RESEARCH COMMUNICATION. sirna Mediated Silencing of NIN1/RPN12 Binding Protein 1 Homolog Inhibits Proliferation and Growth of Breast Cancer Cells
|
|
|
- Meagan Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH COMMUNICATION sirna Mediated Silencing of NIN1/RPN12 Binding Protein 1 Homolog Inhibits Proliferation and Growth of Breast Cancer Cells Wei-Yi Huang, Dong-Hui Chen, Li Ning, Li-Wei Wang* Abstract The gene encoding the Nin one binding (NOB1) protein which plays an essential role in protein degradation has been investigated for possible tumor promoting functions. The present study was focused on NOB1 as a possible therapeutic target for breast cancer treatment. Lentivirus mediated NOB1 sirna transfection was used to silence the NOB1 gene in two established breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231, successful transfection being confirmed by fluorescence imaging. NOB1 deletion caused significant decline in cell proliferation was observed in both cell lines as investigated by MTT assay. Furthermore the number and size of the colonies formed were also significantly reduced in the absence of NOB1. Moreover NOB1 gene knockdown arrested the cell cycle and inhibited cell cycle related protein expression. Collectively these results indicate that NOB1 plays an essential role in breast cancer cell proliferation and its gene expression could be a therapeutic target. Keywords: Breast cancer - NOB1 - proliferation - colony formation - sirna Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev, 13, Introduction Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death among women worldwide. Therefore, identification of effective treatments to prevent breast cancer is highly researched. As breast cancers are tend to arise due to genetic alterations in cells which will lead to uncontrolled growth and survival advantage (Hanahan, 2000). Therefore, it could be suggested that the regulation of genes involved in breast cancer progression would be a promising target for breast cancer therapy. In that regard RNA interference (RNAi) mediated cancer therapy has been identified as a novel and effective method of treatment compared to conventional methods (Mello, 2004). In the last few years, small interference RNA (sirna) has gained more attention as a more specific and efficient approach of cancer therapy. The function of sirna mediated cancer therapy is to down regulate the mutant cancer relevant transcripts and restoring wild-type function in heterozygous cancer cell models (Størvold, 2006). For this therapy identification of genes which have a significant role in cancer development and progression is of utmost importance. In malignant the ubiquitin proteasome pathway of protein degradation which plays a critical role in gene transcription, signal transduction and modulation of protein turnover in cell cycle is mostly mutated (Hershko, 1998; Ferrell, 2000). This mutation directly leads to cancer development and malignancy. Nin one binding protein (NOB1p), encoded by the NOB1 gene plays a crucial role in protein degradation pathway as it binds together the 20S proteasome with the 19S regulatory particle in the nucleus to facilitate the maturation of the 20S proteasome (Tone, 2002). Recently it has been found that the down regulation of over expressed NOB1 in ovarian cancer tissues lead to the suppressed cancer cell survival. Therefore, it was suggested that NOB1 may act as an oncogenic factor and it could be used as a therapeutic marker (Lin, 2012). In the light of these previous experiments we hypothesized that highly malignant breast cancer cells may have higher expression levels of this oncogenic gene NOB1 and silencing this gene would be effective for the regulation of breast cancer cell progression. To test this hypothesis highly malignant breast cancer cell models were used and tested for the expression levels of NOB1 and lentivirus mediated transfection of NOB1 sirna was used as an approach to silence the NOB1 gene. Then the effect of silencing NOB1 on the breast cancer cell proliferation and survival was analyzed. Materials and Methods Reagents and plasmids AgeI, EcoRI, and SYBR Green Master Mix Kits were purchased from TaKaRa (Dalian, China). pvsvg, pfh1ugw, pcmvyr 8.92 plasmids were purchased from Hollybio (Shanghai, China). RNeasy Midi Kit was from Qiagen (Valencia, CA, USA). Dulbecco s Department of Oncology, Affiliated People s 1st Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Shanghai, China *For correspondence: leewaiwang@126.com Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 13,
