 2 and a) Pituitary Estrogen Progesterone b) FSH Estrogen LH c) Pituitary FSH LH d) Pituitary Testosterone Estrogen 5. Days 1-5 in the menstrual cycle are referred to as 1 and days are referred to as a) Menstrual phase Proliferation phase b) Proliferation phase Secretory phase c) Menstrual phase Secretory phase d) Secretory phase Menstrual phase 6. In females, progesterone is responsible for: a) Preparing the uterus for implantation and stimulating the production of milk in pregnant women b) The degeneration of the uterine lining, causing females to get their periods c) Causing the release of ova from the ovaries. 7. In the female, once fertilization takes place, the embryo implants itself in the a) Endometrium b) Ovaries c) Fallopian tube 8. What hormone is responsible for ovulation? a) FSH b) LH c) Estrogen 9. True or False: a- Hormones secrete glands b- The male hormones are testosterone, FSH and LH c- The primary sexual characteristic for males is the start of their cycle and sperm production d- A penis must be erect on order to ejaculate. e- A female cannot get pregnant form pre-mature ejaculation.
4 10. Give three secondary sexual characteristics which occur in females only. 11. Give a secondary sexual characteristic which occurs in both males and females. 12. Name the two hormones responsible for the maturation of the follicle What is the difference between an oocyte and an ovum? 14. Define infertility. 15. What are all of the methods couples can use to help have a child when they are deemed infertile? 16. List 2 pros and 2 cons that accompany assisted reproduction. Nutrition & Digestion 1. Fill in the table Function Protein Carbohydrates Fats Examples of it Number of grams needed per day What you multiply to get from grams (g) into kj The amount of kj needed per day 2. What 4 nutrients are responsible for regulating metabolism?
5 3. Calculate the kj intake of the cookies: 15 g of carbohydrates 8 g of fat 3 g of protein 4. Give the definitions of the following terms: Chemical breakdown or change Metabolism Physical breakdown or change Gland Enzyme Peristalsis _ Absorption 5. What is the passageway food follows when it is digested and give the mechanical breakdown that occurs at each place? Location Mechanical Breakdown 6. What are the 5 glands of the digestive system and what enzyme do they release? Gland Enzyme
6 7. Write all the chemical breakdowns chicken will go through to bring it to its simplest form so absorption of the nutrient can occur. Include the locations of the chemical breakdown and the enzyme involved. 8. Write all the chemical breakdown pasta will go through to bring it to its simplest form so absorption of the nutrient can occur. Include the locations of the chemical breakdown and the enzyme involved. 9. Write all the chemical breakdown butter will go through to bring it to its simplest form so absorption of the nutrient can occur. Include the locations of the chemical breakdown and the enzyme involved. 10. Where does the absorption of all the simple nutrients occur? Why can it occur there? 11. Where does the absorption of water, vitamins and minerals occur? 12. Explain the reason constipation occurs and give possible solutions. 13. Explain the reason diarrhea occurs and give possible solutions. 14. What is the function of the digestive system?
7 15. Fill in passageway on the diagram. 16. Complete the following table concerning the digestive system: Part Mechanical Transformation Chemical Transformation Gland
8 Organization of, Properties of, and Changes to Matter 1. State whether the following are examples of chemical (c) or physical (p) changes: a- Ice melting d- Mixing salt and water g- Toasting bread b- A bike rusting c- A fire occurring e- Making Jell-0 f- Water evaporating h- Separating a compound i- Making a compound 2. What reactions (signs) tell you a chemical change occurred? 3. Fill in the table Give the 4 pure substances Give their definition Give an example Use symbols to show an example 4. Explain what a decomposition reaction is. Give an example, and two reactions (signs) that tell you something was decomposed. 5. Explain what a synthesis reaction is. Give an example and explain two reactions (signs) that tell you a something new was produced. 6. Give the 4 types of properties and two examples of each.. 7. What is the definition of density and what is the density of water?
