JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
|
|
|
- Harriet Jordan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: ISSN (e) x ISSN (p) DOI: Comparison of Brain Magnetic Reasoning Imaging (MRI) Image Information between T1 Turbo Inversion Recovery (TIR) With T2 Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (Flair) in Case of Epilepsy Authors Jeffri Ardiyanto 1, Agung Tri Pambudi 2, Sudiyono 3, Rasyid 4, Dwi Rochmayanti 5, Edy Susanto 6, Ardi Soesilo W 7 1,3,4,5,6,7 Poltekkes Kemenkes Semarang, 2 RS Dr.Sutomo jeffri-ardiyanto@hotmail.com ABSTRACT Background: Examination MRI of brain coronal oblique slices in is usually performed using T1 turbo inversion recovery (TIR) or T2 fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences. Objective: The purpose of this research is to determine the differences in MRI of brain image information between the sequences of and coronal oblique slices in and to find out the better image information between the two sequences. Methods: This research is a quantitative study with an experimental approach. Data were collected from June to August 2016 in Radiology of General Hospital Haji Surabaya by using a questionnaire to the two respondents. Wilcoxon test is used to determine the means differences in image information generated by and sequences. The calculation is aided with SPSS 16 software. Results: There are differences in MRI brain image information between and sequences coronal oblique slices in with a p-value = (p <0.05). This difference is due to the characteristics of different parameters between the two sequences and time inversion 0f is shorter than. The results show that the mean rank of is 5.00 and is At MRI brain coronal oblique slices in the case of epilepsy, sequence is better than the because it can reveal the anatomy of the brain more clear and informative as well as the anatomy of the gray matter, white matter, and hippocampus while on the anatomy of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) there is no significant difference between and sequences. Conclusion: There are differences in MRI brain image information between and sequences coronal oblique slices in. Keywords: MRI brain,,, coronal oblique slices, epilepsy. INTRODUCTION Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio frequencies to visualize and analyze bodily tissues, bloodstream, and body's metabolic functions. In its application, the magnetic field strength used Tesla -1.5 Tesla (Notosiswoyo, 2004). The brain is very vital organs for humans. There are a lot of abnormalities in the human brain, Jeffri Ardiyanto et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 06 June 2017 Page 23186
2 among others, epilepsy, hydrocephalus, Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and cancer. Among the various brain diseases, epilepsy became one of the diseases in the brain that need special attention because besides the cases are quite common and influences the quality of life of people (deboer, 2008). Image evaluation in epileptic disease progresses rapidly with the CT scan in early 1970, because it can reveal a good soft tissue contrast, multi-planar imaging, and least artifacts. But the disorder of epilepsy can be visualized with a much more sensitive and accurate with Magnetic Reasoning Imaging (MRI). Thus, Currently, MRI is of choice for displaying high-resolution structural imaging in epilepsy (Karis, 2008). Selection of the proper sequence on MRI brain in epilepsy clinic is very important to show abnormalities clearly so that they can be treated with the proper diagnosis. According to Karis (2008), epilepsy patients need watching the signs of their mesial temporal sclerosis (atrophy of the hippocampus), the internal structure of the chaotic and hyperintensity on T2 weighting. But among the signs, the atrophy of the hippocampus is the most often found. This condition is rare in children under the age of 10 years. If the pathogenesis is not known, there might be a correlation with infection and seizure due to fever when they were children. This condition is characterized by atrophy of the hippocampus and the best sequences to look at it is T2 weighted FLAIR coronal oblique because the lost volume of hippocampus will be joined by increased T2 signal and loss of contrast between gray matter and white matter. According to Hajnal JV et al (1992), T2 weighted FLAIR coronal sequences are very useful to confirm the abnormalities of the hippocampus and to detect abnormalities in the cortex and sub-cortex. According to Karel & Eric (2008), the optimal imaging of the hippocampus and the medial temporal lobe is done with slices of 2-3 mm coronal oblique images orthogonal to the long axis of the hippocampus. So far the "gold standard" MRI brain scanning protocol in are T1 Inversion Recovery (T1 IR) sequences coronal and FLAIR coronal sequences. In the implementation of the hospital to confirm the abnormalities of the hippocampus in the case of epilepsy, some hospitals besides using oblique coronal also use coronal oblique. Some use them