Anatomy in the resting state? Taking a look at receptor patterns
|
|
|
- Logan Chase
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy in the resting state? Taking a look at receptor patterns Karl Zilles Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine INM- Research Centre Jülich and University Hospital of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics, RWTH Universität Aachen
2 Regionally and functionally specific endowment of the brain with neurotransmitter receptors. How to visualize receptors at high spatial resolution throughout the entire brain Zilles, K., Schleicher, A., Palomero-Gallagher, N., Amunts, K.: Quantitative analysis of cyto- and receptorarchitecture of the human brain, pp In: Brain Mapping: The Methods, 2nd edition (A.W. Toga and J.C. Mazziotta, eds.). Academic Press (22)
3 Quantitative in vitro Receptor Autoradiography: Method () MRI autopsy in situ post mortem MRI 3D MR volume unfixed post mortem brain mounting on the cryomicrotome chuck dissection into slabs
4 Serial sections (2 µm) mounted onto glass slides
5 Preincubation: re-hydrate sections. Remove endogenous substances Main incubation: buffer solution with [ 3 H]-ligands which specifically bind to a given receptor type Washing step: terminate binding procedure and eliminate surplus [ 3 H]- ligand and buffer salts Exposition of labeled sections and scales of known radioactivity concentrations to tritiumsensitive film Digitization of the films, measurement of receptor densities in fmol/mg protein, and color coding Histological staining of alternating sections for cell bodies and myelinated fibers Examined receptor binding sites Neurotransmitter Receptor [ 3 H] Ligand Glutamate Kainate MK-8 GABA GABA A muscimol, GABA B CGP GABA A BZ Flumazenil Acetylcholine M pirenzepine M 2 M 3 oxotremorine-m, AF-DX DAMP nicotinic a 4 b 2 epibatidine Noradrenaline a prazosin a 2 UK 4,34 RX-822 Serotonin 5-HT A 8-OH-DPAT 5-HT 2 ketanserin Dopamine D SCH 2339
6 Grey values Image processing C S a K L L D [fmol/mg protein] 4 5-HT A Radioactivity concentration (cpm) 5 Linearised and color-coded autoradiograph grey values or colors encode receptor densities
7 Regionally and functionally specific endowment of the brain with neurotransmitter receptors 2. Regional and laminar distribution of single receptor types in the cerebral cortex
8 The amygdala must be further subdivided based on it s distinct and heterogenous receptor distribution l bm bl basomedial basolateral lateral Structural MRI at 4 Tesla: spatial resolution 35 mm isotrop GABA muscarinic receptor M A receptor 2 Receptor autoradiography
9 The termination fields of the trisynaptic pathway in the hippocampus show distinct regional and laminar expression patterns of different glutamatergic receptors Perforant path to CA and molecular layer of DG Mossy fibers from DG to CA3 Schaffer collaterals from CA3 to CA fmol/mg protein 82 CA sub CA2 633 CA3 464 mol 295 fmol/mg protein Glutamatergic terminals of the perforant path and the Schaffer collaterals fmol/mg protein CA mol Kainate Glutamatergic terminals of the perforant path and the Schaffer collaterals Glutamatergic terminals of the mossy fibers
10 Cholinergic muscarinic M 2 receptor and primary sensory areas: Matching receptor- and myeloarchitecture Receptor autoradiography Myelin staining fmol/mg protein V layers II-IVa layer IVc layer IVb Gennari stripe = layer IVb V V V V V
11 Cholinergic muscarinic M 2 receptor and primary sensory areas: Receptorarchitecture sc motor cortex primary somatosensory cortex area 3b motor cortex primary somatosensory cortex area 3b sc primary auditory cortex BA4 primary auditory cortex BA4 Human Brain 84 fmol/mg protein 42 Macaque Brain
12 Multiple receptors and anterior cingulate cortex p32 p32 Glutamate receptor Noradrenaline a 2 receptor pacc p32 Glutamate 32 24c d receptor pd24 cv/cd amcc * p24a/b 24c v 24ab pv24c s24a s24b s32 sacc 25 pmcc p24b 24dd 24dv p24ab 33 Palomero-Gallagher et al., unpublished p24a p24b pd24cd pd24cv 33 Acetylcholine Glutamate M 2 receptor receptor pd24cv pd24cd Dopamine D receptor p24a 33 Palomero-Gallagher, Mohlberg, Zilles, Vogt (28) J Comp Neurol 58: Palomero-Gallagher & Zilles (29) In: Cingulate Neurobiology & Disease. Oxford University Press, pp
13 Regionally specific endowment of the brain with neurotransmitter receptors 3. Regional and laminar distribution of multiple receptor types in the cerebral cortex - RECEPTOR FINGERPRINTS -
14 5-HT A, 5-HT 2 serotonin glutamate,, GABA B GABA dopamine D, D 2, D 4 a, a 2 noradrenaline glutamate,,,, glutamate GABA GABA A, GABA A /BZ nicotinic, M, M 2, M 3 acetylcholine noradrenaline a, a 2 GABA A, GABA A /BZ GABA acetylcholine nicotinic, M, M 2, M 3 D, D 2, D 4 dopamine GABA GABA B GABA B GABA glutamate,, 5-HT A, 5-HT 2 serotonin GABA GABA A, GABA A /BZ GABA A, GABA A /BZ GABA GABA GABA A, GABA A /BZ axon terminal receptor
