MIT 9.14 Class 9a. Autonomic nervous system structures. A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins
|
|
|
- Dwayne Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 5: Differentiation of the brain vesicles MIT 9.14 Class 9a Autonomic nervous system structures
2 Autonomic nervous system Overview of functions Schematic overview Formation of sympathetic ganglia from the neural crest (REVIEW) Sympathetic innervation pattern (thoracicolumbar system) Cf. parasympathetic innervation (cranio-sacral system); dual innervation of smooth muscles and glands. Chemical mediation at synapses: discovery by Otto Loewi in 1921.
3 Closure of neural tube; formation of sympathetic ganglia Neural plate Ectoderm Notochord Neural groove Neural tube and neural crest Roof plate Alar plate Basal plate Floor plate
4 Autonomic nervous system Overview of functions Schematic overview Formation of sympathetic ganglia from the neural crest Sympathetic innervation pattern (thoracicolumbar system) Cf. parasympathetic innervation (cranio-sacral system); dual innervation of smooth muscles and glands. Chemical mediation at synapses: discovery by Otto Loewi in 1921.
5 INTERNAL STRUCTURE OF THE SPINAL CORD Dorsal Root Fibers Nuc cornucommissuralis Posterior Fasc. Gracilis Substantia Gelatinosa Nuc. Posteromarginalis Internal Structure Spinal Cord Segment C1 Internal structure of Ventral Root Fibers Nuc. Motorii Medialis Zone of Lissauer Lat. Corticospinal Tr. Nuc. Proprius Cornu Dorsalis Nuc. Reticularis Nuc. Dorsalis (of Clarke) Ant. Spinocerebellar Tr. Lat. Spinothalamic Tr. Nuc. Motorii Lateralis Fasc. Proprius Ant. Spinothalamic Tr. Vestibulospinal Tr. Segment C5 Segment C8 Segment T2 spinal cord: II III IV I Segment T10 Note the V VI Segment L1 lateral horn X M VIII IX VII IX IX IX Segment L4 Segment S4 Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare.
6 Sympathetic nervous system axons, schematic section of spinal cord, thoracic level xxxxx xxxxx xx Descending reticulospinal fibers Paravertebral ganglion Prevertebral ganglion, e.g., celiac Dorsal root ganglion Spinal nerve Smooth muscle: Glands; intestinal tract; blood vessels, erector pili (hairs); sweat glands. Cardiac muscle To striated muscles
7 Sympathetic Innervation (P. Brodal) Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare.
8 Autonomic nervous system Overview of functions Schematic overview Formation of sympathetic ganglia from the neural crest Sympathetic innervation pattern (thoracicolumbar system) Parasympathetic innervation (cranio-sacral system); dual innervation of smooth muscles and glands. Chemical mediation at synapses: discovery by Otto Loewi in 1921.
9 Vagus nerve (10 th cranial nerve)
10 MESENCEPHALON Visceral Efferent Oculomotor Nucleus (Edinger-Westphal) Ciliary Ganglion Oculomotor Nerve MEDULLA OBLONGATA MEDULLA OBLONGATA Superior Salivary Nucleus Maxillary Nerve Intermediate Nerve Greater Petrosal Nerve Facial Nerve Chorda Dorsal Motor Tympani Vagus Nucleus Mandibular Nerve Glossopha- Ryngeal Nerve Vagus Nerve Tympanic Nerve Pterygopalatine Ganglion Lingual Nerve Submandibular Ganglion Otic Ganglion Pupillary Sphincter Muscle Ciliary Muscle Lacrimal Gland Nasal & Palatal Gland Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Parotid Gland Auriculo-Temporal Nerve Pharynx Esophagus Trachea, Bronchi Lungs Parasympathetic Innervation (P. Brodal) MEDULLA SPINALIS (S 3 - S 4 ) Ganglia & Plexuses Pelvic Nerve Sympathetic Trunk Heart Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine Liver, Pancreas Gallbladder Large Intestine (Lower) Rectum Bladder Genitals Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare.
