Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice
|
|
|
- Patience Mason
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Online Sumissions: fice doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): ISSN (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Curcumin ttenutes Nrf2 signling defect, oxidtive stress in muscle nd glucose intolernce in high ft diet-fed mice Hui-Jun He, Guo-Yu Wng, Yun Go, Wen-Hu Ling, Zhi-Wen Yu, Tin-Ru Jin Hui-Jun He, Guo-Yu Wng, Yun Go, Wen-Hu Ling, Zhi- Wen Yu, Tin-Ru Jin, Deprtment of Nutrition, School of Pulic Helth, Sun Yt-sen University, Room 17, 74 Zhongshn 2 nd Rod, Gungzhou 18, Gungdong Province, Chin Author contriutions: He HJ performed the experiments throughout the study nd wrote the drft of this mnuscript; Wng GY nd Go Y prticipted in the intrperitonel glucose tolernce test experiments nd mice tissue collection; Ling WH provided his dvice on feeding nd the dosge of curcumin in this study; Yu ZW designed the study, provided technicl guidnce nd edited this pper; Jin TR coordinted the study, provided importnt guidnce nd finl editing of the mnuscript. Supported y A Ntionl Nturl Science Foundtion of Chin Grnt, No to Jin TR nd Yu ZW Correspondence to: Dr. Zhi-Wen Yu, Associte Professor, Deprtment of Nutrition, School of Pulic Helth, Sun Yt-sen University, Room 17, 74 Zhongshn 2 nd Rod, Gungzhou 18, Gungdong Province, Chin. yuzhiwen@yhoo.com Telephone: Fx: Received: Jnury 29, 212 Revised: April 19, 212 Accepted: My 11, 212 Pulished online: My 1, 212 Astrct AIM: To investigte the signling mechnism of ntioxidtive ction y curcumin nd its impct on glucose disposl. METHODS: Mle C7BL/6J mice were fed with either norml diet (n = 1) or high ft diet () (n = 2) to induce oesity nd insulin resistnce. After 16 wk, 1 -fed mice were further treted with dily curcumin orl gvge t the dose of mg/kg ody weight (BW) ( + curcumin group). After 1 d of the curcumin supplementtion, n intrperitonel glucose tolernce test ws performed. Fsting lood smples were lso collected for insulin nd glucose mesurements. Insulin-sensitive tissues, including muscle, dipose tissue nd the liver, were isolted for the ssessments of mlondildehyde (MDA), rective oxygen species (ROS) nd nucler fctor erythroid-2-relted fctor-2 (Nrf2) signling. RESULTS: We show here tht in mouse model, short-term curcumin gvge ttenuted glucose intolernce without ffecting -induced BW gin. Curcumin lso ttenuted -induced elevtions of MDA nd ROS in the skeletl muscle, prticulrly in its mitochondril frction, ut it hd no such n effect in either dipose tissue or the liver of -fed mice. Correspondingly, in skeletl muscle, the levels of totl or nucler content of Nrf2, s well s its downstrem trget, heme oxygense-1, were reduced y -feeding. Curcumin intervention drmticlly reversed these defects in Nrf2 signling. Further nlysis of the reltionship of oxidtive stress with glucose level y regression nlysis showed positive nd signi ficnt correltion etween the re under the curve of glucose tolernce test with MDA levels either in muscle or musculr mitochondri. CONCLUSION: These findings suggest tht the shortterm tretment of curcumin in -fed mice effectively meliortes musculr oxidtive stress y ctivting Nrf2 function tht is novel mechnism for its effect in improving glucose intolernce. 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. Key words: Oxidtive stress; Insulin resistnce; Glucose tolernce; Nucler fctor erythroid-2-relted fctor-2; Curcumin; Mitochondri Peer reviewers: Suresh T Mthews, Professor, Deprtment of Nutrition nd Food Science, Auurn University, Auurn, AL 36849, United Sttes;; Dr. Serp Ylin, Phrmcy Fculty, Mersin University, Mersin 33169, Turkey He HJ, Wng GY, Go Y, Ling WH, Yu ZW, Jin TR. Curcumin ttenutes Nrf2 signling defect, oxidtive stress in muscle nd glucose intolernce in high ft diet-fed mice. World J Dietes 94 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
2 He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce 212;; 3(): Aville from: URL: wjgnet.com/ /full/v3/i/94.htm DOI: org/239/wjd.v3.i.94 INTRODUCTION Oesity is ssocited with high incidence of mny metolic disorders, including type 2 dietes mellitus nd crdiovsculr diseses [1,2]. Insulin resistnce is recognized s core mechnism for these oesity-relted diseses. Extensive recent studies hve shown tht chronic ctivtion of inflmmtory signling, endoplsmic reticulum (ER) stress nd mitochondril dysfunction remongthe mong etiologiclicl fctors of insulinresistnce [3,4]. In ddition, the cusl reltionship etween oxidtive stress nd the development of insulin resistnce [-7] hs een suggested for long time, while ithsginedmuchmorettention more ttention recently due to the recognitionof of theinvolvementof of mitochondril-derived oxidtive stress in the etiology of insulin resistnce [4,8]. Over nutrition supply or high ft diet () consumption led to incresed mitochondril oxidtive phosphoryltion nd inevitle rective oxygen species (ROS) )over-production [7,8]. Mmmls however, hve evolved endogenous nti-oxidtive systems to prevent oxidtive stress nd mintin insulin sensitivity. The trnscription nucler fctor erythroid-2-relted fctor-2 (Nrf2) plys mjor role in mintining redox lnce. In resting cell, Nrf2 molecules minly reside in cell cytosol nd re nchored with its negtive regultor Kelch-like ECH-ssocited protein 1 (Kep1). The coupling etween Nrf2 nd Kep1 leds to Nrf2 protesoml degrdtion [9]. When oxidtive stress occurs, Nrf2 nd Kep1 will e seprted, leding to the elevtion of free Nrf2 level nd the increse of Nrf2 nucler trnsloction. Nucler Nrf2 will then ind to the consensus nucleotide sequence, nmely ntioxidnt response element (ARE), in the promoter regions of ttery of genes tht encode ntioxidnt enzymes [9,1]. Since oxidtive stress is n importnt etiologicl fctor in ging, inflmmtion nd tumor growth, it is not surprising tht Nrf2 cn modulte the progress of these diseses [11,12]. Interestingly, certin nturl phyto-compounds, including curcumin, re Nrf2 ctivtors nd hve potentil therpeutic effect for diseses, including inflmmtion, tumor, hert filure, neurodegenertive diseses nd ischemi [13-16]. Curcumin hs lso een shown to sensitize insulin ction in -fed dietic models [17]. The understnding of moleculr mechnisms underlying the insulin sensitizing ction y curcumin is essentil for the genertion of interventionl pproches. Most in vivo investigtions hve een conducted to explore long-term effect of curcumin nd its eneficil effect on insulin signling minly vi reducing ody weight (BW) gin nd inhiiting inflmmtory rections [17,18]. However, in spite of the documented nti-oxidtive function of curcumin [14], no ttempt hs een mde to correlte the role of curcuminmedited nti-oxidtive function nd its impct on insulin sensitivity. Since curcumin hs een shown to ctivte Nrf2 in cultured cells [1], here we sked whether curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 system in vivo nd whether the ctivtion leds to improved insulin signling. To investigte whether the eneficil effect of curcumin cn e chieved independent of its BW lowering effect, we delivered low dose of curcumin y gvge short-term to void BW chnge. MATERIALS A METHODS Mterils Mle C7BL/6J mice (8 wk of ge) were purchsed from the Lortory Animl Center of Sun Yt-sen University. Curcumin (curcuminoid content 94%), common chemicls nd protese inhiitors were otined from Sigm Chemicl Compny (St Louis, MO). Norml