together, but some only use one of the sequences. METHODS This research is a quantitative study with an experimental approach. Data were collected from June to August 2016 in Radiology RSU Haji Surabaya. Population and sample is the image of MRI brain images of the two groups paired with sequences coronal oblique slices of the 10 patients with the inclusion criteria of men/women with age years old, been indicated abnormalities in the brain epilepsy, while for exclusion criteria were patients of claustrophobia, given anesthetic drugs and using the contrast media. The subjects of this study are two radiologists who assesses the results of image research through questionnaires. Sliced assessed were slices of hippocampus displaying the most obvious image. Data analysis was performed statistical tests with applications SPPS 16 using test Cohen's Kappa to determine the level of agreement of the second respondent, the Wilcoxon test because the data in the form of ordinal to determine the level difference information image of MRI brain between with sequences slice coronal in with the value of α = 0.05 (p <0.05), the mean rank of the Wilcoxon test to find out information better image. RESULT 1. Characteristics of Samples This study was conducted on 10 patients with MRI examinations of the brain performed with and sequences oblique coronal slices in with a total time of scanning for both sequences for each patient during 7 minutes. Jeffri Ardiyanto et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 06 June 2017 Page 23187
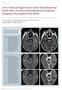
3 Table 1. Description of the research sample Categories Classification Numbers Percentage (%) Men 4 40 sex women 6 60 Total years old 7 70 age years old 3 30 Total Table 4. Result of difference test in image information all criteria between with T2 FLAIR sequences coronal oblique slices in cases of epilepsy Sequences p-value explanation TSE GRE Significant 2. Differences in Image Information of MRI Brain Between with Before performing the different test, respondents were tested beforehand to determine the level of agreement or objectivity of ratings to the image of the cervical spine of MRI brain by using Cohen's Kappa statistical test. Table 2. Result of Cohen s Kappa test on two respondents Sequences Level of agreement Cohen s Kappa Amount of Data 0, , Based on Table 2, the level of agreement from respondents in sequence of 0.708, while the sequence of Wilcoxon test is then performed to determine the difference of the image information between T1 TIR with to see the significance value of (p-value). a. Differences Test in Image Information for Each Criterion Between with T2 FLAIR Table 3. Result of difference test in image information each of criteria between with sequences coronal oblique slices in Criteria Sequences p-value Explanation gray matter 0,024 significant white matter 0,033 significant CSF Not 0,257 significant Hippocampus 0,011 significant b. Differences Test in Image Information for All Criteria Between with Figure 1. The research sample coronal oblique slices image parallel to the hippocampus on T1 TIR (A) with sequences (B) Note: 1. gray matter 2. white matter 3. cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 4. hippocampus 3. The Better Image Information of MRI Brain Between with The results of assessment on the image information is analyzed with to determine the mean rank for the better image information between with sequences oblique coronal slices in a. The Better Image Information for Each Criterion Between with. Table 5 Result of mean rank Wilcoxon test of image information each criterion between with sequences oblique coronal slices in Criteria Sequences Mean rank gray matter white matter CSF Hippocampus Jeffri Ardiyanto et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 06 June 2017 Page 23188
4 b. The Better Image Information for All Criteria Between with Table 6 Result of Wilcoxon test's mean rank on image information for all criteria between with sequences oblique coronal slices in Sequences Mean Rank DISCUSSION The result of Cohen s Kappa test shows that the level of agreement in sequence is while the sequence is According to Sim and Wraight (2005), a measure of agreement between the two assessors in classifying some subjects into one of two categories is a consensus (objective) if the value of Cohen's Kappa in the range 0 (poor), 0.01 to 0.2 (slight), 0.21 to 0.40 (fair) 0.41 to 0.60 (moderate), 0.61 to 0.80 (substantial) and 0.81 to 1.00 (almost perfect). Based on Cohen's Kappa test results, it is concluded that the ratings of two respondents are objective. 