An improved method for primary culture of rat podocytes
|
|
|
- Sara Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 & 26 International Society of Nephrology technical notes An improved method for primary culture of rat podocytes K Katsuya 1,2, E Yaoita 1, Y Yoshida 1, Y Yamamoto 2 and T Yamamoto 1 1 Department of Structural Pathology, Institute of Nephrology, Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Niigata, Japan and 2 Central Pharmaceutical Research Institute, Pharmaceutical Frontier Research Laboratories, Japan Tobacco Inc., Yokohama, Kanagawa, Japan A gentle method to isolate glomeruli simply by cutting renal cortices without forced sieving was devised in our previous study of primary podocyte culture. Yields of glomeruli isolated by this method, however, were too small to perform subculture or biological assays. In the present study, we tried an isolation method with magnetic beads and collagenase to increase the yields. Rat kidneys were perfused with magnetic particles. Renal cortices were digested with collagenase and filtered. Utilizing magnetic particles trapped within glomeruli, glomeruli were collected by attractive power of a magnet and cultured. The number of glomeruli isolated from one adult rat was more than 2 and the purity was more than 97%. About half of them were attached to culture dishes and exhibited cellular outgrowths, which were identified as podocytes by their distinct staining for podocyte markers. After 3 days of primary culture, the cellular outgrowths were subcultured. Approximately 6 podocytes were obtained per attached glomerulus. Their significant expression of podocytes markers was demonstrated by immunostaining and quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. The isolation method with magnetic beads and collagenase provides a number of glomeruli suitable for primary podocyte culture. Kidney International (26) 69, doi:1.138/sj.ki.5398; published online 19 April 26 KEYWORDS: glomerulus; epithelial cell; podocyte; primary culture; polygonal cell Correspondence: E Yaoita, Department of Structural Pathology, Institute of Nephrology, Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences, Asahimachi-dori, Niigata , Japan. ren-path@med.niigata-u.ac.jp Received 14 May 25; revised 25 August 25; accepted 5 October 25; published online 19 April 26 Cell culture has been used to elucidate the physiological and pathophysiological characteristics of podocytes. Recently, there has been a tremendous increase in studies dealing with cultured podocytes, to which immortalized mouse 1,2 and human 3 podocyte cell lines have made great contributions. However, cell lines exhibit some phenotypes different from cells in vivo. Their transcriptional levels of podocyte-specific genes are very low, although novel cell lines with stable expression of nephrin have been reported recently. 2 Primary cultured cells play a role as a bridge between cell lines and cells in vivo. Owing to the short-term culture, primary cultured podocytes, especially just after growing out from isolated glomeruli, are assumed to retain phenotypes in vivo. Podocytes, however, are easily damaged during isolation of glomeruli by the conventional sieving method. 4,5 We devised a gentle isolation method without forced sieving. 6 Consequently, a substantial number of podocytes grew out from glomeruli devoid of Bowman s capsule in the primary culture. The cells retain podocyte markers, and exhibit a unique morphology, which is different from polygonal cells with a cobblestone-like appearance. The polygonal cells have been reported as dedifferentiated podocytes in primary culture. 7 Our isolation method had a serious shortcoming since the number of retrieved glomeruli was very small. Only a few hundred glomeruli were obtained from one rat. For this reason, primary cultures of glomeruli isolated by this method are not suitable for subculture or quantitative bioassay. Recently, Takemoto et al. 8 reported on a new isolation method using kidney perfusion of magnetic beads and collagenase digestion for large-scale isolation of glomeruli from mice. Podocytes on the isolated glomeruli morphologically remains intact as confirmed by electron microscopy. In the present study, we applied this isolation method to rat primary podocyte culture and succeeded in getting a number of podocyte outgrowths sufficient for subculture, thus enabling us to evaluate their gene expression. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Isolation of glomeruli from rat kidneys Isolation procedures were based on the report of Takemoto et al. 8 for the mouse kidney. Two modifications were Kidney International (26) 69,
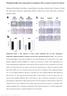