11 Autonomic nervous system Overview of functions Schematic overview Formation of sympathetic ganglia from the neural crest Sympathetic innervation pattern (thoracicolumbar system) Parasympathetic innervation (cranio-sacral system); dual innervation of smooth muscles and glands. Chemical mediation at synapses: discovered by Otto Loewi in 1921 (REVIEW)
12 Autonomic pathways with neurotransmitters showing accelerator & decelerator nerves of the heart
13 An advance in PNS anatomy in the late part of the 20 th century: The enteric nervous system The little brain in the gut: A semi-autonomous network that may contain as many neurons as the entire spinal cord. In the wall of the intestine, this network contains multiple plexi: Myenteric plexus (the outer plexus) Submucous plexus (the middle plexus) Villous plexus (inner plexus) Periglandular plexus (inner plexus) Innervation by vagus nerve Cf. Cardiac Ganglion: Does the heart have a brain? Various neurotransmitters are used in this system.
14 Levels of autonomic control The enteric nervous system shows autonomy at the lowest level, in control of the alimentary tract. Within the CNS, there are lower levels of control of the internal environment capable of some autonomy. Temperature regulation is a good example. For this function, each higher level adds more refinement.
15 Levels of control in the ANS: the temperature regulation systems Temperature is regulated by mechanisms operating at all levels: spinal, hindbrain, midbrain, hypothalamus of the tweenbrain. Each higher level adds refinements: for endothermic animals, this means speed and a narrower range of target temperatures. See reviews by Evelyn Satinoff. For other functions, there is probably a similar hierarchy.
16 A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 5: Differentiation of the brain vesicles MIT 9.14 Class 9b Differentiation of the brain vesicles: Introduction to hindbrain and segmentation
17 The encephalon* (brain) Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) Midbrain (mesencephalon) Forebrain (prosencephalon) Tweenbrain (diencephalon) Endbrain (telencephalon) * In the head
18 The embryonic neural tube above the spinal cord What are the "flexures" in the neural tube? (See, e.g., Nauta & Feirtag, pp )
19 The flexures of the developing neural tube s rostral end, human (From Nauta & Feirtag) Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare.
20 Origin of the term rhombencephalon What happens to the roof plate where the pontine flexure (bend) forms? (See, e.g., Nauta & Feirtag, p. 162)
21 a. Spinal cord a. Spinal a. Spinal cord cord b. Hindbrain b. Hindbrain (rhombencephalon) b. Hindbrain (rhombencephalon (rhombencephalon c. Midbrain c. Midbrain (mesencephalon) c. Midbrain (mesencephalon) (mesencephalon) d. Tweenbrain d. Tweenbrain (diencephalon) d. Tweenbrain (diencephalon) (diencephalon) e. Endbrain e. Endbrain (telencephalon) e. Endbrain (telencephalon) (telencephalon) Forebrain Basic subdivisions, embryonic neural tube: Where is the rhombus? What is it? Reminder: Students should understand and know this figure! (prosencephalon)
22 Terminology: What is the obex? Find it in the previous picture.
23 The hindbrain (rhombencephalon) topics Basic structural organization compared with spinal cord Basic functions Cell groupings; origins Sensory channels and the trigeminal nerve The "distortions" in the basic organization
24 Basic organization: "a glamorized spinal cord" Alar and basal plates; widened roof plate (with widened ventricle the 4 th ventricle) No more law of roots; some cranial nerves are "mixed nerves" containing both sensory and motor components.
25 Cell groupings Secondary sensory nuclei (cell groups) in the alar plate Motor nuclei (groups of motor neurons) in the basal plate The arrangement can be understood as a simple modification of spinal cord organization.