1. Differences in Image Information MRI of Brain Between with Sequences Coronal of oblique Slices In Cases of Epilepsy Initial hypothesis assumes that there is a significant difference to the criteria of the gray matter, white matter, and hippocampus in the MRI brain image between with T2 FLAIR sequences. The value of significance (pvalue) of anatomy criteria shows that gray matter = 0.024; white matter = 0.033; hippocampus = 0.011, while on anatomical criteria CSF has a value of significance (pvalue) of 0.257, indicating that Ho is accepted as the p-value is > meaning there is no significant difference for anatomical criteria hippocampus on MRI brain images between T1 TIR to sequences coronal of oblique slices. Wilcoxon test on the overall image information indicates that there is a significant difference in image information for the overall criterion with the p-value of (p <0.05) for MRI brain images between T1 with TIR sequences coronal of oblique slices. The difference happens as each sequence has advantages and disadvantages. In this study, each sequence has the characteristics of different parameters, such as time inversion (TI), repetition time (TR) and the acquisition time to obtain a good image in every sequence, in this case, the and apply sequences coronal of oblique slices. At the image of MRI brain coronal oblique slices, it has a higher contrast than T1 TIR. Background image in sequences is gray while in is black. The length of time inversion recovery sequences is shorter than, which is 400 ms compared to 2500 ms. This is in accordance with Moran et. al (1986) that the has the background of mid gray color air supplied because it uses a polarity gradient M (z) phase corrected and parameters normally used to sequences are TR = 7000 ms, TI = 400 ms and TE = 70. sequences have black background as it only uses gradient magnitude M (z) and the parameters used in the sequence is very long TR ms, TI range is about 2000 to 2500 ms and for the null signal from CSF and TE are approximately ms (Hajnal, et. al, 1992). 2. The Better Image Information of MRI Brain Between with The better image Information in MRI brain between with sequences oblique with coronal slices obtained from the mean rank of Wilcoxon test per the criteria of image information is described below: a. Gray Matter From the results of the Wilcoxon test criteria anatomy gray matter, sequences has a higher mean rank (3.50) value than the T2 FLAIR (0.00). According to the authors, it is because of the differential factor time inversion sequences and. Timing parameters that control the contrast inversion Jeffri Ardiyanto et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 06 June 2017 Page 23189
5 are the inversion time (TI). TI on is shorter than the TI so that the contrast of gray matter is more optimal. While contrasting gray matter on sequences looks hipper -intense. sequences have a short time inversion of 400 ms which not to allow a longitudinal full recovery (Moran et al, 1986), while sequences have a range about 2000 to 2500 ms inversion time to null signal from CSF enabling the longitudinal full recovery (Hajnal, et al, 1992). This is consistent with the theory of Redpath et.al (1994), that the sequence of T1 TIR gray matter in the organs are very good for the gray matter and is a selective sequence, in particular, suppress signal on gray matter organ. b. White matter In the anatomy of white matter criteria, Wilcoxon test results showed that the mean rank is higher than sequences in the amount of 4.64 against According to the authors, it is because of the differential factor time inversion (TI) between and sequences. Time inversion on T1 TIR is shorter than in so that the contrast of the white matter is more intermediated when compared with sequences which are more hypo-intense. This is consistent with the theory of Redpath et. al (1994), that the sequence of organ white matter on sequences looked intermediated but lighter than the gray matter. c. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) On anatomical criteria of CSF, Wilcoxon test results showed that the mean rank between T1 TIR and is 2.67 and sequences are higher than but the difference in value between the sequences are relatively small in the amount of According to the authors, the difference in relatively small different value to the mean rank between and sequences on signal intensity because the two sequences are equally hypo-intense. This is consistent with the theory of Moran et. al (1986), that the sequence anatomy CSF seemed darkest (hypo-intense) because these sequences were using the inverse correction phase recovery that maintains information about the polarity of Mz, the more negative the value is given the darker. Meanwhile, according to Hajnal (1992), the sequences anatomy CSF appears dark because of the sequence is using the value of TI from 2000 to 2500 to zero signals from the CSF, coupled with a very long TR (8000+) and TE ( ) to make T2 weighting. d. Hippocampus Wilcoxon test criteria anatomy for hippocampus, indicates that sequences (4.00) have a higher mean value than the sequences (0.00). According to the author, this because of the differential factor in time inversion (TI) between sequences with. TI on is shorter than the TI T2 FLAIR so that the contrast of the intermediated hippocampus than sequences which are hipper intense. According to Fajar (2012), suspicion of epilepsy is due to the density of components and the integrity of an overview of certain pyramidal cells in the cortex included in the hippocampus that is vulnerable to seizure activity. According to Hajnal et. al (1992), the use of TI in sequences is longer than making it difficult to distinguish when there is a pathology (lesions) on the organ because both have hipper intense signal intensity. While on T1 TIR sequences have a short TI thus minimizing phase error, and if there is any pathology (lesions), it becomes more apparent and detail boundaries between surrounding tissue are visible. Jeffri Ardiyanto et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 06 June 2017 Page 23190
