Supporting online material
|
|
|
- Aldous Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supporting online material 1. Materials and Methods 2. Preparation of highly purified peptidoglycans from Gram-negative and Grampositive bacteria 3. Analysis of N. meningitidis peptidoglycan by reverse-phase HPLC and mass spectroscopy 4. Supporting online figures 5. Supporting online references 1. Materials and Methods Bacterial strains and products Bacterial strains used in these studies are the following: S. typhimurium strain C52 and C52- delta flagellin (flic::apha-3(km)fljb5001::mud(cm)); E. coli K12; S, flexneri 5a M90T; B. subtilis (from Agnès Fouet, Institut Pasteur); S. aureus (from livier Chesneau, Institut Pasteur); L. casei (from Raphaëlle Bourdet-Sicard, Danone Vitapole); L. monocytogenes (Strain EGD, from Pascale Cossart, Institut Pasteur); N. meningitidis LNP8013. Bacterial extracts were prepared from overnight cultures of bacterial strains, diluted to an D600 of 0.3, sonicated 3 min and filtered (0.2 micron). Commercial LPS and lipid A were from E. coli 111:B4 (Sigma). Commercial S. aureus peptidoglycan was from Fluka Chemicals. Commercial Pam3Cys-Ser-Lys 4 -H lipopeptide was from Roche Diagnostics (Mannheim) and E. coli lipoproteins preparations were provided by Emmanuelle Bouveret and Roland Lloubes (UPR 9027, Marseille). Pure RE-LPS was from E. coli F515 and purified as previously described (6). Synthetic GM-dipeptide was purchased from Sigma. Peptidoglycans of E. coli, S. flexneri and N. meningitidis were purified as described by Glauner et al (S1). peptidoglycans of B. subtilis and S. aureus were purified as described by de Jonge et al (S2). See also supporting text for additional details concerning peptidoglycan preparations and quality controls.
2 Expression plasmids and transient transfections The expression plasmid for Flag-tagged Nod1 was from Gabriel Nuñez and has been previously described (S7). The HA-tagged, DN-Nod1 ( aa) and myc-tagged LRR (1-644aa) Nod1 were generated by PCR and cloned into pcdna3 (Invitrogen) and prk5 (from Alan Hall, ICRF, London), respectively. DN-MyD88 was from Marta Muzio and the expression plasmid for vsv-tagged DN-Rip2 (7-425aa) was provided by Margot Thome and Jurg Tschopp (University of Lausanne, Switzerland). Transfections were carried out in HEK293 as previously described (S8). NF-kB activation assays For NF-kB activation assays in digitonin-permeabilized cells, 1 x 10 5 HEK293 were grown in 24 well plates and then transfected for 24h with 75 ng of NF-kB-luciferase reporter gene (Igkluciferase) as previously described (S8). Cells were then incubated for 30 min at 37 C with 25µl of sonicated bacterial extracts in 500 µl of permeabilization buffer (50 mm HEPES, ph 7, 100mM KCl, 3mM MgCl 2, 0.1mM DTT, 85mM sucrose, 0.2% BSA, 1mM ATP and 0.1mM GTP) with or without 10µg/ml digitonin (Sigma). Permeabilization buffer was then removed and replaced with medium (DMEM, Gibco) plus 10% fetal-calf serum (Gibco) for 4 hours before processing for luciferase measurements as described previously (S8). For dominant-negative studies presented in Figure 3, increasing amounts of dominant-negative constructs were cotransfected with the NF-kB reporter plasmid. Experiments were then performed as detailed above. Studies examining the activation of NF-kB by LPS, lipid A, lipoproteins or the purified peptidoglycans in cells over-expressing Nod1 were carried out as described by Inohara et al. (S9). Briefly, HEK293 cells were transfected overnight with 10ng of Nod1. At the same time, the LPS, lipoproteins or peptidoglycan preparations were added and the NF-kB-dependent luciferase activation was then measured following 24h of co-incubation. It is presumed that the transfection reagent plus the added DNA aids in the uptake of bacterial products into the cells since extracellular addition of these products to cells previously transfected and washed to remove the liposome reagent does not lead to NF-kB activation (data not shown). 2
