EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE RENAL ARTERY AND VEIN OF THE DOMESTIC PIG AN ENZYME-HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY
|
|
|
- Sheena Parks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2007), 10, No 3, EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE RENAL ARTERY AND VEIN OF THE DOMESTIC PIG AN ENZYME-HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY Summary A. VODENICHAROV 1, P. ATANASSOVA 2, P. YONKOVA 1, G. KOSTADINOV 1 & H. HRISTOV 1 1 Department of Veterinary Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Trakia University, Stara Zagora; 2 Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Medical University, Plovdiv; Bulgaria Vodenicharov, A., P. Atanassova, P. Yonkova, G. Kostadinov & H. Hristov, Expression of lipoprotein lipase in the renal artery and vein of the domestic pig an enzymehistochemical study. Bulg. J. Vet. Med., 10, No 3, Lipoproteinlipase (LPL) expression in the wall of renal artery and vein of 8 (4 male and 4 female), months old slaughtered for consumption Landrace pigs, was studied. In the renal artery, the LPL expression was observed as a irregular thick layer mostly on the luminal surface of endothelial layer and close to both intimal and media sides of the internal elastic membrane. The latter showed a various degree of fragmentation. In two of the animals lipoproteinlipase expression was also established in the Tunica media, between smooth muscle cells. In the renal vein, LPL expression was observed as a slim line on the luminal surface of the endothelium. No positive reaction was detected next to the internal elastic membrane. A large amount of LPL-positive cells was observed in the connective tissue of the venous middle shell of one of investigated animals. On the basis of obtained results, a presumption was made that LPL expression in pig renal artery and vein had a speciesrelated and individual features. Key words: lipoprotein lipase, pig, renal artery, renal vein INTRODUCTION Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) is an important enzyme, involved in the intravascular metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, ingested with food (Goldberg, 1996). It hydrolyzes the triglycerols of chylomicrons, circulating in the bloodstream, to fatty acids and glycerol (Fawcett & Jensh, 2002). LPL is synthesized and secreted by various types of cells, among which the endothelial cells of capillaries and arteries. In fat tissues and muscles, the enzyme is synthesized and secreted in a catalytically active form, by the adipocytes and myocytes, respectively and is then transported to the surface of the capillary endothelium (Pentikäinen et al., 2002). The immunohistochemical expression of LPL is proved in all layers of the arterial wall the intima, the smooth-muscle cells of the media, and the adventitia (Jonasson et al., 1987; Sako et al., 2003; Kojama et al., 2004). LPL belongs to the mammalian triacylglycerol lipase gene family, which also includes pancreatic, liver, and endo-
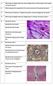
2 Expression of lipoprotein lipase in the renal artery and vein of the domestic pig... thelial lipases (Pentikäinen et al., 2002). The endothelial lipase, synthesized and secreted mostly by the endothelial cells of the blood vessels, is determined as a new member of the lipase gene family (Kojama et al., 2004). The immunological studies of Ruge et al. (2004) showed that LPL in the kidneys of mice and minks is produced by the epithelial cells of the tubules. It was also established that this enzyme can deposit in the glomerules from the blood that passes through them. According to Camps et al. (1990), expression of LPL in the large blood vessels is observed in the smooth-muscle cells of the media, while in the kidneys, a strong immunofluorescence of the vascular endothelium was established, especially in the glomerules. Recently, in our studies on renal blood vessels of a control group of dogs, and a group fed a high-calorie diet, a positive expression of LPL only in the blood vessels of the latter was established, while no such reaction was observed in the control group (Yonkova et al., 2007). In available literature, we could not find any data from similar studies on renal blood vessels of pigs, that is why we aimed to study the expression of LPL in the wall of the renal artery and vein on material, obtained from pigs, slaughtered for consumption. MATERIALS AND METHODS We studied the renal artery and vein of 8 pigs (4 male and 4 female) from the Belgian Landrace breed, aged 8 12 months, weighing kg, with a well-developed layer of subcutaneous fat. The material for the study was obtained immediately after the animals were slaughtered in a slaughterhouse, and transported in a refrigerated case to the laboratory. After careful preparation of the structures in the area of the chylus with the aid of a magnifying glass, little pieces (1 cm 3 ) with included renal artery and vein, as well as surrounding tissues, were formed and frozen in a cryostat at 20 0 С. From them, 5 7 µm cryostat cuts were prepared, upon which the enzyme-histochemical