9 8. How are the following properties determined (measured/calculated)? Mass Volume Density Regular solid Irregular solid Liquid 9. Fill in the table. Carbon dioxide Oxygen Hydrogen Test to ID Reaction Observed 10. Fill in the table for what reaction will be observed. RLP BLP CCP Conductivity Saltwater Distilled water Alcohol Acid Base 11. What are the definitions of the following? Malleability Luster 12. From a scale of 0-14 give the range of an acid, a base and a neutral solution. 13. Which of the following are not characteristic properties of water? a) boils at 100 b) dissolves sugar c) has a ph of 7 d) freezes at 0 e) volume of 25mL f) is transparent g) density of 1g/mL h) tasteless 14. Which of the following best describes the behaviour of the particles (use particle model)? 1. The bonds in a solid become stronger when phased into a liquid 2. The more the temperature increases, the more the particles vibrate in a liquid 3. The change from gas to solid allows the particles to stay as far away from each other as possible 4. An increase in temperature will cause the bonds of a liquid to weaken
10 15. Select the best definition of a characteristic property: 1. A property of a solid, liquid or gas, which is unique to that substance. 2. A property of a metal and nonmetal that describes where on the period table the element appears. 3. A property that is not unique to individual substances. 4. A property of any object or living thing, such as mass and colour. 16. Match the gas with the appropriate test: i- Hydrogen A. Turns limewater cloudy ii- Carbon dioxide iii- Oxygen B. Causes a flaming splint to pop C. Causes a glowing splint to re-light a) i -A, ii-b, iii-c b) i-c, ii-a, iii-b c) i-b, ii-c, iii-a d) i-b, ii-a, iii-c 17. Bobby needs to find the density of a solid. Use the table below he created after conducting his experiment to find the objects mass and volume (by water displacement). Mass Volume Water Volume Water + Solid g 12.0 ml 16.8 ml How could Bobby solve for the density of the solid? (show all work) Density: 18. Decomposition is the transformation of complex molecules into simpler molecules or into atoms. What is the reverse process known as? Reverse process: 19. When 2 clear liquids are mixed together and result in a yellow solid being produced. What type of change took place? Solids can be produced in a chemical reaction with liquids. What do we call this solid? a) Type of change? b) Justification c) Name of solid?
11 Respiratory System and Fluids 1. Which gas, referred to as an oxidizing agent, makes the combustion of nutrients possible? 2. During inhalation, in which direction does the diaphragm move? 3. True or False a) The volume of the rib cage increases during exhalation b) Air pressure in the lungs decreases during inhalation 4. List three functions of the nasal cavities: 5. What body parts are shared by the digestive system and the respiratory system? 6. What defense do we have against foreign particles like pollen, dust and pollution? 7. Give the definition of a fluid. What substances are fluids? 8. What fluids are incompressible? Explain incompressibility is using the particle theory of matter. 9. What fluids are compressible? Explain compressibility using the particle theory of matter.
12 10. Label the diagram below: 11. Below is a diagram of a lung and it components. Label the diagram using the following words: Cluster of Alveoli Capillaries Alveolus Bronchiole
13 12. Place the following statements below in the order that they occur during inspiration: a. the molecule enters the alveolus b. the molecule crosses the trachea c. the molecule crosses the pharynx d. the molecule enters a bronchiole e. the molecule enters the nasal cavity f. the molecule crosses the larynx g. the molecule enters one of the bronchi 13. In order for inspiration to occur, does the air pressure inside the lungs have to be higher or lower than surrounding air pressure? Why? 14. Explain why a gas is considered a fluid? 15. Explain why a liquid is considered an incompressible fluid? 16. At a birthday party you fill balloons with helium and they all rise to the ceiling. The next morning the balloons were still floating but had fallen quite a bit. By nighttime the balloons had fallen to the floor and the volume has decreased greatly. What term describes why the balloons have fallen down? Why was the helium able to escape? Explain in detail, why the volume of the balloon decreases. 17. a) What is the respiration formula? b) Where does this reaction occur and why does it occur there?