2 t e c h n i c a l n o t e s K Katsuya et al.: Primary culture of rat podocytes a c e Figure 1 Phase-contrast microscopy of isolated glomeruli and their cellular outgrowths. (a) Isolated collagenase-digested glomeruli, (b) their primary outgrowths after 1 day, (c) 2 days, and (d) 3 days of culture, (e) subcultured cells from these outgrowths, and (f) subcultured polygonal cells from glomeruli isolated by the conventional sieving method. At 1 day after starting to culture glomeruli, cellular outgrowths are observed (arrows in b). Bar: 1 mm. necessary to apply the procedures to the rat kidney. First, kidneys were perfused with a mixture of Dynabeads (f4.5 mm) and iron powder (f6 mm) instead of perfusion only with Dynabeads in the original method. This modification brought in more than a two-fold yield of isolated glomeruli. As a result, the number of glomeruli isolated from one adult rat was (mean7s.d., n ¼ 11), which was comparable to those of conventional sieving methods. Second, tissues were additionally rinsed on 7 mm nylon mesh after magnetic treatment to remove small tubular fragments. The purity of glomeruli devoid of Bowman s capsule increased to % (Figure 1a). Podocytes growing out from collagenase-digested glomeruli Approximately 4 6% of cultured collagenase-digested glomeruli adhered to the culture dishes. Cellular outgrowths were first detected within 24 h of culture (Figure 1b). They were irregular and often arborized shaped cells with long cytoplasmic processes, and often multinucleated (Figure 1c and d). Their morphology was identical to that of primary cultured podocytes as described previously, 6 and quite different from cobblestone-like appearance of polygonal cells growing out from glomeruli isolated by the conventional sieving method. 7 Subculture, namely detachment of cells from culture dishes followed by recultivation on new dishes, was first performed after 3 days of the primary culture to remove remaining glomerular cores and phagocytic cells. The b d f yield of subcultured cells was cells per cultured glomerulus used for primary culture (n ¼ 5), that is, approximately 6 cells per attached glomerulus attaching to the culture dish. The subcultured cells fundamentally exhibited the same morphology (Figure 1e) in marked contrast to polygonal cells obtained by the conventional sieving method (Figure 1f). Podocyte origin of the irregular and arborized cells was confirmed by distinct staining for podocyte markers such as podocalyxin, podocin, and synaptopodin (Figure 2), although the hypertrophic cells were likely to reduce the staining intensity. No staining for cytokeratins using anti-pan Cytokeratin antibody (Sigma, St Louis, USA) or lu-5 (Dianova, Hamburg, Germany) was found in the cultured podocytes. Significant nephrin staining was not detected in any cultured cells. In addition, the cultured podocytes exhibited desmin and connexin43 staining, which is one of the major pathological responses of podocytes in vivo 9,1 (Figure 2b,c,f,g). These findings suggest that cultured podocytes exhibit the phenotype of a pathologically activated cell in vivo. Subculture was repeated every 5 days after the first subculture. In the second and third subcultures, the cultured cells did not proliferate but gradually decreased in number, and underwent distinct hypertrophy. Their immunostaining for podocin and podocalyxin was distinctly weakened. Thus, podocytes obtained just after the first subculture are the most suitable for biological assays. Other glomerular cells growing out from collagenasedigested glomeruli Mesangial cells (Thy-1-positive cells) were less than.5% of subcultured cells (Figure 3a). The limited outgrowths of mesangial cells may be caused by the short duration of primary culture and a low concentration of fetal bovine serum in the culture medium. 11 Macrophages ED-1-positive cells were % (n ¼ 5) of subcultured cells in the case where the removal of phagocytic cells was not performed (Figure 3b). Numbers of ED-1-positive cells in the culture are likely to originate from bone marrow-derived phagocytes as reported by Schreiner and Unanue. 12 When subcultured, phagocytic cells were fed with immune complex-coated magnetic beads (Figure 3c), and removed by using a magnet. Consequently, ED- 1-positive cells decreased to % (n ¼ 4) (Figure 3d). Polygonal cells were hardly seen in the primary culture and the subculture. Our previous study showed that polygonal cells mainly come from parietal epithelial cells of Bowman s capsule. 6 Pressing tissues through a 1 mm mesh after collagenase digestion may be effective to remove Bowman s capsule, because a considerable number of polygonal cells appeared in the culture when a 15 mm mesh was used instead of a 1 mm one. None of the outgrowing cells showed staining for von Willebrand factor or rat endothelial cell antigen-1 (endothelial markers). 212 Kidney International (26) 69,
