1. Non Infectious, Non Neoplastic 2. Non Infectious, Neoplastic. 3. Infectious. Pituitary tumors (D) (adenomas>> carcinomas)
|
|
|
- Dora Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Famous Rat Pathology (Phenotypes) Discussion Plan 1. Non Infectious, Non Neoplastic 2. Non Infectious, Neoplastic 1 Cory Brayton, D.V.M., D.A.C.L.A.M., D.A.C.V.P. Associate Professor, Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology Director, Phenotyping Core Johns Hopkins University, School of Medicine Baltimore, MD TEL: FAX: phenocore@jhmi.edu Infectious NOT Neoplastic 4 Famous Rat Phenotypes Nephropathy (D) (mineralization, Parathyroid hyperplasia) Cardiomyopathy (D) (Degeneration, fibrosis, inflammation) Arteritis polyarteritis Axonal degeneration Infectious/parasitic BOLD possible likely COD CCOD Not bold Incidental finding/phenotype to expect D Role of Diet I Role of Infectious agents? E.g. MYCOPLASMA, Trichosomoides crassicauda Neoplastic Pituitary tumors (D) (adenomas>> carcinomas) Mammary tumors (D) (fibroadenoma etc) Pheochromocytomas Hematopoietic (I) Histiocytic sarcomas Fibromas, sarcomas Adrenal cortical, Thyroid follicular or C cell; Zymbal Gland, Urinary bladder (I) 4 5 Famous Rat lesions (phenotypes) 1. Non Infectious, Non Neoplastic a. Nephropathy b. Arteritis c. Cardiomyopathy etc 2. Non Infectious, Neoplastic a. Skin Tumors (most commonly seen) b. Hematopoietic (most? Famous) c. Pituitary etc (most? Common killer) etc 3. Infectious 6 1.a. Rat Nephropathy Most common significant lesion or COD in many studies, especially Older studies/diets Ad lib feeding Gross : Lumpy bumpy kidneys LARGER then smaller AKA CPN Chronic progressive nephropathy CRD Chronic Renal Disease ORN Old rat nephropathy 7 1.a. Rat Nephropathy Glomeruli Large Mesangium Cellularity Synechiae Small Sclerotic Tubules Dilated, protein Degen, regen Mineral +/ Interstitium Inflammation Fibrosis RodentPath 7 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
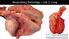
2 1.a. Rat Nephropathy Glomeruli Large Mesangium Cellularity Synechiae Small Sclerotic Tubules Dilated, protein Degen, regen Mineral +/ Interstitium Inflammation 8 Fibrosis RodentPath 8 9 Soft tissue mineralization Severe nephropathy. Enlarged parathyroid. Soft tissue mineralization Severe nephropathy? Enlarged parathyroids? HEART, arteries LUNG septa Soft tissue mineralization Severe nephropathy? Enlarged parathyroids? Stomach Muscle b. Arteritis, periarteritis (aka polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)) Gross: Thick, nodular, multicolored arteries, mesenteric arcade, pancreas, spermatic cord etc Histology: Inflammation neutrophilic lymphohistiocytic, transmural periarterial Mural periarterial thickening by inflammation, proliferation (fibroplasia;) hemorrhage fibrinoid, mineralization /+Thrombi laminated, recanalized etc 1.b. Rat PAN Nodular thickening Arteritis, periarteritis, chronic, lymphohistiocytic, transmural proliferative with Fibroplasia Fibrinoid Thrombi Mineral etc 15 RodentPath 15 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
3 1.b. Rat periarteritis / polyarteritis Rat PAN Aka Polyarteritis Nodosa (PAN) Earliest in mesentery, pancreas, spermatic cord Most obvious in mesentery SD, SHR, hypertensive rats Nodular thickening +/ hemorrhage, 16 mineral RodentPath Earliest? In Pancreas Mesentery Spermatic cord Best gross in Mesentery Veins Spared Thrombi Fibrinoid deposition Disrupted elastic lamina Proliferation Subintimal Medial Adventitial Inflammation Rat PAN Rat PAN Disrupted elastic lamina Proliferation Subintimal Medial Adventitial Inflammation Rat crystals are blood (Hb) origin c. Rat Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy Myofiber degeneration loss Replacement fibrosis Mild chronic inflammation Cf human MI +/ mineral usually with ORN 20 RodentPath = heart muscle abnormality IN pets & people Impaired function diagnosed by ECG, US Big dilated? Hypertrophic? Small fibrotic HOCM COCM RCM cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
4 Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy IN TOX refers to spontaneous changes Typically multifocal Inflammation (Rats > mice) Myofiber degeneration /necrosis/ loss) Fibroplasia +/ collagen vs toxic myocardial degeneration Usually extensive global Jokinen & al Jokinen & al TP Etc NON neoplastic Lungs Alveolar histiocytosis White spots = foam cell foci Alimentary Ulcers gastric/duodenal Stressors, including dehydration, water / diet restriction Crystals 25 Etc: Alveolar histiocytosis Renne & Al intra alveolar macrophages containing foamy cytoplasm Often subpleural in aged animals Increased with hi fat diet Fldodh Magnuson Magnuson 1974 Rat WYD? 1. Etc Non Neoplastic A. Alveolar histiocytosis B. Acidophilic macrophage Pneumonia C. Pneumocystosis D. Induced alveolar proteinosis WYD? A. YM1 crystals B. Blood derived hemoglobin crystals C. Charcot leyden Crystals D. Oxalate crystals 26 Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology Roger Renne et al. Toxicol Pathol 2009;37:5S-73S 28 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
5 WYD? A. YM1 crystals B. Blood derived hemoglobin crystals C. Charcot leyden Crystals D. Oxalate crystals 1. Etc Non Neoplastic Etc: Rat crystals Eosinophilic crystals, Rat lung; Rectangular and linear; Extracellular, alveoli and capillaries. No associated inflammation, nor resemblance to eosinophilic crystalline pneumonia Inset: Okajima stain for hemoglobin. Considered an artifact of freezing, intracardiac puncture, and barbiturate euthanasia. found only in euthanized rats and not in rats found dead or killed in snap traps. likely crystalized hemoglobin J. L. Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015; & Cause/s? A. Vaginal septa B. E coli Rats WYD? Which is Normal? Rats WYD? 6. Normal vagina, rat. 7. Vagina, rat, vaginal septum with necro-hemorrhagic fluid accumulation. 8. Vagina, rat, thin vaginal septum. 9. Vagina, rat, thick vaginal septum. 10. Vagina, rat, mucus plug accumulation in the proximal part of the vagina. 31 S. Lezmi et al. Vet Pathol 2010;48: S. Lezmi et al. Vet Pathol 2010;48: Great Rat lesions (phenotypes) 2.a. Skin Tumors Non Infectious, Non Neoplastic 2. Non Infectious, Neoplastic a. Skin / Mammary most obvious b. Hematopoietic most famous c. Pituitary most common? etc e.g. Adrenal, Thyroid, insuloma; mesothelioma; reproductive; urinary tract etc 3. Infectious 34 Mammary Fibroadenoma (F >> M) Most common tumor identified clinically Gross: small big, soft firm Often resectable Histo Mesenchymal often predominates Glands can be hard to find Fibromas Sarcomas (M > F?) Gross: small big, soft firm Histo Mesenchymal Fibrosarcoma collagen Trichrome Myxoid myxomatous bluish Alcian blue PNST like (peripheral nerve sheath tumor ) cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
6 2.a. Skin Tumors Mammary fibroadenoma More common in Female 40 70% incidence in SD! Associated with hi prolactin, But not necessarily pituitary tumors Case 4 RAT 18 month old female Strain: 35 RodentPath 35 c HCD Rat Mammary Tumors F344 ad lib Strain Diet F344 DR F344 SD CIT Max % SD WIS LE Fibroadenoma Adenofibroma 24 Adenoma Cystadenoma 10 Adenocarcinoma Ductular carcinoma 14 ref Thurman 94 Thurman 94 Sommer 97 Attia 95 Sommer 97 Sommer 97 Sommer Rat Mammary Tumors Associated with increased or decreased mammary tumors? Exposure to estrogen Increased prolactin levels Parity Ovariectomy Pituitary tumors Body weight (Ad lib feeding) What (2) are associated with increased pituitary and mammary tumors Estrogens & body weight 2.a. Skin Tumors 2.a. Skin Tumors Mammary fibroadenoma More common in Female 40 70% incidence in SD! Associated with hi prolactin, But not necessarily pituitary tumors Trichrome stains collagen Fibro ~ blue (Adeno (glands) ~pink/red) 43 RodentPath 43 Fibroma More likely? than fibroadenoma in male Sarcomas are invasive Myxoid PNST Osteo Hemangio (Histiocytic Sarcoma) 44 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
