OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
|
|
|
- Junior Wiggins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shara M. Marshall, M.S.
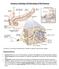
2 Chapter 1- The Human Bdy: An Orientatin Anatmy: OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Subdivisins: Physilgy: Subdivisins: Ex. Principle f Cmplementarity Anatmy and physilgy are inseparable. Levels f Structural Organizatin Chemical: Cellular: Tissue: Organ: Organ system: Organismal: Overview f Organ Systems Nte majr rgans and functins f the 11 rgan systems (Fig. 1.3) 2
3 Survival Needs Nutrients Oxygen Essential fr: 3. Water Site f: Nrmal bdy temperature 5. Apprpriate atmspheric pressure Hmestasis Definitin: A dynamic state f equilibrium Hmestatic Cntrl Mechanisms Invlve: Cmpnents f a Cntrl Mechanism 1. Receptr (sensr) 2. Cntrl center Determines: Receives: Determines: 3. Effectr Receives: 3
4 Prvides: Negative Feedback Examples: Regulatin f bdy temperature Regulatin f bld vlume by ADH Negative Feedback: Regulatin f Bld Vlume by ADH Receptrs sense: Cntrl center (in hypthalamus) stimulates: ADH causes: Psitive Feedback The respnse: May exhibit: Usually cntrls infrequent events: Enhancement f labr cntractins by xytcin Platelet plug frmatin and bld cltting Anatmical Psitin Standard anatmical bdy psitin: Directinal Terms Superir (cranial)- Inferir (caudal)- Ventral (anterir)- Drsal (psterir)- Medial- Lateral- Intermediate- POSITIONAL TERMS AND TERMINOLOGY 4
5 Prximal- Distal- Superficial- Deep- Bdy Planes Plane: Sagittal plane Midsagittal (median) plane Parasagittal plane Frntal (crnal) plane Transverse (hrizntal) plane Oblique sectin Bdy Cavities Drsal cavity Tw subdivisins: Cranial cavity Vertebral cavity Ventral cavity Tw subdivisins (separated by diaphragm): Ventral Bdy Cavities Thracic cavity subdivisins: Tw pleural cavities Mediastinum 5
6 Pericardial cavity Abdminpelvic cavity subdivisins: Abdminal cavity Pelvic cavity Serus Membranes (Sersae) Definitin: Parietal sersa: Visceral sersa: Sersae named accrding t their site and rgan assciatin Pleura: Pericardium: Peritneum: Abdminpelvic Regins Nine divisins used primarily by anatmists Abdminpelvic Quadrants Divisins used primarily by medical persnnel 6
7 Other Bdy Cavities Oral and digestive cavities Nasal cavity- Orbital cavities Middle ear cavities- Synvial cavities - Chapter 2-Chemistry Cmes Alive BASIC CHEMISTRY Matter Definitin: States f matter: Slid Liquid Gas Energy Definitin: Types f energy: Kinetic Ptential Frms f Energy Chemical energy Electrical energy Mechanical energy Radiant r electrmagnetic energy Energy Frm Cnversins Cmpsitin f Matter Elements 7
8 Majr elements f the human bdy: Each has unique prperties: Physical Prperties Chemical Prperties Atms: Three imprtant subatmic particles in atms: Atmic Structure Neutrns Mass = Prtns Mass= Electrns Mass= Identifying Elements Atms f different elements cntain different numbers f subatmic particles Cmpare hydrgen, helium and lithium Atmic number = Mass number = Istpes = Atmic weight = Radiistpes 8
9 Mlecules and Cmpunds Mst atms cmbine chemically with ther atms t frm mlecules and cmpunds Mlecule (e.g., H 2 r C 6 H 12 O 6 ) Chemical Bnds Cmpund (e.g., C 6 H 12 O 6 ) Octet rule: Chemically Inert Elements Chemically Reactive Elements Types f Chemical Bnds: Cvalent, Inic, Hydrgen Cvalent Bnds Frmed by: Allws: Sharing f electrns may be equal r unequal Equal sharing prduces: Ex. CO 2 Unequal sharing by atms with different electrn-attracting abilities prduces: Ex. H 2 O Atms with six r seven valence shell electrns are electrnegative, e.g., xygen Inic Bnds Ins are frmed by transfer f valence shell electrns between atms Anins ( charge): Catins (+ charge): Attractin f ppsite charges results in: Inic cmpunds frm crystals instead f individual mlecules Ex. NaCl (sdium chlride) 9
10 Hydrgen Bnds Attractive frce between: Imprtant in intramlecular bnds, hlding a large mlecule in a three-dimensinal shape CHEMICAL REACTIONS Synthesis Reactins A + B AB Always invlve: Anablic Endergnic reactins- Decmpsitin Reactins AB A + B Reverse synthesis reactins Invlve: Catablic- Exergnic reactins- Rate f Chemical Reactins Rate f reactin is influenced by: Temperature: Cncentratin: Particle size: Catalysts: Enzymes: Classes f Cmpunds Inrganic cmpunds Organic cmpunds 10
11 Water Salts Ins (electrlytes) are: Acids and Bases Bth are electrlytes Acids : HCl H + + Cl Bases: NaOH Na + + OH Acid-Base Cncentratin Acid slutins cntain [H + ] As [H + ] increases: Alkaline slutins cntain bases (e.g., OH ) As [H + ] decreases (r as [OH ] increases): ph= Neutral slutins: ph = Acidic slutins ph = Alkaline slutins ph= Organic Cmpunds Many are plymers: Examples: 11
12 Synthesized by: Brken dwn by: Carbhydrates Cntain C, H, and O [(CH 2 0) n ] Three classes Mnsaccharides- Disaccharides- Plysaccharides- Functins: Majr functin: Als functin in: Lipids Mstly insluble in: Cntain: Fur Main types: Triglycerides, Phsphlipids, Sterids, Eicsanids Triglycerides Triglycerides Cmpsed f: Main functins Saturatin f Fatty Acids Saturated fatty acids Have: Fund in: 12
13 Unsaturated fatty acids Have: Reduced number f: Fund in: Phsphlipids Mdified triglycerides: Cmpsed f: Head and Tail regins: Imprtant in: Sterids Have: Examples f sterids include: Prteins Functin in: Cntain: Exhibit fur levels f rganizatin Primary Secndary Tertiary Quaternary Fibrus and Glbular Prteins Fibrus (structural) prteins Examples: keratin, elastin, cllagen, and certain cntractile fibers Glbular (functinal) prteins Specific functinal regins called: Examples: antibdies, hrmnes, mlecular chapernes, and enzymes Prtein Denaturatin Definitin: Reversible in mst cases 13
14 Enzymes Functin: Characteristics f Enzymes The enzyme binds t: The enzyme is released: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Prtein Synthesis DNA is: Gene: Triplets f nucletide bases: Each triplet specifies: Rles f the Three Main Types f RNA Messenger RNA (mrna) Ribsmal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNAs (trnas) Transcriptin Transfers: RNA plymerase 14
15 Translatin Cnverts: Invlves use f: Genetic Cde Each triplet in DNA is represented by a cdn Cdn Steps f Translatin mrna: Anticdn f a trna: New amin acids: Nucleic Acids DNA and RNA are: Cntain: Cmpsed f: Dexyribnucleic Acid (DNA) Cntains fur nitrgen cntaining bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytsine (C), and thymine (T) Prvides: 15
16 Ribnucleic Acid (RNA) Cntains fur nitrgen cntaining bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytsine (C), and uracil (U) Three varieties f RNA carry ut the DNA rders fr prtein synthesis mrna: trna: rrna: Adensine Triphsphate (ATP) Functin: Phsphrylatin: Such primed mlecules: Chapter 3-Cells: The Living Units Generalized Cell All cells have sme cmmn structures and functins Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane THE PLASMA MEMBRANE Cytplasm Nucleus Plasma Membrane Separates: 16
