Physiological and pathological properties of EMTassociated
|
|
|
- Harry Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physiological and pathological properties of EMTassociated plasticity Stéphane Ansieau Inserm UMR 1050, CNRS UMR 8256 Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Lyon, France
2 EMT: a reversible phenotypic and functional switch EMT Primary epithelium Loss of cell polarity Loss of cell to cell contact Cytoskeleton reorganization Disruption of the basal membrane Gain in motility / invasion Resistance to anoikis Phenotypic switch Functional consequences E Cell plasticity M External signals MET EMT is a transient, reversible, and highly regulated transdifferentiation process Secondary epithelium The phenotypic switch is associated with a profound genetic reprogramming
3 EMT: a prerequisite for both morphogenesis and organogenesis during the embryonic development First wave Second waves Cell plasticity Third waves Thiery JP et al., Cell 2009
4 EMT and wound-healing Arnoux V. et al. Rise and fall of Epithelial Phenotype: Concepts of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition edited by P. Savagner Eurekah. Com and Kluwer Academic / Plenum Publishers
5 Pathological EMT: the metastatic cascade initiation Polyak K & RA Weinberg, Nature Reviews 2009
6 EMT, MET & the metastatic cascade Primary tumor Secondary tumor 1 5 EMT 3 MET 2 EMT 4 EMT 6 Differentiated tumor cell Cancer cell in EMT Stromal cell Immune cell 1. Dissemination 2. Intravasation 3. Migration in the flux 4. Extravasation 5. Colonisation
7 Schematic representation of the EMT process Wnt, TGFβ, Hdg, Notch mechanical constraint, hypoxia Zeb Snail Twist Epithelial markers (E-cadherin) Attached cells Non-motile Proliferative Mesenchymal markers (N-cadherin /vimentin) Individual cells Motile and invasive (MMP) Poorly proliferative
8 A complex mirna-emt-tf interactome TGFβ Mir-200 ZEB1 Targets Diaz-Lopez A. et al. Cancer Manadgment & Res. 2014
9 EMT is regulated by four interconnected regulatory networks De Craene B. & G. Berx, Nature Reviews Cancer, 2013
10 Observation of EMT figures EMT-TF & permissive environment Protein expression analysis E M Epithelial markers E-cadherin vimentin Mesenchymal markers Acquisition of migratory properties Wound healing (scratch) assay
11 Acquisition of migratory and invasive properties (Boyden chamber) EMT features Crystal violet Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay Bio-luminescence xenografted or injected in the caudal vein
12 Experimental demonstration of the biological relevance of EMT in vivo LacZ Myc WAP Cre Mammary epithelial cells Experimental control Lox-STOP-Lox LacZ LacZ ST LacZ+ epithelial cells Cytokeratin + Fibronectin- T T: tumor ST: stroma Breast carcinoma Trimboli AJ et al. Cancer Res. 2008
13 Reversion to an epithelial phenotype is a prerequisite for the second site colonization Healthy keratenocytes Non invasive carcinoma Invasive carcinoma K5 rtta Twist1 DMBA +TPA Twist1 + Dox Twist1 (Topical Dox) EMT transiently induced (Oral Dox) Primary tumor volume control topical oral Secondary tumors Constitutive EMT Tsai JH et al., Cancer Cell 2012 temps O T O T Control Twist1
14 Schematic representation of the EMT process Wnt, TGFβ, Hdg, Notch mechanical constraint, hypoxia Zeb Snail Twist Self-renewal potential Secondary tumor formation Cancer stem cell properties Tumorigenic potential Differential potential Intratumoral heterogeneity
15 EMT associates with a gain in stem-like cell properties epithelial cells EMT (even partial) EMT-TF + Oncogene + EMT permissive environment Tumorigenic potential Stemness properties Tumor subtype WAP: KRASG12D; TWIST1 MaSC Bipotent progenitor Mesenchymal Claudin-low Basal Progenitors Differentiated cells Luminal Luminal Myoepithelial Luminal Mani et al., Cell 2008, Morel et al. PLos ONE 2008; Morel et al., PLoS Genet. 2012
16 EMT associates with a gain in stem-like cell properties Organoid-forming efficiency Competitive mammary fad pat reconstitution assay GFP SNAIL2-GFP MEC (Myoepithelial progenitors) dsred dsred - SNAIL2 + SNAIL2 Rudimentary structures Elaborated ductal tree Luminal differentiated cells - SNAIL2 + SNAIL2 GFP dsred SNAIL2/Sox9-GFP dsred SOX9 SNAIL2 + SOX9 Cooperation with endogenous stemness program Organoid-forming efficiency Guo W. et al. Cell 2012
17 EMT and chemoresistance Genotoxic or cytotoxic stress Definition of an universal EMT signature Epithelial Mesenchymal M Breast (doxorubicin + cyclophosmamide) Ovary (Platinium based Therapy) Mesenchymal Intermediate Epithelial chemoresistance chemoresistance Tan et al., EMBO Mol Med 2014 CR: complete response; PR partial response; SD stable disease; PD progressive disease
18 Gain in migratory and invasive properties Cell commitment to EMT Gain in stemness Gain in chemoresitance As easy as that?...