6 CONCLUSION In comparing the use of brain MRI between T1 TIR with sequences coronal oblique slices, to see better overall criteria, using sequences is better because it has a mean rank higher than sequences, amounting to 5.00 versus These values indicate that the image information on sequence is much better than the. 9. Sim, Julius dan Chris C. Wraight, 2005, The Kappa Statistic in Realibity Studies: Use, Interpretation and Sample Size Requirements, Physical Therapy Volume 85 REFERENCES 1. DeBoer HM, Mula M, Sander JW, 2008, The Global Burden And Stigma Of Epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior, 12, Fajar, H N, 2012, Predikator Kejaidan Kejang Pasca Operasi Bedah Epilepsi Lobus Temporal Pada Penderita Epilepsi Lobus Temporal, Universitas Diponegoro 3. Hajnal JV, Bryant DJ, Kasuboski L, et al, 1992, Use of Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) pulse sequences in MRI of the brain, J Computer Assist Tomography 4. Karel D, Eric Achten, 2008, Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Epilepsy. European radiology 18, Karis, JP, 2008, Epilepsy, for the Expert Panel on Neurologic Imaging, ACR Appropriateness Criteria 6. Moran PR, Kumar NG, Karstaedt N, Jackels SC, 1986, Tissue contrast enhancement: image reconstruction algorithm selection of TI in inversion recovery MRI, Magn Reson Imaging 7. Notosiswoyo M, 2004, Media Litbang Kesehatan, Pemanfaatan Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Sebagai Sarana Diagnose Pasien, No.3, Vol XIV 8. Redpath, T W dan F W Smith, 1994, Technical note : Use of a double inversion recovery pulse sequence to image selectively gray or white brain mater, The British Jurnal of Radiology Jeffri Ardiyanto et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 06 June 2017 Page 23191
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.84 Anatomical Differences Between T2 WI FSE
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.84 Anatomical Differences Between T2 WI FSE
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Yin-Hui Siow MD, FRCPC Director of Nuclear Medicine Southlake Regional Health Centre
 Yin-Hui Siow MD, FRCPC Director of Nuclear Medicine Southlake Regional Health Centre Today Introduction to CT Introduction to MRI Introduction to nuclear medicine Imaging the dementias The Brain ~ 1.5
Yin-Hui Siow MD, FRCPC Director of Nuclear Medicine Southlake Regional Health Centre Today Introduction to CT Introduction to MRI Introduction to nuclear medicine Imaging the dementias The Brain ~ 1.5
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
2D-Sigmoid Enhancement Prior to Segment MRI Glioma Tumour
 2D-Sigmoid Enhancement Prior to Segment MRI Glioma Tumour Pre Image-Processing Setyawan Widyarto, Siti Rafidah Binti Kassim 2,2 Department of Computing, Faculty of Communication, Visual Art and Computing,
2D-Sigmoid Enhancement Prior to Segment MRI Glioma Tumour Pre Image-Processing Setyawan Widyarto, Siti Rafidah Binti Kassim 2,2 Department of Computing, Faculty of Communication, Visual Art and Computing,
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods
 Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Fat Suppression in the Abdomen
 Clinical How I do it? Fat Suppression in the Abdomen Wilhelm Horger Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany Introduction Due to the different chemical environment, hydrogen nuclei in - and in -tissue
Clinical How I do it? Fat Suppression in the Abdomen Wilhelm Horger Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany Introduction Due to the different chemical environment, hydrogen nuclei in - and in -tissue
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note
 High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
A new Method on Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection
 2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 1 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology A new Method on Brain MRI Preprocessing for Tumor Detection ABSTRACT D. Arun Kumar
2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 1 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology A new Method on Brain MRI Preprocessing for Tumor Detection ABSTRACT D. Arun Kumar
6/23/2009. Inversion Recovery (IR) Techniques and Applications. Variations of IR Technique. STIR, FLAIR, TI and TI Null. Applications of IR
 The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Mesial Temporal Sclerosis (MTS): What radiologists ought to know?