14 18. What is the waste product of respiration, where is it produced and why is it produced there? 19. What is the functional unit of the lungs? Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems 1. Give three differences between arterial and venous blood? Fill in the table Blood component Function(s). 3. What is the largest artery? 4. What is the function of the systemic and pulmonary circulation? 5. What type of blood vessel allows for diffusion? Where does diffusion occur?
15 6. Fill in the table. Passageway Type of Blood Type of Circulation Left ventricle 7. Explain what blood pressure and pulse measures. 8. What is the minimum of a high blood pressure reading? Explain why a person will have a high blood pressure result. What are things that a person does that might cause them to have high blood pressure?
16 9. Fill in the diagram What is the function of the circulatory system? 11. Give 3 differences between white blood cells and red blood cells What makes blood red? 13. Describe what happens when an antigen enters the body:
17 14. Define the following terms: Term Definition Antigen Antibody Vaccine Immunity Blood transfusion Diffusion Semi permeable membrane 15. Complete the chart Blood vessel Description and Function Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Vein Aorta Vena Cava Arteries Veins
18 16. On the heart diagram put in the following parts: right ventricle, pulmonary vein, superior vena cava and left atrium 17. Give the description and function of the parts mentioned in question 16. Part of the Heart Description and Function right ventricle pulmonary vein superior vena cava left atrium
19 18. Where are the following structures located (relative to the heart) and what are their functions: Structure: Function: Pulmonary Artery Aorta Inferior Vena Cava 19. Describe the pathway of Pulmonary Circulation. 20. Describe the pathway of Systemic Circulation. 21. How do the digestive and circulatory systems work together to achieve cellular respiration? 22. What can happen when there is a blockage in the circulatory system? 23. Explain the purpose of a vaccination and how it works.
20 24. What is the function of antibodies? 25. What are the 2 ways someone will acquire immunity? 26. Explain how blood donation and receiving works. 27. Can O- donate to B+, why? 28. Can B+ donate to O-, why? 29. Why is O- the universal donor? 30. Why is AB+ the universal recipient?
21 31. Complete the table: Donate A+ B+ AB+ O+ A- B- AB- O- Receive 32. During a blood typing lab, how can we determine what our blood type is? 33. Complete the following table regarding the lymphatic system Terms Definition Lymph Lymph Nodes Phagocytosis Extracellular Fluid Antibody Antigen 34. Our bodies are defended by Defense mechanisms: Mechanism Action Phagocytosis
Review for Midyear Exam (2016) ANSWERS
 Name: Cells and Genetics Review for Midyear Exam (2016) ANSWERS 1. Which cells in the human body normally have a diploid number of chromosomes in their nuclei? a) all cells b) only cells produced by mitosis
Name: Cells and Genetics Review for Midyear Exam (2016) ANSWERS 1. Which cells in the human body normally have a diploid number of chromosomes in their nuclei? a) all cells b) only cells produced by mitosis
Review for Midyear Exam ( )
 Name: Cells and Genetics Review for Midyear Exam (2017-18) 1. Which cells in the human body normally have a diploid number of chromosomes in their nuclei? a) all cells b) only cells produced by mitosis
Name: Cells and Genetics Review for Midyear Exam (2017-18) 1. Which cells in the human body normally have a diploid number of chromosomes in their nuclei? a) all cells b) only cells produced by mitosis
Review for Midyear Exam (2016)
 Name: Cells and Genetics Review for Midyear Exam (2016) 1. Which cells in the human body normally have a diploid number of chromosomes in their nuclei? a) all cells b) only cells produced by mitosis c)
Name: Cells and Genetics Review for Midyear Exam (2016) 1. Which cells in the human body normally have a diploid number of chromosomes in their nuclei? a) all cells b) only cells produced by mitosis c)
Grade 9 Science Midyear Review
 Grade 9 Science Midyear Review Density a) Find the density of a mysterious liquid with a mass of 4.5 grams and a volume of 16 ml. b) Find the mass of an unknown substance with a density of 7.8 g/ml and
Grade 9 Science Midyear Review Density a) Find the density of a mysterious liquid with a mass of 4.5 grams and a volume of 16 ml. b) Find the mass of an unknown substance with a density of 7.8 g/ml and
Reproduction Worksheet