19 Complete EMT is dispensable for cancer cell dissemination Breast carcinomagenesis model (MMTV-PyMT) with lung metastasis Tracing experiments to follow fully EMT-committed cells (independently of their outcome) Epithelial (RFP,Red), mesenchymal (GFP,Green) No epithelial GFP+ cells in primary and secondary tumors (Same results with MMTv-Neu and vimentin-cre-ert2) Tumor-derived RFP cells Orthotopic tumors RFP+-cells Primary tumor Metastasis These few GFP cells do not contribute to lung metastasis (not detectable in lung) Few positive GFP cells No positive GFP cells
20 Removal of the primary tumor Tumor-derived RFP+ cells CTX: cyclophosmamide EMT associates with chemoresistance Enrichment in EMT cells Fischer KR et al. Nature 2015 Lineage tracing to mark carcinoma cells need to fill two criteria: - Cre/Cre-ER driver needs to be expressed in all cells that transiently undergo EMT activation - When activated the Cre/Cre-ER protein needs to activate the GFP reporter in all cells where Cre/Cre-ER cells are expressed. Fsp1 Snail1-YFP; MMTV-PyMT Vim Fsp1 Vim Snail1 + Zeb1 + Ye X et al. Nature 2017
21 Interfering with EMT plasticity pertubs its contribution to metastasis? Murine pancreatic carcinomagenesis model (activated KRAS and loss of p53 function): KPC Compare KPC with KPC Twist1 KO or with Twist1 Snail1 KO Carcinoma cell tracing with YFP. In absence of Twist/Snail, reduction of YFP+/α-SMA+ cells Similar primary tumor growth Similar local invasion Similar number of DTCs Similar metastatic potential Zheng et al. Nature 2015
22 Inhibition of EMT sensitizes KPC tumors to gentamycin Treatment with gentamycin Zheng et al. Nature α-sma is not a good EMT marker -Reduction of snail2/zeb1 following Twist/Snail depletion is very partial. Aiello NM et al. Nature Difficulty to trace EMT-committed cells: no universal marker - Not a single EMT but EMTs - A highly dynamic process, needs more flexible tools
23 Direct evidence of EMT obtained in unpertubed breast tumors All cancer cells are YFP+ Epithelial cells are blue Ecad-mCFP high (Epi) Ecad-mCFP low (partial EMT) Ecad-mGFP low Specific signature Primary tumors Ecad-mGFP low cancer cells are similar to human mesenchymal CTCs
24 Direct evidence of EMT obtained in unpertubed breast tumors Ecad-mCFP high (Epi)/ orthotopic injection Multi-photon microscopy YFP CFP Nonmigratory field YFP No difference in their ability to extravasate Shift back to an epithelial phenotype CFP Migratory field Similar self-renewal potential Finger-like projection Beerling et al., Cell Reports 2016
25 Cells partially committed to EMT display CSC properties E or M cells Adherent Mammospheres HMEC SV40/RAS Epithelial cells (E) Mesenchymal Cells (M) Mammospheres Single cell RNAseq Shift to an EM gene expression profile Epithelial signature Mesenchymal signature EM signature Breast cancers Coexpression of M and E genes predict poor outcomes Grosse-Wilde A et al., 2015
26 Integrin-β4 segregates partial to fully EMT-committed cells Fully committed to EMT Partially committed to EMT ZEB1 Bierie A et al., 2017
27 Conclusions EMT is a dynamic continuum between an epithelial and a mesenchymal phenotype The partial EMT-committed cells contribute to metastasis EMT-inducers are transiently induced and need to be studied as such. Permanently expressing or deleting them aberrantly fix the epithelial or mesenchymal phenotype.
