Physics (CT VI-Cone Beam CT)
|
|
|
- Briana George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SSK15 Physics (CT VI-Cone Beam CT) W ednesday, Dec. 2 10:30AM - 12:00PM Location: S403B CT PH AMA PRA Category 1 Credits : 1.50 ARRT Category A+ Credits: 1.50 Stephen J. Glick, PhD, Silver Spring, MD (Moderator) Nothing to Disclose Bruce R. Whiting, PhD, Pittsburgh, PA (Moderator) Nothing to Disclose Sub-Events SSK15-01 Accurate Perfusion Maps from C-arm Cone Beam CT Perfusion Acquisition: A Canine Study SSK15-02 W ednesday, Dec. 2 10:30AM - 10:40AM Location: S403B Kai Niu, MS, Madison, WI (Presenter) Nothing to Disclose Pengfei Yang, Shanghai, China (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Beverly A. Kienitz, MD, DDS, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Ke Li, PhD, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Sebastian Schafer, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Consultant, Siemens AG Kevin Royalty, PhD,MBA, Hoffman Estates, IL (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Siemens AG Charles M. Strother, MD, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Research Consultant, Siemens AG Research support, Siemens AG License agreement, Siemens AG Guang-Hong Chen, PhD, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Research funded, General Electric Company; Research funded, Siemens AG C-arm cone beam CT perfusion (CBCTP) has shown promise to generate relatively accurate perfusion parameters. However, high noise, inadequate temporal resolution and temporal sampling due to the inferior detector dynamic range and slow gantry rotation can limit this accuracy. In this study we address these problems using newly developed techniques. Seven canines underwent endovascular surgery with IACUC approval. Acute ischemic stroke was introduced in five of the subjects through large vessel occlusion, with the remaining two subjects serving as controls with no stroke imparted. CTP was performed 3.5 hours post-induction and immediately followed by a CBCTP acquisition with a bi plane system. CTP images were reconstructed using vendor's software, CBCTP images were reconstructed and post processed to reduce noise (using Prior Image Constrained Compressed Sensing (PICCS)) and to enhance temporal resolution and sampling (using the TEmporal REsolution and SAmpling Recovery (TERESAR)). The CTP and CBCTP images were co registered, reformatted into 5mm slices and processed with the same software to compute perfusion maps. Arterial input functions (AIF) were selected at the same region (basilar artery) for both datasets. The maps were then randomized and reviewed by two experienced interventional neuroradiologists. Image quality scores as well as the confidence of diagnostic decision were recorded. The noise in the post-processed CBCTP images was greatly reduced and 0.5s temporal resolution and sampling was achieved. The AIF was well recovered compared to the CTP dataset. Image quality scores show no statistical difference between CTP and CBCTP maps, and the confidence evaluations indicate strong agreement between the two imaging modalities for making stroke diagnoses. By improving contrast to noise ratio and enhancing both temporal resolution and sampling density for CBCTP scans, perfusion maps were generated that correlate well with conventional CTP acquisitions. With the ability to produce accurate perfusion maps with C- arm systems in interventional suites, we now have the possibility to perform CBCTP scans pre- and post-interventional treatment for rapid patient diagnosis without transferring the patient. The workflow of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke patient can be further optimized using this technique, potentially delivering improved patient outcomes. Time-resolved Contrast-enhanced Cone Beam CT Imaging of Livers in Rabbits W ednesday, Dec. 2 10:40AM - 10:50AM Location: S403B Yuncheng Zhong, PhD, Houston, TX (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Sanjay Gupta, MD, Houston, TX (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Chao-Jen Lai, PhD, Houston, TX (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Tianpeng Wang, Houston, TX (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Chris C. Shaw, PhD, Houston, TX (Presenter) Nothing to Disclose Currently available cone beam CT (CBCT) imaging methods do not allow temporal information with a single scan. We investigated the use of a time-resolved CBCT method to generate multiple phase imaging with a single post-injection scan and measured the contrast time-density curves in rabbit livers. Such information may help guide and transcatheter arterial interventional procedures.
2 Contrast agents were injected into hepatic artery of rabbits with implanted VX-2 hepatic tumors with a rate of 0.5 ml/second and 8 ml in total. Two CBCT scans were made before and after the injection. Two flat panel (Varian 4030CB and Perkin Elmer 1621) x-ray imaging systems oriented at right angle to each other were used to simultaneously acquire two sets of projection images over 360 at a rate of 7.5 frames/second during each scan. Following the scans, regular CBCT image sets were reconstructed from the projections and the pre-injection image set was subtracted from the post-injection image set to form a 3D contrast map. Each of the two orthogonal post-injection projection sets was then divided into 12 subsets, thus creating 12 orthogonal pairs of 30 limited angle projection sets which were then reconstructed to form 12 3D image sets corresponding to 12 consecutive phases over the scanning time. A maximum likelihood estimation iterative algorithm was applied for image reconstruction with the contrast map used as the constraint. We have successfully reconstructed 4D images of contrast flow and used them to obtain time-density curves over various regionsof-interest (ROIs). We have demonstrated differences of flow patterns between implanted tumors and normal tissues with the timedensity curves measured from the reconstructed 4D image data. Dual-gantry image acquisition and constrained iterative reconstruction algorithm may help obtain multi-phasic CT images with a single post-injection scan allowing contrast flow to be dynamically imaged and quantified, which may help guide transcatheter arterial interventional procedures for liver tumors. This work was supported in part by research grants: CA and CA124585, EB from NIBIB, CA138502A1, and a subcontract from NIST-ATPs. Our method provides the capability of imaging contrast injection process in organs and the measured time-density curves may be of interest to differentiate malignant and benign tumors. SSK15-03 SSK15-04 Evaluation of H(L)ctr on CBCT with a Stationary Source W ednesday, Dec. 2 10:50AM - 11:00AM Location: S403B Sarah E. McKenney, PhD, Washington, DC (Presenter) Consultant, RadCal Corporation Donovan M. Bakalyar, PhD, Detroit, MI (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Vivek Singh, PhD, Detroit, MI (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Background The equilibrium dose Deq and rise to equilibrium H(L) are recognized as dose metrics that more fully capture the contributions of scattered radiation in multi-detector CT (MDCT). Deq and H(L) are not limited to MDCT, these metrics can be used to characterize cone beam CT (CBCT) systems as well. Evaluation Five sections from two TG200/ICRU polyethylene phantoms, with a total length of 1 m, were used as the scattering material. The phantom was centered at isocenter of an interventional system (Axiom Artis dta, Siemens). A 0.6 cc thimble chamber with a realtime digitizer was centered within the middle section of the phantom. Because of symmetry at isocenter, rotation of the source was unnecessary. Serial integrated dose measurements were made with a series of 10 s exposures at collimation widths of mm at 81 kv and 0 mm of Cu. A real-time dose profile, using the same technique factors, was obtained by translating the patient gantry at a constant speed of 14.7 cm/s. H(L)ctr was calculated from the dose profile. Additional acquisitions of the dose profile were performed at tube potentials of 50 kv; the maximum and minimum collimation; and 0.9 mm Cu beam filtration. Discussion Significant cone-angle effects at the wide collimation lengths require an offset, dependent on collimation width, for equivalence to the H(L)ctr determined using the real-time dose measurements. Because of the limited fan angle, the beam does not intercept the entire diameter of the phantom and so the radial dose behavior differs substantially in form from that typical of MDCT, particularly near the edge. Conclusion Though the radial dose distribution is altered near the edge due to the small