Radiographic Positioning. Small Animal Abdominal Radiography. Lecture Outline. Matthew Paek, VMD, MS, DACVR
|
|
|
- Frank Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Small Animal Abdominal Radiography Matthew Paek, VMD, MS, DACVR 7/30/ Lecture Outline Radiographic technique Introduction to systematic review and principles of interpretation Basic abdominal radiographic anatomy 7/30/ Radiographic Positioning Multiple projections should always be obtained 2 D image of 3 D structures Superimposi on, Summa. on, and Silhouetting of structures Obtain at least 2 orthogonal (90 o ) views Important for lesion localization Additional projections can be helpful 7/30/2018 3
2 Radiographic Positioning For the abdomen, typically 2 projections obtained Ventrodorsal (VD) Lateral projection Left (preferred) or Right (GDV) Lateral Remember Projections named for the direction of the x ray beam through the patient to the film Ventrodorsal: Dorsal recumbency Dorsoventral: Sternal recumbency Right lateral (Left Right lateral): Right side down Left lateral (Right Left lateral): Left side down 7/30/ Radiographic Positioning Include the entire abdomen Cranial extent: Diaphragm Caudal extent: Greater trochanter Large dogs: May not fit on a single radiograph Radiograph the cranial and caudal aspects separately for each view 7/30/ Radiographic Projection Projection obtained at maximal (end) expiration Less superimposition of structures Longer respiratory pause Goal: Take the radiograph with no movement versus Thoracic radiographs Obtained at maximal (peak) inspiration 7/30/2018 6
3 Positioning Aids Trough Sandbags Foam blocks or wedges Sedation Troughs Tape Rope Tape 7/30/ Puppy VD projection Radiographic Positioning Proper positioning is important! Aids in recognition of normal versus pathology Poor radiographs are at best inconclusive and at worst misleading. 7/30/ So now you have a radiograph Confirm appropriate positioning and technique Entire abdomen included Patient is straight VD/DV: Dorsal spinous process on midline superimposed over the vertebrae Lateral: Transverse processes, ilium, and rib heads superimposed (mildly rotated) 7/30/2018 9
4 So now you have a radiograph Check for artifacts Positioning aids, Markers, IV tubes, ECG wires, Collars, etc Wet hair Motion 7/30/ Cat Wet Hair Artifact Cat - Motion Artifact Possible Search Methods Be Consistent Organ systems Body condition Structures outside of the abdomen Abdominal wall Serosal detail, Peritoneal and retroperitoneal spaces Liver Spleen Kidneys Urinary bladder (Prostate, Uterus) Gastrointes nal tract 7/30/2018 Dog 11 Possible Search Methods Be Consistent Organ systems Body condi on Structures outside of the abdomen Abdominal wall Serosal detail, Peritoneal and retroperitoneal spaces Liver (&GB) Spleen Kidneys Urinary bladder (Prostate, Uterus) Gastrointestinal tract 7/30/2018 Dog 12
5 Possible Search Methods Organ systems Be Consistent Body condi on Structures outside of the abdomen Abdominal wall Serosal detail, Peritoneal and retroperitoneal spaces Liver (&GB) Spleen Kidneys Urinary bladder (Prostate, Uterus) Gastrointestinal tract Cecum Colon 7/30/2018 Dog 13 Systematic Approach Describe the radiographic signs (any changes or abnormalities) Roentgen signs Radiographic opacities Skipping this step and going straight to a diagnosis may lead to misdiagnosis! Establish a Radiographic diagnosis Make a list of differential diagnoses Roentgen signs: 1. Location 2. Number 3. Opacity 4. Size 5. Shape 6. Margin 7. Function or functional implications 7/30/ Metal Radiographic Opacities: 1. Air 2. Fat 3. Soft-tissue / Fluid 4. Mineral Factors Affecting Visualization of Abdominal Organs Projection Differences in radiopacity Normal variations 7/30/
