RT 2 Profiler PCR Array:
|
|
|
- Mariah Gilmore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RT 2 Profiler PCR Array: Rat Cell Cycle Catalog Number For Real-Time Instruments: PARN-020A ABI Standard Blocks; Bio-Rad icycler, MyiQ, and (MJ Research) Chromo 4; and Stratagene Mx3005p, Mx3000p PARN-020C ABI 7500 and 7900HT FAST 96-Well Blocks, ABI StepOnePlus PARN-020D Bio-Rad (MJ Research) Opticon and Opticon 2, Stratagene Mx4000 PARN-020E ABI 7900HT 384-Well Block PARN-020F Roche LightCycler well Block PARN-020G Roche LightCycler well Block Description The Rat Cell Cycle RT 2 Profiler PCR Array profiles the expression of 84 genes key to cell cycle regulation. This array contains genes that both positively and negatively regulate the cell cycle, the transitions between the each of the phases, DNA replication, checkpoints and arrest. Using real-time PCR, you can easily and reliably analyze expression of a focused panel of genes related to the cell cycle with this array. Functional Gene Groupings G1 Phase and G1/S Transition: Camk2a, Camk2b, Gpr132, Itgb1, LOC (Nfatc1), RGD (Myb), LOC (Slfn1), Ppp3ca, RGD (Skp2), Taf10. S Phase and DNA Replication: Dnajc2 (Zrf2), LOC (Mcm3), Mcm2, Mcm4, Mki67, Mre11a, Msh2, Pcna, Rad17, Rad51, Sumo1. G2 Phase and G2/M Transition: Chek1, Dnajc2 (Zrf2), Ppm1d. M Phase: Brca2, Ccna1 (Cyclin A1), Ccnb1, Cdc25a, Cdc25b, Cdk2, LOC (Pes1), MGC (Rad21), Nek2, Npm2, Prm1, Ran, Shc1, Smc1l1, Stag1, Terf1, Tnfsf5ip1, Wee1. Cell Cycle Checkpoint and Cell Cycle Arrest: Ak1, Apbb1, Brca2, Casp3, Cdk5rap1, Cdkn1a, Cdkn1b, Cdkn2a, Cdkn2b, Chek1, Ddit3 (CHOP), Dst, Gadd45a, Inha, LOC (Hus1), LOC (Slfn1), Mad2l1, Mdm2, Msh2, Notch2, Pkd1, Pmp22, Ppm1d (WIP1), Rad9, RGD (Sestrin 2), Sfn (Stratifin), Smc1l1, Tsg101. Regulation of the Cell Cycle: Abl1, Bcl2, Brca2, Ccna1, Ccna2, Ccnb1, Ccnb2, Ccnc, Ccnd1, Ccnd2, Ccne1, Ccnf, Cdk4, Cdkn1a, E2f1, E2f4, Gadd45a, Itgb1, RGD (E2f3), Rad9, Ran, RGD (Skp2), Sfn (Stratifin), Shc1, Tcfdp2 (Tfdp2), Tnfsf5ip1. Negative Regulation of the Cell Cycle: Apbb1, Atm, Brca1, Casp3, Cdkn2a, Inha, LOC (Rbl1), Rbl2, Tp53, Trp63. Storage Conditions Please check the kit components immediately after you receive this package. We are only responsible for missing items reported within two (2) business days of receipt. Storage Conditions: PCR Arrays are shipped at ambient temperature. Keep plates at -20 ºC for long-term storage. NOTE: Be sure that you have the correct PCR Array format for your instrument before starting the experiment. Page 1 of 5
2 References 1. Nurse, P. (2000) A Long Twentiety Century Of The Cell Cycle And Beyond. Cell 100: Sherr, C. J. and Roberts, J. M. (1999) CDK Inhibitors: Positive And Negative Regulators Of G1-Phase Progression. Genes & Development 13: Harbour, J. W. and Dean, D. C. (2000) Rb Function In Cell-Cycle Regulation And Apoptosis. Nature Cell Biology 2: E Deshaies, R. J. (1995) The Self-Destructive Personality Of A Cell Cycle In Transition. Current Biology 7: Gardner R. D. and Burke D. J. (2000) The Spindle Checkpoint: Two Transition, Two Pathways. Trends in Cell Biology 10: Dasika, G. K., Lin, S. C., Zhao, S., Sung, P., Tomkinson, A., and Lee, E. Y. (1999) DNA Damage-Induced Cell Cycle Checkpoints And DNA Strand Break Repair In Development And Tumorigenesis. Oncogene 18: Amati, B. and Vlach, J. (1999) Kip1 Meets SKP2: New Links in Cell-Cycle Control. Nature Cell Biology 1: E Muller, H. and Helin, K. (2000) The E2F Transcription Factors: Key Regulators of Cell Proliferation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1470: M Bottazzi, M. E. and Assoian, R. K. (1997) The Extracellular Matrix And Mitogenic Growth Factors Control G1 Phase Cyclins And Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors. Trends in Cell Biology 7: Sherr C. J. and Weber J. D. (2000) The ARF/p53 Pathway. Curr Opin Genet. Dev 10: Page 2 of 5