17 Interstitial fluid (IF) = ECF that surrunds cells Membrane Lipids 75% phsphlipids (lipid bilayer) Phsphate heads: Fatty acid tails: 5% glyclipids 20% chlesterl Membrane Prteins Integral prteins are: Integral prteins functin as: Peripheral prteins are: Peripheral prteins functin as: Functins f Membrane Prteins (See Figure 3.4) Membrane Junctins Three types: Tight junctin - Desmsme - Gap junctin - Membrane Transprt Plasma membranes are: As substances mve within r thrugh cells they d s alng a cncentratin gradient which is defined asz: Types f Membrane Transprt Passive transprt prcesses Active transprt prcesses Passive Transprt What determines whether r nt a substance can passively permeate a membrane? 1. Lipid slubility f substance 2. Size f the mlecule passing (therefre the size f the channel/carrier) Three Passive Transprt Prcesses: 17
18 Simple diffusin Facilitated diffusin (carrier r channel mediated) Osmsis (fr slvent mvement nly) Passive Transprt: Simple Diffusin In simple diffusin: Passive Transprt: Facilitated Diffusin In facilitated diffusin: Exhibit: Are saturable: Can be regulated: Passive Transprt: Osmsis Osmsis is: Water diffuses thrugh plasma membranes thrugh: Osmlarity: When slutins f different smlarity are separated by a membrane: When smsis ccurs in cells: Tnicity Tnicity: Istnic: Hypertnic: Hyptnic: Summary f Passive Prcesses Als see Table 3.1 and Figure 3.7 Active Transprt Requires carrier prteins that: 18
19 Active Transprt: Primary In primary active transprt: The Sdium-ptassium pump (Na + -K + ATPase) is a specific type f primary active transprt Lcated in: Invlved in: Maintains: Membrane Ptential Due t: Resting membrane ptential (RMP): Ranges frm 50 t 100 mv in different cells Results frm diffusin and active transprt f ins (mainly K + ) Active Transprt: Secndary Secndary active transprt depends n: Can invlve ctransprters which: Symprt system: Antiprt system: Vesicular Transprt Vesicular transprt is used t mve: Tw Main Types: Excytsis Endcytsis ORGANELLES OF THE CYTOPLASM Cytplasm Lcated between: Cytsl Cytplasmic rganelles (prtein, salts, sugars, etc.) Cytplasmic Organelles Membranus Mitchndria Perxismes 19
20 Lyssmes Endplasmic reticulum Glgi apparatus Nnmembranus Cytskeletn Centriles Ribsmes Mitchndria Prvide: Cntain: Ribsmes Site f: Free ribsmes: Membrane-bund ribsmes (n rugh ER): Endplasmic Reticulum (ER) System f: Cntinuus with: Tw varieties: Rugh and Smth ER Rugh ER External surface: Manufactures: Synthesizes: Smth ER Its enzymes catalyze reactins invlved with:: In the liver: In testes: Synthesis f In skeletal and cardiac muscle: Glgi Apparatus Prteins exit via: 20
21 Lyssmes Spherical membranus rganelles cntaining: Can degrade/breakdwn: Ingested bacteria, viruses, and txins nnfunctinal rganelles Break dwn and release glycgen Break dwn bne t release Ca 2+ Perxismes Membranus sacs cntaining: Cytskeletn Elabrate series f rds thrughut cytsl Micrtubules Micrfilaments Intermediate filaments- Centriles Invlved in: Fund within: Cellular Extensins Flagella Cilia mve: Micrvilli Nucleus Genetic library with: Respnds t: Surrunded by: Cntains threadlike strands f DNA (30%), histne prteins (60%), and RNA (10%) called: 21
22 Als cntains nucleli: CELL GROWTH AND REPRODUCTION The Cell Life Cycle Includes: Interphase Perid frm: Interphase has three subphases: G 1 (gap 1) S phase (synthetic phase) G 2 (gap 2) DNA Replicatin Occurs During the S-phase f Interphase Helicase: Each nucletide strand: DNA Plymerase: End result: This prcess is called: Cell Divisin (Mitsis) Essential fr: Des nt ccur in mst mature cells f nervus tissue, skeletal and cardiac muscle Cell Divisin Includes tw distinct events 1. Mitsis fur stages f nuclear divisin: Prphase Metaphase Anaphase Telphase 2. Cytkinesis divisin f cytplasm by cleavage furrw 22
23 Prphase Metaphase Anaphase Telphase Cytkinesis Chapter 4-Tissue: The Living Fabric Fur tissue types in the bdy Epithelial tissue Cnnective tissue Muscle tissue Nerve tissue TISSUES Epithelial Tissue (Epithelium) Tw main types (by lcatin): 1. Cvering and lining epithelia 2. Glandular epithelia 23
24 Characteristics f Epithelial Tissue 1. Cells have: Apical surface: Basal surface: 2. Are cmpsed f: 3. Supprted by: Bth laminae frm: 4. Avascular 5. High rate f regeneratin Classificatin f Epithelia T Classify Epithelia ask tw questins: 1. Hw many cell layers? 1 = >1 = 2. What type f cell? Squamus- Cubidal- Clumnar (If stratified, name accrding t apical layer f cells) Epithelial Tissue Types *Fr each f the fllwing types f epithelia, nte descriptin, functin and lcatin* Simple Epithelia Simple Squamus Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Tw ther lcatins f simple squamus epithelia: Prvides a slick, frictin reducing lining fr lymphatic vessels and hllw rgans f Cardivascular System= Fund in serus membranes lining the ventral bdy cavity and cvering its rgans= 24
25 Simple Cubidal Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Simple Clumnar Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Pseudstratified Clumnar Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Stratified Epithelia Stratified Squamus Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Stratified Cubidal and Clumnar Stratified cubidal: Stratified clumnar: Transitinal Epithelium Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Glandular Epithelia Sme epithelial tissue is mdified int glands that prduce and secrete prducts Endcrine Glands- Excrine Glands- Unicellular Excrine Glands- 25
26 Multicellular Excrine Glands- Mercrine- Hlcrine- Apcrine- Cnnective Tissue Mst abundant and widely distributed tissue type Fur classes Cnnective tissue prper Cartilage Bne tissue Bld Majr Functins f Cnnective Tissue Characteristics f Cnnective Tissue Cnnective tissues have: Structural Elements f Cnnective Tissue Grund substance- Allws: Cmpnents: Prteglycans: Three types f fibers Cllagen Elastic 26
27 Reticular Cells blast cell types: cyte cell types: Fibrblasts: Chndrblasts and chndrcytes: Osteblasts and stecytes: Hematpietic stem cells: Fat cells- White bld cells- Mast cells- Macrphages Cnnective Tissue Prper Tw subclasses: Lse cnnective tissue- Dense Cnnective tissue- Lse Cnnective Tissue Arelar Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Adipse Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: 27
28 Reticular Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Dense cnnective tissue Dense regular Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Dense irregular Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Elastic Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Cartilage Cnnective Tissue Three types f cartilage: Hyaline Cartilage Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Elastic Cartilage Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Fibrcartilage Descriptin: Functin: 28