28 Partial EMT as a driver of metastasis Epithelial cells Partially committed cells Fully committed cells Epithelial shape Epithelial shape Mesenchymal shape Associates with a collective migration rather than single cells (collective migration frequently observed in patients). A metastable phenotype? CTC clusters intra- and extravasate more efficiently than fully committed EMT CTCs and form 50x time more tumors. Coexpression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers is an hallmark of aggressive tumors. mir200 ZEB Higher tumor-initiating and stem-like properties than fully committed EMT cells. Phenotypic Stability Factors (OVOL, GRHL2) Watanabe K et al., Dev. Cell 2014; Jolly MK et al., Oncotarget 2016
29 Partial EMT reflects an underestimated level of regulation Nieto MA et al., Cell 2016
30 EMT-TFs but not only. Failsafe program inhibition (RB and p53 dependent) Modulation of differentiation programs Modification of the cell metabolism ZEB2, SNAIL2 + Differentiation Tumor per mouse WT +/- -/- Twist1 MITF rheostat - ZEB1, TWIST1 Survival Proliferation RAS + p53 KO Dose-dependent activity TSG/oncogenic properties (cell context dependent) Glycolyse induced (increased glucose uptake & macromolecule biosynthesis) Beck B. et al, Cell Stem Cell 2015;Caramel J.. et al. Cancer Cell 2013;Dong C et al. Cancer Cell 2013
31 Concomitant fail-safe program escape and EMT induction ErbB2 Twist1 ErbB2 + Twist1 Sénescence prématurée Cellules épithéliales Cellules mésenchymateuses Ansieau S et al., Cancer Cell 2008
32 Early metastatic dissemination MMTV-ErbB2 Premalignant lesions edccs Malignant progression Her2 +, Twist1 +, Ecad low, DCCs (30% Twist1 + ) (MET) Dormancy Secondary tumors Schardt JA et al. Cancer Cell 2004; Hüsemann Y et al. Cancer Cell 2008, Harper et al., Nature 2016; Hosseini et al., 2016
Cell Polarity and Cancer
 Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells. Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles
 Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles Stem cell properties Differentiation Self-renewal Tumor
Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles Stem cell properties Differentiation Self-renewal Tumor
Cancer Biology Course. Invasion and Metastasis
 Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium. Rosita Winkler
 Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition
 EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
TITLE: Microenvironments and Signaling Pathways Regulating Early Dissemination, Dormancy, and Metastasis
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0296 TITLE: Microenvironments and Signaling Pathways Regulating Early Dissemination, Dormancy, and Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: John Condeelis CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0296 TITLE: Microenvironments and Signaling Pathways Regulating Early Dissemination, Dormancy, and Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: John Condeelis CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Concomitant Gain of Function of Notch and Loss of p53 Signalling trigger an EMT Like Programme Driving Metastatic Intestinal Cancers
 8 AVRIl 2015 8 Avril 2015 Concomitant Gain of Function of Notch and Loss of p53 Signalling trigger an EMT Like Programme Driving Metastatic Intestinal Cancers Daniel LOUVARD UMR 144 / CNRS - Institut Curie
8 AVRIl 2015 8 Avril 2015 Concomitant Gain of Function of Notch and Loss of p53 Signalling trigger an EMT Like Programme Driving Metastatic Intestinal Cancers Daniel LOUVARD UMR 144 / CNRS - Institut Curie
1. The metastatic cascade. 3. Pathologic features of metastasis. 4. Therapeutic ramifications. Which malignant cells will metastasize?
 1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis
 Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Molecular factors influencing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer
 Molecular factors influencing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer Gisela Nilsson Department of Medical Biochemistry and Cell Biology Institute of Biomedicine Sahlgrenska Academy at University
Molecular factors influencing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer Gisela Nilsson Department of Medical Biochemistry and Cell Biology Institute of Biomedicine Sahlgrenska Academy at University
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Update of mixed tumours of the GI tract, the pancreas and the liver Introduction to the concept of mixed tumours and clinical implication Jean-Yves SCOAZEC Surgical
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in carcinoma metastasis
 REVIEW Epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in carcinoma metastasis Jeff H. Tsai 1 and Jing Yang 1,2,3 1 Department of Pharmacology, 2 Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, University of California
REVIEW Epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in carcinoma metastasis Jeff H. Tsai 1 and Jing Yang 1,2,3 1 Department of Pharmacology, 2 Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, University of California
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer 2 The So Called Pre-Neoplastic Lesions and Carcinoma In Situ
 Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Contents 1 The Windows of Susceptibility to Breast Cancer... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Risk Factor and Etiological Agents... 2 1.3 The Concept of the Windows of Susceptibility to Carcinogenesis... 5
Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelialmesenchymal
 Related Commentary, page 2528 Research article Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelialmesenchymal transition Erica L. McCoy,
Related Commentary, page 2528 Research article Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelialmesenchymal transition Erica L. McCoy,
Dual reporter genetic mouse models of pancreatic cancer identify an epithelial to mesenchymal transition independent metastasis program
 Dual reporter genetic mouse models of pancreatic cancer identify an epithelial to mesenchymal transition independent metastasis program Yang Chen, Valerie S. LeBleu, Julienne L. Carstens, Hikaru Sugimoto,
Dual reporter genetic mouse models of pancreatic cancer identify an epithelial to mesenchymal transition independent metastasis program Yang Chen, Valerie S. LeBleu, Julienne L. Carstens, Hikaru Sugimoto,
Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer?