26 Embyonic spinal cord & hindbrain compared Embryonic spinal cord (in cross section) Ventricular zone Intermediate zone Marginal zone Alar plate Basal plate Embryonic hindbrain Sulcus limitans Secondary sensory cell groups in intermediate zone of alar plate Alar plate Motor neuron cell groups in intermediate zone of basal plate Basal plate
27 Hindbrain functions Routine maintenance: the support services area of the CNS, for centralized control of spinal functions Vital functions (control of breathing, blood pressure & heart rate, & other visceral regulation) Motor coordination (cerebellum, vestibular system) Fixed Action Pattern generators: swallowing, vomiting, eyeblink, grooming, smiling, frowning, righting, etc. Widespread modulation of brain activity: sleep & waking; arousal effects [See following illustrations] Role in mammalian higher functions: movement control for functions of more rostral brain systems for speech (tongue, lip, breath control) for emotional displays, especially in facial expressions for eye movements
28 Neurons of the reticular formation Isodendritic core of the brainstem (Ramon-Moliner & Nauta) Neuropil segments Axons with very wide distributions Contrast: isodendritic & idiodendritic
29 Dendritic orientation of reticular formation neurons in hindbrain, forming a series of neuropil segments: Collaterals of pyramidal tract axons have similar distributions. For contrast, cells of the hypoglossal nucleus are also shown Figure removed due to copyright restrictions. Golgi stain, parasagittal section of hindbrain, young rat. From Scheibel & Scheibel, 1958
30 Neuron of hindbrain reticular formation: Axon has ascending and descending branches, each with widespread distribution of terminations Figure removed due to copyright restrictions. 2-day old rat, Rapid Golgi stain, from Scheibel & Scheibel, 1958
31 Notes on hindbrain origins: definitions Segmentation above the segments of the spinal cord: The somitomeres & branchial arches in the mesoderm, and the rhombomeres of the CNS See Nauta & Feirtag, ch.11, p. 170, on the branchial motor column -- in addition to the somatic and visceral motor columns. Sulcus limitans Visceral motor column Somatic motor column Branchial motor column Reticular formation Basal plate Alar plate
32 Three segmented systems, 3-day chick embryo: somites, branchial arches, rhombomeres s10 s2 r1 Rhombomeres r2 of Hindbrain r3 r4 r5 r6 r7 r8 Somites b1 b2 b3 b4 Limb Bud s20 MidBrain Branchial Arches Branchial arches of the mesoderm, innervated by the Trigeminal Motor & the Facial Nucleus and by Nucleus Ambiguus. (Functions of Nuc. Ambiguus: swallowing and vocalization) The branchial arches in humans form jaws, the auditory ossicles, the hyoid, and the pharyngeal skeleton including thyroid cartilage. Wolpert, 2002 Fig Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare.
33 Hox gene expression in the mouse embryo after neurulation The mesoderm below the head region becomes segmented: Somites, 2-day chick embryo Figure removed due to copyright restrictions. Somites, 2-day chick embryo Please see: Wolpert, Lewis, et al. Principles of Development. 2nd ed. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2002, p. 22. ISBN: (Photo from Wolpert, 2002, p. 22)
34 Genes underlying segmentation topics Ancient origins of segmentation along the A-P axis, with corresponding nervous system differentiation The homeobox genes: What are they? Examples of gene expression patterns
35 Homeobox genes in Drosophila, and 13 paralogous groups in 4 chromosomes of mouse Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare.
36 Hox gene expression along the antero-posterior axis of the mouse mesoderm Figure removed due to copyright restrictions. Please see: Figure 4.11 from Wolpert, Lewis, et al. Principles of Development. 2nd ed. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, ISBN: E 9.5 mouse embryos, immunostained using antibodies specific For the protein products of the indicated Hox genes. (Wolpert, 2002, fig. 4.11)
37 Hox gene expression along the antero-posterior axis of the mouse mesoderm Vertebral regions Posterior Caudal Sacral Lumbar Thoracic Anterior Cervical Hox genes d3 d4 d8 d9 d10 d11 d12 d13 c5 c6 c8 c9 b1 b4 b5 b9 b7 a1 a4 a5 a6 a7 a10 a11 Anterior margins of expression Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare. (Wolpert, 2002, fig. 4.12)
38 Figure removed due to copyright restrictions. Allman, John Morgan. "Scanning Electron Microscope Photo." In Evolving Brains. New York, NY: Scientific American Library: Distributed by W.H. Freeman and Co., ISBN: Rhombomeres: the 8 segments of the rhombencephalon (Scanning e.m. photo from Allman, 2000)
39 r7 r6 r5 r4 r3 r2 r1 r6 r5 r4 r3 r2 Gene Expression Kreisler Krox-20 Sek-1 Sek-2 Sek-3 Sek-4 Ebk Elk-L Elf-2 Elk-L3 Hoxa-1 Hoxb-1 Hoxa-2 Hoxb-2 Hoxa-3 Hoxb-3 Hoxd-3 Hoxd-4 Hoxb-4 Hoxa-4 and Rhombomeres (Lumsden & Krumlauf 96) Fgf-3 Follistatin CRABP-1 RAR α RAR β Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare.
