MicroRNA-663 Targets TGFB1 and Regulates Lung Cancer Proliferation
|
|
|
- Mavis Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
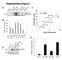
1 MicroRNA-663 Targets TGFB1 and Regulates Lung Cancer Proliferation RESEARCH COMMUNICATION MicroRNA-663 Targets TGFB1 and Regulates Lung Cancer Proliferation Liu Zhi-Yong 1&, Zhang Guang-Ling 2&, Wang Mei-Mei 2, Xiong Ya-Nan 2, Cui He-Qin 3* Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) play critical roles in many different cellular processes, including metabolism, apoptosis, differentiation, and development. In this study, mir-663 was shown to be highly expressed in patients with lung cancer. Furthermore, mir-663 contributed to lung cancer cell proliferation of by regulating TGFB1, P53, Bax, and Fas directly or indirectly. Our results demonstrated that mir-663 plays an important role in the biology of lung cancer and may be useful in developing therapies targeting genes. Keywords: mir lung cancer - oncogene - A549 - TGFB1 Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev, 12, Introduction Lung cancer is a disease that is characterized by frequent mutations, amplifications, and epigenetic changes in various cancer-related genes, and is the major cause of death from neoplastic disease worldwide. The main types of lung cancer are small cell lung carcinoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma (Tiozzo et al., 2009; Young et al., 2009). The most common cause of lung cancer is longterm environmental exposure and genetic predisposition. Early studies suggest potential involvement of altered regulation of micrornas (mirnas) in the pathogenesis of a limited range of human cancers (Hiyoshi et al., 2009; Aguda et al., 2008; Mathonnet et al., 2007). MicroRNAs (mirnas) are a class of endogenous small, single-stranded, non-coding RNAs. MicroRNAs negatively regulate the expression of target genes through interacting with complementary sites in the 3 untranslated region (3 UTR) of their target genes (Bartel et al., 2004). MiRNAs are considered to play crucial roles in many cellular processes, such as proliferation, development, differentiation, and apoptosis (Agrawal et al., 2009; Matsubara et al., 2007; Venugopal et al., 2010). Studies have shown that mirnas may function as a novel class of oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. These oncogene mirnas usually promote tumor development by negatively inhibiting tumor suppressor genes. The amplification of an oncogenic mirna could eliminate the expression of a mirna-target tumor suppressor gene and lead to cancer progression (Osada et al., 2007). In the present study, we looked for alterations of mir-663 in ten patients with lung cancer. We here have documented the first evidence of frequent and marked overexpression of mir-663 in lung cancers. We also have shown an inhibitory effect of mir-663 on the expression of TGFB1, which we preselected based on the potential significance of its putative TargetScan algorithm predicted target genes. TGFB1 is a potent growth inhibitor implicated in the development of several cancers (Elliott et al., 2005). In addition, our findings suggest that mir- 663 regulates lung cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis through targeting TGFB1, and also represents a promising therapeutic approach in lung cancer. Materials and Methods Cell culture The A549 cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 (Gibco, Grand Island) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100U/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/ml streptomycin at 37ºC in humidified air containing 5% carbon dioxide. RNA extraction and real-time analysis Briefly, total RNA was extracted from 10 paired samples of lung cancer and normal lung tissues by using Trizol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer s instructions. These tissues were provided by Tian Jin hospital. The mature species of mir-663 was then measured by quantitative real-time PCR specific for mir-663 [23]. Accordingly, 2 μg total RNA was reverse transcribed to cdna using the following stem loop RT primers, 5 - GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTGCACTGGAT ACGACGCGG TCC -3. The PCR primers were mir-663-forward, 5 - TGCGGAGGCGGGGCGCCGC GGG -3, and reverse, 5 -CCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3. The PCR cycles were as follows: initial denaturation at 94 C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 94 C for 30 s, 56 C for 30 s, and 72 C for 30 s. Concentrations of the mir- 663 were normalized by the average of the control samples. Transfection A549 cells were plated at a density of cells per well in 6-well plates. Transfection was performed using Lipofectamine 2000 at a final concentration of 1 μg/ml (Invitrogen, USA). The final concentrations of DNA transfected into A549 cells were oligonucleotides (200 nm), and plasmids (1 μg/ ml). 1 Hebei United University Affiliated Hospital, 2 Basic Medical College, 3 Life Science College, Hebei United University, Tang Shan, China & Equal contributions *For correspondence: cuiheqin@yahoo.cn Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12,