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Mesial Temporal Sclerosis (MTS): What radiologists ought to know? Poster No.: C-0856 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Singh, G. Mittal, R. Kaur, K.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Mesial Temporal Sclerosis (MTS): What radiologists ought to know? Poster No.: C-0856 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Singh, G. Mittal, R. Kaur, K.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Imaging in Epilepsy. Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015
 Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/26921 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Doan, Nhat Trung Title: Quantitative analysis of human brain MR images at ultrahigh
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/26921 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Doan, Nhat Trung Title: Quantitative analysis of human brain MR images at ultrahigh
International Journal of Research (IJR) Vol-1, Issue-6, July 2014 ISSN
 Developing an Approach to Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection Mr. B.Venkateswara Reddy 1, Dr. P. Bhaskara Reddy 2, Dr P. Satish Kumar 3, Dr. S. Siva Reddy 4 1. Associate Professor, ECE Dept,
Developing an Approach to Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection Mr. B.Venkateswara Reddy 1, Dr. P. Bhaskara Reddy 2, Dr P. Satish Kumar 3, Dr. S. Siva Reddy 4 1. Associate Professor, ECE Dept,
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
mri sequences 8267BD21D03EEA3AE7926DD1904E7425 Mri Sequences 1 / 6
 Mri Sequences 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Mri Sequences An MRI sequence is a number of radiofrequency pulses and gradients that result in a set of images with a particular appearance. This article presents a simplified
Mri Sequences 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Mri Sequences An MRI sequence is a number of radiofrequency pulses and gradients that result in a set of images with a particular appearance. This article presents a simplified
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol
 MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
MR Imaging with the CCSVI or Haacke protocol Reports from the Haacke protocol are often made available to the patients. The report consists of four major components: 1. anatomical images of major neck
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging
 Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
Magnetic susceptibility artefact on MRI mimicking lymphadenopathy: description of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient
 Case Report on Focused Issue on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Magnetic susceptibility artefact on MRI mimicking lymphadenopathy: description of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient Feng Zhao
Case Report on Focused Issue on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Magnetic susceptibility artefact on MRI mimicking lymphadenopathy: description of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma patient Feng Zhao
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy - a diagnostic performance of standardized MRI protocol in detection of epileptogenic lesion
 Pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy - a diagnostic performance of standardized MRI protocol in detection of epileptogenic lesion Poster No.: C-2226 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy - a diagnostic performance of standardized MRI protocol in detection of epileptogenic lesion Poster No.: C-2226 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Practical CT and MRI Anthony J. Fischetti, DVM, MS, DACVR Department Head of Diagnostic Imaging The Animal Medical Center, New York OBJECTIVE:
 Practical CT and MRI Anthony J. Fischetti, DVM, MS, DACVR Department Head of Diagnostic Imaging The Animal Medical Center, New York OBJECTIVE: This lecture describes the most common indications for referred
Practical CT and MRI Anthony J. Fischetti, DVM, MS, DACVR Department Head of Diagnostic Imaging The Animal Medical Center, New York OBJECTIVE: This lecture describes the most common indications for referred
Refractory focal epilepsy: findings by MRI.
 Refractory focal epilepsy: findings by MRI. Doctors Nicolás Sgarbi, Osmar Telis Clinical Radiology Department Hospital de Clínicas Montevideo- Uruguay ABSTRACT Epilepsy is one of the most frequent neurological
Refractory focal epilepsy: findings by MRI. Doctors Nicolás Sgarbi, Osmar Telis Clinical Radiology Department Hospital de Clínicas Montevideo- Uruguay ABSTRACT Epilepsy is one of the most frequent neurological
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class III
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class III Black Blood Imaging & IR Blue= O2 poor blood Red=O2 rich blood Inversion pulses can produce black blood imaging in GRE pulse sequences. Specially on the
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class III Black Blood Imaging & IR Blue= O2 poor blood Red=O2 rich blood Inversion pulses can produce black blood imaging in GRE pulse sequences. Specially on the
Assessment of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-FLAIR Mismatch: Comparison between Conventional FLAIR versus Shorter-Repetition-Time FLAIR at 3T
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:88-94 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.88 Assessment of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-FLAIR Mismatch: Comparison between Conventional FLAIR versus Shorter-Repetition-Time
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:88-94 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.2.88 Assessment of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-FLAIR Mismatch: Comparison between Conventional FLAIR versus Shorter-Repetition-Time
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist
 mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques. Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology
 Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2014 Rationale for the Course
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2014 Rationale for the Course
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Comparison of T1-weighted fast spin-echo and T1-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images of the lumbar spine at 3.