7 2.a. Skin Tumors Other skin tumors Histiocytic sarcoma in skin Also in literature as Fibrous histiocytoma or MFH Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma Papilloma Squamous cell carcinomas Uncommon unless induced (skin paint) Zymbal gland tumors Sebaceous gland anteroventral to external canal Sebaceous squamous feature 2.b. Rat Hematopoietic Tumors Lymphoma, leukemia, histiocytic sarcoma Arguably most Famous rat tumors everyone has heard of them LGL leukemia aka mononuclear leukemia especially F344 Other lymphomas Histiocytic sarcoma anywhere in rat Lung Lymphomas? 2.b. Rat Hematopoietic Tumors LGL leukemia aka mononuclear leukemia Especially F344 Splenomegaly (homogeneously enlarged on gross) Arise in spleen marginal zone Hepatomegaly later Leukemia circulating mononuclear cells with azurophilic granules Pale rat with watery blood Brayton Williford F344 rat LGL leukemia Diagnoses Splenomegaly Icterus Hepatopathy (neoplasia) Icterus dt? 50 Photos by E Ihms 51 Photos by E Ihms cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
8 Diagnosis Pigment nephropathy case 2 F344 Rat Intravascular leukocytosis Leukemia Special stains? IHC? Cause? Hemolysis Immune mediated? 52 Smear: Spherocytosis, polychromasia/anisocytosis, thrombocytopenia, neutrophilia, leukemia Photos by E Ihms Mononuclear cell leukemia LGL leukemia Heterogeneous NonT, non B, NK activity Usually Lysosyme, Esterase negative TOX PROBLEM equivocals Relevant human condition? Rare aggressive NK LGL leukemia? 2.b. Rat Hematopoietic Tumors Spleen Nodules Lymphoma Histiocytic Sarcoma? cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
9 2.b. Rat Hematopoietic Tumors Histiocytic Sarcoma Pleomorphic histiocytoid cells Spleen 2.b. Rat Hematopoietic Tumors Lung Lymphoma? Association with M pulmonis. 58 RodentPath RodentPath 59 2.c. Pituitary Tumors MOST common tumors in some chronic studies 30% 80% Important COD in some often Bloody Cystic Large Prolactin secreting galactorrhea month old female Long Evans Rat Axillary mass; pituitary mass Rat Brain tumors RodentPath 64 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
10 65 2.c. PituitaryTumors Usually Pars Distalis Cords of epithelial cells in vascular stroma Chromophobe > acidophil or basophil Prominent nucleoli 2.b. Pituitary Tumors Usually pars distalis / intermedia / nervosa? Usually adenomas / carcinomas? Usually secrete? Most common in Males or females? age Female % Male % SD old Attia 1995 usually with mammary neoplasia in females (uterine changes suggest estrogen exposure??) SD 2y McMartin & al 1992 Wistar 110 w Nataraju estrogen induced F344 2y Thurman & al 1994 reduced by food restriction in M 68 LOBUN Hi? P ll d S d 69 2.b. Pituitary Tumors Origin of most common pituitary tumor in Human / Rat / Mouse Pars distalis Pars intermedia Pars nervosa Most common secretory product Prolactin (+ GH in human) Likely clinical Signs Galactorrhea in males; acromegalic features or growing nose in elderly humans 70 Rat Pituitary Changes Usually pars distalis Pituitary adenomas compressive May have Pseudocapsule, hemorrhage, cystic changes Chromophobes, acidophilic, basophilic, mixed Hyperplastic Foci = proliferation of cells of normal size, no evidence of pseudocapsule and no significant compression of adjacent pituitary tissue. Nodules of hypertrophic cells = larger cells without evidence of encapsulation Pituitary carcinomas are rare and require evidence of invasion or distant metastasis for their diagnosis. Rat Pituitary Changes Myths? Chromophobe adenomas that secrete prolactin Also Eosinophilic cells Estrogen influence Takekoshi & al A Histopathological Study of Multi-hormone Producing Proliferative Lesions in Estrogen-induced Rat Pituitary Prolactinoma. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 47(4): Etc Rat Endocrine Tumors Adrenal: Cortical F> M? Medullary pheochromocytoma M > F? Up to 70% in Wistar rats Some with Ganglioneuroma Thyroid: Follicular tumors thyroglobulin + / Follicular, cystic, papillary, solid Interstitial C cell (M>F) Calcitonin + more common than in mice esp in BN, WH? Islets insulinoma BN rats Vs hypertrophy in fat insulin resistant rats? cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
11 Etc Rat Endocrine Tumors Pheochromocytoma Adrenal Pheochromocytoma (medullary) Often Bloody Large Invade Vessels (ORN also here) ~80% Wistar!! ~30% SD & F344 Often bloody Invades vasculature Pheochromocytoma Ganglioneuroma packeted neuroendocrine pattern Look like Ganglion cells Usually w pheo Also in Trp53 TM mice Reproductive: 2. etc tumors Testes: Interstitial C cell (F344!!) > Sertoli, seminoma Vagina /cervix / uterus polyps, stromal tumors Urinary tract Kidney renal carcinoma (LE rats, Eker rats); nephroblastoma Ureter/Bladder BN rats T crassicauda? Mesothelioma especially F344 Etc. 2.c. OTHER Rat Tumors Mesothelioma 82 Spermatic cord disseminates Another tumor? Likely Strain? RodentPath 82 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
12 68040 Another expected finding in F344 male >1yo? 55. Rat testis. Adenoma, Leydig cell. 56. Rat testis. Adenoma, Leydig cell. Differing cellular characteristics with pale foamy vacuolated cells and small basophilic fusiform cells. 57. Rat testis. Adenoma, Leydig cell, retiform. 58. Rat testis. Adenoma, Leydig cell, retiform. 59. Rat testis. Carcinoma, Leydig cell. 60. Rat testis. Carcinoma, Leydig cell. Creasey & al Photos by E Ihms 84 Creasy et al. Toxicol Pathol 2012;40:40S-121S Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology Interstitial Cell Tumors Aka Leydig cell tumors Most common testicular tumor in? 1. Rat 2. Cat 3. Dog 4. Bull Hyperplastic lesions focal/diffuse? Size? Usually more diffuse Usually < 3 seminiferous tubules in diameter Rat seminiferous epithelium PAS. PAS stains carbohydrates and emphasizes the glycoproteins contained in the acrosomes (A). Acrosomes, which cap the nuclei of spermatids (St a), play an important role in the fertilization of the oocyte. Note the presence of basophilic residual bodies (R) along the surface of the epithelium. These cytoplasmic bodies separate from the spermatozoa, as these cells detach from the seminiferous epithelium (see Figure 15.10). These residual bodies are eliminated by the phagocytic activity of Sertoli cells. Some pachytene spermatocytes (Sc) are also labelled. Note that the thin limiting membrane of rat tubules is composed of a single layer of myoid cells (My). Stain: PAS Hematoxylin Magnification: Creasy et al. Toxicol Pathol 2012;40:40S-121S Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology WYD 87 Creasy et al. Toxicol Pathol 2012;40:40S-121S Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology 90 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
13 Granulosa Cell tumor wo female Rat SD with Thy1:GFP transgene Synonym(s) Tumor, sex cord stromal, benign, granulosa cell type. Non cystic, solid proliferative lesion larger than a CL. Cell morphology resembles normal granulosa cells. >70% granulosa cells. (+ Stromal component) Variable luteinization Atypia can be Minimal. Mitotic figures may be rare few. Call Exner bodies uncommon. Cystic, microfollicular, solid, trabecular but usually NOT subclassified by pattern. Hemorrhage necrosis lipofuscin in larger tumors. Benign: Compressive Malignant: Invasion/metastasis, size, hemorrhage, necrosis, atypia 91 Dixon&al female Repro INHAND 2014 JTP wo female Rat wo female Rat SD with Thy1:GFP transgene SD with Thy1:GFP transgene WYD? Likely strain? EKER rat (or LE ) Hereditary RCC Tsc2 (tuberous sclerosis2) tumor suppressor gene insertion mutation Autosomal dominant Homozygous lethal Arose in inbred Wistar Mcdorman & Wolf 2002 Tox Path 96 Who is this famous rat? What is its famous mutation? cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