2 Wei-Yi Huang et al modified Eagle s medium (DMEM) and fetal bovine serum (FBS) were obtained from Gibco (Cambrex, MD, USA). Lipofectamine 2000, TRIzol and Super ScriptII reverse transcriptase were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). All other chemicals were obtained from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). The antibodies used were as follows: anti-nob1 (1:1,000 dilution; Abcam, ab87151); anti-gapdh (glyceraldehyde-3- phosphate dehydrogenase, 1:2,000 dilution; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., sc-32233) anti-p21 (1:1,000 dilution; Cell signaling, #2947); anti-cdk4 (1:2,000 dilution; Cell signaling, #2906); Cyclin D1 (1:500 dilution; Marine Biological Laboratory, MD-17-3). Cell culture Breast cancer cells (MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231) and human embryonic kidney cells (293T) were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC). The cells were maintained in Penicillin/streptomycin treated DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS at 37 in humidified atmosphere of 5% CO 2. Construction and of NOB1 shrna lentivirus The corresponding sequences of the NOB1 short hairpin RNA (shrna) and non-silencing control shrna were 5 - CTAGCCCGGTTCTCCGAACGTGTCA CGTATCTCGAGATACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAATT TTTTTAAT-3 and 5 -CTAGCCCGGCC AAGGAAGTGCAATTGGTTTTTTGTTAAT-3, respectively. shrna expressing vector pfh1ugw and lentiviral packing vectors pvsvg and pcmvyr 8.92 (Shanghai, Hollybio, China) was used to insert these shrna into the plasmid. DNA sequencing was performed to confirm the lentiviral based shrna expressing vectors. Then the lentiviral basedsh-rna were transfected into HEK293T cells cultured in 10 cm dishes at a cell density of using standard protocols (Soneoka, 1995). Two hours before transfection, the medium was replaced with serum-free DMEM and the three plasmids including 20 µg of silencing sequence or non-silencing sequence, 15 µg packaging vecto and 10 µg VSVG expression plasmid were added to 200 µl Opti-MEM and 15 µl of Lipofectamine The supernatant was collected 48 h after transfection and lentiviral particles were harvested by ultra-centrifugation (4,000 g) at 4 for 10 min. NOB1 shrna infection into the breast cancer cells NOB1 and non-silencing control shrna were infected into breast cancer cells seeded in 96 well plates (50,000 cells per well) by replacing the medium with Opti-MEM medium containing the lentivirus. After 24h, the virus containing medium was replaced with fresh medium and further incubated for another 72 h. The successful infection was examined by counting the green fluorescence emitted by the green florescence protein (GFP) containing lentivirus particles under fluorescence microscopy following 96 h of infection. RNA extraction and real-time PCR analysis RNA for RT-PCR was extracted from breast cancer cells after 5 days of infection. Cells were lysed with 1824 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 13, 2012 Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) and total RNA was extracted from the lysate using standard procedures. The cdna synthesis was carried out using Promega M-MLV cdna synthesis kit according to the manufactures instructions. For the RT-PCR analysis Actin was used as the reference housekeeping gene. The forward and reverse primers used are; for NOB1 forward primer 5 -AAGTGAGGAGG AGGAGGAG-3 and reverse primer 5 -ACTTTCTTC AGGGTCTTGTTC -3, Actin forward primer 5 -GTGGACATCCGCAAAGAC -3 and reverse primer 5 -AAAGGGTGTAACGCAACTA-3. Relative gene expression levels compared to Actin was calculated using 2 -ΔΔCT analysis method. Western Blot analysis Total protein was isolated from cells infected for 5 days and the isolated protein was quantified by BSA protein analysis method. Protein (20 µg) was loaded onto a 10% SDS-PAGE and electrophoresed at 60 V for 4 h. Then the protein in the gel was transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membrane following electrophoresis (Millipore). The proteins levels were detected by respective antibodies following detection with ECL kit (Amersham) and exposed to X-ray film. The GAPDH was used as control and detected by an anti-gapdh antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology). Bands on X-ray films were quantified with an ImageQuant densitometric scanner (Molecular Dynamics). MTT analysis Breast cancer cells were seeded into a 96 well plate 5 days after infection at a concentration of 2,000 cells/well. MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide) analysis was performed in different time intervals (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 days after incubation) to find the viability of cells at tested time periods. After the specified incubation time, 20 μl of MTT solution (5 mg/ml) was added to each well and incubated at 37 for 4 h. then the medium and MTT from the wells were removed and 100 μl of DMSO was added to each well. The optical density was, measured using a microplate reader at 490 nm. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Colony forming assay The cells were transfected for 5 days and seeded into 6 well plates at a density of 500 cells per well. The medium was changed every 3 days until 2 weeks of culture. Then the cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and the fixed cells were stained by adding freshly prepared diluted Giemsa stain for 20 min. The cells were rinsed with distilled water and colonies with more than 50 cells were counted under a fluorescence microscope. Cell cycle analysis The cell cycle distributions in the infected cells were analyzed using flow cytometer following propidium iodide (PI) staining. The infected cells were seeded on a 6 well plate at a cell density of After 24 h the cells were collected, washed with ice cold PBS and were fixed with 70% ethanol and incubated for another 30 min at 4. The
3 Figure 1. Silencing of NOB1 Suppressed the NOB1 mrna and Protein Expression Levels in MCF-7 Cells. A. Light microscopic and fluorescent microscopic pictures of MCF-7 cells 96 h after infection with lentivirus containing NOB1 sirna and non-silencing sirna at the magnification of 200. B. Quantitative real time PCR data of sirna mrna levels following the silencing compared to non-silenced control group. C. NOB1 protein expression levels of NOB1 in NOB1 sirna infected and control sirna infected MCF-7 cells. The values represents the mean from three independent experiments; bars represent SD. **P<0.01 in comparison with control ethanol was removed by centrifugation and the remaining cell pellets were suspended in 100 µg/ml of DNase-free RNase for 30 min at 37. Finally, the PI solution (100 μg/ml) was added to the cell suspension and analyzed by flow cytometer (FACS Cali-bur, BD Biosciences) after filtering through a 50-µm nylon mesh. Statistical analysis All data were expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments conducted in triplicates. The Students t test was used to evaluate the differences between the control cells and NOB1 silenced cells in SPSS 13.0 software. P < 0.01 was considered as statistically significant. Results NOB1 expression down regulation by NOB1 sirna The successful infection with lentivirus mediated NOB1 RNAi is observed by florescence imaging. The NOB1 sirna infected cells were detected as GFP positive cells under the green florescence as GFP is also transfected to the cells together with NOB1 sirna. As shown in Figure 1A and 4A both the breast cancer cells MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 are successfully infected with the NOB1 sirna. Further the gene expression levels of NOB1 following NOB1 sirna infection was observed by real time PCR and Western blot analysis. As shown in Fig. 1B the relative mrna expression level of NOB1 in MCF-7 cells were significantly (p<0.01) reduced with the NOB1 sirna infection compared to non-silencing control sirna infected group. Similarly the NOB1 protein expression was also markedly inhibited due to NOB1 sirna infection in both MCF-7 (Figure 1C) and MDA- MB-231 cells (Figure 4B). Therefore, it was confirmed that the lentiviral mediated infection of NOB1 sirna is an effective method to reduce the higher expression level Figure 2. Effect of NOB1 Silencing on the Proliferation and Colony Forming Ability of MCF-7 Cells. A. The 75.0 cell proliferation levels in NOB1 silenced and non-silenced MCF-7 cells. The values represent the mean from three independent experiments; bars represent SD. B. Giemsa staining of the cancer cell colonies under light microscope C. Numerical representation of the number of colonies in the NOB1 silenced group and non-silenced group. D. Images of a single colony after Giemsa staining, in bright field and under fluorescence microscope. The values represents the mean from 25.0 three independent experiments; bars represent SD. **P<0.01 in comparison with control of NOB1 in breast cancer cells. NOB1 sirna infection suppressed the proliferation of breast cancer