3 NF-kB-dependent luciferase assays were performed in duplicate and data represent at least 3 independent experiments. Data show mean ± SEM and are expressed as fold activation compared to vector expressing cells or as fold synergy compared to the level of NF-kB activation of Nod1-expressing cells (for 10ng of Nod1, NF-kB activation is approximately 5 fold compared to vector-expressing cells). For immunofluorescence studies, NF-kB activation was assessed by nuclear translocation of NF-kB p65 in HeLa, Caco-2 or isolated intestinal epithelial cells following microinjection of bacterial products (diluted 1:1 with FITC-dextran) as previously described (S10). At least 50 microinjected cells were examined per coverslip and experiments were performed at least 2 times independently with similar results. Interleukin-8 production To measure Nod1-dependent IL-8 produced in epithelial cells by muropeptides, 5 X 10 5 HeLa cells were seeded into each well of a twelve well plate and transfected the following day with 10 ng Nod1 plus the individual muropeptides (as described above) or treated with IL-1 as a positive control. Eighteen hours later, supernatants were collected and assayed for IL-8 as previously described (S10) using an ELISA kit (R and D Systems). Western blot and immunoprecipitations Western blot and immunoprecipitations were carried out as previously described (S8). The Nod1 polyclonal antibody was obtained by immunization of rabbits with two peptides corresponding to aa 1-15 and of Nod1. Serum was collected, affinity purified and verified to be specific for Nod1. The Nod2 polyclonal antibody was from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, MI). Generation of Nod1-deficient mice Details of the construction of the Nod1-deficient mice and the description of one of the phenotypes of these mice will be described elsewhere (S11). Isolation of intestinal epithelial cells from mice 3
4 The preparation of the small intestine primary cultures was based on the protocol described by Evans et al. (S12) and modified by Athman et al. (S13). The small intestines of four-week old wild-type and Nod1-deficient mice were removed, slit open and cut into 2-3 mm lengths. After 3 washes in 20ml of Hank's balanced salt solution (HBSS, Gibco) with vigorous shaking, the tissue was cut into <1 mm 3 pieces. The pieces were transferred to a flask with 7.5 ml of an enzyme solution (0,1 mg/ml dispase I + 300U/ml collagenase) and incubated for 30 minutes at 25 C with vigorous shaking. The solution was then submitted to 2x five minutes of vigorous pipetting in order to dissociate the cells and the contents were left to sediment under gravity for 1 minute. The supernatant was removed and an equal volume of D-MEM-S (D-MEM + 2% sorbitol +2;5% FBS) was added The solution was centrifuged at 600 r.p.m./min for 5 minutes. After eliminating the supernatant, the pellet was resuspended in D-MEM containing 2.5% of FBS and 1 mg/ml of glutamine and plated onto glass coverslips. The cells were used between the second and fifth day of culture. 2. Preparation of highly purified peptidoglycans from Gram-negative and Grampositive bacteria Bacterial strains used to prepare peptidoglycan are the following: E. coli K12; S, flexneri 5a M90T (wild-type); N. meningitidis; B. subtilis 168; S. aureus CL (from livier Chesneau, Institut Pasteur). Peptidoglycans of E. coli and S. flexneri were purified as described by Glauner et al (S1). peptidoglycans of B. subtilis and S. aureus were purified as described by de Jonge et al (S2). Briefly, bacteria were harvested in exponential growth phase at an optical density (600 nm) of and quickly chilled in an ice-ethanol bath to minimize peptidoglycan hydrolysis by endogeneous autolysins. Pellets were resuspended in ice-cold water and added drop by drop to 8% boiling SDS. Samples were boiled for 30 minutes allowing immediate inactivation of autolysins. Polymeric peptidoglycan, which is insoluble, was recovered by centrifugation and washed several times until no SDS could be detected. SDS assay was done as described by Hayashi (S3). SDS treatment removes contaminating proteins, non-covalently bound lipoproteins and LPS. Gram-positive bacterial samples were physically broken with acid washed 4