14 Rat Zymbal s gland what is it? multilobulated sebaceous holocrine gland located anterior ventral to the ear canal 3 4 lobules each have intralobular ducts (Squamous epithelium) that empty into the excretory duct and then into ear canal. Do mice have it? How common are spontaneous tumors? Not very common but ~ 1% or less in aging studies in various strains Zymbal s gland neoplasia? WYD? Types Sebaceous cell adenoma, Squamous cell papilloma, Carcinoma of sebaceous and/or ductal epithelial origin Causes of Zymbal s gland neoplasia? target organ of many carcinogens incidence a high as 67% (versus 0% in controls) E.g.2 Acetylaminofluorine, Tris carbonium pamoate, urethan, heterocyclic amines, benzene, 3 3 dichlorobenzidine, 4 aminostilbene, azoxymethane, methychorlanethrene, and cupferron WYD? QUIZ WYD? cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
15 Etc. spontaneous conditions in recent literature: PubMed SEARCH vet pathol [jo] 2015 mice vet pathol [jo] 2015 rats toxicol pathol [jo] 2015 mice jaalas [jo] 2015 mice toxicol pathol [jo] 2015 rats jaalas [jo] 2015 rats j comp path [jo] 2015 mice j comp path [jo] 2015 rats Comp med [jo] 2015 mice Comp med [jo] 2015 rats lab anim [jo] 2015 mice lab anim [jo] 2015 rats 1. Pets 2. Lunch 3. Toxicity What are rats good for? PK! 4. Cancer 5. Behavior 6. Metabolic dz What are rats good at? Amazing Rats! SURVIVAL ayer_detailpage&v=0t2vpbf6kp Great Rat lesions (phenotypes) Non Infectious, Non Neoplastic 2. Non Infectious, Neoplastic 3. Infectious a. Viruses b. Bacteria c. Eukaryota a. Fungi b. Protozoa c. Metazoa a. Helminths b. Arthropod cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
16 FELASA 2014 recommendations Rats Viruses FELASA 2014 recommendations Rats Bacteria & Fungi 3 month testing 1. Parvovirus Kilham rat virus 2. Parvovirus Rat minute virus 3. Parvovirus Rat parvovirus 4. Parvovirus Toolan sh 1 virus 5. PVM 6. Rat coronavirus (SDAV) 7. Rat theilovirus 8. Hantaviruses x Annual testing 1. MAD1 (FL) 2. MAD2 (K87) 3. Reovirus type 3 4. Sendai virus 3 month testing 1. Clostridium piliforme 2. Helicobacter spp. + H bilis 3. Mycoplasma pulmonis 4. Pasteurella pneumotropica 5. Strep b haemolytic (not group D) 6. Streptococcus pneumoniae Annual testing 1. CAR bacillus 2. Pneumocystis spp. 3. Salmonella spp. 4. Streptobacillus moniliformis NO FUNGI FELASA 2014 recommendations RATS Other Agents Bacteria etc 1. Bordetella bronchiseptica 2. Corynebacterium kutscheri 3. Encephalitozoon cuniculi 4. Klebsiella oxytoca, 5. Klebsiella pneumoniae 6. Other Pasteurellaceae 7. Pseudomonas aeruginosa 8. Staphylococcus aureus Unlikely in contemporary colonies Found in healthy animals & Too common to practically exclude Rat Serology: Results Pritchett Corning, K. R., J. Cosentino, et al. (2009). "Contemporary prevalence of infectious agents in laboratory mice and rats." Lab Anim 43(2): Prevalence % Agent (assay abbreviation) Method N NA Europe Total Adenovirus (MAV 1 and 2) Serology 35, Hantaviruses (HANT) Serology 23, Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) Serology 37, Parvovirus generic assay (NS-1) Serology 63, H-1 (Toolan's) Serology 79, Rat virus (RV, KRV) Serology 86, Rat minute virus (RMV) Serology 47, Rat parvovirus (RPV) Serology 85, Pneumonia virus of mice (PVM) Serology 79, Rat coronavirus (RCV/SDAV) Serology 82, Rat respiratory virus (RRV) Histopathology na 6.36 Rat theilovirus (RTV, GD-VII) Serology 35, Reovirus-3 (REO-3) Serology 72, Sendai virus (SEND) Serology 80, Virus prevalence Rats (P car) RRV Parv NS-1 RTV Virus type a Sample type Family or genus No. of pools Most similar species Known Serum Anelloviridae 22 Unclassified anellovirus Serum Bocavirus 9 Porcine bocavirus Serum Mastadenovirus 1 Murine adenovirus A Serum Parvovirus 19 Kilham rat virus Fecal Bocavirus 16 Porcine bocavirus Fecal Calhevirus 10 Calhevirus 1 Fecal Cardiovirus 21 Boone cardiovirus / Rat theilovirus 1 Fecal Circovirus 21 Pig stool-associated circular ssdna virus Chicken anemia virus Fecal Hunnivirus 19 Ovine hungarovirus Fecal Mamastrovirus 19 Rat astrovirus / Murine astrovirus Fecal Mastadenovirus 18 Murine adenovirus A Fecal Parvovirus 24 Kilham rat virus Fecal Rotavirus 3 IDIR agent Fecal Other 31 Novel Serum Arterivirus 2 Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Serum Hepacivirus 16 Rodent hepacivirus Serum Orbivirus 3 African horse sickness virus / Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus Serum Pegivirus 15 Rodent pegivirus Serum Pestivirus 4 Bungowannah virus / Classical swine fever virus Fecal Hepeviridae-like 1 Hepatitis E virus / Betatetravirus Fecal Kobuvirus 19 Mouse kobuvirus / Aichi virus Fecal Parechovirus 5 Ljungan virus / Sebokele virus Fecal Phlebovirus 1 Echarate virus Fecal Picobirnavirus 22 Human picobirnavirus / Otarine picobirnavirus Fecal Picornaviridae 33 Feline picornavirus / Bat picornavirus Fecal Rosavirus 20 Rosavirus M-7 S i NYC rats 201 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
17 127 3.a. Rat Viruses Boring usually subclinical seroconversion 1. Parvoviruses Seroconversion = only sign? 2. Rat Theilovirus Seroconversion = only sign? 3. SDAV clinical Disease Cowpoxvirus ZOONOTIC Pet rat reports Not in standard surveillance or FELASA lists 128 Rat Parvoviruses (RV, H 1, RMV, RPV 1a) Parvoviridae nonenveloped SS DNA viruses. Incidence: low.? Transmission: Direct contact, fomites. Clinical: Usually none; except maybe RV Pathology: Usually none; except maybe RV Diagnosis: serology MFI, IFA; fecal PCR (or mesenteric nodes) 129 Rat Parvoviruses (RV, H 1, RMV, RPV 1a) No disease recognized in natural infections by Toolan s H1 virus Rat Parvovirus 1 Rat Minute virus Rare disease in natural infections by Kilham rat virus aka Rat virus (RV) Immune effects? Lymphotropic/lympholytic? Tumor effects? oncolytic? RPV 1a is a Model oncolytic agent Transient? biliary hyperrplasia? 130 Pathology, organ distribution, and immune response after single and repeated intravenous injection of rats with clinical grade parvovirus H1. Parvovirus H1 (H1PV) natural host is rat. Nonpathogenic except in rat and hamster fetuses and newborns. Strongly oncolytic in human cancer models Clinical grade H1PV was produced according to Good Manufacturing Practices. Minimal effects (IgG & biliary hyperplasia) in rats Due to the confirmation of the favorable safety profile of H1PV in a permissive animal model, a phase I/IIa clinical trial of H1PV in brain tumor patients could be initiated. Geletneky & al 2015 Comp Med. Rat Parvoviruses Rat Virus (RV) Clinical: usually none; may cause: fertility, fetal resorption, small litters, runting. Juvenile young adult male: lethal hemorrhage Pathology: usually none infects actively replicating cells CPE cytolysis IN utero infection: cerebellar hypoplasia in young males hemorrhage, thrombi, infarction Notably: Scrotal hemorrhage Liver multi focal degeneration/ necrosis, hypertrophy Rat cerebellar hypoplasia dt experimental RV in utero cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