15 WT KO On the way to understand specificity and mechanisms behind receptor fingerprints: Conditional 5-HT A receptor knockout 5-HT A receptor a receptor 64 fmol/mg protein fmol/mg protein 9
16 V2 V V2 mglur2/3 V2 low Human primary visual cortex * * * GABA A GABA B M nic a 4 b 2 V V * * * V2 high Zilles, Palomero Gallagher: Comparative analysis of receptor subtypes that identify primary cortical sensory areas. In (Kaas, Striedter, Krubitzer, Herculano-Houzel, Preuss, eds.) Evolution of the Nervous System. Elsevier, Oxford (27) V2 V2 a 5-HT A 5-HT 2 D * * * *
17 Fingerprints: functional specificity primary somatosensory primary motor primary auditory 3b 5-HT A 5-HT 2 D a GABA A GABA B 4 5-HT A 5-HT 2 D a GABA A GABA B 4 5-HT A 5-HT 2 D a GABA A GABA B a BZ a BZ a BZ N M 3 M 2 M N M 3 M 2 M N M 3 M 2 M primary (V), and higher (V2, V3) visual areas V 5-HT 2 D 3 2 V2 5-HT 2 D 3 2 V3 5-HT 2 D HT A GABA A 5-HT A GABA A 5-HT A GABA A a 2 GABA B a 2 GABA B a 2 GABA B a BZ a BZ a BZ N M N M N M M 3 M 2 M 3 M 2 M 3 M 2
18 Ventral visual areas in human extrastriate cortex (FG2, FG2) FG2 FG FG2 FG FG2 FG FG2 FG FG FG2 FG FG2 FG FG2 FG FG2 (pfus) Weiner, K., Golarai, G., Caspers, J., Mohlberg, H., Zilles, K., Amunts, K., Grill-Spector, K.: The mid-fusiform sulcus: A landmark identifying both cytoarchitectonic and functional divisions of the human fusiform gyrus. Neuroimage 84: (24) Gomez, J., Barnett, M.A., Natu, V.S., Mezer, A., Palomero-Gallagher, N., Weiner, K.S., Amunts, K., Zilles, K., Grill-Spector, K. (26). Growth of tissue in human cortex is coupled with the development of face processing. Science 355: 68-7 (27)
19 Receptor fingerprint of FG Hierarchical Cluster Analysis ventral stream Receptor fingerprint of FG2 auditory somatosensory motor Caspers, J., Palomero-Gallagher, N., Caspers, S., Schleicher, A., Amunts, K., Zilles, K.: Receptor architecture of cytoarchitectonic visual areas FG and FG2 of the posterior fusiform gyrus. Brain Struct. Funct. 22: (25)
20 FG GABA B FG2 (pfus) GABA 5-HT A bz b.s. A
21 /BZ V 4 2 /BZ V2v 4 2 /BZ V3v 4 2 /BZ 3b 4 2 /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ L 4 2 /BZ /BZ 4 2 /BZ /BZ supragranular granular infragranular /BZ PFm 4 2 Zilles K, & Palomero-Gallagher N: Transmitter receptor fingerprints in regions and layers of the human cerebral cortex. Frontiers Neuroanat (submitted)
22 /BZ V /BZ V2v /BZ V3v /BZ 3b /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ PFm /BZ L /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ /BZ supragranular granular infragranular Zilles K, & Palomero-Gallagher N: Transmitter receptor fingerprints in regions and layers of the human cerebral cortex. Frontiers Neuroanat (submitted)
23 Dimension Multi-receptor fingerprints systematically differ between cortical layers V2d 3b V2v V V2d V3A V3d V3d V3v 4 V4v V3A 4 V2v V4v V3v 5M 4 PGp b 23 5L PGa V3d V3A 3a 4 FG2 5L V4v FG 44 3a FG2 3 5M PGa 3b PGa PFm FG 2 PFt PFt 37M PFm B 3 5M 37B 37M 4 PGp 37L 38 5L 37L 22 PFm 6 47 PFt 6 38 FG 22 L L 3a 37B 9 M L M 2 37M PGp 9 M FG L Dimension Zilles K, & Palomero-Gallagher N: Transmitter receptor fingerprints in regions and layers of the human cerebral cortex. Frontiers Neuroanat (submitted) 32 V V3v V2v V2d V Strata supragranular (layers I-III) granular (layer IV) infragranular (layers V-VI)
24 Receptors and the Default Mode Network
25 L 3a,3b 2 PFt PFm PGa PGp L L V4v V3d L 5M V3A V3d V V2d V2v V3v V4v FG 37M 37B 36 Hi EC 38 s24 p24 32 M DMN areas defined by Buckner et al. (28) Ann NY Acad Sci 24: -38 Cytoarchitectonic areas defined by Brodmann (99) and JuBrain
26 2nd Principal Component Principal component analysis of receptor densities (averaged over all cortical layers) and default mode network DMN FG 9 8 FG p24 M EC 36 37L L PGp 37M 4 PFt PFm 3 37B 38 PGa 5L s24 3a 5M DMN 24 Broca V3A 3b V3v early visual primary sensory V2 V posterior cingulate cortex (BA23) precuneus (BA3) anterior cingulate cortex (p24, s24) ventral medial prefrontal cortex (m, BA32, BA) dorsal medial prefrontal cortex (medial part of BA9) inferior parietal lobule (PGa, PGp, PFm, PFt) lateral temporal cortex (BA2, BA2) anterior temporal pole (BA38) hippocampus, entorhinal (EC), and parahippocampal (BA36) cortex 6 45 V4v motor V3d -3 HIP st Principal Component
27 SCORE Discriminance analysis of the densities (averaged over all cortical layers) of all receptor types between default mode network DMN areas and Non-DMN areas DMN Networks Non-DMN p =.2 Contribution of each receptor type to the segregation between DMN and Non-DMN areas Receptor Standardized score M Kainate a HT M GABA B.695 D a 4 b HT A a GABA A /BZ GABA A.235 M -.22