cells The effect of silencing NOB1 on breast cancer cell proliferation was analyzed by MTT assay. It could be clearly observed that the proliferation of both NOB1 sirna infected MCF-7 (Figure 2A) and MDA-MB-231 (Figure 4C) cell proliferation was time dependently decreased. At the 5th day of observation, the cell viability was significantly (p<0.01) reduced in both cell lines compared to the non-silencing control sirna infected cell groups. These results indicate that the higher expression levels of NOB1 are closely related to the proliferation of breast cancer cells. Colony formation of breast cancer cells were suppressed by the silencing of NOB1 Both MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells are growing in groups and therefore the effect of NOB1 silencing on this colony forming ability of breast cancer cells was investigated by performing colony formation assay following Giemsa staining. The number and the size of the colonies were observed in both NOB1 sirna infected cell group and the non-silencing control sirna infected group. The reduction in the number and the size of the colonies were clearly observed under the light microscope in NOB1 sirna infected MCF-7 cells (Figure 2B). Further the numbers of colonies were counted in both cell lines infected with NOB1 and control sirna. As shown in Figure 2C and Figure 4D NOB1 sirna infection significantly (p<0.01) reduced the number of colonies by 69.8% in MCF-7 cells and 59.5% in MDA-MB-231 cells. The Figure 2D evidently show that the GFP expressing NOB1 sirna infected cell colonies have reduced size compared to the control group. Collectively, these results strongly support that in the absence of NOB1 both the Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 13,
4 Wei-Yi Huang et al expression was markedly increased in the NOB1 absent cell group. Therefore, it is clear that the presence of NOB1 is a determining factor of breast cancer cell proliferation and cell cycle progression. Discussion Figure 3. Effect of NOB1 Silencing on the Cell Cycle Distribution of MCF-7 Cells. A. The histograms obtained from flow cytometric analysis of NOB1 silenced and nonsilenced cells. B. The percentages of MCF-7 cells at different phases of the cell cycle following NOB1 sirna or non-silencing sirna infection. C. The protein expression levels of cell cycle and apoptosis related proteins. The values represents the mean from three independent experiments; bars represent SD. **P<0.01 in comparison to control Figure 4. The Effect of NOB1 Deletion on the MDA- MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. A. Light microscopic and fluorescent microscopic pictures of MDA-MB-231 cells 96 h after infection with lentivirus containing NOB1 sirna and non-silencing sirna at the magnification of 200. B. NOB1 protein expression level in the absence and presence of NOB1 gene. C. The effect of NOB1 silencing on the proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells. D. The effect of NOB1 silencing on the colony forming ability of the MDA-MB-231 cells. The values represents the mean from three independent experiments; bars represent SD. **P<0.01 in comparison with control number and the size of the colonies are suppressed. Infection with NOB1 sirna arrested the cell cycle of MCF-7 cells The effect of NOB1 on the cell cycle progression was analyzed by flow cytometry by using both NOB1 silenced and non-silenced MCF-7 cells. As depicted in the Figure 3A and 3B thenumber of cells in the G0/G1 phase has increased by 9.9% due to NOB1 sirna infection. And also the number of events in the S phase of the cell cycle is decreased by 47.8% and the events in G2/M phase have increased by 57.8% as a result of NOB1 gene knockdown. This significant (p<0.01) arrest of cell cycle in NOB1 silenced MCF-7 cells were further confirmed by investigating cell cycle related protein expression levels. As shown in Figure 3C the cell cycle related proteins CDK4 and cyclin D1 are inhibited due to the absence of NOB1. Furthermore, the anti-proliferative protein p Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 13, 2012 Breast cancer is the most common mortality cause of women worldwide despite of higher research on controlling the cancer progression. Therefore, novel methods of cancer treatments are approached recently. Among them cancer therapy at the gene level through understanding of the molecular functions of cancer cell survival has gained more attention. This study was focused to identification of an oncogenic target in breast cancer