diet () (8% clories from ft) nd (6% clories from ft) were provided y Gungdong Animl Center, (Gungzhou, Gungdong, Chin). Nrf2 ntiody ws from Snt Cruze Biotechnology (Snt Cruz, CA). Heme oxygense-1 (HO-1) nd -ctin ntiodies were from the Proteintech Group (Chicgo, IL). Histone H3 ntiody ws otined from Cell Signling Technology (Denvers, MA, United Sttes). Bicinchoninic cid (BCA) ssy kit ws purchsed from Pierce Bio-technology, Inc. (Rockford, IL). Enhnced chemiluminescence (ECL) ws purchsed from Thermo Scientific (Rockford, IL). Blood glucose meter ws otined from ACON Lortories, Inc. (Sn Diego, CA). ROS ssy kit ws purchsed from GENMED Scientifics (Shnghi, Chin). Mlondildehyde (MDA) ssy kit ws purchsed from ZeptoMetrix (Bufflo, NY). Animl cre nd tretment The niml experiments were performed in ccordnce with the Guide for Cre nd Use of Experimentl Animls (Sun Yt-sen University, SYSU). Thirty mice were housed in n environmentlly controlled room t 22 ± 2. nd % ± % humidity with 12-h: 12-h light/drk cycle. The mice hd ccess to food nd wter d liitum. After one week dptive period, the mice were rndomly divided into two weight-mtched groups. Ten mice were fed with nd the rest of them (2 mice) were fed with. BW ws mesured weekly. After 16 wk of feeding, -fed mice were further divided into two weight-mtched groups, e.g., group (n = 1) nd plus curcumin treted group (n = 1). Curcumin ws given dily y orl gvge t the dose of mg/kg BW in 1% croxymethyl cellulose uffer solution for 1 d. Mice in the nd group were gvged with vehicle only. For lood smple nd tissue collection, ll mice were euthnized fter fsting for 6 h. Blood smples were tken nd centrifuged t 4 t 3 rpm for 1 min for collecting the serum. Menwhile, skeletl muscle in qudriceps, livers nd epididyml ft pds were rpidly isolted, followed y immedite freezing in liquid nitrogen nd then stored t -8 efore further nlyses. 9 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
3 He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce Intrperitonel glucose tolernce test Intrperitonel glucose tolernce test ws performed s previously descried [19]. Briefly, mice were fsted overnight, followed y glucose (1 g/kg) injection intrperitonelly. Blood smples collected from til vein were used for glucose mesurement. Mitochondril nd nucler frctiontion Nucler nd mitochondril frctiontion were performed s previously descried [2,21] with slight modifiction. Aout 3 mg skeletl muscle ws homogenized in 1 ml ice-cold uffer contining 2 mmol/l HEPES (ph 7.4), 2 mmol/l sucrose, 1 mmol/l KCl, 1. mmol/l MgCl2, 1 mmol/l EDTA, 1 mmol/l EGTA, 1 mmol/l dithiothreitol nd the protese inhiitors [2 μg/ml protinin, μg/ml leupeptin nd 2 mmol/l phenylmethyl sulphonyl fluoride (PMSF)]. Following the homogeniztion procedure, smples were incuted on ice for 2 min. Centrifugtion ws then crried out t 72 g t 4 for min. The nucler pellet ws dispersed y the uffer nd pssed through 21G needle 2 times. The smples were then centrifuged gin t 72 g t 4 for 1 min. After removing the superntnt, the nucler pellet ws re-suspended in μl nucler lysis uffer contining 2 mmol/l Tris (ph 7.), 137 mmol/l NCl, 2 mmol/l EDTA, 1 mmol/l CCl2, 1 mmol/l MgCl2, 1% Nonidet P-4 (NP-4), 2 mmol/l sodium orthovndte, 1 mmol/l sodium fluoride, 1 mmol/l sodium pyrophosphte, 1% glycerol,.1% sodium dodecyl sulfte (SDS) nd the forementioned protese inhiitors. The nucler pellet ws sonicted riefly for 3 s nd sved for western lotting. For mitochondril frctiontion whole cell lyste fter removing the nuclei ws centrifuged t 1 g, 4 for 1 min nd sved the pellet s mitochondril frction t -8. MDA nlysis in serum nd tissues MDA level ws determined y the thiorituric cid (TBA) method [22]. TBA rection ws performed ccording to mnufctory guidnce. To ssess MDA level in serum, 1 L serum ws used. For tissue MDA ssy out 3 mg of tissues (skeletl muscle, liver or dipose tissue) or mitochondri extrcted from 3 mg skeletl muscle were homogenized in 3 L ice-cold PBS. TBA rection ws performed ccording to mnufctory guidnce. Briefly, smples were incuted with TBA nd SDS t 9 for 1 h, followed y centrifugtion t 8 g for 1 min. Superntnts were trnsferred to 96-well plte nd the sornce ws mesured t 32 nm. The protein concentrtion in smples ws determined y BCA ssy kit. Serum MDA level ws clculted ccording to the formul provided y the compny guidnce, i.e., serum MDA (nmol/ml) = (smple OD vlue-ckground OD)/( Stndrd OD-lnk OD) stndrd concentrtion (1 nmol/ml) smple dilution times, while tissue MDA level fter the clcultion ws further corrected y smple protein concentrtion (mg protein/ml). MDA equivlents were expressed s nmol/mg tissue protein or nmol/ml serum. ROS mesurements in tissues Skeletl muscles were homogenized nd ROS level nlysis ws performed using 2,7 -dichlorofluorescein dicette fluorescent dye s proe nd fluorescence density ws mesured t 49/2 nm ccording to mnufctory guidnce nd the mesured vlues of opticl density [ reltive fluorescence unit (RFU)] were corrected y the protein concentrtions of smples nd were expressed s RFU/ g protein. Insulin nd glucose mesurements nd homeostsis model ssessment - insulin resistnce index After the mice were fsted for 6 h, lood smples were collected. To ssess plsm insulin levels, n ELISA sed method (Mercodi AB, Uppsl, Sweden) ws used, the method ws ccording to mnufctory guidnce nd expressed s g/l. Plsm glucose ssy levels were determined using glucose ssy kit from Sigm-Aldrich (Sint Louis, United Sttes), with the method provided y the mnufcturer. The level of the originl plsm glucose concentrtion ws mesured t 4 nm nd expressed s mg/dl. Homeostsis model ssessment- insulin resistnce index (HOMA-IR) ws clculted s [fsting plsm glucose (mmol/l) fsting serum insulin ( IU/mL)] /22. [23]. Tissue protein preprtion nd western lotting Methods for tissue protein preprtion nd western lotting were performed s descried [19]. A frction of liver, dipose tissue nd skeletl muscle were homogenized in ice-cold lysis uffer contining 2 mmol/l Tris (ph 7.), 137 mmol/l NCl, 2 mmol/l EDTA, 1 mmol/l CCl2, 1 mmol/l MgCl2, 1% NP-4, 2 mmol/l sodium orthovndte, 1 mmol/l sodium fluoride, 1 mmol/l sodium pyrophosphte, 1% glycerol, 2 g/ml protinin, g/ml leupeptin nd 2 mmol/l PMSF. The homogentes were then sonicted on ice cold conditions three times for 2 s nd centrifuged t 12 rpm for 1 min t 4. The superntnt ws collected. The protein concentrtion ws determined y BCA ssy kit. Equl mounts of proteins were used for western lot nlysis. The proteins were heted t 9 for min in SDS smple loding uffer nd underwent SDS-PAGE nlysis s descried in the following. The cellulr proteins were seprted y SDS-PAGE (1%) nd trnsferred to nitrocellulose memrnes. Following the trnsfer, the memrnes were incuted for 1. h t room temperture in the uffer contining 2 mmol/l Tris (ph 7.6), 14 mmol/l NCl,.1% Tween-2 nd % skimmed milk. The memrnes were then proed with ntiody overnight t 4. The memrnes were wshed nd incuted with secondry ntiody conjugted to horserdish peroxidse. Immunorective proteins were visulized with ECL. The intensities of the nds were quntified y phosphorimger nlysis using NIH imge softwre. 96 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
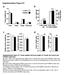