28 Ratio between and GABA A receptor densities Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) EC s24 /GABA A Hippocampus M 8 L p24 2 PFt PFm 5M PGa 3 PGp y = -.844x R² =.52 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) ( ) and GABA A ( ) 5 Hip 38 M EC L s24 PFm PFt p24 5M PGa 3 PGp Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) areas of the DMN non-dmn areas Metabolic data from: Hyder F, Herman P, Bailey CJ, Møller A, Globinsky R, Fulbright RK, Rothman DL, Gjedde A (26) Uniform distributions of glucose oxidation and oxygen extraction in gray matter of normal human brain: No evidence of regional differences of aerobic glycolysis. J Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 36(5): 93 96
29 Thanks to: Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-), Research Center Jülich: Katrin Amunts Mareike Bacha-Trams Sebastian Bludau Julian Caspers Svenja Caspers Nicola Palomero-Gallagher Filip Scheperjans Axel Schleicher Stanford University: Kalanit Grill-Spector Kevin Weiner Institute of Developmental Genetics, German Research Center for Environmental Health München: Wolfgang Wurst Max Planck Institute Leipzig: Angela Friederici Brain Mapping Center, UCLA: John C. Mazziotta Arthur Toga
30 A receptor fingerprint is 5-HT 2 D HT A a 2 5 GABA A GABA B a BZ caudate nach M 3 M 2 M putamen area 4
31 Receptor Fingerprints of the primary visual cortex: layer specificity L. I 5-HT 2 D 3 2 Ll. II-III 5-HT 2 D 3 2 L. IV 5-HT 2 D HT A GABA A 5-HT A GABA A 5-HT A GABA A a 2 GABA B a 2 GABA B a 2 GABA B a BZ a BZ a BZ N M N M N M M 3 M 2 M 3 M 2 M 3 M 2 In/output Synapse L. V D 3 L. VI D 5-HT HT I II I II I II 5-HT A a 2 a N M GABA A BZ GABA B 5-HT A a 2 a N M GABA A BZ GABA B III IV V III III IV V M 3 M 2 M 3 M 2 VI VI
32 Dimension Multidimensional scaling analysis of receptor densities (averaged over all cortical layers) and default mode network DMN 24 EC 6 motor 32 p L PGp M 37M L 42 5L 5M 2 2 PGa 22 PFt 3 s24 37B PFm 3a 4 3b FG2 V3v FG V4v Broca V3d V3A 4 primary sensory V2 early visual V posterior cingulate cortex (BA23) precuneus (BA3) anterior cingulate cortex (p24, s24) ventral medial prefrontal cortex (m, BA32, BA) dorsal medial prefrontal cortex (medial part of BA9) inferior parietal lobule (PGa, PGp, PFm, PFt) lateral temporal cortex (BA2, BA2) anterior temporal pole (BA38) hippocampus, entorhinal (EC), and parahippocampal (BA36) cortex -4 HIP Dimension
33 Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) 5 y = -57.8x R² =.3239 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) y = 255.6x R² =.656 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) 3 2 y = -.2x GABA A 5-HT A R² =.4852 y = 22.6x R² =.422 p=. y = 278.8x R² =.432 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) 5 5 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) Metabolic data from: Hyder F, Herman P, Bailey CJ, Møller A, Globinsky R, Fulbright RK, Rothman DL, Gjedde A (26) Uniform distributions of glucose oxidation and oxygen extraction in gray matter of normal human brain: No evidence of regional differences of aerobic glycolysis. J Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 36(5): 93 96
34 Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) y = x y = x M 2 R² =.5852 a R² =.92 p=.9 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) HT 2 y = x R² =.323 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) DMN: cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption decreases with increasing, 5-HT A and a receptor densities, but increases with increasing GABA A receptor densities Non-DMN: cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption increases with increasing, GABA A, M 2 and 5-HT 2 receptor densities Metabolic data from: Hyder F, Herman P, Bailey CJ, Møller A, Globinsky R, Fulbright RK, Rothman DL, Gjedde A (26) Uniform distributions of glucose oxidation and oxygen extraction in gray matter of normal human brain: No evidence of regional differences of aerobic glycolysis. J Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 36(5): 93 96
35 Ratio between and GABA A Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) receptor densities receptor densities /GABA A y = -.962x R² =.299 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of glucose consumption (mmol/g/min) ( ) and GABA A ( ) Cerebral metabolic rate of glucose consumption (mmol/g/min) Ratio between and GABA A /GABA A y = x R² =.538 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) ( ) and GABA A ( ) Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption (mmol/g/min) Metabolic data from: Hyder F, Herman P, Bailey CJ, Møller A, Globinsky R, Fulbright RK, Rothman DL, Gjedde A (26) Uniform distributions of glucose oxidation and oxygen extraction in gray matter of normal human brain: No evidence of regional differences of aerobic glycolysis. J Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 36(5): 93 96