18 clinical grade parvovirus h1 (H1PV) RAT THEILOVIRUS (RTV1) nonpathogenic except in rat and hamster fetuses and newborns natural host is rats IV in adult rats No significant pathology! Antivirus Ig G Studied for oncolytic brain tumor treatment! Geletneky & al. (2015). Picornaviridae non enveloped, SSRNA virus. Incidence: Incidence of infection is moderate. Transmission: Fecoral Clinical: usually none Pathology: usually none Diagnosis: Serology MFI, IFA; fecal PCR Rat coronaviruses SDAV RCV RCV causes respiratory infection SDAV infects upper respiratory tract, Submandibular + parotid glands sialoaedintis Harderian + exorbital glands dacryoadenitis, Pulmonary disease is possible in young rats. Clinical: Usually none, or classic SDA Neck swelling Sialoadenitis Porphyrin oculonasal discharge DacryoAdenitis Also exophthalmos keratitis &corneal ulcers. 137 Rat coronaviruses SDAV RCV Etiology: enveloped RNA virus Rat coronavirus (RCV or Parker s rat coronavirus) Sialodacryoadenitis virus (SDAV) Incidence: low. Transmission: highly contagious by aerosol etc. Clinical & Pathology findings: can be none worst in immunodeficient w SDAV Diagnosis: Serology MFI, IFA; PCR in acute dz SDAV from Harderian or submandibular gland. RCV from lung 138 Rat coronaviruses SDAV RCV Gross: Large salivary glands + EDEMA Large Cervical lymph nodes Rhinitis, maybe pneumonia Occasional eye lesions (keratoconjunctivitis, corneal opacities, megaloglobus, hypopyon, hyphema, etc.) Histology: Necrosis of gland & ductal epithelium of parotid and submaxillary and lacrimal glands Squamous metaplasia common during healing Then fibrosis in chronic disease Sublingual gland usually spared 139 SDAV CLINICAL Disease!! in competent animal Hi morbidity (Outbreak) Swollen neck Salivary gland edema Chromodacryorrhea Consider dehydration & stressors RodentPath 139 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
19 3.a. Rat Viruses Summary WYD? Figure 2. Skin. Cause? 141 Boring usually subclinical seroconversion Historically significant SDAV not so common but still around Zoonotic Cowpox pet rats Hantavirus wild rodents LCMV wild rodents, immunodeficient 142 A. Breithaupt et al. Vet Pathol 2012;49: B. 6) Pharynx 7) Pharynx 8) Lung 9) Lung 10) Skin 11) Brain Name the inclusion 143 A. Breithaupt et al. Vet Pathol 2012;49: B. NYC Rats Firth & al 2014 Virus type a Sample type Family or genus No. of pools Most similar species Known Serum Anelloviridae 22 Unclassified anellovirus Serum Bocavirus 9 Porcine bocavirus Serum Mastadenovirus 1 Murine adenovirus A Serum Parvovirus 19 Kilham rat virus Fecal Bocavirus 16 Porcine bocavirus Fecal Calhevirus 10 Calhevirus 1 Fecal Cardiovirus 21 Boone cardiovirus / Rat theilovirus 1 Fecal Circovirus 21 Pig stool-associated circular ssdna virus Chicken anemia virus Fecal Hunnivirus 19 Ovine hungarovirus Fecal Mamastrovirus 19 Rat astrovirus / Murine astrovirus Fecal Mastadenovirus 18 Murine adenovirus A Fecal Parvovirus 24 Kilham rat virus Fecal Rotavirus 3 IDIR agent Fecal Other 31 Novel Serum Arterivirus 2 Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus Serum Hepacivirus 16 Rodent hepacivirus Serum Orbivirus 3 African horse sickness virus / Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus Serum Pegivirus 15 Rodent pegivirus Serum Pestivirus 4 Bungowannah virus / Classical swine fever virus Fecal Hepeviridae-like 1 Hepatitis E virus / Betatetravirus Fecal Kobuvirus 19 Mouse kobuvirus / Aichi virus Fecal Parechovirus 5 Ljungan virus / Sebokele virus Fecal Phlebovirus 1 Echarate virus Fecal Picobirnavirus 22 Human picobirnavirus / Otarine picobirnavirus Fecal Picornaviridae 33 Feline picornavirus / Bat picornavirus 3 Fecal Rosavirus 20 Rosavirus M Fecal Sapovirus 13 Human sapovirus / Porcine sapovirus Table 2. Incidents/outbreaks identified by the review, by zoonotic agent and animal category. 3.b. Bacteria Mostly opportunists today Most research rats are immune sufficient 1. Gram positive: S aureus ~ 23% 2. Helicobacters ~ 6% 3. Gram Negative: P pneumotropica > others Halsby KD, Walsh AL, Campbell C, Hewitt K, Morgan D (2014) Healthy Animals, Healthy People: Zoonosis Risk from Animal Contact in Pet Shops, a Systematic Review of the Literature. PLoS ONE 9(2): e doi: /journal.pone Mycoplasmosis should be rare now. M pulmonis usually with CARbacillus in Chronic Respiratory Disease cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
20 Rat Bacteriology: Results 2009 Pritchett Corning, Cosentino & Clifford 2009" Bacterial prevalence Rats PREVALENCE % J facilities Bacterium Method N NA Europe Total NH 07 Bordetella bronchiseptica Culture Cilia-associated respiratory bacillus Serology 26, Corynebacterium kutscheri Culture Helicobacter genus (any sp.)* PCR Gram Helicobacter hepaticus PCR Helicobacter bilis PCR Klebsiella oxytoca Culture Klebsiella pneumoniae Culture Culture nt 0.06 Mycoplasma pulmonis Serology 81, ? PCR nt 0.29 Culture Pasteurella multocida Pasteurella pneumotropica Culture Other Pasteurella spp. Culture Salmonella sp. Culture Staphylococcus aureus Culture ~40% Streptobacillus moniliformis Culture Streptococcus pneumoniae Culture Streptococcus sp. β-haemolytic, Group B Culture Streptococcus sp. β-haemolytic, Group G Culture Clostridium 151 piliforme ~2% H hep H bil H any P pneum S aureus Staphylococci in rats Gram positive cocci S aureus, S xylosus Incidence: VERY common Transmission: contact, fomites, wounds Clinical & Pathology Findings: Usually none Opportunistic infections Diagnosis: Culture, PCR, histopathology Staphylococci in rats Common isolates from normal skin or Dermatitis Furunculosis in nude rats Helicobacters in rats Gram negative, microaerophilic spiral motile H. bilis, ganmani, H. muridarum, H. rodentium, H. trogontum H. typhlonius Incidence: The incidence of infection is moderate. Incidence: pretty common Transmission: fecal oral Clinical & Pathology Findings: Usually none Diagnosis: Fecal PCR 156 Helicobacters in rats Identified by PCR Uncertain significance Hepatobiliary dz? Zoonotic concern? H spp, H ganmani > H hepaticus or bilis H bilis in nu/nu rats Proliferative and ulcerative typhlitis, colitis, proctitis Haines, D.C., et al., Inflammatory large bowel disease in immunodeficient rats RodentPath 156 naturally and experimentally infected with Helicobacter bilis. Vet Pathol, (3): p cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
21 157 Rat Helicobacters H bilis in nu/nu rats Proliferative and ulcerative typhlitis, colitis, proctitis 1. Colon 2. Cecum Haines, D.C., et al., Inflammatory large bowel disease in immunodeficient rats RodentPath 157 naturally and experimentally infected with Helicobacter bilis. Vet Pathol, (3): p Pasteurella pneumotropica Gram negative, short pleomorphic rod Poor gram staining on histo Incidence: common in mice & rats Transmission: aerosol, fecal oral, contact Clinical: Often none, opportunist Conjunctivitis, respiratory, reproductive tract infections Pathology: often none Inflammation necrosis, inconspicuous bacteria Diagnosis: PCR most sensitive, specific Feces + infection sites 3.b. Bacteria summary 1. Gram positive: S aureus ~ 23%! (S xylosus) Dermatitis, Abscesses, opportunist infections 2. Helicobacters ~6% Enterohepatic lower GI Tract 3. Gram Negative: P pneumotropica Opportunists, inflammatory lesions, abscesses + HISTORICAL RARE + Zoonotic 3.b. Bacteria summary HISTORICAL RARE Mycoplasma pulmonis + CARbacillus (CRD) Cl Piliforme megaloileitis + liver necrosis Salmonella enterica typhimurium liver necrosis C kutscheri pseudotuberculosis (abscessed Lymph nodes +/ pneumonia) Klebsiella pneumoniae Murine Respiratory Mycoplasmosis Pneumonia Bronchiectasis Neutrophilic chronic + upper respiratory disease Perivascular peribronchiolar lymphocytic cuffing M pulmonis & CARbacillus are lymphocyte mitogens Murine Respiratory Mycoplasmosis M pulmonis & CARbacillus MRM, Chronic Respiratory Disease of rats M pulmonis mollicutes Tiny, lack a cell wall Cilia associated respiratory (CAR) bacillus Gram negative filamentous rod, motil Similar to Flavobacterium, Flexibacter Incidence: Rare now; historical significance cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
