Processes of Tubulogenesis. Processes of Tubulogenesis. Tube Formation is critical to forming: There are three types of tubes:
|
|
|
- Camron Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology Developmental Genetics Tubular Organs Lecture #8 - Tube Formation I Tube Formation is critical to forming: 1. Lung* 2. Kidney* 3. Mammary gland 4. Blood vessels* 5. Fly trachea 6. C. elegans excretory system (1 cell!) There are three types of tubes: 1. Multicellular 2. Unicellular, with autocellular junction 3. Unicellular, seamless From Nelson, 2003 From Lubarsky and Krasnow, 2003 Processes of Tubulogenesis Processes of Tubulogenesis From Lubarsky and Krasnow, 2003 From Lubarsky and Krasnow,
2 Genetic Programs involved in Tube Formation MDCK Cells in Collagen Gels - HGF +HGF From Nelson, 2003 MDCK in collagen starts with a polarized cyst Upon addition of HGF, some cells form an extension outward on their basolateral side Gp135 = apical, red b-catenin = basolateral, green From Pollack et al, 98; Zegers et al, 03 E-cadherin, basolateral Gp135, apical From Pollack et al, 98 The extended cell divides, and cells in the extension express E-cadherin but not gp135 As the lumen begins to reform in the extension, gp135 is re-expressed on the new apical surface E-cadherin, basolateral Gp135, apical From Pollack et al, 98 E-cadherin, basolateral Gp135, apical From Pollack et al, 98 2
3 As lumen formation continues, cells re-establish basolateral expression of E-cadherin E-cadherin, basolateral Gp135, apical From Pollack et al, 98 Model derived from this study: 1. Stimulation of migration is the first step in tubulogenesis 2. Apical/basal polarity is transiently lost and then restored 3. Discontinuous lumens form in tubules 4. Cell-cell contacts are retained throughout the process Apical membrane biogenesis is important For lumen formation in MDCK cells Tube formation requires and stabilizes apicalbasolateral polarity From Lubarsky and Krasnow, 03 From Bryant and Mostov, 08 Tube formation requires and stabilizes apicalbasolateral polarity Drosophila Tracheal System Simple structure Powerful genetics Easy observation From Bryant and Mostov, 08 3
4 Embryonic Tracheal Development Drosophila Trachea Has Four Types of Tubes II I IV III Drosophila Trachea Has Four Types of Tubes 4-5 µm 1 µm 1 µm or 4-5 µm 0.5 µm 2-5 cells compose the lumen circumference single tube-shaped cells with AJ encircle the lumen doughnut shaped cells with no AJ protrusions from single cells without AJ Specification of Tracheal Cells Invagination of Tracheal Placode Trh = trachealess (bhlh PAS transcription factor) Tgo=Tango (bhlh Pas transcription factor, binding partner for Trh) Vvl/Dfr = Ventral veinless-drifter (POU domain transcription regulator) EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor Spitz=EGFR ligand Rho = Rhomboid (EGF pathway activator) From Affolter and Shilo, 2000 From Affolter and Shilo,
5 Model of Tracheal Cell Invagination Trh, Vvl Rho (EGF pathway) Apical Actin Enrichment Localized Apical Cell Constriction Ordered Cell invagination Brodu V and Casanova J 2006 Branches of the Drosophila Trachea Determination of branch identity DB = dorsal branch DTa/p = dorsal trunk (anterior/posterior) VB = visceral branch SB = spiracular branch LTa/p = lateral trunk (anterior/posterior) LTp is also called GB or ganglionic branch EGF αps1 integrin From Cabernard et al, 2004 EGF=Epidermal growth factor : GB and DT Wg= wigless: DT Dpp = Decapentaplegic (Transforming growth factor β-like): DB, LT From Affolter M 2002 FGF Signaling Directs Primary Branch Outgrowth bnl/fgf = blue Btl/FGFR in Trachea cells = brown From Cabernard et al,
6 Primary Branching Requires Bnl/Btl Signaling green = actin-gfp (WT) Red = cells lacking Btl/FGFr From Cabernard et al, 2004 Dpp Signaling is Required for Dorsal Branch Migration in Addition to FGF Signaling Branch Migration Requires Slit/Robo Signaling Dpp (ligand) Pnt (receptor) Affolter M 2002 blue= tracheal lumen Brown =DSRF (GB marker) From Englund et al, 2002 Branch Elongation via Cell Rearrangements AJ Remodeling during Intercalation Process Type I Type I Type II Type II From Cabernard et al, 2004 From Ribeiro C et al
7 Formation of Specialized Tracheal Cells Specification of tracheal cells (tracheal placodes) Invagination of the tracheal placode DB migration requires Dpp signaling GB migration requires slit-robo signaling Tube elongation through cell intercalation Fusion process Terminal branching Fusion Process Migration Contact Adhesion Dysfusion is Expressed in Tracheal Fusion Cells Invagination Lumen Formation DB DT E-Cadherin Membrane Cytoskeleton Lumen LT btl-lacz dys Misexpression Causes Inhibition of Migration Dys Specification of tracheal cells (tracheal placodes) Invagination of the tracheal placode Wild type DB migration requires Dpp signaling GB migration requires slit-robo signaling Tube elongation through cell intercalation btl-gal4; UAS-dys Fusion process Terminal branching Mab 2A12 Dys 7