2 Liu ZhiYong et al Growth curve A549 cells were plated at a density of per well in 6-well plates, and were transfected as described above after 24 h of incubation. After transfection, the cells were counted once per day for 10 days. Each treatment was carried out in triplicate. MTT assay Cells were seeded into 96-well plates at a density of 20% per well in a fixed volume of 100 μl and incubation under 5% CO2 at 37 C overnight. Then cells were tranfected. After 72 h incubation, 20 μl of MTT solution (5mg/mL)were added to each well. Incubation with MTT was terminated. Then, the 96-well plate was kept at 5 C for 1-2 h. Finally, the absorption was measured at 570 nm. Soft agar assay for colony formation For colony formation assay, 5 x103 cells in 2 RPMI 1640 mixed equally with 1% agar were distributed on a total of ten 6-cm-diameter dishes, and were incubated at 37. A colony was counted only if it contained more than 50 cells, and the number of colonies was counted the 9th day after seeding. Each treatment was carried out in triplicate. DNA construction and fluorescent reporter assays TGFB1 expression plasmid with 3 UTR or without 3 UTR was cloned. These two DNA fragments from cdna library both cloned into pcdna3.1 vector by EcoRI/XbaI site. Primers of full length TGFB1 without 3 UTR: forward primer, 5 -CCGGAATTCGCCACCATGCCGCCCTCCGGGCTG-3 ; reverse primer, 5 -CTAGTCTAGA TCAGCTGCACTTGCAGGAG-3. Primers of full length TGFB1 with 3 UTR: forward primer, 5 -CCGGAATTCGCCACCATGCCGCCCTCCGGGCTG-3 ; reverse primer, 5 - CTAGTCTAGA CCGCAGTCCTCTCTCCATC-3. The 3 UTR of TGFB1 (144 bp) containing the TGFB1-miR-663 response element was cloned into the PmeI/XbaI site of pmirglo Luciferase vector (Promega). Mutant 3 UTR of TGFB1 lacks 1-54 gene fragment were synthesized and cloned into the PmeI/XbaI site of pmirglo Luciferase vector (Promega). We transfected A549 cells with 0.2 μg of the pmirglo Vector reporter vector with wild TGFB1 3 UTR or mutation TGFB1 3 UTR and 0.1 μg of the pmirglo control vector. Twenty-four hours after transfection, we transfected cells with 200 ng of mir-663 LNA; and the control LNA was transfected in parallel. We collected and assayed luciferase expression level 48 h after transfection. Each treatment was carried out in triplicate. Western blot Cells were resuspended in protein extraction buffer, as described previously[18]. Proteins were separated on 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel, and electrophoretically transferred to Immobilon-P membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The membranes were incubated with antibodies overnight at 4. TGFB1 antibodies and β-tublin were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA, USA). The antibodies were used at 1:100 and 1:2,000 dilutions, as indicated. After incubating the membranes with secondary antibodies conjugated to peroxidase, the signal was revealed with Immobilon Western (Millipore, USA). Statistical Analysis Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis utilized two-tailed Student s t test and statistical significance was set as P < Results MiR-663 was highly expressed in lung cancer patients To validate the expression pattern of mir-663 of lung cancer, we first performed microrna specific qrt-pcr on 10 pairs of lung cancer tissues and their adjacent normal tissues. Moreover, the lung cancer A549 cells were also analyzed. As shown in Figure 1, mir-663 was markly up-regulated in lung cancer tissues and A549 cells. Reduction of mir-663 inhibits the proliferation ablility of A549 cells Because mir-663 is expressed at a high level in lung cancer cells, the mir-663 LNA (locked nucleic acid) was Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12, Figure 1. Expression of the Mature Species of the MiR After extracting the total RNA from 10 specimens of lung cancer and from 10 specimens of normal lung, mir-663 level was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. U6snRNA was used as endogenous normalizer. The histogram shows the relative levels of mir-663 expression. A Figure 2. Reduction of MiR-663 Inhibits the Proliferation of A549 Cells. A. A549 cells were plated at a density of per well in 6-well plates, and were transfected with mir-663 LNA or control LNA. Starting at 24 h after transfection, the cells were counted once per day for 7 days. Each data point represents the average of three independent experiments. B. A549 cells were plated at a density of per well in 6-well plates, and treated as in A, after 10 days, the number of visible colonies was counted using a dissecting microscope. Each data point represents the average of three transfected into