beam angle, CBCT can still be characterized along the longitudinal axis. A series of measurements with known collimation widths can be used to determine H(L)ctr. While measurements performed with the real-time dosimeter can be obtained with a single exposure, a correction must be applied. Development of a Dedicated Cone-beam CT System for Imaging of Intracranial Hemorrhage W ednesday, Dec. 2 11:00AM - 11:10AM Location: S403B Jennifer Xu, Baltimore, MD (Presenter) Research Grant, Carestream Health, Inc Alejandro Sisniega, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Carestream Health, Inc Wojciech Zbijewski, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Carestream Health, Inc Hao Dang, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Carestream Health, Inc Joseph W. Stayman, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Elekta AB; Research Grant, Varian Medical Systems, Inc Xiaohui Wang, PhD, Rochester, NY (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Carestream Health, Inc David Foos, MS, Rochester, NY (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Carestream Health, Inc Nafi Aygun, MD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Vassiliss Koliatsos, MD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Jeffrey H. Siewerdsen, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Siemens AG; Consultant, Siemens AG; Research Grant, Carestream Health,Inc; License agreement, Carestream Health,Inc; License agreement, Elekta AB; ; ; Prompt detection of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) is essential to accurate diagnosis of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and stroke. This work reports development of a dedicated cone-beam CT (CBCT) system that overcomes conventional limitations to low-contrast
3 imaging performance to provide reliable detection of acute ICH at the point of care. An imaging performance model for task-based detectability index provided the foundation for system design and optimization, including system geometry, imaging technique, and detector choice. Experimentation on a CBCT bench investigated the influence of three important factors on image quality and dose: (1) bowtie filters formed from Al and Ti with various degrees of beam flattening; (2) optional incorporation of an antiscatter grid with grid ratio ranging from 6:1 to 12:1; and (3) selection of detector readout mode (low-gain (LG), high-gain (HG), and dynamic gain (DG) readout). Performance was quantified in CBCT images of an anthropomorphic head phantom with simulated ICH inserts in terms of image uniformity, noise magnitude and correlation, CNR, and spatial resolution, and dose was measured using a Farmer chamber throughout a 16 cm CTDI phantom. CBCT images of the head acquired using optimal system geometry (source-axis and source-detector distance 75 and 110 cm, respectively) and technique (90 kv, mas / projection) exhibited good visualization of low-contrast ICH inserts: LG readout yielded CNR = 5.5; HG readout provided a 15% increase in CNR (6.3) but suffered skin line artifacts and HU inaccuracy due to barebeam saturation; DG readout yielded a 12% increase in CNR (6.2) and avoided saturation artifacts. Use of an Al bowtie filter in HG mode improved CNR by 23.4% (6.8), permitting lighter grids (or no grid) and reducing CTDIW by ~47% (10.1 mgy). A CBCT head scanner designed according to task-based performance optimization and physical experimentation exhibited image quality suitable to ICH detection. Further improvement will be gained by integration with model-based image reconstruction and artifact correction. The work supports development of a scanner prototype now underway for clinical studies. A dedicated CBCT system will permit detection of acute ICH and improve diagnosis and treatment of patients with brain injuries at the point of care in the ICU, urgent care, and mobile environments. SSK15-05 SSK15-06 Respiratory and Cardiac Motion-Compensated 5D Cone-Beam CT (CBCT) of the Thorax Region W ednesday, Dec. 2 11:10AM - 11:20AM Location: S403B Sebastian Sauppe, Heidelberg, Germany (Presenter) Nothing to Disclose Marcus Brehm, Baden-Dattwil, Switzerland (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Varian Medical Systems, Inc Pascal Paysan, PhD, Baden-Dattwil, Switzerland (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Varian Medical Systems, Inc Marc Kachelriess, PhD, Heidelberg, Germany (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose To provide motion artifact-free 5D CBCT images from a conventional flat detector-based CBCT scan. Image quality of retrospectively respiratory- and cardiac-gated volumes from flat detector cone-beam CT scans is deteriorated by severe sparse projection artifacts. These artifacts further complicate motion estimation, as it is required for motion compensated (MoCo) image reconstruction. For high quality 5D CBCT images at the same x-ray dose and the same number of projections as today's 3D CBCT we developed a double motion compensation approach based on the motion vector fields (MVFs) of respiratory as well as cardiac motion. In a first step our previously published artifact-specific cyclic motion-compensation (acmoco) approach is applied to compensate for the respiratory patient motion, thus leading to high fidelity 4D CBCT images. With this information a cyclic phase-gated deformable heart registration algorithm is applied to the respiratory motion-compensated 4D CBCT data, thus resulting in cardiac MVFs and thereby in respiratory and cardiac motion-compensated 5D CBCT images. Our new 5D MoCo approach is validated using simulated rawdata obtained by deforming a clinical patient dataset by realistic deformation fields, and by processing patient data acquired with the TrueBeam 4D CBCT system (Varian Medical Systems), as it is used in radiation therapy. The typical streak artifacts in gated, but non motion-compensated 4D CBCT reconstruction become even more severe when cardiac gating is additionally applied: In scenarios with a 10% respiratory and a 10% cardiac window only 1% of the initial data are available for reconstruction. Our double MoCo approach turned out to be very efficient and removed nearly all streak artifacts due to making use of 100% of the projection data for each reconstructed frame. The simulations show that the 5D MVFs represent the ground truth very well. The 5D MoCo patient data show fine details and no motion blurring, even in regions close to the heart where motion is fastest. Our preliminary results indicate that the proposed double motion-compensated 5D CBCT results in high quality 5D images with full dose usage. This is guaranteed because now all data contribute to each time frame. High quality 5D images are a prerequisite for precise adaptive radiation treatment. Our approach may also be useful for interventional imaging with C-arm systems. Polyenergetic Known Component Reconstruction (KCR) for Flat-panel CBCT with Unknown Material Compositions and Unknown X-ray Spectra W ednesday, Dec. 2 11:20AM - 11:30AM Location: S403B Shiyu Xu, Carbondale, IL (Presenter) Nothing to Disclose Wojciech Zbijewski, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Carestream Health, Inc Ali Uneri, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Jeffrey H. Siewerdsen, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Siemens AG; Consultant, Siemens AG; Research Grant, Carestream Health,Inc; License agreement, Carestream Health,Inc; License agreement, Elekta AB; ; ; A. Jay Khanna, MD, Bethesda, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose
4 Joseph W. Stayman, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Elekta AB; Research Grant, Varian Medical Systems, Inc Many imaging scenarios involve known devices in the field-of-view (e.g., intraoperative imaging of metal implants). Known component reconstruction (KCR), which integrates device shape and material information into the reconstruction, has demonstrated great potential to reduce metal artifacts and required x-ray exposures. However, accurate KCR requires spectral characterization of system and components (e.g., through pre-scans of devices in air - greatly reducing the practicality of KCR). In this work, we develop a calibration-free KCR that jointly estimates the patient volume and a spectral transfer function (STF) for homogeneous components from a single diagnostic scan. Because KCR decouples patient anatomy and known components, we may target high-fidelity models where they are needed most. Specifically, we adopt a polyenergetic component model while maintaining a simple monoenergetic model for the patient anatomy. We modify KCR to jointly estimate a STF with the reconstruction and component registration using alternating optimizations. We evaluate this new calibration-free KCR in cone-beam CT (CBCT) scans of objects containing metal pedicle screws with unknown material composition. The proposed methodology is compared with filtered-backprojection (FBP) and KCR using calibration scans. STFs estimated using precalibration and the modified KCR were very similar and provided a good fit to air-scan data. In CBCT studies, FBP exhibited substantial metal artifacts due to beam hardening and photon starvation while KCR methods showed a strong capability for artifact reduction. The calibration-free KCR showed better performance, likely due to its ability to adapt to additional physical effects in the diagnostic scans (e.g. increased beam hardening due to surrounding tissues). Calibration-free KCR has the capability to reduce artifacts through high-fidelity device models, outperforming FBP and a more cumbersome KCR method with precalibration. Improved image quality facilitates assessment of pedicle screw placement (including visualizations of possible complications near the device) as well as potential dose reductions. Metal artifacts are common in interventional imaging where implant knowledge is available. The proposed approach has potential widespread application in situations where visualization near implant boundaries is critical. SSK15-07 High Quality Time-resolved C-arm Cone Beam CT Angiography Images for Large Vessel Occlusion Diagnosis W ednesday, Dec. 2 11:30AM - 11:40AM Location: S403B Kai Niu, MS, Madison, WI (Presenter) Nothing to Disclose Pengfei Yang, Shanghai, China (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Yijing Wu, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Tobias Struffert JR, MD, Erlangen, Germany (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Arnd Dorfler, Erlangen, Germany (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Sebastian Schafer, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Consultant, Siemens AG Kevin Royalty, PhD,MBA, Hoffman Estates, IL (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Siemens AG Yu Deuerling-Zheng, MD, Forchheim, Germany (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Siemens AG Charles M. Strother, MD, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Research Consultant, Siemens AG Research support, Siemens AG License agreement, Siemens AG Guang-Hong Chen, PhD, Madison, WI (Abstract Co-Author) Research funded, General Electric Company; Research funded, Siemens AG With the demonstrated feasibility of measuring perfusion parameters, C-arm cone beam CT perfusion (CBCTP) scans performed directly in the interventional suite potentially enable faster patient triaging and improved patient outcomes. In this work, a method for creating time-resolved cone beam CT angiography (4D-CBCTA) images from the CBCTP acquisition and its potential benefits are discussed. Under IRB approval, 21 C-arm cone beam CT dynamic perfusion scans of 17 patients with acute ischemic strokes were acquired. For each multi-sweep CBCTP dataset, a 3D isotropic filtered back projection (FBP) image volume of each rotation was reconstructed and co-registered. All image volumes were post processed using Prior Image Constrained Compressed Sensing (PICCS) to reduce noise and TEmporal REsolution and SAmpling Recovery (TERESAR) to enhance temporal resolution and improve the temporal sampling density. The final image volumes were then imported into a research workstation enabling display of time-resolved volumetric renderings of a patient's cerebral vasculature.two experienced interventional radiologists independently evaluated the image quality and diagnosed each case. Cronbach's alpha coefficients and ROC analysis were used to evaluate the inter-observer agreement and diagnostic value of this novel image presentation. Post processing greatly reduced the noise contained in each volume and a half-second temporal resolution was achieved. Observers agreed that image quality for large cerebral arteries was very good and ROC curves demonstrated excellent diagnostic value for detecting large vessel occlusions (AUC=0.987 and 1). 4D-CBCTA derived from CBCTP datasets provides high quality images that allow accurate diagnosis of large vessel occlusions. With the ability to acquire both CBCTP images and high quality 4D-CBCTA images from a single C-arm acquisition, it may greatly reduce the time needed to transfer acute ischemic stroke patient between CT/MR room and interventional room. This technique can reduce the time from arrival to endovascular treatment for stroke patients, achieving better patient outcomes.
5 This technique can reduce the time from arrival to endovascular treatment for stroke patients, achieving better patient outcomes. SSK15-08 SSK15-09 Should Dental CBCT Devices be Equipped with Cu-filters? A Monte Carlo Organ Dose Comparison Study W ednesday, Dec. 2 11:40AM - 11:50AM Location: S403B Andreas Stratis, Leuven, Belgium (Presenter) Nothing to Disclose Guozhi Zhang, Leuven, Belgium (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Reinhilde Jacobs, Leuven, Belgium (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Ria Bogaerts, Herestraat 49, Belgium (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Hilde Bosmans, PhD, Leuven, Belgium (Abstract Co-Author) Co-founder, Qaelum NV Research Grant, Siemens AG To investigate the influence of different x-ray tube filter combinations on organ doses in a dental CBCT exam. Promax 3D Max x-ray tube (Planmeca, Finland) is equipped with 0.5mmCu and 2.5mmAl. Its equivalent source model (energy spectrum and filter description) was specified via half value layer (HVL) and air kerma measurements across the detector and by applying the Matlab Spektr tool (Mathworks,Inc). The tube housing (TH) equivalent Al filtration was also determined. Equivalent sources for different filter combinations were designed, employed to the x-ray tube and simulated: from (0 mmcu, 2.5mmAl) to (0.5mmCu, 2.5mmAl) in 0.1mmCu steps and from (0mmCu,2.5mmAl) to (0mmCu,10mmAl) in 2.5mmAl steps. Each spectrum was raytraced through a 10 cm thick water phantom to determine the attenuation each spectrum undergoes. A spectrum specific scaling factor was calculated as the quotient of the total number of photons in the spectrum to the total number of photons of the lowest HVL spectrum (0 mmcu, 2.5mmAl) which yields the same amount of energy to the detector. Each source model was then used in an EGSnrc based Monte Carlo framework to simulate the jaw protocol (FOV: 130x90 mm2, 96kV, 85.2mAs) for the Zubal head voxel model. Organ doses were calculated for each different filtration such that the detector always receives the same amount of energy. Increasing the HVL from 6.09mmAl (0mmCu,2.5mmAl,TH) to 9.05mmAl (0.5mmCu, 2.5mmAl,TH) results in dose decrease of 21.3% in skin, 9.4% decrease in cranial bone, 16.3% decrease in muscle, 6.5% decrease in ET and 16.6% decrease in blood doses. On the other hand, there is a 9.7% increase in the dose to brain, 4.5% increase in spinal bone marrow dose, 5.6% increase in eye lens dose and a 3.6 % dose increase to the thyroid. In absolute values these doses remain very low. The beam hardening impact of Cu filtration results in reducing the dose to the skin. On the other hand, the higher mean photon energy results in higher doses outside the primary beam due to more scatter radiation. For the jaw protocol, this is the case for the thyroid and the eye lenses. To determine whether or not the implementation of Cu filtration has a benefit on organ dose reduction. Ultra-High Resolution Quantitative Cone Beam CT of the Extremities with a CMOS X-ray Detector W ednesday, Dec. 2 11:50AM - 12:00PM Location: S403B Wojciech Zbijewski, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Presenter) Research Grant, Carestream Health, Inc Qian Cao, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Nothing to Disclose Joseph W. Stayman, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Elekta AB; Research Grant, Varian Medical Systems, Inc John Yorkston, PhD, Rochester, NY (Abstract Co-Author) Employee, Carestream Health, Inc Shadpour Demehri, MD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research support, General Electric Company; Researcher, Carestream Health, Inc; Consultant, Toshiba Corporation Jeffrey H. Siewerdsen, PhD, Baltimore, MD (Abstract Co-Author) Research Grant, Siemens AG; Consultant, Siemens AG; Research Grant, Carestream Health,Inc; License agreement, Carestream Health,Inc; License agreement, Elekta AB; ; ; Early detection of pathological alterations in trabecular bone could accelerate treatment and improve prognosis in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis, but is currently challenged by a