8 Larval Tracheal System II I IV III VB that has ramified to form dozens of fine terminal branches on the gut Ghabrial and Krasnow MA 2003 Terminal branch expansion in response to Hypoxia induced branchless Model for Patterning of Terminal Branching by Bnl Type IV tube Jarecki J, Johnson E and Krasnow MA 1999 Jarecki J, Johnson E and Krasnow MA 1999 Branch-specific outgrowth is controlled by regional signals and branch identity genes Branch identity dentermination 8
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were
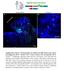 Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Electroporation of a stable form of β-catenin causes masses protruding into the IV ventricle. HH12 chicken embryos were electroporated with β- Catenin S33Y in PiggyBac expression
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Supplemental Figure 1. Quantification of proliferation in thyroid of WT, Ctns -/- and grafted Ctns -/- mice. Cells immunolabeled for the proliferation marker (Ki-67) were counted in sections (n=3 WT, n=4
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
04_polarity. The formation of synaptic vesicles
 Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Rac function in epithelial tube morphogenesis
 Developmental Biology 290 (2006) 435 446 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio Rac function in epithelial tube morphogenesis Carolyn Pirraglia, Rakhi Jattani, Monn Monn Myat Department of Cell and Developmental
Developmental Biology 290 (2006) 435 446 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio Rac function in epithelial tube morphogenesis Carolyn Pirraglia, Rakhi Jattani, Monn Monn Myat Department of Cell and Developmental
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space
 I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
Daniela Drummond-Barbosa, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
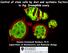 Control of stem cells by diet and systemic factors in the Drosophila ovary Daniela Drummond-Barbosa, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Multiple levels of stem cell regulation local
Control of stem cells by diet and systemic factors in the Drosophila ovary Daniela Drummond-Barbosa, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Multiple levels of stem cell regulation local
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Tissues. Definition. A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function.
 Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Chapter 4 - Tissues Tissues Definition A group of similar cells and their intercellular substances specialized to perform a specific function. Tissues Epithelial covers exposed surfaces, lines internal
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
Report. Transcriptional Profiling Identifies TNS4 Function in Epithelial Tubulogenesis
 Current Biology 21, 161 166, January 25, 2011 ª2011 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2010.12.037 Transcriptional Profiling Identifies TNS4 Function in Epithelial Tubulogenesis Report
Current Biology 21, 161 166, January 25, 2011 ª2011 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2010.12.037 Transcriptional Profiling Identifies TNS4 Function in Epithelial Tubulogenesis Report
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
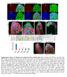 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
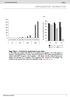 b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
b 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 E0 E10 E50 Number of organoids per well 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 R0 R50 R100 R500 1st 2nd 3rd Noggin 100 ng/ml Noggin 10 ng/ml Noggin
Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues
 Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues Tissues Definition A group of closely associated cells that work together to perform a specific function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement
Chapter 4 - Epithelial Tissues Tissues Definition A group of closely associated cells that work together to perform a specific function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Development of the Urinary System. 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney Structures
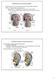 Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
They cells can not function death.
 Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Histology. Marcello Malpighi ( ) is regarded as Father of Histology.
 Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
Histology The branch of biology which deals about tissue is called Histology. Marcello Malpighi (1628 1694) is regarded as Father of Histology. Tissue:- Group of identical or, unidentical cells which associate
Histology and development of the respiratory system
 Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Epithelial Tissue. SAC Request. Epithelial Tissue 27/06/12. Linings and? BIOL241
 Epithelial Tissue Linings and? BIOL241 SAC Request From Audrey Rose Cabinet Coordinator Student Administrative Council SAC is looking for dedicated students to apply for the Student Cabinet, Fee Board,
Epithelial Tissue Linings and? BIOL241 SAC Request From Audrey Rose Cabinet Coordinator Student Administrative Council SAC is looking for dedicated students to apply for the Student Cabinet, Fee Board,
5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Glandular epithelium Gland: Is a collection of epithelial cells the secrets a certain product, like: proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. Secretion : A certain material that is produced
5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Glandular epithelium Gland: Is a collection of epithelial cells the secrets a certain product, like: proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. Secretion : A certain material that is produced
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
يراهظلا( يئلاطلا جيسنلا
 Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Chapter 11 Intercellular Communication and Tissue Architecture
 Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter 11 Multicellular organisms such as the human body consist of various tissues such as epithelial tissues, bones and nerves, and organs such as heart and
Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter 11 Multicellular organisms such as the human body consist of various tissues such as epithelial tissues, bones and nerves, and organs such as heart and
Urogenital Development
 2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
Functional Characterization of a Cathepsin L in Drosophila Melanogaster
 Western Kentucky University TopSCHOLAR Masters Theses & Specialist Projects Graduate School Summer 2015 Functional Characterization of a Cathepsin L in Drosophila Melanogaster Qian Dong Western Kentucky
Western Kentucky University TopSCHOLAR Masters Theses & Specialist Projects Graduate School Summer 2015 Functional Characterization of a Cathepsin L in Drosophila Melanogaster Qian Dong Western Kentucky
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
EMT 2.0: shaping epithelia through collective migration Céline Revenu and Darren Gilmour
 Available online at EMT 2.0: shaping epithelia through collective migration Céline Revenu and Darren Gilmour Epithelial mesenchymal transitions (EMTs) drive epithelial remodelling by converting cohesive,
Available online at EMT 2.0: shaping epithelia through collective migration Céline Revenu and Darren Gilmour Epithelial mesenchymal transitions (EMTs) drive epithelial remodelling by converting cohesive,
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
MCB Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly- Prof. David Rivier
 MCB 252 -Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly- Prof. David Rivier MCB 252 Spring 2017 MCB 252 Cell Biology Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly Reading: Lodish 17.2-17.3, 17.7 MCB 252 Actin Cytoskeleton
MCB 252 -Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly- Prof. David Rivier MCB 252 Spring 2017 MCB 252 Cell Biology Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly Reading: Lodish 17.2-17.3, 17.7 MCB 252 Actin Cytoskeleton
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTION. biology that deals with the normal functions of living
 PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTION Dr.H.B.Mahesha, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Musuru. Physiology: The branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts. Or
PHYSIOLOGY OF DIGESTION Dr.H.B.Mahesha, Yuvaraja s College, University of Mysore, Musuru. Physiology: The branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts. Or
The world of epithelial sheets
 The Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists Develop. Growth Differ. (2017) 59, 306 316 doi: 10.1111/dgd.12350 Review Article The world of epithelial sheets Hisao Honda 1,2 * 1 Department of Physiology
The Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists Develop. Growth Differ. (2017) 59, 306 316 doi: 10.1111/dgd.12350 Review Article The world of epithelial sheets Hisao Honda 1,2 * 1 Department of Physiology
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
a 0,8 Figure S1 8 h 12 h y = 0,036x + 0,2115 y = 0,0366x + 0,206 Labeling index Labeling index ctrl shrna Time (h) Time (h) ctrl shrna S G2 M G1
 (GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
(GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
 Wright et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2015) 15:33 DOI 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
Wright et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2015) 15:33 DOI 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Supplemental material Wang and Page-McCaw, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201403084/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Extracellular anti-wg staining is specific. Note
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi
 Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Epithelium. Connective tissue. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Basal surface.
 Chapter 4: Tissues A Tissue is a group of closely associated cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. Four Basic Tissue Types and Basic Functions: Epithelial covering (Chapters
Chapter 4: Tissues A Tissue is a group of closely associated cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. Four Basic Tissue Types and Basic Functions: Epithelial covering (Chapters
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Inner ear development Nervous system development
 Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
The Role of Oxygen Supply in the Regulation of Neural Stem Cell Proliferation in the Brain of Drosophila
 The Role of Oxygen Supply in the Regulation of Neural Stem Cell Proliferation in the Brain of Drosophila Bach. Martín Baccino A thesis submitted for the Degree of Master of biological sciences Programa
The Role of Oxygen Supply in the Regulation of Neural Stem Cell Proliferation in the Brain of Drosophila Bach. Martín Baccino A thesis submitted for the Degree of Master of biological sciences Programa
Intercellular indirect communication
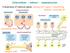 Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Circulatory System Function Move circulatory fluid (blood) around body Gas Transport Nutrient Transport Excretory Product Transport
 Lecture 37 Introduction to Circulation BY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Functions of the Heart Generating blood pressure Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations Ensuring one-way
Lecture 37 Introduction to Circulation BY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Functions of the Heart Generating blood pressure Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations Ensuring one-way
Cell Polarity and Cancer
 Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. 2 3 4 DOI: 10.1038/NMAT4893 EGFR and HER2 activate rigidity sensing only on rigid matrices Mayur Saxena 1,*, Shuaimin Liu 2,*, Bo Yang 3, Cynthia Hajal
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. 2 3 4 DOI: 10.1038/NMAT4893 EGFR and HER2 activate rigidity sensing only on rigid matrices Mayur Saxena 1,*, Shuaimin Liu 2,*, Bo Yang 3, Cynthia Hajal
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Tetrapod Limb Development
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
Muscle tissue. 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue.
 Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Brain Development III
 Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced
 Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Anatomy Arthur H. Cohen Richard J. Glassock The topic of normal vascular and glomerular anatomy is introduced here to serve as a reference point for later illustrations of
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal
 glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
glial cells missing and gcm2 Cell-autonomously Regulate Both Glial and Neuronal Development in the Visual System of Drosophila Carole Chotard, Wendy Leung and Iris Salecker Supplemental Data Supplemental
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Fig.9.2. Structure of embryonic brain
 T Chapter 9 Development of Ectodermal Organs he ectoderm gives rise to 3 separate cell populations: neural(plate) ectoderm, neural crest cells, and epiderm (general body ectoderm). A primordium (anlage)
T Chapter 9 Development of Ectodermal Organs he ectoderm gives rise to 3 separate cell populations: neural(plate) ectoderm, neural crest cells, and epiderm (general body ectoderm). A primordium (anlage)
Physiology sheet #2. The heart composed of 3 layers that line its lumen and cover it from out side, these layers are :
 Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland 1. Endocrine Glands 2. Exocrine Glands Endocrine Glands Exocrine Glands
 Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Lec.2 Histology Glandular Epithelium A gland is one or more cells that produce and secrete a specific product. The product is always a water-based fluid (aqueous) and usually contains proteins (the product
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Tight junction biology and kidney dysfunction
 Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290: F20 F34, 2006; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00052.2005. Tight junction biology and kidney dysfunction David B. N. Lee, 1,2 Edmund Huang, 2,3 and Harry J. Ward 2,4 Divisions of Nephrology,
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290: F20 F34, 2006; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00052.2005. Tight junction biology and kidney dysfunction David B. N. Lee, 1,2 Edmund Huang, 2,3 and Harry J. Ward 2,4 Divisions of Nephrology,
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CELL JUNCTIONS AND TISSUES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
Toxicology in the 21 st Century
 Toxicology in the 1 st Century A Road Map for the National Toxicology Program Dr. Christopher J. Portier Associate Director, National Toxicology Program National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
Toxicology in the 1 st Century A Road Map for the National Toxicology Program Dr. Christopher J. Portier Associate Director, National Toxicology Program National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Tissues Review 4 type
 Tissues Review 4 type Tissues Definition: a group of closely associated cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure Between cells: nonliving extracellular material Four basic types
Tissues Review 4 type Tissues Definition: a group of closely associated cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure Between cells: nonliving extracellular material Four basic types
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE CASZ1-DEPENDENT MECHANISMS UNDERLYING VERTEBRATE BLOOD VESSEL DEVELOPMENT. Marta S. Charpentier
 CHARACTERIZATION OF THE CASZ1-DEPENDENT MECHANISMS UNDERLYING VERTEBRATE BLOOD VESSEL DEVELOPMENT Marta S. Charpentier A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel
CHARACTERIZATION OF THE CASZ1-DEPENDENT MECHANISMS UNDERLYING VERTEBRATE BLOOD VESSEL DEVELOPMENT Marta S. Charpentier A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel
Anatomy PHL 212. Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan. -
 Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Anatomy PHL 212 Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor College of Pharmacy (Female Section) Sattam Bin Abdulaziz University Al kharj / Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Email :- da.hassan@psau.edu.sa 1 Anatomy
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen. Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang
 Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
2/2/2011. Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
DEVELOPMENT OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Development of Endodermal Organs Primitive Gut Tube Proctodeum and Stomodeum Stomach Duodenum Pancreas Liver and Biliary Apparatus Spleen Midgut Wednesday, February
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
TISSUES. Objectives. Tissues
 TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance
 Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
The contribution of TGF-β in Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): Down-regulation of E-cadherin via snail
 Neoplasma 62, 1, 2015 1 doi:10.4149/neo_2015_002 The contribution of TGF-β in Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): Down-regulation of E-cadherin via snail Minireview H. YU, Y. SHEN, J. HONG, Q. XIA,
Neoplasma 62, 1, 2015 1 doi:10.4149/neo_2015_002 The contribution of TGF-β in Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT): Down-regulation of E-cadherin via snail Minireview H. YU, Y. SHEN, J. HONG, Q. XIA,
Lecture Overview. CT Framework of the Body. Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11. Connective tissue framework of the body
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
TYPES OF EPITHELIA. Epithelia can be divided into two main groups. A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia.
 TYPES OF EPITHELIA Epithelia can be divided into two main groups A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia. Glands Glandular epithelial cells may synthesize, store, and secrete:
TYPES OF EPITHELIA Epithelia can be divided into two main groups A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia. Glands Glandular epithelial cells may synthesize, store, and secrete:
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