A549 cells. We then used cell growth curve and colony formation assay to validate the effects of mir-663 on the proliferation of A549 cells. As shown in Figure 2, these results clearly demonstrate that decreased level of mir-663 can significantly inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells. TGFB1 is a direct target of mir-663 Recent studies indicate that mirnas repress gene expression through targeting the 3 UTR region. Thus we used the mirna target prediction program Targetscan to find the candidate target genes of mir-663. As shown in figure 3A, TGFB1 was select for the candidate target gene of mir-663 because the 3 UTR of TGFB1 mrna carries several binding sites matching with the seed region of mir-663. Then we investigate the protein expression level of TGFB1 in A549 with altered expression levels of mir-663 by Western blotting. We transfected mir-663 LNA into A549 cells and scrambled oligonucleotides were used as negative control. As shown in figure 3B and 3C, TGFB1 protein level were up-regulated in A549 cells at 48 h after transfection with mir-663 LNA. To validate the direct interaction of TGFB1 and mir-663, we cloned the 3 UTR of TGFB1 (predicted to interact with mir-663) into a luciferase reporter vector, and co-transfected with mir-663 LNA or scrambled oligonucleotides into the A549 cells. We found that suppression of the expression of mir-663 in A549 cells could pecifically enhance the B
3 MicroRNA-663 Targets TGFB1 and Regulates Lung Cancer Proliferation Figure 3. Identification of TGFB1 as a Direct Target Gene of MiR-663. A. The 3 UTR of TGFB1 mrna Figure 4. Highly Expressed TGFB1 Inhibits A549 Cell carries a binding site for mir-663 and the mutation sites Proliferation. A. A549 cells were plated at a density of per well in 6-well plates, and were transfected with pcdna3/ of mir-663 seed region. B. A549 cells were transfected TGFB1 or pcdna3 as control. After 10 days, 31.3 the number of with luciferase reporter plasmid with wild type TGFB1 visible colonies was counted using a dissecting microscope. B 3 UTR (TGFB1-3 UTR) along with either mir-663 LNA and C. A549 cells were plated at a density of per well in or control LNA. The luciferase intensity was detected 96-well plates, and were trasfected as in A. 48 h after transfection, 25.0 and normalized by the amount of total protein. C. A549 cell viability was analyzed 38.0 by MTT assay. Each data point cells were transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid represents 31.3 the average of three with WT TGFB1 3 UTR or Mut TGFB1 3 UTR along with either mir-663 LNA or control.lna. The luciferase 0 intensity was detected and normalized by the amount of total protein. The fluorescence value of TGFB1-3 UTR group was set at 1, and the relative luciferase intensity is shown. Each data point represents the average of three expression level of a reporter gene that carries a TGFB1 3 UTR. Moreover, no marked difference were observed in cells transfected with mutant TGFB1-3UTR no matter the real level of mir-663 (p > 0.05). These results demonstrated that mir-663 can specifically interacted with TGFB1 mrna and repress TGFB1 expression at post-transcriptional level. TGFB1 inhibits A549 cell proliferation In order to verify that mir-663 regulates A549 cell proliferation through targeting TGFB1, we further elucidate the real role of TGFB1 in vitro. We constructed the plasmid expressing TGFB1 (pcdna3/tgfb1, without 3 UTR) to increase the protein level of TGFB1 in A549 cells and investigated the possible effects of TGFB1 on cell proliferation ability. As shown in Figure 4A, the protein level of TGFB1 was increased when pcdna3/ TGFB1 was transfected into A549 cells. Furthermore, the viability and capacity of cell proliferation were both significantly reduced through MTT and a soft agar assay (Figure 4B and 4C). Newly diagnosed without treatment Newly diagnosed with treatment Figure 5. A549 cells were plated at a density of per well in 6-well plates, and were transfected with mir-663 LNA or control LNA as control. 48 h after transfection, cells were lysated, and the protein level of TGFB1, Bax, Fas, and P53 were detected. β-tubulin was used as the loading control. MiR-663 regulates P53, Fas, and Bax expression through targeting TGFB1 Since mir-663 and TGFB1 has been shown to be related with cell growth and proliferation and TGFB1 is a direct target of mir-663, we further investigate the possible mechanism in lung cancer proliferation about mir-663 and TGFB1. It has been reported that TGFB1 is a multifunctional cytokine and involved in mulitiple cell progesses including cell apoptosis and proliferation. Therefore, we test the expression level of three apoptosisrelated genes, P53, Fas, and Bax, in the situations of alternated levels of mir-663 and TGFB1. As shown in figure 5, obviously increased level of these three genes were observed in TGFB1 over-expressed