-80 Figure 1. Identification of dopaminergic neurons in. VTA slices (a) Micrographs demonstrate the location of the VTA with
|
|
|
- Chester Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Potential (mv) A B C Potential (mv) D E F Biocytin TH Merge R G H Supplemental -8-8 Figure 1. Identification of dopaminergic neurons in -1 VTA slices. -1 (a) Micrographs demonstrate the location of the VTA with -12 the landmark -12 of the substantia nigra compacta (SNc) in a brain slice Time (s) Time (ms) Scale bar, 5 μm, (b) where the stimulating electrode (S) was placed rostral to the recording microelectrode (R). Scale bar, 2 μm, (c) when recording from a VTA neuron. Scale bar, 25 μm. (d) Micrographs of a recorded VTA neuron filled with biocytin and (e) expressing tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), and (f) a superimposed image. Scale bar, 4 μm. Inset in (f): Membrane currents elicited by voltage steps from -7 mv to -5 to -14 mv, in -1 mv-increments in this dopaminergic neuron. Scale bars, 2 ms and 4 pa. Besides, (g) dopaminergic neurons have lower basal firing rates. Scale bars, 1s and 2 mv, (h) wider action potentials, Scale bars, 5 ms and 2 mv. and stronger firing adaptation than GABA neurons. Note that robust Ih currents were elicited by hyperpolarizing voltage steps. VTA: Ventral Tegmental Area, SNc: Substantia Nigra compacta, SNr: Substantia Nigra reticulate.
2 Te mv Te mv Current (pa) Current (pa) IPSC (% of Baseline) 14 1 nm Orexin A Time (ms) Time (ms) Sw 122/123 Time Sw (ms) 121/ Time 2 3 Supplemental Figure 2. Long term treatment with orexin A did not cause receptor desensitization. Time courses of effects of orexin A (1 nm) on IPSCs (n=4). Upper panels are the representative IPSC traces taken at time point 1, 2 and 3, respectively, from a neuron. Scale bars, 5 ms and 2 pa.
3 Current (pa) Te pa EPSC (% of Baseline) nm Orexin A Time (ms) Sw 151 Time (ms) Time (ms) Sw 153/153 Sw 152/ Time (min) Supplemental Figure 3. Orexin A did not depress evoked EPSCs Time courses of effects of orexin A (1 nm) on EPSCs (n=5). Upper panels are the representative IPSC traces taken at time point 1, 2 and 3, respectively, from a neuron. Scale bars, 5 ms and 2 pa. 3
4 A B IPSC (% of Baseline) 3 M AM nm Orexin A Time (min) IPSC (% of Baseline) ** (3) Orexin A Orexin A + AM251 # Supplemental Figure 4. Orexin A depressed IPSCs in dopaminergic neurons of mouse VTA slices in a manner reversed by a CB1R antagonist. (a) The time course of the effect of orexin A (1 nm) on the IPSC amplitude before and after treatment with AM 251 (3 μm). (b) The effect of orexin A (n=3) (black bar) alone or in combination with AM 251 (right slashed bar) on the IPSC amplitude. Data analysis and presentation are the same as Fig. 1. **p<.1 (one sample t test); # p<.5 vs. orexin A alone (paired t test)
5 PAG fr mm VTA -3.8 mm MM SNc mm SNr mm Supplemental Figure 5. Reconstructed bilateral injection sites in the VTA are shown in drawn midbrain coronal sections. Distance from bregma is shown to the right of each section (in millimeters) 1. Injection sites from mice used in the stress induced reinstatement experiment, on site (closed circles); off site (open circles). fr: fasciculus retroflexus, MM: Medial Mammill, PAG: Periaqueductal gray, SNc: Substantia Nigra compacta, SNr: Substantia Nigra reticulate,vta: Ventral Tegmental Area.