 Name: Date: Reproduction Worksheet Directions: Base your answers to questions 1-4 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. 1. Identify the structure in which sperm is produced. What is the name
Name: Date: Reproduction Worksheet Directions: Base your answers to questions 1-4 on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. 1. Identify the structure in which sperm is produced. What is the name
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Physiology Quiz (30 Points)
 Physiology Quiz (30 Points) Name: 1. What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses? A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation. B. Viruses have no RNA. C. Viruses have no metabolism. D. Viruses
Physiology Quiz (30 Points) Name: 1. What prevents antibiotics from being effective against viruses? A. Viruses have a high rate of mutation. B. Viruses have no RNA. C. Viruses have no metabolism. D. Viruses
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice
 Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Student Academic Learning Services Page 1 of 5 Reproductive System Practice Fill in the blanks using the words listed: accessory glands, vas deferens, penis, scrotum, fallopian tube, testes, urethra, vagina,
Secondary 3 Final Exam Review
 Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
1 Food and its use by the body (pp )
 Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
Checkup Chapter 6 1 Food and its use by the body (pp. 160 172) 1. This is what Veronica ate for supper: 1 grilled Atlantic salmon steak 1 baked potato 5 ml of butter (on the potato) 3 boiled broccoli florets
1 The cell. Checkup Chapter 5. (pp ) 1. Look at the following illustration.
 Checkup Chapter 5 1 The cell (pp. 126 131) 1. Look at the following illustration. a) What three cell components are visible under a light (optical) microscope? Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus b) What is
Checkup Chapter 5 1 The cell (pp. 126 131) 1. Look at the following illustration. a) What three cell components are visible under a light (optical) microscope? Cell membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus b) What is
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into 2
 Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Reproduction (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Asexual Reproduction o Production of genetically identical offspring from one parent o E.g. - Bacteria Reproduce by binary fission a cell to divide into
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
LIFE SCIENCES Grade 12 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014
 REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
REPRODUCTION 30 JUNE 2014 Checklist Make sure you Can describe different reproductive strategies of vertebrates Are able to identify the structure and function of the male and female reproductive organs
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Grade 9 Science Review
 Grade 9 Science Review You are not allowed your notes, a memory aid, and formulas will NOT be written on the board so study! Chapter 1 - Organisation of matter 1. Find the density of a mysterious liquid
Grade 9 Science Review You are not allowed your notes, a memory aid, and formulas will NOT be written on the board so study! Chapter 1 - Organisation of matter 1. Find the density of a mysterious liquid
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Review Questions for June Exam
 Review Questions for June Exam Term 1 Topic 1 Cells and Genetics 1. A cell with 20 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? 2 Each daughter cell has 20 chromosomes. 2. What are
Review Questions for June Exam Term 1 Topic 1 Cells and Genetics 1. A cell with 20 chromosomes undergoes mitosis. How many daughter cells are created? 2 Each daughter cell has 20 chromosomes. 2. What are
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Unit 2 Reproduction & Genetics Grade 9 Science SCI 10F Mr. Morris
 Unit 2 Reproduction & Genetics Grade 9 Science SCI 10F Mr. Morris This booklet belongs to: Lesson 1 Cells and Organelles Lesson 1 SCI10F A short list of Organelles (little organs): Nucleus Cytoplasm Chromosome
Unit 2 Reproduction & Genetics Grade 9 Science SCI 10F Mr. Morris This booklet belongs to: Lesson 1 Cells and Organelles Lesson 1 SCI10F A short list of Organelles (little organs): Nucleus Cytoplasm Chromosome
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System
 Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System 1. Which of the following is NOT related to a cell s surface area to volume ratio? a. Cell size b. Number of nuclei c.