group. These result indicated that mir-663 may exert its function through target TGFB1 and other three genes, P53, Fas, and Bax, may be the downstream genes of TGFB1 in regulating lung cancinogenesis. Discussion Work in recent years has identified over 1000 kinds of micrornas in humans. MicroRNAs play critical roles in many different cellular processes, including metabolism, apoptosis, differentiation, and development (Agrawal et al., 2009; Matsubara et al., 2007; Venugopal et al., 2010). Our data presented herein demonstrate that mir-663 is highly expressed in lung cancer, and plays a critical role in lung cancer proliferation. To find the direct target genes of mir-663, we performed bioinformatics analysis. According to the microrna target prediction database Targetscan, we identified TGFB1 as a candidate target gene of mir-663. We further validated TGFB1 as a direct Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12, Persistence or recurrence Remission None 5 3
4 Liu ZhiYong et al target gene of mir-663 through a luciferase reporter assay. TGFB1 is a multifunctional cytokine that involved in the control of several biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and apoptosis (Datto et al., 1995; Berndt et al., 2007; Mao et al., 2006; Aluwihare et al., 2009). It is one of the most commonly altered cellular signaling pathways in human cancers (Wrana et al., 1994). In mammalian cells, TGFB1 is the most abundant isoform of TGF-ß family (which includes TGFB1, TGFB2, and TGFB3). TGFB1 signals the target cell by binding to a heterodimeric complex of two transmembrane receptors, transforming growth factor beta receptor types I and II (TGFRBI and TGFBRII). Once bound to TGFB1, TGFBR2 recruits and phosphorylates the type I TGF-ß receptor (TGFBR1). Activated TGFBR1 then phosphorylates two downstream transcription factors, SMAD2 and SMAD3, allowing them to bind to SMAD4 (Attisano et al., 2002; Shi et al., 2003; Nakao et al., 1997). Early studies also have suggested that TGFB1 interacts with oncogenes and tumor suppressed genes (Katakura et al., 1999; Inman et al., 2000; Ewan et al., 2002; Depoortere et al., 2000). Some of the downstream targets of TGF-β signaling are important cell-cycle checkpoint genes, including CDKN1A (p21), CDKN1B (p27) and CDKN2B (p15), and their activation leads to growth arrest (Massaguéet al., 2000). Therefore, TGF-β serves as a tumor suppressor in the normal intestinal epithelium by inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis. Studies indicate that TGFB1 inhibits the proliferation of normal intestinal epithelial cells, but promotes the growth of malignant colorectal cancer cells (Derynck al., 2001). But in MCF-7 cells, TGFB1 can suppress leptinstimulated cell proliferation (Perera al., 2008). In addition, TGFB1 Suppresses Nonmetastatic Colon Cancer at an Early Stage of Tumorigenesis (Engle al., 1999). In our study, TGFB1 was found to inhibit cell proliferation and down-regulated in mir-663 over-expressed A549 cells. After inhibit mir-663 express, TGFB1 and some tumor suppressor genes, P53, Bax, and Fas, were all upregulated. All of the three genes are play important role in anti cancer mechanism. The result indicate that mir-663 can regulate the expression level P53, Bax, and Fas directly or mediated by TGFB1. In conclusion, we have presented herein the novel finding that mir-663 contributes to A549 cell proliferation through regulation of the expression of TGFB1, P53, Bax, and Fas directly or indirectly. Owing to its dual complex role in cancer, TGFB1 still remains a challenge as a potential therapeutic target. Thus, understanding of the precise mechanisms of mir-663 and TGFB1 will improve patient stratification and provide new therapeutic targets for improving the efficacy of cancer therapy. References Tiozzo C, De Langhe S, Yu M, et al (2009). Deletion of Pten expands lung epithelial progenitor pools and confers resistance to airway injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 180, Young RP, Hopkins RJ, Hay BA, et al (2009). A gene-based risk score for lung cancer susceptibility in smokers and exsmokers. Postgrad Med J, 85, Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12, Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Karashima R, et al (2009). MicroRNA-21 Regulates the Proliferation and Invasion in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res, 15, Aguda B D, Kim Y, Piper-Hunter M G, et al (2008). MicroRNA regulation of a cancer network: Consequences of the feedback loops involving mir-17-92, E2F, and Myc. PNAS, 105, Mathonnet G, Fabian M R, Svitkin Y V, et al (2007). MicroRNA Inhibition of Translation Initiation in Vitro by Targeting the Cap-Binding Complex eif4f. Science, 317, Bartel D P (2004). MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell, 116, Agrawal R, Tran U, Wessely O (2009). The mir-30 mirna family regulates Xenopus pronephros