5 glass beads (<100 nm). The peptidoglycan fraction was recovered by differential centrifugation to remove cellular debris. All peptidoglycans were further treated with a-amylase to remove any glycogen and with trypsin (3x crystallized trypsin, Worthington) digestions to remove covalently bound proteins (LPXTG proteins in Gram-positive bacteria) or lipoproteins (Gram-negative bacteria). Samples were further boiled in 1% SDS to inactivate trypsin and were washed to remove SDS. Gram-positive bacterial samples were treated with 49% hydrofluoridic acid during 48 hours at 4 C. This mild acid hydrolysis allows removal of secondary polysaccharides covalently bound to the peptidoglycan by phosphodiester bonds such as teichoic acid, capsules, poly-(b,1-6 GlcNAc), etc. Further treatment of both Gram-positive and Gram-negative peptidoglycans included washes with 8 M LiCl, 0.1 M EDTA to remove any polypeptidic contaminations and with acetone to remove lipoteichoic acids or any traces of LPS. Samples were lyophilized to measure peptidoglycan amounts. Purity of samples was assessed by HPLC amino acid and saccharide analysis after HCl hydrolysis (see also Fig. S1). 3. Analysis of N. meningitidis peptidoglycan by reverse-phase HPLC and mass spectroscopy Peptidoglycans of N. meningitidis or S. flexneri were digested by the muramidase mutanolysin (M1, Sigma) to generate the entire spectrum of muropeptides for both species. The muropeptides were reduced with sodium borohydride and separated by reverse-phase HPLC as described by Glauner (S1). Individual muropeptide peaks were collected and directly used for biological assays. For mass spectrometry analysis, the different muropeptide fractions from N. meningitidis peptidoglycan were further desalted by HPLC as described by Garcia-Bustos and Dougherty (S4). Desalted muropeptides were analyzed by MALDI-TF as described by Xu et al. (S5). These molecular masses were found for the following analyzed fractions : fraction 3 [M+H] + 871,6214 m/z ; [M+Na] + : 893,3633 m/z ; [M+2Na-H] + 915,3518 m/z which is consistent with the GlcNAc-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-mesoDAP structure (calculated mass 870); fraction 6 [M+H] + 942,4512 m/z; [M+Na] + 964,4689 m/z, [M+2Na-H] + 986,4429 m/z ; [M+3Na- 5
6 2H] ,4321 m/z which is consistent with a GlcNAc-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-mesoDAP-D- Ala structure (calculated mass 941); fraction 17 a mixture of two muropeptide species : 1) [M+H] + 851,3460 m/z ; [M+Na] + 873,3422 m/z, [M+2Na-H] + 895,3219 m/z ; [M+3Na- 2H] + 917,3115 m/z which is consistent with a GlcNAc-anhydro-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-GlumesoDAP structure (calculated mass 850) and 2) [M+H] ,5588 m/z ; [M+Na] ,5331 m/z, [M+2Na-H] ,5753 m/z ; [M+3Na-2H] ,5625 m/z which is consistent with the muropeptide dimer GlcNAc-MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-mesoDAP(GlcNAc- MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-mesoDAP-D-Ala)-D-Ala structure (calculated mass 1864). 4. Supporting online figures Figure S1: Experimental procedure followed to prepare highly purified peptidoglycans from Gram-negative or Gram-positive bacteria. Figure S2: Nod1 detects peptidoglycan through its leucine-rich repeat domain. Figure S3: Schematic representation of the muropeptides derived from peptidoglycans of various bacteria. Figure S4 Figure S5: Intracellular detection of Gram-negative but not Gram-positive bacterial products in epithelial cells through Nod1/Rip2 but not MyD88 Figure S6: Nod1 and Nod2 are expressed in HeLa and HEK 293 epithelial cells. Figure S7: Intestinal epithelial cells from mice deficient in Nod1 do not respond to bacterial supernatants. 6
7 Supporting online figures S1 Pelleted bacteria 1. Removes non-covalent associations to PGN (LPS, LTA, proteins, lipoproteins, ) 1. Boiling SDS PGN 2. Removes covalent associations to PGN (lipoproteins, ) Contaminant-free PGN (Gram -) 2. a-amylase trypsine (3x) SDS Polypeptide-free PGN (Gram +) 3. Removes TA, LTA and capsule from Gram+ PGN 3. HF Contaminant-free PGN (Gram +) Figure S1: Experimental procedure followed to prepare highly purified peptidoglycans (PGNs) from Gram-negative or Gram-positive bacteria. See supporting online text for details.
8 S2 NF-kB activation (fold synergy) Nod1 DLRR Nod1 PGN E.coli Figure S2: Nod1 detects peptidoglycan through its leucine-rich repeat domain. No synergistic activation of NF-kB bye. coli peptidoglycan (1µg/ml) was observed in cells expressing DLRR- Nod1.