29 Lcatin: Bne (Osseus) Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Bld Cnnective Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Nervus Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Three Types f Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Cardiac Muscle Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: Smth Muscle Tissue Descriptin: Functin: Lcatin: BODY MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes The Cutaneus membrane: Mucus membranes Serus Membranes 29
30 Always ccur in pairs: Inflammatin TISSUE REPAIR Organizatin and restred bld supply Regeneratin and fibrsis Develpmental Aspects Primary germ layers: ectderm, mesderm, and endderm Specialize t frm fur primary tissues Nerve tissue arises frm: Muscle and cnnective tissue arise frm: Endderm gives rise t: Epithelial tissues arise frm: Chapter-5 The Integumentary System INTEGUMENT Skin (Integument) Cnsists f three majr regins 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Hypdermis (superficial fascia) 30
31 Epidermis Tissue type: Cells f epidermis Keratincytes Melancytes: Epidermal dendritic (Langerhans) cells Tactile (Merkel) cells Layers f the Epidermis: Stratum Basale (Basal Layer) Als called stratum germinativum: Takes days Layers f the Epidermis: Stratum Spinsum (Prickly Layer) Layers f the Epidermis: Stratum Granulsum (Granular Layer) Layers f the Epidermis: Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer) Layers f the Epidermis: Stratum Crneum (Hrny Layer) Functins: 31
32 Prtects frm: Barrier against: Dermis Tw layers: Layers f the Dermis: Papillary Layer Papillary layer Dermal papillae cntain: Layers f the Dermis: Reticular Layer Reticular layer Skin Markings: Frictin Ridges Skin Clr Three pigments cntribute t skin clr: 1. Melanin Freckles and pigmented mles are: 2. Cartene 3. Hemglbin Derivatives f the epidermis APPENDAGES OF THE SKIN 32
33 Sweat Glands Tw main types f sweat (sudriferus) glands 1. Eccrine (mercrine) sweat glands Sweat: 2. Apcrine sweat glands cnfined t axillary and angenital areas Sebum: Ducts cnnect t: Specialized apcrine glands Ceruminus glands Mammary glands-- Sebaceus (Oil) Glands Sebum Hair Functins Distributin Cnsists f: Cntains: Hair pigments: Gray/white hair: Hair Fllicle Tw-layered wall: 33
34 Hair bulb: Hair fllicle receptr (rt hair plexus): Sensry nerve endings arund each hair bulb Arrectr pili Types f Hair Vellus Terminal Hair Thinning and Baldness Alpecia True (frank) baldness Structure f a Nail Structures t knw: nail matrix, nail rt, bed and free edge, hypnychium and epnychium Functins f the Integumentary System Prtectin three types f barriers Chemical Physical/mechanical barriers Bilgical barrier Bdy temperature regulatin 34
35 Cutaneus sensatins Metablic functins 5. Bld reservir 6.Excretin DISORDERS OF THE SKIN Skin Cancer Risk factrs Three majr types: Basal cell carcinma Squamus cell carcinma Melanma Basal Cell Carcinma Arises frm: Appearance: Squamus Cell Carcinma Arises frm: Appearance: Melanma Can begin: 35
36 Appearance: The American Cancer Sciety suggests that peple shuld apply the ABCD rule: A: Asymmetry; B: Brder C: Clr D: Diameter Burns Heat, electricity, radiatin, certain chemicals Burn (tissue damage, denatured prtein, cell death) Immediate threat: Dehydratin and electrlyte imbalance, leading t renal shutdwn and circulatry shck The Rule f Nines is used t estimate the vlume f fluid lss frm burns by cmputing the percentage f bdy surface burned This methd: Partial-Thickness Burns First degree Secnd degree Full-Thickness Burns Third degree Chapter 6-The Skeletal System Functins f Bnes Supprt Prtectin BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES 36
37 Mvement Strage Bld cell frmatin (hematpiesis) in: Triglyceride (energy) strage in: There are fur types f bnes classified by their vshapes: Lng bnes- Ex. humerus, radius, ulna, femur, tibia, phalanges Shrt bnes- Sesamid bnes- Flat bnes- Ex. Sternum, ribs, mst skull bnes Irregular bnes Ex. cxal, vertebrae Types f Osseus Tissue Cmpact bne (dense) - Spngy (cancellus) - Bne Markings (Refer t Table 6.1) Bne Markings: Prjectins Prjectins that are sites f muscle and ligament attachment Tubersity Crest Trchanter Line Tubercle Epicndyle Spine Prcess Prjectins that help t frm jints Head- 37
38 Facet- Cndyle- Ramus- Depressins and Openings fr the passage f bld vessels and nerves Meatus - Sinus- Fssa- Grve- Fissure- Framen- Structure f a Lng Bne Diaphysis (shaft) - Epiphyses Epiphyseal line r plate- Membranes Peristeum The uter fibrus layer The inner stegenic layer: Endsteum Als cntains: Shrt, Irregular, and Flat Bnes all share a simple design: They all cnsist f thin plates f: Diplë Lack: Lcatin f Hematpietic Tissue (Red Marrw) Red marrw cavities f adults Trabecular cavities f the heads f: Trabecular cavities f : Red marrw f newbrn infants Micrscpic Anatmy f Bne: Cmpact Bne Haversian system, r Osten = structural unit 38
39 Lamellae Cncentric Interstitial Circumferential - Central (Haversian) canal - Perfrating (Vlkmann s) canals - Ostecytes Canaliculi Micrscpic Anatmy f Bne: Spngy Bne Organic Cmpnents Osteid- Inrganic Cmpnents Hydrxyapatites [Ca 10 (PO 4 ) 6 (OH) 2 ]- Ostegenesis (ssificatin) BONE DEVELOPMENT Tw Types f Bne Frmatin Intramembranus ssificatin- Used fr: Steps Develpmental Aspects: Fetal Skull Infant skull has mre bnes than the adult skull Skull bnes such as the mandible and frntal bnes are unfused 39
40 At birth, skull bnes are cnnected by fntanelles Fntanelles Fur fntanelles Endchndral ssificatin - Used fr: Steps 1. Frmatin f bne cllar arund hyaline cartilage mdel 2. Deteriratin f cartilage matrix 3. Frmatin f spngy bne by peristeal bud Peristeal bud- 4. Frmatin f medullary cavity 5. Ossificatin f epiphyses Grwth in Length f Lng Bnes Als called interstitial grwth Epiphyseal plate cartilage abutting the diaphysis rganizes int fur functinal znes: Prliferatin, Hypertrphic, Calcificatin, & Ossificatin Grwth in the epiphyseal plate is accmpanied by remdeling f epiphyseal ends The tp layer (epiphyseal plate) f the hyaline cartilage plate cntains: Older chndrcytes (clser t diaphysis):: Osteblasts secrete: Sex hrmnes (teststerne and estrgen): At the end f adlescence: 40
41 Appsitinal Grwth Appsitinal Grwth- Osteblasts: Osteclasts: Bne Remdeling- BONE REMODELING AND REPAIR Remdeling ccurs: In healthy adults, the rate f bne resrptin = Remdeling ccurs: Bne Depsit Osteblasts depsit: Requires a diet rich in prtein; vitamins C, D, and A; calcium; phsphrus; magnesium; and manganese Hrmnal cntrl Calcitnin- Bne Resrptin Osteclasts secrete: Osteclasts may: Digested prducts: Hrmnal cntrl Parathyrid hrmne (PTH) - Repair f Bne Fractures Fracture - Fracture Types Simple 41
42 Cmpund- Cmminuted- Cmpressin- Depressed Impacted- Spiral- Greenstick- Phases f Repair 1. Hematma frmatin- 2.Fibrcartilaginus callus frmatin 3.Bny callus frmatin 4.Bne callus remdeling Final structure resembles riginal Hmestatic Imbalances Ostemalacia - BONE IMBALANCES Rickets - Osteprsis 42