development and targets the transcription factor Xlim1/Lhx1. Development, 136, Matsubara H, Takeuchi T, Nishikawa E, et al (2007). Apoptosis induction by antisense oligonucleotides against mir-17-5p and mir-20a in lung cancers overexpressing mir Oncogene, 26, Epub 2007 Mar 26 Venugopal SK, Jiang J, Kim TH, et al (2010). Liver fibrosis causes down-regulation of mirna-150 and mirna-194 in hepatic stellate cells and their over-expression causes decreased stellate cell activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 298, G Osada H, Takahashi T (2007). MicroRNAs in biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis, 28, Elliott RL, Blobe GC (2005). Role of transforming growth factor β in human cancer. J Clin Oncol, 23, Datto MB, Li Y, Panus JF, et al (1995). Transforming growth factor beta induces the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 through a p53-independent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 92, Berndt SI, Huang WY, Chatterjee N, et al (2007). Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFB1) gene polymorphisms and risk of advanced colorectal adenoma. Carcinogenesis, 28, Mao JH, Saunier EF, de Koning JP, et al (2006). Genetic variants of Tgfb1 act as context-dependent modifiers of mouse skin tumor susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103, Aluwihare P, Mu Z, Zhao Z, et al (2009). Mice that lack activity of alphavbeta6- and alphavbeta8-integrins reproduce the abnormalities of Tgfb1- and Tgfb3-null mice. J Cell Sci, 122, Wrana JL, Attisano L, Wieser R, et al (1994). Mechanism of activation of the TGF-beta receptor. Nature, 370, Attisano L, Wrana JL (2002). Signal transduction by the TGFbeta superfamily. Science, 296, Shi Y, Massagué J (2003). Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell, 113, Nakao A, Imamura T, Souchelnytskyi S, et al (1997). TGF-beta receptor-mediated signalling through Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4. EMBO J, 16, Katakura Y, Nakata E, Miura T, et al (1999). Transforming growth factor beta triggers two independent-senescence programs in cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 255, Inman GJ, Allday MJ (2000). Apoptosis induced by TGF-beta 1 in Burkitt s lymphoma cells is caspase 8 dependent but is death receptor independent. J Immunol, 165, Ewan KB, Henshall-Powell RL, Ravani SA, et al (2002). Transforming growth factor-beta1 mediates cellular response to DNA damage in situ. Cancer Res, 62, Depoortere F, Pirson I, Bartek J, et al (2000). Transforming growth factor beta(1) selectively inhibits the cyclic AMPdependent proliferation of primary thyroid epithelial cells by preventing the association of cyclin D3-cdk4 with nuclear
5 p27(kip1). Mol Biol Cell, 11, Massagué J, Blain SW, Lo RS (2000). TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell, 103, Derynck R, Akhurst RJ, Balmain A (2001). TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Nat Genet, 29, Perera CN, Chin HG, Duru N, et al (2008). Leptin-regulated gene expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: mechanistic insights into leptin-regulated mammary tumor growth and progression. J Endocrinol, 199, Epub 2008 Aug 20 Engle SJ, Hoying JB, Boivin GP, et al (1999). Transforming growth factor beta1 suppresses nonmetastatic colon cancer at an early stage of tumorigenesis. Cancer Res, 59, MicroRNA-663 Targets TGFB1 and Regulates Lung Cancer Proliferation Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12,
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Ling Xu, Wei-Qi Dai, Xuan-Fu Xu, Fan Wang, Lei He, Chuan-Yong Guo*
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.7.3203 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Multiple-target Anti-microRNA Antisense Oligodeoxyribonucleotides on Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells Ling
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.7.3203 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Multiple-target Anti-microRNA Antisense Oligodeoxyribonucleotides on Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells Ling
MiRNA-202 impacts proliferation and apoptosis of granulose cells
 MiRNA-202 impacts proliferation and apoptosis of granulose cells Liqiong Huang, Bo Zheng*, Yi He Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Xianning Central Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital Of Hubei
MiRNA-202 impacts proliferation and apoptosis of granulose cells Liqiong Huang, Bo Zheng*, Yi He Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Xianning Central Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital Of Hubei
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway
 Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression
 1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Figure 1
 A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors. Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation?
 Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation? Transforming Activities From Condition Media from a Tumor Cell Line Condition
Control of Cell Proliferation by Peptide Growth Factors Autocrine Growth Factor Production Causes Malignant Transformation? Transforming Activities From Condition Media from a Tumor Cell Line Condition
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Material The Androgen Receptor is a negative regulator of eif4e Phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the use of mtor inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer Supplementary Figures Supplemental
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
CH Cho *, J Yu, WKK Wu 1,2
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Identification of pathogenic micrornas in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer using a combined approach of animal study and clinical sample
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Identification of pathogenic micrornas in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer using a combined approach of animal study and clinical sample
Human Lung Cancer Pathology and Cellular Biology Mouse Lung Tumor Workshop
 Human Lung Cancer Pathology and Cellular Biology Mouse Lung Tumor Workshop Jan 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Brigitte Gomperts, MD University of California, Los Angeles Lung Structure and Function Airway Epithelial
Human Lung Cancer Pathology and Cellular Biology Mouse Lung Tumor Workshop Jan 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Brigitte Gomperts, MD University of California, Los Angeles Lung Structure and Function Airway Epithelial
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Article Identification of IRF1, PPP2R5E and IL-6R, the target genes of mir-23a in gastric cancer cells
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10055-10062 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022207 Original Article Identification of IRF1, PPP2R5E and IL-6R, the target genes of mir-23a in gastric cancer cells Li-Hua
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):10055-10062 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022207 Original Article Identification of IRF1, PPP2R5E and IL-6R, the target genes of mir-23a in gastric cancer cells Li-Hua
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of
 Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION. sirna Mediated Silencing of NIN1/RPN12 Binding Protein 1 Homolog Inhibits Proliferation and Growth of Breast Cancer Cells
 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION sirna Mediated Silencing of NIN1/RPN12 Binding Protein 1 Homolog Inhibits Proliferation and Growth of Breast Cancer Cells Wei-Yi Huang, Dong-Hui Chen, Li Ning, Li-Wei Wang* Abstract
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION sirna Mediated Silencing of NIN1/RPN12 Binding Protein 1 Homolog Inhibits Proliferation and Growth of Breast Cancer Cells Wei-Yi Huang, Dong-Hui Chen, Li Ning, Li-Wei Wang* Abstract
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Supplementary Information. Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of HOXA5
 Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Supplementary Information Induction of p53-independent apoptosis by ectopic expression of in human liposarcomas Dhong Hyun Lee 1, *, Charles Forscher 1, Dolores Di Vizio 2, 3, and H. Phillip Koeffler 1,
Long non coding RNA GAS5 suppresses pancreatic cancer metastasis through modulating mir 32 5p/PTEN axis
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-017-0192-0 Cell & Bioscience RESEARCH Open Access Long non coding RNA GAS5 suppresses pancreatic cancer metastasis through modulating mir 32 5p/PTEN axis Zhi Qiang Gao *,
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-017-0192-0 Cell & Bioscience RESEARCH Open Access Long non coding RNA GAS5 suppresses pancreatic cancer metastasis through modulating mir 32 5p/PTEN axis Zhi Qiang Gao *,
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
MiR-181a promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting TGIF2
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4835-4843 MiR-181a promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting TGIF2 C. ZHIPING 1,2, T. SHIJUN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4835-4843 MiR-181a promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting TGIF2 C. ZHIPING 1,2, T. SHIJUN
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
mir-132 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4
 Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Role of TGFB1 polymorphism in the development of metastatic brain tumors in non-small cell lung cancer patients
 Role of TGFB1 polymorphism in the development of metastatic brain tumors in non-small cell lung cancer patients H.B. Wang, W.G. Song, H.Q. Liu, F. Fang and Y. Xiao Department of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
Role of TGFB1 polymorphism in the development of metastatic brain tumors in non-small cell lung cancer patients H.B. Wang, W.G. Song, H.Q. Liu, F. Fang and Y. Xiao Department of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro
 Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
HIF-inducible mir-191 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment.