9 S3a MurNAc D-Glu D-Ala H H NH HN L-Ala NH H HN NH 2 NH H H MesoDAP MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-mesoDAP-D-Ala S3c MurNAc D-Glu H H H NH HN NH HN L-Ala L-Lys S3b MurNAc D-Glu D-Ala H H H NH HN NH HN NH H L-Ala Amidated-DAP NH 2 NH 2 MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-Amidated-DAP-D-Ala D-Ala NH 2 NH H MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala Figure S3: Schematic representation of the muropeptides derived from peptidoglycans of various bacteria. a, muropeptide found in Gram-negative bacteria, containing a mesodap amino acid. b, muropeptide found in some Gram-positive bacteria such as B. subtilis. Instead of the mesodap, an amidated-dap is found. c, muropeptide found in most Gram-positive bacteria, containing a L-lysine as third amino acid. Note that the only differences between these muropeptides take place at the third amino acid position.
10 S4a S4b NF-kB activation (fold) CTR S. flexneri extract + TLR2 CTR P.K/Boiled S. aureus extract NF-kB p65 FITC- Dextran Buffer S. flexneri S. aureus UTSIDE stimulation Microinjection Figure S4 : a,we aimed to determine the relative peptidoglycan content of the bacterial extracts prepared. To this end, TLR2-overexpressing HEK293 cells were stimulated by extracellular addition of bacterial extracts treated or not with proteinase K and boiling, which affects lipoprotein activity. In this way we could analyze the relative contribution of bacterial lipoproteins versus peptidoglycan towards TLR2 stimulation. We observed that bacterial extracts from Gram-negative bacteria displayed much less peptidoglycan activity than extracts from Gram-positive bacteria cultured to the same optical density. This finding is not surprising since it is well known that Gram-negative bacteria contain less peptidoglycan than Gram-positive bacteria and also recycle peptidoglycan to a higher extent during growth. b, Bacterial extracts from S. flexneri and S. aureus were micro-injected together with FITC-Dextran into Caco-2 epithelial cells. After 30 minutes, the cells were fixed and analyzed for NF-kB activation by immunofluorescence. NF-kB activation was assessed by translocation of the NF-kB p65 subunit from the cytosol to the nucleus in microinjected cells. Activation of NF-kB was observed only in Caco-2 cells microinjected with bacterial extracts from Gram-negative bacteria. We also observed the lack of NF-kB activation in Caco-2 cells following extracellular addition of bacterial extracts, suggesting that these cells do not display a functional endogenous TLR sensing system.
11 S5a 30 NF-kB activation (fold) CTR S. typhimurium D F extract IL-1 DN-Myd88 S5b 30 S5c 30 NF-kB activation (fold) NF-kB activation (fold) CTR DN-Nod1 0 CTR DN-Rip2 S. flexneri extract S. typhimurium D F extract E. coli extract S. typhimurium D F extract Figure S5 : Intracellular detection of Gram-negative but not Gram-positive bacterial products in epithelial cells through Nod1/Rip2 but not MyD88. a, No effect of dominant-negative MyD88 (DN-MyD88; 0, 20, 50ng) on Gram-negative bacterial extracts-induced NF-kB activity, yet inhibition of IL-1-induced NF-kB activation (IL-1, 10ng/ml). b, Inhibition of Gram-negative bacterial extracts-induced NF-kB activity in digitonin-permeabilized HEK293 cells transfected with Nod aa (DN-Nod1; 0, 200, 400ng). c, Inhibition of Gram-negative bacterial extractsinduced NF-kB activity by dominant-negative Rip2 (DN-Rip2; 0, 50, 100ng).
12 S6a Cell extracts HeLa HEK HEK/ Nod1 WB: a Nod1 Nod1 HeLa HEK HEK/ Nod2 WB: a Nod2 Nod2 S6b Immunoprecipitations (IP) IP: a Nod1 IP: a IgG HeLa HEK HeLa HEK WB: a Nod1 Nod1 IP: a Nod2 IP: a IgG HeLa HEK HeLa HEK WB: a Nod2 Nod2 Figure S6: Nod1 and Nod2 are expressed in HeLa and HEK 293 epithelial cells. a, Protein extracts ( cells/lane) from HeLa and HEK 293 cells were directly analyzed by western blot for endogenous expression of Nod1 and Nod2, using specific polyclonal antibodies raised against human forms of Nod1 and Nod2, respectively (see Methods section). Note that endogenous expressions of Nod1 and Nod2 remained undetectable using this technique, and therefore protein extracts from HEK 293 transiently transfected with expression vectors for Nod1 (HEK/Nod1) and Nod2 (HEK/Nod2) were analyzed in parallel in order to show the specificity of the antibodies. b, Protein extracts (10 7 cells/lane) from HeLa and HEK 293 cells were immunoprecipitated using Nod1, Nod2 or control IgG antibodies prior to analysis by western blot as indicated. This immunoprecipitation technique was required to detect the presence of the endogenous forms of Nod1 and Nod2, since it allowed for the concentratation of Nod1 and Nod2 present in cell extracts by ~ 500 fold.