6 Factors Affecting Visualization of Abdominal Organs Projection Structures closer to the detector better evaluated Changes in position of gas and fluid Gas goes up, Fluid goes down Alterations from interventions and disease 7/30/2018 Dog 16 Factors Affecting Visualization of Abdominal Organs Differences in radiopacity Most abdominal organs are so ssue opacity Low subject contrast between structures in the abdomen Bone Air Metal Bone Soft tissue and Fluid Fat Dog 7/30/2018 Fat Metal 17 Air Factors Affecting Visualization of Abdominal Organs Differences in radiopacity Abdominal and retroperitoneal fat prevents silhouetting of adjacent soft tissue structures Increased Bone Air Metal Bone Soft tissue and Fluid ST Dog 7/30/2018 Fat Metal 18 Fat Air
7 Cats Factors Affecting Visualization of Abdominal Organs Fat Content Obese Good subject contrast Emaciated Very poor subject contrast 7/30/ Factors Affecting Visualization of Abdominal Organs Normal variations In SIZE Stomach, Colon, Urinary bladder Canine: Spleen In CONTENT Of the GI tract: Gas, Fluid, Food, Feces Body conformation Species, Breed Body condition Respiratory phase 7/30/ Interpreting the Radiograph 7/30/
8 Abdomen Dog 7/30/ Abdomen as a Whole Body condition Affects subject contrast and therefore visualization of organs Abdominal wall Abdominal distension Body wall defects 7/30/2018 Cats 23 Abdomen as a Whole Peritoneum Serosal detail Retroperitoneum Demarcated ventrally by the parietal peritoneum & dorsally by the sublumbar musculature Extends caudally to the pelvic inlet Kidneys, ureters, adrenal glands, aorta, caudal vena cava, sublumbar lymph nodes cisterna chyli 7/30/
9 Serosal Detail The ability to see the serosal margins of abdominal viscera due to the presence of outlining fat Alterations may be focal or diffuse 7/30/ Dog Serosal Detail Fat Cat Very good serosal detail Very Thin (Cachectic) Cat 7/30/2018 Poor serosal detail 26 Serosal Detail Causes of decreased serosal detail Poor technique Underexposure Immaturity Young dogs and cats due to brown fat Lack of abdominal fat Thin or poor body condition, Emaciation, Cachexia Peritoneal effusion (any type of fluid) Mass effect Mass or enlarged structure results in displacement and silhouetting of adjacent organs Peritonitis Carcinomatosis 7/30/
10 Serosal Detail Mottled serosal detail Ground glass appearance Differential diagnoses: Peritonitis Carcinomatosis Ground glass 7/30/ Dog Serosal Detail Increased Serosal Detail (free abdominal gas) Differential diagnoses: Perforated Intestine Gas Producing Bacteria Penetrating Wound Recent Laparotomy Ground glass 7/30/ Dog 8 year old Germ Shep PC: abdominal distension and retching Intestinal Perforation 7/30/
11 Abdominal Organs Visible organs Gastrointestinal tract Portions of the stomach, small intestines, and large intestine Liver Ventral and caudal ventral margins Spleen Especially in dogs Kidneys In dogs, especially the left Urinary bladder Prostate (Intact male dogs) 7/30/ Abdominal Organs Not routinely visualized Gallbladder Pancreas Sometimes seen in fat cats on VD projection Lymph nodes Adrenal glands Ovaries Uterus Prostate (Cats or neutered dogs) 7/30/ Gastrointestinal Tract Stomach Small intestines Colon 7/30/
12 GI Tract Stomach Cardia and Fundus Left craniodorsal abdomen Caudal to the left diaphragmatic crus Body Ventral Pyloric antrum (canal) Right ventrolateral abdomen 7/30/ GI Tract Stomach Appearance depends on Radiographic projection Species and Body conformation Gastric contents 7/30/ GI Tract Stomach Radiographic projection Location of the gas and fluid changes with patient position Anatomy Gravity Gas goes up, Fluid goes down Can help identify the projection RIGHT LEFT 7/30/
13 Right Lateral Radiograph RLR Gas in Fundus Fluid in Antrum 7/30/2018 Cr 37 Left Lateral Radiograph Gas in Antrum Fluid in Fundus LLR 7/30/2018 Cr 38 DV versus VD Gas in Fundus Fluid in body Gas in body (+/- antrum) Fluid in Fundus & Antrum DV VD 7/30/
14 GI Tract Stomach Species Cats VD/DV projection: J shaped The pyloric antrum is on or slightly to the right of midline on the VD/DV Cat Dog 7/30/ GI Tract Stomach Gastric axis Line from the fundus to the antrum Lateral view: Perpendicular to the spine or parallel to the ribs VD/DV: Perpendicular to the spine 7/30/ GI Tract Stomach Body conformation Dogs Gastric axis Barrel chested breeds: Parallel with the ribs Deep chested breeds: Perpendicular to the spine Barrel- Chested Average Deep- Chested Lateral 7/30/ VD View
