Title: Niche-dependent regulations of metabolic balance in high-fat diet induced diabetic mice by mesenchymal stromal cells
|
|
|
- Christiana Johnson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pge 1 of 3 Dietes Title: Niche-dependent regultions of metolic lnce in high-ft diet induced dietic mice y mesenchyml stroml cells Authors: Andre Tung-Qin Ji, 1 Yun-Chung Chng, 1 Yun-Ju Fu, 1 Oscr K Lee, 2,3,4* Jennifer H Ho 1,5,6* * Corresponding uthors Affilitions: 1 Center for Stem Cell Reserch, Wn Fng Hospitl, Tipei Medicl University, Tipei, Tiwn 2 Deprtment of Orthopedic Surgery, Tipei City Hospitl, Tipei, Tiwn 3 Institute of Clinicl Medicine, Ntionl Yng-Ming University, Tipei, Tiwn 4 Stem Cell Reserch Center, Ntionl Yng-Ming University, Tipei, Tiwn 5 Deprtment of Ophthlmology, Wn Fng Hospitl, Tipei Medicl University, Tipei, Tiwn 6 Grdute Institute of Clinicl Medicine, Tipei Medicl University, Tipei, Tiwn Corresponding uthors: Jennifer Hui-Chun Ho, MD, PhD Grdute Institute of Clinicl Medicine, Tipei Medicl University, 25 Wu-Hsing Street, Tipei 11, Tiwn, R.O.C. Telephone numer: ext 2946 Fx numer: E-mil ddress: wh981@yhoo.com.tw AND Oscr Kung-Sheng Lee, MD, PhD Tipei Veterns Generl Hospitl Institute of Clinicl Medicine, Ntionl Yng-Ming University, 155 Linong Street, Sec. 2, Tipei 112, Tiwn, R.O.C. Telephone numer: Fx numer: E-mil ddress: kslee@vghtpe.gov.tw One Sentence Summry: Niche-dependent metolic regultion y MSCs 1 Dietes Pulish Ahed of Print, pulished online Octoer 2, 214
2 Dietes Pge 2 of 3 Astrct: Mesenchyml stroml cells (MSCs) hve gret potentils to mintin glucose homeostsis nd metolic lnce. Here, we demonstrte tht, in mice continuously feed with high-ft diet (HFD) nd developed non-insulin dependent dietes, two episodes of systemic MSC trnsplnttions effectively improve the glucose tolernce, lood sugr homeostsis nd reduce the ody weight through trgeting pncres nd insulin-sensitive tissues nd orgns vi sitespecific mechnisms. MSCs support pncretic islet growth y direct differentition into insulinproducing cells nd y mitigting the cytotoxicity of interleukin (IL)-1 nd tumor necrosis fctor lph (TNF-α) in the pncres. Locliztion of MSCs in the liver nd skeletl muscles in dietic nimls is lso enhnced nd therefore improves glucose tolernce, lthough long-term engrftment is not oserved. MSCs prevent HFD-induced ftty liver development nd restore glycogen storge in heptocytes. Incresed expression of IL-1 receptor ntgonist nd Glut4 in skeletl muscles fter MSC trnsplnttion result in etter lood sugr homeostsis. Intriguingly, systemic MSC trnsplnttion does not lter dipocyte numer, ut it decreses HFD-induced cell infiltrtion in dipose tissues nd reduces serum levels of dipokines, including leptin nd TNF-α. Tken together, systemic MSC trnsplnttion meliortes HFD-induced oesity nd restores metolic lnce through multi-systemic regultions which re niche-dependent. Such findings hve supported systemic trnsplnttion of MSCs to correct metolic imlnce. Key Words: dietes, ftty liver, inflmmtion, insulin-producing cell differentition, mesenchyml stroml cells, oesity 2
3 Pge 3 of 3 Dietes Introduction Impirment of glucose tolernce nd insulin resistnce initites type 2 dietes; however, exhustion of the insulin supply due to et (β)-cell poptosis is the ultimte pthomechnism of oth type 1 nd 2 dietes (1,2). The liver, dipose tissues, skeletl muscles, nd vsculr tissues re insulin-sensitive tissues responsile for lood sugr homeostsis (1,3). Inflmmtion dversely ffects insulin sensitivity nd worsens dietic retinopthies, neuropthies, nd vsculopthies (4-6). Proinflmmtory cytokines produced y mcrophges, such s tumor necrosis fctor lph (TNF-α) nd interleukin (IL)-1, crete vicious cycle of reduced insulin sensitivity (3,7-9). To the present, more thn 3 clinicl trils of mesenchyml stem/stroml cell (MSC) trnsplnttions hve een conducted worldwide with wide clinicl ppliction trgeting more thn 5 indictions ( Systemic trnsplnttion is the most fvorle route for MSC delivery from sfety nd systemic regultion point of view, nd 56% of MSC clinicl trils is llogenic trnsplnttion (1). It is well ccepted tht the mjority of MSCs re initilly distriuted in vitl orgns (11-16), nd re lso frequently found in tissues of mesenchyml origin (11,12) when systemiclly dministered. Nevertheless, the long-term engrftment of MSCs is miniml, nd the engrftment rte is not correlted with therpeutic response in humn studies (17). The cutely disesed nd dmged tissues show incresed locliztion of MSCs from the circultion (13-16). Regrding the possiility of treting dietes with MSC trnsplnttion, n in vitro study of directly co-culturing MSCs with islet cells hs demonstrted the potentil of MSCs to give rise to insulin-producing cells (18). In niml experiments of MSC trnsplnttion for treting 3
4 Dietes Pge 4 of 3 hyperglycemi nd dietes-relted complictions, it is indicted tht prcrine nd ntiinflmmtory effects of MSCs re the primry mechnisms of ction (19-22) rther thn direct engrftment nd differentition into insulin-producing cells (23, 24). IL-1 receptor ntgonist (IL-1 RA) produced y MSCs hs een postulted to medite ntiinflmmtory nd nti-firotic effects (25, 26), which is responsile for the modultion of dietogenesis in the niml experiment (25). We hve previously reported tht indolemine 2,3- dioxygense (IDO), IL-1 (hil-1), solule TNF receptor II (stnf RII), nd IL-1 RA re inducile immune-modultors produced y humn MSCs in response to the stimultion of mcrophge-produced IL-1α, β nd TNF-α (27). We hve lso demonstrted tht, in murine model of type 1 dietes, systemic trnsplnttion of MSCs regultes lood sugr homeostsis y differentition into insulin-producing cells in liver when islet cells re totlly depleted in the pncres; nd such heterotopic engrftment is not oserved in non-dietic mice (28). All the ove findings indicte tht the therpeutic mechnism of MSCs vi systemic dministrtion my e guided y specific tissue nd orgn micro-environments; nd the micro-environments in type 1 dietes re different from those in non-dietic conditions. However, the interction etween MSCs nd pncres s well s insulin-sensitive tissues in type 2 dietes remins elusive so fr. The purpose of this study is to investigte how MSCs contriute to the mintennce of lood sugr homeostsis in type 2 dietes. Herein, experimentl model of type 2 dietes is estlished in mice under continuous high-ft diet (HFD) feeding for 6 months. Therpeutic effects of systemic MSC trnsplnttion on the correction of ody weight nd the mintennce of lood sugr homeostsis, s well s the mechnism of ction in the pncres nd insulinsensitive tissues/orgns including liver, skeletl muscles, nd dipose tissues re to e elucidted 4