6 Supplementary Table 1. Endocannabinoid levels in the VTA of extinguished mice with and without restraint stress. No Stress Stress Endocannabinoids (pmol/g tissue) 2-AG ± ± 42.73* 2-OG ± ± 32.8 P-Gly ± ± PEA ± ± SEA ± ± OEA ± ± 1.11 LEA ± ± 3.79 Mice were randomly divided into restrained and non-restrained groups. Both groups received the same cocaine-conditioning and extinction training in the CPP test. After extinction, the restrained, but not the non-restrained, group received a 3-min restraint stress. Brain tissue containing the VTA was quickly isolated after the restraint stress. Endocannabinoids were extracted and measured by LC/MS/MS as described in Methods. Data are presented as means ± SE. *p<.5, n=8 for each group. 2-AG, 2-arachidonyl glycerol; 2-OG, 2-oleoylglycerol; P-Gly, N-palmitoleoyl glycine; PEA, palmitoylethanolamine; SEA, stearoylethanolamine; OEA, oleoylethanolamine
7 and LEA, dihomo-γ-linolenoylethanolamine.
8 Supplementary References 1. Paxinos G, Franklin K. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Deluxe Edition), Second edn. Academic Press, California, USA (21).
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplemental Information. Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons. Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses
 Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Supplementary Information. Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels. in cell attached patch clamp recordings
 Supplementary Information Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels in cell attached patch clamp recordings Stephen R. Williams 1,2 and Christian Wozny 2 1 Queensland Brain Institute,
Supplementary Information Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels in cell attached patch clamp recordings Stephen R. Williams 1,2 and Christian Wozny 2 1 Queensland Brain Institute,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
GABA injected into the anterior dorsal tegmentum ADT of the midbrain blocks stepping initiated by stimulation of the hypothalamus
 Ž. Brain Research 766 1997 271 275 Short communication Ž. GABA injected into the anterior dorsal tegmentum ADT of the midbrain blocks stepping initiated by stimulation of the hypothalamus H.M. Sinnamon
Ž. Brain Research 766 1997 271 275 Short communication Ž. GABA injected into the anterior dorsal tegmentum ADT of the midbrain blocks stepping initiated by stimulation of the hypothalamus H.M. Sinnamon
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response
 A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Activation of lateral habenula inputs to the ventral midbrain promotes behavioral avoidance
 B r i e f com m u n i c at i o n s npg 212 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Activation of lateral habenula inputs to the ventral midbrain promotes behavioral avoidance Alice M Stamatakis 1 & Garret
B r i e f com m u n i c at i o n s npg 212 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. Activation of lateral habenula inputs to the ventral midbrain promotes behavioral avoidance Alice M Stamatakis 1 & Garret
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche
 Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT
 ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
Supplementary Figure 1. Recording sites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
In Vivo Activation of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons via Sensitized, High-Affinity a6* Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
 Neuron Article In Vivo Activation of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons via Sensitized, High-Affinity a6* Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Ryan M. Drenan, 1 Sharon R. Grady, 2 Paul Whiteaker, 2,6 Tristan McClure-Begley,
Neuron Article In Vivo Activation of Midbrain Dopamine Neurons via Sensitized, High-Affinity a6* Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Ryan M. Drenan, 1 Sharon R. Grady, 2 Paul Whiteaker, 2,6 Tristan McClure-Begley,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
Etv4 BU EMM Etv5 BC MMM UI-M-BH3- Elk1 BC MMM
 Supplementary Tables In situ hybridization probes Genbank Gene Accession Number Clone ID Cat. No Etv1 BC005645 PCR Etv4 BU053662 5062538 EMM1002-5544031 Etv5 BC034680 4036564 MMM1013-7511524 Fev AI876263
Supplementary Tables In situ hybridization probes Genbank Gene Accession Number Clone ID Cat. No Etv1 BC005645 PCR Etv4 BU053662 5062538 EMM1002-5544031 Etv5 BC034680 4036564 MMM1013-7511524 Fev AI876263
Supralinear increase of recurrent inhibition during sparse activity in the somatosensory cortex
 Supralinear increase of recurrent inhibition during sparse activity in the somatosensory cortex Christoph Kapfer 1,2, Lindsey L Glickfeld 1,3, Bassam V Atallah 1,3 & Massimo Scanziani 1 The balance between
Supralinear increase of recurrent inhibition during sparse activity in the somatosensory cortex Christoph Kapfer 1,2, Lindsey L Glickfeld 1,3, Bassam V Atallah 1,3 & Massimo Scanziani 1 The balance between
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Thalamic control of cortical states
 Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
The ventral tegmental area revisited: is there an electrophysiological marker for dopaminergic neurons?
