Structure and Function. Interactive Notebook Activity
|
|
|
- Katherine Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structure and Function Interactive Notebook Activity
2 Cell Organelles Structure and Function Directions: For the Pocket Cut along the outer solid lines. Fold on the dotted lines. Place a small amount of glue on the pieces labeled 1, 2, and 3. Use these pieces to secure the front of the pocket to the back of the pocket. For the Inserts Cut along the outer solid lines of each square. Cut out each piece. Identify each cell organelle or structure. On the same side of the picture, write the name of the organelle or structure. On the other side of the square, write the function of the organelle and if the structure is found in plant cells, animal cells, or both. When finished, place the pieces in the pocket and fold the top flap down. Science From The South Cell Organelles Structure and Function 2 3
3
4 Cell Membrane Nucleus and Nucleolus Smooth and Rough ER Small Vacuole Golgi Bodies Cell Wall Centrioles Lysosomes Large Vacuole Chloroplast Mitochondria Ribosomes
5 Cell Membrane Structure found in all cells. It is essential in maintaining homeostasis by controlling what gets in and out of the cell. Smooth and Rough ER The smooth ER contains enzymes that aid in cell function. The rough ER is responsible for transporting proteins. It acts like a highway of the cell. Nucleus and Nucleolus The nucleus is the boss of the cell. It holds the DNA (instructions for making proteins). The nucleolus is the center of the nucleus where ribosomes are made. Small Vacuole Also known as a vesicle, they are used as storage and transportation vesicles to move materials in and out of the cell. Smaller ones are found in animal cells. Golgi Bodies Responsible for inspecting and packaging proteins before they are shipped out to their target areas. Cell Wall Thick, rigid outer wall found in plant cells, but not animal cells. It provides support and protection for the cell. Centrioles Structures found in animal cells that aid in cell division. Lysosomes Responsible for cleaning up the cell, by getting rid of waste. Found in animal cells only. NOTE: Some scientists believe they are found in plant cells but rarely visible. Large Vacuole Large storage compartment used for storing water and other materials needed. Larger vacuoles are found in plant cells. Chloroplast The site of photosynthesis. It is found in plant cells but not in animal cells. Mitochondria The power house of the cell responsible for cellular respiration. Ribosomes Responsible for making proteins in the cell. Found attached to the rough ER and free floating in the cytoplasm.
6 Cell Membrane Structure found in all cells. It is essential in maintaining homeostasis by controlling what gets in and out of the cell. Smooth and Rough ER The smooth ER contains enzymes that aid in cell function. The rough ER is responsible for transporting proteins. It acts like a highway of the cell. Nucleus and Nucleolus The nucleus is the boss of the cell. It holds the DNA (instructions for making proteins). The nucleolus is the center of the nucleus where ribosomes are made. Small Vacuole Also known as a vesicle, they are used as storage and transportation vesicles to move materials in and out of the cell. Smaller ones are found in animal cells. Golgi Bodies Responsible for inspecting and packaging proteins before they are shipped out to their target areas. Cell Wall Thick, rigid outer wall found in plant cells, but not animal cells. It provides support and protection for the cell. Centrioles Structures found in animal cells that aid in cell division. Lysosomes Responsible for cleaning up the cell, by getting rid of waste. Found in animal cells only. NOTE: Some scientists believe they are found in plant cells but rarely visible. Large Vacuole Large storage compartment used for storing water and other materials needed. Larger vacuoles are found in plant cells. Chloroplast The site of photosynthesis. It is found in plant cells but not in animal cells. Mitochondria The power house of the cell responsible for cellular respiration. Ribosomes Responsible for making proteins in the cell. Found attached to the rough ER and free floating in the cytoplasm.