3 Array Layout: Rat Cell Cycle RT 2 Profiler PCR Array A Abl1 Ak1 Apbb1 Atm Brca1 Brca2 Camk2a Camk2b Casp3 Ccna1 Ccna2 Ccnb1 B Ccnb2 Ccnc Ccnd1 Ccnd2 Ccne1 Ccnf Cdc25a Cdc25b Cdk2 Cdk4 Cdk5rap1 Cdkn1a C Cdkn1b Cdkn2a Cdkn2b Chek1 Ddit3 Dnajc2 Dst E2f1 E2f4 Gadd45a Gpr132 Inha D Itgb1 LOC RGD LOC RGD LOC LOC BCL2 LOC Mad2l1 Mcm2 Mcm4 E Mdm2 MGC Mki67 Mre11a Msh2 Nek2 Notch2 Npm2 Pcna Pkd1 Pmp22 Ppm1d F Ppp2r3a Ppp3ca Prm1 Rad17 Rad51 Rad9 Ran LOC Rbl2 RGD RGD Sfn G Shc1 Smc1l1 Stag1 Sumo1 Taf10 Terf1 Tcfdp2 Tnfsf5ip1 Tp53 Trp63 Tsg101 Wee1 H Rplp1 Hprt Rpl13a Ldha Actb RGDC RTC RTC RTC PPC PPC PPC Gene Table Position UniGene GenBank Symbol Description A01 Rn.3105 XM_ Abl1 V-abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (mapped) A02 Rn NM_ Ak1 Adenylate kinase 1 A03 Rn NM_ Apbb1 Amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein-binding, family B, member 1 A04 Rn XM_ Atm Ataxia telangiectasia mutated homolog (human) (mapped) A05 Rn NM_ Brca1 Breast cancer 1 A06 Rn NM_ Brca2 Breast cancer 2 A07 Rn NM_ Camk2a Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, alpha A08 Rn.9743 NM_ Camk2b Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, beta A09 Rn NM_ Casp3 Caspase 3, apoptosis related cysteine protease A10 Rn NM_ Ccna1 Cyclin A1 A11 Rn NM_ Ccna2 Cyclin A2 A12 Rn.9232 NM_ Ccnb1 Cyclin B1 B01 Rn NM_ Ccnb2 Cyclin B2 B02 Rn XM_ Ccnc Cyclin C B03 Rn NM_ Ccnd1 Cyclin D1 B04 Rn NM_ Ccnd2 Cyclin D2 B05 Rn XM_ Ccne1 Cyclin E B06 Rn XM_ Ccnf Cyclin F B07 Rn NM_ Cdc25a Cell division cycle 25 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) B08 Rn NM_ Cdc25b Cell division cycle 25 homolog B (S. cerevisiae) B09 Rn NM_ Cdk2 Cyclin dependent kinase 2 B10 Rn.6115 NM_ Cdk4 Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 B11 Rn NM_ Cdk5rap1 CDK5 regulatory subunit associated protein 1 B12 Rn NM_ Cdkn1a Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A C01 Rn NM_ Cdkn1b Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B C02 Rn NM_ Cdkn2a Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A C03 Rn NM_ Cdkn2b Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B (p15, inhibits CDK4) C04 Rn NM_ Chek1 Checkpoint kinase 1 homolog (S. pombe) C05 Rn NM_ Ddit3 DNA-damage inducible transcript 3 C06 Rn NM_ Dnajc2 DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily C, member 2 C07 Rn XM_ Dst_predicted Dystonin (predicted) C08 Rn XM_ E2f1 E2F transcription factor 1 C09 Rn XM_ E2f4_predicted E2F transcription factor 4 (predicted) C10 Rn NM_ Gadd45a Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible 45 alpha C11 Rn XM_ Gpr132_predicted G protein-coupled receptor 132 (predicted) C12 Rn.8831 NM_ Inha Inhibin alpha D01 Rn NM_ Itgb1 Integrin beta 1 (fibronectin receptor beta) D02 Rn.9521 XM_ LOC Similar to PES1 protein D03 Rn XM_ RGD _predicted Similar to E2f3 protein (predicted) Page 3 of 5