15 GI Tract Stomach Gastric contents Type Volume (degree of gastric distension) Unless distended, it is normally within the costal arch (rib cage margin) and does not project caudal to the last ribs Dog - Stomach markedly distended with food 7/30/ year old Germ Shep PC: abdominal distension and retching Gastric Dilatation and Volvulus with Gastric Pneumatosis 7/30/ /30/
16 Feline GDV 7/30/ Guinea Pig GDV 7/30/ year old Labradoodle Vomiting and Inappetance Gastric Outflow Obstruction Fruit Pit 7/30/
17 8 year old FS DSH PC: Vomiting and Inappetance Gastric Mass Large Cell Lymphoma 7/30/ GI Small Intestines Duodenum Right sided Proximally is against the caudal surface of the liver Descending duodenum courses parallel to the body wall Dogs: Lateral, adjacent to the body wall Cats: More medial course than dogs Fat Cat 7/30/ Dog GI Small Intestines Jejunum & Ileum Variable position in the mid abdomen Distribution depends on: Body conformation Size, shape, and position of adjacent viscera Distended organs and masses displace the SI Mass effect What projection??? 7/30/
18 GI Small Intestines Obese dogs and cats Intraabdominal fat tends to displace SI into the central midabdomen In obese cats, most located in the right mid abdomen Cat 7/30/ year Lab PC abdominal distension Intraperitoneal Lipoma Cat 7/30/ GI Tract Small Intestines Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum Contains variable amounts of intraluminal gas Cats have less intraluminal gas Peristalsis Cats: String of pearls What projection??? Cat 7/30/ Barium Upper GI Study R
19 GI Tract Small Intestines Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum Maximal Diameter (serosa to serosa) Dogs: <1.6x the height of L5 at the midbody (narrowest) < 2 3x the width of a rib < width of an intercostal space *The lateral projection is used to evaluate vertebral body height b c a 7/30/ GI Tract Small Intestines Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum Maximal Diameter (serosa to serosa) Cats: < 2x the height of L4 at the midbody < 2x the height of the cranial L2 endplate < 12 mm (US) b a *The lateral projection is used to evaluate vertebral body height 7/30/ GI Tract Small Intestines Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum Maximal Diameter (serosa to serosa) Similar in diameter to each other Abnormal if > 1.5 2x (50 100%) larger than other segments = Two populations (little/normal ones & big ones) (Duodenum may normally be mildly larger than other segments) Duodenum 7/30/
20 3 year old DSHA PC: Vomiting 7/30/ year old Mixed Breed PC: Vomiting Linear foreign body anchored in the stomach 7/30/ Year Old Pitbull PC: Vomiting 7/30/
21 8 year old Germ Shep PC: Vomiting, abdominal pain, recumbent 7/30/ Mesenteric Torsion 7/30/ GI Tract Large Intestines Cecum (c): Right mid, Level of L3 Dogs: cork screw or C shaped Often contains gas Cats: Small, Not usually visible Ascending colon (a): Right mid to cranial Transverse colon (t): Caudal to stomach Descending colon (d): Left Rectum (r): Pelvic canal and caudal Dog Cat 7/30/
22 GI Tract Large Intestines Cecum Colon 7/30/ year old Jack Russel Terrier PC: vomiting and inappetance. Recently ate a cow bone Signs and Symptoms: 7/30/ year old Jack Russel Terrier PC: vomiting and inappetance. Recently ate a cow bone Post Pneumocolonogram Mineral material within the ileum 7/30/
23 7yo Lab Straining to defecate and pacing 7/30/ /30/ /30/
24 7/30/ Liver Cranial abdomen Caudal to and conforms to the diaphragm Caudoventral margin: Right lateral view: Right medial lobe Left lateral view: Left lateral lobe 7/30/ Liver Cranial abdomen Caudal to and conforms to the diaphragm Caudoventral margin: Right lateral view: Right medial lobe Left lateral view: Left lateral lobe 7/30/