7 Cell Membrane Structure found in all cells. It is essential in maintaining homeostasis by controlling. Smooth and Rough ER The smooth ER contains enzymes that aid in cell function. The rough ER is responsible for transporting proteins. It acts like a of the cell. Nucleus and Nucleolus The nucleus is the boss of the cell. It holds the (instructions for making proteins). The nucleolus is the center of the nucleus where are made. Small Vacuole Also known as a vesicle, they are used as and transportation vesicles to move materials in and out of the cell. Smaller ones are found in animal cells. Golgi Bodies Responsible for and packaging proteins before they are shipped out to their target areas. Cell Wall Thick, rigid outer wall found in plant cells, but not animal cells. It provides and protection for the cell. Centrioles Structures found in animal cells that aid in. Lysosomes Responsible for the cell, by getting rid of waste. Found in animal cells only. NOTE: Some scientists believe they are found in plant cells but rarely visible. Large Vacuole Large compartment used for storing water and other materials needed. Larger vacuoles are found in plant cells. Chloroplast The site of. It is found in plant cells but not in animal cells. Mitochondria The power house of the cell responsible for. Ribosomes Responsible for making in the cell. Found attached to the rough ER and free floating in the cytoplasm.
8 Thank you for your download! If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to let me know. Your 100% satisfaction is valued. Feedback and ratings are greatly appreciated. Teacher s Notes: You can use this product in many different ways. See some examples below! Interactive notebook Manipulative Pre-assessment, practice assignment, assessment (match pictures with descriptions) Cooperative learning As a station For early finishers Differentiated for you already (give students with special needs labeled squares and descriptions and have them match). Race to complete Game Credits Tangstar Science eractive-notebook-templates-mega-pack-over Templates The Painted Crow Painted-Crow
9 Check out Science From The South for other interactive assessments and assignments!
Structure and Function. Interactive Notebook Activity
 Structure and Function Interactive Notebook Activity Cell Organelles Structure and Function Directions: For the Pocket Cut along the outer solid lines. Fold on the dotted lines. Place a small amount of
Structure and Function Interactive Notebook Activity Cell Organelles Structure and Function Directions: For the Pocket Cut along the outer solid lines. Fold on the dotted lines. Place a small amount of
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS. All living things are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all of the processes of life.
 CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
CHAPTER 4 - CELLS Objectives Name the scientists who first observed living and nonliving cells. Summarize the research that led to the development of the cell theory. State the three principles of the
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
 Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Image Guide. Do NOT Write on this page. It is an Image guide for test questions.
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Structure & Function Quiz Prompts 1. The cell s managing structure; it contains most of the cell s genetic material (DNA, which stores information used to make proteins for cell
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Parts Exam Study Guide
 Cell Parts Exam Study Guide Define these organelles: Cell wall- the definite boundary or wall of a plant cell that provides protection and structural support. Cell membrane- the outer layer that surrounds
Cell Parts Exam Study Guide Define these organelles: Cell wall- the definite boundary or wall of a plant cell that provides protection and structural support. Cell membrane- the outer layer that surrounds
Cell Structure and Function. Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells
 Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Bellringer. Objectives. Chapter 3. Chapter 3. Vocabulary. Cell Wall. Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell.
 Bellringer Objectives Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell. Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. Plant cells and animal cells have many cell parts in common. But they also
Bellringer Objectives Identify the different parts of a eukaryotic cell. Explain the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell. Plant cells and animal cells have many cell parts in common. But they also
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
 Name Date Period Cells Alive Webquest Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and
Name Date Period Cells Alive Webquest Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and
centriole cytoskeleton plays a role in cell division centriole protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
 centriole plays a role in cell division plays a role in cell division centriole cytoskeleton protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
centriole plays a role in cell division plays a role in cell division centriole cytoskeleton protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell protein fibers that provide a framework for the cell cytoskeleton
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
By: Brooke Sheppard
 By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
Journey to the World of Cells
 Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Cells. A typical animal cell THE CELL MEMBRANE FIRST STOP
 WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
Parts (organelles) of the Cell
 Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Name Class Date. What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Cells: A Busy Factory. Adapted from:
 Cells: A Busy Factory Adapted from: http://www.beyondbooks.com/lif71/4a.asp Imagine a bustling factory manufacturing the latest musthave gadget. Whether they make bicycles, cell phones, or hot air balloons,
Cells: A Busy Factory Adapted from: http://www.beyondbooks.com/lif71/4a.asp Imagine a bustling factory manufacturing the latest musthave gadget. Whether they make bicycles, cell phones, or hot air balloons,
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell.
 Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
The World of Cells. Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or Both
 The World of Cells Name Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or Both CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS NUCLEAR MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CHROMATIN SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
The World of Cells Name Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or Both CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS NUCLEAR MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CHROMATIN SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
Draw and Complete the Chart.
 Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
Draw and Complete the Chart. In this True/False Activity; you and your partner will discuss the question, record your response (both), and share your answer with the class. Be prepared to justify your
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14
 Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
Cell Structure and Organelles SBI4U 2016/10/14 Inside the cell These are generalizations, not rules! Everything inside the cell membrane besides the nucleus is called the cytoplasm; The liquid is known
Biology Study Guide Answers. Cells/Cell Transport
 Biology Study Guide Answers Cells/Cell Transport 1 1.) All living things are made of cells. 2.) Cells are the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.) Cells come from pre-existing
Biology Study Guide Answers Cells/Cell Transport 1 1.) All living things are made of cells. 2.) Cells are the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. 3.) Cells come from pre-existing
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Cellular Boundaries. Cell Organelles. The Nucleus and Cell Control. Cell Membrane. Cell Wall. Nucleus 10/11/2012. Cell Membrane Cell Wall
 Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
Cell Organelles Cellular Boundaries Protects cell Support and shape Controls what comes in and out of the cell Selectively permeable the process in which a membrane allows some molecules to pass through
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Organelles Defined. Class Copy CELL STUDY NOTES Class Copy
 Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
You and plants have something in common! 1
 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure & Function These are micrographs of cells you will see in this week's lab. One is plant (onion epithelium), the other animal (human cheek epithelium). Determine which is which
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure & Function These are micrographs of cells you will see in this week's lab. One is plant (onion epithelium), the other animal (human cheek epithelium). Determine which is which
Structures of the CELL
 Structures of the CELL How do cell organelles interact to maintain life? EQ EQ Cell Structures ORGANELLES aka Organelle means little organ Just like organs are the functional units in an organism, ORGANELLES
Structures of the CELL How do cell organelles interact to maintain life? EQ EQ Cell Structures ORGANELLES aka Organelle means little organ Just like organs are the functional units in an organism, ORGANELLES
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Smart cell lesson (1).notebook February 02, 2015
 Cells 1 TEKS Related to the Lesson (12) Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The
Cells 1 TEKS Related to the Lesson (12) Organisms and environments. The student knows that living systems at all levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Cells. Cells are the best!
 Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
Cells Cells are the best! All living things are made of cells Some life forms are just one teeny, tiny cell We are made of trillions of cells! (1,000,000,000,000 = 1 trillion) Cells are really, really
The manager in a factory is responsible for controlling everything that happens within the factory and decides what the factory makes.
 The manager in a factory is responsible for controlling everything that happens within the factory and decides what the factory makes. This is similar to the role of the nucleus in a cell. The nucleus
The manager in a factory is responsible for controlling everything that happens within the factory and decides what the factory makes. This is similar to the role of the nucleus in a cell. The nucleus
Answer Key. Chapter Test A
 Answer Key Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company Chapter Test A Multiple Choice 1. c 2. b 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. b 7. c 8. c 9. d 10. a 11. b 12. a 13. d 14. b 15. c Short Answer
Answer Key Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company Chapter Test A Multiple Choice 1. c 2. b 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. b 7. c 8. c 9. d 10. a 11. b 12. a 13. d 14. b 15. c Short Answer
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE
 CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Name: Per/row: Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology
 Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
Cell Structure and Function Practice: Use Ch 4 in Mader Biology Name: Per/row: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the box next to its description/function. Cell membrane Centrioles Chloroplast Chromatin
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Cellular Structure and Function
 7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Structure Characteristics Function. Double layer of phospholipid molecules studded with proteins
 CELL BOOKLETS: Instructions for creating the pages Take 4 pieces of white computer type paper. Cut them so that you have 4 slips from each page that measure 8-1/2 x 2-3/4 inches. You will have 8 slips
CELL BOOKLETS: Instructions for creating the pages Take 4 pieces of white computer type paper. Cut them so that you have 4 slips from each page that measure 8-1/2 x 2-3/4 inches. You will have 8 slips
Looking Inside Cells
 Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
Objectives. To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles.
 Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
A Tour of the Cell Period
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Name Date Period California State standard covered within this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
The Cell. The building blocks of life
 The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
The Cell The building blocks of life Learning Goals I can describe the cell theory. I can differentiate between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell. I can describe the similarities and differences between
Cell Organelles and their Functions. Chapter 4 Section 2
 Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Directions: Use Aim # 7-13 (Unit 2) to complete this study guide. Part I. Aim # 7 Inorganic and Organic Molecules. Building Blocks (monomers)
 Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 2 Biochemistry and The Cell Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 2 Important Topics: Aim # 7: Inorganic and Organic Molecules Aim # 8: Organic Macromolecules
Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 2 Biochemistry and The Cell Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 2 Important Topics: Aim # 7: Inorganic and Organic Molecules Aim # 8: Organic Macromolecules
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Topic 1: Living Things
 Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Objectives. By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles
 Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
Biology 11 THE Cell Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles Types of Cells There are two types of cells:
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Cell Theory. Cells are the basic unit of life.
 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
3.1 7.1 Cell Theory Cells are the basic unit of life. 3.1 7.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists Galileo (1610) made the first microscope Hooke (1665) made up the term
1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells.
 CELL ORGANELLES - NOTES CELL THEORY Cells are the basic unit of life. The Cell Theory states that: 1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells. 2) All cells carry
CELL ORGANELLES - NOTES CELL THEORY Cells are the basic unit of life. The Cell Theory states that: 1) All organisms are made up of one or more cells and the products of those cells. 2) All cells carry
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION
 CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION CHAPTER 2 https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Cellular components of animal & plant cells https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Plant Cells Cell wall Plasma membrane
CELL STRUCTURE AND CELL ORGANISATION CHAPTER 2 https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Cellular components of animal & plant cells https://wickedbiology.wordpress.com Plant Cells Cell wall Plasma membrane
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
The most valuable lipid ever?
 The most valuable lipid ever? Spermaceti whale oil Used by sperm whales in a special organ in the huge head cavity Largely comprised of cetyl palmitate ww.thisrecording.com www.greenpeace.org Peer Instruction
The most valuable lipid ever? Spermaceti whale oil Used by sperm whales in a special organ in the huge head cavity Largely comprised of cetyl palmitate ww.thisrecording.com www.greenpeace.org Peer Instruction
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
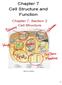 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7, Section 2 Cell Structure Cell as a Factory 1 A. Cell Organization The Cell is like a Factory: Many different workers performing different functions in order
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7, Section 2 Cell Structure Cell as a Factory 1 A. Cell Organization The Cell is like a Factory: Many different workers performing different functions in order
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided.
 Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Same bacteria on pinhead Fig. 4-1c, p.50 Review: Ionic Bonds Na has 11p and 10e making it (+) Cl has 18e and 17 p making it (-) The attraction
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Household pin w/ bactera. Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
St. Brigid Catholic Academy AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells:
 Name: St. Brigid Catholic Academy Date: Science AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells: Below are two types of cells. What similarities
Name: St. Brigid Catholic Academy Date: Science AIM: Do-Now: What is a cell? Jot down what you remember from last year about cells: There are two types of cells: Below are two types of cells. What similarities
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment
 Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Cell Basics. Basic Unit of Life. Prokaryotic. Eukaryotic. Plant Cell. Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Bacteria. Very Complex.
 Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per:
 Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Lysosome ( lie-so-so-m ) Golgi body ( goal-gee ) Vacuole ( vack-u-ol )
 Chapter 31: Page 304 So far, you have looked at four organelles that you can find in both plant and animal cells: the nucleus, ribosomes, ER, and mitochondria. Every eukaryotic cell uses these small structures
Chapter 31: Page 304 So far, you have looked at four organelles that you can find in both plant and animal cells: the nucleus, ribosomes, ER, and mitochondria. Every eukaryotic cell uses these small structures