5 Pge 5 of 3 Dietes in this study. We hypothesize tht improvement of lood sugr homeosttsis fter MSC trnsplnttion is medited y multiple niche-specific regultory mechnisms in pncres nd other insulin-sensitive tissues/orgns. Reserch Design nd Methods Animls Seven-week-old mle B6 mice were purchsed from the Ntionl Lortory Animl Center (NLAC, Tipei, Tiwn) nd housed following the niml cre guidelines of the NLAC. The use of nimls ws pproved y the Institutionl Animl Cre nd Use Committee of Wn Fng Hospitl, Tipei Medicl University (TMU-WFH). Isoltion nd Culture of MSCs MSCs were isolted from humn oritl ft tissues following previously reported protocol (29), An Institutionl Review Bord pprovl ws otined prior to the commencement of the study of isolting MSCs, nd written informed consents to donte oritl ft tissues were otined from ptients prior to lephroplstic surgery. Induction of Dietes Dietes ws induced y continuous feeding of HFD (D12492, Reserch Diets, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) (3). Thirty six mice were used in the study of systemic MSC trnsplnttion. Mice were divided into four groups: (1) eight mice with norml diet (ND)-fed mice (D1245B, Reserch Diets) receiving two PBS injections (ND), (2) ten mice with ND-fed mice receiving two MSC injections (ND+MSCs), (3) eight mice with HFD-fed mice receiving two PBS injections (HFD), nd (4) ten mice HFD-fed mice receiving two MSC injection (HFD+MSCs). The ody weight nd fsting lood glucose level were mesured weekly. A glucose tolernce test (GTT) ws performed every 2 weeks efore the onset of dietes. The 5
6 Dietes Pge 6 of 3 onset of dietes in mice fed the HFD ws defined s n elevted fsting lood glucose level on two consecutive tests plus impired glucose tolernce on two consecutive GTTs compred to mice fed the ND. After the onset of dietes, GTT ws performed t 2 weeks efore the first dose of MSC trnsplnttion (week 1) nd 2 weeks fter ech MSC trnsplnttion (week 14 nd week 22). Blood Sugr Mesurement nd the GTT Blood sugr mesurement nd the GTT were performed following the sme protocol s in our previous study (3). Briefly, the til cpillry lood sugr level ws mesured using OneTouch Ultr meter (LifeScn, Milpits, CA, USA) fter mouse ws strved for 8 h. For the GTT, 1 g/kg ody weight of glucose in.9% NCl ws intrperitonelly injected, nd til cpillry lood sugr levels were mesured efore ( min) nd 3, 6, 9, nd 12 min fter the glucose injection. MSC Trnsplnttion For systemic MSC trnsplnttion, 4.2 x 1 7 cells/kg ody weight in.2 ml PBS for ech dose, the sme therpeutic dose s in our previous experiments used for type 1 dietes (28) nd cute lung inflmmtion (31), were slowly injected into mice vi the til vein. The sme volume of PBS ws injected into control mice. Mesurement of Serum Insulin, IL-1, Leptin, nd TNF-α Levels The serum level of mouse insulin ws mesured with Mercodi Mouse Insulin Enzyme-linked Immunosorent Assy (ELISA) Enzyme immunossy (Mercodi AB, Uppsl, Sweden), nd humn insulin ws detected with Mercodi Ultrsensitive Insulin ELISA (Mercodi AB) s per the mnufcturer's instructions. Mouse IL-1, leptin, nd TNF-α levels were determined using regents of the ELISA kits (ebioscience, Sn Diego, CA, USA) ccording to the mnufcturer's 6
7 Pge 7 of 3 Dietes instructions. All ELISA dt were nlyzed with n ELISA reder (Spectr MAX 25, Spectr Devices, Sunnyvle, CA, USA). Six mice were used in ech group of ech experiment. Histopthology nd Quntifiction of Adipocyte Numers Tissues/orgns were hrvested, fixed in formlin, nd emedded in prffin locks for sectioning (t thickness of 3~4 µm). For the histopthologicl evlution, tissue sections were stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin (Sigm-Aldrich). For dipocyte numer clcultion, six imges of dipose tissue sections under the 2x mgnifiction were cptured in ech smple, nd six mice were used in ech group. Immunohistochemicl nd Periodic cid Schiff (PAS) Stining For immunohistochemicl stining, pncres sections were incuted with rit ntiodies ginst humn β2 microgloulin (hβ2m; 1:8, Acm, Cmridge, MA, USA), rit ntiodies ginst humn insulin (1:1, Acm), or rit ntiodies ginst mouse insulin (1:3, ImmunoStr, Hudson, WI, USA) t room temperture for 1 h, followed y got ntiodies ginst rit immunogloulin (IgG; 1:2, Acm) for nother 4~6 min. For PAS stining, tissue sections were covered with.1% Triton X-1 (Sigm-Aldrich) for 5 minutes, followed y 1% Periodic-cid (Sigm-Aldrich) for 1 minutes, nd finl Schiff s fuchsin-sulfite regent (Sigm-Aldrich) in the drk for 3 minutes. Tissue sections were ssessed y fluorescence microscopy (Leitz, Wetzlr, Germny). Imge cquisition ws performed with the SPOT RT Imging system (Dignostic Instruments, Sterling Heights, MI, USA). Quntittive rel-time RT-PCR Totl RNAs were reverse-trnscried into cdnas using n Omniscript RT kit (Qigen). A reltime RT-PCR ws performed using SYBR supermix kit (Bio-Rd). Smples from ech niml were sujected to 4 cycles of 95 C for 15 s, followed y 6 C for 3 s nd 72 C for 3 s. A primer for detecting oth mouse nd humn 18s rrna ws included in every plte s n internl loding control. The mrna level of ech smple for ech gene ws normlized ginst tht of 7
8 Dietes Pge 8 of 3 18s rrna mrna. The reltive mrna level ws determined s 2 [(Ct/18S rrna Ct/gene of interest)]. Primers for the rel-time RT-PCR in this study were listed in tle 1. Quntittive Western Blot Anlysis Protein smples were prepred ccording to previously descried protocol (3). Proteins (3 µg) from ech smple ws sujected to SDS-PAGE (1% (w/v) crylmide) nd trnsferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride memrnes (Amershm Biosciences, Uppsl, Sweden). The memrnes were lotted with rit ntiodies ginst mouse crnitine plmitoyltrnsferse (Cpt) 1A (1:2, Proteintech Group, Chicgo, IL, USA), or rit ntiodies ginst mouse Glut4 (1:2, Acm) followed y horserdish peroxidse-conjugted secondry ntiody (1:5, Acm). Protein intensities were determined using n enhnced chemiluminescence regent (PerkinElmer Life Sciences, Wlthm, MA, USA) nd the density of protein nds from t lest three nimls in ech group ws ssessed using computing densitometer with Imge-J softwre (LWorks, UVP, Uplnd, CA, USA). Sttisticl Anlysis Sttisticl nlyses were performed using the Sttisticl Pckge for Socil Science softwre (Version 16, SPSS, Chicgo, IL, USA). Differences in lood glucose levels for the ND nd HFD groups t the sme time point were ssessed using two-tiled, non-pired t-test, nd p<.5 ws considered sttisticlly significnt. Differences in lood sugr levels nd ody weights t the sme time point mong ND, ND+MSCs, HFD, nd HFD+MSCs groups, or differences in ny test mong three nd more thn three groups were sttisticlly nlyzed y ANOVA with Bonferroni's post-hoc tests t 95% CI. Different levels of sttistic significnce were represented y different lpheticl letters. Letter, represent sttisticlly significnt difference etween level nd. In Figure 1, 2A nd 2B, four chrcters were shown in ech time point, nd ment no sttisticl difference mong the four groups t the sme time point, while represented 2 of the 4 with level t the sme sttisticl level nd 8
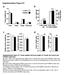