 J Physiol 577.3 (2006) pp 907 924 907 The ventral tegmental area revisited: is there an electrophysiological marker for dopaminergic neurons? Elyssa B. Margolis 1,Hagar Lock 2,Gregory O. Hjelmstad 1,3
J Physiol 577.3 (2006) pp 907 924 907 The ventral tegmental area revisited: is there an electrophysiological marker for dopaminergic neurons? Elyssa B. Margolis 1,Hagar Lock 2,Gregory O. Hjelmstad 1,3
Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies
 Behavioural Brain Research 101 (1999) 129 152 Review article Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies William J. McBride
Behavioural Brain Research 101 (1999) 129 152 Review article Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies William J. McBride
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of GlyT2::eGFP fibers in the mouse thalamus at three different coronal levels. Note the innervation centered in the rostral (CL, PC) and caudal (PF) nuclear groups of
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of GlyT2::eGFP fibers in the mouse thalamus at three different coronal levels. Note the innervation centered in the rostral (CL, PC) and caudal (PF) nuclear groups of
The Pitx3-deficient aphakia mouse: a naturally occurring mouse model of dopamine deficiency van den Munckhof, P.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The Pitx3-deficient aphakia mouse: a naturally occurring mouse model of dopamine deficiency van den Munckhof, P. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The Pitx3-deficient aphakia mouse: a naturally occurring mouse model of dopamine deficiency van den Munckhof, P. Link to publication Citation for published version
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits
 Neuron, Volume 66 Supplemental Information Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits Yusuf Tufail, Alexei Matyushov, Nathan Baldwin, Monica L. Tauchmann, Joseph Georges, Anna Yoshihiro,
Neuron, Volume 66 Supplemental Information Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits Yusuf Tufail, Alexei Matyushov, Nathan Baldwin, Monica L. Tauchmann, Joseph Georges, Anna Yoshihiro,
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA3 output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity
 Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease
 Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11436 Supplementary Figure 1. CRF peptide is localized cholinergic interneurons throughout the nucleus accumbens. Immunofluorescent images demonstrating localization of CRF peptide, tyrosine
doi:10.1038/nature11436 Supplementary Figure 1. CRF peptide is localized cholinergic interneurons throughout the nucleus accumbens. Immunofluorescent images demonstrating localization of CRF peptide, tyrosine
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters. motor- and cue- dependent behaviors
 Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
-Opioid Agonists Directly Inhibit Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons
 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9981 9986 9981 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive -Opioid Agonists Directly Inhibit Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons Elyssa B. Margolis, 1 Gregory O. Hjelmstad,
The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9981 9986 9981 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive -Opioid Agonists Directly Inhibit Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons Elyssa B. Margolis, 1 Gregory O. Hjelmstad,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
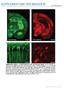 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12107 Supplementary Figure 1. CLARITY preserves GFP and TdTomato signals. (a) 3D rendering of a 1mm-thick Thy1-EGFP M line mouse brain block processed by CLARITY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12107 Supplementary Figure 1. CLARITY preserves GFP and TdTomato signals. (a) 3D rendering of a 1mm-thick Thy1-EGFP M line mouse brain block processed by CLARITY
Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE. The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in
 1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
Synaptic plasticity and addiction
 Synaptic plasticity and addiction Julie A. Kauer* and Robert C. Malenka Abstract Addiction is caused, in part, by powerful and long-lasting memories of the drug experience. Relapse caused by exposure to
Synaptic plasticity and addiction Julie A. Kauer* and Robert C. Malenka Abstract Addiction is caused, in part, by powerful and long-lasting memories of the drug experience. Relapse caused by exposure to
The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience
 J Physiol 595.4 (217) pp 1393 1412 1393 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience Excitation of lateral habenula neurons as a neural mechanism underlying ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion Shashank
J Physiol 595.4 (217) pp 1393 1412 1393 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience Excitation of lateral habenula neurons as a neural mechanism underlying ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion Shashank