 HIF-inducible mir-9 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment. Neha Nagpal, Hafiz M Ahmad, Shibu Chameettachal3, Durai Sundar, Sourabh
HIF-inducible mir-9 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment. Neha Nagpal, Hafiz M Ahmad, Shibu Chameettachal3, Durai Sundar, Sourabh
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat. synovial cells
 Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7
 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1
 Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
Liu et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:53 DOI 10.1186/s12943-017-0625-8 RESEARCH Open Access mir-19a promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting TIA1 Yanqing Liu 1, Rui Liu 2, Fei
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Inhibition of the Growth of Raji Cells by Precursor MicroRNA-15a
 22 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2010) 7: 22-26 DOI 10.1007/s11805-010-0022-1 Inhibition of the Growth of Raji Cells by Precursor MicroRNA-15a Dong-mei HE Qin CHEN Institute of Hematology, Medical College of
22 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2010) 7: 22-26 DOI 10.1007/s11805-010-0022-1 Inhibition of the Growth of Raji Cells by Precursor MicroRNA-15a Dong-mei HE Qin CHEN Institute of Hematology, Medical College of
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery & VP Integrated Health Services University of Saskatchewan & Saskatoon Health Region
 Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
Downregulation of microrna-196a inhibits human liver cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FOXO1
 2148 Downregulation of microrna-196a inhibits human liver cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FOXO1 Liu Yang 1, Fei Peng 2, Jian Qin 3, Henghua Zhou 4 and Bing Wang 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
2148 Downregulation of microrna-196a inhibits human liver cancer cell proliferation and invasion by targeting FOXO1 Liu Yang 1, Fei Peng 2, Jian Qin 3, Henghua Zhou 4 and Bing Wang 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology,
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
http / /cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology A431 . Western aza-dC FUT4-siRNA
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: 807-820, 2019 MicroRNA 98 suppresses cell growth and invasion of retinoblastoma via targeting the IGF1R/k Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway LONG GUO 1, YU BAI 2, SHUZHE
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
Published online 17 July 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, No doi: /nar/gkq637
 Published online 17 July 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, No. 21 7673 7688 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq637 GAM/ZFp/ZNF512B is central to a gene sensor circuitry involving cell-cycle regulators, TGFb
Published online 17 July 2010 Nucleic Acids Research, 2010, Vol. 38, No. 21 7673 7688 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq637 GAM/ZFp/ZNF512B is central to a gene sensor circuitry involving cell-cycle regulators, TGFb
Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus entry
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
The inhibitory effect of mir-375 targeting sp1 in colorectal cancer cell proliferation
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 405-411 The inhibitory effect of mir-375 targeting sp1 in colorectal cancer cell proliferation X.-H. LIU, J. WANG, Y.-H. DONG Department
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 405-411 The inhibitory effect of mir-375 targeting sp1 in colorectal cancer cell proliferation X.-H. LIU, J. WANG, Y.-H. DONG Department
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Posttranscriptional upregulation of HER3 by HER2 mrna induces trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer
 Li et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:113 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0862-5 RESEARCH Open Access Posttranscriptional upregulation of HER3 by HER2 mrna induces trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer
Li et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:113 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0862-5 RESEARCH Open Access Posttranscriptional upregulation of HER3 by HER2 mrna induces trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Inhibiting mirna-30a-3p has anti-tumor effects in glioma cancer via PTEN
 Inhibiting mirna-30a-3p has anti-tumor effects in glioma cancer via PTEN Liexiang Zhang 1,3,*, Wei Jin 2, Jing Zheng 3, Yuxiang Dai 2,Yue Song 1, Hongbin Ni 2, 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Nanjing Drum
Inhibiting mirna-30a-3p has anti-tumor effects in glioma cancer via PTEN Liexiang Zhang 1,3,*, Wei Jin 2, Jing Zheng 3, Yuxiang Dai 2,Yue Song 1, Hongbin Ni 2, 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Nanjing Drum
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
MicroRNA-30a functions as tumor suppressor and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells by down-regulation of SIX1
 Human Cell (2017) 30:290 299 DOI 10.1007/s13577-017-0170-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE MicroRNA-30a functions as tumor suppressor and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells by down-regulation
Human Cell (2017) 30:290 299 DOI 10.1007/s13577-017-0170-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE MicroRNA-30a functions as tumor suppressor and inhibits the proliferation and invasion of prostate cancer cells by down-regulation
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research
 MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