9 Pge 9 of 3 Dietes the other 2 with level were t sttisticl level higher thn. Error rs shown in ll figures represented the stndrd devition of the mens. Results Chrcteriztion of MSCs MSCs were firolst-like, dherent cells. The osteogenic, chondrogenic nd dipogenic differentition cpcities hve een tested s previously reported (29). Immuno-phenotypiclly, these cells were negtive for CD34, CD133, CD31, CD16, CD146, CD45, CD14, CD117 nd humn leukocyte ntigen (HLA)-DR, nd were highly expressed CD29, CD49, CD49e, CD44, CD49d, CD58, CD9, CD15, nd HLA-ABC (29). Blood sugr more sensitive to systemic MSC trnsplnttions thn ody weight chnges Fsting lood sugr nd ody weight of mice were regulrly recorded every 2 weeks. In ND-fed group, systemic MSC trnsplnttion did not lter lood sugr levels (Fig. 1A, ND vs. ND+MSCs). In ND nimls, MSC trnsplnttion slightly decresed the ody weight fter the second MSC trnsplnttion (Fig. 1B, ND vs. ND+MSCs). In HFD-fed groups, the first dose of MSCs given t week 12 rogted the progression of hyperglycemi for 8 weeks (Fig. 1A, HFD vs. HFD+MSCs); nd the second dose of MSCs given t week 2 further dropped the lood sugr level (Fig. 1A, ND vs. HFD+MSCs). Significnt HFD-induced ody weight gin ws noted fter week 8, nd single MSC trnsplnttion did not lter the ody weight till the second dose of MSCs given t week 2 (Fig. 1B, HFD vs. HFD+MSCs). Improvement of glucose tolernce correlted with locliztion of MSCs in liver nd skeletl muscles 9
10 Dietes Pge 1 of 3 Although the fsting lood sugr level in HFD-fed mice ws still higher thn tht in ND-fed mice fter two doses of MSC trnsplnttions (Fig. 1A, ND vs. HFD+MSCs), systemic MSC trnsplnttion effectively corrected HFD-induced glucose impirment (Fig. 2A) fter ech episode of MSC trnsplnttion (Fig. 2B nd C). One month fter the second dose of MSC trnsplnttion, quntittion of DNA from humn MSCs y humn-specific house keeper gene hβ2m versus DNA from tissue cells y humn/mouse house keeper gene 18s rrna ws mesured. In ND mice, humn DNA ws detectle in the mouse pncres, liver, ft, skeletl muscles, hert, lungs, spleen, nd kidneys, ut the intensity of hβ2m ws reltively low (<.5) compred to 18s rrna (Fig. 2D). Moreover, type 2 dietic environment enhnced the io-distriution of MSCs in insulin-responsive tissues such s the liver nd skeletl muscles, ut not dipose tissues (Fig. 2D). Differentition of MSCs into insulin-producing cells in type 2 dietic pncres In control mice, MSC trnsplnttion did not lter the histologicl ppernce of pncretic islets (Fig. 3A, ND v.s. ND+MSCs). After HFD feeding, mice with persistently high lood glucose levels showed decrese in islet size (Fig. 3A, HFD); while trnsplnted MSCs promoted islet growth (Fig. 3A, HFD+MSCs). Immuno-histochemicl stined for mouse insulin nd humn insulin in two consecutive sections of pncres in HFD-fed mice reveled tht only mouse nd no humn insulin-expressing cells were found in ny single islet of the dietic pncres (Fig. 3B, HFD, mouse insulin v.s. humn insulin). In dietic pncres fter MSC trnsplnttions, 32 islets were counted in the tissue sections nd 25% (8/32) islets showed consisting of oth mouse nd humn insulin-producing cells (Fig. 3B, HFD+MSCs, mouse insulin v.s. humn insulin). Before MSC trnsplnttion, humn insulin ws non-detectle (N.D.); fter MSC trnsplnttions, humn insulin could e detected in the circultion, nd serum level of humn insulin in dietic mice ws higher thn in norml mice (Fig. 3C). 1
11 Pge 11 of 3 Dietes Cytoprotection of pncres islet y MSCs Next, we mesured the expression of IL-1 nd TNF-α, two criticl pro-inflmmtory cytokines relted to the development of dietes, in pncres. It ws found tht MSC trnsplnttion significntly down-regulted the expression of IL-1α, IL-1β, nd TNF-α in pncres elevted y HFD (Fig. 3D). After two MSC trnsplnttions, humn (h) IDO (hido), hil-1, hstnf RII, ut not hil-1 RA mrna expressions were detectle in pncres; however, only hstnf RII ws up-regulted y n HFD (Fig. 3E). Prevention of ftty liver development nd restortion of heptic glycogen storge y MSCs We previously reported tht persistent HFD feeding resulted in ftty liver, nd over-expression of Cpt 1A s well s decrese in glycogen storge ility in heptocytes ccounted for liverrelted glucose impirment nd insulin resistnce (3). Here, MSCs did not lter the morphology (Fig. 4A, ND v.s. ND+MSCs), glycogen storge (Fig. 4B, ND v.s. ND+MSCs), or Cpt 1A level (Fig. 4C, ND v.s. ND+MSCs) in the liver. Systemic MSC trnsplnttion prevented the development of HFD-induced ftty liver (Fig. 4A, HFD v.s. HFD+MSCs) nd reduced HFDinduced overexpression of Cpt1A (Fig. 4C, HFD v.s. HFD+MSCs). Therefore, HFD-induced loss of glycogen storge ility in those fomy heptocytes could e restored y MSCs (Fig. 4B, HFD v.s. HFD+MSCs). However, long-term engrftment of MSCs in the liver ws not found regrdless of whether mice were fed with ND or HFD (dt not shown). IL-1 RA produced y MSCs ssocited with glucose uptke enhncement in dietic skeletl muscles In skeletl muscles, neither MSCs nor the HFD induced significnt pthologicl chnges (Fig. 5A). After MSC trnsplnttion, hido, hil-1, hil-1 RA nd hstnf RII in skeletl muscle 11
12 Dietes Pge 12 of 3 were detectle, nd only hil-1 RA ws responsive to n HFD (Fig. 5B). Similr to hil-1 RA, Glut4 level in skeletl muscle fter MSC trnsplnttion ws lso enhnced in response to n HFD (Fig. 5C). Long-term skeletl muscle engrftment of MSCs ws neither oserved in mice fed with ND nor HFD (dt not shown). Regultion of dipokines y MSC trnsplnttion In mice fed with ND, the numers of dipocytes nd the morphology in the ft tissues remined unchnged fter systemic MSC trnsplnttion (Figs. 6A nd B, ND v.s. ND+MSCs). HFD feeding resulted in inflmmtory cell infiltrtion into ft tissues nd lso incresed dipocyte numers; while systemic MSC trnsplnttion reduced the inflmmtion in ft tissues ut hd no effect on dipocyte numers (Figs. 6C nd D, HFD v.s. HFD+MSCs). Two doses of systemic MSC trnsplnttions did not lter serum diponectin levels in mice with HFD feeding (Fig. 6C). However, serum leptin level ws effectively decresed y MSCs fter the first trnsplnttion (Fig. 6D). After two MSC infusions, oth circulting TNF-α (Fig. 6E) nd IL-1 (Fig. 6F) levels were reduced in mice fed the HFD. Discussion In this study, we discover tht systemic MSC trnsplnttion improves the glucose tolernce in type 2 dietes through comined mechnism in tissue-specific mnner. The mjority of trnsplnted MSCs in the pncres support islet growth y mitigting the cytotoxicity from IL-1 nd TNF-α. Some trnsplnted MSCs differentite into insulin-producing cells in the dietic pncres to increse circulting insulin level. In type 2 dietes, MSCs increse the iodistriution in the liver nd skeletl muscles without long term engrftment. MSCs improve insulin sensitivity in the liver y preventing ftty liver formtion s well s restoring glycogen 12