13 S7 S. aureus extract S. flexneri extract NF-kB p65 FITC- Dextran Nod 1 +/+ NF-kB p65 FITC- Dextran Nod 1 -/- Figure S7: Intestinal epithelial cells from mice deficient in Nod1 do not respond to bacterial supernatants. Additional immunofluorescence images from Figure 4 are displayed here.
14 5. Supporting online references S1. B. Glauner, Anal. Biochem. 172, 451 (1988). S2. B. L. de Jonge, Y. S. Chang, D. Gage, A. Tomasz, J. Biol. Chem. 267, (1992). S3. K.A. Hayashi, Anal. Biochem. 67, 503 (1975). S4. J.F. Garcia-Bustos, T.J. Dougherty, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 31, 178 (1987). S5. N. Xu, Z.H. Huang, B.L. de Jonge, D.A. Gage, Anal. Biochem. 248, 7 (1997). S6. P. M. Sanchez Carballo, E. T. Rietschel, P. Kosma, U. Zahringer, Eur. J. Biochem. 261, 500 (1999). S7. N. Inohara et al., J. Biol. Chem. 274, (1999). S8. S.E. Girardin et al., EMB Rep. 2, 736 (2001). S9. N. Inohara, Y. gura, F.F. Chen, A. Muto, G. Nunez, J. Biol. Chem. 276, 2551 (2001). S10. D.J. Philpott, S. Yamaoka, A. Israel, P.J. Sansonetti, J. Immunol. 165, 903 (2000). S11. A.J. Coyle et al. (submitted). S12. G.S. Evans, N. Flint, A.S. Somers, B. Eyden, C.S. Potten, J. Cell. Sci. 101, 219 (1992). S13. Athman R., Niewohner J., Louvard D., Robine S., Methods in Microbiology 3, 93 (2001). 7
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was grown in a casein-based semisynthetic medium (C+Y) supplemented with yeast extract (1 mg/ml of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Bacterial strains and growth conditions. Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R36A was grown in a casein-based semisynthetic medium (C+Y) supplemented with yeast extract (1 mg/ml of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplemental material Chairoungdua et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201002049/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Expression of CD9 and CD82 inhibits Wnt/ -catenin
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab)
 Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIPs) Protocol (Mirmira Lab) Updated 12/3/02 Reagents: ChIP sonication Buffer (1% Triton X-100, 0.1% Deoxycholate, 50 mm Tris 8.1, 150 mm NaCl, 5 mm EDTA): 10 ml 10 % Triton
supplementary information
 Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit
 Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Mitochondrial DNA Isolation Kit Catalog Number KA0895 50 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Mouse primary keratinocytes preparation
 Mouse primary keratinocytes preparation 1. Fill a 150 X 25 mm petri dish with ice. Put newborn mice (2 3 days old) in the petri dish and insert it in an ice bucket. Leave the mice in the ice bucket for
Mouse primary keratinocytes preparation 1. Fill a 150 X 25 mm petri dish with ice. Put newborn mice (2 3 days old) in the petri dish and insert it in an ice bucket. Leave the mice in the ice bucket for
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Nuclear Extraction Kit NBP2-29447 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 888.506.6887 - technical@novusbio.com Novus kits are
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Nuclear Extraction Kit NBP2-29447 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 888.506.6887 - technical@novusbio.com Novus kits are
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit User Manual (v5)
 Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Minute TM Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation and Cell Fractionation Kit Catalog number: SM-005 Description Minute TM plasma membrane (PM) protein isolation kit is a novel and patented native PM protein
Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin Anna R. Arnold, Andy Zhou, and Jacqueline K. Barton Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Characterization of the DNA-mediated Oxidation of Dps, a Bacterial Ferritin Anna R. Arnold, Andy Zhou, and Jacqueline K. Barton Division of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, California
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Supplementary Material Nuclear import of purified HIV-1 Integrase. Integrase remains associated to the RTC throughout the infection process until provirus integration occurs and is therefore one likely
Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit
 Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit Cat #:DP022MD/ DP022MD-50 Size:10/50 reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a rapid, simple
Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit Cat #:DP022MD/ DP022MD-50 Size:10/50 reactions Store at RT For research use only 1 Description: The Midi Plant Genomic DNA Purification Kit provides a rapid, simple
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3
 Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