lack of high resolution imaging modality capable of resolving the trabecular structure (~100 µm) while simultaneously providing diagnostic soft-tissue contrast. We investigate the feasibility of ultra-high resolution invivo imaging of trabecular bone by implementation of a CMOS x-ray detector on a previously developed extremities cone-beam CT (CBCT). CMOS detectors offer lower electronic noise (~500 electrons/pixel), faster read-out (up to 30 frames/second for 30x30 cm field of view) and higher resolution than asi flat panel detectors (FPDs) typically used in CBCT. Initial evaluation of CMOS-based extremities CBCT employed a Dalsa Xineos 1515 detector (99 µm pixels, 600 µm CsI scinitillator) and a rotating anode x-ray source (0.3 mm focal spot). Magnification was 1.25 (matching that of extremities CBCT prototype). A contrast phantom, a resolution phantom with a 127 µm Tungsten wire for measurement of Point Spread Function (PSF), and a hand phantom (real skeleton in soft tissueequivalent plastic) were imaged at 90 kvp, mas/frame and 720 projections (0.5º steps). Reconstructions of the contrast phantom show satisfactory soft tissue discrimination with adipose-to-water contrast-to-noise ratio ranging from 2.6 at 0.1 mas/frame to 5.1 at 0.5 mas/frame. Full-width half maximum of the PSF was 0.26 mm, indicating high spatial resolution. Further improvement of resolution via optimization of CsI thickness is being investigated. Images of the hand phantom show excellent visualization of the cancellous bone, with clearly delineated trabecular architecture down to ~0.2 mm. CMOS-based extremities CBCT provides high spatial resolution and diagnostic soft tissue contrast, establishing a novel platform for
6 CMOS-based extremities CBCT provides high spatial resolution and diagnostic soft tissue contrast, establishing a novel platform for in-vivo imaging of bone microarchitecture. When combined with model-based reconstruction with advanced models of detector blur, the system is anticipated to reach ~100 µm detail size, opening applications in quantitative bone morphometrics for early detection of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Major improvement in spatial resolution of extremities CBCT is achieved with a CMOS detector, enabling in-vivo quantitative trabecular morphometry for early detection of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
Cone-Beam CT for MSK Extremities
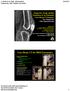 8/6/0 Diagnostic Image Quality Evaluation of an Extremity Cone-Beam CT Scanner: Pre-Clinical and First Clinical Results Abdullah Muhit Wojciech Zbijewski, J Webster Stayman John Yorkston, Nathan Packard,
8/6/0 Diagnostic Image Quality Evaluation of an Extremity Cone-Beam CT Scanner: Pre-Clinical and First Clinical Results Abdullah Muhit Wojciech Zbijewski, J Webster Stayman John Yorkston, Nathan Packard,
Dual-Energy Imaging of Bone Marrow Edema on a Dedicated Multi-Source Cone-Beam CT System for the Extremities
 Dual-Energy Imaging of Bone Edema on a Dedicated Multi-Source Cone-Beam CT System for the Extremities W Zbijewski, 1 A Sisniega, 1 JW Stayman, 1 N Packard, 2 J Yorkston, 2 G Thawait, 3 S Demehri, 3 J Fritz,
Dual-Energy Imaging of Bone Edema on a Dedicated Multi-Source Cone-Beam CT System for the Extremities W Zbijewski, 1 A Sisniega, 1 JW Stayman, 1 N Packard, 2 J Yorkston, 2 G Thawait, 3 S Demehri, 3 J Fritz,
Extremities CBCT. Advances in Cone-Beam CT and Emerging Applications: Clinical Motivation 7/14/2015
 JHU Radiology 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 JHU Radiology Advances in Cone-Beam CT and Emerging Applications: Extremities CBCT W Zbijewski Department of Biomedical
JHU Radiology 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 JHU Radiology Advances in Cone-Beam CT and Emerging Applications: Extremities CBCT W Zbijewski Department of Biomedical
Breast CT and Dosimetry
 2013 ICTP/IAEA Training Course on Radiation Protection of Patients Trieste Breast CT and Dosimetry John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FSBI, FACR Professor and Vice Chair (Research) of Radiology Professor of
2013 ICTP/IAEA Training Course on Radiation Protection of Patients Trieste Breast CT and Dosimetry John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FSBI, FACR Professor and Vice Chair (Research) of Radiology Professor of
Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT
 GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements
 Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements Jonas Andersson Medical Physicist, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Sciences University Hospital of Norrland, Umeå Sweden Contents The Computed
Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements Jonas Andersson Medical Physicist, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Sciences University Hospital of Norrland, Umeå Sweden Contents The Computed
X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT
 Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Toshiba Aquillion 64 CT Scanner. Phantom Center Periphery Center Periphery Center Periphery
 Comparison of radiation dose and imaging performance for the standard Varian x-ray tube and the Richardson Healthcare ALTA750 replacement tube for the Toshiba Aquillion CT scanners. by Robert L. Dixon,
Comparison of radiation dose and imaging performance for the standard Varian x-ray tube and the Richardson Healthcare ALTA750 replacement tube for the Toshiba Aquillion CT scanners. by Robert L. Dixon,
Acknowledgments. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Lung Nodule Detection. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Chest CT Protocols. Chest CT Protocols
 Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY. L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
 IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
IAEA Training Material on Radiation Protection in Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology RADIATION PROTECTION IN DIAGNOSTIC AND INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY L19: Optimization of Protection in Mammography
AAPM Task Group 180 Image Guidance Doses Delivered During Radiotherapy: Quantification, Management, and Reduction
 AAPM Task Group 180 Image Guidance Doses Delivered During Radiotherapy: Quantification, Management, and Reduction Parham Alaei, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology University of Minnesota NCCAAPM Fall
AAPM Task Group 180 Image Guidance Doses Delivered During Radiotherapy: Quantification, Management, and Reduction Parham Alaei, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Oncology University of Minnesota NCCAAPM Fall
Typical PET Image. Elevated uptake of FDG (related to metabolism) Lung cancer example: But where exactly is it located?
 Typical PET Image Elevated uptake of FDG (related to metabolism) Lung cancer example: But where exactly is it located? PET/CT Oncology Imaging Anatometabolic fusion images are useful in the management
Typical PET Image Elevated uptake of FDG (related to metabolism) Lung cancer example: But where exactly is it located? PET/CT Oncology Imaging Anatometabolic fusion images are useful in the management
Patient Dosimetry in Mammography and Tomosynthesis:
 2013 ICTP/IAEA Training Course on Radiation Protection of Patients Trieste Patient Dosimetry in Mammography and Tomosynthesis: What to measure, why and how John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FSBI, FACR Professor
2013 ICTP/IAEA Training Course on Radiation Protection of Patients Trieste Patient Dosimetry in Mammography and Tomosynthesis: What to measure, why and how John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FSBI, FACR Professor
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT. Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
 ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches
 Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
THE TUFFEST STUFF CT REGISTRY REVIEW Live Lecture Seminar SATURDAY CURRICULUM
 1. The CT Imaging Chain-10 major components & their functions a. The x-ray tube b. Generator c. Filter d. Pre-patient collimator e. Pre-detector collimator f. Detector system g. Analog to digital converter
1. The CT Imaging Chain-10 major components & their functions a. The x-ray tube b. Generator c. Filter d. Pre-patient collimator e. Pre-detector collimator f. Detector system g. Analog to digital converter
Mammography. Background and Perspective. Mammography Evolution. Background and Perspective. T.R. Nelson, Ph.D. x41433
 - 2015 Background and Perspective 2005 (in US) Women Men Mammography Invasive Breast Cancer Diagnosed 211,240 1,690 Noninvasive Breast Cancer Diagnosed 58,940 Deaths from Breast Cancer 40,410 460 T.R.