cells and investigation of the effects of silencing the respective gene on breast cancer cell proliferation. NOB1 gene was found as an oncogene responsible for the higher rates of proliferation in cancer cells. In humans NOB1 gene is located on chromosome 16q22.1, composed of nine exons and 1,749 bp long (Zhang, 2005). The translation product of NOB1, NOB1 protein is mainly localized in the nucleus of the mammalian cells. It has been found that NOB1 plays essential roles in proteasome biogenesis (Pertschy, 2009). And several recent studies have reported that repression of NOB1 gene inhibit the growth of ovarian cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma (Lin, 2012; Lu, 2012). Therefore, this study the level of NOB1 proliferation in highly malignant breast cancer cell models MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 were investigated and the results showed that both cell lines expressed significantly high levels of NOB1. These significant higher levels of NOB1 expression was down regulated by transfecting with NOB1 sirna in order to find whether NOB1 down regulation has any effect on the breast cancer cell survival. The results demonstrated that sirna mediated silencing of NOB1 gene has a significant influence on the survival of breast cancer cells. The proliferation rate, colony forming ability and the cell cycle progression was strongly inhibited by the absence of NOB1 gene. Hence it is clear that NOB1 gene has played an important role in the proliferation and progression of breast cancer cells. The eukaryotic proteasome which degrade or process intracellular proteins control the cell cycle proteins such as cyclins, CDK4 and apoptosis proteins (Adams, 2004). NOB1 protein plays a major role in the proteasome by forming a complex between 19S regulatory particle of the 26S proteasome where the latter catalyze the protein degradation through ubiquitin proteasome pathway for the cell cycle progression (Shirane, 1999; Xu, 2008; Fasanaro, 2010). Therefore, it could be suggested that by silencing the NOB1 gene the functions of the NOB1 protein in cell cycle progression was inhibited and thereby the breast cancer cells proliferation is suppressed. In conclusion through this study identifies NOB1 as a critical gene in the breast cancer cell survival and growth. Therefore, sirna mediated silencing of the NOB1 gene has inhibitory effects on the breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the cell cycle progression. Collectively, this study showed potential future prospects
5 of using NOB1 gene therapy as an effective breast cancer treatment method. References Adams J (2004). The proteasome: a suitable antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer, 4, Fasanaro P, Capogrossi MC, Martelli F (2010). Regulation of the endothelial cell cycle by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Cardiovasc Res, 85, Ferrell K, Wilkinson CR, Dubiel W, Gordon C (2000). Regulatory subunit interactions of the 26S proteasome, a complex problem. Trends Biochem Sci, 25, Hanahan Da WRA (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 100, Hershko Aa CA (1998). The ubiquitin system. Annual Review Biochem, 67, Lin Y, Peng S, Yu H, Teng H, Cui M (2012). RNAi-mediated downregulation of NOB1 suppresses the growth and colonyformation ability of human ovarian cancer cells. Med Oncol, 29, Lu Z, Guo Q, Shi A, Xie F, Lu Q (2012). Down regulation of NIN/RPN12 binding protein inhibit the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Biol Rep, 39, Mello CC, Conte D Jr. (2004). Revealing the world of RNA interference. Nature, 431, Pertschy B, Schneider C, Gnadig M, et al (2009). RNA helicase prp43 and its co-factor Pfa1 promote 20 to 18S rrna processing catalyzed by the endonuclease Nob1. J Biol Chem, 284, Shirane M, Harumiya Y, Ishida N, et al (1999). Down-regulation of p27(kip1) by two mechanisms, ubiquitin-mediated degradation and proteolytic processing. J Biol Chem, 274, Soneoka Y, Cannon PM, Ramsdale E, et al (1995). A transient three-plasmid expression system for the production of high titer retroviral vectors. Nucleic Acids Res, 23, Størvold GL, Andersen TI, Perou CM, Frengen E (2006). sirna: a potential tool for future breast cancer therapy? Crit Rev Oncog, 12, Tone Y, Toh-E A (2002). Nob1p is required for biogenesis of the 26S proteasome and degraded upon its maturation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev, 16, Xu G, Bernaudo S, Fu G, et al (2008). Cyclin G2 is degraded through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and mediates the antiproliferative effect of activin receptor-like kinase 7. Mol Biol Cell, 19, Zhang Y, Ni J, Zhou J, et al (2005). Cloning, expression and characterization of the human NOB1 gene. Mol Biol Rep, 32, Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 13,