13 Pge 13 of 3 Dietes storge in heptocytes. In the skeletl muscle, MSCs increse IL-1 RA production nd enhnce the glucose uptke from circultion. MSCs hve no effect on reducing the numer of dipocytes induced y n HFD. Nevertheless, trnsplnttion of MSCs modultes dipokines such s leptin nd TNF-α contriuting the inhiition of inflmmtion in dipose tissues. Body weight reduction in HFD-induced oesity is lso chieved y systemic trnsplnttion of MSCs fter metolic lnce. Si et l. report tht islet size is decresed in n insulin-independent dietic pncres, nd systemic MSC trnsplnttion preserves the islet size without the differentition (32). According to our results, it is clerly demonstrted tht the fte of trnsplnted MSCs depends on the sttus of islets in pncres. In our previous study of type 1 dietic model, pncretic islets were totlly depleted y streptozocin, nd the environment of pncres ws not fvorle for MSC engrftment; so we oserved tht the liver served s n lterntive niche for β-cell differentition of MSCs (28). In type 2 dietes, lthough the islets were reltively trophic nd dysfunctionl (Figs. 3A nd B, HFD), such pncretic environment preserved niche for MSCs differentition into insulin-secreting cells in the islets (Figs. 3B nd C). In this study, only 25% of islets in dietic pncres possessed the ility to provide humn insulin fter humn MSC trnsplnttion (Fig. 3B), nd the level of humn insulin in the serum ws much lower thn tht in type 1 dietes we reported in the previous study (28), indicting tht differentition into insulin producing cells is one of the therpeutic mechnisms of MSC trnsplnttion for type 2 dietes. We reson tht prcrine support of islet growth nd immunemodultion in insulin-sensitive tissues re criticl for lood sugr regultion (Figs. 3-6). MSCs hd een reported to meliorte hyperglycemi in type 2 dietic rts (32, 33) through islet protection nd regultion of insulin sensitivity in peripherl insulin-sensitive tissues (32). In this 13
14 Dietes Pge 14 of 3 study, we explored tht the mechnism of islet protection nd insulin-sensitive tissues regultion y MSCs were niche-dependent (Figs. 3-6). Free ftty cids in n HFD induce mcrophge-medited inflmmtion vi relesing TNF-α nd IL-1, which leds to poptosis of islet cells (7-9) nd initites series of inflmmtory responses in vivo (34). It is known tht relese of solule immune-modultory fctors from MSCs is induced y TNF-α, IL-1, nd interferon (IFN)-γ (35,36). Recently, we nd others report tht MSCs exert their nti-inflmmtory ction vi producing IDO, IL-1, IL-1 RA nd stnf RII y themselves nd reducing TNF-α nd IL-1 level from mcrophges (27, 37). In coculture study, MSCs show their protective effect on oth islet cells nd β-cells ginst IFN-γ-, TNF-α-, nd IL-1β-induced poptosis (38). Herein, we demonstrted tht MSCs rogted HFDinduced elevtion of IL-1α, IL-1β, nd TNF-α in the pncres (Fig. 3D), nd which protected islet cells from IL-1- nd TNF-α-medited tissue injury nd inflmmtion in vivo. Solule TNF RII is secreting receptor inding to TNF-α for rogting the effect from receptor-lignd interction (39). The expression of hstnf RII ws response to dietic environment in pncres (Fig. 3E), suggesting tht MSCs meliorte the cytotoxicity of TNF-α towrd islet cells through oth the secretion of solule neutrlizing receptor nd the inhiition of TNF-α production. In n HFD-induced ftty liver, mssive mount of sturted ftty cids ccumulted in heptocytes results in insulin resistnce vi inhiiting insulin signling through c-jun N- terminl kinse-dependent mechnism (9,4) nd turning off glucose metolism in heptocytes with ctive β-oxidtion (3). Systemic MSC trnsplnttion restored insulin sensitivity in the liver y preventing ftty liver formtion induced y n HFD (Fig. 4A), nd susequently resumed the ility of heptocytes to metolize/storge glucose (Fig. 4B nd C). 14
15 Pge 15 of 3 Dietes Skeletl muscle cells ply crucil role in regulting lood sugr levels y tking glucose up from the circultion into cells vi Glut4 (41). Free ftty cids induce mcrophge-medited suclinicl inflmmtion in skeletl muscles through TNF-α, which results in insulin resistnce nd reduced Glut4 expression (9,42,43). Although circulting levels of TNF-α nd IL-1 in HFDfed mice decresed with systemic MSC trnsplnttion (Figs. 6E nd F), MSC-enhnced Glut4 expression ws ssocited with IL-1 RA production in skeletl muscles (Figs. 5B nd C). IL-1 RA hs een found to e dietogenic modultor produced y MSCs (25). In this study, the level of hil-1 RA in pncres ws undetectle (Fig. 3E) ut strongly incresed y HFD in the skeletl muscle (Fig. 5B), suggesting tht IL-1 RA modultes dietic development y trgeting on the skeletl muscles insted of the pncres. The effect of MSCs on dipose tissues ws the meliortion of HFD-induced inflmmtion (Fig. 6A), which ws ssocited with reduced leptin production triggered y n HFD (Fig. 6D). Leptin is n dipokine minly secreted y white dipose tissues, nd its circulting level is proportionl to the totl mount of ft in the ody (44). Circulting leptin not only cts on the hypothlmus to regulte food intke nd energy expenditure (45), ut lso cts s proinflmmtory nd mitogenic fctor for immune cells (46,47). Therefore, leptin is mrker of dipose tissue-exerted inflmmtion (46, 47). In this study, the chnge in leptin y trnsplnttion of MSCs (Fig. 6D), similr to glucose tolernce (Figs. 3B nd 3C), ws more consequentil to TNF-α nd IL-1 regultion (Figs. 6E nd F) nd ody weight control (Fig. 1B), indicting tht correction of HFD-induced oesity y MSCs is the result of inflmmtion inhiition nd the chievement of metolic lnce. 15
16 Dietes Pge 16 of 3 In generl, the doses of MSCs in niml studies re higher thn those used in clinicl trils, s the volume of distriution of mice is very different from tht of humn. In future clinicl trils, crefully designed dose escltion study will e performed to decide the optiml therpeutic dosge. Tken together, systemic MSC trnsplnttion improves glucose tolernce nd metolic lnce in type 2 dietes through multi-systemic regultion with tissue-specific mechnisms. The unique ilities of MSCs to chieve intricte multi-systemic regultion strongly support further investigtion of the fesiility to use these cells to enhnce, mintin nd correct lood sugr homeostsis nd the relevnt metolic lnce in ptients suffering from such prolems. 16
17 Pge 17 of 3 Dietes Acknowledgments Funding The uthors cknowledge the support of reserch grnts from the Ntionl Science Council, Tiwn (NSC B MY3, NSC I-1-53, nd NSC M-1-2 to JHH nd OKL; nd NSC B-1-3-MY3, NSC B-1-9, nd NSC I-1-53 to OKL). This work ws lso supported in prt y the UST-UCSD Interntionl Center of Excellence in Advnced Bio-engineering sponsored y the Tiwnese Ntionl Science Council I-RiCE Progrm under grnt no. NSC I The uthors lso cknowledge the finncil support from Wn Fng Hospitl, Tipei Medicl University (13swf4 to JHH nd OKL), nd reserch grnt support from Tipei Medicl University nd Steminent Biotherpeutics (A-11-23). Author contriutions A.T.J. reserched dt nd wrote the mnuscript; Y.C.C. reserched dt; Y.J.F. reserched dt; O.K.L contriuted to study design nd reviewed/edited the mnuscript; J.H.H. designed the study nd wrote the mnuscript. Conflict of Interest Sttement No potentil conflicts of interest relevnt to this rticle were reported. Gurntor Sttement Dr. J.H.H is the gurntor of this work nd, s such, hd full ccess to ll the dt in the study nd tkes responsiility for the integrity of the dt nd the ccurcy of the dt nlysis. 17