22 Brayton Rat CARbacillus Wild Urban Rats WYD? Cause? Lymphoplasmacytic cuffs, lung Increased macrophages in adjacent alveoli Significantly associated (P.02) with CARbacillus and M pulmonis J. L. Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015; Wild Urban Rats Norway (Rattus norvegicus) and black rats (Rattus rattus) BALT hyperplasia Peribronchiolar and perivascular lymphocytic cuffs may not actually be inflammatory lesions but rather inducible BALT ibalt, May be response to M. pulmonis, a recognized B and T cell mitogen in rats, or to antigens of CARBacillus which was identified more commonly WYD? Cause? Wild Urban Rats 5. Nose, rhinitis Lumen purulent exudate Submucosa Lymphocytes and plasma cells 6. Nose, rhinitis Basophilic bacilli between cilia (tangled cilia) Inset: Steiner s silver stain. Black filamentous bacteria among the cilia. CARBacillus 165 J. L. Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015; J. L. Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015; Other mycoplasmas Rat WYD? Mycoplasma haemomuris (Hemobartonella muris) Extracellular RBC parasite infectious anemia or splenomegaly in rodents. Dx by PCR, blood smear transmitted by rat louse Polyplax sp Mycoplasmas in tissue culture Common Most are NOT transmissible to rodents a) Pneumonia b) Bronchopneumonia c) Interstitial d) Embolic e) M pulmonis f) CARbacillus g) Streptococcus pneumoniae h) Corynebacterium kutscheri i) Murine Pseudotuberculsosis cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
23 Wild Urban Rats URI Cause (s) Lymphoplasmacytic cuffs, lung Associated with what agents? 171 J. L. Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015;52: Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015;52: b. Bacteria Zoonotic Human/rodent helicobacters? 175 H bilis? hepaticus? ganmani? Leptospirosis rat urine contaminated water Salmonella enterica typhimurium RBF = rat bite fever due to Spirillum minus spirillary RBF, sodoku, Haverhill fever Streptobacillus moniliformis Streptobacillary RBF Yersinia pestis? black plague Via rat fleas? 176 Helicobacter pylori, Helicobacter bilis, Helicobacter hepaticus, Helicobacter ganmani. trend of a higher presence of Helicobacter spp. in patients with biliary tract cancers compared with normal controls or those with benign biliary diseases Shen & al 2014 Fatal Rat Bite Fever in a Child San Diego County, California, CDC.gov Healthy 10yo boy rigors, fevers, vomiting, headaches, leg pains, death PCR Pos Streptobacillus moniliformis (Lung, liver, epiglottis) owned 2 pet rats; 1 PCR Pos oropharyngeal swab Streptobacillus moniliformis Nearly all domestic and wild rats carry S. moniliformis. Elliot % of NYC R norvegicus Firth& al Or may be not. Blaming gerbils from Asia now. cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
24 3.c. Eukaryotes 1. Fungi & Protists P carinii (RRV common) T mentagrophytes Ringworm unlikely E cuniculi microsporidia unlikely 2. Protozoa Entamoebae & flagellates > Giardia & Spironucleus 3. Helminths Pinworms S muris > S obvelata etc Bladder worm T crassicauda unlikely Cestodes (Hymenolepis, Rodentolepis, Cysticercus) 4. Arthropods Mites Fur mites & mesostigmatid > Fleas & lice Rat Eukaryota: Results Pritchett Corning, K. R., J. Cosentino, et al. (2009). "Contemporary prevalence of infectious agents in laboratory mice and rats." Lab Anim 43(2): PREVALENCE % Agent Method N NA Europe Total Encephalitozoon cuniculi Serology 22, Lice Direct nr 0.00 Mites Direct Oxyurids* Aspiculuris tetraptera Direct Syphacia muris Direct Syphacia obvelata Direct Protozoa Chilomastix sp. Wet mount nr 1.65 Entamoeba sp. Wet mount nr 3.18 Giardia sp. Wet mount Hexamastix sp. Wet mount nr 4.60 Monocercomonoides sp. Wet mount nr 0.09 Retortamonas sp. Wet mount nr 0.17 Spironucleus sp. Wet mount nr 0.19 Trichomonads Wet mount nr Fungi Pneumocystis (formerly protozoan) P carinii & P wakefieldii in rats P carinii = RRV Trichophyton mentagrophytes Ringworm no recent reports Microsporidian (also formerly in protozoa) Encephalitozoon cuniculi UNLIKELY Unless rats or mice from pet store 184 Pneumocystis carinii Typical pneumocystosis in immunodeficient Formerly known as RRV, Rat Respiratory Virus in immunocompetent mice Not a virus It s a fungus Used to be classified as protozoan Pathology in competent rats is very different from findings in immunodeficient animals that can not clear the agent RADIL scientists prove there is no RRV; instead it s P. carinii fulfilled Koch s postulates by proving that P. carinii is an etiologic agent of the idiopathic pneumonia historically associated with rat respiratory virus ( RRV ) infection. AALAS Albers T M et al. Vet Pathol 2009;46: cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
25 RRV Fig. 1. Percentage of 8 rats sampled each week that had gross lung lesions consistent with interstitial pneumonia. Fig. 4. Lung; rat 7 weeks after exposure. Fig. 2. Lung; rat 7 weeks after exposure. 189 Albers T M et al. Vet Pathol 2009;46: Albers T M et al. Vet Pathol 2009;46: Pneumocystis Pneumocystis carinii Formerly known as Rat Respiratory Virus 192 Only 4 spp?: In rats P carinii P wakefieldiae In mice P murina In humans P jirovecii (ICBN) Li & al Common (~6%) Consider this with seronegative lung disease Relationship to BN rat allergic? Pneumonia? Diagnosis by pathology Now ELISA + PCR Gross patchy lung lesions resolve Be concerned about Sendai, Mycoplasma Histology perivascular interstitial pneumonia mostly mononuclear Resolves completely 194 Pcp vs Brown Norway Pneumonia BN used to Model allergic/reactive airway disease asthma Consider stimulants/irritants in bedding, environment PCR neg for Pc These control BAL were similar to OVA treated FELASA Rat annual testing Parasites /protozoa Protozoa 1. Entamoeba 2. Giardia 3. Spironucleus 4. Tritrichomonas muris Ectoparasites 1. Fleas 2. Mesostigmatid mites 3. Polyplax 4. Radfordia Helminths 1. Aspiculuris 2. Syphacia 3. Hymenolepis 4. Rodentolepis cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
26 Protozoa Helminths 197 Mostly commensals & pests Small intestine potentially pathogenic Giardia Spironucleus Coccidia Large Intestine Entamoebae Trichomonads Chilomastix etc Most Least common: 1. Hexamastix sp. 2. Entamoeba sp. 3. Chilomastix sp. 4. Trichomonads 5. Spironucleus sp. 6. Retortamonas sp. 7. Monocercomonoides sp. 8. Giardia sp. 198 Nematodes Pinworms Bladder threadworm T crassicauda Rat Lungworm A cantonensis Hepatic capillariasis Calodium hepaticum Cestodes Cysticerci intermediate hosts Hymenolepid (Rodentolepis, Hymenolepis) 199 Pinworms Syphacia muris >>>> S obvelata Tape test, eggs flat on 1 side S muris eggs are smaller x µm. S obvelata eggs x µm more curve Larvae + adults in cecum Adults in colon Eggs on perineum Diagnosis: Tape test? Direct exam? PCR is increasingly efficient 200 Syphacia muris Meade & Watson JAALAS 2014 recommend that perianal tape testing be as close as possible to the peak egg shedding time of 1400, to maximize sensitivity Sex of the host had no consistent effect on egg shedding. Egg shedding showed periodicity, decreasing to 0 at 2 to 3 wk intervals. Neither cecal examin nor tape tests alone reliably predicted pinworm infestation, Eggs aged up to 7 mo remained viable, Gaseous chlorine dioxide ClO2 was an effective ovicidal agent, kill rate of 99.7%. 202 Arthropods 3.c. Eukaryotes Summary Fur mites Radfordia ensifera (look like Myocoptes) Expected 1. Fungi Incidence: low. P carinii (RRV common) Distribution: intrascapular dorsal cervical 2. Protozoa the usual Entamoebae & flagellates > Giardia & Spironucleus Clinical Signs: usually none 3. Helminths the usual Diagnosis: fur pluck etc, PCR more reliable Pinworms S muris > S obvelata etc Mesostigmatid mites blood sucking 4. Arthropods the usual Ornithonyssus bacoti Fur mites Radfordia & mesostigmatid Laelaps echidninus Lice Historical / unexpected Zoonotic Polyplax spinulosa is the sucking louse of rats 203 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