4 Position UniGene GenBank Symbol Description D04 Rn.8800 XM_ LOC Similar to nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1 D05 Rn XM_ RGD _predicted Similar to Nanos2 (predicted) D06 Rn XM_ LOC Similar to DNA replication licensing factor MCM3 (DNA polymerase alpha holoenzymeassociated protein P1) (P1-MCM3) D07 Rn XM_ LOC Similar to Hus1 homolog D08 Rn.9996 NM_ Bcl2 B-cell leukemia/lymphoma 2 D09 Rn XM_ LOC Similar to schlafen 1 D10 Rn XM_ Mad2l1_predicted MAD2 (mitotic arrest deficient, homolog)-like 1 (yeast) (predicted) D11 Rn XM_ Mcm2_predicted Minichromosome maintenance deficient 2 mitotin (S. cerevisiae) (predicted) D12 Rn.8341 XM_ Mcm4 Minichromosome maintenance deficient 4 homolog (S. cerevisiae) E01 Rn XM_ Mdm2 Transformed mouse 3T3 cell double minute 2 E02 Rn NM_ MGC Similar to HR21spA E03 Rn XM_ Mki67_predicted Antigen identified by monoclonal antibody Ki-67 (predicted) E04 Rn NM_ Mre11a Meiotic recombination 11 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) E05 Rn.3174 NM_ Msh2 MutS homolog 2 (E. coli) E06 Rn XM_ Nek2 NIMA (never in mitosis gene a)-related expressed kinase 2 E07 Rn NM_ Notch2 Notch gene homolog 2 (Drosophila) E08 Rn NM_ Npm2 Nucleophosmin/nucleoplasmin 2 E09 Rn.223 NM_ Pcna Proliferating cell nuclear antigen E10 Rn XM_ Pkd1 Polycystic kidney disease 1 homolog E11 Rn.1476 NM_ Pmp22 Peripheral myelin protein 22 E12 Rn XM_ Ppm1d_predicted Protein phosphatase 1D magnesium-dependent, delta isoform (predicted) F01 Rn XM_ Ppp2r3a Protein phosphatase 2 (formerly 2A), regulatory subunit B'', alpha F02 Rn.6866 NM_ Ppp3ca Protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, alpha isoform F03 Rn NM_ Prm1 Protamine 1 (mapped) F04 Rn NM_ Rad17 RAD17 homolog (S. pombe) F05 Rn XM_ Rad51_predicted RAD51 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (predicted) F06 Rn XM_ Rad9_predicted RAD9 homolog (S. pombe) (predicted) F07 Rn NM_ Ran RAN, member RAS oncogene family F08 Rn XM_ LOC Similar to Retinoblastoma-like protein 1 (107 kda retinoblastoma-associated protein) (PRB1) (P107) F09 Rn NM_ Rbl2 Retinoblastoma-like 2 F10 Rn XM_ Similar to S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (F-box protein Skp2) (F-box/WD-40 protein RGD _predicted 1) (predicted) F11 Rn XM_ RGD _predicted Similar to Sestrin 2 (Hi95) (predicted) F12 Rn XM_ Sfn_predicted Stratifin (predicted) G01 Rn NM_ Shc1 Src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein C1 G02 Rn NM_ Smc1l1 Structural maintenance of chromosomes 1 like 1 (S. cerevisiae) G03 Rn XM_ Stag1_predicted Stromal antigen 1 (predicted) G04 Rn.1221 NM_ Sumo1 SMT3 suppressor of mif two 3 homolog 1 (yeast) G05 Rn XM_ Taf10_predicted TAF10 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factor (predicted) G06 Rn NM_ Terf1 Telomeric repeat binding factor 1 G07 Rn XM_ Tcfdp2_predicted Transcription factor Dp 2 (predicted) G08 Rn XM_ Tnfsf5ip1_predicted Tumor necrosis factor superfamily, member 5-induced protein 1 (predicted) G09 Rn NM_ Tp53 Tumor protein p53 G10 Rn NM_ Trp63 Transformation related protein 63 G11 Rn.7410 NM_ Tsg101 Tumor susceptibility gene 101 G12 Rn NM_ Wee1 Wee 1 homolog (S. pombe) H01 Rn.973 NM_ Rplp1 Ribosomal protein, large, P1 H02 Rn.47 NM_ Hprt Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase H03 Rn NM_ Rpl13a Ribosomal protein L13A H04 Rn NM_ Ldha Lactate dehydrogenase A H05 Rn NM_ Actb Actin, beta H06 N/A U26919 RGDC Rat Genomic DNA Contamination H07 N/A SA_00104 RTC Reverse Transcription Control H08 N/A SA_00104 RTC Reverse Transcription Control H09 N/A SA_00104 RTC Reverse Transcription Control H10 N/A SA_00103 PPC Positive PCR Control H11 N/A SA_00103 PPC Positive PCR Control H12 N/A SA_00103 PPC Positive PCR Control Page 4 of 5
5 Page 5 of 5