reaction for detection of lipoproteinlipase was performed by the Tween method of Gomori (Pearse, 1960). Positive reaction was registered by appearance of clusters of dark brown granules. The detection of the reaction was performed by a semi-quantitative analysis usign the score system of Atanassova (2000) to present enzyme activity as followed: (0) lack of enzyme activity; (+) weak, (++) medium and (+++) strong enzyme activity. RESULTS The light microscope studies showed that, in both blood vessels, there was an expression of lipoproteinlipase, which was manifested at different extents in the layers of vascular walls in the individual animals (Table 1). In the wall of the renal artery, LPL expression was observed in all test animals on the lumen surface of the intimal endothelial cells, and around the inner elastic membrane. On the lumen surface of the endothelium, the LPL expression was positive in the form of a dark layer with a different width along the vessel s circumference. Around the internal elastic membrane, LPL reactivity was present as a thin layer right next to the two sides (toward the intima and the media) of the membrane (Fig. 1). It should be noted that in all studied arteries, the internal elastic membrane showed different degrees of fragmentation. 156 BJVM, 10, No 3
3 A. Vodenicharov, P. Atanassova, P. Yonkova, G. Kostadinov & H. Hristov Тable 1. LPL activity in the walls of renal artery and vein Blood vessel Number and gender of dogs Renal artery Intimal coat (Tunica intima) Medium coat (Tunica media) Renal vein Intimal coat (Tunica intima) Medium coat (Tunica media) (0) lack of enzyme activity; (+) weak, (++) medium and (+++) strong enzyme activity. * * * * * * * Fig. 1. Lipoproteinlipase expression on the lumen surface (*) of endothelial cells, and on both sides of the internal elastic membrane (arrows). Bar = 50 µm. In two of the studied individuals (1 male and 1 female), i.e. 25% of all cases we found a clear LPL expression in the medium coat (Tunica media) of the two renal (left and right) arteries. Here, the positive reaction product was observed between the smooth-muscle cells of the media, and, relatively rarely, in the smooth muscle cells themselves (Fig. 2). In the renal vein s wall, the LPL expression was observed as a thin yet dense layer on the lumen surface of the endothelium. Around the internal elastic membrane, no expression of LPL was established. In one of the male pigs (12.5% of all cases), large amounts of LPL-positive cells in the connective tissue of the media in both studied veins were observed (Fig. 3). BJVM, 10, No 3 157
4 Expression of lipoprotein lipase in the renal artery and vein of the domestic pig... Fig. 2. Part of the media of a renal artery. The arrows point at the positive LPL expression in and around smooth muscle cells. Bar = 40 µm. Fig. 3. Wall of a renal vein. LPL expression on the lumen surface of the endothelium (arrows) and in the media (arrow heads). Bar = 120 µm. In the adventitia of the studied arteries and veins, the expression of LPL enzyme activity was weak. DISCUSSION Data from the performed light-microscope tests showed convincingly the presence of LPL activity in the renal artery and vein of domestic pigs. Even though the animals, from which the material was obtained, had a well-developed layer of subcutaneous fat, only in a relatively small portion of them 25% for arteries, and 12.5% for veins, did we discover reaction for LPL in the middle coat. The reaction product was 158 BJVM, 10, No 3
5 A. Vodenicharov, P. Atanassova, P. Yonkova, G. Kostadinov & H. Hristov observed mainly around the smooth muscles, and rarely in them. In this regard, our results about the renal artery differ, to an extent, from the data of Camps et al. (1990) about the presence of LPL in smooth-muscle cells in the media of large arteries, one of which is the renal artery. We consider that the established positive LPL expression, mainly outside the smooth-muscle cells in the media, probably originates from the circulating LPL, and is related to components of the extracellular matrix, as suggested by Pentikäinen et al. (2000). The observed deposition of LPL around the internal elastic membrane, fragmented at varying extent, is described for the first time, yet this localization is probably related to the initial processes of atherogenesis in the arterial wall. Because we did not observe any LPL-positive cells (mostly macrophages) in the intima, we consider that this is most probably a case of lipids penetrating from the bloodstream. An item of interest is the marked expression of LPL on the lumen surface of endothelial cells of the renal vein, since we could not find information on such a finding in any reference. The strongly expressed enzyme activity gives us reason to believe that the vein endothelium takes an active role in the destruction of chylomicrons in the blood that exits the kidney. It could be, however, hard to determine whether LPL is synthesized in the endothelium of the renal vein. Unlike the dogs who became obese after a high-calorie diet, for which there was a LPL expression in the media of the renal artery