36 Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) Receptor density (fmol/mg protein) y = x R² =.2679 p=.63 M y = 242.8x R² =.387 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of glucose consumption (mmol/g/min) 5-HT A y = -46.8x R² =.3729 p= Cerebral metabolic rate of glucose consumption Cerebral metabolic rate of glucose consumption DMN: cerebral metabolic rate of glucose consumption decreases with increasing and 5-HT A receptor densities Non-DMN: cerebral metabolic rate of glucose consumption increases with increasing and M receptor densities Metabolic data from: Hyder F, Herman P, Bailey CJ, Møller A, Globinsky R, Fulbright RK, Rothman DL, Gjedde A (26) Uniform distributions of glucose oxidation and oxygen extraction in gray matter of normal human brain: No evidence of regional differences of aerobic glycolysis. J Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 36(5): 93 96
37 Summary High densities of receptors significantly correlate, or show a non-significant trend, with low cerebral metabolic rates of glucose or oxygen consumption in DMN areas. A notable exception is the positive correlation of the densities of inhibitory GABA A receptors with the cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen consumption. High densities of receptors significantly correlate, or show a non-significant trend, with high cerebral metabolic rates of glucose or oxygen consumption in non-dmn areas (mainly primary and higher sensory areas, motor areas).
Receptorarchitecture and Neural Systems
 Receptorarchitecture and Neural Systems Karl Zilles Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine INM-1 Research Centre Jülich and University Hospital of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics RWTH Universität
Receptorarchitecture and Neural Systems Karl Zilles Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine INM-1 Research Centre Jülich and University Hospital of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics RWTH Universität
Receptorarchitecture and Neural Systems
 Receptorarchitecture and Neural Systems Karl Zilles Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine INM-1 Research Centre Jülich and University Hospital of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics RWTH Universität
Receptorarchitecture and Neural Systems Karl Zilles Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine INM-1 Research Centre Jülich and University Hospital of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics RWTH Universität
Where macroscopy fails: going to microscopic architecture
 Where macroscopy fails: going to microscopic architecture Nicola Palomero-Gallagher Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-1) Research Centre Jülich and Department of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and
Where macroscopy fails: going to microscopic architecture Nicola Palomero-Gallagher Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-1) Research Centre Jülich and Department of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Organization of the Human Inferior Parietal Lobule Based on Receptor Architectonics
 Cerebral Cortex March 2013;23:615 628 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs048 Advance Access publication February 28, 2012 Organization of the Human Inferior Parietal Lobule Based on Receptor Architectonics Svenja Caspers
Cerebral Cortex March 2013;23:615 628 doi:10.1093/cercor/bhs048 Advance Access publication February 28, 2012 Organization of the Human Inferior Parietal Lobule Based on Receptor Architectonics Svenja Caspers
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
CEREBRUM. Dr. Jamila EL Medany
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila EL Medany Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral ventricle). Describe
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions
 Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
Supplementary Material S3 Further Seed Regions Figure I. Changes in connectivity with the right anterior insular cortex. (A) wake > mild sedation, showing a reduction in connectivity between the anterior
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
10/10/2011. Tools for Visualization and Labeling. SPM MRIcron MRIcroGL xjview MARINA FreeSurfer Talairach Daemon SPM Anatomy Toolbox WFU Pickatlas