4 Body weights (g) He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce A curcumin c B t/wk Adipose weight (g) C Liver weight (g) Sttisticl nlysis All the vlues were expressed s men ± SE. Sttisticl comprisons of mens mong three groups were crried out y using nlysis of vrince nd the P vlue less thn. ws considered to e sttisticlly significnt. d + curcumin + curcumin Figure 1 Effects of short term curcumin gvge on weights of whole ody, epididyml ft tissue nd liver. A: Body weight. The ody weight of mice ws mesured weekly following norml diet or high ft diet feeding during the period of 18 wk. The rrow indictes the strting time of curcumin gvge; B: Weight of epididyml dipose tissue; C: Liver weight. The mice were fed with either norml diet (, n = 1) or high ft diet (, n = 2) for 16 wk. The fed mice then received gvge of either curcumin ( mg/kg per dy, n = 1) or vehicle (1% croxymethyl cellulose uffer, n = 1) for 1 d. The fed mice were lso gvged with the vehicle. The mice were scrificed for tissue isoltion nd weighing. P <.1, or + curcumin vs ; P <.1, + curcumin vs ; c P <.1 + curcumin vs ; d P <., + curcumin vs. Four mice from nd four mice from + curcumin group died during the gvge procedure. The correltion etween re under the curve (AUC) nd MDA or ROS ws tested with the method of multiple liner regressions. RESULTS Short-term curcumin tretment does not lter BW Firstly, we fed the mice with to induce oesity nd insulin resistnce. As shown in Figure 1A, mice who received feeding exhiited more rigorous BW gin when compred with the mice of the group. The difference reched sttisticl significnce t 11 wk fter feeding. Curcumin ws supplemented fter 16 wk feeding during consumption, which ws different from the previous studies when curcumin ws dministered t the eginning of feeding nd prevented -induced oesity [17,18]. A short-term nd low dose of curcumin dministrtion ws designed to void its BW lowering effect in order to detect the primry mechnism of its ction. We gvged group of -fed mice with mg/kg BW of curcumin consecutively for 1 d. The control mice received the vehicle solution. This curcumin tretment did not lter BW gin in mice while fed with (Figure 1A). To further detect its effect on oesity, the weight of epididyml ft pds (n indictor of viscerl ft mss) ws mesured. We oserved tht induced out n 8-fold increse in the weight of epididyml ft pds compred to mice (:.21 ±.7 g vs : 1.6 ±.12 g, P <.1, Figure 1B), while curcumin gvge only modertely reduced the weight of epididyml ft in mice who received ( + curcumin: 1.19 ±.2 g vs : 1.6 ±.12 g, P <., Figure 1B) nd compred with mice in the group, the increse of the weight of epididyml ft in curcumintreted mice ws still out -fold (:.21 ±.7 g vs + curcumin: 1.19 ±.2 g, P <.1, Figure 1B). We lso mesured the weight of the liver nd there ws no sttisticl difference mong the three groups (Figure 1C). Curcumin improves glucose disposl nd insulin sensitivity As indicted previously, curcumin dministrtion signifi- 97 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
5 AUC (mmol/l 12 min) Serum insulin ( IU/mL) He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce A 3 + curcumin Blood glucose (mmol/l) e t/min B 3 c C d e f 1 2 D + curcumin E + curcumin Serum glucose (mmol/l) curcumin HOMA-IR e + curcumin Figure 2 Effects of short term curcumin gvge on glucose tolernce nd insulin sensitivity. A: Intrperitonel glucose tolernce test in the norml diet group (n = 1), high ft diet group (n = 6) nd high ft diet plus curcumin group (n = 6); B: Are under the curve of glucose tolernce test; C: Are under the curve; D: Fsting plsm glucose levels; E: Homeostsis model ssessment - insulin resistnce index vlues. The mice were fed with different diets nd gvged with curcumin s indicted in Figure 1. At the end of 18 wk following norml diet (), high ft diet () nd +curcumin tretments, intrperitonel glucose tolernce test ws performed nd lood glucose levels were mesured. P <.1, or + curcumin vs t ech time point; P <.1, vs ; c P <.1, vs ; d P <., + curcumin vs ; e P <.1, + curcumin vs ; f P <., +curcumin vs. AUC: Are under the curve; HOMA-IR: Homeostsis model ssessment- insulin resistnce index. cntly prevented -induced insulin resistnce y longterm supplementtion [17]. To ssess whether curcumin could reverse insulin insensitivity in n estlished oese model or to test its tretment efficcy, we performed n intrperitonel glucose tolernce test (IPGTT). As shown in Figure 2A, fter 18 wk feeding of, glucose levels following the i.p. injection were significntly higher when compred with those in -fed mice. Curcumin tret- 98 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
6 He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce A 2 B 4 Serum MDA (mmol/l) Muscle MDA (mmol/l) C 6 + curcumin D + curcumin Muscle ROS (RFU/ g) Mitochondril MDA (mmol/mg) curcumin + curcumin Figure 3 Effects of short term gvge of curcumin on mlondildehyde levels. A: Serum mlondildehyde levels; B: Mlondildehyde levels in skeletl muscle; C: Rective oxygen species level in whole cell lystes of skeletl muscle; D: Mlondildehyde levels in mitochondri of skeletl muscle. The mice were fed with indicted diets nd gvged with curcumin or vehicle. At the end of 18 wk following norml diet (, n = 1), high ft diet (, n = 6) nd + curcumin (n = 6) tretments, the mice were scrificed for lood nd tissue collections. Serum ws isolted, tissues were homogenized nd mitochondri were isolted. Mlondildehyde ssessments or rective oxygen species ssy were performed s descried in Mterils nd Methods. P <.1, vs ; P <.1 + curcumin vs ; c P <.1, + curcumin vs. MDA: Mlondildehyde; ROS: Rective oxygen species. ment reduced lood glucose levels (Figure 2A). The nlysis of AUC of the IPGTT during the tested 12 min lso showed tht induced out 2-fold increse in the AUC index compred to tht in mice, while curcumin normlized this elevtion y more thn % (Figure 2B). Furthermore, in order to ssess whether insulin sensitivity ws enhnced y curcumin, we mesured fsting glucose nd insulin levels (Figure 2C nd D) nd clculted the HOMA-IR index (Figure 2E). We found tht induced lmost 3-fold increse in this index while curcumin significntly reversed this normlity. These results indicte tht the effect of curcumin on improving glucose disposl is vi enhncing insulin ction nd this ction of curcumin in -fed mice is disposle with its effect on ttenuting BW gin. Curcumin meliortes -induced oxidtive stress in skeletl muscle nd mitochondri Incresed evidence indictes tht oxidtive stress plys cusl role in the development of insulin resistnce [7,24,2]. We tested whether nd curcumin lter redox lnce y ssessing MDA levels, stle indictor of oxidtive stress [22]. As shown in Figure 3A, induced pproximtely 2% elevtion of serum MDA level, while short-term curcumin gvge completely reversed this elevtion (: ±. nmol/ml vs + curcumin: ±.91 nmol/ml, P <.1). We then ssessed MDA levels in the insulin sensitive tissues. MDA level in the skeletl muscle of -fed mice ws incresed pproximtely 2-fold when compred with tht in the mice (Figure 3B). Curcumin dministrtion decresed musculr MDA content to the level tht ws comprle with tht in the mice (Figure 3B). Furthermore, musculr ROS content ws incresed out 4% y feeding while curcumin tretment completely locked this elevtion (: ± 4.3 RFU/ g vs : 1.7 ± 4.92 RFU/ g vs P <.1; : 1.7 ± 4.92 RFU/ g vs + curcumin: 3.18 ± 6.66 RFU/ g, P <.1, Figure 3C). Since mitochondril oxidtive stress plys mjor custive role in insulin resistnce in the condition of nutrition over consumption [4,8], we mesured the MDA level in the mitochondril frction of skeletl muscles. 99 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