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Comparison of T1-weighted fast spin-echo and T1-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Comparison of T1-weighted fast spin-echo and T1-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity. Overview
 Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2
 Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
Synthesized Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Synthesized Magnetic Resonance Imaging and SyMRI Theory and Application A White Paper Marcel Warntjes, PhD. Table of contents SyMRI technical overview Synthesized MR image acquisition and reconstruction
Synthesized Magnetic Resonance Imaging and SyMRI Theory and Application A White Paper Marcel Warntjes, PhD. Table of contents SyMRI technical overview Synthesized MR image acquisition and reconstruction
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011
 Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011 Samuel Wiebe, MD University of Calgary Canada American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure University of Calgary Hopewell Professorship of Clinical
Imaging for Epilepsy Diagnosis December 2, 2011 Samuel Wiebe, MD University of Calgary Canada American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure University of Calgary Hopewell Professorship of Clinical
POC Brain Tumor Segmentation. vlife Use Case
 Brain Tumor Segmentation vlife Use Case 1 Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation using CNN Background Brain tumor segmentation seeks to separate healthy tissue from tumorous regions such as the advancing tumor,
Brain Tumor Segmentation vlife Use Case 1 Automatic Brain Tumor Segmentation using CNN Background Brain tumor segmentation seeks to separate healthy tissue from tumorous regions such as the advancing tumor,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results
 Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/19768 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Langevelde, Kirsten van Title: Are pulmonary embolism and deep-vein thrombosis
Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to
 125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
125 A B C Fig. 1. Localized single voxel proton MR spectroscopy was performed along the long axis of right hippocampus after extension of patient s head to obtain entire dimension of the hippocampal body.
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy
 Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy Poster No.: C-2190 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Puiu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Neuroradiology brain,
Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy Poster No.: C-2190 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Puiu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Neuroradiology brain,
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol. for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS. David K.B.
 Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Advantages of the Spin Echo-type Radial Scan of the Cranial Region
 Advantages of the Spin Echo-type Radial Scan of the Cranial Region Poster No.: C-0969 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Gomi 1, M. Hasegawa 2, N. Murata 2, A. Tabata 2, M. Tsunoo
Advantages of the Spin Echo-type Radial Scan of the Cranial Region Poster No.: C-0969 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Gomi 1, M. Hasegawa 2, N. Murata 2, A. Tabata 2, M. Tsunoo
Neuro-Imaging in dementia: using MRI in routine work-up Prof. Philip Scheltens
 Neuro-Imaging in dementia: Philip Scheltens Alzheimer Center VU University Medical Center Amsterdam The Netherlands 1 Outline of talk Current guidelines Imaging used to exclude disease Specific patterns
Neuro-Imaging in dementia: Philip Scheltens Alzheimer Center VU University Medical Center Amsterdam The Netherlands 1 Outline of talk Current guidelines Imaging used to exclude disease Specific patterns
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Study of Mastoid Air Cells Diseases using Spiral CT
 Global Journal of Medical research Diseases Volume 13 Issue 3 Version 1. Year 13 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
Global Journal of Medical research Diseases Volume 13 Issue 3 Version 1. Year 13 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist. Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation
 Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
The Asymmetric Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR
 The Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR Alexander C. Mamourian, Lawrence Rodichok, and Javad Towfighi PURPOSE: To determine whether mamillary body atrophy
The Mamillary Body: Association with Medial Temporal Lobe Disease Demonstrated with MR Alexander C. Mamourian, Lawrence Rodichok, and Javad Towfighi PURPOSE: To determine whether mamillary body atrophy
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans
 Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Initial Clinical Experience of TOSHIBA 3T MRI
 The 21st Conference of the Japanese Society of Cardiovascular Imaging & Dynamics Sponsored Seminar The Leading Edge of CT/MRI Diagnosis for the Cardiovascular System Initial Clinical Experience of TOSHIBA
The 21st Conference of the Japanese Society of Cardiovascular Imaging & Dynamics Sponsored Seminar The Leading Edge of CT/MRI Diagnosis for the Cardiovascular System Initial Clinical Experience of TOSHIBA
MR Angiography in the evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
 March 2001 MR Angiography in the evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Ted Mau, Harvard Medical School Year III Objectives We will cover: Indications for Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Basic
March 2001 MR Angiography in the evaluation of Lower Extremity Arterial Disease Ted Mau, Harvard Medical School Year III Objectives We will cover: Indications for Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Basic
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Redlich R, Opel N, Grotegerd D, et al. Prediction of individual response to electroconvulsive therapy via machine learning on structural magnetic resonance imaging data. JAMA
Supplementary Online Content Redlich R, Opel N, Grotegerd D, et al. Prediction of individual response to electroconvulsive therapy via machine learning on structural magnetic resonance imaging data. JAMA
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Phase-Sensitive T1 Inversion Recovery Imaging: A Time-Efficient Interleaved Technique for Improved Tissue Contrast in Neuroimaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1432 1438, June/July 2005 Phase-Sensitive T1 Inversion Recovery Imaging: A Time-Efficient Interleaved Technique for Improved Tissue Contrast in Neuroimaging Ping Hou, Khader M.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1432 1438, June/July 2005 Phase-Sensitive T1 Inversion Recovery Imaging: A Time-Efficient Interleaved Technique for Improved Tissue Contrast in Neuroimaging Ping Hou, Khader M.