 Tools for Visualization and Labeling Visualization and Labeling SPM MRIcron MRIcroGL xjview MARINA FreeSurfer Talairach Daemon SPM Anatomy Toolbox WFU Pickatlas Gesture imitation with variable memory load
Tools for Visualization and Labeling Visualization and Labeling SPM MRIcron MRIcroGL xjview MARINA FreeSurfer Talairach Daemon SPM Anatomy Toolbox WFU Pickatlas Gesture imitation with variable memory load
Cytoarchitecture of the cerebral cortex More than localization
 Commentary Cytoarchitecture of the cerebral cortex More than localization K. Amunts, a,b, A. Schleicher, c and K. Zilles a,c a Institute of Neurosciences and Biophysics-Medicine (INB 3), Research Centre
Commentary Cytoarchitecture of the cerebral cortex More than localization K. Amunts, a,b, A. Schleicher, c and K. Zilles a,c a Institute of Neurosciences and Biophysics-Medicine (INB 3), Research Centre
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama
 CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
CEREBRUM Dr. Jamila Elmedany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: List the parts of the cerebral hemisphere (cortex, medulla, basal nuclei, lateral
Anatomy of the Hippocampus
 Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Supplementary Digital Content
 Supplementary Digital Content Contextual modulation of pain in masochists: involvement of the parietal operculum and insula Sandra Kamping a, Jamila Andoh a, Isabelle C. Bomba a, Martin Diers a,b, Eugen
Supplementary Digital Content Contextual modulation of pain in masochists: involvement of the parietal operculum and insula Sandra Kamping a, Jamila Andoh a, Isabelle C. Bomba a, Martin Diers a,b, Eugen
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
Chapter 2: Studies of Human Learning and Memory From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Medium Spiny Neuron A Current Conception of the major memory systems in the brain Figure
LIMBIC SYSTEM. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
FRONTAL LOBE. Central Sulcus. Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Sulcus. Cingulate Sulcus. Lateral Sulcus
 FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
FRONTAL LOBE Central Ascending ramus of the Cingulate Cingulate Lateral Lateral View Medial View Motor execution and higher cognitive functions (e.g., language production, impulse inhibition, reasoning
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits
 Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
Text to brain: predicting the spatial distribution of neuroimaging observations from text reports (submitted to MICCAI 2018)
 1 / 22 Text to brain: predicting the spatial distribution of neuroimaging observations from text reports (submitted to MICCAI 2018) Jérôme Dockès, ussel Poldrack, Demian Wassermann, Fabian Suchanek, Bertrand
1 / 22 Text to brain: predicting the spatial distribution of neuroimaging observations from text reports (submitted to MICCAI 2018) Jérôme Dockès, ussel Poldrack, Demian Wassermann, Fabian Suchanek, Bertrand
Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The largest part of the brain. Ovoid shape. Two incompletely separated cerebral hemispheres. The outer surface of the cerebral
Cerebrum-Cerebral Hemispheres Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University The largest part of the brain. Ovoid shape. Two incompletely separated cerebral hemispheres. The outer surface of the cerebral
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
Supplemental Digital Content 4: Effect sizes
 Supplemental Digital Content 4: Effect sizes Effect size within each of the pre-defined regions of interest for each studied network across experimental conditions and for the correlation analysis. Legend
Supplemental Digital Content 4: Effect sizes Effect size within each of the pre-defined regions of interest for each studied network across experimental conditions and for the correlation analysis. Legend
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2006 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
C:\Documents and Settings\sstensaas\Desktop\dental visual 2010\VisualPath dental 2010.docVisualPath dental 2010.doc
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas April 8, 2010, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15, Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch 7 THE VISUAL PATHWAY Objectives: 1. Describe the pathway of visual information from
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas April 8, 2010, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15, Computer Resources: HyperBrain Ch 7 THE VISUAL PATHWAY Objectives: 1. Describe the pathway of visual information from
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy
 Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: Describe the anatomy and main functions of the thalamus. Name and identify different nuclei