and vein in 100% of the cases (Yonkova et al., 2007), in our research, this percentage was significantly lower. According to us, this could be due to species-related, as well as individual peculiarities, associated above all to an acquired resistance towards the infiltration of lipids in the vascular wall. The grounds for this suggestion is the statement of Anestiady & Nagornev (1982), who believed that the individual reactivity of an organism is highly significant in the process of formation and regression of lipid deposits in arteries. The results from our research give us a reason to suggest that the observed expression of LPL in the media of the renal artery and vein in a comparatively low percentage of studied animals is most probably caused by individual characteristics. It should not be overruled that there is a possibility along with age advancement and the increasing extent of fatness LPL expression to be found in more, if not all, animals. It is obvious that further research into the matter of age-related peculiarities is necessary. REFERENCES Anestiady, V. & V. A. Nagornev, The Morphogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Shtiinsa Publishers, Kishinev pp Atanassova, P., Histogenesis and differentiation of subcutaneous adipose cells in the early human embryogenesis in situ. Ph.D. thesis, Medical University, Plovdiv. Camps, M., M. Reina, M. Llobera, S. Vilaro & T. Olivecrona, Lipoprotein lipase: Cellular origin and functional distribution. American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology, 258, No 4, Fawcett, D. W. & R. P. Jensh, Bloom & Fawcett s Concise Histology, 2 nd edn. Arnold, London, pp Goldberg, I. J., Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: Central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis. Journal of Lipid Research, 37, BJVM, 10, No 3 159
6 Expression of lipoprotein lipase in the renal artery and vein of the domestic pig... Jonasson, L., G. Bondjers & G. K. Hansson, Lipoprotein lipase in atherosclerosis: Its presence in smooth muscle cells and absence from macrophages. Journal of Lipid Research, 28, Kojama, Y., K. Hirata, T. Ischida, Y. Shimokawa, N. Inoue, S. Kawashima, T. Quertermous & M. Yokoyama, Endothelial lipase modulates monocyte adhesion to the vessel wall. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 52, No 279, Pearse, A., Lipases, lipases methods. In: Histochemistry, Theoretical and Applied, J. & A. Churchill, Ltd., London, pp , Pentikäinen, M. O., K. Öörni & P. T. Kovanen, Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) strongly links native and oxidized low density lipoprotein particles to decorincoated collagen: Roles for both dimeric and monomeric forms of LPL. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, Pentikäinen, M. O., R. Oksjoki, K. Öörni & P. T. Kovanen, Lipoprotein lipase in the arterial wall. Linking LPL to the arterial extracellular matrix and much more. Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, 22, Ruge, T., L. Neuger, V. Sukonina, G. Wu, S. Barath, J. Gupta, B. Frankel, B. Christophersen, K. Nordstoga, T. Olivecrona & G. Olivecrona, Lipoprotein lipase in the kidney: Activity varies widely among animal species. American Journal of Physiology and Renal Physiology, 287, Sako, T., E. Uchida, Y. Kagawa, K. Hirayama, T. Nakade & H. Taniyama, Immunohistochemical detection of apolipoprotein A-I and B-100 in canine atherosclerotic lesions. Veterinary Pathology, 40, No 3, Yonkova, P., P. Atanassova, A. Vodenicharov & M. Andonova, Enzyme histochemical expression of lipoproteilipase (LPL) in renal blood vessels in dogs fed a high calorie diet. Acta Morphologica and Anthropologica, 13, (in press). Paper received ; accepted for publication Correspondence: Assoc. Prof. A. Vodenicharov Department of Veterinary Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Trakia University, Student s Campus, 6000 Stara Zagora, Bulgaria 160 BJVM, 10, No 3
ENZYME HISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE LIVER AND ADRENAL GLANDS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY RABBITS
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2011), 14, No 3, 137 141 ENZYME HISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE LIVER AND ADRENAL GLANDS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY RABBITS Summary P. Y. YONKOVA
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2011), 14, No 3, 137 141 ENZYME HISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE LIVER AND ADRENAL GLANDS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY RABBITS Summary P. Y. YONKOVA
LOCALIZATION AND ACTIVITY OF TISSUE LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN FELINE PROSTATE GLAND
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2010), 13, No 1, 13 17 LOCALIZATION AND ACTIVITY OF TISSUE LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN FELINE PROSTATE GLAND Summary R. DIMITROV, P. YONKOVA, K. STAMATOVA, D. YOVCHEV
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2010), 13, No 1, 13 17 LOCALIZATION AND ACTIVITY OF TISSUE LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN FELINE PROSTATE GLAND Summary R. DIMITROV, P. YONKOVA, K. STAMATOVA, D. YOVCHEV