- 2015 Background and Perspective 2005 (in US) Women Men Mammography Invasive Breast Cancer Diagnosed 211,240 1,690 Noninvasive Breast Cancer Diagnosed 58,940 Deaths from Breast Cancer 40,410 460 T.R.
Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL
 Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL Conflict of Interest Disclaimer Employee of Aspirus Wausau
Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL Conflict of Interest Disclaimer Employee of Aspirus Wausau
True Dual Energy. Dr. Stefan Ulzheimer, Siemens Healthcare GmbH. DEfinitely Siemens
 DEfinitely Siemens True Dual Energy Dr. Stefan Ulzheimer, Siemens Healthcare GmbH International version. Not for distribution in the US. Unrestricted Siemens AG 2015 All rights reserved. The products/features
DEfinitely Siemens True Dual Energy Dr. Stefan Ulzheimer, Siemens Healthcare GmbH International version. Not for distribution in the US. Unrestricted Siemens AG 2015 All rights reserved. The products/features
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Article. Reference. Comparison of organ doses and image quality between CT and flat panel XperCT scans in wrist and inner ear examinations
 Article Comparison of organ doses and image quality between CT and flat panel XperCT scans in wrist and inner ear examinations DAMET, J, et al. Abstract The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare
Article Comparison of organ doses and image quality between CT and flat panel XperCT scans in wrist and inner ear examinations DAMET, J, et al. Abstract The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare
Peripheral Quantitative CT (pqct) Using a Dedicated Extremity Cone-Beam CT Scanner
 SPIE Medical Imaging 23 Peripheral Quantitative CT (pqct) Using a Dedicated Extremity Cone-Beam CT Scanner A. A. Muhit, a S. Arora, a M. Ogawa, a Y. Ding, a W. Zbijewski, a J. W. Stayman, a G. Thawait,
SPIE Medical Imaging 23 Peripheral Quantitative CT (pqct) Using a Dedicated Extremity Cone-Beam CT Scanner A. A. Muhit, a S. Arora, a M. Ogawa, a Y. Ding, a W. Zbijewski, a J. W. Stayman, a G. Thawait,
Bone Densitometry. Total 30 Maximum CE 14. DXA Scanning (10) 7
 STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
The Bone Densitometry Examination
 The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric
 Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
CT SCAN PROTOCOL. Shoulder
 CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
GATE MONTE CARLO DOSIMETRY SIMULATION OF MARS SPECTRAL CT
 GATE MONTE CARLO DOSIMETRY SIMULATION OF MARS SPECTRAL CT R Aamir, C Lowe, J Damet, P Carbonez, A P H Butler, N Schleich, N G Anderson MARFO, Emmanuel Geant4 User Workshop 2017, Wollongong Overview MARS
GATE MONTE CARLO DOSIMETRY SIMULATION OF MARS SPECTRAL CT R Aamir, C Lowe, J Damet, P Carbonez, A P H Butler, N Schleich, N G Anderson MARFO, Emmanuel Geant4 User Workshop 2017, Wollongong Overview MARS
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS ARRT BOARD APPROVED: JANUARY 2017 IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
True Low Dose. Exact time to display image on screen may vary upon computer and network configuration.
 RAYSCAN ALPHA PLUS True Low Dose Cone Beam CT Industry Leading Resolution High resolution images provide all the clinical information needed while keeping radiation exposure low. Endodontics - Smallest
RAYSCAN ALPHA PLUS True Low Dose Cone Beam CT Industry Leading Resolution High resolution images provide all the clinical information needed while keeping radiation exposure low. Endodontics - Smallest
PACS: ERGONOMIC CONSIDERATIONS 1
 RADIOLOGY RESEARCH Radiographic Tomosynthesis: Acquisition Parameters Michael J. Flynn, PhD Henry Ford Health System Detroit, MI Learning Objectives Learn.. 1. Appreciate the importance of scan direction,
RADIOLOGY RESEARCH Radiographic Tomosynthesis: Acquisition Parameters Michael J. Flynn, PhD Henry Ford Health System Detroit, MI Learning Objectives Learn.. 1. Appreciate the importance of scan direction,
SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report
 www.siemens.com/healthcare SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report Table of contents 1 Dosimetry and imaging performance report 5 1.1 Dose information 5 1.1.1 General
www.siemens.com/healthcare SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report Table of contents 1 Dosimetry and imaging performance report 5 1.1 Dose information 5 1.1.1 General
CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC
 CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Acknowledgments John Boone, PhD Michael McNitt-Grey,
CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Acknowledgments John Boone, PhD Michael McNitt-Grey,
Imaging of Scattered Radiation for Real Time Tracking of Tumor Motion During Lung SBRT
 Imaging of Scattered Radiation for Real Time Tracking of Tumor Motion During Lung SBRT April 25 nd, 2015 Lung Cancer Lung cancer is the most lethal cancer: Over 224,000 new diagnoses in the U.S. predicted
Imaging of Scattered Radiation for Real Time Tracking of Tumor Motion During Lung SBRT April 25 nd, 2015 Lung Cancer Lung cancer is the most lethal cancer: Over 224,000 new diagnoses in the U.S. predicted
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging
 Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Managing Radiation Risk in Pediatric CT Imaging Mahadevappa Mahesh, MS, PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FACMP, FSCCT. Professor of Radiology and Cardiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Chief Physicist
Radiation Dose Reduction: Should You Use a Bismuth Breast Shield?
 Radiation Dose Reduction: Should You Use a Bismuth Breast Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. Michael V. Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT
Radiation Dose Reduction: Should You Use a Bismuth Breast Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. Michael V. Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING. Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
Introduction. Modalities used in imaging guidance. Flat panel detector. X-ray Imaging Dose to Patients in the Era of Image-Guided Radiation Therapy
 X-ray Imaging Dose to Patients in the Era of Image-Guided Radiation Therapy George Ding, Ron Price, Charles Coffey Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN Introduction
X-ray Imaging Dose to Patients in the Era of Image-Guided Radiation Therapy George Ding, Ron Price, Charles Coffey Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, TN Introduction
Head to new heights with your imaging SCANORA 3D
 SCANORA 3D Head to new heights with your imaging Benefits at a glance The solution for dentomaxillofacial and ENT imaging Easy Patient seated for added stability during exposure. Clear, self-explinatory
SCANORA 3D Head to new heights with your imaging Benefits at a glance The solution for dentomaxillofacial and ENT imaging Easy Patient seated for added stability during exposure. Clear, self-explinatory
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic)
 Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions
 CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
SenoBright Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography Technology. Ann-Katherine Carton Sylvie Saab-Puong Matt Suminski
 SenoBright Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography Technology Ann-Katherine Carton Sylvie Saab-Puong Matt Suminski White Paper October 2012 SenoBright Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography Technology Ann-Katherine
SenoBright Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography Technology Ann-Katherine Carton Sylvie Saab-Puong Matt Suminski White Paper October 2012 SenoBright Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography Technology Ann-Katherine
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use?
 Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy: Dosimetric Aspects & Commissioning Strategies
 Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy: Dosimetric Aspects & Commissioning Strategies ICPT School on Medical Physics for Radiation Therapy Justus Adamson PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation
Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy: Dosimetric Aspects & Commissioning Strategies ICPT School on Medical Physics for Radiation Therapy Justus Adamson PhD Assistant Professor Department of Radiation
Varian Edge Experience. Jinkoo Kim, Ph.D Henry Ford Health System
 Varian Edge Experience Jinkoo Kim, Ph.D Henry Ford Health System Disclosures I participate in research funded by Varian Medical Systems. Outline of Presentation Review advanced imaging in Varian Edge Linear
Varian Edge Experience Jinkoo Kim, Ph.D Henry Ford Health System Disclosures I participate in research funded by Varian Medical Systems. Outline of Presentation Review advanced imaging in Varian Edge Linear
Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner
 Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner Zhen Qian, Gustavo Vasquez, Sarah Rinehart, Parag Joshi, Eric Krivitsky, Anna Kalynych, Dimitri Karmpaliotis,
Validation of CT Perfusion Imaging Against Invasive Angiography and FFR on a 320-MDCT Scanner Zhen Qian, Gustavo Vasquez, Sarah Rinehart, Parag Joshi, Eric Krivitsky, Anna Kalynych, Dimitri Karmpaliotis,
On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding
 Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
Title On the feasibility of speckle reduction in echocardiography using strain compounding Author(s) Guo, Y; Lee, W Citation The 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS 2014), Chicago, IL.,
Measurement of organ dose in abdomen-pelvis CT exam as a function of ma, KV and scanner type by Monte Carlo method
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 1(4): 187-194 Measurement of organ dose in abdomen-pelvis CT exam as a function of ma, KV and scanner type by Monte Carlo method M.R. Ay 1, M. Shahriari 2, S. Sarkar 3, P.
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 1(4): 187-194 Measurement of organ dose in abdomen-pelvis CT exam as a function of ma, KV and scanner type by Monte Carlo method M.R. Ay 1, M. Shahriari 2, S. Sarkar 3, P.
Feasibility of improving cone-beam CT number consistency using a scatter correction algorithm.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Medicine Faculty Papers Department of Medicine 11-4-2013 Feasibility of improving cone-beam CT number consistency using a scatter correction
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Medicine Faculty Papers Department of Medicine 11-4-2013 Feasibility of improving cone-beam CT number consistency using a scatter correction
DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING. OPTIMIZED.
 ABOUT LED DENTAL SEE THE DIFFERENCE Using our years of business insight and clinical experience as a foundation, LED Dental takes the uncertainty out of your imaging purchase decision. We offer our clients
ABOUT LED DENTAL SEE THE DIFFERENCE Using our years of business insight and clinical experience as a foundation, LED Dental takes the uncertainty out of your imaging purchase decision. We offer our clients
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals. Massimo Marenzana
 CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know
 Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
Unrivaled, End-to-End
 PHANTOMS Unrivaled, End-to-End Stereotactic QA Industry-leading 0.1mm accuracy minimizes errors at each link in the stereotactic quality assurance chain. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is governed by
PHANTOMS Unrivaled, End-to-End Stereotactic QA Industry-leading 0.1mm accuracy minimizes errors at each link in the stereotactic quality assurance chain. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is governed by
MAX-HD SRS PHANTOM THE COMPREHENSIVE END-TO-END SRS PHANTOM SCAN PLAN LOCALIZE TREAT. distributed by:
 SRS PHANTOM SCAN PLAN LOCALIZE TREAT THE COMPREHENSIVE END-TO-END SRS PHANTOM distributed by: Tel: +33 (0) 42 88 68 41 info@orion-france.com www.orion-france.com 2, Avenue du General Balfourier 75016 Paris,
SRS PHANTOM SCAN PLAN LOCALIZE TREAT THE COMPREHENSIVE END-TO-END SRS PHANTOM distributed by: Tel: +33 (0) 42 88 68 41 info@orion-france.com www.orion-france.com 2, Avenue du General Balfourier 75016 Paris,
Opportunities and Innovations in Digital Mammography John M. Sandrik, Ph.D. GE Healthcare Milwaukee, WI
 Opportunities and Innovations in Digital Mammography John M. Sandrik, Ph.D. GE Healthcare Milwaukee, WI john.sandrik@med.ge.com with many thanks to Vince Polkus, Advanced Applications Product Mgr. 1 Content
Opportunities and Innovations in Digital Mammography John M. Sandrik, Ph.D. GE Healthcare Milwaukee, WI john.sandrik@med.ge.com with many thanks to Vince Polkus, Advanced Applications Product Mgr. 1 Content
Practical Reference Dosimetry Course April 2015 PRDC Program, at a glance. Version 1.0. Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4
 Practical Reference Dosimetry Course 21-24 April 2015 PRDC 2015 Program, at a glance Version 1.0 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Quantities and Units Free air chambers Uncertainties Brachytherapy traceability
Practical Reference Dosimetry Course 21-24 April 2015 PRDC 2015 Program, at a glance Version 1.0 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Quantities and Units Free air chambers Uncertainties Brachytherapy traceability
Introduction. Measurement of Secondary Radiation for Electron and Proton Accelerators. Introduction - Photons. Introduction - Neutrons.
 Measurement of Secondary Radiation for Electron and Proton Accelerators D. Followill, Ph.D. Radiological Physics Center U. T. M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Introduction Patients undergoing radiation therapy
Measurement of Secondary Radiation for Electron and Proton Accelerators D. Followill, Ph.D. Radiological Physics Center U. T. M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Introduction Patients undergoing radiation therapy
Improving personal dosimetry of medical staff wearing radioprotective garments: Design of a new whole-body dosimeter using Monte Carlo simulations
 Improving personal dosimetry of medical staff wearing radioprotective garments: Design of a new whole-body dosimeter using Monte Carlo simulations Clarita Saldarriaga Vargas, Corinne Amalberto, Lara Struelens,
Improving personal dosimetry of medical staff wearing radioprotective garments: Design of a new whole-body dosimeter using Monte Carlo simulations Clarita Saldarriaga Vargas, Corinne Amalberto, Lara Struelens,
Learning objective. Outline. Acknowledgements. KV CBCT Imaging Part I. R Hammoud AAPM 2008 CE-Therapy (SAM) 1
 1 2 KV CBCT Imaging Part I Rabih Hammoud, MS, DABR Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Acknowledgements Indrin Chetty, PhD Teamour Nurushev, PhD Harrison Guan, PhD Jinkoo Kim, PhD JianYue Jin, PhD
1 2 KV CBCT Imaging Part I Rabih Hammoud, MS, DABR Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan Acknowledgements Indrin Chetty, PhD Teamour Nurushev, PhD Harrison Guan, PhD Jinkoo Kim, PhD JianYue Jin, PhD
Liver Perfusion Analysis New Frontiers in Dynamic Volume Imaging. Case Study Brochure Chang Gung Memorial Hospital.
 New Frontiers in Dynamic Volume Imaging dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Chang Gung Memorial Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2010-2011. All rights
New Frontiers in Dynamic Volume Imaging dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Chang Gung Memorial Hospital http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2010-2011. All rights
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT
 Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
4 Essentials of CK Physics 8/2/2012. SRS using the CyberKnife. Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest
 SRS using the CyberKnife Sonja Dieterich, PhD, DABR Associate Professor University of California Davis Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest Consulting agreements with Broncus Medical and CyberHeart, Inc. Scientific
SRS using the CyberKnife Sonja Dieterich, PhD, DABR Associate Professor University of California Davis Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest Consulting agreements with Broncus Medical and CyberHeart, Inc. Scientific
InTouch Center Local Customer Teams InTouch Agreements Parts Support
 Essential. Perfect. Fundamental Ultrasound. For advanced performance you can rely on day after day, look no further than Toshiba s Aplio 300. Scalable and versatile, it provides superior image quality
Essential. Perfect. Fundamental Ultrasound. For advanced performance you can rely on day after day, look no further than Toshiba s Aplio 300. Scalable and versatile, it provides superior image quality
Disclosures. Outline. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Introduction. Stereotactic Breast Biopsy vs Mammography: Image Quality and Dose.