18 Dietes Pge 18 of 3 References: 1. Bour-Hlfon S nd Zick Y. Phosphoryltion of IRS proteins, insulin ction, nd insulin resistnce. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 29; 296:E Schenk S, Seri M nd Olefsky JM. Insulin sensitivity: modultion y nutrients nd inflmmtion. J Clin Invest 28; 118: Yn M, Meht JL, Zhng W nd Hu C. LOX-1, oxidtive stress nd inflmmtion: novel mechnism for dietic crdiovsculr complictions. Crdiovsc Drugs Ther 211; 25: Lee MS, Chng I nd Kim S. Deth effectors of et-cell poptosis in type 1 dietes. Mol Genet Met 24; 83: Wd J nd Mkino H. Inflmmtion nd the pthogenesis of dietic nephropthy. Clin Sci (Lond) 213; 124: Yellowlees Dougls J, Bhtwdekr AD, Li Clzi S, Shw LC, Crnegie D, Cllero S, Li Q, Stitt AW, Rizd MK nd Grnt MB. Bone mrrow-cns connections: implictions in the pthogenesis of dietic retinopthy. Prog Retin Eye Res 212; 31: Ot T. Chemokine systems link oesity to insulin resistnce. Dietes Met J 213; 37: Bstrd JP, Mchi M, Lgthu C, Kim MJ, Cron M, Vidl H, Cpeu J nd Feve B. Recent dvnces in the reltionship etween oesity, inflmmtion, nd insulin resistnce. Eur Cytokine Netw 26; 17: Tck CJ, Stienstr R, Joosten LA nd Nete MG. Inflmmtion links excess ft to insulin resistnce: the role of the interleukin-1 fmily. Immunol Rev 212; 249: Ankrum JA, Ong JF nd Krp JM. Mesenchyml stem cells: immune evsive, not immune privileged. Nt Biotechnol. 214;32: Allers C, Sierrlt WD, Neuuer S, River F, Minguell JJ nd Conget PA. Dynmic of distriution of humn one mrrow-derived mesenchyml stem cells fter trnsplnttion into dult unconditioned mice. Trnsplnttion 24; 78: Jeong YS, Kim EJ, Shim CK, Hou JH, Kim JM, Choi HG, Kim WK nd Oh YK. Modultion of iodistriution nd expression of plsmid DNA following mesenchyml progenitor cell-sed delivery. J Drug Trget 28; 16: Kritchmn DL, Ttsumi M, Gilson WD, Ishimori T, Kedziorek D, Wlczk P, Segrs WP, Chen HH, Fritzges D, Izudk I, Young RG, Mrcelino M, Pittenger MF, Soliyppn M, Boston RC, Tsui BM, Whl RL nd Bulte JW. Dynmic imging of llogeneic mesenchyml stem cells trfficking to myocrdil infrction. Circultion 25; 112: Detnte O, Moisn A, Dimstromtteo J, Richrd MJ, Riou L, Grillon E, Brier E, Desruet MD, De Fripont F, Segerth C, Jillrd A, Hommel M, Ghezzi C nd Remy C. Intrvenous dministrtion of 99mTc-HMPAO-leled humn mesenchyml stem cells fter stroke: in vivo imging nd iodistriution. Cell Trnsplnt 29; 18: Gholmreznezhd A, Mirpour S, Bgheri M, Mohmdnejd M, Alimoghddm K, Adolhzdeh L, Sghri M nd Mlekzdeh R. In vivo trcking of 111In-oxine leled mesenchyml stem cells following infusion in ptients with dvnced cirrhosis. Nucl Med Biol 211; 38: Kng JW, Prk KD, Choi Y, Bek DH, Cho WS, Choi M, Prk JH, Choi KS, Kim HS nd Yoo TM. Biodistriution nd in vivo efficcy of geneticlly modified humn mesenchyml stem cells systemiclly trnsplnted into mouse one frcture model. Arch Phrm Res 213; 36: von Bhr L, Btsis I, Moll G, Hägg M, Szkos A, Sunderg B, Uzunel M, Ringden O nd Le Blnc K. Anlysis of tissues following mesenchyml stroml cell therpy in humns indictes limited long-term engrftment nd no ectopic tissue formtion. Stem Cells. 212;3:
19 Pge 19 of 3 Dietes 18. Kroz E, Okcu A, Unl ZS, Susi C, Sglm O nd Duruksu G. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchyml stroml cells efficiently differentite into insulin-producing cells in pncretic islet microenvironment oth in vitro nd in vivo. Cytotherpy 213; 15: Mottghi S, Lrijni B nd Shrifi AM. Atorvsttin: n efficient step forwrd in mesenchyml stem cell therpy of dietic retinopthy. Cytotherpy 213; 15: Li XY, Zheng ZH, Li XY, Guo J, Zhng Y, Li H, Wng YW, Ren J nd Wu ZB. Tretment of foot disese in ptients with type 2 dietes mellitus using humn umilicl cord lood mesenchyml stem cells: response nd correction of immunologicl nomlies. Curr Phrm Des 213; 19: Yn J, Tie G, Xu TY, Cecchini K nd Messin LM. Mesenchyml stem cells s tretment for peripherl rteril disese: current sttus nd potentil impct of type II dietes on their therpeutic efficcy. Stem Cell Rev 213; 9: Zhng H, Qiu X, Shindel AW, Ning H, Ferretti L, Jin X, Lin G, Lin CS nd Lue TF. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells meliorte dietic ldder dysfunction in type II dietic rt model. Stem Cells Dev 212; 21: Volrevic V, Arsenijevic N, Lukic ML nd Stojkovic M. Concise review: Mesenchyml stem cell tretment of the complictions of dietes mellitus. Stem Cells 211; 29: El-Bdri N nd Ghoneim MA. Mesenchyml stem cell therpy in dietes mellitus: progress nd chllenges. J Nucleic Acids 213; 213: Volrevic V, Al-Qhtni A, Arsenijevic N, Pjovic S nd Lukic ML. Interleukin-1 receptor ntgonist (IL-1 RA) nd IL-1 RA producing mesenchyml stem cells s modultors of dietogenesis. Autoimmunity 21; 43: Ortiz LA, Dutreil M, Fttmn C, Pndey AC, Torres G, Go K nd Phinney DG. Interleukin 1 receptor ntgonist medites the ntiinflmmtory nd ntifirotic effect of mesenchyml stem cells during lung injury. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A 27; 14: Lien GS, Liu JF, Chien MH, Hsu WT, Chng TH, Ku CC, Ji AT, Tn P, Hsieh TL, Lee LM, Ho JH. The ility to suppress mcrophge-medited inflmmtion in oritl ft stem cells is controlled y mir-671-5p. Stem Cell Res Ther 214; 5: Ho JH, Tseng TC, M WH, Ong WK, Chen YF, Chen MH, Lin MW, Hong CY nd Lee OK. Multiple intrvenous trnsplnttions of mesenchyml stem cells effectively restore long-term lood glucose homeostsis y heptic engrftment nd et-cell differentition in streptozocininduced dietic mice. Cell Trnsplnt 212; 21: Ho JH, M WH, Tseng TC, Chen YF, Chen MH nd Lee OK. Isoltion nd chrcteriztion of multi-potent stem cells from humn oritl ft tissues. Tissue Eng Prt A 211; 17: Ho JH, Lee OK, Fu YJ, Shih HT, Tseng CY, Chung CC, Hn CL nd Chen YJ. An itraq proteomic study revels n ssocition etween diet-induced enhnced ftty cid metolism nd the development of glucose intolernce in predietic mice. J Proteome Res 213; 12: Chien MH, Bien MY, Ku CC, Chng YC, Po HY, Yng YL, Hsio M, Chen CL nd Ho JH. Systemic humn oritl ft-derived stem/stroml cell trnsplnttion meliortes cute inflmmtion in lipopolyscchride-induced cute lung injury. Crit Cre Med 212; 4: Si Y, Zho Y, Ho H, Liu J, Guo Y, Mu Y, Shen J, Cheng Y, Fu X nd Hn W. Infusion of mesenchyml stem cells meliortes hyperglycemi in type 2 dietic rts: identifiction of novel role in improving insulin sensitivity. Dietes 212; 61: Ho H, Liu J, Shen J, Zho Y, Liu H, Hou Q, Tong C, Ti D, Dong L, Cheng Y, Mu Y, Liu J, Fu X nd Hn W. Multiple intrvenous infusions of one mrrow mesenchyml stem cells reverse hyperglycemi in experimentl type 2 dietes rts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 213; 436:
20 Dietes Pge 2 of Hnd T nd Yoshimur A. Regultion of cytokine signling nd inflmmtion. Cytokine Growth Fctor Rev 22; 13: Keting A. Mesenchyml stroml cells. Curr Opin Hemtol 26; 13: English K, Brry FP, Field-Corett CP nd Mhon BP. IFN-gmm nd TNF-lph differentilly regulte immunomodultion y murine mesenchyml stem cells. Immunol Lett 27; 11: Engel AU, Bn CC, Peeters AM, Weimr W nd Hoogduijn MJ. Interction etween dipose tissue-derived mesenchyml stem cells nd regultory T-cells. Cell Trnsplnt 213; 22: Yeung TY, Seeerger KL, Kin T, Adesid A, Jomh N, Shpiro AM nd Korutt GS. Humn mesenchyml stem cells protect humn islets from pro-inflmmtory cytokines. PLoS One 212; 7:e Diez-Ruiz A, Tilz GP, Zngerle R, Bier-Bitterlich G, Wchter H nd Fuchs D. Solule receptors for tumour necrosis fctor in clinicl lortory dignosis. Eur J Hemtol 1995; 54: Solins G, Nugler W, Glimi F, Lee MS nd Krin M. Sturted ftty cids inhiit induction of insulin gene trnscription y JNK-medited phosphoryltion of insulin-receptor sustrtes. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A 26; 13: Bouzkri K, Koistinen HA nd Zierth JR. Moleculr mechnisms of skeletl muscle insulin resistnce in type 2 dietes. Curr Dietes Rev 25; 1: Steinerg GR. Inflmmtion in oesity is the common link etween defects in ftty cid metolism nd insulin resistnce. Cell Cycle 27; 6: Boden G. Ftty cid-induced inflmmtion nd insulin resistnce in skeletl muscle nd liver. Curr Di Rep 26; 6: Mffei M, Hls J, Rvussin E, Prtley RE, Lee GH, Zhng Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lllone R, Rngnthn S nd et l. Leptin levels in humn nd rodent: mesurement of plsm leptin nd o RNA in oese nd weight-reduced sujects. Nt Med 1995; 1: Hls JL, Gjiwl KS, Mffei M, Cohen SL, Chit BT, Rinowitz D, Lllone RL, Burley SK nd Friedmn JM. Weight-reducing effects of the plsm protein encoded y the oese gene. Science 1995; 269: Lord GM, Mtrese G, Howrd JK, Bker RJ, Bloom SR nd Lechler RI. Leptin modultes the T-cell immune response nd reverses strvtion-induced immunosuppression. Nture 1998; 394: Fntuzzi G nd Fggioni R. Leptin in the regultion of immunity, inflmmtion, nd hemtopoiesis. J Leukoc Biol 2; 68:
21 Pge 21 of 3 Dietes Figure legends: Figure 1. Chnge in lood sugr more sensitive thn chnge in ody weight under systemic mesenchyml stem/stroml cell (MSC) regultion (A) A single systemic MSC trnsplnttion rogted the progression of high-ft diet induced hyperglycemi, nd the second dose of MSCs decresed the hyperglycemi. (B) Continued HFD feeding incresed the ody weight of mice, nd MSCs grdully stilized the ody weight fter the second trnsplnttion. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI t the sme time point, n=6 in A nd B) Figure 2. Improvement of glucose tolernce correlted with enhnced distriution of MSCs in liver nd skeletl muscle (A) Persistent HFD intke induced impirment of glucose tolernce. In norml conditions, MSCs did not lter the lood sugr level in response to glucose chllenging, ut significntly improved the impirment of glucose tolernce induced y HFD with one (B) nd two doses (C) of MSCs. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI t the sme time point, n=6 in A-C). (D) One month fter the second MSC trnsplnttion, the rtio of humn DNAs proed y humn et2 microgloulin (hβ2m) versus housekeeper genes (18s rrna for oth mouse nd humn species) ws less thn.1, nd dietic environment cused the trnsplnted MSCs to enhnce their distriution in the liver nd skeletl muscles ut decrese it in ft tissues (lck r). (Student s t- test; * p<.5, n=4) Figure 3. Islet protection nd β-cell differentition of MSCs in dietic pncres (A) Systemic MSCs did not lter the morphology of islets in helthy pncres, nd promoted islet growth in dietic pncres (white rrows) (n=6). (B) Decrese in islet size nd no humn insulin-expressing cells were noted in HFD-induced dietic pncres, while mixed mouse- 21
22 Dietes Pge 22 of 3 nd humn insulin-producing cells were found in some islets of dietic pncres fter MSC trnsplnttion (n=3). (C) Humn insulin ws non-detectle (N.D.) efore trnsplnttion, nd could e detected fter MSC trnsplnttions, nd serum level of humn insulin in dietic mice ws higher thn in norml mice. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=6) (D) MSC trnsplnttion rogted IL-1α, IL-1β, nd TNF-α relese from mouse cells triggered y the HFD. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI, n=4) (E) After MSC trnsplnttion, humn indolemine 2,3-dioxygense (hido), humn (h)il-1, nd humn solule TNF receptor II (hstnf RII) expressions were detectle in pncreses, nd hstnf RII in pncres ws up-regulted y the HFD. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=4) Figure 4. Prevention of ftty liver nd mintennce of glycogen storge y MSCs (A-C) Systemic MSC trnsplnttion neither ltered the morphology nor liver function in norml condition. (A) MSCs prevented HFD-induced fomy chnge in heptocytes (n=6). (B) Periodic cid-schiff (PAS) stining of glycogen demonstrted tht loss of glycogen storge ility in those fomy heptocytes, nd which could e rescued y MSCs (n=3). (C) MSCs significntly reduced HFD-induced the crnitine plmitoyltrnsferse 1A (Cpt 1A) protein expression in the dietic liver. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI, n=3). Figure 5. Up-regultion of interleukin-1 receptor ntgonist (IL-1 RA) y MSCs ssocited with enhnced glucose uptke in dietic skeletl muscles (A) Neither MSCs nor HFD induced significnt pthologicl chnge in skeletl muscles (n=6). (B) Humn IDO, hil-1, hil-1 RA nd hstnf RII were detectle in skeletl muscles nd hil- 1 RA ws strongly responsile for the HFD. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=4) (C) MSC trnsplnttion significntly enhnced Glut4 production in dietic skeletl muscles compred to the norml control. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=3) 22
23 Pge 23 of 3 Dietes Figure 6. Ameliortion of dipose-derived inflmmtion vi dipokine regultion y MSCs (A, B) After systemic MSC trnsplnttion, ft tissues mintined norml ppernce (A) nd norml dipocyte numers (B) in mice fed ND, while HFD triggered inflmmtory cell infiltrtion into ft tissues (A) nd incresed dipocyte numers (B). MSCs reduced HFDinduced inflmmtion in ft tissues (A) ut hd no effect on dipocyte numer reduction (B). (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI, n=6 in A nd B) Systemic MSC trnsplnttion did not lter serum diponectin level (C), ut effectively decresed serum leptin level (D) in dietic mice. After two MSC infusions, circulting TNF-α (E) nd IL-1 (F) levels were reduced in HFD-fed mice. (Student s t-test; * p<.5 t the sme time point, n=6 in C-F) 23
24 Dietes Pge 24 of 3 Tle 1. Primers for Rel-Time Reverse Trnscription-Polymerse Chin Rection β2m: et2 mcrogloulin; IDO: indolemine 2,3-dioxygense; IL-1: interleukin-1; stnf RII: solule tumor necrosis fctor receptor II; IL-1α: interleukin-1 lph; IL-1β: interleukin-1et; TNFα: tumor necrosis fctor lph; 18s rrna: 18s riosoml rionucleic cid. 24
25 Figure 1 Pge 25 of 3 Dietes A HFD MSC (1) MSC (2) GTT (1) GTT (2) GTT (3) Fsting lood sugr (mg/dl) B Bodt weight (g) HFD Before weeks fter HFD feeding c ND ND+MSCs HFD HFD+MSCs, c MSC (1) MSC (2), weeks fter HFD feeding c c,c c c d c c ND ND+MSCs HFD HFD+MSCs Before c c Figure 1. Chnge in lood sugr more sensitive thn chnge in ody weight under systemic mesenchyml stem/stroml cell (MSC) regultion (A) A single systemic MSC trnsplnttion rogted the progression of high-ft diet induced hyperglycemi, nd the second dose of MSCs decresed the hyperglycemi. (B) Continued HFD feeding incresed the ody weight of mice, nd MSCs grdully stilized the ody weight fter the second trnsplnttion. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI t the sme time point, n=6 in A nd B)
26 Figure 2 Dietes Pge 26 of 3 A Blood sugr (mg/dl) D GTT (1) * * * * * ND HFD B Blood sugr (mg/dl) Before hours fter glucose injection hβ2m/18s rrna expression GTT (2), c c c Blood sugr (mg/dl) C c GTT (3) c c c d 3 c 2, ND HFD 1 ND HFD ND+OFSCs ND+MSCs HFD+MSCs HFD+OFSCs ND+OFSCs ND+MSCs HFD+OFSCs HFD+MSCs Before Before hours fter glucose injection hours fter glucose injection * * * ND+MSCs HFD+MSCs pncres liver ft skeletl muscle hert lung spleen kidney d Figure 2. Improvement of glucose tolernce correlted with enhnced distriution of MSCs in liver nd skeletl muscle (A) Persistent HFD intke induced impirment of glucose tolernce. In norml conditions, MSCs did not lter the lood sugr level in response to glucose chllenging, ut significntly improved the impirment of glucose tolernce induced y HFD with one (B) nd two doses (C) of MSCs. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI t the sme time point, n=6 in A-C). (D) One month fter the second MSC trnsplnttion, the rtio of humn DNAs proed y humn et2 microgloulin (hβ2m) versus housekeeper genes (18s rrna for oth mouse nd humn species) ws less thn.1, nd dietic environment cused the trnsplnted MSCs to enhnce their distriution in the liver nd skeletl muscles ut decrese it in ft tissues (lck r). (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=4)