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Stability of the hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype
 /, Advance Publications 2016 Stability of the hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype Mohit Kumar Jolly 1,2, Satyendra C. Tripathi 8,*, Dongya Jia 1,5,*, Steven M. Mooney 7, Muge Celiktas 8, Samir M. Hanash
/, Advance Publications 2016 Stability of the hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal phenotype Mohit Kumar Jolly 1,2, Satyendra C. Tripathi 8,*, Dongya Jia 1,5,*, Steven M. Mooney 7, Muge Celiktas 8, Samir M. Hanash
The Z-cad dual fluorescent sensor detects dynamic changes between the epithelial and mesenchymal cellular states
 Toneff et al. BMC Biology (2016) 14:47 DOI 10.1186/s12915-016-0269-y METHODOLOGY ARTICLE The Z-cad dual fluorescent sensor detects dynamic changes between the epithelial and mesenchymal cellular states
Toneff et al. BMC Biology (2016) 14:47 DOI 10.1186/s12915-016-0269-y METHODOLOGY ARTICLE The Z-cad dual fluorescent sensor detects dynamic changes between the epithelial and mesenchymal cellular states
Supplementary Table S1. Tumor samples used for analysis Tumor size (cm) BNG (grade) ERα PR. pn-
 Supplementary Table S1. Tumor samples used for analysis Sample# Age Tumor size (cm) pn- Stage Stage BNG (grade) ERα PR HER2 (FISH) Triple negative T1 46 3 N1a III 2 Pos Neg N T2 58 1 N(i-) I 3 Pos Neg
Supplementary Table S1. Tumor samples used for analysis Sample# Age Tumor size (cm) pn- Stage Stage BNG (grade) ERα PR HER2 (FISH) Triple negative T1 46 3 N1a III 2 Pos Neg N T2 58 1 N(i-) I 3 Pos Neg
The Role of EZH2 in Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis
 The Role of EZH2 in Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis by Heather Marie Moore A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Cellular
The Role of EZH2 in Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis by Heather Marie Moore A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Cellular
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER. Andrew Leask.
 CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
Dynamic cohesin-mediated chromatin architecture controls epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in cancer
 Article Dynamic cohesin-mediated chromatin architecture controls epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in cancer Jiyeon Yun,, Sang-Hyun Song, Hwang-Phill Kim, Sae-Won Han,, Eugene C Yi & Tae-You Kim,,, Abstract
Article Dynamic cohesin-mediated chromatin architecture controls epithelial mesenchymal plasticity in cancer Jiyeon Yun,, Sang-Hyun Song, Hwang-Phill Kim, Sae-Won Han,, Eugene C Yi & Tae-You Kim,,, Abstract
Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization
 Correction Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization Ilaria Malanchi, Albert Santamaria-Martínez, Evelyn Susanto, Hong Peng, Hans-Anton Lehr, Jean-Francois Delaloye
Correction Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization Ilaria Malanchi, Albert Santamaria-Martínez, Evelyn Susanto, Hong Peng, Hans-Anton Lehr, Jean-Francois Delaloye
Review Article Pathways to Breast Cancer Recurrence
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation ISRN Oncology Volume 2013, Article ID 290568, 16 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/290568 Review Article Pathways to Breast Cancer Recurrence Aamir Ahmad Department of
Hindawi Publishing Corporation ISRN Oncology Volume 2013, Article ID 290568, 16 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/290568 Review Article Pathways to Breast Cancer Recurrence Aamir Ahmad Department of
A Novel CTC-Detecting Technique Using TelomeScan and Its Clinical Applications
 A Novel CTC-Detecting Technique Using TelomeScan and Its Clinical Applications Yasuo Urata CEO and President Oncolys BioPharma Inc. February 16, 2013 Telomere Length is a Limiting Factor for Cell Replication
A Novel CTC-Detecting Technique Using TelomeScan and Its Clinical Applications Yasuo Urata CEO and President Oncolys BioPharma Inc. February 16, 2013 Telomere Length is a Limiting Factor for Cell Replication
Ichan School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, NY Fort Detrick, Maryland Distribution Unlimited
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0365 TITLE: Macrophage Functions in Early Dissemination and Dormancy of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nina Linde CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Ichan School of Medicine at
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0365 TITLE: Macrophage Functions in Early Dissemination and Dormancy of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Nina Linde CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Ichan School of Medicine at
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
The 5th International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention Versailles, France, October 20 24, 2009
 Cancer Microenvironment (2010) 3:1 5 DOI 10.1007/s12307-010-0039-2 EDITORIAL The 5th International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention Versailles, France, October
Cancer Microenvironment (2010) 3:1 5 DOI 10.1007/s12307-010-0039-2 EDITORIAL The 5th International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention Versailles, France, October
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank
 @QMBCI bartscancerinstitute 3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank Richard Grose Barts Cancer Institute Ed Carter Normal Breast Architecture Calponin / CK8 Myoepithelial
@QMBCI bartscancerinstitute 3D in vitro modelling using material from the Breast Cancer Now Tissue Bank Richard Grose Barts Cancer Institute Ed Carter Normal Breast Architecture Calponin / CK8 Myoepithelial
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
Stem Cells. Induced Stem Cells
 Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
Skin squamous cell carcinoma propagating cells increase with tumour progression and invasiveness
 Manuscript EMBO-2012-83706 Skin squamous cell carcinoma propagating cells increase with tumour progression and invasiveness Gaëlle Lapouge, Benjamin Beck, Dany Nassar, Christine Dubois, Sophie Dekoninck
Manuscript EMBO-2012-83706 Skin squamous cell carcinoma propagating cells increase with tumour progression and invasiveness Gaëlle Lapouge, Benjamin Beck, Dany Nassar, Christine Dubois, Sophie Dekoninck
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century.
 Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or
 Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
 Rath, N., and Olson, M. (2016) Regulation of pancreatic cancer aggressiveness by stromal stiffening. Nature Medicine, 22(5), pp. 462-463. There may be differences between this version and the published
Rath, N., and Olson, M. (2016) Regulation of pancreatic cancer aggressiveness by stromal stiffening. Nature Medicine, 22(5), pp. 462-463. There may be differences between this version and the published
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer. PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C.
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0306 TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C. Bocanegra CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Leland Stanford Junior University Stanford,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0306 TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C. Bocanegra CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Leland Stanford Junior University Stanford,
Liquid Biopsy: Implications for Cancer Staging & Therapy
 Prof. Klaus Pantel, MD, PhD Institut für Tumorbiologie Liquid Biopsy: Implications for Cancer Staging & Therapy Tumor cell dissemination and cancer dormancy Primary tumor Local relapse Cancer cells disseminate
Prof. Klaus Pantel, MD, PhD Institut für Tumorbiologie Liquid Biopsy: Implications for Cancer Staging & Therapy Tumor cell dissemination and cancer dormancy Primary tumor Local relapse Cancer cells disseminate
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Table S1: Analysis of Notch gene rearrangements in triple negative breast cancer subtypes
 Supplemental Tables Table S1: Analysis of Notch gene rearrangements in triple negative breast cancer subtypes NOTCH1 or NOTCH2 Basal Immune Luminal AR Mesenchymal Stem Like WT 27 (87%) 24 (100%) 4 (66%)
Supplemental Tables Table S1: Analysis of Notch gene rearrangements in triple negative breast cancer subtypes NOTCH1 or NOTCH2 Basal Immune Luminal AR Mesenchymal Stem Like WT 27 (87%) 24 (100%) 4 (66%)
Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Glioblastoma Multiforme Highly malignant, invasive, difficult-to-treat primary brain tumor" " Frequency: 9,000 cases/year (peak age, 55 65 years)" " Recurrence: rapid growth; size may double every 10 days"
Glioblastoma Multiforme Highly malignant, invasive, difficult-to-treat primary brain tumor" " Frequency: 9,000 cases/year (peak age, 55 65 years)" " Recurrence: rapid growth; size may double every 10 days"
The splicing regulation and clinical significance of epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 in invasion and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer
 The splicing regulation and clinical significance of epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 in invasion and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer Jie Tang MD, Ph.D, Professer Vice director of Department
The splicing regulation and clinical significance of epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 in invasion and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer Jie Tang MD, Ph.D, Professer Vice director of Department
Characterization of cell lines derived from breast cancers and normal mammary tissues for the study of the intrinsic molecular subtypes
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2013) 142:237 255 DOI 10.1007/s10549-013-2743-3 PRECLINICAL STUDY Characterization of cell lines derived from breast cancers and normal mammary tissues for the study of the intrinsic
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2013) 142:237 255 DOI 10.1007/s10549-013-2743-3 PRECLINICAL STUDY Characterization of cell lines derived from breast cancers and normal mammary tissues for the study of the intrinsic
SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT AND FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT AND FIGURES Prrx1 isoform switching regulates pancreatic cancer invasion and metastatic colonization Shigetsugu Takano, Maximilian Reichert, Basil Bakir, Koushik K. Das, Takahiro Nishida,
SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT AND FIGURES Prrx1 isoform switching regulates pancreatic cancer invasion and metastatic colonization Shigetsugu Takano, Maximilian Reichert, Basil Bakir, Koushik K. Das, Takahiro Nishida,
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue
 Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Cell Therapy for Diabetes: Generating Functional Islets from Human Exocrine Tissue Kevin Docherty University of Aberdeen ELRIG Drug Discovery 2016 ACC Liverpool 14 th October 2016 Autoimmune destruction
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cells
 9 Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cells Gaoliang Ouyang 1,2 1 State Key Laboratory of Stress Cell Biology, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, 2 Laboratory of Stem