 Disclosures Stereotactic Biopsy vs Mammography: and Dose None Vikas Patel, PhD, DABR Upstate Medical Physics 2014 Annual Meeting The American Association of Physicists in Medicine Austin, TX Learning Objectives
Disclosures Stereotactic Biopsy vs Mammography: and Dose None Vikas Patel, PhD, DABR Upstate Medical Physics 2014 Annual Meeting The American Association of Physicists in Medicine Austin, TX Learning Objectives
Les Outils Cliniques de Demain en Scanner Cardiaque. Cardiaque Status en ECR 2018 From Diagnosis to Prognosis
 ECR 2018 From Diagnosis to Prognosis ECR 2018 From Diagnosis to Prognosis Thursday, March 1, 2018/08:30-10:00/Room N Les Outils Cliniques de Demain en Scanner Cardiaque Cardiaque Status en 2018 Rodrigo
ECR 2018 From Diagnosis to Prognosis ECR 2018 From Diagnosis to Prognosis Thursday, March 1, 2018/08:30-10:00/Room N Les Outils Cliniques de Demain en Scanner Cardiaque Cardiaque Status en 2018 Rodrigo
The Optimum Choice for Implantologist
 The Optimum Choice for Implantologist What is essential for your practice? What s the best way to choose a 3D X-ray machine for implant treatment planning? 02 Doctor says.. There are diagnostic limitations
The Optimum Choice for Implantologist What is essential for your practice? What s the best way to choose a 3D X-ray machine for implant treatment planning? 02 Doctor says.. There are diagnostic limitations
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement
 Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Outcomes in the NLST. Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening
 Outcomes in the NLST Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening Denise R. Aberle, MD Professor of Radiology and Bioengineering David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 Disclosures I have
Outcomes in the NLST Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening Denise R. Aberle, MD Professor of Radiology and Bioengineering David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 Disclosures I have
MR QA/QC for MRgRT. Rick Layman, PhD, DABR Department of Radiology July 13, 2015
 MR QA/QC for MRgRT Rick Layman, PhD, DABR Department of Radiology July 13, 2015 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute
MR QA/QC for MRgRT Rick Layman, PhD, DABR Department of Radiology July 13, 2015 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute
Calculation of Effective Doses for Radiotherapy Cone-Beam CT and Nuclear Medicine Hawkeye CT Laura Sawyer
 Calculation of Effective Doses for Radiotherapy Cone-Beam CT and Nuclear Medicine Hawkeye CT Laura Sawyer Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, Royal United Hospital, Bath Overview Varian Acuity
Calculation of Effective Doses for Radiotherapy Cone-Beam CT and Nuclear Medicine Hawkeye CT Laura Sawyer Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, Royal United Hospital, Bath Overview Varian Acuity
SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties
 SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties Sonja Dieterich, PhD Linac/CyberKnife Technological Uncertainties 1 Linac Mechanical/Radiation Isocenters Depuydt, Tom, et al. "Computer aided analysis
SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties Sonja Dieterich, PhD Linac/CyberKnife Technological Uncertainties 1 Linac Mechanical/Radiation Isocenters Depuydt, Tom, et al. "Computer aided analysis
Mineral Density Of Subchondral Bone May Be Quantitatively Evaluated Using A Clinical Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scanner
 Mineral Density Of Subchondral Bone May Be Quantitatively Evaluated Using A Clinical Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scanner Mikael J. Turunen, PhD 1, Juha Töyräs, PhD 1, Harri Kokkonen, PhD 2, Jukka S.
Mineral Density Of Subchondral Bone May Be Quantitatively Evaluated Using A Clinical Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scanner Mikael J. Turunen, PhD 1, Juha Töyräs, PhD 1, Harri Kokkonen, PhD 2, Jukka S.
Why is CT Dose of Interest?
 Why is CT Dose of Interest? CT usage has increased rapidly in the past decade Compared to other medical imaging CT produces a larger radiation dose. There is direct epidemiological evidence for a an increase
Why is CT Dose of Interest? CT usage has increased rapidly in the past decade Compared to other medical imaging CT produces a larger radiation dose. There is direct epidemiological evidence for a an increase
The Computed Tomography Examination
 CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS The Computed Tomography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Computed Tomography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive
CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS The Computed Tomography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Computed Tomography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive
PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR.
 GE Healthcare PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR. MR Radiation Oncology Suite MAXIMIZE YOUR PRECISION. HELP MINIMIZE PATIENT COMPLICATIONS. Our goal in MR radiation oncology is to
GE Healthcare PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR. MR Radiation Oncology Suite MAXIMIZE YOUR PRECISION. HELP MINIMIZE PATIENT COMPLICATIONS. Our goal in MR radiation oncology is to
Dosimetry in digital mammography
 Dosimetry in digital mammography Professor David Dance NCCPM, Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford, United kingdom Outline Why do dosimetry? History Essentials of European breast dosimetry protocol
Dosimetry in digital mammography Professor David Dance NCCPM, Royal Surrey County Hospital, Guildford, United kingdom Outline Why do dosimetry? History Essentials of European breast dosimetry protocol
CT Dosimetry in the Clinical Environment: Methods and Analysis
 CT Dosimetry in the Clinical Environment: Methods and Analysis Manuel Arreola, Ph.D. DABR Associate Chair of Radiology Director, Medical Physics Graduate Program Department of Radiology University of Florida
CT Dosimetry in the Clinical Environment: Methods and Analysis Manuel Arreola, Ph.D. DABR Associate Chair of Radiology Director, Medical Physics Graduate Program Department of Radiology University of Florida
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS EFFECTIVE: JANUARY 1, 2016
 Computed Tomography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled with selected clinical experiences,
Computed Tomography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled with selected clinical experiences,
Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET
 Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET M. Soret, C. Riddell, S. Hapdey, and I. Buvat Abstract-- The influence of tumor diameter, tumor-tobackground activity ratio, attenuation, spatial resolution,
Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET M. Soret, C. Riddell, S. Hapdey, and I. Buvat Abstract-- The influence of tumor diameter, tumor-tobackground activity ratio, attenuation, spatial resolution,
A comparison of radiation doses from modern multi-slice Computed Tomography angiography and conventional diagnostic Angiography:
 A comparison of radiation doses from modern multi-slice Computed Tomography angiography and conventional diagnostic Angiography: Rob Loader Oliver Gosling Introduction Approached by Dr Oliver Gosling (Research
A comparison of radiation doses from modern multi-slice Computed Tomography angiography and conventional diagnostic Angiography: Rob Loader Oliver Gosling Introduction Approached by Dr Oliver Gosling (Research
Verification of treatment planning system parameters in tomotherapy using EBT Radiochromic Film
 Verification of treatment planning system parameters in tomotherapy using EBT Radiochromic Film E.B.Rajmohan¹, Pratik Kumar¹, Bhudatt Paliwal,² David Westerly², N.Gopishankar³, R.K.Bisht³, D.Tewatia²,
Verification of treatment planning system parameters in tomotherapy using EBT Radiochromic Film E.B.Rajmohan¹, Pratik Kumar¹, Bhudatt Paliwal,² David Westerly², N.Gopishankar³, R.K.Bisht³, D.Tewatia²,
Monte Carlo Modelling: a reliable and efficient tool in radiation dosimetry
 Monte Carlo Modelling: a reliable and efficient tool in radiation dosimetry G. Gualdrini, P. Ferrari ENEA Radiation Protection Institute, Bologna (Italy) Contribution to the Italy in Japan 2011 initiative
Monte Carlo Modelling: a reliable and efficient tool in radiation dosimetry G. Gualdrini, P. Ferrari ENEA Radiation Protection Institute, Bologna (Italy) Contribution to the Italy in Japan 2011 initiative
An Update of VirtualDose Software Used for Assessing Patient Organ Doses from CT Examinations
 An Update of VirtualDose Software Used for Assessing Patient Organ Doses from CT Examinations Aiping Ding, X. George Xu Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Troy, NY USA http://rrmdg.rpi.edu 1 Acknowledgements
An Update of VirtualDose Software Used for Assessing Patient Organ Doses from CT Examinations Aiping Ding, X. George Xu Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Troy, NY USA http://rrmdg.rpi.edu 1 Acknowledgements
Cone Beam CT Protocol Optimisation for Prostate Imaging with the Varian Radiotherapy OBI imaging system. Dr Craig Moore & Dr Tim Wood
 Cone Beam CT Protocol Optimisation for Prostate Imaging with the Varian Radiotherapy OBI imaging system Dr Craig Moore & Dr Tim Wood Background With the increasing use of CBCT imaging alongside complex
Cone Beam CT Protocol Optimisation for Prostate Imaging with the Varian Radiotherapy OBI imaging system Dr Craig Moore & Dr Tim Wood Background With the increasing use of CBCT imaging alongside complex
Dental ConeBeam Computed Tomography (CBCT) X-ray Systems
 Dental ConeBeam Computed Tomography (CBCT) X-ray Systems PROPOSED REVISIONS TO 4732.XXXX, 1.0 4732.#### DENTAL CONEBEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CBCT) X-RAY SYSTEMS; STATIONARY AND MOBILE. Subpart 1. Applicability.