25 Liver Quadrate - Near midline, Ventral Left medial - Cranial, Ventral Right medial - Cranial, Ventral Left lateral - Caudal, Ventral Right lateral - Cranial, more dorsal Caudate - Caudal-dorsal 7/30/ Liver Assessment: Does not extend caudal to the costal arch Sharp caudoventral margins (not rounded) Normal gastric axis // to ribs or to spine 7/30/ Liver Assessment: Does not extend caudal to the costal arch ( ) Sharp caudoventral margins (not rounded) Normal gastric axis // to ribs or to spine 7/30/
26 Liver Assessment: Gastric axis Normal: // to ribs, to spine Normal 7/30/ Liver Assessment: Hepatomegaly: Caudal displacement of antrum (gastric axis) Extends caudal to costal arch Rounded margins Hepatomegaly Normal 7/30/ Liver Assessment: Microhepatica: Cranial displacement of antrum (gastric axis) Hepatomegaly Normal Microhepatica 7/30/
27 Case 11 year Mixed Breed PC: Vomiting, abdominal pain, clinician is suspicious of sepsis 7/30/ Hepatic Abscess with Septic Peritonitis 7/30/ Gall bladder Right cranioventral abdomen Not usually seen Cats: When distended, may produce a bulge along the ventral hepatic silhouette Cat 7/30/
28 Gall bladder Right cranioventral abdomen Not usually seen Cats: When distended, may produce a bulge along the ventral hepatic silhouette Differential diagnosis: Hepatic nodule or mass Cat 7/30/ year Mixed Small Breed PC: Lethargy, tachypnea, recent vomiting 7/30/ Emphysematous Cholecystitis Spleen Flat, elongated Dorsal extremity Left, cranial, dorsal, lateral Caudal to the gastric fundus Ventral extremity Dogs: Variable Cats: Not seen ventrally on lateral projection Enlarged if seen along ventral abdomen 7/30/2018 Dog 84
29 Spleen Flat, elongated Dorsal extremity Left, cranial, dorsal, lateral Caudal to the gastric fundus Ventral extremity Dogs: Variable Cats: Not seen ventrally on lateral projection Enlarged if seen along ventral abdomen What projection??? VD 7/30/2018 Dog 85 8 year old Germ Shep PC: Vomiting, abdominal pain Splenic Torsion 7/30/ Kidneys Retroperitoneal Ureters not seen More mobile in cats Dog 7/30/2018 Cat 87
30 Kidneys L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 Retroperitoneal Ureters not seen More mobile in cats Right kidney: More difficult to visualize Adjacent to & silhouettes with caudate liver lobe Cranial margin: Dog: ~ T13 L1 Cat: ~ L1 L2 Dog L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 7/30/2018 Cat 88 Kidneys L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 Retroperitoneal Ureters not seen More mobile in cats Right kidney: Cranial margin: Dog: ~ T13 L1 Cat: ~ L1 L2 Left kidney: Cranial margin: Dog: ~ 1 vertebral body caudal to Right kidney Cat: ~ L1 L3 7/30/2018 Cat 89 Dog L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 Kidneys Kidney size: Ratio: Renal length to L2 body length VD projection Dog: x length of L2 Cats: Intact: x length of L2 Neutered: x length of L2 Dog 7/30/ Cat
31 Kidneys Kidney size: Ratio: Renal length to L2 body length VD projection Dog: x length of L2 Cats: Intact: x length of L2 Neutered: x length of L2 Dog 7/30/ Cat Case 13 year old FS DSH PC: Vomiting, Anorexia, Azotemia 7/30/ Case 13 year old FS DSH PC: Vomiting, Anorexia, Azotemia Renal Lymphoma 7/30/
32 9 yo MN DSH Underlying GI IBD Urinary Bladder Ectopic R Kidney 7/30/ Adrenal Glands Retroperitoneal Craniomedial to kidney Not normally seen Cats: Incidental mineralization Dogs: Mineralization associated with neoplasia Lateral Kidneys Cats 7/30/ Lateral VD 13 year old Beagle PC: Abdominal distension, PU/PD Mineralized Adrenal Mass 7/30/
33 Urinary Bladder Caudal ventral abdomen Cranial to pubis Ventral to descending colon and rectum Cat 7/30/ Urinary Bladder Caudal ventral abdomen Round, Tear or Pear shaped Variably sized Exerts mass effect when large Cat Mass Effect 7/30/ yo MN Scottish Terrier PC: Recurrent urinary tract infections 7/30/
34 12yo MN Scottish Terrier PC: Recurrent urinary tract infections Transitional Cell Carcinoma 7/30/ yo MI Boston Terrier PC: Straining to Urinate/Defecate with a perineal mass What s not there? 7/30/ yo MI Boston Terrier PC: Straining to Urinate/Defecate with a perineal mass Perineal hernia with bladder herniation 7/30/