3 K Katsuya et al.: Primary culture of rat podocytes t e c h n i c a l n o t e s a Podocalyxin b Desmin c Merge d Podocin e Synaptopodin f Podocalyxin + desmin g Podocalyxin + connexin43 Figure 2 Double-labeled immunofluorescence microscopy of cellular outgrowths from glomeruli and subcultured cells. Green color shows staining for (a, c, f, and g) podocalyxin, (d) podocin, and (e) synaptopodin. Red color shows staining for (b, c, and f) desmin and (g) connexin43. Nuclei are colored blue with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. The insets in (d) and (e) show podocin and synaptopodin staining at higher power, respectively. (a) Podocalyxin is stained diffusely on cultured cells. (d) Podocin and (g) connexin43 are localized mainly at cell cell contact sites in addition to the Golgi apparatus. (e) Synaptopodin staining exhibits stress fiber-like appearance and cross striation at higher power magnification. (a e) Outgrowths after 3 days of primary culture. (f, g) Cells 1 day after subculture. Glomeruli. Bar: 5 mm. Gene expression of podocyte-specific markers in cultured podocytes Quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis was performed to examine the transcriptional levels of podocyte-specific markers. The mrna levels were compared among primary cultured podocytes, subcultured podocytes, and polygonal cells (Figure 4). The polygonal cells were subcultured from cellular outgrowths from glomeruli isolated by the conventional sieving method. Expression of nephrin, podocin, and podocalyxin was detected in both primary cultured and subcultured podocytes, but not in polygonal cells. The expression levels of subcultured podocytes were lower than those of primary cultured cells. Although no immunostaining for nephrin was found, significant levels of nephrin transcripts were detected in cultured podocytes. The reason for this discrepancy presently remains unknown, but it might be caused by too low levels of expression to detect by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibody or the protein instability in this culture system. In the second and third subcultures, podocytes dramatically decreased the transcriptional levels of nephrin, podocin, Kidney International (26) 69,
4 t e c h n i c a l n o t e s K Katsuya et al.: Primary culture of rat podocytes a c Thy-1+desmin b d ED-1+desmin ED-1+desmin Figure 3 Mesangial cells and macrophages in subcultured cells. Double-labeled immunofluorescence microscopy using antibody against (a) Thy-1 or (b) ED-1 with antidesmin antibody shows the presence of mesangial cells and macrophages (arrows in a and b). Green color indicates staining for (a) Thy-1 and (b) ED-1. Red color indicates staining for desmin. Immune complex-coated magnetic beads were easily phagocytized by small round cells in culture (arrows in c). (d) Trapping the phagocytic cells on a magnet took ED-1-positive cells off the subculture. Glomerulus, Bar: 5 mm. podocalyxin, but did not decrease those of synaptopodin, NEPH-1, or CD2-associated protein (CD2-AP) (data not shown). Especially, the expression of nephrin and podocin was hardly detected after the second and third subculture, respectively. Synaptopodin, NEPH-1 and ZO-1 were expressed in primary cultured podocytes, subcultured podocytes, and polygonal cells, although mrna levels in the polygonal cells were lower than those in the others (Figure 4). It is unlikely that podocytes constituted a part of polygonal cell population to contribute to the expression, because compatible expression of nephrin, podocin, or podocalyxin was not detected in the polygonal cells. Our previous study showed that polygonal cells from parietal epithelial cells exhibited significant staining for podocyte-specific proteins, including WT-1, synaptopodin, HSP27, and P Thus, it is possible that synaptopodin and NEPH-1 expression in polygonal cell population were attributed to cultured parietal epithelial cells. Conclusion We present here the improved method to isolate glomeruli and culture rat podocytes. The primary cultured cells retain Nephrin Podocin Podocalyxin Synaptopodin NEPH-1 ZO CD2-AP GAPDH β-actin Figure 4 mrna levels of podocyte-specific genes in cultured cells. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using mrna from primary cultured podocytes at day 4, which were the whole-cellular outgrowths from collagenase-digested glomeruli (1), from subcultured podocytes, which were cultured one more day after trypsin digestion at day 3 of primary culture of collagenase-digested glomeruli (2), or from subcultured polygonal cells, which were cultured one more day after trypsin digestion at day 5 of primary culture of glomeruli isolated by the conventional sieving method (3). ZO-1 primer pair was designed for the region common to two isoforms, namely ZO-1 a þ and ZO-1 a. Data represent means7s.d. (n ¼ 3). Po.5, Po Kidney International (26) 69,