27 2016 Brayton 5 POLA Rat Path 3.c. Eukaryotes Summary Des escargots pour le dîner? Historical/unexpected in laboratory rats Fungi & Protists Unlikely T mentagrophytes Ringworm E cuniculi microsporidia Helminths Unlikely but GREAT LESIONS A cantonensis rat lungworm C hepaticum hepatic capillariasis T crassicauda Bladder threadworm Cysticercus fasciolaris where s the cat? Rodentolepis nana, Hymenolepis diminuta Arthropods Unlikely but important disease (?) 204 Fleas xenopsylla black plague? Lice polyplax Mycoplasma haemomuris 205 Angiostrongyus cantonensis Calodium hepaticum Hepatic capillariasis (Capillaria hepatica) Wild rats etc rodents, AND rabbits Rat lungworm Wild rats etc Snail intermediate host dog, human etc infections Embryonated and non embryonated strongyle eggs in lungs 206 Askjpc.org Urban rats Capillarid eggs with bipolar plugs Simoes & al Trichosomoides crassicauda (Bladder threadworm) Trichosomoides crassicauda Bladder threadworm Incidence: rare (in Laboratory rats). Distribution: Urinary bladder, ureter renal pelvis. Clinical Signs: Usually None Pathology: Proliferative cystitis, calculi, worms Diagnosis: eggs in urine, fecal PCR; Path Still around. Female: ~10 mm! Male ~1mm in female repro tract eggs: ~50x70µ, brown, w bipolar plugs cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
28 210 Hymenolepid cestodes Rodentolepis nana = dwarf tapeworm R microstoma in bile ducts usually mice? Hymenolepis diminuta = rat tapeworm Incidence: rare. Transmission: ingested intermediate hosts fleas, flour beetles, cockroaches Direct cycle: Rodentolepis only. Ingested eggs. Distribution: Small intestine larva in mucosa. Clinical: Usually none Diagnosis: Fecal flotation; Path Hymenolepid cestodes Diagnostic morphology: Rodentolepis nana Adults mm + armed rostellum Strobelocerci (cysticerci) in lamina propria Eggs: 40 60u, oval 2 membranes; 3 pairs polar filaments Hymenolepis diminuta Adults: 10 60x3 4 wide without hooks Eggs: µm, yellow, spherical ZOONOTIC POTENTIAL? 211 ZOONOTIC POTENTIAL? Rodent tapeworms (& humans) Rodentolepis (Hymenolepis) nana common tapeworm in children SAME? Species WAS common in rats, mice Still found in pet stores & wild rodents Roble & al 2012 Human isolates do NOT infect mice, rats Macnish & al 2002 Tough to do the human infection expt Cysticerci (Strobilocerci) Cysticercus fasciolaris (Cysticercus taeniaformis, Strobilocercus fasciolaris) Mice rats = INTERMEDIATE host Cat/carnivore = DEFINITIVE host Incidence: should not occur Transmission: ingestion of cat/carnivore feces Distribution: liver. Clinical Signs: usually none Diagnosis: Path: Cysticerci in liver WYD? Figure 1. Liver; wild rat. Coinfection with Calodium hepatica and Cysticercus fasciolaris.hepatic Parasites in Korean Wild Rats (Rattus norvegicus) and Their Association With Pulmonary Arteriolar Medial 214Hypertrophy 215 J.-Y. Yi et al. Vet Pathol 2009;47: Taenia Larval forms in Intermediate Hosts Cysticercus intermediate host cystic structure with a single scolice Taenia saginata, Taenia solium, Taenia hydatigena, Taenia pisiformis, Taenia crassiceps, Taenia hydatigena and Taenia ovis Strobilocercus (everted) scolice + body (strobila) + bladder Taenia taeniaeformis uses a strobilocercus form Coenurus numerous scolices (inverted) per cyst Taenia multiceps, Taenia serialis and Taenia cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
29 Sarcoma? Strobilocercus fasciolaris 3.c. Eukaryotes summary Zoonotic Pneumocystis? Species specific Giardia? (G muris vs G lamblia) Hymenolepis / rodentolepis tapeworms? Syphacia? Angiostrongylus cantonensis Beware of snails Fleas Xenopsylla cheopis Yersinia pestis? Beware of gerbils Rat testing FELASA Recommendations pdf Immune deficient, gnotobiotics & other needs may warrant different testing. 219 FELASA Rats annual testing by SEROLOGY 1. RCV (SDAV) 2. Parvovirus(es) NS 1 3. Parvovirus KRV 4. Parvovirus H 1 5. Parvovirus RPV 6. Sendai 7. PVM 8. REO3 9. RTV 10. MAD1 11. MAD2 12. Hantavirus (Seoul) Mycoplasma pulmonis Clostridium piliforme 12 viruses + 2 bacteria FELASA Rat/Mouse testing RATS By BACTERIOLOGY 1. Bordetella bronchiseptica 2. Corynebacterium kutscheri 3. Pasteurella pneumotropica 4. Salmonella spp. 5. Streptococcus pneumoniae 6. β hemolytic Streptococcus By MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS Helicobacter 1. Helicobacter spp. 2. H. hepaticus 3. H. typhlonius 4. H. bilis 5. H. rodentium 6. H. ganmani 7. H. mastomyrinus Streptobacillus moniliformis Not so much rat breeding in research facilities More all in, all out studies More clean rats from commercial vendors Try pet stores to see good infectious disease. A few more rat lesions cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
30 Cotton rats WYD? Pregnant females Hemochorial placentation Trophoblast emboli La Perle, & al (2014). Cotton rat WYD? 223 Laperle et al. Vet Pathol S. Lezmi et al. Vet Pathol 2010;48: Key Largo Woodrats (Neotoma floridana smalli) Neotoma sp 225 WYD? Causes? S. P. Terrell et al. Vet Pathol 2011;49: /5 also had signs of diabetes Patchy glomerular immunoreactivity for IgG in 2 cases, but Not IgA and IgM CPN. ad libitum high protein diet. 226 S. P. Terrell et al. Vet Pathol 2011;49: WYD? What are these rats used to study? Psammomys obesus Heterocephalus Glaber WYD? 1. Conspecific trauma 2. Calcinosis cutis 3. Calcinosis circumscripta 4. Calcinosis circumscripta 5. CPN 6. CPN 227 T. J. Steinbach, and J. D. Kane Vet Pathol 2012;50: M. A. Delaney et al. Vet Pathol 2013;50: cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
31 Heterocephalus Glaber 229 WYD? 6. Testis 7. ICH 8. Liver 9. Hemosiderosis 10. Adrenal cortex hyperplasia 11. Heart myofiber variation 12. Normal lungs M. A. Delaney et al. Vet Pathol 2013;50: Figures 1 6. Heterocephalus glaber WYD?? M. A. Delaney et al. Vet Pathol 2015;53: RAT WYD RAT Acute Vacuolation, pyknosis, hemorrhage Chronic Lipid laden macrophages 231 De Jonghe et al. Toxicol Pathol 2015;43: Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology 232 De Jonghe et al. Toxicol Pathol 2015;43: Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology WYD Match # to letter: 1) Benign granular cell tumor, 2) Benign granular cell tumor - PAS 3) Medulloblastoma 4) Malignant highgrade astrocytoma 5) Malignant highgrade oligodendroglioma, 6) Malignant lowgrade-mixed glioma Bertrand et al. Toxicol Pathol 2014;42: Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology Bertrand et al. Toxicol Pathol 2014;42: Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
32 Figures 1 6 RATS Tissue? Diagnoses? Cause? 235 Bertrand et al. Toxicol Pathol 2014;42: Copyright by Society of Toxicologic Pathology 236 J. L. Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015;52: RATS HYPOGEOMYS ANTIMENA Tissues? Diagnoses? Cause? g/doi/full/ / R1.1 Species? Developmmental stage? J. L. Rothenburger et al. Vet Pathol 2015;52: Figures HYPOGEOMYS ANTIMENA g/doi/full/ / R1.1 WYD? 239 cbrayton@jhmi.edu of 32
AUSTRALIAN PHENOMICS FACILITY HEALTH REPORTS
 S Zone 2 - Level 3 High - High Barrier - No Researcher Access Room - 3.71, 3.72, 3.75, 3.76, 3.79, 3.80, 3.83, 3.84, 3.87, 3.88 Random Sampling and Sentinel screening by Cerberus Sciences Last Test Date