Supporting Online Material Material and Methods References Supplemental Figures S1, S2, and S3 Sarbassov et al. 1 Material and Methods Materials Reagents were obtained from the following sources: protein
NLRX1: 5 -GCTCCATGGCTTAGAGCATC-3 (forward) 5 -AACTCCTCCTCCGTCCTGAT-3 (reverse) β-actin
 NLRX1 β-actin 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 NLRX1 (667 bp) β-actin (523 bp) Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NLRX1 in human cell lines. 1: HeLa, 2: HEK293T, 3: MCF-7, 4:Ramos, 5:Jurkat, 6: THP1. The following
NLRX1 β-actin 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 6 NLRX1 (667 bp) β-actin (523 bp) Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NLRX1 in human cell lines. 1: HeLa, 2: HEK293T, 3: MCF-7, 4:Ramos, 5:Jurkat, 6: THP1. The following
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary Figure 1. Method development.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Method development. Titration experiments to determine standard antibody:lysate concentration. Lysates (~2 mg of total proteins) were prepared from cells expressing FLAG- tagged
Supplementary Figure 1 Method development. Titration experiments to determine standard antibody:lysate concentration. Lysates (~2 mg of total proteins) were prepared from cells expressing FLAG- tagged
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Catalog number: AR0155 Boster s Mammalian Membrane Protein Extraction Kit is a simple, rapid and reproducible method to prepare cellular protein fractions highly
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
ab Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions.
 ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
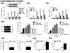 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535
 Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Nuclear Extraction Kit
 Nuclear Extraction Kit Item No. 10009277 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials
Nuclear Extraction Kit Item No. 10009277 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Trident Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Cat. No. Size Shelf life GTX16373 5/ 20 tests 12 months at the appropriate storage temperatures (see below) Contents Component Storage Amount for 5 tests Amount for 20 tests Buffer A -20 o C 2.5 ml 10
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples:
 Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Western Immunoblotting Preparation of Samples: Total Protein Extraction from Culture Cells: Take off the medium Wash culture with 1 x PBS 1 ml hot Cell-lysis Solution into T75 flask Scrap out the cells
Data Sheet. Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509
 Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
Data Sheet Notch Pathway Reporter Kit Catalog # 60509 6042 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. NOTCH signaling
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
The nature of adhesion factors which lie on the surfaces of Lactobacillus adhering to cells
 Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 2012, 3, 153-157 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/abb.2012.32023 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/abb/) ABB The nature of adhesion factors which
Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 2012, 3, 153-157 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/abb.2012.32023 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/abb/) ABB The nature of adhesion factors which
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Recipes for Media and Solution Preparation SC-ura/Glucose Agar Dishes (20mL/dish, enough for 8 clones)
 Protocol: 300 ml Yeast culture preparation Equipment and Reagents needed: Autoclaved toothpicks Shaker Incubator set at 30 C Incubator set at 30 C 60 mm 2 sterile petri dishes Autoclaved glass test tubes
Protocol: 300 ml Yeast culture preparation Equipment and Reagents needed: Autoclaved toothpicks Shaker Incubator set at 30 C Incubator set at 30 C 60 mm 2 sterile petri dishes Autoclaved glass test tubes
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II. Table of Contents
 E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
Human Obestatin ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
Human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (A.T.C.C., Manassas, VA) were cultured in DMEM, F-12
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Cell cultures Human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (A.T.C.C., Manassas, VA) were cultured in DMEM, F-12 Ham with 25 mm HEPES and NaHCO 3 (1:1) and supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS, 1.0
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Cell cultures Human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells (A.T.C.C., Manassas, VA) were cultured in DMEM, F-12 Ham with 25 mm HEPES and NaHCO 3 (1:1) and supplemented with 10% (v/v) FBS, 1.0