5 K Katsuya et al.: Primary culture of rat podocytes t e c h n i c a l n o t e s podocyte characteristics in vivo, as shown by immunostaining as well as gene expression analysis. The improved method will allow us to investigate podocyte characteristics in vitro. MATERIALS AND METHODS Isolation and culture of glomeruli Male Sprague Dawley rats at ages of 7 9 weeks (Charles River Japan Atsugi, Japan) were anesthetized by an inhalation of diethyl ether. A 21-gauge butterfly needle was inserted into the abdominal aorta below the level of the renal arteries. The abdominal aorta was ligated above the renal arteries and at the site of needle insertion. A cut was made in the vena cava and the kidneys were perfused with 12 ml of phosphate-buffered saline containing Dynabeads (f4.5 mm) (Dynal ASA, Oslo, Norway) and 12 mg of iron powder (f6 mm) (Wako Chemical, Osaka, Japan). The kidney cortices were dissected and cut into small pieces (1 2 mm cubes) with a surgical blade in Hanks balanced salt solution (Invitrogen, Gland Island, NY, USA). The tissues were digested in collagenase solution containing 1 mg/ml collagenase A (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and.2 mg/ml deoxyribonuclease I (Roche Diagnostics GmbH) in Hanks balanced salt solution at 371C for 6 min with gentle agitation. The collagenase-digested tissues were gently pressed through a 1 mm cell strainer (BD Biosciences, Stockholm, Sweden) using a flattened pestle. Glomeruli containing Dynabeads and iron powder in the cell suspension were gathered by a magnetic particle concentrator (Dynal ASA) and washed at least four times with phosphate-buffered saline. Finally, collected glomeruli were suspended in suitable amount of phosphate-buffered saline and the suspension was poured onto a 7-mm cell strainer. The cell strainer was washed with phosphate-buffered saline and glomeruli on the cell strainer were carefully collected. During the procedure, kidney tissues were kept at 41C except for the collagenase digestion at 371C. Isolated glomeruli were cultured on type I collagen-coated culture dishes or glass coverslips (Asahi techno glass, Tokyo, Japan) in D-MEM/F-12 (1:1) containing 5% fetal bovine serum (Cansera International, Canada) supplemented with.5% Insulin Transferrin Selenium-A liquid media supplement (Invitrogen), 1 U/ml penicillin, and 1 mg/ml streptomycin. Cultures were incubated in a 371C humidified incubator with 5% CO 2. Subculture of glomerular outgrowths Subculture of primary cultured podocytes was performed after 3 days of culture of isolated glomeruli. Cellular outgrowths were detached with Trypsin ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid solution (Sigma, St Louis, USA) and passed through a 25 mm sieve to remove the remaining glomerular cores. The filtered cells were cultured on collagen I-coated dishes or glass coverslips for one more day, and processed for immunohistochemical analysis or RNA preparation. To remove phagocytic cells from the culture, immune complexcoated magnetic beads were prepared by sequential binding of Dynabeads M-28 Sheep anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (f2.8 mm, beads/ml) (Dynal ASA) to rabbit anti-ovalbumin antibody (1 mg/ml) (Chemicon International, Temecula, CA, USA), ovalbumin (1 mg/ml) (Sigma), and fresh rat serum. The opsonized beads were mixed with culture media, and added to the primary culture at day 3. After 6 h, cells were detached with Trypsin ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid solution and passed through a 25 mm sieve. After removing cells with phagocytized beads using a magnetic particle concentrator, remaining cells were cultured for further analyses. Immunofluorescence microscopy Podocytes cultured on glass coverslips were fixed in methanol, and processed for double-label immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies specific for podocytes, endothelial cells, mesangial cells, or macrophages as described previously. 6 Quantitative RT-PCR analysis Total RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Micro kit (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) and quantified by using the RNA 6 LabChip (Agilent Technology, Waldbronn, Germany) on a 21 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technology) as described by the manufacturer. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed on ABI PRISM 77 sequence detection system using TaqMan EZ RT-PCR Core Reagent Kit (Applied Biosystems, Branchburg, NJ, USA) and SYBER Green (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) as a probe, according to the manufacturer s direction. Four nanograms of total RNA was used for quantitative RT-PCR except that 24 ng total RNA was used to quantify nephrin expression. Target gene forward and reverse primers were designed using Primer Express 1.5 (Applied Biosystems). Commercially available predeveloped TaqMan assay reagents (Applied Biosystems) were used for the internal standard (glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and b-actin). Statistics All data were presented as means7s.d. Statistical assessment of the significance between control animals and PAN-treated animals was made by Student s t-test. Differences were considered statistically significant at Po.5. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported in part by a Grand-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Japanese Ministry for Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology. We thank Dr H Tsukaguchi (Tokushima, Japan), Dr MG Farquhar (San Diego, USA), and Dr H Kawachi (Niigata, Japan) for providing antibodies against podocin, podocalyxin (1A), and nephrin (5-1-6), respectively. We also thank Dr H Sasai, Dr M Kamada, Dr Y Saito, and Dr H Kodama (Yokohama, Japan) for discussion and Dr Y Numata (Yokohama, Japan) for primers design. REFERENCES 1. Mundel P, Reiser J, Zuniga Mejia Borja A et al. Rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell lines. Exp Cell Res 1997; 236: Schiwek D, Endlich N, Holzman L et al. Stable expression of nephrin and localization to cell cell contacts in novel murine podocyte cell lines. Kidney Int 24; 66: Saleem MA, O Hare MJ, Reiser J et al. A conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating nephrin and podocin expression. JAm Soc Nephrol 22; 13: Nørgaard JOR. Rat glomerular epithelial cells in culture: parietal or visceral epithelial origin? Lab Invest 1987; 57: Ishikawa Y, Kitamura M. Spontaneous apoptosis of podocytes in explanted glomeruli. Kidney Int 1998; 54: Yaoita E, Kurihara H, Sakai T et al. Phenotypic modulation of parietal epithelial cells of Bowman s capsule in culture. Cell Tissue Res 21; 34: Mundel P, Reiser J, Kriz W. Induction of differentiation in cultured rat and human podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol 1997; 8: Takemoto M, Asker N, Gerhardt H et al. A new method for large-scale isolation of kidney glomeruli from mice. Am J Pathol 22; 161: Kidney International (26) 69,
6 t e c h n i c a l n o t e s K Katsuya et al.: Primary culture of rat podocytes 9. Yaoita E, Kawasaki K, Yamamoto T, Kihara I. Variable expression of desmin in rat glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Pathol 199; 136: Yaoita E, Yao J, Yoshida Y et al. Up-regulation of connexin43 in glomerular podocytes in response to injury. Am J Pathol 22; 161: Foidart JB, Dechenne CA, Mahieu P et al. Tissue culture of normal rat glomeruli. Isolation and morphological characterization of two homogeneous cell lines. Invest Cell Pathol 1979; 2: Schreiner GF, Unanue ER. Origin of the rat mesangial phagocyte and its expression of the leukocyte common antigen. Lab Invest 1984; 51: Kidney International (26) 69,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplemental Experimental Procedures
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 2 Supplemental Data A Temporal Switch from Notch to Wnt Signaling in Muscle Stem Cells Is Necessary for Normal Adult Myogenesis Andrew S. Brack, Irina M. Conboy, Michael J. Conboy,
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES
 How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reshape and Provoke Proliferation of Articular. State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, East China University of
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reshape and Provoke Proliferation of Articular Chondrocytes by Paracrine Secretion Lei Xu, Yuxi Wu, Zhimiao Xiong, Yan Zhou, Zhaoyang Ye *, Wen-Song Tan * State Key Laboratory of
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reshape and Provoke Proliferation of Articular Chondrocytes by Paracrine Secretion Lei Xu, Yuxi Wu, Zhimiao Xiong, Yan Zhou, Zhaoyang Ye *, Wen-Song Tan * State Key Laboratory of
Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Cytochrome C (10 M) Z-VAD-fmk. Procaspase-3. Cleaved caspase-3. actin. Z-VAD-fmk
 A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
A HeLa actin - + + - - + Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk PMN - + + - - + actin Cytochrome C (1 M) Z-VAD-fmk Figure S1. (A) Pan-caspase inhibitor z-vad-fmk inhibits cytochrome c- mediated procaspase-3 cleavage.
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
References. Plasma renin activity (PRA) PRA was measured by a radioimmunoassay kit (Wallac, Tokyo, Japan).
 Detailed Methods Experiment I enos / mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, USA). C57BL/6J mice on the same genetic background were purchased from KBT Oriental (Hamamatsu, Japan). Eleven-week-old
Detailed Methods Experiment I enos / mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, USA). C57BL/6J mice on the same genetic background were purchased from KBT Oriental (Hamamatsu, Japan). Eleven-week-old
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Supplemental methods. Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and
 Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
Title. CitationJournal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 100(1): 12. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title Effect of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid on Author(s)Nishimoto, Shohei; Takagi, Mutsumi; Wakitani, Shigey CitationJournal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 100(1): 12 Issue Date 2005-07
Title Effect of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid on Author(s)Nishimoto, Shohei; Takagi, Mutsumi; Wakitani, Shigey CitationJournal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 100(1): 12 Issue Date 2005-07
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
10/18/2012. A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why. What?