7 He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce A 7 B curcumin MDA of dipose tissue (nmol/mg) Liver MDA (nmol/mg) + curcumin Figure 4 Effects of curcumin on dipose nd liver mlondildehyde levels. A: Mlondildehyde levels in dipose tissue; B: Mlondildehyde levels in liver. The mice were fed with indicted diets nd gvged with curcumin or vehicle. At the end of 18 wk following norml diet (, n = 1), high ft diet (, n = 6) nd + curcumin (n = 6) tretments, the mice were scrificed, tissues were homogenized nd mlondildehyde levels were mesured s indicted in the Mterils nd Methods. P <.1, or +curcumin vs. MDA: Mlondildehyde. Indeed, the MDA level in the mitochondril frction ws pronouncedly elevted in the -fed mice (4-fold elevtion compred to mice) nd curcumin significntly ttenuted the effect of (: 33.7 ± 1.16 nmol/mg vs + curcumin: 1. ± 2.9 nmol/ mg, P <.1, Figure 3D). We, however, did not detect chnge of MDA level in liver or dipose tissue y curcumin gvge (Figure 4). By performing regression nlysis on the musculr MDA level nd the AUC vlue in IPGTT, we found tht there ws significntly positive correltion etween them (P <.). The regression nlysis ws lso performed on the musculr mitochondril MDA level nd the AUC vlue in IPGTT. A more significntly positive correltion ws oserved (P <.1). These dt suggest the existence of tight link etween musculr mitochondril redox lnce nd the ility of the whole ody on glucose disposl. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 signling in skeletl muscles Curcumin hs een shown to ctivte the Nrf2 system in cell culturing systems [1]. To further explore the potentil mechnism of n nti-oxidtive effect of curcumin, we determined whether curcumin stimultes Nrf2 signling in vivo. We prepred whole lystes of tissues from the three groups of mice nd exmined the levels of Nrf2 s well s one of its trget gene products, HO-1 y western lotting. As shown in Figure A, when compred with the control mice, feeding reduced Nrf2 level pproximtely % in muscles, wheres curcumin dministrtion significntly ttenuted the repressive effect of (Figure A). We however, did not see n pprent chnge in the protein levels of Nrf2 nd HO-1 in the liver nd the ft tissue y this short-term curcumin tretment (Figure C nd D). Consistently, Nrf2 content in the nuclei of skeletl muscle ws reduced in mice while curcumin tretment reversed this reduction (Figure B). Furthermore, feeding led to reduced level of HO-1 wheres curcumin significntly reversed this reduction. These results collectively suggest tht feeding impirs the function of Nrf2 system while short-term tretment with curcumin significntly ctivtes the Nrf2-ARE signling pthwy in skeletl muscles of -fed mice. DISCUSSION Long-term curcumin dministrtion in mice hs een shown to improve insulin signling nd glucose disposl y ttenuting inflmmtion nd oesity [17,26]. However, it is not cler whether curcumin could exert its insulinsensitizing ction y nti-oxidtive stress. Prticulrly, very few studies hve een conducted to exmine the cute effect of curcumin in n lredy insulin resistnt model. We showed here tht short-term curcumin gvge improved glucose disposl in -induced mouse model in the sence of n pprent chnge of BW. We then oserved tht short-term curcumin dministrtion meliorted oxidtive stress in oth serum nd muscles of mice, prticulrly in musculr mitochondri. Furthermore, we detected tht these eneficil effects were ccompnied y reversl of impired Nrf2 signling, including incresed Nrf2 expression, its nucler loction nd the expression of the trget ntioxidnt enzyme, HO-1. We hence suggest tht the ctivtion of the mjor nti-oxidtive defense mchinery Nrf2 in muscle is novel mechnism for curcumin in the tretment of insulin resistnce nd ssocited metolic disorders. In -induced insulin resistnt model, severl mechnisms hve een proposed to explin the cusl role of consumption in the development of insulin insensitivity. Inflmmtion, ER stress nd mitochondril dysfunction re ll reported to e involved [3,6-8]. However, these normlities could e the chronic etiology fctors of insulin resistnce. It is still not known which fctor initilly induces insulin resistnce. It is resonle to elieve tht in the condition of nutrition over supply, mitochondril oxidtive phosphoryltion metolism would produce lrger mount ROS nd if nti-oxidtive mchinery could not eliminte the mitochondril derived oxidnts, oxidtive stress will occur, resulting in insulin 1 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
8 Nrf2 (opticl density) Nrf2 (opticl density) Nrf2 (opticl density) He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce A Muscle + curcumin C Liver + curcumin Totl Nrf2 Nrf2 HO-1 HO-1 -ctin -ctin 1..8 c d HO-1 (opticl density) curcumin d HO-1 (opticl density) curcumin + curcumin + curcumin D Adipose tissue + curcumin B Nrf2 Muscle nuclei + curcumin Nrf2 HO-1 Hostine H3 -ctin Nucler Nrf2 (opticl density) d + curcumin c + curcumin Figure Effects of curcumin on nucler fctor erythroid-2-relted fctor-2 signling. A: The protein levels of nucler fctor erythroid-2-relted fctor-2 (Nrf2), heme oxygense-1 (HO-1) in skeletl muscle (β-ctin s the loding control of totl protein); B: Nucler Nrf2 contents in skeletl muscle were proed with Nrf2 ntiody (Histone H3 s the nucler protein loding control). C, D: The levels of Nrf2 nd HO-1 in livers were exmined y western lotting. The nlysis of reltive opticl density on western lots ws presented in the lower pnels or the right pnel for corresponding figures. The mice were fed with indicted diets nd gvged with curcumin or vehicle. At the end of 18 wk, the mice were scrificed nd tissues were collected for protein or nucler preprtion. Western lotting ws performed with indicted ntiodies. P <., P <.1, c P <.1, or +curcumin vs ; d P <., + curcumin vs. : High ft diet; : norml diet. HO-1 (opticl density) curcumin 11 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
9 He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce resistnce. In support, recent investigtions hve indicted tht muscle mitochondril derived ROS cn cutely impir glucose disposl [27,28] nd the dministrtion of mitochondril specific ntioxidnt corrects this defect [7,2]. Interestingly, curcumin hs n nti-oxidnt effect nd in vitro studies hve indicted its ction on triggering Nrf2 signling [14,1]. We therefore proposed the working hypothesis of this study tht short-term curcumin supplementtion could improve glucose homeostsis in mice y its nti-oxidtive ction vi Nrf2 ctivtion. Firstly, we exmined the redox sttus in the three groups of mice y MDA ssy. We demonstrte here tht induces severe oxidtive stress in skeletl muscle especilly in mitochondri, while curcumin dministrtion reverses this deleterious effect. The regression nlysis on the AUC dt of IPGTT nd MDA level hs further scertined the reltionship of muscle mitochondril redox sttus with insulin sensitivity. We hence suggest tht musculr mitochondri re initil nd importnt working sites for curcumin in ttenuting oxidtive stress nd improving glucose tolernce. Detiled mechnisms underlying mitochondril redox sttus in regulting insulin ction re currently uncler. One possiility is tht ROS impirs mitochondril function, followed y reduced lipid oxidtion nd incresed lipid ccumultion in muscle. The elevtion of muscle lipid content then ctivtes protein kinse C, which