35 Prostate Dog Caudal abdomen / Cranial pelvic canal Caudal to bladder, Ventral to rectum Not normally seen in cats or neutered dogs 7/30/ Prostate Caudal abdomen / Cranial pelvic canal Caudal to bladder, Ventral to rectum Fat triangle: between body wall (ventral), bladder (caudoventral margin), prostate (cranioventral margin), Not normally seen in cats or neutered dogs Bladder Prostate Dog 7/30/ Prostate Intact male dogs: Lateral: Length or height as % of Pubic brim to sacral promontory dimension Normal: < 70% (mean 56%) VD: < 50% of the pelvic inlet width 7/30/
36 9yo MN Terrier Mix PC: Straining to Urinate & Limping Prostatic Mass with Metastatic Disease 7/30/ yo MN Terrier Mix PC: Straining to Urinate & Limping 7/30/ Thank You 7/30/
Close window to return to IVIS. in collaborazione con RICHIESTO ACCREDITAMENTO. organizzato da certificata ISO 9001:2000
 in collaborazione con Close window to return to IVIS RICHIESTO ACCREDITAMENTO SOCIETÀ CULTURALE ITALIANA VETERINARI PER ANIMALI DA COMPAGNIA SOCIETÀ FEDERATA ANMVI organizzato da certificata ISO 9001:2000
in collaborazione con Close window to return to IVIS RICHIESTO ACCREDITAMENTO SOCIETÀ CULTURALE ITALIANA VETERINARI PER ANIMALI DA COMPAGNIA SOCIETÀ FEDERATA ANMVI organizzato da certificata ISO 9001:2000
GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN. VMB 960 March 25, 2013
 GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN VMB 960 March 25, 2013 REFERENCE Chapters 35-36 Pages 650-678 Chapter 37 Pages 694-701 Chapter 3 Pages 38-49 OBJECTIVES Radiography and Ultrasound
GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN VMB 960 March 25, 2013 REFERENCE Chapters 35-36 Pages 650-678 Chapter 37 Pages 694-701 Chapter 3 Pages 38-49 OBJECTIVES Radiography and Ultrasound
ABDOMINAL RADIOLOGY UNDERSTANDING
 ABDOMINAL RADIOLOGY UNDERSTANDING CACVT 2017 SPRING CONFERENCE - GREENWOOD VILLAGE, CO Amy Newfield, CVT, VTS (ECC) BluePearl Massachusetts - Waltham, MA INTRODUCTION As a technician you will likely be
ABDOMINAL RADIOLOGY UNDERSTANDING CACVT 2017 SPRING CONFERENCE - GREENWOOD VILLAGE, CO Amy Newfield, CVT, VTS (ECC) BluePearl Massachusetts - Waltham, MA INTRODUCTION As a technician you will likely be
General Abdominal Radiography
 General Abdominal Radiography Tony Pease, DVM, MS Assistant Professor of Radiology North Carolina State University Objectives Acquisition of radiographs Abdominal radiographic anatomy Radiographic patterns
General Abdominal Radiography Tony Pease, DVM, MS Assistant Professor of Radiology North Carolina State University Objectives Acquisition of radiographs Abdominal radiographic anatomy Radiographic patterns
GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN
 GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN VMB 960 March 25, 2013 REFERENCE Chapters 35-36 Pages 650-678 Chapter 37 Pages 694-701 Chapter 3 Pages 38-49 OBJECTIVES Radiography and Ultrasound
GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN VMB 960 March 25, 2013 REFERENCE Chapters 35-36 Pages 650-678 Chapter 37 Pages 694-701 Chapter 3 Pages 38-49 OBJECTIVES Radiography and Ultrasound
Abdominal Ultrasound
 Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging Control Buttons Depth The organ imaged should take up 3/4 of the screen Frequency = Penetration Use high frequencies (harmonics) for fluid filled and superficial structures
Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging Control Buttons Depth The organ imaged should take up 3/4 of the screen Frequency = Penetration Use high frequencies (harmonics) for fluid filled and superficial structures
Gastrointestinal Tract Imaging. Objectives. Reference. VMB 960 April 6, Stomach Small Intestine Colon. Radiography & Ultrasound
 Gastrointestinal Tract Imaging VMB 960 April 6, 2009 Stomach Small Intestine Colon Objectives Radiography & Ultrasound Contrast Examination of the Small Intestine Reference Chapters 45 47 Pages 750 805
Gastrointestinal Tract Imaging VMB 960 April 6, 2009 Stomach Small Intestine Colon Objectives Radiography & Ultrasound Contrast Examination of the Small Intestine Reference Chapters 45 47 Pages 750 805
What is Your Diagnosis?