Applied Biosystems models 7500 (Fast block), 7900HT (Fast block), StepOnePlus, ViiA 7 (Fast block)
 RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition
 Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
Tumour growth environment modulates Chk1 signalling pathways and sensitivity to Chk1 inhibition Andrew J Massey Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure S1. Related to Fig. 1. (a) HT29 or U2OS cells
For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression
 ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
ExProfile TM Human HIV Infection and Host Response Related Gene qpcr Array For focused group profiling of human HIV infection and host response genes expression Cat. No. QG023-A (1 x 96-well plate, Format
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Regulation of cell cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
Regulation of cell cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Control of cell cycle: Checkpoints Are the cell cycle controls mechanisms in eukaryotic cells. These checkpoints verify whether the processes at each phase
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
CELL CYCLE MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS Summary of the regulation of cyclin/cdk complexes during celll cycle Cell cycle phase Cyclin-cdk complex inhibitor activation Substrate(s) G1 Cyclin D/cdk 4,6
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2)
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Genomic instability. Amin Mahpour
 Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, sensitizes lung cancer cells to treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary
PD 0332991, a selective cyclin D kinase 4/6 inhibitor, sensitizes lung cancer cells to treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary
Cell cycle control (mammalian)
 Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I. Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017
 Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Propranolol enhances cell cycle-related gene expression in pressure overloaded hearts
 1917..1928 BJP British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01504.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1504 Propranolol enhances cell cycle-related gene expression in pressure overloaded
1917..1928 BJP British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01504.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1504 Propranolol enhances cell cycle-related gene expression in pressure overloaded
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Chapter 12. Regulation of Cell Division Coordination of cell division! Multicellular organism " need to coordinate across different parts of organism! timing of cell division! rates of cell division "
Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage
 1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
1 Cancer Biology How a cell responds to DNA Damage Jann Sarkaria Department of Oncology Mayo Clinic 2 EDUCATIONAL GOALS How proteins can transmit signals to each other. The definition of a tumor suppressor
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
U118MG. Supplementary Figure 1 U373MG U118MG 3.5 A CCF-SSTG
 A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK
 TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
C) The graph should look exactly like the graph on the left (Mut1 cells + Mating Pheromone for 3 hours at 25 degrees). The cells arrest in G1.