9 Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cells Gaoliang Ouyang 1,2 1 State Key Laboratory of Stress Cell Biology, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, 2 Laboratory of Stem
Identifying genomic signatures in circulating breast tumour cells
 Identifying genomic signatures in circulating breast tumour cells 9 th ISMRC 2013, Paris, France September 25th, 2013 NISHA KANWAR PhD Candidate Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathobiology University
Identifying genomic signatures in circulating breast tumour cells 9 th ISMRC 2013, Paris, France September 25th, 2013 NISHA KANWAR PhD Candidate Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathobiology University
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs)
 GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0184 TITLE: In Vivo Tagging of Lung Epithelial Cells To Define the Early Steps of Tumor Cell Dissemination PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hasmeena Kathuria, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0184 TITLE: In Vivo Tagging of Lung Epithelial Cells To Define the Early Steps of Tumor Cell Dissemination PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hasmeena Kathuria, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
The Role of Tenascin-C in Metastasis Formation
 Chapter 3 The Role of Tenascin-C in Metastasis Formation Metastasis occurs when tumor cells spread from the primary site and form a new tumor at a different site within the same or another organ. This
Chapter 3 The Role of Tenascin-C in Metastasis Formation Metastasis occurs when tumor cells spread from the primary site and form a new tumor at a different site within the same or another organ. This
MIT Student EMT variations in cancer
 MIT Student EMT variations in cancer Epithelial mesenchymal transition is a transformative process that normal cells, as well as cancer cells, undertake, Throughout the life cycle of a tumor, the environmental
MIT Student EMT variations in cancer Epithelial mesenchymal transition is a transformative process that normal cells, as well as cancer cells, undertake, Throughout the life cycle of a tumor, the environmental
MASTER EN ONCOLOGÍA MOLECULAR 2011 TGF-BETA
 MASTER EN ONCOLOGÍA MOLECULAR 2011 TGF-BETA Joan Seoane ICREA Research Professor Vall d Hebron Institute of Oncology Vall d Hebron University Hospital Barcelona jseoane@vhio.net Glioma Stupp et al. New
MASTER EN ONCOLOGÍA MOLECULAR 2011 TGF-BETA Joan Seoane ICREA Research Professor Vall d Hebron Institute of Oncology Vall d Hebron University Hospital Barcelona jseoane@vhio.net Glioma Stupp et al. New
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4. Clinical Case: Pathologic Features
 Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
Breast Pathology Evening Specialty Conference Case #4 K.P. Siziopikou, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Breast Pathology and Breast Pathology Fellowship Program Northwestern University Feinberg
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
Mohamed Bentires-Alj
 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, December 6-10, 2016 Mohamed Bentires-Alj Professor of experimental surgical oncology Department of Biomedicine University of Basel University Hospital Basel m.bentires-alj@unibas.ch
San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, December 6-10, 2016 Mohamed Bentires-Alj Professor of experimental surgical oncology Department of Biomedicine University of Basel University Hospital Basel m.bentires-alj@unibas.ch
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
TITLE: Microenvironments and Signaling Pathways Regulating Early Dissemination, Dormancy, and Metastasis
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0296 TITLE: Microenvironments and Signaling Pathways Regulating Early Dissemination, Dormancy, and Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: John Condeelis CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0296 TITLE: Microenvironments and Signaling Pathways Regulating Early Dissemination, Dormancy, and Metastasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: John Condeelis CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Lab Med Breast Cancer: From Basics to Beyond. Basic Cancer Biology and Model Systems ZENA WERB. 4:30-6 pm November 1, 2010
 Lab Med 180.04 Breast Cancer: From Basics to Beyond Basic Cancer Biology and Model Systems ZENA WERB 4:30-6 pm November 1, 2010 Advantages of mice as breast cancer models hlp://mammary.nih.gov/atlas/histology/
Lab Med 180.04 Breast Cancer: From Basics to Beyond Basic Cancer Biology and Model Systems ZENA WERB 4:30-6 pm November 1, 2010 Advantages of mice as breast cancer models hlp://mammary.nih.gov/atlas/histology/
Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells or Tumor-Initiating Cells
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6624-6648; doi:10.3390/ijms14046624 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Stem
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6624-6648; doi:10.3390/ijms14046624 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Stem