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر. Zaid. Th. Jaber
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS زيد ثامر جابر Zaid. Th. Jaber Objectives 1- Review the normal histological features of blood vessels walls. 2-define the atherosclerosis. 3- display the risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Histopathology: Vascular pathology
 Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: Vascular pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System
 Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System Piryaei May 2011 Circulatory System Heart Blood Vessels Macrovasculature (More than 0.1mm) Elastic Artery Muscular (Distributing) Artery Large Arteriol Small Vein Muscular
Part 1 Risk Factors and Atherosclerosis. LO1. Define the Different Forms of CVD
 Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Week 3: Cardiovascular Disease Learning Outcomes: 1. Define the difference forms of CVD 2. Describe the various risk factors of CVD 3. Describe atherosclerosis and its stages 4. Describe the role of oxidation,
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Lipids digestion and absorption, Biochemistry II
 Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
INFLAMM-O-WARS ACTIVITY 4B. Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis. Student Activity Page 4B. Introduction. Background A LOOK AT ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Student Activity Page 4B Introduction Chances are that every one in your class knows somebody who has had a heart attack, but how many really understand what
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Student Activity Page 4B Introduction Chances are that every one in your class knows somebody who has had a heart attack, but how many really understand what
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
The Circulatory System Dr. Sami Zaqout The circulatory system Circulatory system Blood vascular systems Lymphatic vascular systems Blood vascular systems Blood vascular systems The circulatory system Circulatory
Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy. Student Information Page 3A
 Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy Student Information Page 3A Activity Introduction: Once you get home from running around all day, your throat is probably a little dry. You go to your kitchen, get
Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy Student Information Page 3A Activity Introduction: Once you get home from running around all day, your throat is probably a little dry. You go to your kitchen, get
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease
 Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth J. Kligerman, MD Pathology of Coronary Artery Disease Seth Kligerman, MD Assistant Professor Medical Director of MRI University of Maryland Department of Radiology
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Effect of Glomerulonephritis on -A Special Reference to the Glomeru Aortic Intima- Ohi, Junji Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1987, 32 Issue Date
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Lipoproteins Metabolism
 Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism I. Chylomicrons (exogenous pathway) A. 83% triacylglycerol, 2% protein, 8% cholesterol plus cholesterol esters, 7% phospholipid (esp. phosphatidylcholine)
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism I. Chylomicrons (exogenous pathway) A. 83% triacylglycerol, 2% protein, 8% cholesterol plus cholesterol esters, 7% phospholipid (esp. phosphatidylcholine)
Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall
 Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
Histol Histopath (1 990) 5: 161-1 67 Histology and Histopathology Distribution of type IV collagen, laminin, nidogen and fibronectin in the haemodynamically stressed vascular wall Reinhold Kittelberger,
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1813 1819 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON MAJOR SALIVARY GLANDS IN PRENATAL BUFFALO (Bubalus
Histological Features of the Renal Arteries in Indian Goat (Capra hircus)
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 04 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.704.271
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
CHM333 LECTURE 34: 11/30 12/2/09 FALL 2009 Professor Christine Hrycyna
 Lipid Metabolism β-oxidation FA Acetyl-CoA Triacylglycerols (TAGs) and glycogen are the two major forms of stored energy in vertebrates Glycogen can supply ATP for muscle contraction for less than an hour
Lipid Metabolism β-oxidation FA Acetyl-CoA Triacylglycerols (TAGs) and glycogen are the two major forms of stored energy in vertebrates Glycogen can supply ATP for muscle contraction for less than an hour
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
OpenStax-CNX module: m49689 1 Cardivascular System Module 5: Structure and Function of Blood Vessels * Donna Browne Based on Structure and Function of Blood Vessels by OpenStax This work is produced by
Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance?