Geography of the Forehead
 5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
5. Brain Areas Geography of the Forehead Everyone thinks the brain is so complicated, but let s look at the facts. The frontal lobe, for example, is located in the front! And the temporal lobe is where
Supporting online material for: Predicting Persuasion-Induced Behavior Change from the Brain
 1 Supporting online material for: Predicting Persuasion-Induced Behavior Change from the Brain Emily Falk, Elliot Berkman, Traci Mann, Brittany Harrison, Matthew Lieberman This document contains: Example
1 Supporting online material for: Predicting Persuasion-Induced Behavior Change from the Brain Emily Falk, Elliot Berkman, Traci Mann, Brittany Harrison, Matthew Lieberman This document contains: Example
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Brain anatomy tutorial. Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics
 Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4
 Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4 Table S1: Brain regions involved in the adapted classification learning task Brain Regions x y z Z Anterior Cingulate
Supplementary Online Material Supplementary Table S1 to S5 Supplementary Figure S1 to S4 Table S1: Brain regions involved in the adapted classification learning task Brain Regions x y z Z Anterior Cingulate
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table. Neuroimaging studies on the premonitory urge and sensory function in patients with Tourette syndrome. Authors Year Patients Male gender (%) Mean age (range) Adults/ Children
Theory of mind skills are related to gray matter volume in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia
 Theory of mind skills are related to gray matter volume in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia Supplemental Information Table of Contents 2 Behavioral Data 2 Table S1. Participant demographics
Theory of mind skills are related to gray matter volume in the ventromedial prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia Supplemental Information Table of Contents 2 Behavioral Data 2 Table S1. Participant demographics
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Exam 1 PSYC Fall 1998
 Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Exam 1 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) Briefly describe the difference between a dualistic and a materialistic explanation of brain-mind relationships. (1 point) True or False. George Berkely was a monist.
Lisa M. Giocomo & Michael E. Hasselmo
 Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Stuttering Research. Vincent Gracco, PhD Haskins Laboratories
 Stuttering Research Vincent Gracco, PhD Haskins Laboratories Stuttering Developmental disorder occurs in 5% of children Spontaneous remission in approximately 70% of cases Approximately 1% of adults with
Stuttering Research Vincent Gracco, PhD Haskins Laboratories Stuttering Developmental disorder occurs in 5% of children Spontaneous remission in approximately 70% of cases Approximately 1% of adults with
Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines
 Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines Altmann A. 1,2,7 *, Schröter M.S. 1,3 *, Spoormaker V.I. 1, Kiem S.A. 1, Jordan D. 4, Ilg R. 5,6,
Validation of non- REM sleep stage decoding from resting state fmri using linear support vector machines Altmann A. 1,2,7 *, Schröter M.S. 1,3 *, Spoormaker V.I. 1, Kiem S.A. 1, Jordan D. 4, Ilg R. 5,6,
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
What can connectomics tell us about latelife depression? Olusola Ajilore, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor ADAA 2014
 What can connectomics tell us about latelife depression? Olusola Ajilore, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor ADAA 2014 Disclosures No Financial Conflict of Interests Funding NIMH Overview Background Structural
What can connectomics tell us about latelife depression? Olusola Ajilore, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor ADAA 2014 Disclosures No Financial Conflict of Interests Funding NIMH Overview Background Structural
Supplemental Information. Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion
 Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion Luke J. Chang, Alec Smith, Martin Dufwenberg, and Alan G. Sanfey Supplemental Information
Neuron, Volume 70 Supplemental Information Triangulating the Neural, Psychological, and Economic Bases of Guilt Aversion Luke J. Chang, Alec Smith, Martin Dufwenberg, and Alan G. Sanfey Supplemental Information
An Introduction to the Structure, Function and Aging of the Human Brain.