 What is Your Diagnosis? Izabela Ragan, Class of 2014 Signalment Species: Canine Breed: English Bulldog Sex: Male castrated Date of birth: 04/14/11 Presenting Complaint Dog was presented for vomiting and
What is Your Diagnosis? Izabela Ragan, Class of 2014 Signalment Species: Canine Breed: English Bulldog Sex: Male castrated Date of birth: 04/14/11 Presenting Complaint Dog was presented for vomiting and
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Ultrasonography of Peritoneal and Retroperitoneal Spaces and Abdominal Lymph Nodes
 IMAGING Ultrasonography of Peritoneal and Retroperitoneal Spaces and Abdominal Lymph Nodes Clifford R. Berry, DVM, DACVR; Elizabeth Huyhn, DVM; and Danielle Mauragis, CVT University of Florida Welcome
IMAGING Ultrasonography of Peritoneal and Retroperitoneal Spaces and Abdominal Lymph Nodes Clifford R. Berry, DVM, DACVR; Elizabeth Huyhn, DVM; and Danielle Mauragis, CVT University of Florida Welcome
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
What s Your Diagnosis? Allison Crow, Class of 2014
 What s Your Diagnosis? Allison Crow, Class of 2014 Signalment: 13 year old male castrated mixed breed dog History: The patient presented to the rdvm for pain in the hind end, weakness and neck stretching
What s Your Diagnosis? Allison Crow, Class of 2014 Signalment: 13 year old male castrated mixed breed dog History: The patient presented to the rdvm for pain in the hind end, weakness and neck stretching
A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology. Outline. Technique. Technique. Principles of interpretation. Case Examples. Optimize image quality
 A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology Kacie Schmitt Felber, DVM, DACVIM Cardiology Thursday, May 17 th, 2018 Mid Atlantic States Veterinary Clinic Conference Outline Technique Principles of interpretation
A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology Kacie Schmitt Felber, DVM, DACVIM Cardiology Thursday, May 17 th, 2018 Mid Atlantic States Veterinary Clinic Conference Outline Technique Principles of interpretation
Calvin 9 year old NM DLH. Dr. Norman Ackerman Memorial Radiography Case Challenge
 September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
Radiography of the Acute Abdomen
 The 3 rd Annual Vet Education Online Veterinary Conference - July 2012 Radiography of the Acute Abdomen Dr Angela Hartman DVM Dipl. ACVR Massy University, New Zealand Vet Education Pty Ltd Vet Education
The 3 rd Annual Vet Education Online Veterinary Conference - July 2012 Radiography of the Acute Abdomen Dr Angela Hartman DVM Dipl. ACVR Massy University, New Zealand Vet Education Pty Ltd Vet Education
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to:
 RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
What s your diagnosis?
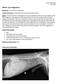 What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING: LIVER DISEASE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING: LIVER DISEASE Author : Abby Caine Categories : Vets Date : February 1, 2010 ABBY CAINE reviews both established
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING: LIVER DISEASE Author : Abby Caine Categories : Vets Date : February 1, 2010 ABBY CAINE reviews both established
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1-
 Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
Radiology of the abdomen Lecture -1- Objectives To know radiology modalities used in abdomen imaging mainly GI tract. To know advantages and disadvantages of each modality. To know indications and contraindications
GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING IN SMALL ANIMAL ONCOLOGY
 GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING IN SMALL ANIMAL ONCOLOGY Jantra Ngosuwan Suran, DVM, Dipl. ACVR, Cert Clin Res University of Pennsylvania, School of Veterinary Medicine 3900 Delancey St, Philadelphia, PA 19104
GENERAL DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING IN SMALL ANIMAL ONCOLOGY Jantra Ngosuwan Suran, DVM, Dipl. ACVR, Cert Clin Res University of Pennsylvania, School of Veterinary Medicine 3900 Delancey St, Philadelphia, PA 19104
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
In the name ofgod. Abdomen 3. Dr. Zahiri
 In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Imaging the Urogenital System
 maging the Urogenital System Tony Pease, DVM, MS, DACVR Assistant Professor of Radiology North Carolina State University Reading Thrall Chapters 42-46 Prostate Gland Not visible radiographically in normal
maging the Urogenital System Tony Pease, DVM, MS, DACVR Assistant Professor of Radiology North Carolina State University Reading Thrall Chapters 42-46 Prostate Gland Not visible radiographically in normal
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract
 Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
OUTLINE ANATOMY, RADIOGRAPHY,
 16 ABDOMEN R OUTLINE SUMMARY OF PROJECTIONS, 84 ANATOMY, 85 Abdominopelvic cavity, 85 SUMMARY OF ANATOMY, 86 SUMMARY OF PATHOLOGY, 86 EXPOSURE TECHNIQUE CHART, 87 ABBREVIATIONS, 87 RADIOGRAPHY, 88 Abdominal
16 ABDOMEN R OUTLINE SUMMARY OF PROJECTIONS, 84 ANATOMY, 85 Abdominopelvic cavity, 85 SUMMARY OF ANATOMY, 86 SUMMARY OF PATHOLOGY, 86 EXPOSURE TECHNIQUE CHART, 87 ABBREVIATIONS, 87 RADIOGRAPHY, 88 Abdominal
Instructions. Print out all three tabs of the guide to be used as a reference.