 1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (C.T.) Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Enumerate the general characteristics of C.T. 2. Classify C.T into C.T. proper and special types of C.T.
Acute coronary syndrome. Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA
 Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Acute coronary syndrome Dr LM Murray Chemical Pathology Block SA13-2014 Acute myocardial infarction (MI) MI is still the leading cause of death in many countries It is characterized by severe chest pain,
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System. Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD
 Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman, PhD hemn.othman@univsul.edu.iq What is the circulatory system? The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from
SHORT-TERM AND LONG-TERM EFFECT OF OXYTOCIN ON THE MORPHOLOGY AND FUNCTIONAL ACTIVITY OF FEMALE RAT SUBCUTANEOUS ADIPOSE TISSUE. P.
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 739 743) SHORT-TERM AND LONG-TERM EFFECT
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 739 743) SHORT-TERM AND LONG-TERM EFFECT
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Histology of the Cardiac System. Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department
 Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Histology of the Cardiac System Dr. Nabil Khoury Anatomy Department Objectives 1. Identify the 3 layers of the heart endocardium, myocardium, epicardium 2. Differentiate cardiacmuscle 3. Define intercalated
Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water vapour Nitrogen
 1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
1. The table shows the percentage of various gases in atmospheric air, exhaled air and in air samples collected from the alveoli and the trachea of a healthy human. Gas Atmospheric air(inhaled air) Exhaled
General pathophysiology LIPID METABOLISM
 General pathophysiology LIPID METABOLISM 1. Alimentary chylomicronemia is sustained in: 1. Lipoprotein lipase deficiency. 2. Inhibited lipoprotein lipase. 3. Hypoalbuminemia. 4. Hyperalbuminemia. 2. Direct
General pathophysiology LIPID METABOLISM 1. Alimentary chylomicronemia is sustained in: 1. Lipoprotein lipase deficiency. 2. Inhibited lipoprotein lipase. 3. Hypoalbuminemia. 4. Hyperalbuminemia. 2. Direct
BIOL2171 ANU TCA CYCLE
 TCA CYCLE IMPORTANCE: Oxidation of 2C Acetyl Co-A 2CO 2 + 3NADH + FADH 2 (8e-s donated to O 2 in the ETC) + GTP (energy) + Heat OVERVIEW: Occurs In the mitochondrion matrix. 1. the acetyl portion of acetyl-coa
TCA CYCLE IMPORTANCE: Oxidation of 2C Acetyl Co-A 2CO 2 + 3NADH + FADH 2 (8e-s donated to O 2 in the ETC) + GTP (energy) + Heat OVERVIEW: Occurs In the mitochondrion matrix. 1. the acetyl portion of acetyl-coa
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas
 Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
CVS HISTOLOGY. Dr. Nabil Khouri.
 CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
7 ANIMALS Blood Vessels.notebook. January 11, Human Blood Vessels
 Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
Human Blood Vessels 1 Arteries All arteries take blood AWAY from the heart, and most arteries carry oxygenated blood. The one exception is the PULMONARY ARTERY which carries de oxygenated blood to the
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System No cell is further than that carries nutrients. Your circulatory system km of blood vessels. Your heart beats about from the beginning of life until death. During an average lifetime,
The Circulatory System No cell is further than that carries nutrients. Your circulatory system km of blood vessels. Your heart beats about from the beginning of life until death. During an average lifetime,
Connective Tissue. Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease: A Tertiary Care Hospital Based Autopsy Study
 Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Article History Received: 03 Feb 2016 Revised: 05 Feb 2016 Accepted: 08 Feb 2016 *Correspondence to: Dr. Alpana Jain Senior demonstrator SMS Medical College, Jaipur, Rajasthan, INDIA. dr.alpana.jain@gmail.com
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID
 HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
HISTOLOGY Lecture TWO DR. ASHRAF SAID Start Of this lecture TISSUES TISSUE: A DEFINITION A group of connected and interdependent cells that cooperate to perform a specific function CONNECTIVE TISSUE The
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Annals of RSCB Vol. XV, Issue 1
 AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
AFFECTION OF SANGUINE VESSELS AND BILIARY DUCTS IN CHRONIC INTERSTITIAL FIBROUS HEPATITIS CAUSED BY MIGRATION OF ASCARIS SUUM LARVAE THROUGH PIGLETS LIVER A. F. Gal, V. Miclăuş, C. Cătoi, V. Rus, L. Oana,
The use of pathology surrogate markers in Fabry Disease. Beth L. Thurberg MD PhD Vice President of Pathology Genzyme
 Disclaimer: Presentation slides from the Rare Disease Workshop Series are posted by the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases for educational purposes only. They are for use by drug development professionals
Disclaimer: Presentation slides from the Rare Disease Workshop Series are posted by the EveryLife Foundation for Rare Diseases for educational purposes only. They are for use by drug development professionals
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
KEY COMPONENTS. Metabolic Risk Cardiovascular Risk Vascular Inflammation Markers
 CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
CardioMetabolic Risk Poor blood sugar regulation and unhealthy triglyceride and lipoprotein levels often present long before the diagnosis of type 2 Diabetes. SpectraCell s CardioMetabolic and Pre-Diabetes
PPAR history of research
 PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
Vasoprotective Properties of Aronia Melanocarpa a Histological and Morphometric Study
 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 22 Sofia 2015 Morphology Vasoprotective Properties of Aronia
Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum Bulgarian Anatomical Society Acta morphologica et anthropologica, 22 Sofia 2015 Morphology Vasoprotective Properties of Aronia
Blood. Hematopoietic Tissue
 Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
THROMBOSIS. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan
 THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
THROMBOSIS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology Pathology Department University of Jordan NORMAL BLOOD VESSEL HISTOLOGY THROMBOSIS Pathogenesis (called Virchow's triad): 1. Endothelial*
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
TISSUES. Objectives. Tissues
 TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS
 UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
UNIT 4: BLOOD VESSELS Dr. Moattar Raza Rizvi NRS237, Physiology Generalized Structure of Blood Vessels 1 Tunica interna (tunica intima) Endothelial layer that lines the lumen of all vessels In vessels
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
DRUG DISTRIBUTION. Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding
 DRUG DISTRIBUTION Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding DRUG DISTRIBUTION Drug distribution is a reversible transport of drug through the body by the systemic circulation The drug molecules
DRUG DISTRIBUTION Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding DRUG DISTRIBUTION Drug distribution is a reversible transport of drug through the body by the systemic circulation The drug molecules
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
Reducing the risk of CVD
 1 The risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) can be reduced in several ways. Lowering blood cholesterol levels and lowering blood pressure are two ways of reducing CVD. (a) (i) Complete the diagram
1 The risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) can be reduced in several ways. Lowering blood cholesterol levels and lowering blood pressure are two ways of reducing CVD. (a) (i) Complete the diagram
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
Rheological, mechanical and failure properties of biological soft tissues at high strains and rates of deformation
 Rheological, mechanical and failure properties of biological soft tissues at high strains and rates of deformation Society of Rheology Conference Salt Lake City, Utah October 10, 2007 Martin L. Sentmanat,
Rheological, mechanical and failure properties of biological soft tissues at high strains and rates of deformation Society of Rheology Conference Salt Lake City, Utah October 10, 2007 Martin L. Sentmanat,
Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease
 Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease Shu Chien Dept. of Bioengineering & Medicine UC, San Diego Presented by Ming-Shaung Ju Dept. of Mech. Eng., NCKU, Tainan Background
Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease Shu Chien Dept. of Bioengineering & Medicine UC, San Diego Presented by Ming-Shaung Ju Dept. of Mech. Eng., NCKU, Tainan Background
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