RESEARCH COMMUNICATION
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.3.1043 Functional Role of COPS3 in Lung Caner Proliferation RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Silencing of the COPS3 Gene by sirna Reduces Proliferation of Lung Cancer
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.3.1043 Functional Role of COPS3 in Lung Caner Proliferation RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Silencing of the COPS3 Gene by sirna Reduces Proliferation of Lung Cancer
RNAi-mediated downregulation of NOB1 suppresses the growth and colony-formation ability of human ovarian cancer cells
 Med Oncol (2012) 29:311 317 DOI 10.1007/s12032-010-9808-5 ORIGINAL PAPER RNAi-mediated downregulation of NOB1 suppresses the growth and colony-formation ability of human ovarian cancer cells Yang Lin Shuai
Med Oncol (2012) 29:311 317 DOI 10.1007/s12032-010-9808-5 ORIGINAL PAPER RNAi-mediated downregulation of NOB1 suppresses the growth and colony-formation ability of human ovarian cancer cells Yang Lin Shuai
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Effect of specific silencing of EMMPRIN on the growth and cell cycle distribution of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 Effect of specific silencing of EMMPRIN on the growth and cell cycle distribution of MCF-7 breast cancer cells X.Q. Yang 1, J. Yang 1, R. Wang 1, S. Zhang 1, Q.W. Tan 1, Q. Lv 1, W.T. Meng 2, X.M. Mo 2
Effect of specific silencing of EMMPRIN on the growth and cell cycle distribution of MCF-7 breast cancer cells X.Q. Yang 1, J. Yang 1, R. Wang 1, S. Zhang 1, Q.W. Tan 1, Q. Lv 1, W.T. Meng 2, X.M. Mo 2
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Role of the CKIP1 gene in proliferation and apoptosis of the human lung cancer cell line H1299
 Role of the CKIP1 gene in proliferation and apoptosis of the human lung cancer cell line H1299 G.M. Chen 1, R.F. Ding 2, Y.D. Tan 2, X.B. Pan 2, G.M. Jiang 2, J.F. He 3, S.H. Lin 2, C. Liu 2 and Y. Jia
Role of the CKIP1 gene in proliferation and apoptosis of the human lung cancer cell line H1299 G.M. Chen 1, R.F. Ding 2, Y.D. Tan 2, X.B. Pan 2, G.M. Jiang 2, J.F. He 3, S.H. Lin 2, C. Liu 2 and Y. Jia
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel
 KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 2671-2676, 2015 Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer JIE CHEN *, JUNKAI WANG *, XINGANG CUI, YUSHAN LIU, LEI YIN, YAO LI,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 2671-2676, 2015 Positive nin one binding protein expression predicts poor outcome in prostate cancer JIE CHEN *, JUNKAI WANG *, XINGANG CUI, YUSHAN LIU, LEI YIN, YAO LI,
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
~Lentivirus production~
 ~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
~Lentivirus production~ May 30, 2008 RNAi core R&D group member Lentivirus Production Session Lentivirus!!! Is it health threatening to lab technician? What s so good about this RNAi library? How to produce
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant molecular mechanism.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (14): 6350-6354 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Research on the inhibitory effect of metformin on human oral squamous cell carcinoma SCC-4 and CAL-27 cells and the relevant
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues. suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by
 Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Marine Streptomyces sp. derived antimycin analogues suppress HeLa cells via depletion HPV E6/E7 mediated by ROS-dependent ubiquitin proteasome system Weiyi Zhang 1, +, Qian Che 1, 2, +, Hongsheng Tan 1,
Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
LncRNA LET function as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer development
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 6002-6007 LncRNA LET function as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer development C.-X. ZHOU, X. WANG, N. YANG, S.-K. XUE, W.-C. LI, P.-P.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 6002-6007 LncRNA LET function as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer development C.-X. ZHOU, X. WANG, N. YANG, S.-K. XUE, W.-C. LI, P.-P.