S Zone 2 - Level 3 High - High Barrier - No Researcher Access Room - 3.71, 3.72, 3.75, 3.76, 3.79, 3.80, 3.83, 3.84, 3.87, 3.88 Random Sampling and Sentinel screening by Cerberus Sciences Last Test Date
IDEXX BioResearch Case # Received: 3/3/2014 Completed: 3/13/2014 Submitted By Sentinels
 FINAL REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION 4011 Discovery Drive, Columbia, MO 65201 1-800-669-0825 1-573-499-5700 idexx-radil@idexx.com www.idexxbioresearch.com IDEXX BioResearch Case # 8518-2014 Received:
FINAL REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION 4011 Discovery Drive, Columbia, MO 65201 1-800-669-0825 1-573-499-5700 idexx-radil@idexx.com www.idexxbioresearch.com IDEXX BioResearch Case # 8518-2014 Received:
AUSTRALIAN PHENOMICS FACILITY HEALTH REPORTS
 AUSTRALIAN PHENOMICS FACILITY HEALTH REPORTS Zone 2 - Level 3 High - High Barrier - No Researcher Access Room - 3.71, 3.72, 3.75, 3.76, 3.79, 3.80, 3.83, 3.84, 3.87, 3.88 Random Sampling and Sentinel screening
AUSTRALIAN PHENOMICS FACILITY HEALTH REPORTS Zone 2 - Level 3 High - High Barrier - No Researcher Access Room - 3.71, 3.72, 3.75, 3.76, 3.79, 3.80, 3.83, 3.84, 3.87, 3.88 Random Sampling and Sentinel screening
IDEXX BioAnalytics Case # Received: 9/18/2018 Completed: 9/26/2018 Submitted By Justin Wilson
 FINAL REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION 4011 Discovery Drive, Columbia, MO 65201 1-800-669-0825 1-573-499-5700 idexxbioanalytics@idexx.com www.idexxbioanalytics.com IDEXX BioAnalytics Case # 26931-2018
FINAL REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION 4011 Discovery Drive, Columbia, MO 65201 1-800-669-0825 1-573-499-5700 idexxbioanalytics@idexx.com www.idexxbioanalytics.com IDEXX BioAnalytics Case # 26931-2018
Price List. Effective 1 October Effective 1 October SAHMRI 2126/B SAHMRI 2126/B
 Price List Effective 1 October 2013 Effective 1 October 2013 1 SEROLOGY EIA $14.50 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** IFA $25.00 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** ***A 20% discount is applied to each submission with 30 or more
Price List Effective 1 October 2013 Effective 1 October 2013 1 SEROLOGY EIA $14.50 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** IFA $25.00 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** ***A 20% discount is applied to each submission with 30 or more
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY
 AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
Price List Effective 1 September 2016
 Price List Effective 1 September 2016 SEROLOGY EIA $15.20 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** IFA $26.30 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** ***A 10% discount is applied to each submission with 30 or more serum samples for an
Price List Effective 1 September 2016 SEROLOGY EIA $15.20 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** IFA $26.30 PER INDIVIDUAL TEST*** ***A 10% discount is applied to each submission with 30 or more serum samples for an
2015 Lab Animal 8/22/ Mouse. 2. Rat. 3. Mouse. Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse
 1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
IDEXX BioResearch Case # Received: 12/10/2014 Completed: 12/22/2014 Submitted By Beata Muszynska-Furas
 FINAL REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Mörikestr. 28/3, D 71636 Ludwigsburg, Germany 001-877-635-4036 (International toll free number) IdexxBioresearch-Europe@idexx.com www.idexxbioresearch.com/europe
FINAL REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Mörikestr. 28/3, D 71636 Ludwigsburg, Germany 001-877-635-4036 (International toll free number) IdexxBioresearch-Europe@idexx.com www.idexxbioresearch.com/europe
FINAL ANIMAL HEALTH MONITORING REPORT
 101 Blacks Road Gilles Plains SA 5086 T +61 8 8128 4617 F +61 8 8261 2280 info@compath.com.au www.compath.com.au FINAL ANIMAL HEALTH MONITORING REPORT Requested By University of Adelaide - Medical School
101 Blacks Road Gilles Plains SA 5086 T +61 8 8128 4617 F +61 8 8261 2280 info@compath.com.au www.compath.com.au FINAL ANIMAL HEALTH MONITORING REPORT Requested By University of Adelaide - Medical School
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Rodent Pathogens. Judy Hickman-Davis, DVM, PhD, DACLAM. Associate Professor, VPM
 A Review of Common Rodent Pathogens Judy Hickman-Davis, DVM, PhD, DACLAM Clinical Veterinarian, ULAR Associate Professor, VPM Purpose of Sentinel Rodents To monitor the health status t in each colony animal
A Review of Common Rodent Pathogens Judy Hickman-Davis, DVM, PhD, DACLAM Clinical Veterinarian, ULAR Associate Professor, VPM Purpose of Sentinel Rodents To monitor the health status t in each colony animal
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
FELASA profile in 7 days!
 Lab Animal Health Screening & Biological Sample Testing FELASA profile in 7 days! Your Lab Animal Health Surveillance Partner We believe our work adds value to scientific research, and that every facility
Lab Animal Health Screening & Biological Sample Testing FELASA profile in 7 days! Your Lab Animal Health Surveillance Partner We believe our work adds value to scientific research, and that every facility
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
Endocrine Lab. Heather Fenton VPM 222 November
 Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS
 COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
COMPREHENSIVE STOOL ANALYSIS Intestinal parasites: Normal value = 0 (not marked) Reference range: 0 (negative) - 4 (heavy presence) Specimens fixed and transported in SAF and concentrated using CONSED
Schistosome life cycle.
 Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data. March, 2003
 Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data March, 2003 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
Spontaneous Neoplasms and Survival in Wistar Han Rats: Compilation of Control Group Data March, 2003 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1
Alveolar Histiocytosis. Non-infectious conditions of Rats. Alveolar Histiocytosis
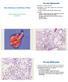 Non-infectious conditions of Rats Charles B Clifford, DVM, PhD, DACVP Charles River Alveolar Histiocytosis Synonym: Alveolar lipidosis Prevalence: Very high in aged rats, moderate in younger animals may
Non-infectious conditions of Rats Charles B Clifford, DVM, PhD, DACVP Charles River Alveolar Histiocytosis Synonym: Alveolar lipidosis Prevalence: Very high in aged rats, moderate in younger animals may
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Rat Serology Results INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF LABORATORY RATS
 INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF LABORATORY RATS Charles River Laboratories Charles Louis Davis, DVM Foundation Madison, WI July 2007 Charles B. Clifford, DVM, PhD, DACVP Rat Serology Results Agent/Assay NS-1 H-1
INFECTIOUS DISEASES OF LABORATORY RATS Charles River Laboratories Charles Louis Davis, DVM Foundation Madison, WI July 2007 Charles B. Clifford, DVM, PhD, DACVP Rat Serology Results Agent/Assay NS-1 H-1
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ORGANIZED BY SOCIETY FOR TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY IN INDIA (STPI) OCTOBER 29-31, 2010 The Atria Hotel, # 1, Palace Road, Bangalore - 560 001
CONTINUING EDUCATION IN TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ORGANIZED BY SOCIETY FOR TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY IN INDIA (STPI) OCTOBER 29-31, 2010 The Atria Hotel, # 1, Palace Road, Bangalore - 560 001
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Neoplasia literally means "new growth.