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment
 Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience lec9_ neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy
 Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Cogs 107b Systems Neuroscience www.dnitz.com lec9_02042010 neuromodulators and drugs of abuse principle of the week: functional anatomy Professor Nitz circa 1986 neurotransmitters: mediating information
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Roseti et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907324106 A MTLE B AFCD C PFCD I (%) GABA 100 70 6 th untreated ANR152 6 th 6 th 6 th 6 th 6 th oocytes 40 0 100 200 0 100 200 0 100 200 Fig. S1. The
Supporting Information Roseti et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907324106 A MTLE B AFCD C PFCD I (%) GABA 100 70 6 th untreated ANR152 6 th 6 th 6 th 6 th 6 th oocytes 40 0 100 200 0 100 200 0 100 200 Fig. S1. The
Firing properties and functional connectivity of substantia nigra pars compacta neurones recorded with a multi-electrode array in vitro
 J Physiol 588.10 (2010) pp 1719 1735 1719 Firing properties and functional connectivity of substantia nigra pars compacta neurones recorded with a multi-electrode array in vitro Nicola Berretta 1, Giorgio
J Physiol 588.10 (2010) pp 1719 1735 1719 Firing properties and functional connectivity of substantia nigra pars compacta neurones recorded with a multi-electrode array in vitro Nicola Berretta 1, Giorgio
AIR POLLUTION AND THE BRAIN
 AIR POLLUTION AND THE BRAIN Michael Kleinman University of California, Irvine A&WMA International Specialty Conference: Leapfrogging Opportunities for Air Quality Improvement Background Evidence from epidemiological
AIR POLLUTION AND THE BRAIN Michael Kleinman University of California, Irvine A&WMA International Specialty Conference: Leapfrogging Opportunities for Air Quality Improvement Background Evidence from epidemiological
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Dynamic Nigrostriatal Dopamine Biases Action Selection
 Article Dynamic Nigrostriatal Dopamine Biases Action Selection Highlights d Nigrostriatal dopamine signaling is associated with ongoing action selection Authors Christopher D. Howard, Hao Li, Claire E.
Article Dynamic Nigrostriatal Dopamine Biases Action Selection Highlights d Nigrostriatal dopamine signaling is associated with ongoing action selection Authors Christopher D. Howard, Hao Li, Claire E.
S100B+ Cell Density day Spine Formation (%)
 b * CP * HC CP Th DAPI S100B ** 50 40 30 * 20 10 0-10 -20 * * ** 9 6 3 0 0-50 50-100 100-150 150-200 Distance from Prism Face (um) 1-day Spine Formation (%) 1-day Spine Elimination (%) 12 Distance from
b * CP * HC CP Th DAPI S100B ** 50 40 30 * 20 10 0-10 -20 * * ** 9 6 3 0 0-50 50-100 100-150 150-200 Distance from Prism Face (um) 1-day Spine Formation (%) 1-day Spine Elimination (%) 12 Distance from
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches
 Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Cholinergic Activation of M2 Receptors Leads to Context- Dependent Modulation of Feedforward Inhibition in the Visual Thalamus
 Cholinergic Activation of M2 Receptors Leads to Context- Dependent Modulation of Feedforward Inhibition in the Visual Thalamus Miklos Antal., Claudio Acuna-Goycolea., R. Todd Pressler, Dawn M. Blitz, Wade
Cholinergic Activation of M2 Receptors Leads to Context- Dependent Modulation of Feedforward Inhibition in the Visual Thalamus Miklos Antal., Claudio Acuna-Goycolea., R. Todd Pressler, Dawn M. Blitz, Wade
Opioids Excite Dopamine Neurons by Hyperpolarization Interneurons
 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1992, f.?(2): 483-488 Opioids Excite Dopamine Neurons by Hyperpolarization Interneurons of Local S. W. Johnson and R. A. North Vellum Institute, Oregon Health Sciences
The Journal of Neuroscience, February 1992, f.?(2): 483-488 Opioids Excite Dopamine Neurons by Hyperpolarization Interneurons of Local S. W. Johnson and R. A. North Vellum Institute, Oregon Health Sciences
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of. parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala
 Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
Molecular and Physiological Diversity of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in the Midbrain Dopaminergic Nuclei
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 2001, 21(5):1452 1463 Molecular and Physiological Diversity of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in the Midbrain Dopaminergic Nuclei Ruby Klink, 1 Alban de Kerchove
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 1, 2001, 21(5):1452 1463 Molecular and Physiological Diversity of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in the Midbrain Dopaminergic Nuclei Ruby Klink, 1 Alban de Kerchove
Na + /Cl - -dependent Neurotransmitter Transporters. Outline. Synaptic Transmission. How did the neurotransmitter cross the membrane?