 An Introduction to the Structure, Function and Aging of the Human Brain. These lectures will discuss the anatomy and workings of this amazing organ, that is thought to be the most complex structure to
An Introduction to the Structure, Function and Aging of the Human Brain. These lectures will discuss the anatomy and workings of this amazing organ, that is thought to be the most complex structure to
Hippocampal brain-network coordination during volitionally controlled exploratory behavior enhances learning
 Online supplementary information for: Hippocampal brain-network coordination during volitionally controlled exploratory behavior enhances learning Joel L. Voss, Brian D. Gonsalves, Kara D. Federmeier,
Online supplementary information for: Hippocampal brain-network coordination during volitionally controlled exploratory behavior enhances learning Joel L. Voss, Brian D. Gonsalves, Kara D. Federmeier,
Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
 American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Structure and Function of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems (Fall 2014) Auditory Cortex (1) Prof. Xiaoqin Wang
 580.626 Structure and Function of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems (Fall 2014) Auditory Cortex (1) Prof. Xiaoqin Wang Laboratory of Auditory Neurophysiology Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns
580.626 Structure and Function of the Auditory and Vestibular Systems (Fall 2014) Auditory Cortex (1) Prof. Xiaoqin Wang Laboratory of Auditory Neurophysiology Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Finding the Central Sulcus MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Finding the Central Sulcus MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Co-ac&va&on mapping and Parcella&on
 Co-ac&va&on mapping and Parcella&on Sarah Genon Jülich Research Centre, Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine, Brain and Behavior (INM-7) Meta-Analyses Topic based meta-analyses: derive brain regions
Co-ac&va&on mapping and Parcella&on Sarah Genon Jülich Research Centre, Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine, Brain and Behavior (INM-7) Meta-Analyses Topic based meta-analyses: derive brain regions
LEC 1B ANATOMY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Cogs 17 * UCSD
 LEC 1B ANATOMY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Cogs 17 * UCSD Cerebral Cortex A 6-layer sheet of cells, unfolded = < 1 m square X 3 mm thick Cortex 6 layers of cells Nissl Stain for Cell Bodies Info projected to
LEC 1B ANATOMY OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Cogs 17 * UCSD Cerebral Cortex A 6-layer sheet of cells, unfolded = < 1 m square X 3 mm thick Cortex 6 layers of cells Nissl Stain for Cell Bodies Info projected to
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Devenney E, Bartley L, Hoon C, et al. Progression in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: a longitudinal study. JAMA Neurol. Published online October 26, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.2061.
Supplementary Online Content Devenney E, Bartley L, Hoon C, et al. Progression in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia: a longitudinal study. JAMA Neurol. Published online October 26, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.2061.
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS. specifications
 NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
NEOCORTICAL CIRCUITS specifications where are we coming from? human-based computing using typically human faculties associating words with images -> labels for image search locating objects in images ->
APPLICATION OF PHOTOGRAMMETRY TO BRAIN ANATOMY
 http://medifitbiologicals.com/central-nervous-system-cns/ 25/06/2017 PSBB17 ISPRS International Workshop APPLICATION OF PHOTOGRAMMETRY TO BRAIN ANATOMY E. Nocerino, F. Menna, F. Remondino, S. Sarubbo,
http://medifitbiologicals.com/central-nervous-system-cns/ 25/06/2017 PSBB17 ISPRS International Workshop APPLICATION OF PHOTOGRAMMETRY TO BRAIN ANATOMY E. Nocerino, F. Menna, F. Remondino, S. Sarubbo,
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
-Zeina Assaf. -Omar Odeh. - Maha Beltagy
 -3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
-3 -Zeina Assaf -Omar Odeh - Maha Beltagy 1 P a g e The Inferior Surface Of The Brain The inferior surface of the brain is divide by the stem of the lateral fissure into 2 parts : The orbital surface and
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation
 Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
NeuroImage. Probabilistic fibre tract analysis of cytoarchitectonically defined human inferior parietal lobule areas reveals similarities to macaques
 NeuroImage 58 (2011) 362 380 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Probabilistic fibre tract analysis of cytoarchitectonically defined human
NeuroImage 58 (2011) 362 380 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect NeuroImage journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ynimg Probabilistic fibre tract analysis of cytoarchitectonically defined human
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Theories of memory. Memory & brain Cellular bases of learning & memory. Epileptic patient Temporal lobectomy Amnesia
 Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Distinct Value Signals in Anterior and Posterior Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex
 Supplementary Information Distinct Value Signals in Anterior and Posterior Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex David V. Smith 1-3, Benjamin Y. Hayden 1,4, Trong-Kha Truong 2,5, Allen W. Song 2,5, Michael L.
Supplementary Information Distinct Value Signals in Anterior and Posterior Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex David V. Smith 1-3, Benjamin Y. Hayden 1,4, Trong-Kha Truong 2,5, Allen W. Song 2,5, Michael L.
Announcement. Overview. Words Describing Sectional Planes. Words Describing Spatial Orientation. Explore! Basic neuroscience terminology
 Announcement Explore! The reading list is a good place to start, especially the Perspectives section. Overview Basic neuroscience terminology A Roadmap to the course Also, check out short articles in the
Announcement Explore! The reading list is a good place to start, especially the Perspectives section. Overview Basic neuroscience terminology A Roadmap to the course Also, check out short articles in the
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Two cortical systems for memoryguided
 Two cortical systems for memoryguided behaviour Charan Ranganath 1,2 and Maureen Ritchey 2 Abstract Although the perirhinal cortex (PRC), parahippocampal cortex (PHC) and retrosplenial cortex (RSC) have
Two cortical systems for memoryguided behaviour Charan Ranganath 1,2 and Maureen Ritchey 2 Abstract Although the perirhinal cortex (PRC), parahippocampal cortex (PHC) and retrosplenial cortex (RSC) have
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
correlates with social context behavioral adaptation.