locks insulin receptor sustrte-1 phosphoryltion nd downstrem insulin signling [29]. Further experiments re needed to ssess whether curcumin is le to improve insulin signling vi locking this pthologicl signling pthwy. Redox lnce is determined y oth ROS production nd nti-oxidtive function (ROS elimintion). Recent studies hve indicted tht n inility of the Nrf2 system in the elimintion of ROS leds to the development of insulin resistnce, wheres phrmcologicl or genetic ctivtion of Nrf2 cn improve insulin signling, long with improved glucose metolism [19,3]. To further investigte the underlying mechnism of curcumin on regulting redox lnce, we exmined Nrf2 signling in insulin sensitive tissues. We found tht repressed Nrf2 function in muscles y reducing oth totl Nrf2 content nd its nucler portion, wheres curcumin mrkedly reversed these defects. Furthermore, curcumin lso incresed the expression of HO-1, downstrem trget of Nrf2 nd n essentil nti-oxidtive enzyme. These dt re consistent with the reversl of oxidtive stress in muscle ut not in ft tissue or the liver. Therefore, these results suggest tht curcumin-induced Nrf2 ction is novel mechnism ginst -induced oxidtive stress nd to ttenute glucose intolernce. In line with the positive regultion of the Nrf2/HO-1 system on insulin sensitivity, HO-1 hs een shown to repress oxidtive stress nd inflmmtion [31], nd the dministrtion of HO-1 inducer improves insulin sensitivity [32,33]. Due to the tight link of oxidtive stress with inflmmtion [31], further studies should e conducted to ddress whether the ctivtion of Nrf2 y curcumin is relted to its nti- inflmmtory effect. It should lso e pointed out tht lthough 1 d curcumin supplementtion did not reduce the BW in -fed nimls, we egn to see the effect of curcumin on reducing ft mss. We hence cnnot rule out the possiility tht curcumin-evoked Nrf2 signling modulte lipid metolism, dipogenesis, dipocyte differentition, indirectly ffecting glucose metolism [17-19]. Curry contining curcumin, populr nturl spice in Indi, hs een used s trditionl drug to tret inflmmtion, wheres modern studies further demonstrte the potentil of curcumin to tret other mjor lifethretening diseses, such s hert filure, neurodegenertive diseses nd dietes [13,17,18,34]. The reltive high sfety nd low cost of curcumin would lso encourge its therpeutic pplictions in the future. In ddition to the preventive effect of curcumin on insulin resistnce, we demonstrted here tht fter the induction of oesity y, short-term curcumin gvge still reversed glucose intolernce, clerly suggesting the therpeutic ppliction of curcumin in the tretment of insulin resistnce-relted metolic disorders. In light of its clinicl usge, studies hve een conducted nd verified the effectiveness of curcumin in treting hyperglycemi-induced oxidtive stress nd relted disorders, such s dietic nephropthy [3,36]. In ccordnce, the present study provides significnt mechnism of Nrf2 ctivtion y which curcumin cn defend oxidtive stress nd mitochondril redox imlnce nd ttenute the normlity of glucose metolism in the condition of nutritionl oversupply. Together these findings would plce Nrf2 nd curcumin s the new therpeutic trgets nd pproches for the tretment of hyperglycemi, s well s oxidtive stressrelted diseses. COMMENTS Bckground Curcumin intervention ttenutes insulin resistnce nd improves glucose dis- posl invriousrodentmodelsofinsulinresistncenddietes.thecurrent rodent of insulin resistnce nd dietes. current mechnistic understnding on these eneficileffectsislimitedlthough effects islimitedlthough curcumin hseenshowntottenuteodyweight(bw) shown ttenute ody weight ginndinflmmtorynd inflmmtory response during high ft diet consumption. Whether curcumin improves insulin signling vi ctivting the endogenous nucler fctor erythroid-2-relted fctor-2 (Nrf2) nti-oxidtive stress system nd whether the improvement involves the ttenution of mitochondril oxidtive stressreunknown. Reserch frontiers The use of nturlly occurring compound in intervention is n optimum pproch for the tretment nd prevention of dietes nd oesity. Mitochondri re primry site of production of free rdicls. Extensive recent studies hve reveled the fundmentl importnce of mitochondril oxidtive stress in the etiology of insulin resistnce. The ctivtion of the mjor nti-oxidtive stress systemnrf2wsshowntoimproveinsulinsignlingndglucosedisposl shown to insulin signling nd glucose disposl in vivo. Curcumin is le to ctivte Nrf2 signling in vitro. Here the uthors ddressed the question whether curcumin, nturlly-occurring compound, improves insulin signling vi ttenuting oxidtive stress in mitochondri, vi ctivting the Nrf2 signling pthwy. Innovtions nd rekthroughs The study showed hereforthefirsttimethestimultoryeffectofcurcuminincti- first time stimultory effect of curcumin in ctivting endogenous Nrf2 system in vivo. This finding will initite further investigtions on mechnistic explortion of the stimultion of Nrf2 system y nturllyoccurring plnt compounds. 12 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
10 He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce The uthors demonstrtedherethtcurcuminimprovedinsulinsignling tht improved insulin signling nd glucose disposl, ssocited with the ttenution of muscle mitochondril oxidtive stress. This finding defined muscle mitochondri s novel trgets for curcumin. The improvement oserved in this niml model is independent of the BW lowering effect of curcumin. The uthors hve hence not only deepened the mechnistic understnding of the therpeutic effect of curcumin, ut lso reveled tht ttenution of endogenous nti-oxidtive stress is n importnt pthologicl event of high ft diet consumption. Applictions This studyidentifiednewtrgetforcurcuminndothernturlly-occurring new trget for nd other nturlly-occurring compounds in improving insulinsensitivity.itfurthersupportsthehypothesistht sensitivity. supports the hypothesis tht curcumin cn e utilized in the tretment nd prevention of dietes nd other metolic disorders tht involve insulin resistnce. Terminology Insulin resistnce is the pthophysiologicl condition tht insulin cn not exert norml function on itstrgetingtissuesorcells,includingmuscle,livernd trgeting tissues including,livernd dipose tissue, or higher concentrtion of insulin is required to evokeinsulin signling nd glucose uptke. The normlityisthesisforthedevelopment of insulin-resistnt diseses, including type2dietesmellitus,hypertension nd certin crdiovsculr diseses.nrf2 nti-oxidtive system:in thecondition of oxidtive stress, cytosol Nrf2 will e trnslocted into the nucleus.it Itwillthen then ind to ttery of specifictrgetgenesintheirpromoterregions,stimultingthe genes in theirpromoterregions,stimultingthe regions, stimulting trnscription of these genes. Nrf2 trget genes encode series of nti-oxidnt enzymes, including HO-1. Peer review The present study showed thtshorttermtretmentwithcurcuminctivtesnrf2 term tretment ctivtes signling nd lowers lood glucose levels nd oxidtive stress in C7BL/6J mice fed on high-ft diet. It hs two strengths. Firstly,,demonstrtionofNrf2ctivtion of ctivtion nd nucler trnsloction following curcumin tretment in n niml model of high-ft diet induced oesity nd insulin resistnce. Secondly,,demonstrtionof of reversl of high ft diet-induced mlondildehyde elevtions in serum, muscle nd muscle mitochondri. REFERENCES 1 Reven GM. Insulin resistnce: the link etween oesity nd crdiovsculr