 Na /Cl - -dependent Neurotransmitter Transporters Stine Meinild Lundby The Neurobiology Group Molecular, Cellular, and Integrative Physiology Section November 26 th, 2007 slide 1 Outline Synaptic neurotransmission
Na /Cl - -dependent Neurotransmitter Transporters Stine Meinild Lundby The Neurobiology Group Molecular, Cellular, and Integrative Physiology Section November 26 th, 2007 slide 1 Outline Synaptic neurotransmission
Kappa Opioid Receptor Activation Potentiates the Cocaine-Induced Increase in Evoked Dopamine Release Recorded In Vivo in the Mouse Nucleus Accumbens
 (214) 39, 336 348 & 214 American College of. All rights reserved 893-133X/14 www.neuropsychopharmacology.org Kappa Opioid Receptor Activation Potentiates the aine-induced Increase in Evoked Dopamine Release
(214) 39, 336 348 & 214 American College of. All rights reserved 893-133X/14 www.neuropsychopharmacology.org Kappa Opioid Receptor Activation Potentiates the aine-induced Increase in Evoked Dopamine Release
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers
 Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH).
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of the type II spiral ganglion neurons (SGN) via immunofluorescence of peripherin protein (PRPH). (a), (b), PRPH immunolabelling of cryosections from post-natal day
Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC
 Supplementary information Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC Pathway in Pancreatic -Cells Authors: Hodaka Yamada 1,*, Masashi Yoshida 1,*, Kiyonori Ito 1, Katsuya
Supplementary information Potentiation of Glucose-stimulated Insulin Secretion by the GPR40 PLC TRPC Pathway in Pancreatic -Cells Authors: Hodaka Yamada 1,*, Masashi Yoshida 1,*, Kiyonori Ito 1, Katsuya
Cocaine-evoked synaptic plasticity: persistence in the VTA triggers adaptations in the NAc
 aine-evoked synaptic plasticity: persistence in the VTA triggers adaptations in the NAc Manuel Mameli 1, Briac Halbout, Cyril Creton 1, David Engblom, Jan Rodriguez Parkitna, Rainer Spanagel & Christian
aine-evoked synaptic plasticity: persistence in the VTA triggers adaptations in the NAc Manuel Mameli 1, Briac Halbout, Cyril Creton 1, David Engblom, Jan Rodriguez Parkitna, Rainer Spanagel & Christian
Cholinergic Modulation of GABAergic and Glutamatergic Transmission in the Dorsal Subcoeruleus: Mechanisms for REM Sleep Control
 Mechanisms of REM Sleep Control Cholinergic Modulation of GABAergic and Glutamatergic Transmission in the Dorsal Subcoeruleus: Mechanisms for REM Sleep Control David S. Heister, PhD; Abdallah Hayar, PhD;
Mechanisms of REM Sleep Control Cholinergic Modulation of GABAergic and Glutamatergic Transmission in the Dorsal Subcoeruleus: Mechanisms for REM Sleep Control David S. Heister, PhD; Abdallah Hayar, PhD;
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
Target-specific M1 inputs to infragranular S1 pyramidal neurons
 J Neurophysiol 116: 1261 1274, 216. First published June 22, 216; doi:1.1152/jn.132.215. Target-specific M1 inputs to infragranular S1 pyramidal neurons Amanda K. Kinnischtzke, Erika E. Fanselow, and Daniel
J Neurophysiol 116: 1261 1274, 216. First published June 22, 216; doi:1.1152/jn.132.215. Target-specific M1 inputs to infragranular S1 pyramidal neurons Amanda K. Kinnischtzke, Erika E. Fanselow, and Daniel
The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience
 J Physiol 593.22 (215) pp 495 4922 495 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience High dendritic expression of I h in the proximity of the axon origin controls the integrative properties of nigral dopamine
J Physiol 593.22 (215) pp 495 4922 495 The Journal of Physiology Neuroscience High dendritic expression of I h in the proximity of the axon origin controls the integrative properties of nigral dopamine