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3
 Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document
 Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods:
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods: Cell viability assay. Cells were seeded overnight at a density of 2,000 cells per well in 96-well plates in RPMI with 10% FBS and then treated with the relevant
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods: Cell viability assay. Cells were seeded overnight at a density of 2,000 cells per well in 96-well plates in RPMI with 10% FBS and then treated with the relevant
Knockdown of Rab7a suppresses the proliferation, migration and xenograft tumor growth of breast cancer cells
 Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document
 Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
Graveley Lab shrna knockdown followed by RNA-seq Biosample Preparation and Characterization Document Wet Lab: Sara Olson and Lijun Zhan Computational Lab: Xintao Wei and Michael Duff PI: Brenton Graveley
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
 The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
Supplemental Information Tobacco-specific Carcinogen Induces DNA Methyltransferases 1 Accumulation through AKT/GSK3β/βTrCP/hnRNP-U in Mice and Lung Cancer patients Ruo-Kai Lin, 1 Yi-Shuan Hsieh, 2 Pinpin
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from murine
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. Physical properties of murine DC-derived exosomes. a, Electron micrograph of phosphotungstanic acid-stained exosomes derived from
Effect of ABCE1-silencing gene, transfected by electrotransfer, on the proliferation, invasion, and migration of human thyroid carcinoma SW579 cells
 Effect of ABCE1-silencing gene, transfected by electrotransfer, on the proliferation, invasion, and migration of human thyroid carcinoma SW579 cells X. Qu 1,2 and L. Zhang 1 1 ENT and Maxillofacial Oncology,
Effect of ABCE1-silencing gene, transfected by electrotransfer, on the proliferation, invasion, and migration of human thyroid carcinoma SW579 cells X. Qu 1,2 and L. Zhang 1 1 ENT and Maxillofacial Oncology,
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of rhomboid domain containing 1 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 377-381, 2015 Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of rhomboid domain containing 1 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth JUNYI HAN 1,2*, JUNCHAO BAI 3*, YAO YANG 2, HUA YIN 2,
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 12: 377-381, 2015 Lentivirus-mediated knockdown of rhomboid domain containing 1 inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth JUNYI HAN 1,2*, JUNCHAO BAI 3*, YAO YANG 2, HUA YIN 2,
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7
 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins
 Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
Pre-made Lentiviral Particles for Fluorescent Proteins Catalog# Product Name Amounts Fluorescent proteins expressed under sucmv promoter: LVP001 LVP001-PBS LVP002 LVP002-PBS LVP011 LVP011-PBS LVP012 LVP012-PBS
http / /cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology A431 . Western aza-dC FUT4-siRNA
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Silencing of Rac3 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Lung Cancer Cells
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.7.3061 RESEARCH ARTICLE Silencing of Rac3 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Lung Cancer Cells Tie-Qin Liu 1, Ge-Bang Wang 1, Zheng-Jun Li
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2015.16.7.3061 RESEARCH ARTICLE Silencing of Rac3 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis of Human Lung Cancer Cells Tie-Qin Liu 1, Ge-Bang Wang 1, Zheng-Jun Li
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Supplementary Figure 1
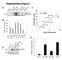 A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
http / / cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology COX-2 NTera-2 NTera-2 RT-PCR FasL caspase-8 caspase-3 PARP.