 A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why What? 1 First recognized in mice during 1930 s and 1940 s. Mouse (murine) experiments with tumors Independent observations were made in humans with leukoagglutinating
A primer in HLA: The who, what, how and why What? 1 First recognized in mice during 1930 s and 1940 s. Mouse (murine) experiments with tumors Independent observations were made in humans with leukoagglutinating
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL DIAGNOSTIC TEST USING PODOCYTURIA AS A BIOMARKER FOR DETECTION OF KIDNEY DAMAGE. An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis
 DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL DIAGNOSTIC TEST USING PODOCYTURIA AS A BIOMARKER FOR DETECTION OF KIDNEY DAMAGE An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by EESHA FAROOQI Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research
DEVELOPMENT OF A NOVEL DIAGNOSTIC TEST USING PODOCYTURIA AS A BIOMARKER FOR DETECTION OF KIDNEY DAMAGE An Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by EESHA FAROOQI Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis EasySep Mouse Monocyte Isolation Kit Catalog #19861 For processing 1 x 10^9 cells Description Isolate untouched and highly purified monocytes from mouse
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis EasySep Mouse Monocyte Isolation Kit Catalog #19861 For processing 1 x 10^9 cells Description Isolate untouched and highly purified monocytes from mouse
Detection of Apoptosis in Primary Cells by Annexin V Binding Using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Detection of Apoptosis in Primary Cells by Annexin V Binding Using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer Application Note Samuel D. H. Chan Marc Valer and Tobias Preckel, Introduction The Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer
Detection of Apoptosis in Primary Cells by Annexin V Binding Using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer Application Note Samuel D. H. Chan Marc Valer and Tobias Preckel, Introduction The Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit
 INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
INSTRUCTIONS Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit 88281 Number Description 88281 Pierce Primary Cardiomyocyte Isolation Kit, contains sufficient reagents to isolate cardiomyocytes from 50 neonatal
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Pu Duann, MD, PhD Hideki G. Kawanishi, MD Eugene J. Gross, BS Prasun K. Datta, PhD Elias A. Lianos, MD, PhD
 Detection of Injury-induced Changes in Gene Expression of the Glomerular Epithelial Cell-specific Marker, Wilm s Tumor-1, by Laser Capture Microdissection Pu Duann, MD, PhD Hideki G. Kawanishi, MD Eugene
Detection of Injury-induced Changes in Gene Expression of the Glomerular Epithelial Cell-specific Marker, Wilm s Tumor-1, by Laser Capture Microdissection Pu Duann, MD, PhD Hideki G. Kawanishi, MD Eugene
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
10.00 PBS OVA OVA+isotype antibody 8.00 OVA+anti-HMGB1. PBS Methatroline (mg/ml)
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
RESEARCH ARTICLE Penh (100% of PBS) 1 PBS 8.00 +anti-hmgb1 6.00 4.00 p=0.054 Cellular & Molecular Immunology advance online publication, PBS 3.12 6.25 Methatroline (mg/ml) Neutrophil isolation and culture
COMPONENT NAME COMPONENT # QUANTITY STORAGE SHELF LIFE FORMAT. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze. Store at 2-8 C. Do not freeze.
 This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
This document is available at www.stemcell.com/pis Catalog #18765 EasySep Mouse CD4+CD62L+ T Cell Isolation Kit For processing 1x 10^9 cells Description Isolate highly purified naïve CD4+ T cells (CD4+CD62L+)
Instructions. Fuse-It-Color. Overview. Specifications
 Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
Journal Club. 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal
 Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Keiji Kobayashi, Hidetoshi Nojiri, Yoshitomo Saita, Daichi Morikawa, Yusuke Ozawa, Kenji
 Supplementary Information Mitochondrial superoxide in osteocytes perturbs canalicular networks in the setting of age-related osteoporosis Keiji Kobayashi, Hidetoshi Nojiri, Yoshitomo Saita, Daichi Morikawa,
Supplementary Information Mitochondrial superoxide in osteocytes perturbs canalicular networks in the setting of age-related osteoporosis Keiji Kobayashi, Hidetoshi Nojiri, Yoshitomo Saita, Daichi Morikawa,
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Introduction Kit Components Cat. # # of vials Reagent Quantity Storage
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Protocol for Thawing Cryopreserved Hepatocytes
 cell and tissue-based products Protocol for Thawing Cryopreserved Hepatocytes Product Instruction The following procedure may be carried out in a biosafety containment hood to reduce the risk of contamination
cell and tissue-based products Protocol for Thawing Cryopreserved Hepatocytes Product Instruction The following procedure may be carried out in a biosafety containment hood to reduce the risk of contamination
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol
 L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Studying Kidney Injury using the Operetta System: Analysis of the Podocyte Cytoskeleton on CYTOO Micropatterns
 APPLICATION NOTE Cellular Imaging and Analysis Key Features Nephrotoxicity screening on the Operetta system Cell normalization on CYTOO micropatterns Visualization of compound effects through calculation
APPLICATION NOTE Cellular Imaging and Analysis Key Features Nephrotoxicity screening on the Operetta system Cell normalization on CYTOO micropatterns Visualization of compound effects through calculation
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT 2B receptor in chronic liver disease.
 Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT 2B receptor in chronic liver disease. Mohammad R Ebrahimkhani, Fiona Oakley, Lindsay B Murphy, Jelena Mann, Anna Moles, Maria J Perugorria,
Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT 2B receptor in chronic liver disease. Mohammad R Ebrahimkhani, Fiona Oakley, Lindsay B Murphy, Jelena Mann, Anna Moles, Maria J Perugorria,
Item Catalog Number Manufacturer 1,4-Dithioerythritol (1 g) D9680 Sigma-Aldrich
 SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
SOP: Nuclei isolation from fresh mouse tissues and DNaseI treatment Date modified: 01/12/2011 Modified by: E. Giste/ T. Canfield (UW) The following protocol describes the isolation of nuclei and subsequent
Human Mammary Luminal Epithelial Cells. Manual
 Human Mammary Luminal Epithelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL SHIPPING CONDITIONS ZBM0071.00 Human Mammary Luminal Epithelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada
Human Mammary Luminal Epithelial Cell Manual INSTRUCTION MANUAL SHIPPING CONDITIONS ZBM0071.00 Human Mammary Luminal Epithelial Cells Orders are delivered via Federal Express courier. All US and Canada
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY
 ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY Protocol for Protein Extraction Stock Solution 1. Leupeptin/hydrochloride (FW 463.0,
ASSAY OF SPHINGOMYELINASE ACTIVITY Protocol for Protein Extraction Stock Solution 1. Leupeptin/hydrochloride (FW 463.0,
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen. Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang
 Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Marker expression, behaviors, and responses vary in different lines of conditionally immortalized cultured podocytes
 Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 301: F660 F671, 2011. First published June 1, 2011; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00234.2011. Marker expression, behaviors, and responses vary in different lines of conditionally immortalized
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 301: F660 F671, 2011. First published June 1, 2011; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00234.2011. Marker expression, behaviors, and responses vary in different lines of conditionally immortalized
Original Article. Rapid Downregulation of Ç-actin-based CAG Promoter and Filamentous Actin in Injured Podocytes
 J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 129 134 Original Article Rapid Downregulation of Ç-actin-based CAG Promoter and Filamentous Actin in Injured Podocytes Takako Asano 1,3, Taiji Matsusaka 2, Shuki Mizutani 3 and
J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 129 134 Original Article Rapid Downregulation of Ç-actin-based CAG Promoter and Filamentous Actin in Injured Podocytes Takako Asano 1,3, Taiji Matsusaka 2, Shuki Mizutani 3 and
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system
 Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system Françoise Bruyère, Laurence Melen-Lamalle, Silvia Blacher, Guy Roland, Marc Thiry, Lieve Moons, Francis Frankenne, Peter Carmeliet, Kari
Modeling lymphangiogenesis in a three-dimensional culture system Françoise Bruyère, Laurence Melen-Lamalle, Silvia Blacher, Guy Roland, Marc Thiry, Lieve Moons, Francis Frankenne, Peter Carmeliet, Kari
Lab 3, case 1. Is this an example of nephrotic or nephritic syndrome? Why? Which portion of the nephron would you expect to be abnormal?
 Lab 3, case 1 12-year-old Costa Rican boy is brought into clinic by his parents because of dark brownish-red urine over the last 24 hours. The family has been visiting friends in Indianapolis for two weeks.
Lab 3, case 1 12-year-old Costa Rican boy is brought into clinic by his parents because of dark brownish-red urine over the last 24 hours. The family has been visiting friends in Indianapolis for two weeks.
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Instructions. Fuse-It-mRNA easy. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Isolating glomeruli from mice: A practical approach for beginners
 1322 Isolating glomeruli from mice: A practical approach for beginners XIAODAN LIU, QIULING FAN, GANG YANG, NAN LIU, DONG CHEN, YI JIANG and LINING WANG Department of Nephrology, The First Affiliated Hospital,
1322 Isolating glomeruli from mice: A practical approach for beginners XIAODAN LIU, QIULING FAN, GANG YANG, NAN LIU, DONG CHEN, YI JIANG and LINING WANG Department of Nephrology, The First Affiliated Hospital,
Early changes in gene expression that influence the course of primary glomerular disease
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology original article Early changes in gene expression that influence the course of primary glomerular disease LC Clement 1,4,
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology original article Early changes in gene expression that influence the course of primary glomerular disease LC Clement 1,4,
RNA/DNA Stabilization Reagent for Blood/Bone Marrow
 For general laboratory use. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. RNA/DNA Stabilization Reagent for Blood/Bone Marrow For simultaneous cell lysis and stabilization of nucleic acids
For general laboratory use. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. FOR IN VITRO USE ONLY. RNA/DNA Stabilization Reagent for Blood/Bone Marrow For simultaneous cell lysis and stabilization of nucleic acids
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber
 Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354480, 354481 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200 (U.S.) CLSTechServ@Corning.com www.corning.com/lifesciences