43 Risk factrs Pagets Disease Chapter 7 - The Skeletn THE SKELETON The skeletn accunts f 20% f bdy mass There are 206 bnes in the human skeletn Ligaments Divisins f the Skeletn The Axial Skeletn Axial Skeletn & Appendicular Skeletn- Cntains f 80 bnes that cllectively frm the axis f the bdy trunk Prtect the brain and spinal crd and rgans within the thracic cavity Three majr regins f the axial skeletn Skull Vertebral clumn Thracic cage Hyid The Skull General Characteristics Cmpsed f: Cranial bnes: Facial bnes: Mst bnes f the skull are: 43
44 Majr Sutures f the Skull Fur sutures mark the articulatins f parietal bnes with frntal, ccipital, and tempral bnes: Crnal (frntal) suture- Sagittal suture- Lambdid suture- Squamus suture- The Skull Calvaria Cranial base (flr) f the skull is divided int three regins: Anterir cranial fssa- Middle cranial fssa- Psterir cranial fssa- Cavities Fur pair f cavities within the skull bnes called: The fur pair are: Sphenid Ethmid Maxillary Frntal Each cavity is lined with mucus membranes that frm mucus, which drains int the nasal cavity The Orbits Cmpsed f: The Nasal Cavity The rf, superir/lateral walls and superir prtin f the nasal septum are frmed by: The flr is frmed anterirly by The cavity is divided int right and left halves by Nasal cnchae n the lateral walls: The cnchae and septum are lined with a mucus secreting mucsa that mistens & warms air, helps cleanse it f debris Cribrifrm plate - 44
45 The Vertebral Clumn General Characteristics Cntains 33 vertebrae,sme f which are fused in adults. Intervertebral discs- Inner part Nucleus pulpsus- Outer part Annulus fibrsus- Herniated disc- Vertebral Clumn: Curvatures Increase the resilience and flexibility f the spine Fur nrmal curvatures Tw primary curvatures- Tw secndary curvatures- The Appendicular Skeletn Characteristics Includes: REVIEW ALL APPENDICULAR BONES LISTED IN YOUR LAB MANUAL. KNOW THE LOCATION, LISTED STRUCTURES, AND ARTICULATIONS. Ntes n Articulatins: The scapula is the nly attachment the arms have t the trunk f the bdy. The fibula des nt articulate with the femur. The tibia articulates superirly with the femur and the fibula. Bth the tibia and fibula articulate with the talus bne distally t frm the ankle (medial and lateral mallelus) Cmparisn f the Male and Female Pelvis: The true pelvis is: The pubic angle is in females and in males. The acetabula are: Chapter 8-Jints JOINTS Intrductin Jint (Articulatin) - Functins f jints: 45
46 Classificatin f Jints There are tw ways t classify jints: Functinal Classificatin f Jints based n amunt f mvement allwed by the jint Synarthrses Amphiarthrses Diarthrses Structural Classificatin f Jints - Based n material binding bnes tgether and whether r nt a jint cavity is present (Fibrus, Cartilaginus, Synvial) Fibrus jints- Three types f fibrus jints: Sutures- Syndesmses- Gmphses- Cartilaginus Jints- Tw types f cartilaginus jints Synchndrses- Symphyses- Synvial Jints General Structure f Synvial Jints Articular cartilage- Jint (synvial) cavity A duble-layered jint capsule- Synvial fluid May have wedges f: Fibrus (bursae) lined with: Types f Synvial Jints Plane Jints- Hinge Jints Pivt Jints Cndylid Jints Saddle Jints Ball-and-Scket Jints 46
47 Cmmn Jint Injuries Sprains Cartilage injuries Dislcatins Bursitis and Tendnitis Arthritis Acute frms: Chrnic frms: Gliding mvements MOVEMENTS AT SYNOVIAL JOINTS Examples: Intercarpal, intertarsal jints; between articular prcesses f vertebrae Angular mvements Mvements that ccur alng the sagittal plane: Flexin - Extensin - Hyperextensin- Mvements that ccur alng the frntal plane: Abductin Adductin Circumductin Rtatin Examples: Between C 1 and C 2 vertebrae Rtatin f humerus and femur Special mvements Mvements f radius arund ulna: Supinatin Prnatin 47
48 Mvements f the ft: Drsiflexin- Plantar flexin- Inversin Eversin Mvements in a transverse plane: Prtractin Retractin Elevatin Depressin Oppsitin f the thumb - Chapter 9-Muscles and Muscle Tissue MUSCLES AND MUSCLE TISSUES Muscle Functins Overview f Muscle Tissue Three Types f Muscle Tissue 1. Skeletal muscle tissue: 2.Cardiac muscle tissue: 3.Smth muscle tissue: 48
49 SKELETAL MUSCLE STRUCTURE Each muscle is served by ne artery, ne nerve, and ne r mre veins Three layers f cnnective tissue sheaths surrund skeletal muscle: Epimysium (fascia)- Perimysium- Endmysium - Tendn - Muscle Actin Actin Attachments Origin Insertin - Functinal Classificatin Prime mver- Synergist Antagnist - Skeletal Muscle Fiber Structure Myfibrils A muscle fiber is cmpsed f thusands f stacked, cylindrical, cntractile structures called: Each myfibril cnsists f smaller cntractile units called: Each sarcmere cntains an rderly arrangement f rd-like prtein filaments called: Thick filaments Micrscpic Anatmy Sarcplasm Myglbin Thin filaments Sarclemma- T (transverse) tubules - Sarcplasmic Reticulum - 49
50 Terminal cisternae - Sarcmere Structure Sarcmere Myfilaments- filaments that cnstitute myfibrils A sarcmere extends frm Z disc t Z disc Z line (band) Sarcmere Regins H zne (band) A band I band - M line- NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION The Neurmuscular Junctin Mtr Neurns Skeletal muscle is innervated by: Each muscle is served by: Neurn axns: Mtr unit Neurmuscular Junctin includes: Each axn terminal frms: Synaptic cleft Axn Terminal Synaptic vesicles Acetylchline (Ach) When a nerve impulse reaches the axn terminal, Ca2+: This causes: 50
51 Excytsis f: The Mtr End Plate Cntains: Respnsible fr: End plate ptential: THE ACTION POTENTIAL AND THE SARCOLEMMA Resting Membrane Ptential Sarclemma The difference between the charge inside and utside the membrane is called: Actin Ptential Generatin Steps: Ach Binding f Ach t receptrs causes: This allws: Deplarizatin This prduces: This causes: Prpagatin - The deplarizatin wave spreads t: Deplarizatin travels dwn the sarclemma: 51
52 Once a threshld vltage is reached: The AP: Replarizatin- Due t: Abslute refractry perid The actin ptential includes all f the abve steps: Deplarizatin, Prpagatin, and Replarizatin Destructin f Acetylchline Effects are quickly terminated by: Prevents: Sliding Filament Mechanism CONTRACTION OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBER When a muscle fiber cntracts: In a relaxed state: During a cntractin: Ultra structure f Myfilaments The structure f actin and mysin play a majr rle in the sliding filament mechanism Thick Filament (Mysin) Structure- The head f each mysin mlecule: Mysin heads: Mysin: Thin Filament (Actin) Structure Tw actin strands: Trpnin (prtein) mlecules: Nrmally, the trpmysin strand: 52