 Instructions For the Learner 1) The purpose of the observation checklist is to help evaluate the skills obtained from the course. It is also a reference and reminder for what was learned in this course.
Instructions For the Learner 1) The purpose of the observation checklist is to help evaluate the skills obtained from the course. It is also a reference and reminder for what was learned in this course.
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg
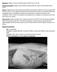 Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Signalment: Gidget, 12 year old, female spayed, Scottish Terrier, 10.7 kg Presenting Complaint: Gidget presented after having elevated liver enzymes, patchy alopecia and PU/PD. History: Gidget had been
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Imaging the Urinary Tract
 Imaging the Urinary Tract Laura Armbrust, DVM, DACVR Gregory F. Grauer, DVM, MS, DACVIM Kansas State University Radiographic and ultrasound imaging in addition to history, physical examination, and clinicopathologic
Imaging the Urinary Tract Laura Armbrust, DVM, DACVR Gregory F. Grauer, DVM, MS, DACVIM Kansas State University Radiographic and ultrasound imaging in addition to history, physical examination, and clinicopathologic
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
Corso Base di Cardiologia Unisvet 2012
 Principi di Radiologia del torace Dr Luca Ferasin DVM PhD CertVC PGCert(HE) DipECVIM-CA (Cardiology) MRCVS European and RCVS Recognised Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Introduction Thoracic radiography
Principi di Radiologia del torace Dr Luca Ferasin DVM PhD CertVC PGCert(HE) DipECVIM-CA (Cardiology) MRCVS European and RCVS Recognised Specialist in Veterinary Cardiology Introduction Thoracic radiography
What s Your Diagnosis??? Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012
 Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
What s Your Diagnosis? Sara Alves, Class of Signalment: 9-year-7-month old female spay American Miniature Eskimo dog
 What s Your Diagnosis? Sara Alves, Class of 2018 Signalment: 9-year-7-month old female spay American Miniature Eskimo dog Presenting Complaint: The patient presented on 5/30/17 with signs of lethargy and
What s Your Diagnosis? Sara Alves, Class of 2018 Signalment: 9-year-7-month old female spay American Miniature Eskimo dog Presenting Complaint: The patient presented on 5/30/17 with signs of lethargy and
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Concepts in Small Animal Thoracic Radiology Thoracic Radiology
 Concepts in Small Animal Thoracic Radiology + Radiology of the Pleural Space VMB 960 2/21/2011 Optimizing Image Quality Inherent subject contrast Thorax has high inherent subject contrast c/f abdomen Primarily
Concepts in Small Animal Thoracic Radiology + Radiology of the Pleural Space VMB 960 2/21/2011 Optimizing Image Quality Inherent subject contrast Thorax has high inherent subject contrast c/f abdomen Primarily
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING OF THE NORMAL
 DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING OF THE NORMAL COMMON MARMOSET (Callithrix jacchus) by Wencke M. Wagner Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of M.Med.Vet (Diagnostic Imaging) in the Faculty
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING OF THE NORMAL COMMON MARMOSET (Callithrix jacchus) by Wencke M. Wagner Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of M.Med.Vet (Diagnostic Imaging) in the Faculty
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
Abdominal Assessment
 Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
Abdominal Exam. Winter Quarter Adapted from previous years by Amanda Kocoloski, OMS IV
 Abdominal Exam Winter Quarter 2010 Adapted from previous years by Amanda Kocoloski, OMS IV Agenda ó History ó Anatomy ó Physical ó Prac4ce cases ó 2 gastrointes4nal complaints ó Work on incorpora4ng GI
Abdominal Exam Winter Quarter 2010 Adapted from previous years by Amanda Kocoloski, OMS IV Agenda ó History ó Anatomy ó Physical ó Prac4ce cases ó 2 gastrointes4nal complaints ó Work on incorpora4ng GI
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol
 Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol Romolo Gaspari CHAPTER 3 GOAL OF THE FAST EXAM Demonstrate free fluid in abdomen, pleural space, or pericardial space. EMERGENCY ULTRASOUND