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School of. Integrative Biosciences
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School of Integrative Biosciences THE REGULATION OF MESENCHYMAL AND CANCER STEM CELL PHENOTYPES IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA A Dissertation in Molecular Medicine
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School of Integrative Biosciences THE REGULATION OF MESENCHYMAL AND CANCER STEM CELL PHENOTYPES IN HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA A Dissertation in Molecular Medicine
The Beauty of the Skin
 The Beauty of the Skin Rose-Anne Romano, Ph.D Assistant Professor Department of Oral Biology School of Dental Medicine State University of New York at Buffalo The Big Question How do approximately 50 trillion
The Beauty of the Skin Rose-Anne Romano, Ph.D Assistant Professor Department of Oral Biology School of Dental Medicine State University of New York at Buffalo The Big Question How do approximately 50 trillion
(A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square),
 Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Validation of EMT-selective small molecules (A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square), and HMLE_Twist (black diamond) cells
Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Validation of EMT-selective small molecules (A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square), and HMLE_Twist (black diamond) cells
Mario Giuliano Trieste Novembre 2015
 Mario Giuliano Trieste 20-21 Novembre 2015 Metastatic Cascade Main Actors A small fraction of cells detaching from primary tumors end up forming metastatic lesions. 1 0 Tumor Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
Mario Giuliano Trieste 20-21 Novembre 2015 Metastatic Cascade Main Actors A small fraction of cells detaching from primary tumors end up forming metastatic lesions. 1 0 Tumor Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
Mitosis. Single Nano Micro Milli Macro. Primary. PCNA expression
 a b c DAPI YFP CC3 DAPI YFP PCNA DAPI YFP ph3 DAPI YFP KI67 e 6 Mitosis f 1 PCNA expression %ph3 + /YFP + n= 63 87 61 3 13 8 n= 15 3 9 1 5 %PCNA+/YFP+ 8 6 Supplementary Figure 1. Proliferation/apoptosis
a b c DAPI YFP CC3 DAPI YFP PCNA DAPI YFP ph3 DAPI YFP KI67 e 6 Mitosis f 1 PCNA expression %ph3 + /YFP + n= 63 87 61 3 13 8 n= 15 3 9 1 5 %PCNA+/YFP+ 8 6 Supplementary Figure 1. Proliferation/apoptosis
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1796 (2009) 293 308 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbacan Review Metastasis mechanisms Thomas
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1796 (2009) 293 308 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbacan Review Metastasis mechanisms Thomas
Transcriptomic classification of genetically engineered mouse models of breast cancer identifies human subtype counterparts
 Pfefferle et al. Genome Biology 2013, 14:R125 RESEARCH Transcriptomic classification of genetically engineered mouse models of breast cancer identifies human subtype counterparts Open Access Adam D Pfefferle
Pfefferle et al. Genome Biology 2013, 14:R125 RESEARCH Transcriptomic classification of genetically engineered mouse models of breast cancer identifies human subtype counterparts Open Access Adam D Pfefferle
TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TMA-BERN COHORT-2
 Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Paracrine and Autocrine Signals Induce and Maintain Mesenchymal and Stem Cell States in the Breast
 Paracrine and Autocrine Signals Induce and Maintain Mesenchymal and Stem Cell States in the Breast The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Paracrine and Autocrine Signals Induce and Maintain Mesenchymal and Stem Cell States in the Breast The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
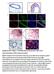 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Quantitative Data Analysis Assignment Sample Newessays.co.uk
 Absorbance Quantitative Data Analysis Assignment Sample Newessays.co.uk Part A: Results of the Study Is there a difference of curve profile between the MTT assay and the cell number? What do the different
Absorbance Quantitative Data Analysis Assignment Sample Newessays.co.uk Part A: Results of the Study Is there a difference of curve profile between the MTT assay and the cell number? What do the different
Antithetical NFATc1-Sox2 and p53-mir200 signaling networks govern pancreatic cancer cell plasticity
 The EMBO Journal Peer Review Process File - EMBO-2014-89574 Manuscript EMBO-2014-89574 Antithetical NFATc1-Sox2 and p53-mir200 signaling networks govern pancreatic cancer cell plasticity Shiv K. Singh,
The EMBO Journal Peer Review Process File - EMBO-2014-89574 Manuscript EMBO-2014-89574 Antithetical NFATc1-Sox2 and p53-mir200 signaling networks govern pancreatic cancer cell plasticity Shiv K. Singh,
Pancreatic cancer cell invasion: mesenchymal switch or just hitchhiking?