53 Steps in the Sliding Filament Mechanism In a relaxed state, the actin filaments: ATP binds t the mysin head and: The energy released is stred and the mysin head is: An actin ptential travels dwn the sarclemma and dwn the T-tubules The T-tubules: The impulse causes: Ca2+ ins: Trpnin and trpmysin cmplex: The active sites fr binding f the mysin head are uncvered. Mysin heads bind t Actin Once each mysin head binds t actin: As the mysin head tilts inward it pulls the actin filament twards the M line This inward pulling f the actin: Once the pwer strke has ccurred: Binding f the ATP: The newly attached ATP: This prcess: SKELETAL MUSCLE CONTRACTION Muscle Twitch A muscle twitch is: There are three phases f a twitch: Latent perid: Perid f cntractin: Perid f relaxatin: Graded Muscle Respnses Variatins in the degree f muscle cntractin are called: 53
54 Required fr: There are tw ways t grade a muscle respnse: Changing the frequency f stimulatin Changing the strength f stimulatin Wave Summatin If a secnd stimulus is delivered t a muscle in rapid successin: Since the muscle is already partially cntracted when the secnd cntractin begins: The cntractins: This will nt be true if: Tetanus Increase frequency f stimulus- This leads t: Further increase in stimulatin rate: Prlnged tetanus will ultimately result in muscle fatigue. Multiple Mtr Unit Summatin (Recruitment) Threshld stimulus: Maximal stimulus: At maximal stimulus: Muscle Tne A state f: Results in: Due t: 54
55 Types f Cntractins Istnic cntractins- Ismetric cntractins- MUSCLE METABOLISM Energy fr Cntractin ATP Muscles: It is needed fr: Muscles: There are three pathways that a muscle can use t generate ATP: Direct phsphrylatin f ADP by creatine phsphate (CP) Anaerbic pathway Aerbic pathway Creatine Phsphate When ATP is depleted in a muscle cell: Creatine phsphate reserves: During inactivity: Aerbic Respiratin Glucse is brken dwn (with the use f xygen) t: This prcess requires: Mst f this prcess ccurs in: This prcess: Mst f the energy: Enugh energy t allw fr: Glucse + Oxygen Carbn Dixide + Water + ATP 55
56 Anaerbic Glyclysis and Lactic Acid Frmatin (Anaerbic Respiratin) Glyclysis Occurs: Occurs in: If xygen is available: If xygen is nt available: Anaerbic glyclysis Occurs withut: Occurs within: Prduces: Prvides: Use f Energy Systems Energy Systems Used During Activities ATP and Creatinine Phsphate Reserves Anaerbic Glyclysis Aerbic Respiratin 56
57 Muscle Fatigue Defined as: Occurs when: Oxygen Debt Heat Prductin The bdy respnds by: Rapid muscle cntractins will: FORCE VELOCITY AND DURATION OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION Frce f Muscle Cntractin The strength r frce f muscle cntractin is affected by: The number f muscle fibers cntracting The relative size f the muscle Series-elastic elements Cntracting myfibrils generate: Endmysium, perimysium, epimysium and tendns: When the cntractin ends: Degree f muscle stretch (what is the ptimal perating length?) Length-tensin relatinship ccurs when: 57
58 Velcity and Duratin f Cntractin Influenced by: Lad If lad exceeds muscles maximum tensin: Muscle fiber types Slw Oxidative Fibers Fast Glyclytic Fibers Fast Oxidative Fibers Mst muscles cntain: The percentage f each fiber type is: 58
59 EFFECT OF EXERCISE ON MUSCLE Adaptatins t Exercise Aerbic (endurance) exercise results in the fllwing changes: Disuse Atrphy Results in: Caused by: Micrscpic Structure f Smth Muscle Spindle-shaped fibers: Cnnective tissue: SR: Puchlike infldings called cavelae: Innervatin f Smth Muscle Varicsities (bulbus swellings): SMOOTH MUSCLE Myfilaments in Smth Muscle Rati f thick t thin filaments (1:13) is much lwer than in skeletal muscle (1:2) N trpnin cmplex; prtein calmdulin binds Ca 2+ Myfilaments are spirally arranged, causing smth muscle t cntract in a crkscrew manner 59
60 Cntractin f Smth Muscle Sliding filament mechanism Final trigger is intracellular Ca 2+ Ca 2+ is btained frm the SR and extracellular space Chapter 15-The Special Senses THE EYE The Eye and Visin Accessry Structures f the Eye -Prtect the eye and aid in eye functin Eye brws - Eyelids (palpebrae)- Levatr palpabrae superiris muscle - Tarsal plates - Palpebral fissure - Medial and Lateral Canthi - Caruncle - Cntains: Eyelashes - Tarsal (Meibmian) Glands Prduce: 60
61 Ciliary glands Cnjunctiva Transparent mucus membrane Palpebral cnjunctiva: Bulbar cnjunctiva: Lacrimal Apparatus Cnsists f: Releases: The slutin als cntains: The slutin drains via: Extrinsic Eye Muscles The mvement f the eye is cntrlled by six muscles n the external surface f each eye: Superir rectus: Inferir rectus: Lateral rectus: Medial rectus: Inferir blique: Superir blique: The innervatins t each muscle can be remembered by the fllwing equatin: (LR 6 SO 4 )O 3 Which means: Lateral rectus: Superir blique: All thers: Structure f the Eyeball Wall f eyeball cntains three layers Fibrus layer- Vascular layer- Sensry layer- 61
62 Structures r Substances t Knw: Sclera Crnea Chrid Ciliary bdy, muscle and prcesses Suspensry ligaments Ora Serrata Iris Pupil Anterir segment divided int anterir and psterir chambers Psterir segment Vitreus humr Aqueus humr Lens Macula Lutea Fvea Centralis Optic disc Optic nerve Central artery and vein Canal f Schlemm 62
63 PHYSIOLOGY OF VISION Light and Optics Refractin Light is refracted (bent) as it passes thrugh 3 areas f the Since the lens shape can be changed, it can be used t: Fcusing Light n the Retina Fcusing fr Distant Visin Fcusing fr Clse Visin Light frm a clse bject diverges as it appraches the eye. Three prcesses must ccur t prduce clear visin: Accmmdatin - Cnstrictin f the pupils Cnvergence f the Eyeballs- 63
64 Prblems f Refractin Emmetrpia - Mypia Hyperpia - Phtreceptin and the Retina Structure f the Retina Pigmented Layer- Neural Layer Cmpsed f three layers: Phtreceptrs The rds and cnes are adjacent t: Rds Outer segment Inner segment Cnes Biplar Cells- Ganglin Cells- 64
65 Visual Pigments and Stimulatin f Phtreceptrs Retinal - Tw ismers: Cnversin f 11-cis-retinal t all-trans-retinal: Stimulatin f the Phtreceptrs Excitatin f the rds In the dark: When light is absrbed: all-trans-retinal: Excitatin f the cnes There are 3 types f cnes: Breakdwn and regeneratin f visual pigments: The threshld fr activatin f cnes is: Phtreceptr Imbalances Nyctalpia (night blindness) Caused by: 65
66 Clr Blindness Due t: THE VISUAL PATHWAY TO THE BRAIN Optic Nerve ptic chiasma fibers frm medial regin f each eye crss ver t the ppsite side ptic tracts lateral geniculate bdy f the thalamus ptic radiatins primary visual crtex in the ccipital lbe f the brain cnscius perceptin f the image. The Ear: Hearing and Balance Three parts f the ear The External (uter) ear Pinna THE EAR External auditry (acustic) canal (meatus) Lined with: Tympanic membrane The Middle Ear (tympanic cavity) Three bnes (ssicles)- 66
67 Tw tiny skeletal muscle prevent damage due t large vibratins: Tensr tympani- Stapedius muscle- Pharyngtympanic (auditry) tubes The Inner Ear Cnsists f the bny (sseus) and membranus labyrinth Bny labyrinth - Three regins Vestibule - Cntains tw sacs Saccule- Cchlea Utricle - Semicircular canals Membranus labyrinth EQUILIBRIUM The Maculae and Static Equilibrium Maculae - Each maculae cntains: Otlithic membrane Otliths - 67