Dental ConeBeam Computed Tomography (CBCT) X-ray Systems PROPOSED REVISIONS TO 4732.XXXX, 1.0 4732.#### DENTAL CONEBEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CBCT) X-RAY SYSTEMS; STATIONARY AND MOBILE. Subpart 1. Applicability.
Joint ICTP/IAEA Advanced School on Dosimetry in Diagnostic Radiology and its Clinical Implementation May 2009
 2033-4 Joint ICTP/ Advanced School on Dosimetry in Diagnostic Radiology and its Clinical Implementation 11-15 May 2009 Dosimetry for General Radiology and Clinical Uncertainty Peter Homolka EFOMP Training
2033-4 Joint ICTP/ Advanced School on Dosimetry in Diagnostic Radiology and its Clinical Implementation 11-15 May 2009 Dosimetry for General Radiology and Clinical Uncertainty Peter Homolka EFOMP Training
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR
 Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Managing the imaging dose during image-guided radiation therapy
 Managing the imaging dose during image-guided radiation therapy Martin J Murphy PhD Department of Radiation Oncology Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond VA Imaging during radiotherapy Radiographic
Managing the imaging dose during image-guided radiation therapy Martin J Murphy PhD Department of Radiation Oncology Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond VA Imaging during radiotherapy Radiographic
Cardiac Computed Tomography
 Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
Cardiac Computed Tomography Authored and approved by Koen Nieman Stephan Achenbach Francesca Pugliese Bernard Cosyns Patrizio Lancellotti Anastasia Kitsiou Contents CARDIAC COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Page 1.
Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Thorax Cone Beam CT Image Quality across Multiple Imaging Systems
 Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Thorax Cone Beam CT Image Quality across Multiple Imaging Systems Matthew Williams Pre-registration Clinical Scientist Velindre NHS Trust, Cardiff Computed Tomography
Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of Thorax Cone Beam CT Image Quality across Multiple Imaging Systems Matthew Williams Pre-registration Clinical Scientist Velindre NHS Trust, Cardiff Computed Tomography
Leila E. A. Nichol Royal Surrey County Hospital
 2 nd UK and Ireland Dosimetry Check User Meeting Symposium Clatterbridge Cancer Centre, 24 th October 2012 Leila E. A. Nichol Royal Surrey County Hospital Leila.Nichol@nhs.net *My experience with Dosimetry
2 nd UK and Ireland Dosimetry Check User Meeting Symposium Clatterbridge Cancer Centre, 24 th October 2012 Leila E. A. Nichol Royal Surrey County Hospital Leila.Nichol@nhs.net *My experience with Dosimetry
IGRT1 technologies. Paweł Kukołowicz Warsaw, Poland
 IGRT1 technologies Paweł Kukołowicz Warsaw, Poland Minimal prerequisite for good, efficient radiotherapy ICTP 2015 Paweł Kukołowicz 2/29 Minimal prerequisite for good, efficient radiotherapy Well trained
IGRT1 technologies Paweł Kukołowicz Warsaw, Poland Minimal prerequisite for good, efficient radiotherapy ICTP 2015 Paweł Kukołowicz 2/29 Minimal prerequisite for good, efficient radiotherapy Well trained
CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy. Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017
 CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017 Objectives Components and work flow of CyberKnife Motion management of CyberKnife
CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017 Objectives Components and work flow of CyberKnife Motion management of CyberKnife
Metal Artifact Reduction by Dual Energy CT
 Metal Artifact Reduction by Dual Energy CT Poster No.: C-0108 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper T. Johnson, F. Bamberg, A. Dierks, H.-C. Becker, M. F. Reiser; Munich/DE
Metal Artifact Reduction by Dual Energy CT Poster No.: C-0108 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper T. Johnson, F. Bamberg, A. Dierks, H.-C. Becker, M. F. Reiser; Munich/DE
Technical Study. Institution University of Texas Health San Antonio. Location San Antonio, Texas. Medical Staff. Daniel Saenz. Niko Papanikolaou.
 Technical Study Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Elekta Versa HD and Monaco Accuracy of a single isocenter, multiple brain metastases VMAT plan delivered to a pseudo-patient dosimetric gel phantom Institution
Technical Study Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Elekta Versa HD and Monaco Accuracy of a single isocenter, multiple brain metastases VMAT plan delivered to a pseudo-patient dosimetric gel phantom Institution
Uozu city/jp, Minatoku, Tokyo/JP Bones, Extremities, CT, Surgery, Physics, Artifacts, Image verification /ecr2014/C-0462
 Metal Artifact Reduction Algorithm enablesreduce metal artifacts and improvement of diagnosis in the postoperative Pedicle screws implant for Spinal Fusion: A Phantom Study Poster No.: C-0462 Congress:
Metal Artifact Reduction Algorithm enablesreduce metal artifacts and improvement of diagnosis in the postoperative Pedicle screws implant for Spinal Fusion: A Phantom Study Poster No.: C-0462 Congress:
8/3/2016. DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis. Tomosynthesis Pedigree
 DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
Low Dose Excellent Image Quality Rapid Reconstruction
 Low Dose Excellent Image Quality Rapid Reconstruction Efficient 3 in 1 Dental X-ray System CBCT > Precise 3-D Anatomical structures - Accurate diagnosis for doctors - Safe implant for patients > Significant
Low Dose Excellent Image Quality Rapid Reconstruction Efficient 3 in 1 Dental X-ray System CBCT > Precise 3-D Anatomical structures - Accurate diagnosis for doctors - Safe implant for patients > Significant