 706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
Regulation of Cell Division. AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2006-2007 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death
 02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
02.17.10 Lecture 14 - The cell cycle and cell death The cell cycle: cells duplicate their contents and divide The cell cycle may be divided into 4 phases The cell cycle triggers essential processes (DNA
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Regulation of the Cell Cycle 21 I. OVERVIEW Quiescent differentiated cell / can be induced to re-enter the active cell cycle. urvival Cell division Apoptosis 1 Daughter cells Apoptic cell enescent cell
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12)
 Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division (Ch. 12) Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs critical for normal growth, development &
Regulation of Cell Division
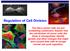 Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Regulation of Cell Division Two HeLa cancer cells are just completing cytokinesis. Explain how the cell division of cancer cells like these is misregulated. Identify genetic and other changes that might
Cell Cycle and Cancer
 142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
142 8. Cell Cycle and Cancer NOTES CELL CYCLE G 0 state o Resting cells may re-enter the cell cycle Nondividing cells (skeletal and cardiac muscle, neurons) o Have left the cell cycle and cannot undergo
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall Cell Cycle Effects of Radiation
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 Cell Cycle: Sequence of changes in a cell starting with the moment the cell is created by cell division, continuing through the doubling of the DNA and
Cell Cycle Regulation. Adrian R. Black
 Cell Cycle Regulation Adrian R. Black 845-3090 Adrian.black@roswellpark.org Loss of Growth Control Block of Apoptosis Evasion of Senescence Angiogenesis Invasion hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome
Cell Cycle Regulation Adrian R. Black 845-3090 Adrian.black@roswellpark.org Loss of Growth Control Block of Apoptosis Evasion of Senescence Angiogenesis Invasion hases of the cell cycle Mitosis: Chromosome
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology
 Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Basics of Radiation Biology Sally A. Amundson Columbia University Center for Radiological Research http://www.cmcr.columbia.edu/ Overview Radiation damage to cells DNA Effects of radiation damage on cells
Prognostic value of DNA repair based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma
 Prognostic value of DNA repair based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma Zhuo Lin 1, 2 #, Shi-Hao Xu 3 #, Hai-Qing Wang 4, Yi-Jing Cai 1, 2, Li Ying 3, Mei Song 1, 2, Yu-Qun Wang 1, 2, Shan-Jie
Prognostic value of DNA repair based stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma Zhuo Lin 1, 2 #, Shi-Hao Xu 3 #, Hai-Qing Wang 4, Yi-Jing Cai 1, 2, Li Ying 3, Mei Song 1, 2, Yu-Qun Wang 1, 2, Shan-Jie
Oncolytic virus strategy
 Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
Oncolytic viruses Oncolytic virus strategy normal tumor NO replication replication survival lysis Oncolytic virus strategy Mechanisms of tumor selectivity of several, some of them naturally, oncolytic
CONTENTS. Preface... xii
 CONTENTS Preface... xii 1. Autocrine Transformation: Cytokine Model... 1 James A. McCubrey, Xiao-Yang Wang, Paul A. Algate, William L. Blalock and Linda S. Steelman Abstract... 1 Cytokine Regulation of
CONTENTS Preface... xii 1. Autocrine Transformation: Cytokine Model... 1 James A. McCubrey, Xiao-Yang Wang, Paul A. Algate, William L. Blalock and Linda S. Steelman Abstract... 1 Cytokine Regulation of
Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes
 Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Cancer mutations disrupt cellular homeostasis Oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes Oncogenes: Gain of function mutations Proto-oncogene Tumour suppressor genes: loss of function mutations Normal cell
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Regulation of Cell Division 2008-2009 Coordination of cell division A multicellular organism needs to coordinate cell division across different tissues & organs u critical for normal growth, development
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway
 Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Effect of Acid and Pepsin on LPR-Sensitive Mucins In Vitro
 Novel Drug Targets for Reflux Disease Role of LPR in Injury and Disease is Controversial Nikki Johnston, Ph.D. Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Novel Drug Targets for Reflux Disease Role of LPR in Injury and Disease is Controversial Nikki Johnston, Ph.D. Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences Medical College of Wisconsin Milwaukee,
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available
 Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
Regulation of T cell proliferation by JMJD6 and PDGF-BB during chronic. hepatitis B infection
 Supplemental Materials Regulation of T cell proliferation by JMJD6 and PDGF-BB during chronic hepatitis B infection Cai-Feng Chen 1#, Xia Feng 2#, Hui-Yu Liao 2#, Wen-Jing Jin 1, Jian Zhang 3, Yu Wang
Supplemental Materials Regulation of T cell proliferation by JMJD6 and PDGF-BB during chronic hepatitis B infection Cai-Feng Chen 1#, Xia Feng 2#, Hui-Yu Liao 2#, Wen-Jing Jin 1, Jian Zhang 3, Yu Wang
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture:
 Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada?
 Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada? Alberto Ocana Albacete University Hospital Salamanca May 19th, 2016 WHAT IS PERSONALIZED MEDICINE? Molecular
Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada? Alberto Ocana Albacete University Hospital Salamanca May 19th, 2016 WHAT IS PERSONALIZED MEDICINE? Molecular
Early cell death (FGF) B No RunX transcription factor produced Yes No differentiation
 Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Non-Size Indications for Aortic Replacement
 Blood Test for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm 2 nd International Meeting on Aortic Diseases September 30-October 2, 2010 Liege, Belgium John A. Elefteriades, MD William W.L. Glenn Professor of Cardiothoracic
Blood Test for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm 2 nd International Meeting on Aortic Diseases September 30-October 2, 2010 Liege, Belgium John A. Elefteriades, MD William W.L. Glenn Professor of Cardiothoracic
qpcr-array Analysis Service
 qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Cancer. Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions.
 Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division. Making new cells. Getting the right stuff. Overview of mitosis 1/5/2015
 Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
Why do cells divide? The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division For reproduction asexual reproduction one-celled organisms For growth from fertilized egg to multi-celled organism For repair & renewal replace
Cell cycle and apoptosis
 Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Cell Cycle Checkpoint Genes and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Checkpoint Genes and Cancer Jens Oliver Funk, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Erlangen, Germany and Oncology Research Darmstadt, Global Preclinical R&D, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Several
Cell Cycle Checkpoint Genes and Cancer Jens Oliver Funk, University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, Erlangen, Germany and Oncology Research Darmstadt, Global Preclinical R&D, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Several
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
BL 424 Test pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points.
 BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS. D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH
 E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p <0.01 for 0.01 mm NS-398, 0.1mM ibuprofen and COX-2 RNAi.
 Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1
 Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
Cancer and Gene Alterations - 1 Cancer and Gene Alteration As we know, cancer is a disease of unregulated cell growth. Although we looked at some of the features of cancer when we discussed mitosis checkpoints,
5/25/2015. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork. Replication fork
 Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Mutations Chapter 5 Cellular Functions Lecture 3: and Cell Division Most DNA mutations alter the protein product May Make it function better (rarely) Change its function Reduce its function Make it non-functional
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Cancer. October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month
 Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
Cancer October is National Breast Cancer Awareness Month Objectives 1: Gene regulation Explain how cells in all the different parts of your body develop such different characteristics and functions. Contrast
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Control of Cell Cycle. Unit 2 Part f III
 Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
Control of Cell Cycle Unit 2 Part f III How often do cells divide and why? The timing and rate of cell division in different parts of the plant or animals are crucial to normal growth, development and
IDENTIFICATION OF NF-KAPPAB AND DNA-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE (DNA-PK) AS NEW PLAYERS IN THE REGULATION AND SIGNALING OF THE ONCOGENIC PHOSPHATASE
 IDENTIFICATION OF NF-KAPPAB AND DNA-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE (DNA-PK) AS NEW PLAYERS IN THE REGULATION AND SIGNALING OF THE ONCOGENIC PHOSPHATASE WIP1 A Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate
IDENTIFICATION OF NF-KAPPAB AND DNA-DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE (DNA-PK) AS NEW PLAYERS IN THE REGULATION AND SIGNALING OF THE ONCOGENIC PHOSPHATASE WIP1 A Dissertation submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate
Functional Limitations
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Emerging" hallmarks of cancer, a. Reprogramming of energy metabolism b. Evasion of the immune system, Enabling characteristics, a.
 HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF MAMMALIAN DNA REPAIR AND THE DNA DAMAGE CHECKPOINTS
 Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004. 73:39 85 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073723 Copyright 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on January 20, 2004
Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004. 73:39 85 doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073723 Copyright 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on January 20, 2004
Oncogenes and Tumor. supressors
 Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Oncogenes and Tumor supressors From history to therapeutics Serge ROCHE Neoplastic transformation TUMOR SURESSOR ONCOGENE ONCOGENES History 1911 1960 1980 2001 Transforming retrovirus RSV v-src is an oncogene
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 6 Cell Division, Cell Cycle, Cell Growth and Differentiation, Programmed Cell Death
BIO360 Quiz #1. September 14, Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points)
 Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