27 Figure 3 Pge 27 of 3 A Dietes ND-Pncres ND+MSCs-Pncres HFD-Pncres HFD+MSCs-Pncres D Reltive expression (normlized y mgapdh) B 2 μm 2 μm HFD-Pncres 1 μm HFD+MSCs-Pncres 1 μm Mouse Insulin Mouse Insulin HFD-Pncres 1 μm HFD+MSCs-Pncres 1 μm ND HFD,c c Humn Insulin Humn Insulin mil-1α mil-1β mtnf-α ND+MSCs HFD+MSCs 2 μm C Serum humn insulin level (mu/l) E Reltive expression μm * ND HFD N.D. N.D. Before MSCs (1) MSCs (2) ND+MSCs N.D. N.D. hido hil-1 hil-1 hil-ra hstnf RII * HFD+MSCs * Figure 3. Islet protection nd β-cell differentition of MSCs in dietic pncres (A) Systemic MSCs did not lter the morphology of islets in helthy pncres, nd promoted islet growth in dietic pncres (white rrows) (n=6). (B) Decrese in islet size nd no humn insulin-expressing cells were noted in HFD-induced dietic pncres, while mixed mouse- nd humn insulin-producing cells were found in some islets of dietic pncres fter MSC trnsplnttion (n=3). (C) Humn insulin ws non-detectle (N.D.) efore trnsplnttion, nd could e detected fter MSC trnsplnttions, nd serum level of humn insulin in dietic mice ws higher thn in norml mice. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=6) (D) MSC trnsplnttion rogted IL-1α, IL-1β, nd TNF-α relese from mouse cells triggered y the HFD. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI, n=4) (E) After MSC trnsplnttion, humn indolemine 2,3-dioxygense (hido), humn (h)il-1, nd humn solule TNF receptor II (hstnf RII) expressions were detectle in pncreses, nd hstnf RII in pncres ws up-regulted y the HFD. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=4)
28 Figure 4 Dietes Pge 28 of 3 A ND-Liver ND+MSCs-Liver HFD-Liver HFD+MSCs-Liver 2 μm 2 μm 2 μm 2 μm B ND-Liver ND+MSCs-Liver HFD-Liver HFD+MSCs-Liver 2 μm PAS 2 μm PAS 2 μm PAS 2 μm PAS C Reltive Cpt1A expression Cpt1A ND ND+MSCs HFD HFD+MSCs Figure 4. Prevention of ftty liver nd mintennce of glycogen storge y MSCs (A-C) Systemic MSC trnsplnttion neither ltered the morphology nor liver function in norml condition. (A) MSCs prevented HFD-induced fomy chnge in heptocytes (n=6). (B) Periodic cid- Schiff (PAS) stining of glycogen demonstrted tht loss of glycogen storge ility in those fomy heptocytes, nd which could e rescued y MSCs (n=3). (C) MSCs significntly reduced HFDinduced the crnitine plmitoyltrnsferse 1A (Cpt 1A) protein expression in the dietic liver. (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI, n=3).
29 Figure 5 Pge 29 of 3 Dietes A ND-Skeletl muscle ND+MSCs-Skeletl muscle HFD-Skeletl muscle HFD+MSCs-Skeletl muscle 2 μm 2 μm 2 μm 2 μm B Reltive expression ND+MSCs HFD+MSCs hido hil-1 hil-1 hil-ra RA hstnf RII * C Reltive GLUT4 expression Glut4 * ND+MSCs HFD+MSCs Figure 5. Up-regultion of interleukin-1 receptor ntgonist (IL-1RA) y MSCs ssocited with enhnced glucose uptke in dietic skeletl muscles (A) Neither MSCs nor HFD induced significnt pthologicl chnge in skeletl muscles (n=6). (B) Humn IDO, hil-1, hil-1 RA nd hstnf RII were detectle in skeletl muscles nd hil- 1RA ws strongly responsile for the HFD. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=4) (C) MSC trnsplnttion significntly enhnced Glut4 production in dietic skeletl muscles compred to the norml control. (Student s t-test; * p<.5, n=3)
30 Figure 6 Dietes Pge 3 of 3 A ND-Ft ND+MSCs-Ft HFD-Ft HFD+MSCs-Ft 2 μm 2 μm 2 μm 2 μm B numer of dipocytes/ hgih power field (2x) Numer of dipocytes ND ND+MSCs HFD HFD+MSCs C Serum diponectin (ng/ml) Adiponectin HFD HFD+MSCs Before MSC (1) MSC (2) D Serum leptin level (pg/ml) Leptin * * HFD HFD+MSCs Before MSC (1) MSC (2) E Serum TNF-α (pm/ml) TNF-α * HFD HFD+MSCs Before MSC (1) MSC (2) F Serum IL-1 level (pg/ml) IL-1 * HFD HFD+MSCs Before MSC (1) MSC (2) Figure 6. Ameliortion of dipose-derived inflmmtion vi dipokine regultion y MSCs (A, B) After systemic MSC trnsplnttion, ft tissues mintined norml ppernce (A) nd norml dipocyte numers (B) in mice fed ND, while HFD triggered inflmmtory cell infiltrtion into ft tissues (A) nd incresed dipocyte numers (B). MSCs reduced HFD-induced inflmmtion in ft tissues (A) ut hd no effect on dipocyte numer reduction (B). (ANOVA, Bonferroni's post-hoc test with 95% CI, n=6 in A nd B) Systemic MSC trnsplnttion did not lter serum diponectin level (C), ut effectively decresed serum leptin level (D) in dietic mice. After two MSC infusions, circulting TNF-α (E) nd IL-1 (F) levels were reduced in HFD-fed mice. (Student s t-test; * p<.5 t the sme time point, n=6 in C-F)
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
SYNOPSIS Final Abbreviated Clinical Study Report for Study CA ABBREVIATED REPORT
 Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
11/7/2011. Disclosures. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) DC-STAMP I II III IV. None
 unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Background Pears (Pyrus L.) are one of the leading cultivated fruit trees in China following apples and oranges in planting area and fruit yield.
 Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated β-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling
 Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
Study of Stress Distribution in the Tibia During Stance Phase Running Using the Finite Element Method
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
mir-155 is dispensable in monosodium urate-induced gouty inflammation in mice
 Yng et l. Arthritis Reserch & Therpy (2018) 20:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1550-y RESEARCH ARTICLE mir-155 is dispensle in monosodium urte-induced gouty inflmmtion in mice Qiin Yng 1,3,4, Quno
Yng et l. Arthritis Reserch & Therpy (2018) 20:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1550-y RESEARCH ARTICLE mir-155 is dispensle in monosodium urte-induced gouty inflmmtion in mice Qiin Yng 1,3,4, Quno
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
Supporting Information. In Situ Supramolecular Assembly and Modular Modification of Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels for 3D Cellular Engineering
 Supporting Informtion In Situ Suprmoleculr Assemly nd Modulr Modifiction of Hyluronic Acid Hydrogels for 3D Cellulr Engineering Kyeng Min Prk,, Jeong-A Yng,, Hyunte Jung, c Junseok Yeom, Ji Sun Prk, d
Supporting Informtion In Situ Suprmoleculr Assemly nd Modulr Modifiction of Hyluronic Acid Hydrogels for 3D Cellulr Engineering Kyeng Min Prk,, Jeong-A Yng,, Hyunte Jung, c Junseok Yeom, Ji Sun Prk, d
SESSIONE I: RELATORI. Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signal to metabolic master regulator?
 SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Supporting Information
 Supporting Informtion Yun et l. 1.173/pns.1523236113 SI Mterils nd Methods Humn Sujects. All prticipnts in our study were recruited from the Center for Reproductive Medicine, Shndong Provincil Hospitl
Supporting Informtion Yun et l. 1.173/pns.1523236113 SI Mterils nd Methods Humn Sujects. All prticipnts in our study were recruited from the Center for Reproductive Medicine, Shndong Provincil Hospitl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Effects of Sini San used alone and in combination with fluoxetine on central and peripheral 5-HT levels in a rat model of depression
 Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Input from external experts and manufacturer on the 2 nd draft project plan Stool DNA testing for early detection of colorectal cancer
 Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
ESM Table 1. Characterisation of the human non-diabetic cohort used for MRIbased assessment of pancreatic fat and insulin secretion via OGTT.
 ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
Chromium Alleviates Glucose Intolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic ER Stress in Obese Mice
 nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
Diabetes mellitus secondary to pancreatic diseases (type 3c): The effect of smoking on the exocrine endocrine interactions of the pancreas
 764062DVR0010.1177/1479164118764062Dibetes & Vsculr Disese ReserchŚliwińsk-Mossoń et l. reserch-rticle2018 Originl Article Dibetes mellitus secondry to pncretic diseses (type 3c): The effect of smoking
764062DVR0010.1177/1479164118764062Dibetes & Vsculr Disese ReserchŚliwińsk-Mossoń et l. reserch-rticle2018 Originl Article Dibetes mellitus secondry to pncretic diseses (type 3c): The effect of smoking
Interleukin-4 Restores Insulin Sensitivity in Lipid-Induced Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes
 ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
Serum nesfatin-1 levels are decreased in pregnant women newly diagnosed with gestational diabetes
 originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
The different mechanisms of insulin sensitizers to prevent type 2 diabetes in OLETF rats
 RESEARCH ARTICLE DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Dietes Met Res Rev 2007; 23: 411 418. Pulished online 30 My 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).756 The different mechnisms
RESEARCH ARTICLE DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Dietes Met Res Rev 2007; 23: 411 418. Pulished online 30 My 2007 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).756 The different mechnisms
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Relationship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients
 J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice
 Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA
 Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Metabolic syndrome as a risk factor for high-ocular tension
 Interntionl Journl of Oesity (2010) 1 9 & 2010 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited All rights reserved 0307-0565/10 $32.00 www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE Metolic syndrome s risk fctor for high-oculr K Imi 1,
Interntionl Journl of Oesity (2010) 1 9 & 2010 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited All rights reserved 0307-0565/10 $32.00 www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE Metolic syndrome s risk fctor for high-oculr K Imi 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin
 Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
Effects of immunosuppression on alpha and beta cell renewal in transplanted mouse islets
 Dietologi () :9 DOI.7/s--89-z ARTICLE Effects of immunosuppression on lph nd et cell renewl in trnsplnted mouse islets C. Krutz & S. Wolk & A. Steffen & K.-P. Knoch & U. Ceglrek & J. Thiery & S. Bornstein
Dietologi () :9 DOI.7/s--89-z ARTICLE Effects of immunosuppression on lph nd et cell renewl in trnsplnted mouse islets C. Krutz & S. Wolk & A. Steffen & K.-P. Knoch & U. Ceglrek & J. Thiery & S. Bornstein
The Effect of Substituting Sugar with Artificial. Sweeteners on the Texture and Palatability of Pancakes
 The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
WSU Tree Fruit Research and Extension Center, Wenatchee (509) ext. 265;
 FINAL REPORT WTFRC Project # AH-1-5 WSU Project # 13C-355-3 Project title: PI: Orgniztion: Coopertors: of Sunburn in Apples with RAYNOX Lrry Schrder, Horticulturist WSU Tree Fruit Reserch nd Extension
FINAL REPORT WTFRC Project # AH-1-5 WSU Project # 13C-355-3 Project title: PI: Orgniztion: Coopertors: of Sunburn in Apples with RAYNOX Lrry Schrder, Horticulturist WSU Tree Fruit Reserch nd Extension
Enhanced Chemopreventive Effect by Combining Quercetin and Green tea in Prostate Cancer
 Enhnced Chemopreventive Effect y Comining Quercetin nd Green te in Prostte Cncer Piwen Wng, MD, PhD Assistnt Professor, Division of Cncer Reserch nd Trining Chrles R. Drew University of Medicine nd Science
Enhnced Chemopreventive Effect y Comining Quercetin nd Green te in Prostte Cncer Piwen Wng, MD, PhD Assistnt Professor, Division of Cncer Reserch nd Trining Chrles R. Drew University of Medicine nd Science
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
Bright Futures Medical Screening Reference Table 2 to 5 Day (First Week) Visit
 Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Role of EP2 and EP4 receptor-selective agonists of prostaglandin E 2 in acute and chronic kidney failure
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Role of EP2 nd EP4 receptor-selective gonists of prostglndin E 2 in cute nd chronic kidney filure S Vukicevic 1,
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 26 Interntionl Society of Nephrology originl rticle Role of EP2 nd EP4 receptor-selective gonists of prostglndin E 2 in cute nd chronic kidney filure S Vukicevic 1,
Hormonal networks involved in phosphate deficiencyinduced cluster root formation of Lupinus albus L.
 Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ameliorates lipid and glucose accumulation in C57BL/6J mice via activation of PPAR-α and AMPK
 3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
Food & Function Accepted Manuscript
 Food & Function Accepted Mnuscript This is n Accepted Mnuscript, which hs een through the Royl Society of Chemistry peer review process nd hs een ccepted for puliction. Accepted Mnuscripts re pulished
Food & Function Accepted Mnuscript This is n Accepted Mnuscript, which hs een through the Royl Society of Chemistry peer review process nd hs een ccepted for puliction. Accepted Mnuscripts re pulished
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
TREM-1 regulates macrophage polarization in ureteral obstruction
 sic reserch http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology regultes mcrophge polriztion in ureterl ostruction Tzu-Hn Lo 1,1, Ki-Yu Tseng,1, Wen-Shn Tso, Chih-Y Yng,3, Shie-Ling
sic reserch http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology regultes mcrophge polriztion in ureterl ostruction Tzu-Hn Lo 1,1, Ki-Yu Tseng,1, Wen-Shn Tso, Chih-Y Yng,3, Shie-Ling
Supporting information
 Supporting informtion Multiple Univrite Dt Anlysis Revels the Inulin Effects on the High-ft-diet Induced Metolic Altertions in Rt Myocrdium nd Testicles in the Pre-oesity Stte Yixun Dun #, Ynpeng An #,
Supporting informtion Multiple Univrite Dt Anlysis Revels the Inulin Effects on the High-ft-diet Induced Metolic Altertions in Rt Myocrdium nd Testicles in the Pre-oesity Stte Yixun Dun #, Ynpeng An #,
The RUTHERFORD-2 trial in heterozygous FH: Results and implications
 The RUTHERFORD-2 tril in heterozygous FH: Results nd implictions Slide deck kindly supplied s n eductionl resource by Professor Derick Rl MD PhD Crbohydrte & Lipid Metbolism Reserch Unit University of
The RUTHERFORD-2 tril in heterozygous FH: Results nd implictions Slide deck kindly supplied s n eductionl resource by Professor Derick Rl MD PhD Crbohydrte & Lipid Metbolism Reserch Unit University of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 and STAT6
 ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