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / / cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2012 7 28 7 630 ~ 636 NTera-2 ** ** * 410081 COX-2 NTera-2 MTT NTera-2 NTera-2 Hoechest 33258
Supporting Information. FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce. apoptosis
 1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
1 2 Supporting Information 3 4 5 FADD regulates NF-кB activation and promotes ubiquitination of cflip L to induce apoptosis 6 7 Kishu Ranjan and Chandramani Pathak* 8 9 Department of Cell Biology, School
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression
 1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
(A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square),
 Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Validation of EMT-selective small molecules (A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square), and HMLE_Twist (black diamond) cells
Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Validation of EMT-selective small molecules (A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square), and HMLE_Twist (black diamond) cells
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the
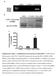 Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Supplementary Figure 1. Establishment of prostacyclin-secreting hmscs. (a) PCR showed the integration of the COX-1-10aa-PGIS transgene into the genomic DNA of hmscs (PGI2- hmscs). Native hmscs and plasmid
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Anti-cancer activity of Aya Thambira Chendooram (ATC) in in-vitro cell line against Breast Carcinoma
 International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 5, Issue 1-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.01.010
International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences ISSN: 2348-8069 www.ijarbs.com DOI: 10.22192/ijarbs Coden: IJARQG(USA) Volume 5, Issue 1-2018 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.01.010
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Supplemental Experimental Procedures: Tissue culture and cell lines Cell culture was conducted as described earlier (Wang et al., 2011). PA-1 and MCF7 were maintained in Eagle's
Supplemental Information Supplemental Experimental Procedures: Tissue culture and cell lines Cell culture was conducted as described earlier (Wang et al., 2011). PA-1 and MCF7 were maintained in Eagle's
Plasmids Western blot analysis and immunostaining Flow Cytometry Cell surface biotinylation RNA isolation and cdna synthesis
 Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Plasmids psuper-retro-s100a10 shrna1 was constructed by cloning the dsdna oligo 5 -GAT CCC CGT GGG CTT CCA GAG CTT CTT TCA AGA GAA GAA GCT CTG GAA GCC CAC TTT TTA-3 and 5 -AGC TTA AAA AGT GGG CTT CCA GAG
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells
 Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
Mahidol University Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2008; 35(1-4): 47-51. Original Article Effects of COX-2 Inhibitor on the Proliferation of MCF-7 and LTED MCF-7 Cells K. Poemsantitham, N. Sookvanichsilp
Supporting Information Nitric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines
 upporting Information itric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines Priya udhesh a, Kaviyarasan Tamilarasan a, Palaniappan Arumugam a and
upporting Information itric oxide releasing photoresponsive nanohybrids as excellent therapeutic agent for cervical cancer cell lines Priya udhesh a, Kaviyarasan Tamilarasan a, Palaniappan Arumugam a and
Silencing Dicer expression enhances cellular proliferative and invasive capacities in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 31: 867-873, 2014 Silencing Dicer expression enhances cellular proliferative and invasive capacities in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma SHUGUANG ZENG 1*, JING YANG 1*, JIANJIANG ZHAO
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 31: 867-873, 2014 Silencing Dicer expression enhances cellular proliferative and invasive capacities in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma SHUGUANG ZENG 1*, JING YANG 1*, JIANJIANG ZHAO
Data Sheet. Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509
 Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information The Effects of Spacer Length and Composition on Aptamer-Mediated Cell-Specific Targeting with Nanoscale PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Hang Xing +, [a] Ji Li +, [a] Weidong Xu,
Supporting Information The Effects of Spacer Length and Composition on Aptamer-Mediated Cell-Specific Targeting with Nanoscale PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Hang Xing +, [a] Ji Li +, [a] Weidong Xu,
Apoptosis and Altered Expression of P53, bax and bcl-2 induced by Formaldehyde in HELF cells
 Apoptosis and Altered Expression of P53, bax and bcl-2 induced by Formaldehyde in HELF cells Sun Rongli 1,, Xiong Mengzhen 1, Zhang Juan 1,Yin Lihong 1, Pu Yuepu 1* 1 Southeast University, Nanjing, China
Apoptosis and Altered Expression of P53, bax and bcl-2 induced by Formaldehyde in HELF cells Sun Rongli 1,, Xiong Mengzhen 1, Zhang Juan 1,Yin Lihong 1, Pu Yuepu 1* 1 Southeast University, Nanjing, China
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
IMMP8-1. Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells
 IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