40 The hindbrain neuromeres (= rhombomeres): A) Expression of transcription factor genes; B) Fate of embryonic precursor cells injected before and after rhombomere formation r1 r2 r3 r4 r5 r6 r7 hox d4 hox b2 hox b3 hox b1 krox 20 A) Gene Expression boundaries B) Lineage restriction boundaries Figure by MIT OpenCourseWare. From Striedter (2005), p. 79
41 MIT OpenCourseWare Brain Structure and Its Origins Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
Autonomic pathways: a selective schematic view
 Autonomic pathways: a selective schematic view Thoraco -lumbar Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with permission. Schneider, G. E. Brain Structure and its Origins: In the Development and in Evolution of Behavior
Autonomic pathways: a selective schematic view Thoraco -lumbar Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with permission. Schneider, G. E. Brain Structure and its Origins: In the Development and in Evolution of Behavior
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
MIT 9.14 Class 9b-10a
 9.14 - Brain Structure and its Origins Spring 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2005
9.14 - Brain Structure and its Origins Spring 2005 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2005
The thickening. embryonic neural tube. Preview: Fig 1.3. Forebrain (prosencephalon)
 9.14 Worksheets Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with permission. Schneider, G. E. Brain structure and its origins: In the Development and in Evolution of Behavior and the Mind. MIT Press, 2014. ISBN: 9780262026734.
9.14 Worksheets Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with permission. Schneider, G. E. Brain structure and its origins: In the Development and in Evolution of Behavior and the Mind. MIT Press, 2014. ISBN: 9780262026734.
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Review of Nervous System Anatomy
 For the real amazement, if you wish to be amazed, is this process. You start out as a single cell derived from the coupling of a sperm and an egg; this divides in two, then four, then eight, and so on,
For the real amazement, if you wish to be amazed, is this process. You start out as a single cell derived from the coupling of a sperm and an egg; this divides in two, then four, then eight, and so on,
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Autonomic Nervous System. Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24
 Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
Autonomic Nervous System Ms. DS Pillay Room 2P24 OVERVIEW OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS PNS BRAIN SPINAL CORD SOMATIC ANS SYMPATHEIC PARASYMPATHEIC LOCATION OF GANGLIA IN THE ANS Short post-ganglionic
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The autonomic nervous system functions
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
!! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: DIVISIONS AND STRUCTURE The Autonomic Nervous System and its Divisions: Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) controls
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Stimulatory
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 15 Part 1 The Autonomic Nervous System and Visceral Sensory Neurons The ANS and Visceral Sensory Neurons
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors. Chapter 9. Autonomic Motor Nerves. Autonomic Neurons. Autonomic Ganglia. Autonomic Neurons 9/19/11
 Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Chapter 9 I. Neural Control of Involuntary Effectors The Autonomic Nervous System Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Autonomic
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 14 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
MITOCW MIT9_14S14_lec09.mp3
 MITOCW MIT9_14S14_lec09.mp3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free.
MITOCW MIT9_14S14_lec09.mp3 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free.
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1)
 I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
I. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) A. Dual Innervation B. Autonomic Motor Pathway 1. Preganglionic Neuron a. Preganglionic Fibers (Axons) (1) Acetylcholine - ACh 2. Ganglion (Ganglia) 3. Ganglionic Neuron
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Organisation of the nervous system
 Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Chapter1 Organisation of the nervous system 1. Subdivisions of the nervous system The nervous system is divided: i) Structurally The central nervous system (CNS) composed of the brain and spinal cord.
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Chapter 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems Anatomy of Autonomic Motor Pathways Preganglionic neuron
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D.
 Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Chapter 20 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 632) 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2.
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic nervous system organization Sympathetic Nervous System division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs. János Hanics M.D.
 Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
Sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic innervation and reflexes of pelvic organs János Hanics M.D. Vegetative (autonomic) nervous system General function: to keep the homeostasis of
Divisions of ANS. Divisions of ANS 2 Divisions dualing innervate most organs. Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9)
 Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9) Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) general properties anatomy Autonomic Effects on Target Organs Subs of Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral
Autonomic Nervous System (Chapter 9) Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) general properties anatomy Autonomic Effects on Target Organs Subs of Nervous System Central nervous system Brain Spinal cord Peripheral
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
Brainstem. Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem
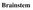 Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni
 Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
Done by: Tymaa Al-zaben & Amin Al-ajalouni ** Hello SERTONIN! SLIDE 3 note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures The Autonomic Nervous System Function : Regulate
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
The Nervous System. Autonomic Division. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
C h a p t e r 17 The Nervous System Autonomic Division PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY
 Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Autonomic Nervous System DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the autonomic nervous system. Describe the structure of autonomic nervous system Trace
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
1/10/2013. What do neurons look like? Topic 14: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves. How do neurons work? The nervous impulse. Specialized Neurons
 Topic 4: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves What do neurons look like? Neurons What do they look like? How do they work? Neuronal and spinal organization What is the difference between neuron & nerve? How
Topic 4: Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves What do neurons look like? Neurons What do they look like? How do they work? Neuronal and spinal organization What is the difference between neuron & nerve? How
4/8/2015. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS. Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: Divisions of the ANS Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Dual innervation ~ All visceral organs served by both divisions, usually cause opposite
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
4/9/2019. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Learn and Understand: What appears to be two separate systems actually work together to maintain homeostasis under varying conditions. Receptors on the membranes of ANS effectors
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE. Thomas Marino, Ph.D.
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Review or skim Ch 12 on the vascular supply of the brain. Just look at pictures and legends for the clinical part at the end.
 Dental Neuroanatomy January 20 and 27, 10-12, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. Dear Students: Please print these notes and bring them with you. My style is to use a Tablet PC and I draw on either a Word
Dental Neuroanatomy January 20 and 27, 10-12, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. Dear Students: Please print these notes and bring them with you. My style is to use a Tablet PC and I draw on either a Word
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 15 The Autonomic Nervous System Comparison of Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems The somatic nervous system includes both sensory and motor
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull. Emphasis on Amniota
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull Emphasis on Amniota Initial introduction to components parts of a vertebrate head. This lecture
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull Emphasis on Amniota Initial introduction to components parts of a vertebrate head. This lecture
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
PSY 215 Lecture #5 (01/26/2011) (Anatomy of the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96
 Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
9.01 Midterm Examination NAME October 27, 2003
 9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
Autonomic Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the CNS components of the ANS 2. Understand the peripheral pathways that connect the ANS with targets in the body. 3. Understand the classes of disorders
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions
 16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
16 Neural Integration II: The Autonomic Nervous System and Higher-Order Functions PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Figure 16-1 An Overview of Neural
cardiac plexus is continuous with the coronary and no named branches pain from the heart and lungs
 Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
Nerves of the Thoracic Region Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes cardiac plexus cardiac brs. of the vagus n. and cervical ; thoracic l nn. the heart and lungs cardiac, cervical cardiac, vagal vagus
1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Cranial Nerve Nuclei MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning materials,
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Cranial Nerve Nuclei MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning materials,
Autonomic Division of NS
 Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
Autonomic Division of NS Compare and contrast the structures of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic divisions, including functions and neurotransmitters. Show the levels of integration in the ANS,
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Laboratory Manual for Comparative Anatomy and Physiology Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
 Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day)
 Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Autonomic Nervous System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Nervous System Divisions of the nervous system The human nervous system consists of the central nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu
 Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system
 Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system 1 The nervous system for topographic indication is divided into two divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) i peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Overview of the autonomic (vegetative) nervous system 1 The nervous system for topographic indication is divided into two divisions: the central nervous system (CNS) i peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Polarity and Segmentation. Chapter Two
 Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
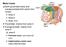 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th
 3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th week differentiates into the CNS = brain development begins
3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th week differentiates into the CNS = brain development begins
The Autonomic Nervous
 Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Basic Organization of the Nervous System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basic Organization of the Nervous System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To introduce some of the basic terminology used throughout the course in describing structures within the central nervous
Basic Organization of the Nervous System George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To introduce some of the basic terminology used throughout the course in describing structures within the central nervous
Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System. Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions. Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers. ANS Neurotransmitters
 Chapter 15 Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers ANS Neurotransmitters Autonomic Nervous System Portion of the nervous
Chapter 15 Introduction to The Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic Divisions Adrenergic and Cholinergic Fibers ANS Neurotransmitters Autonomic Nervous System Portion of the nervous
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