 Editorial Pancreatic cancer cell : mesenchymal switch or just hitchhiking? Rémi Samain, Christine Jean, Corinne Bousquet INSERM U1037, Cancer Research Center of Toulouse, University Toulouse III Paul Sabatier,
Editorial Pancreatic cancer cell : mesenchymal switch or just hitchhiking? Rémi Samain, Christine Jean, Corinne Bousquet INSERM U1037, Cancer Research Center of Toulouse, University Toulouse III Paul Sabatier,
Breast cancer as a systemic disease: a view of metastasis
 Review Click here for more articles from the symposium doi: 10.1111/joim.12084 Breast cancer as a systemic disease: a view of metastasis A. J. Redig 1 & S. S. McAllister 1,2,3 From the 1 Division of Hematology,
Review Click here for more articles from the symposium doi: 10.1111/joim.12084 Breast cancer as a systemic disease: a view of metastasis A. J. Redig 1 & S. S. McAllister 1,2,3 From the 1 Division of Hematology,
!!! Oncology for Scientists (RPN 530) Metastasis and Angiogenesis Chapter 13 and 14 Oct. 28 th 2014
 Oncology for Scientists (RPN 530) Metastasis and Angiogenesis Chapter 13 and 14 Oct. 28 th 2014 Department of Cancer Genetics Masashi Muramatsu, Ph.D. About Exam First, think and understand the concepts.
Oncology for Scientists (RPN 530) Metastasis and Angiogenesis Chapter 13 and 14 Oct. 28 th 2014 Department of Cancer Genetics Masashi Muramatsu, Ph.D. About Exam First, think and understand the concepts.
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz October 11, 2013 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Finite-element analysis of cell cluster dynamics in different cluster trap architectures. (a) Cluster-Chip (b) Filter (c) A structure identical to the Cluster-Chip except that one
Supplementary Figure 1 Finite-element analysis of cell cluster dynamics in different cluster trap architectures. (a) Cluster-Chip (b) Filter (c) A structure identical to the Cluster-Chip except that one
Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells: Allies and Foes in the Tumor Wound Andrei Turtoi, PhD
 Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells: Allies and Foes in the Tumor Wound Andrei Turtoi, PhD Tumor Microenvironment and Resistance to Treatment Lab, IRCM, France Institut de Recherche en Cancérologie de Montpellier
Fibroblasts and Cancer Cells: Allies and Foes in the Tumor Wound Andrei Turtoi, PhD Tumor Microenvironment and Resistance to Treatment Lab, IRCM, France Institut de Recherche en Cancérologie de Montpellier
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
What I Learned from 3 Cases and 3 Antibodies
 What I Learned from 3 Cases and 3 Antibodies Melinda Sanders, M.D Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Pathology Consultant in Breast Pathology Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
What I Learned from 3 Cases and 3 Antibodies Melinda Sanders, M.D Vanderbilt University Medical Center Professor of Pathology Consultant in Breast Pathology Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
Can we prevent metastasis?
 Can we prevent metastasis? A research example to translate from the bench to the bedside Diane Palmieri, Ph.D. Women s Cancers Section Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology CCR, NCI Some Basic Truths Most
Can we prevent metastasis? A research example to translate from the bench to the bedside Diane Palmieri, Ph.D. Women s Cancers Section Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology CCR, NCI Some Basic Truths Most
Therapeutic implications of cellular and molecular biology of cancer stem cells in melanoma
 Kumar et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:7 DOI 10.1186/s12943-016-0578-3 REVIEW Therapeutic implications of cellular and molecular biology of cancer stem cells in melanoma Dhiraj Kumar 1, Mahadeo Gorain
Kumar et al. Molecular Cancer (2017) 16:7 DOI 10.1186/s12943-016-0578-3 REVIEW Therapeutic implications of cellular and molecular biology of cancer stem cells in melanoma Dhiraj Kumar 1, Mahadeo Gorain
Supplement 8: Candidate age-related genes and pathways
 Supplement 8: Candidate age-related genes and pathways Function Untreated cohort (cohort 1) Treated cohort (cohort 2) Genes Gene sets Effect of age Effect of age FDR of 2 nd Effect of age adjusted Effect
Supplement 8: Candidate age-related genes and pathways Function Untreated cohort (cohort 1) Treated cohort (cohort 2) Genes Gene sets Effect of age Effect of age FDR of 2 nd Effect of age adjusted Effect
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#5:(October-18-2010) Cancer and Signals Outline 1 2 Outline 1 2 Cancer is a disease of malfunctioning cells. Cell Lineage: Adult
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#5:(October-18-2010) Cancer and Signals Outline 1 2 Outline 1 2 Cancer is a disease of malfunctioning cells. Cell Lineage: Adult