 REVIEW OF FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURES Main organization of frontal cortex: 1. Motor area (precentral gyrus). 2. Premotor & supplementary motor areas (immediately anterior to motor area). Includes premotor,
REVIEW OF FRONTAL LOBE STRUCTURES Main organization of frontal cortex: 1. Motor area (precentral gyrus). 2. Premotor & supplementary motor areas (immediately anterior to motor area). Includes premotor,
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Connections of basal ganglia
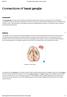 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
How Therapy Changes the Human Brain
 Selected Neural Plasticity References How Therapy Changes the Human Brain Martha S. Burns, Ph.D.,ccc-slp Joint Appointment Professor Northwestern University Bryck & Fisher (2012) Training the Brain: Practical
Selected Neural Plasticity References How Therapy Changes the Human Brain Martha S. Burns, Ph.D.,ccc-slp Joint Appointment Professor Northwestern University Bryck & Fisher (2012) Training the Brain: Practical
Course Calendar
 Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
EDGE DETECTION. Edge Detectors. ICS 280: Visual Perception
 EDGE DETECTION Edge Detectors Slide 2 Convolution & Feature Detection Slide 3 Finds the slope First derivative Direction dependent Need many edge detectors for all orientation Second order derivatives
EDGE DETECTION Edge Detectors Slide 2 Convolution & Feature Detection Slide 3 Finds the slope First derivative Direction dependent Need many edge detectors for all orientation Second order derivatives
Action potentials propagate down their axon
 Action potentials propagate down their axon Larger diameter axons have less resistance to ion flow Speed of conduction is faster in large diameter axons Saltatory conduction in myelinated axons Large myelinated
Action potentials propagate down their axon Larger diameter axons have less resistance to ion flow Speed of conduction is faster in large diameter axons Saltatory conduction in myelinated axons Large myelinated
Online appendices are unedited and posted as supplied by the authors. SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 Appendix 1 to Sehmbi M, Rowley CD, Minuzzi L, et al. Age-related deficits in intracortical myelination in young adults with bipolar SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Intracortical Myelin (ICM)
Appendix 1 to Sehmbi M, Rowley CD, Minuzzi L, et al. Age-related deficits in intracortical myelination in young adults with bipolar SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Intracortical Myelin (ICM)
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Reproducibility is necessary but insufficient for addressing brain science issues.
 1 Reproducibility is necessary but insufficient for addressing brain science issues. GLM promises nothing but the higher amplitude of the experimental trials on the average compared with the control trials.
1 Reproducibility is necessary but insufficient for addressing brain science issues. GLM promises nothing but the higher amplitude of the experimental trials on the average compared with the control trials.
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Cronicon EC NEUROLOGY. Mini Review. Alzheimer s Living with the Disease- Understanding the Brain. Caron Leid* Aspen University, Aspen, Colorado, USA
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Mini Review Alzheimer s Living with the Disease- Understanding the Brain Caron Leid* Aspen University, Aspen, Colorado, USA *Corresponding Author: Caron Leid, Aspen University,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC NEUROLOGY Mini Review Alzheimer s Living with the Disease- Understanding the Brain Caron Leid* Aspen University, Aspen, Colorado, USA *Corresponding Author: Caron Leid, Aspen University,
Differentiated parietal connectivity of frontal regions for what and where memory
 Brain Struct Funct (2013) 218:1551 1567 DOI 10.1007/s00429-012-0476-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Differentiated parietal connectivity of frontal regions for what and where memory C. Rottschy S. Caspers C. Roski
Brain Struct Funct (2013) 218:1551 1567 DOI 10.1007/s00429-012-0476-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Differentiated parietal connectivity of frontal regions for what and where memory C. Rottschy S. Caspers C. Roski
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and the Biological Basis of Individuality
 The Study of Memory Has Two Parts: Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and the Biological Basis of Individuality (1) The Systems Problem of Memory: Where in the brain is memory stored? (2) The Molecular Problem
The Study of Memory Has Two Parts: Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and the Biological Basis of Individuality (1) The Systems Problem of Memory: Where in the brain is memory stored? (2) The Molecular Problem
Human Cognitive Developmental Neuroscience. Jan 27
 Human Cognitive Developmental Neuroscience Jan 27 Wiki Definition Developmental cognitive neuroscience is an interdisciplinary scientific field that is situated at the boundaries of Neuroscience Psychology
Human Cognitive Developmental Neuroscience Jan 27 Wiki Definition Developmental cognitive neuroscience is an interdisciplinary scientific field that is situated at the boundaries of Neuroscience Psychology
Mechanosensation. Central Representation of Touch. Wilder Penfield. Somatotopic Organization
 Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
Mechanosensation Central Representation of Touch Touch and tactile exploration Vibration and pressure sensations; important for clinical testing Limb position sense John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology