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. Identification of acetylation of K68 of SOD2 A B H. sapiens 54 KHHAAYVNNLNVTEEKYQEALAK 75 M. musculus 54 KHHAAYVNNLNATEEKYHEALAK 75 X. laevis 55 KHHATYVNNLNITEEKYAEALAK 77 D. rerio
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Nuclear Extraction Kit
 Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
Supporting Information for: Methylerythritol Cyclodiphosphate (MEcPP) in Deoxyxylulose Phosphate Pathway: Synthesis from an Epoxide and Mechanisms Youli Xiao, a Rodney L. Nyland II, b Caren L. Freel Meyers
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
RayBio Human PPAR-alpha Transcription Factor Activity Assay Kit
 RayBio Human PPAR-alpha Transcription Factor Activity Assay Kit Catalog #: TFEH-PPARa User Manual Jan 5, 2018 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 200 Norcross, GA 30092 Tel: 1-888-494-8555 (Toll Free) or 770-729-2992,
RayBio Human PPAR-alpha Transcription Factor Activity Assay Kit Catalog #: TFEH-PPARa User Manual Jan 5, 2018 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 200 Norcross, GA 30092 Tel: 1-888-494-8555 (Toll Free) or 770-729-2992,
Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples:
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Work-flow: protein sample preparation Precipitation methods Removal of interfering substances Specific examples: Sample preparation for serum proteome analysis Sample
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Data Sheet. NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621
 Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
10.00 PBS OVA OVA+isotype antibody 8.00 OVA+anti-HMGB1. PBS Methatroline (mg/ml)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Enzyme-activatable Probe with a Self-immolative Linker for Rapid and Sensitive
RayBio Human, Mouse and Rat Phospho-NF-kB P65 (Ser536) and Total NF-kB P65 ELISA Kit
 RayBio Human, Mouse and Rat Phospho-NF-kB P65 (Ser536) and Total NF-kB P65 ELISA Kit Catalog #: PEL-NFKBP65-S536-T User Manual Last revised October 10, 2017 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information
RayBio Human, Mouse and Rat Phospho-NF-kB P65 (Ser536) and Total NF-kB P65 ELISA Kit Catalog #: PEL-NFKBP65-S536-T User Manual Last revised October 10, 2017 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Antibodies: LB1 buffer For 50 ml For 10ml For 30 ml Final 1 M HEPES, ph 2.5 ml 0.5 ml 1.5 ml 50mM. 5 M NaCl 1.4 ml 280 µl 0.
 Experiment: Date: Tissue: Purpose: ChIP-Seq Antibodies: 11x cross-link buffer: Regent Stock Solution Final Vol for 10 ml of 11xstock concentration 5 M NaCl 0.1M 0.2 ml 0.5 M EDTA 1 mm 20 ul 0.5 M EGTA,
Experiment: Date: Tissue: Purpose: ChIP-Seq Antibodies: 11x cross-link buffer: Regent Stock Solution Final Vol for 10 ml of 11xstock concentration 5 M NaCl 0.1M 0.2 ml 0.5 M EDTA 1 mm 20 ul 0.5 M EGTA,
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
In-Solution Digestion for proteomics
 In-Solution Digestion for proteomics Guidelines for sample preparation (How to protect your samples from contamination with keratin) 1. Try to avoid any contact of samples and solutions with dust, skin
In-Solution Digestion for proteomics Guidelines for sample preparation (How to protect your samples from contamination with keratin) 1. Try to avoid any contact of samples and solutions with dust, skin
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535
 Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture
 Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
Protocol for purification of recombinant protein from 300 ml yeast culture Equipment and reagents needed: Zirconia beads (0.5 mm diameter from BSP, Germany) Paint Shaker (at 4 C) Tube rotator for 15 ml
NOD1 contributes to mouse host defense against Helicobacter pylori via induction of type I IFN and activation of the ISGF3 signaling pathway
 Research article NOD1 contributes to mouse host defense against Helicobacter pylori via induction of type I IFN and activation of the ISGF3 signaling pathway Tomohiro Watanabe, 1,2 Naoki Asano, 1 Stefan
Research article NOD1 contributes to mouse host defense against Helicobacter pylori via induction of type I IFN and activation of the ISGF3 signaling pathway Tomohiro Watanabe, 1,2 Naoki Asano, 1 Stefan
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Supplementary Information. Cryptochrome Mediates Circadian Regulation of camp. Signalling and Hepatic Gluconeogenesis
 Supplementary Information Cryptochrome Mediates Circadian Regulation of camp Signalling and Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Eric E. Zhang 1,2*, Yi Liu 3,5*, Renaud Dentin 3, Pagkapol Y. Pongsawakul 1, Andrew C.