Unit 5: Cell Cycle, Mitosis, Meiosis & Drug Influence Influence on Nervous System 1. Which of the following is NOT related to a cell s surface area to volume ratio? a. Cell size b. Number of nuclei c.
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
REPRODUCTION The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis.
 1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
1. The diagram below shows a section through seminiferous tubules in a testis. Which cell produces testosterone? 2. A function of the interstitial cells in the testes is to produce A sperm B testosterone
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Interactions Among Animal Systems. Biology 10(A)
 Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Higher Human Biology
 Higher Human Biology Unit 2: Physiology and Health Homework DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET. RETURN THIS BOOKLET TO YOUR TEACHER ON COMPLETION OF THE UNIT 1 Contents Sub-topic Pages (a) Reproductive Organs
Higher Human Biology Unit 2: Physiology and Health Homework DO NOT WRITE ON THIS BOOKLET. RETURN THIS BOOKLET TO YOUR TEACHER ON COMPLETION OF THE UNIT 1 Contents Sub-topic Pages (a) Reproductive Organs
thebiotutor.com 3A Reproduction Time: 55 minutes Total marks available: 55 Total marks achieved: Andy Todd
 thebiotutor.com 3A Reproduction Time: 55 minutes Total marks available: 55 Total marks achieved: Q1. Plants and animals can reproduce asexually and sexually. (a) Give an example of a way that plants can
thebiotutor.com 3A Reproduction Time: 55 minutes Total marks available: 55 Total marks achieved: Q1. Plants and animals can reproduce asexually and sexually. (a) Give an example of a way that plants can
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
Circulation and Respiration
 Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
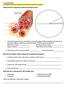 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review
 Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Embryology Lecture # 4
 1 Quick Review: Oogenesis : - Oogonia start appear in the ovary when the age of the fetus 1 is th (5 week). - Then the Oogonia transformed into 1ry Oocyte. - 1ry Oocyte is surrounded by a follicle (cover).
1 Quick Review: Oogenesis : - Oogonia start appear in the ovary when the age of the fetus 1 is th (5 week). - Then the Oogonia transformed into 1ry Oocyte. - 1ry Oocyte is surrounded by a follicle (cover).
Phases of the Ovarian Cycle
 OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16
 Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
Name: Final Test Review Major Concepts from Chapters 1-16 Period: Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Name the levels of structural organization that make up the human body and explain how they are
ARE YOU READY FOR THE JUNE 2016 SECONDARY 3 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXAM?
 ARE YOU READY FOR THE JUNE 2016 SECONDARY 3 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXAM? So what s this document for? This document is designed to help you get prepared for the Secondary 3 Science & Technology exam. Often
ARE YOU READY FOR THE JUNE 2016 SECONDARY 3 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXAM? So what s this document for? This document is designed to help you get prepared for the Secondary 3 Science & Technology exam. Often
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Unit 4 - Reproduction
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Which cell process occurs only in organisms that reproduce sexually? A) mutation B) replication C) meiosis D) mitosis 2. Which sequence represents the
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Which cell process occurs only in organisms that reproduce sexually? A) mutation B) replication C) meiosis D) mitosis 2. Which sequence represents the
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY. 0610/21 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/21
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0610 BIOLOGY 0610/21
Animal Structure and Function
 Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems
 Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
I. Digestive System Salivary Amylase Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) Pepsin Pyloric Sphincter Pancreatic Amylase Pancreatic Lipase Trypsin Chymo tripsin
 Animal Systems I. Digestive System a. Process i. Mouth 1. Salivary Amylase a. Digests starch ii. Esophagus iii. Stomach 1. Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) a. Digests proteins b. Creates a low ph environment for
Animal Systems I. Digestive System a. Process i. Mouth 1. Salivary Amylase a. Digests starch ii. Esophagus iii. Stomach 1. Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) a. Digests proteins b. Creates a low ph environment for