Focused Assessment Sonography of Trauma (FAST) Scanning Protocol Romolo Gaspari CHAPTER 3 GOAL OF THE FAST EXAM Demonstrate free fluid in abdomen, pleural space, or pericardial space. EMERGENCY ULTRASOUND
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC
 IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC Tissue Embedding and Block Banking IMPC_BLK_001 Purpose Collect and fix a standard list of tissues from the complete necropsy (see IMPC Gross Pathology & Tissue Collection
IMPC phenotyping SOPs in JMC Tissue Embedding and Block Banking IMPC_BLK_001 Purpose Collect and fix a standard list of tissues from the complete necropsy (see IMPC Gross Pathology & Tissue Collection
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
X-Rays. Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM
 X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
CEA (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN)
 (CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
(CARCINOEMBRYONIC ANTIGEN) 428 C15.3 Malignant neoplasm of upper third of esophagus C15.4 Malignant neoplasm of middle third of esophagus C15.5 Malignant neoplasm of lower third of esophagus C15.8 Malignant
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Spinal radiographs are indicated for: THORACIC SPINE RADIOGRAPHY SMALL ANIMAL SPINAL RADIOGRAPHY SERIES. ImagIng EssEntIals
 PEER REVIEWED ImagIng EssEntIals SMLL NIML SPINL RDIOGRPHY SERIES THORCIC SPINE RDIOGRPHY Danielle Mauragis, CVT, and Clifford R. erry, DVM, Diplomate CVR Imaging Essentials provides comprehensive information
PEER REVIEWED ImagIng EssEntIals SMLL NIML SPINL RDIOGRPHY SERIES THORCIC SPINE RDIOGRPHY Danielle Mauragis, CVT, and Clifford R. erry, DVM, Diplomate CVR Imaging Essentials provides comprehensive information
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human;
 Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting. Focus on Colic. Indianapolis, IN, USA 2011
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting Focus on Colic Indianapolis, IN, USA 2011 Next Focus Meetings: July 22-24, 2012 - Focus on Hind Limb Lameness
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting Focus on Colic Indianapolis, IN, USA 2011 Next Focus Meetings: July 22-24, 2012 - Focus on Hind Limb Lameness
What s Your Diagnosis? Jessica Eisenbarth. Signalment: Jazz is a female intact 2 year old German Shorthaired Pointer.
 What s Your Diagnosis? Jessica Eisenbarth Signalment: Jazz is a female intact 2 year old German Shorthaired Pointer. Presenting complaint: Jazz was presented to the K-State emergency service on August
What s Your Diagnosis? Jessica Eisenbarth Signalment: Jazz is a female intact 2 year old German Shorthaired Pointer. Presenting complaint: Jazz was presented to the K-State emergency service on August
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University
 Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Understand the components and functions
Dr. Fawzy Elnady Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Cairo University Objectives By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Understand the components and functions
Clinical & Sonographic Approach To GI Disease, Obstructions & Foreign Bodies Parts 1 & 2
 Clinical & Sonographic Approach To GI Disease, Obstructions & Foreign Bodies Parts 1 & 2 Eric Lindquist DMV (Italy), Cert./President IVUSS Further information regarding interventional procedures and case
Clinical & Sonographic Approach To GI Disease, Obstructions & Foreign Bodies Parts 1 & 2 Eric Lindquist DMV (Italy), Cert./President IVUSS Further information regarding interventional procedures and case
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Life is hard. Question? Abdominal Imaging: The practical Utility of Radiography and Ultrasound 2/16/2012
 Abdominal Imaging: The practical Utility of Radiography and Ultrasound Jonathan Hayles, DVM, MS, Dipl ACVR Life is hard Internist Surgeon Oncologist Neurologist Dermatologist Radiologist!!! The digital
Abdominal Imaging: The practical Utility of Radiography and Ultrasound Jonathan Hayles, DVM, MS, Dipl ACVR Life is hard Internist Surgeon Oncologist Neurologist Dermatologist Radiologist!!! The digital
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