Corning BioCoat Matrigel Invasion Chamber Catalog No. 354480, 354481 Guidelines for Use Discovery Labware, Inc., Two Oak Park, Bedford, MA 01730, Tel: 1.978.442.2200 (U.S.) CLSTechServ@Corning.com www.corning.com/lifesciences
Supplementary Materials for
 immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Ectopic Notch Activation in Developing Podocytes Causes Glomerulosclerosis
 Ectopic Notch Activation in Developing Podocytes Causes Glomerulosclerosis Aoife M. Waters,* Megan Y.J. Wu,* Tuncer Onay,* Jacob Scutaru,* Ju Liu, Corrinne G. Lobe, Susan E. Quaggin, and Tino D. Piscione*
Ectopic Notch Activation in Developing Podocytes Causes Glomerulosclerosis Aoife M. Waters,* Megan Y.J. Wu,* Tuncer Onay,* Jacob Scutaru,* Ju Liu, Corrinne G. Lobe, Susan E. Quaggin, and Tino D. Piscione*
FOCUS SubCell. For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions. (Cat. # ) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
 169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II. Table of Contents
 E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
E.Z.N.A. SQ Blood DNA Kit II Table of Contents Introduction and Overview...2 Kit Contents/Storage and Stability...3 Blood Storage and DNA Yield...4 Preparing Reagents...5 100-500 μl Whole Blood Protocol...6
Primary Adult Naïve CD4+ CD45RA+ Cells. Prepared by: David Randolph at University of Alabama, Birmingham
 Primary Adult Naïve CD4+ CD45RA+ Cells Prepared by: David Randolph (drdrdr@uab.edu) at University of Alabama, Birmingham Goal: To obtain large numbers of highly pure primary CD4+ CD45RO- CD25- cells from
Primary Adult Naïve CD4+ CD45RA+ Cells Prepared by: David Randolph (drdrdr@uab.edu) at University of Alabama, Birmingham Goal: To obtain large numbers of highly pure primary CD4+ CD45RO- CD25- cells from
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma
 Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 8 1/2004 Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma L. Davis Lupo and Salvatore T. Butera HIV and Retrovirology Branch,
Excerpt from MACS&more Vol 8 1/2004 Application of μmacs Streptavidin MicroBeads for the analysis of HIV-1 directly from patient plasma L. Davis Lupo and Salvatore T. Butera HIV and Retrovirology Branch,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Correlation between LKB1 and YAP expression in human lung cancer samples. (a) Representative photos showing LKB1 and YAP immunohistochemical staining in human
Edge attributes. Node attributes
 HMDB ID input pane Network view Node attributes Edge attributes Supplemental Figure 1. Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator. The left pane is Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator (code name: rsmetabppi). User
HMDB ID input pane Network view Node attributes Edge attributes Supplemental Figure 1. Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator. The left pane is Cytoscape App MetBridge Generator (code name: rsmetabppi). User
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Diluent B (a phagocytic cell-labeling solution, Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) anti-maci antibody (1:100 dilution, BMA Biomedical, Switzerland)
 Sawada et al. 1 Isolation of two distinct subpopulations of microglia Reagents PKH26 (Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) Diluent B (a phagocytic cell-labeling solution, Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) FITC-labeled IgG (Cappel,
Sawada et al. 1 Isolation of two distinct subpopulations of microglia Reagents PKH26 (Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) Diluent B (a phagocytic cell-labeling solution, Zynaxis, Malvern, PA) FITC-labeled IgG (Cappel,
Product Contents. 1 Specifications 1 Product Description. 2 Buffer Preparation... 3 Protocol. 3 Ordering Information 4
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Quick-RNA Midiprep Kit Catalog No. R1056 Highlights 10 minute method for isolating RNA (up to 1 mg) from a wide range of cell types and tissue samples. Clean-Spin column technology allows
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Start your T cell research right
 Cell Isolation and Expansion Start your T cell research right Dynabeads tube-based cell isolation Cell Isolation and Expansion When you need healthy, pure, and viable T cells Dynabeads for human and mouse
Cell Isolation and Expansion Start your T cell research right Dynabeads tube-based cell isolation Cell Isolation and Expansion When you need healthy, pure, and viable T cells Dynabeads for human and mouse
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2012, 53(1):23 27 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Nanostructural features of diabetic podocytopathy E. MANDACHE, M. PENESCU
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2012, 53(1):23 27 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Nanostructural features of diabetic podocytopathy E. MANDACHE, M. PENESCU
The podocyte, a key cell involved in glomerulosclerosis,
 Podocyte Hypertrophy, Adaptation, and Decompensation Associated with Glomerular Enlargement and Glomerulosclerosis in the Aging Rat: Prevention by Calorie Restriction Jocelyn E. Wiggins,* Meera Goyal,
Podocyte Hypertrophy, Adaptation, and Decompensation Associated with Glomerular Enlargement and Glomerulosclerosis in the Aging Rat: Prevention by Calorie Restriction Jocelyn E. Wiggins,* Meera Goyal,
Overview of glomerular diseases
 Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane
Overview of glomerular diseases *Endothelial cells are fenestrated each fenestra: 70-100nm in diameter Contractile, capable of proliferation, makes ECM & releases mediators *Glomerular basement membrane

 Supplementary Figure 1 (Mu) SBP (mmhg) 2 18 16 p
Supplementary Figure 1 (Mu) SBP (mmhg) 2 18 16 p