Supplementary Information Cryptochrome Mediates Circadian Regulation of camp Signalling and Hepatic Gluconeogenesis Eric E. Zhang 1,2*, Yi Liu 3,5*, Renaud Dentin 3, Pagkapol Y. Pongsawakul 1, Andrew C.
Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada *For correspondence:
 Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Beck et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201011027/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Membrane binding of His-tagged proteins to Ni-liposomes.
Supplemental material Beck et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201011027/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Membrane binding of His-tagged proteins to Ni-liposomes.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany Tuning the Intracellular Bacterial Targeting of Peptidic Vectors** Eric K. Lei, Mark P. Pereira, and Shana O. Kelley* anie_201302265_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2013 69451 Weinheim, Germany Tuning the Intracellular Bacterial Targeting of Peptidic Vectors** Eric K. Lei, Mark P. Pereira, and Shana O. Kelley* anie_201302265_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf
Data Sheet IL-2-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog # 60481
 642 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Tel: 1.858.829.382 Data Sheet IL-2-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog # 6481 Description Human IL-2 reporter construct is stably integrated into the genome
642 Cornerstone Court W, Ste B Tel: 1.858.829.382 Data Sheet IL-2-Luciferase Reporter (Luc) - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog # 6481 Description Human IL-2 reporter construct is stably integrated into the genome
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression. through inhibition of Hsp90
 Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
Instructions. Fuse-It-Color. Overview. Specifications
 Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric*
 SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table S1. Primers and fluorescent probes used for qrt-pcr analysis of relative expression levels of PPP family phosphatases. gene name forward primer, 5-3 probe, 5-3 reverse primer,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table S1. Primers and fluorescent probes used for qrt-pcr analysis of relative expression levels of PPP family phosphatases. gene name forward primer, 5-3 probe, 5-3 reverse primer,
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
PAF Acetylhydrolase Assay Kit
 PAF Acetylhydrolase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1354 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
PAF Acetylhydrolase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1354 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit
 PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit (Cat. # BK050) ORDERING INFORMATION To order by phone: (303) - 322-2254 To order by Fax: (303) - 322-2257 To order by e-mail: cservice@cytoskeleton.com Technical
PhosFree TM Phosphate Assay Biochem Kit (Cat. # BK050) ORDERING INFORMATION To order by phone: (303) - 322-2254 To order by Fax: (303) - 322-2257 To order by e-mail: cservice@cytoskeleton.com Technical
<Supplemental information>
 The Structural Basis of Endosomal Anchoring of KIF16B Kinesin Nichole R. Blatner, Michael I. Wilson, Cai Lei, Wanjin Hong, Diana Murray, Roger L. Williams, and Wonhwa Cho Protein
The Structural Basis of Endosomal Anchoring of KIF16B Kinesin Nichole R. Blatner, Michael I. Wilson, Cai Lei, Wanjin Hong, Diana Murray, Roger L. Williams, and Wonhwa Cho Protein
Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the solubility of amylin and huntingtin in living cells
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Contents Supporting Information Luminescent platforms for monitoring changes in the
Tivadar Orban, Beata Jastrzebska, Sayan Gupta, Benlian Wang, Masaru Miyagi, Mark R. Chance, and Krzysztof Palczewski
 Structure, Volume Supplemental Information Conformational Dynamics of Activation for the Pentameric Complex of Dimeric G Protein-Coupled Receptor and Heterotrimeric G Protein Tivadar Orban, Beata Jastrzebska,
Structure, Volume Supplemental Information Conformational Dynamics of Activation for the Pentameric Complex of Dimeric G Protein-Coupled Receptor and Heterotrimeric G Protein Tivadar Orban, Beata Jastrzebska,
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Manual (Second edition)
 Reagent for RNA Extraction ISOGENⅡ Manual (Second edition) Code No. 311-07361 Code No. 317-07363 NIPPON GENE CO., LTD. Table of contents I Product description 1 II Product content 1 III Storage 1 IV Precautions
Reagent for RNA Extraction ISOGENⅡ Manual (Second edition) Code No. 311-07361 Code No. 317-07363 NIPPON GENE CO., LTD. Table of contents I Product description 1 II Product content 1 III Storage 1 IV Precautions
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual
 Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
Aperto Cell Lysis and Protein Solubilization Users Manual Revision 2 THIS MANUAL APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS: 3A8600 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 20mL 3A8610 Aperto, 5X Cell Lysis Buffer. 100mL