68 Steps f Linear Mvement The Crista Ampullaris and Dynamic Equilibrium Dynamic Equilibrium Detected by: Crista Ampullaris Semicircular canals Three canals are lcated in each ear Endlymph Ampulla Crista Ampullaris Cmpsed f: Cupula Steps f Rtatinal Mvement At rest: During rtatinal acceleratin: As mvement slws: Equilibrium Pathway t the Brain Vestibular nerve - Sund and the Cchlea Sund is detected by: Cchlea The cchlea: Cchlear duct SOUNDS AND MECHANISMS OF HEARING Divides cchlea int three chambers: 68
69 Scala vestibuli Scala tympani Scala media (cchlear duct) Oval windw Rund windw Vestibular membrane Basilar membrane Organ f Crti Tectrial membrane Bending f the cilia: Sund Transmissin Transmissin f Sund t the Inner Ear Sund waves enter: Resnance f the Basilar Membrane- Bending cilia twards kincilium: Bending cilia away frm kincilium: Impulses frm the cchlea: Eventually impulses are sent t: 69
70 HEARING IMBALANCES Deafness Hearing lss can be temprary r permanent. Cmmn causes: Middle ear infectins Cnductin Deafness Can be caused by: Nerve Deafness Can be caused by: Tinnitus Meniere s Syndrme 70
Bio 103 Tissues and Skin 35
 Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
Can exert forces from a fraction of an ounce to > 70 lbs
 Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Al Balqa Applied University. Collage of Medicine. Anatomy Lab Check List
 Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Orbit, Eye and Ear Lab Objectives: Recgnize individual structures related
Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Orbit, Eye and Ear Lab Objectives: Recgnize individual structures related
Topic 11: Senses. Sensory Receptors
 Tpic 11: Senses Sensry Receptrs Part f the nervus system that detects a stimulus A sensry receptr culd be: Types f Sensry Receptrs: Chemreceptrs: detects chemicals ( ) Phtreceptrs: detects light (fund
Tpic 11: Senses Sensry Receptrs Part f the nervus system that detects a stimulus A sensry receptr culd be: Types f Sensry Receptrs: Chemreceptrs: detects chemicals ( ) Phtreceptrs: detects light (fund
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
Human Structure and Function LECTURE 1 ERIN HARRISON
 * Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
* Intrductin t Human Structure and Functin ULO1 = Structure ULO2 = Functin ULO3 = Applicatin f Knwledge TEXTBOOK: Dwnlad - Anatmical Landmarks - Directinal References - Sectinal Planes Structure = Anatmy
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Test 3 Study Guide: Photosynthesis, Respiration, and the Cell Membrane
 Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Prokaryotic cells are placed in two taxonomic domains: o Bacteria o Archaea o
 AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
AP Bilgy Ch. 4 Cellular Structure and Functin 4.1Cellular Level f Organizatin Cell Thery: Name Cell Size Large cells - Small cells EK 2.A.3b: Surface area- t- vlume ratis affect a bilgical system s ability
ANATOMICAL REGIONS, POSITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY
 Shara M. Marshall, M.S. 1 ANATOMICAL REGIONS, POSITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Overview Anatmy: Physilgy: Functin: Levels f Structural Organizatin Chemical: Cellular: Tissue: Organ: Organ system: Organismal:
Shara M. Marshall, M.S. 1 ANATOMICAL REGIONS, POSITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Overview Anatmy: Physilgy: Functin: Levels f Structural Organizatin Chemical: Cellular: Tissue: Organ: Organ system: Organismal:
Topic 1: Cell Biology (Student) Essential Idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure that prokaryotes.
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
ANATOMICAL REGIONS, POSITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY
 Shara M. Marshall, M.S. 1 ANATOMICAL REGIONS, POSITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Overview Anatmy: Physilgy: Principle f Cmplementarity Anatmy and physilgy are inseparable. Levels f Structural Organizatin Chemical:
Shara M. Marshall, M.S. 1 ANATOMICAL REGIONS, POSITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Overview Anatmy: Physilgy: Principle f Cmplementarity Anatmy and physilgy are inseparable. Levels f Structural Organizatin Chemical:
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Function: Life at the Edge
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System S1: Intro to Kinesiology
 S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
S1: Intr t Kinesilgy (1) Intr t Kinesilgy Majr Divisins f the Human Bdy Jints Between Majr Bdy Parts Describing Mvement in the Bdy True Mvement vs. Ging Alng fr the Ride Anatmic Psitin Directinal Terms
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES.! BIOL1040 University of Queensland
 CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
Close to spine/ point of attachment
 Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Module 2. Chapter 4 Anatomy of the Cell
 Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM
 FORBUSH HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM GUIDE TO IDENTIFICATION Arranged by: M.Sewell Bnes and Prcesses t Knw Page 2 f 19 Cntents Bnes and prcesses needed t knw fr Anatmy:... 3 Be able
FORBUSH HIGH SCHOOL ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: SKELETAL SYSTEM GUIDE TO IDENTIFICATION Arranged by: M.Sewell Bnes and Prcesses t Knw Page 2 f 19 Cntents Bnes and prcesses needed t knw fr Anatmy:... 3 Be able
1.6. Topic 1: Cell Biology (Teacher) Essential Idea: Cell division is essential but must be controlled. 1.6 Cell Division
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Teacher) 1.6 Essential Idea: Cell divisin is essential but must be cntrlled. 1.6 Cell Divisin Why d cells divide: - Sa:Vl Rati - Allws fr grwth f the rganism - Allws fr cell differentiatin
Science. Human Biology. New Jersey Quality Single Accountability Continuum (NJQSAC) Department: Course Title
 New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System Module S4 (Leg Ankle and Foot)
 Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) (1) OVERVIEW In this mdule, we ll explre the: Features f the leg & ft bnes Anatmy f the ankle & ft jints Mvements pssible at the ankle & ft Imprtant ligaments f the ankle &
Mdule S4 (Leg Ankle and Ft) (1) OVERVIEW In this mdule, we ll explre the: Features f the leg & ft bnes Anatmy f the ankle & ft jints Mvements pssible at the ankle & ft Imprtant ligaments f the ankle &
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 21. Neural Cntrl and Crdinatin HUMAN NEURAL SYSTEM : The human neural system divided int tw parts The central nervus system (CNS) The peripheral nervus
POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 21. Neural Cntrl and Crdinatin HUMAN NEURAL SYSTEM : The human neural system divided int tw parts The central nervus system (CNS) The peripheral nervus
Chapter 14 Cell division: Continuity of Life means all life originates from other living things of the same type.
 Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Chapter 14 Cell divisin: 2.3 Cell Cntinuity Learning Objectives 2.3.1 2.3.8 The Cell Cycle, Mitsis, Meisis 1. Explain f the terms cell cntinuity and chrmsme. 2. Differentiate between "haplid" and "diplid"
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 Chapter 1: Intrductin 13 Anatmy and Physilgy I ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Anatmy (Greek a cutting up ) Physilgy (Greek relatinship t nature ) is always related t CORE PRINCIPLE IN A&P Structure and Functin
Chapter 1: Intrductin 13 Anatmy and Physilgy I ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Anatmy (Greek a cutting up ) Physilgy (Greek relatinship t nature ) is always related t CORE PRINCIPLE IN A&P Structure and Functin
Module 3. Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions Metabolism Two general types of metabolic reactions: o :
 Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Mdule 3 Chapter 5 Micrbial Metablism Catablic and Anablic Reactins Metablism Tw general types f metablic reactins: : : Recall frm Chapter 2: Energy can be when bnds Energy can be when bnds Catablism Purpse
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Cellular Neurophysiology Membrane Ionic Gradients Concentration gradients and diffusion Membrane transport:
 Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
ASFYT Part I: The Skeletal System Module S3 (Joints)
 Mdule S3 (Jints) (1) Overview f Jints Classificatin f Jints Fibrus Jints Cartilaginus Jints Synvial Jints Factrs Determining the Stability f Synvial Jints Menisci and Articulating Discs Classificatin f
Mdule S3 (Jints) (1) Overview f Jints Classificatin f Jints Fibrus Jints Cartilaginus Jints Synvial Jints Factrs Determining the Stability f Synvial Jints Menisci and Articulating Discs Classificatin f
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Function
 Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Chem 464 Biochemistry Third Hour Exam
 Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
Name: Chem 464 Bichemistry Third Hur Exam Multiple chice (5 pints apiece): 1. Which f the fllwing statements cncerning fatty acids is crrect? A) One is the precursr f prstaglandins. B) Phsphatidic acid
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
4.2 Joint and Movement Type
 TOPIC 4 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 1 4.2 Jint and Mvement Type 4.2.1 - Outline the types f mvement f synvial jints The musculskeletal system is the arrangement f bnes, jints and muscles that permits mvement f the
TOPIC 4 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 1 4.2 Jint and Mvement Type 4.2.1 - Outline the types f mvement f synvial jints The musculskeletal system is the arrangement f bnes, jints and muscles that permits mvement f the
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Biology 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reproductive Systems ANSWERS
 Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
Chapter 13 Forensic Anthropology: What We Learn from Bones By the end of this chapter you will be able to:
 Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
Chapter 13 Frensic Anthrplgy: What We Learn frm Bnes By the end f this chapter yu will be able t: Describe hw bne is frmed Distinguish between male and female skeletal remains Explain hw bnes cntain a
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
The Excretory System. 4 The Excretory System.notebook. May 24, 2017
 4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Rles f Cell Divisin The Key Rles f Cell Divisin CONCEPTS: 12.1 Mst cell divisin results in genetically identical daughter cells 12.2 The mittic phase alternates
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 12: The Cell Cycle: The Key Rles f Cell Divisin The Key Rles f Cell Divisin CONCEPTS: 12.1 Mst cell divisin results in genetically identical daughter cells 12.2 The mittic phase alternates
The eyes and the ocular adnexa (adjoining parts) are sense organs that allow us to see (vision) (sight).
 Mdule 27 The eyes and the cular adnexa (adjining parts) are sense rgans that allw us t see (visin) (sight). Anatmy f the Eye Eye The eye is a rund-shaped rgan cmpsed f three layers called tunica (cat).
Mdule 27 The eyes and the cular adnexa (adjining parts) are sense rgans that allw us t see (visin) (sight). Anatmy f the Eye Eye The eye is a rund-shaped rgan cmpsed f three layers called tunica (cat).
Endocrine glands secrete hormones that mediate slower, but longerlasting. Endocrine system functions more as a regulatory than a command system
 The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
The Endcrine System 1 Tpics Types f cell signalling Fur types f cell signalling (majr) Fur types f hrmnes (majr) Types f hrmnes Hrmne receptrs Majr endcrine glands Majr hrmnes The hypthalamus and pituitary
UNIT 3 - CHAPTER 12: NERVOUS SYSTEM III: SENSES. 1. Differentiate between general senses and special senses.
 LEARNING OUTCOMES: 12.1 Intrductin UNIT 3 - CHAPTER 12: NERVOUS SYSTEM III: SENSES 1. Differentiate between general senses and special senses. 12.2 Receptrs, Sensatin, and Perceptin 2. Name the five types
LEARNING OUTCOMES: 12.1 Intrductin UNIT 3 - CHAPTER 12: NERVOUS SYSTEM III: SENSES 1. Differentiate between general senses and special senses. 12.2 Receptrs, Sensatin, and Perceptin 2. Name the five types
Autonomic. Nervous System
 Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CEREBRAL BLOOD CIRCULATION Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: List the cerebral arteries. Describe
CEREBRAL BLOOD CIRCULATION Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: List the cerebral arteries. Describe
b. Responses/Reflexes Food bulk stretches the fundus of stomach, activating mechanoreceptors GI peptides activate chemoreceptor s o o o
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
Intestinal Hormones Inhibit: Intestinal Hormones Promote:
 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 3 INTESTINAL PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. INTESTINAL PHASE AND FEEDBACK SIGNALS a. Intr Net result f gastric phase is Digestin f prteins in the stmach
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
Metabolism: Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
Metablism: Oxidative Phsphrylatin Hand-ut fr the CBT versin April 2012 1. On average, hw much ATP is needed each day by ur bdy? 2. Which f the fllwing ccurs during cellular respiratin? Bisynthesis f glycgen
Extension: Flexion: Motor neurons: o Only excitatory neurons release acetylcholine (ACh)
 Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Proenza
 CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
The eyes and the ocular adnexa (adjoining parts) are sense organs that allow us to see (vision) (sight).
 Medical Cding Certificatin Review Mdule 27 Eye, Ocular Adnexa, Auditry, and Operating Micrscpe The eyes and the cular adnexa (adjining parts) are sense rgans that allw us t see (visin) (sight). Anatmy
Medical Cding Certificatin Review Mdule 27 Eye, Ocular Adnexa, Auditry, and Operating Micrscpe The eyes and the cular adnexa (adjining parts) are sense rgans that allw us t see (visin) (sight). Anatmy
2N diploid cell replicates division - two daughter cells, each 2N division (without replication)- four daughter cells, each N (haploid)
 Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
Chrmsme - a linear DNA mlecule Hmlgus chrmsmes - chrmsmes that have the same kind f genes in the same rder 1 cpy frm father, 1 cpy frm mther humans have 46 chrmsmes with 23 hmlgus pairs als knw as sister
ANATOMICAL TERMS Anatomical stance
 ANATOMICAL TERMS Anatmical stance Is a stance in which a persn stand erect with the feet flat n the flr and clse tgether, arms at their sides and the palms and face directed frwards? Bdy Planes Sagittal
ANATOMICAL TERMS Anatmical stance Is a stance in which a persn stand erect with the feet flat n the flr and clse tgether, arms at their sides and the palms and face directed frwards? Bdy Planes Sagittal
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Articulations or Joints
 Articulatins r Jints Bnes are cnnected t each ther by jints. The mst cmmn jint type is the diarthrsis f articulating jints, which has a fibrus cnnective tissue capsule (ligament), cntinuus with the peristeum
Articulatins r Jints Bnes are cnnected t each ther by jints. The mst cmmn jint type is the diarthrsis f articulating jints, which has a fibrus cnnective tissue capsule (ligament), cntinuus with the peristeum
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal
 Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Hand Pain & Problems
 Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
Anatmy f the hand: Hand Pain & Prblems The hand is cmpsed f many different bnes, muscles, and ligaments that allw fr a large amunt f mvement and dexterity. There are three majr types f bnes in the hand
The Musculoskeletal System. Chapter 46
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int and ut f the cell.
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int and ut f the cell.
Virginia Western Community College BIO 142 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
 Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Anemia. There are three types of Anemia that effect EB patients. They are Iron Deficiency, Chronic Inflammatory and Nutritional.
 Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
1A Human Biology Food, Digestion and Associated Body Systems
 1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
The Skeletal System. Chapter 4
 The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
The Skeletal System Chapter 4 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Support o Provides shape Protection o Internal organs Movement o Provides structure for muscle to act upon Storage o Minerals & fat Blood
REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014
 REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we revise: the prcess f phtsynthesis the prcesses invlved in cellular respiratin Summary Phtsynthesis (Slutins
REVISION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION 18 JUNE 2014 Lessn Descriptin In this lessn, we revise: the prcess f phtsynthesis the prcesses invlved in cellular respiratin Summary Phtsynthesis (Slutins
Mitosis and Meiosis Lecture Notes
 Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
Bilgy Mitsis and Meisis Lecture Ntes Name Per Learning Gals Quiz #6: December 6th Describe what happens during interphase Identify steps f mitsis/meisis by picture and functin Explain the diseases that
The Nervous System: General and Special Senses Pearson Education, Inc.
 18 The Nervous System: General and Special Senses Introduction Sensory information arrives at the CNS Information is picked up by sensory receptors Sensory receptors are the interface between the nervous
18 The Nervous System: General and Special Senses Introduction Sensory information arrives at the CNS Information is picked up by sensory receptors Sensory receptors are the interface between the nervous
Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Lecture Outline Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Functin Lecture Outline Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane separates the living cell frm its surrundings. This thin barrier, 8 nm thick, cntrls traffic int
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Perid Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview 1. What are the three key rles f cell divisin? State each rle, and give an example. 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Cncept 12.1 Mst cell divisin results
Name Perid Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview 1. What are the three key rles f cell divisin? State each rle, and give an example. 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Cncept 12.1 Mst cell divisin results
The Digestive System. May 16, The Digestive System.notebook
 3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
Anatomy, Histology, & Embryology of the Pancreas
 Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue? a. It
BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue? a. It
Fitness & Weight Training I Manual School Year Revised, Spring 2008
 1 Fitness & Weight Training I Manual 2007-2008 Schl Year Revised, Spring 2008 2 Part! REVIEW MATERIAL. TERMINOLOGY: Vlume The number f sets & reps used in a particular wrkut r phase, i.e. 3 sets f 10 repetitins.
1 Fitness & Weight Training I Manual 2007-2008 Schl Year Revised, Spring 2008 2 Part! REVIEW MATERIAL. TERMINOLOGY: Vlume The number f sets & reps used in a particular wrkut r phase, i.e. 3 sets f 10 repetitins.
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiratin: Harvesting Chemical Energy Lecture Outline Overview: Life Is Wrk T perfrm their many tasks, living cells require energy frm utside surces. Energy enters mst ecsystems as
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiratin: Harvesting Chemical Energy Lecture Outline Overview: Life Is Wrk T perfrm their many tasks, living cells require energy frm utside surces. Energy enters mst ecsystems as
The Senses. Chapter 10 7/8/11. Introduction
 Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
ANAT2011 Anatomy Notes
 ANAT2011 Anatmy Ntes Mdule 1: Hw t Speak Anatmy... 2 Mdule 2: Nervus System... 4 Mdule 3: Sniff, Swallw, Speak!... 14 Mdule 4: Just Breathe... 35 Mdule 5: Wh are the Great 8?... 43 Mdule 6: N Guts, N Glry...
ANAT2011 Anatmy Ntes Mdule 1: Hw t Speak Anatmy... 2 Mdule 2: Nervus System... 4 Mdule 3: Sniff, Swallw, Speak!... 14 Mdule 4: Just Breathe... 35 Mdule 5: Wh are the Great 8?... 43 Mdule 6: N Guts, N Glry...
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Chapter 26: The Urinary System. An Overview of the Urinary System, p The Kidneys, p. 952
 Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
Chapter 26: The Urinary System An Overview f the Urinary System, p. 952 Objective 1. Identify the cmpnents f the urinary system and describe the functins it perfrms. Figure 26-1 The urinary system has
MEMBRANES. Overview of membranes. The chemical components of membranes
 MEMBRANES This text is divided int seven majr sectins: Overview f membranes The chemical cmpnents f membranes Membrane structure Membranes and cmpartmentalizatin Membrane receptrs Sme receptrs invlve secnd
MEMBRANES This text is divided int seven majr sectins: Overview f membranes The chemical cmpnents f membranes Membrane structure Membranes and cmpartmentalizatin Membrane receptrs Sme receptrs invlve secnd
Psychology Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception
 Psychlgy Chapter 5: Sensatin and Perceptin Sensatin: the stimulus-detectin prcess by which ur sense rgans respnd t and translate envirnmental stimuli int nerve impulses that are sent t the brain Perceptin:
Psychlgy Chapter 5: Sensatin and Perceptin Sensatin: the stimulus-detectin prcess by which ur sense rgans respnd t and translate envirnmental stimuli int nerve impulses that are sent t the brain Perceptin:
Human Biological Science 1
 SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Human Bilgical Science 1 SECTION 1 GENERAL INFORMATION Subject Cde: BIOH111 Award/s: Ttal curse credit pints: Level: Bachelr f Health Science (Naturpathy) 128 1 st Year Bachelr
SUBJECT OUTLINE Subject Name: Human Bilgical Science 1 SECTION 1 GENERAL INFORMATION Subject Cde: BIOH111 Award/s: Ttal curse credit pints: Level: Bachelr f Health Science (Naturpathy) 128 1 st Year Bachelr
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Sensory System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Sessin Examinatin f the Sensry System Reviewed & ratified by: Dr D Smith Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr R Davies Cnsultant Neurlgist Dr B Michael Neurlgy Clinical Lecturer Dr J Williamsn
Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015. Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 14.
 Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015 Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 11. 19. 20. 8. 7. 14. 15. 12. 17. 9. 13.
Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015 Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 11. 19. 20. 8. 7. 14. 15. 12. 17. 9. 13.
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION
 SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Al Balqa Applied University. Collage of Medicine. Anatomy Lab Check List
 Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Neuranatmy 1 Lab Objectives: Identify majr cmpnents f brain. Knw majr lbes,
Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Neuranatmy 1 Lab Objectives: Identify majr cmpnents f brain. Knw majr lbes,
 Teacher Ntes fr "Hw d muscles get the energy they need fr athletic activity?" 1 In this activity, students analyze hw aerbic cellular respiratin and anaerbic fermentatin cntribute t ATP prductin in muscle
Teacher Ntes fr "Hw d muscles get the energy they need fr athletic activity?" 1 In this activity, students analyze hw aerbic cellular respiratin and anaerbic fermentatin cntribute t ATP prductin in muscle
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 3 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Integument Support Structures; Axial Skeleton
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 3 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Integument Support Structures; Axial Skeleton Integumentary System Functions Protection Sensory Synthesis The Skin Epidermis
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 3 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Integument Support Structures; Axial Skeleton Integumentary System Functions Protection Sensory Synthesis The Skin Epidermis
Autumn 2012 LEARNING OBJECTIVES BIOL&241
 CELL BIOLOGY This is information that you are expected to have or to acquire on your own. I highly recommend that you have a basic understanding of the following before continuing. Please see me if you
CELL BIOLOGY This is information that you are expected to have or to acquire on your own. I highly recommend that you have a basic understanding of the following before continuing. Please see me if you
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules: The Molecules of Life
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Functin f Large Bilgical Mlecules: The Mlecules f Life Structure and Functin f Large Bi Mlecules: Mlecules f Life CONCEPTS: 5.1 Macrmlecules are plymers, built
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 5: The Structure and Functin f Large Bilgical Mlecules: The Mlecules f Life Structure and Functin f Large Bi Mlecules: Mlecules f Life CONCEPTS: 5.1 Macrmlecules are plymers, built
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