disese. Med Clin North Am 211; 9: Asi F, Brown BW, Lmendol C, McLughlin T, Reven GM. Reltionship etween oesity, insulin resistnce, nd coronry hert disese risk. J Am Coll Crdiol 22; 4: Wellen KE, Hotmisligil GS. In flmmtion, stress, nd dietes. J Clin Invest 2; 11: Mrtínez JA. Mitochondril oxidtive stress nd in flmmtion: n sllom to oesity nd insulin resistnce. J Physiol Biochem 26; 62: Light DW, Desi KM, Gopul NK, Anggård EE, Crrier MJ. Pro-oxidnt chllenge in vivo provokes the onset of NIDDM in the insulin resistnt oese Zucker rt. Br J Phrmcol 1999; 128: Rins JL, Jin SK. Oxidtive stress, insulin signling, nd dietes. Free Rdic Biol Med 211; : Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lnder ES. Rective oxygen species hve cusl role in multiple forms of insulin resistnce. Nture 26; 44: Nkmur S, Tkmur T, Mtsuzw-Ngt N, Tkym H, Misu H, Nod H, Nemoto S, Kurit S, Ot T, Ando H, Miymoto K, Kneko S. Plmitte induces insulin resistnce in H4IIEC3 heptocytes through rective oxygen species produced y mitochondri. J Biol Chem 29; 284: Kspr JW, Niture SK, Jiswl AK. Nrf2: INrf2 (Kep1) signling in oxidtive stress. Free Rdic Biol Med 29; 47: Bloom DA, Jiswl AK. Phosphoryltion of Nrf2 t Ser4 y protein kinse C in response to ntioxidnts leds to the relese of Nrf2 from INrf2, ut is not required for Nrf2 stiliztion/ccumultion in the nucleus nd trnscriptionl ctivtion of ntioxidnt response element-medited NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductse-1 gene expression. J Biol Chem 23; 278: Kundu JK, Surh YJ. Nrf2-Kep1 signling s potentil trget for chemoprevention of in flmmtion-ssocited crcinogenesis. Phrm Res 21; 27: Clrke JD, Dshwood RH, Ho E. Multi-trgeted prevention of cncer y sulforphne. Cncer Lett 28; 269: Morimoto T, Sungw Y, Kwmur T, Tky T, Wd H, Ngsw A, Komed M, Fujit M, Shimtsu A, Kit T, Hsegw K. The dietry compound curcumin inhiits p3 histone cetyltrnsferse ctivity nd prevents hert filure in rts. J Clin Invest 28; 118: Zhou H, Beevers CS, Hung S. The trgets of curcumin. Curr Drug Trgets 211; 12: Blogun E, Hoque M, Gong P, Killeen E, Green CJ, Foresti R, Alm J, Motterlini R. Curcumin ctivtes the hem oxygense-1 gene vi regultion of Nrf2 nd the ntioxidntresponsive element. Biochem J 23; 371: Yng C, Zhng X, Fn H, Liu Y. Curcumin upregultes trnscription fctor Nrf2, HO-1 expression nd protects rt rins ginst focl ischemi. Brin Res 29; 1282: Weiserg SP, Leiel R, Tortoriello DV. Dietry curcumin signi ficntly improves oesity-ssocited in flmmtion nd dietes in mouse models of diesity. Endocrinology 28; 149: Ejz A, Wu D, Kwn P, Meydni M. Curcumin inhiits dipogenesis in 3T3-L1 dipocytes nd ngiogenesis nd oesity in C7/BL mice. J Nutr 29; 139: Yu Z, Sho W, Ching Y, Foltz W, Zhng Z, Ling W, Fntus IG, Jin T. Oltiprz upregultes the nucler fctor (erythroidderived 2)-like 2 [corrected](nrf2) ntioxidnt system nd prevents insulin resistnce nd oesity induced y high-ft diet in C7BL/6J mice. Dietologi 211; 4: Fernández-Vizrr E, López-Pérez MJ, Enriquez JA. Isoltion of iogeneticlly competent mitochondri from mmmlin tissues nd cultured cells. Methods 22; 26: Ackermn EJ, Ikouchev LM. Nucleotide excision repir in oocyte nucler extrcts from Xenopus levis. Methods 2; 22: Del Rio D, Stewrt AJ, Pellegrini N. A review of recent studies on mlondildehyde s toxic molecule nd iologicl mrker of oxidtive stress. Nutr Met Crdiovsc Dis 2; 1: Turner RC, Holmn RR, Mtthews D, Hockdy TD, Peto J. Insulin de ficiency nd insulin resistnce interction in dietes: estimtion of their reltive contriution y feedck nlysis from sl plsm insulin nd glucose concentrtions. Metolism 1979; 28: Tlior I, Yrkoni M, Bshn N, Eldr-Finkelmn H. Incresed glucose uptke promotes oxidtive stress nd PKCdelt ctivtion in dipocytes of oese, insulin-resistnt mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 23; 28: E29-E32 2 Bonnrd C, Durnd A, Peyrol S, Chnseume E, Chuvin MA, Morio B, Vidl H, Rieusset J. Mitochondril dysfunction results from oxidtive stress in the skeletl muscle of diet-induced insulin-resistnt mice. J Clin Invest 28; 118: El-Moselhy MA, Tye A, Shrkwi SS, El-Sisi SF, Ahmed AF. The ntihyperglycemic effect of curcumin in high ft diet fed rts. Role of TNF-α nd free ftty cids. Food Chem Toxicol 211; 49: Brvrd A, Bonnrd C, Durnd A, Chuvin MA, Fvier R, Vidl H, Rieusset J. Inhiition of xnthine oxidse reduces hyperglycemi-induced oxidtive stress nd improves mitochondril ltertions in skeletl muscle of dietic mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 211; 3: E81-E91 28 Yuzefovych L, Wilson G, Rchek L. Different effects of olete vs. plmitte on mitochondril function, poptosis, nd insulin signling in L6 skeletl muscle cells: role of oxidtive stress. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 21; 299: E196-E11 13 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
11 He HJ et l. Curcumin ctivtes Nrf2 nd ttenutes insulin resistnce 29 Roden M. Muscle triglycerides nd mitochondril function: possile mechnisms for the development of type 2 dietes. Int J Oes (Lond) 2; 29 Suppl 2: S111-S11 3 Tn Y, Ichikw T, Li J, Si Q, Yng H, Chen X, Goldltt CS, Meyer CJ, Li X, Ci L, Cui T. Dietic downregultion of Nrf2 ctivity vi ERK contriutes to oxidtive stress-induced insulin resistnce in crdic cells in vitro nd in vivo. Dietes 211; 6: Pine A, Eiz-Vesper B, Blsczyk R, Immenschuh S. Signling to heme oxygense-1 nd its nti-in flmmtory therpeutic potentil. Biochem Phrmcol 21; 8: Li M, Kim DH, Tsenovoy PL, Peterson SJ, Rezzni R, Rodell LF, Aronow WS, Ikehr S, Arhm NG. Tretment of oese dietic mice with heme oxygense inducer reduces viscerl nd sucutneous diposity, increses diponectin levels, nd improves insulin sensitivity nd glucose tolernce. Dietes 28; 7: Nicoli A, Li M, Kim DH, Peterson SJ, Vnell L, Positno V, Gstldelli A, Rezzni R, Rodell LF, Drummond G, Kusmic C, L Ate A, Kpps A, Arhm NG. Heme oxygense-1 induction remodels dipose tissue nd improves insulin sensitivity in oesity-induced dietic rts. Hypertension 29; 3: Begum AN, Jones MR, Lim GP, Morihr T, Kim P, Heth DD, Rock CL, Pruitt MA, Yng F, Hudspeth B, Hu S, Full KF, Teter B, Cole GM, Frutschy SA. Curcumin structurefunction, iovilility, nd ef ficcy in models of neuroinflmmtion nd Alzheimer s disese. J Phrmcol Exp Ther 28; 326: Khjehdehi P, Pkfetrt M, Jvidni K, Azd F, Mlekmkn L, Ns MH, Dehghnzdeh G. Orl supplementtion of turmeric ttenutes proteinuri, trnsforming growth fctor-β nd interleukin-8 levels in ptients with overt type 2 dietic nephropthy: rndomized, doule-lind nd plceo-controlled study. Scnd J Urol Nephrol 211; 4: Rem M, Prdeep R. Dietic retinopthy: n Indin perspective. Indin J Med Res 27; 12: S- Editor Wu X L- Editor Roemmele A E- Editor Wu X 14 My 1, 212 Volume 3 Issue
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Chromium Alleviates Glucose Intolerance, Insulin Resistance, and Hepatic ER Stress in Obese Mice
 nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
nture pulishing group rticles intervention AND prevention Chromium Allevites Glucose Intolernce, Insulin Resistnce, nd Heptic ER Stress in Oese Mice Nir Sreejyn, Feng Dong, Mchender R. Knddi,2, Xioping
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ameliorates lipid and glucose accumulation in C57BL/6J mice via activation of PPAR-α and AMPK
 3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
SESSIONE I: RELATORI. Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signal to metabolic master regulator?
 SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
Interleukin-4 Restores Insulin Sensitivity in Lipid-Induced Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes
 ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
Synergistic effects of metformin, resveratrol, and hydroxymethylbutyrate on insulin sensitivity
 Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Research Article Protective Effect of Short-Term Genistein Supplementation on the Early Stage in Diabetes-Induced Renal Damage
 Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 2013, rticle ID 510212, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/510212 Reserch rticle Protective Effect of Short-Term Genistein Supplementtion on the Erly Stge in Dibetes-Induced
Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 2013, rticle ID 510212, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/510212 Reserch rticle Protective Effect of Short-Term Genistein Supplementtion on the Erly Stge in Dibetes-Induced
Molecular Analysis of BRCA1 in Human Breast Cancer. Cells Under Oxidative Stress
 Moleculr Anlysis of BRCA1 in Humn Brest Cncer Cells Under Oxidtive Stress Brin L. Gilmore 1, Ynping Ling 1, Crly E. Winton 1,2, Ky Ptel 1, Vsile Krgeorge 1, A. Cmeron Vrno 1,3, Willim Dernley 1, Zhi Sheng
Moleculr Anlysis of BRCA1 in Humn Brest Cncer Cells Under Oxidtive Stress Brin L. Gilmore 1, Ynping Ling 1, Crly E. Winton 1,2, Ky Ptel 1, Vsile Krgeorge 1, A. Cmeron Vrno 1,3, Willim Dernley 1, Zhi Sheng
Background Pears (Pyrus L.) are one of the leading cultivated fruit trees in China following apples and oranges in planting area and fruit yield.
 Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Enhanced Chemopreventive Effect by Combining Quercetin and Green tea in Prostate Cancer
 Enhnced Chemopreventive Effect y Comining Quercetin nd Green te in Prostte Cncer Piwen Wng, MD, PhD Assistnt Professor, Division of Cncer Reserch nd Trining Chrles R. Drew University of Medicine nd Science
Enhnced Chemopreventive Effect y Comining Quercetin nd Green te in Prostte Cncer Piwen Wng, MD, PhD Assistnt Professor, Division of Cncer Reserch nd Trining Chrles R. Drew University of Medicine nd Science
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-b and metabolic health
 Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
British Journl of Nutrition (), 6, q The Authors doi:.7/s75 Tretment with oligonol, low-moleculr polyphenol derived from lychee fruit, ttenutes dietes-induced heptic dmge through regultion of oxidtive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Myricetin Ameliorates Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signaling via b-endorphin Signaling in the Skeletal Muscles of Fructose-Fed Rats
 ecam Advnce Access published Mrch 3, 2010 ecam 2010;Pge 1 of 9 doi:10.1093/ecm/neq017 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi b-endorphin Signling in the Skeletl Muscles
ecam Advnce Access published Mrch 3, 2010 ecam 2010;Pge 1 of 9 doi:10.1093/ecm/neq017 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi b-endorphin Signling in the Skeletl Muscles
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
Flaxseed Lignan Increased Glucose Uptake by Human Red Blood Cells
 The Open Nutrceuticls Journl, 29, 2, 81-85 81 Open Access Flxseed Lignn Incresed Glucose Uptke y Humn Red Blood Cells Yeong Rhee * nd Ardith Brunt 351 EML, NDSU Dept. # 262, PO Box 65, North Dkot Stte
The Open Nutrceuticls Journl, 29, 2, 81-85 81 Open Access Flxseed Lignn Incresed Glucose Uptke y Humn Red Blood Cells Yeong Rhee * nd Ardith Brunt 351 EML, NDSU Dept. # 262, PO Box 65, North Dkot Stte
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
Myricetin Ameliorates Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signaling via
 Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 15752, 9 pges doi:1.193/ecm/neq17 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi β-endorphin Signling in
Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 15752, 9 pges doi:1.193/ecm/neq17 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi β-endorphin Signling in
A. Kinoshita 1, L. Locher 2, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S. Dänicke 3, J. Rehage 4, K. Huber 5
 Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Supplemental Materials
 Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
Protective effect of rosuvastatin treatment by regulating oxidized low-density lipoprotein expression in a rat model of liver fibrosis
 BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 311-316, 2016 Protective effect of rosuvsttin tretment by regulting oxidized low-density lipoprotein expression in rt model of liver fibrosis SHUIPING YU 1, XUELING ZHOU 1, BINGZONG
BIOMEDICAL REPORTS 5: 311-316, 2016 Protective effect of rosuvsttin tretment by regulting oxidized low-density lipoprotein expression in rt model of liver fibrosis SHUIPING YU 1, XUELING ZHOU 1, BINGZONG
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Responses of skeletal muscle lipid metabolism in rat gastrocnemius to hypothyroidism and iodothyronine administration: a putative role for FAT/CD36
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 33: E1222 E1233, 212. First pulished Septemer 11, 212; doi:1.1152/jpendo.37.212. Responses of skeletl muscle lipid metolism in rt gstrocnemius to hypothyroidism nd iodothyronine
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 33: E1222 E1233, 212. First pulished Septemer 11, 212; doi:1.1152/jpendo.37.212. Responses of skeletl muscle lipid metolism in rt gstrocnemius to hypothyroidism nd iodothyronine
Physical training prevents oxidative stress in L-NAME-induced hypertension rats
 cell iochemistry nd function Cell Biochem Funct 2013; 31: 136 151. Pulished online 7 Septemer 2012 in Wiley Online Lirry (wileyonlinelirry.com) DOI:.02/cf.2868 Physicl trining prevents oxidtive stress
cell iochemistry nd function Cell Biochem Funct 2013; 31: 136 151. Pulished online 7 Septemer 2012 in Wiley Online Lirry (wileyonlinelirry.com) DOI:.02/cf.2868 Physicl trining prevents oxidtive stress
The effects of Momordica charantia on obesity and lipid profiles of mice fed a high-fat diet
 Nutrition Reserch nd Prctice 2015;9(5):489-495 c2015 The Koren Nutrition Society nd the Koren Society of Community Nutrition http://e-nrp.org The effects of Momordic chrnti on obesity nd lipid profiles
Nutrition Reserch nd Prctice 2015;9(5):489-495 c2015 The Koren Nutrition Society nd the Koren Society of Community Nutrition http://e-nrp.org The effects of Momordic chrnti on obesity nd lipid profiles
Effect of environmental stress on biochemical and physiological features in cultured fish
 Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Serum nesfatin-1 levels are decreased in pregnant women newly diagnosed with gestational diabetes
 originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Effects of Curcumin Attenuated Hepatitis in Mice with Paracetamol Overdose ABSTRACT
 Originl Article 43 Effects of Curcumin Attenuted Heptitis in Mice with Prcetmol Overdose Somnwt K 1 Thong-Ngm D 1 Klikew N 2 ABSTRACT Bckground: N-cetyl-p-minophenol () or prcetmol overdose cuses incresing
Originl Article 43 Effects of Curcumin Attenuted Heptitis in Mice with Prcetmol Overdose Somnwt K 1 Thong-Ngm D 1 Klikew N 2 ABSTRACT Bckground: N-cetyl-p-minophenol () or prcetmol overdose cuses incresing
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE
 THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Dr. Javier Polo Vice President Research & Development
 Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Effects of Sini San used alone and in combination with fluoxetine on central and peripheral 5-HT levels in a rat model of depression
 Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated β-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling
 Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
Irs-2 coordintes Igf-1 receptor-medited β-cell development nd peripherl insulin signlling Dominic J. Withers 1,2 *, Deorh J. Burks 1 *, Hether H. Towery 1, Shri L. Altmuro 1, Crrie L. Flint 1 & Morris
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
Kumar et al. Kumar et al. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013, 13:273
 Umelliferone β-d-glctopyrnoside from Aegle mrmelos (L.) corr. n ethnomedicinl plnt with ntidietic, ntihyperlipidemic nd ntioxidtive ctivity Kumr et l. Kumr et l. BMC Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine
Umelliferone β-d-glctopyrnoside from Aegle mrmelos (L.) corr. n ethnomedicinl plnt with ntidietic, ntihyperlipidemic nd ntioxidtive ctivity Kumr et l. Kumr et l. BMC Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Quercetin modulates Nrf2 and glutathione-related defenses in HepG2. cells. Involvement of p38
 Quercetin modultes Nrf2 nd glutthione-relted defenses in HepG2 cells. Involvement of p38 An Belén Grndo-Serrno, Mrí Angeles Mrtín, Lur Brvo, Luis Goy nd Soni Rmos* Deprtment of Metolism nd Nutrition Institute
Quercetin modultes Nrf2 nd glutthione-relted defenses in HepG2 cells. Involvement of p38 An Belén Grndo-Serrno, Mrí Angeles Mrtín, Lur Brvo, Luis Goy nd Soni Rmos* Deprtment of Metolism nd Nutrition Institute
Food & Function Accepted Manuscript
 Food & Function Accepted Mnuscript This is n Accepted Mnuscript, which hs een through the Royl Society of Chemistry peer review process nd hs een ccepted for puliction. Accepted Mnuscripts re pulished
Food & Function Accepted Mnuscript This is n Accepted Mnuscript, which hs een through the Royl Society of Chemistry peer review process nd hs een ccepted for puliction. Accepted Mnuscripts re pulished
DIETARY FOOD FORTIFIED WITH OROTIC ACID AND LIVER FUNCTION
 MAKARA, SAINS, VOL. 15, NO. 2, NOVEMBER 211: 11-15 DIETARY FOOD FORTIFIED WITH OROTIC ACID AND LIVER FUNCTION Yohnes Bung Deprtment of Chemistry, Fculty of Science nd Engineering, Nus Cendn University,
MAKARA, SAINS, VOL. 15, NO. 2, NOVEMBER 211: 11-15 DIETARY FOOD FORTIFIED WITH OROTIC ACID AND LIVER FUNCTION Yohnes Bung Deprtment of Chemistry, Fculty of Science nd Engineering, Nus Cendn University,
Role of hydroxytyrosol in ameliorating effects of high fat
 Role of hydroxytyrosol in meliorting effects of high ft diet on mle rts CNS Hyder A. N. Al-Zmely, Zen Shkir Mhmoud Al -Tmemi Dept. of physiology nd biochemistry, College of veterinry Medicine, AL-Qssim
Role of hydroxytyrosol in meliorting effects of high ft diet on mle rts CNS Hyder A. N. Al-Zmely, Zen Shkir Mhmoud Al -Tmemi Dept. of physiology nd biochemistry, College of veterinry Medicine, AL-Qssim
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND POLOXAMER 407 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF PIROXICAM
 IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
ESM Table 1. Characterisation of the human non-diabetic cohort used for MRIbased assessment of pancreatic fat and insulin secretion via OGTT.
 ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
Chapter 5: The peripheral nervous system Learning activity suggested answers
 Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulating sodium transport via the PI-3 kinase/sgk1 pathway in a cortical collecting duct cell line
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
Effects of Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Ceylon cinnamon) on blood glucose and lipids in a diabetic and healthy rat model
 PHCOG RES. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Cinnmomum zeylnicum (Ceylon cinnmon) on lood glucose nd lipids in dietic nd helthy rt model Priyng Rnsinghe, Snj Perer, Mngl Guntilke 1, Erng Aeywrdene, Nuwn Gunpl,
PHCOG RES. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Cinnmomum zeylnicum (Ceylon cinnmon) on lood glucose nd lipids in dietic nd helthy rt model Priyng Rnsinghe, Snj Perer, Mngl Guntilke 1, Erng Aeywrdene, Nuwn Gunpl,
Effects of Weight Reduction on Serum Vaspin Concentrations in Obese Subjects: Modification by Insulin Resistance
 nture publishing group rticles Effects of Weight Reduction on Serum Vspin Concentrtions in Obese Subjects: Modifiction by Insulin Resistnce Hye M. Chng 1, He J. Lee 1, Hye S. Prk 1, Je H. Kng 2, Kyung
nture publishing group rticles Effects of Weight Reduction on Serum Vspin Concentrtions in Obese Subjects: Modifiction by Insulin Resistnce Hye M. Chng 1, He J. Lee 1, Hye S. Prk 1, Je H. Kng 2, Kyung
Anti-diabetic and hypolipidaemic properties of garlic (Allium sativum) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
 Int J Dietes & Metolism (27) 15: 18-115 Anti-dietic nd hypolipidemic properties of grlic (Allium stivum) in streptozotocin-induced dietic rts Mrth Thomson, Zin M. Al-Amin, Khled K. Al-Qttn, Lemi H. Shn
Int J Dietes & Metolism (27) 15: 18-115 Anti-dietic nd hypolipidemic properties of grlic (Allium stivum) in streptozotocin-induced dietic rts Mrth Thomson, Zin M. Al-Amin, Khled K. Al-Qttn, Lemi H. Shn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 d MAP2 GFAP e MAP2 GFAP GFAP c f Clindin GFAP Supplementry Figure S1. Neuronl deth nd ltered strocytes in the rin of n ffected child. Neuron specific MAP2 ntiody stining in the hippocmpus
Supplementry Figure S1 d MAP2 GFAP e MAP2 GFAP GFAP c f Clindin GFAP Supplementry Figure S1. Neuronl deth nd ltered strocytes in the rin of n ffected child. Neuron specific MAP2 ntiody stining in the hippocmpus
WWL70 attenuates PGE 2 production derived from 2-arachidonoylglycerol in microglia by ABHD6-independent mechanism
 Tnk et l. Journl of Neuroinflmmtion (2017) 14:7 DOI 10.1186/s12974-016-0783-4 RESEARCH Open Access WWL70 ttenutes PGE 2 production derived from 2-rchidonoylglycerol in microgli y ABHD6-independent mechnism
Tnk et l. Journl of Neuroinflmmtion (2017) 14:7 DOI 10.1186/s12974-016-0783-4 RESEARCH Open Access WWL70 ttenutes PGE 2 production derived from 2-rchidonoylglycerol in microgli y ABHD6-independent mechnism
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Supporting information
 Supporting informtion Multiple Univrite Dt Anlysis Revels the Inulin Effects on the High-ft-diet Induced Metolic Altertions in Rt Myocrdium nd Testicles in the Pre-oesity Stte Yixun Dun #, Ynpeng An #,
Supporting informtion Multiple Univrite Dt Anlysis Revels the Inulin Effects on the High-ft-diet Induced Metolic Altertions in Rt Myocrdium nd Testicles in the Pre-oesity Stte Yixun Dun #, Ynpeng An #,
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
MicroRNA-146a and its adapter proteins are affected by diabetes in rat s heart
 DOI: 10.4149/BLL_2016_031 Brtisl Med J 2016; 117 (3) EXPERIMENTAL STUDY MicroRNA-146 nd its dpter proteins re ffected y dietes in rt s hert Eftekhr E 1, Doustki Zoli M 2, Ktei M 3, Ghdiri Soufi F 3 Deprtment
DOI: 10.4149/BLL_2016_031 Brtisl Med J 2016; 117 (3) EXPERIMENTAL STUDY MicroRNA-146 nd its dpter proteins re ffected y dietes in rt s hert Eftekhr E 1, Doustki Zoli M 2, Ktei M 3, Ghdiri Soufi F 3 Deprtment
Optimizing Metam Sodium Fumigation in Fine-Textured Soils
 Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