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia literally means "new growth. A neoplasm, defined as "an abnormal mass of tissue the growth of which exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues and persists in the
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Tinh hoàn
 Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tinh hoàn Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Mào tinh hoàn Mào tinh hoàn Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh Túi tinh So-called cystadenoma of seminal vesicle. Gross appearance of granulomatous
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
(JPC ) Caprine lungs
 2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
SCOPE OF PRACTICE PGY-5
 Recognize normal cytomorphology of cells derived from the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts, and body fluid (Cerebrospinal fluid, pleural and peritoneal fluid) Recognize normal cytomorphology
Recognize normal cytomorphology of cells derived from the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts, and body fluid (Cerebrospinal fluid, pleural and peritoneal fluid) Recognize normal cytomorphology
Case year female. Routine Pap smear
 Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Case 1 57 year female Routine Pap smear Diagnosis? 1. Atypical glandular cells of unknown significance (AGUS) 2. Endocervical AIS 3. Endocervical adenocarcinoma 4. Endometrial adenocarcinoma 5. Adenocarcinoma
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia. Shannon Martinson, Feb
 Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia Shannon Martinson, Feb 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case #1 Signalment and History: 6-month old feeder lamb found dead on pasture
Disturbances of Circulation, Lab 1: Edema and Congestion/Hyperemia Shannon Martinson, Feb 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case #1 Signalment and History: 6-month old feeder lamb found dead on pasture
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung. Shannon Martinson,
 Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 9 month old DSH cat History: Poor doer with stunted growth One month of lethargy one day the
Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 9 month old DSH cat History: Poor doer with stunted growth One month of lethargy one day the
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
Pathology of the Respiratory System 4: Pneumonia
 Pathology of the Respiratory System 4: Pneumonia Shannon Martinson, March 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 222 Systemic Pathology LUNG PNEUMONIA Review Classification of Pneumonia Diffuse LUNG
Pathology of the Respiratory System 4: Pneumonia Shannon Martinson, March 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 222 Systemic Pathology LUNG PNEUMONIA Review Classification of Pneumonia Diffuse LUNG
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology
 NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
The effects of natural laboratory animal pathogens on research
 The effects of natural laboratory animal pathogens on research Chang-Wu Tsai, D.V.M., Ph.D. Laboratory animal center, college of medicine, NTU 2006/9/7 1 Historical struggle against pathogens of laboratory
The effects of natural laboratory animal pathogens on research Chang-Wu Tsai, D.V.M., Ph.D. Laboratory animal center, college of medicine, NTU 2006/9/7 1 Historical struggle against pathogens of laboratory
Spontaneous Neoplastic Lesions in the CrI:CD-1(ICR) Mouse in Control Groups from 18 Month to 2 year Studies. March, 2005
 Spontaneous Neoplastic Lesions in the CrI:CD-1(ICR) Mouse in Control Groups from 18 Month to 2 year Studies March, 2005 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D 1063
Spontaneous Neoplastic Lesions in the CrI:CD-1(ICR) Mouse in Control Groups from 18 Month to 2 year Studies March, 2005 Information Prepared by Mary L.A. Giknis Ph.D Charles B. Clifford D.V.M, Ph.D 1063
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Western Veterinary Conference 2013
 Western Veterinary Conference 2013 SA283 EMERGING CANINE INFECTIOUS RESPIRATORY DISEASES Stephanie D Janeczko, DVM, MS, Dipl. ABVP (Canine/Feline) ASPCA New York, NY, USA Management of infectious respiratory
Western Veterinary Conference 2013 SA283 EMERGING CANINE INFECTIOUS RESPIRATORY DISEASES Stephanie D Janeczko, DVM, MS, Dipl. ABVP (Canine/Feline) ASPCA New York, NY, USA Management of infectious respiratory
National Unit Specification: General Information
 National Unit Specification: General Information NUMBER D939 12 COURSE - SUMMARY This unit is designed to give candidates a basic introduction to health and disease in laboratory animals. The outcomes
National Unit Specification: General Information NUMBER D939 12 COURSE - SUMMARY This unit is designed to give candidates a basic introduction to health and disease in laboratory animals. The outcomes
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results
 SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia.
 Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
Parasite II Helminths (Worms) General Characteristics: Eukaryotic, multicellular parasites, in the kingdom Animalia. They are worm-like organisms that live and feed off living hosts, receiving nourishment
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION
 PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
Gastroenteritis and viral infections
 Gastroenteritis and viral infections A Large number of viruses are found in the human gut; these include some that are associated with gastroenteritis Rotaviruses Adenoviruses 40/41 Caliciviruses Norwalk-like
Gastroenteritis and viral infections A Large number of viruses are found in the human gut; these include some that are associated with gastroenteritis Rotaviruses Adenoviruses 40/41 Caliciviruses Norwalk-like
Liver Lab #2. Bacterial Hepatitis
 Liver Lab #2 Bacterial Hepatitis Case: O12561-04. Adult ewe. Describe the lesion: Multifocal large nodules ranging in size from 1-3.5cm in greatest diameter are present within the liver and are filled
Liver Lab #2 Bacterial Hepatitis Case: O12561-04. Adult ewe. Describe the lesion: Multifocal large nodules ranging in size from 1-3.5cm in greatest diameter are present within the liver and are filled
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens
 Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
Chapters 21-26: Selected Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens 2. RNA Viral Pathogens 1. DNA Viral Pathogens Smallpox (pp. 623-4) Caused by variola virus (dsdna, enveloped): portal of entry is the respiratory
SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY. Pathology of Muscle
 SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY Pathology of Muscle Lecture 4 Paul Hanna Winter 2018 PARASITIC MYOSITIS several important parasites of domestic animals encyst in muscle &/or cause myositis Figure 8 5 Coiled Trichinella
SYSTEMIC PATHOLOGY Pathology of Muscle Lecture 4 Paul Hanna Winter 2018 PARASITIC MYOSITIS several important parasites of domestic animals encyst in muscle &/or cause myositis Figure 8 5 Coiled Trichinella
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates
 Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION. Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta
 DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
Charles Halsey, DVM, PhD, DACVP Pfizer, Inc. IHC Resources
 Charles Halsey, DVM, PhD, DACVP Pfizer, Inc. IHC Resources 1 IHC Identification Targets Specimens Controls 2 Tissue controls Trouble Spots 3 The Key to Description IHC Description 4 Intermediate Filaments
Charles Halsey, DVM, PhD, DACVP Pfizer, Inc. IHC Resources 1 IHC Identification Targets Specimens Controls 2 Tissue controls Trouble Spots 3 The Key to Description IHC Description 4 Intermediate Filaments
Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770
 Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770 Course Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Recognize reproductive female
Guide to Small Animal Reproductive Imaging using the Vevo 770 Course Objectives: After completion of this module, the participant will be able to accomplish the following: Recognize reproductive female
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: April 2013
 Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Shigella and salmonella
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE
 AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE W. U. GARDNER,' L. C. STRONG,' AND G. M. SMITH (Front the Department of Anatomy, Yale Univerdy School of Medicine)
AN OBSERVATION OF PRIMARY TUMORS OF THE PITUITARY, OVARIES, AND MAMMARY GLANDS IN A MOUSE W. U. GARDNER,' L. C. STRONG,' AND G. M. SMITH (Front the Department of Anatomy, Yale Univerdy School of Medicine)
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Vascular Related Torsion Venous compression Hemorrhagic infarct Young men At night Very painful Can be reduced Scrotal Masses Testicular Tumors (solid
 Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
ACCME/Disclosures 4/13/2016 IDPB
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system
 XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Cytoplasmic changes Nuclear changes
 The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
The presence of infection in the female genital tract may procure certain cellular changes in the epithelium. Such changes are seen in nucleus and cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. Cytoplasmic changes
Charles River Immunodeficient Models Xenograft Data Catalog
 Charles River Immunodeficient Models Xenograft Data Catalog SCID Hairless Outbred (SHO ) Mouse Xenograft Data askcharlesriver@crl.com www.criver.com 214, Charles River Laboratories International, Inc.
Charles River Immunodeficient Models Xenograft Data Catalog SCID Hairless Outbred (SHO ) Mouse Xenograft Data askcharlesriver@crl.com www.criver.com 214, Charles River Laboratories International, Inc.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY. PATHOLOGY of MASS LESIONS and TISSUE DEFECTS -MACROSCOPY Assoc. Professor Rengin Ahıskalı
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of MASS LESIONS and TISSUE DEFECTS -MACROSCOPY Assoc. Professor Rengin Ahıskalı M1 - RENAL TUBERCULOSIS cavitary areas caseous necrosis fibrous
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of MASS LESIONS and TISSUE DEFECTS -MACROSCOPY Assoc. Professor Rengin Ahıskalı M1 - RENAL TUBERCULOSIS cavitary areas caseous necrosis fibrous
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Vascular Lung Diseases
 Vascular Lung Diseases SESSION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES List the major types of vascular lung disease Recognize and describe the pathology of vascular lung disease: Pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, hypertension,
Vascular Lung Diseases SESSION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES List the major types of vascular lung disease Recognize and describe the pathology of vascular lung disease: Pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, hypertension,
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