Spinal injury is very common in Ireland: 19 per 100,000 (1). It poses a significant disease burden.
 MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
Principles of Ultrasound. Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012
 Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
Table 1. Summary of PET and fmri Methods. What is imaged PET fmri BOLD (T2*) Regional brain activation. Blood flow ( 15 O) Arterial spin tagging (AST)
 Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
*smith&nephew. MRI Safety Information & Parameters for Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics AG. Knee Implants
 Knee Implants MRI Safety Information & Parameters for Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics AG Knee Implants *smith&nephew Supporting healthcare professionals for over 150 years Summary All knee implants of Smith
Knee Implants MRI Safety Information & Parameters for Smith & Nephew Orthopaedics AG Knee Implants *smith&nephew Supporting healthcare professionals for over 150 years Summary All knee implants of Smith
Personal use only. MRI Metal Artifact Reduction: Shoulder Implants and Arthroplasty. Reto Sutter, MD
 MRI Metal Artifact Reduction: Shoulder Implants and Arthroplasty Reto Sutter, MD University Hospital Balgrist Zurich University of Zurich Cor PD fat sat 56-year old male patient with positive lift-off
MRI Metal Artifact Reduction: Shoulder Implants and Arthroplasty Reto Sutter, MD University Hospital Balgrist Zurich University of Zurich Cor PD fat sat 56-year old male patient with positive lift-off
Intraventricular CSF Pulsation Artifact on Fast Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR Images: Analysis of 100 Consecutive Normal Studies
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:503 508, March 2000 Intraventricular CSF Pulsation Artifact on Fast Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR Images: Analysis of 100 Consecutive Normal Studies Rohit Bakshi, Shelton
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:503 508, March 2000 Intraventricular CSF Pulsation Artifact on Fast Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR Images: Analysis of 100 Consecutive Normal Studies Rohit Bakshi, Shelton
Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype
 MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
Advances in Clinical Neuroimaging
 Advances in Clinical Neuroimaging Joseph I. Tracy 1, PhD, ABPP/CN; Gaelle Doucet 2, PhD; Xaiosong He 2, PhD; Dorian Pustina 2, PhD; Karol Osipowicz 2, PhD 1 Department of Radiology, Thomas Jefferson University,
Advances in Clinical Neuroimaging Joseph I. Tracy 1, PhD, ABPP/CN; Gaelle Doucet 2, PhD; Xaiosong He 2, PhD; Dorian Pustina 2, PhD; Karol Osipowicz 2, PhD 1 Department of Radiology, Thomas Jefferson University,
Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy
 IJCMR 836 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy Vivek E 1, Abubacker Sulaiman F 2, Srinivasa Mudali K 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Low-back pain (LBP)
IJCMR 836 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy Vivek E 1, Abubacker Sulaiman F 2, Srinivasa Mudali K 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Low-back pain (LBP)
Neurovascular elements of the PCF
 Level I: Neurovascular elements of the PCF Trigeminal and Abducent Superior cerebellar artery and vein Dandy s vein Level II: Facial and Cochleovestibular AICA and internal auditory artery, veins Level
Level I: Neurovascular elements of the PCF Trigeminal and Abducent Superior cerebellar artery and vein Dandy s vein Level II: Facial and Cochleovestibular AICA and internal auditory artery, veins Level
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Susceptibility-weighted MRI ups contrast, offers minute detail 9/15/04 By: Shalmali Pal
 Susceptibility-weighted MRI ups contrast, offers minute detail 9/15/04 By: Shalmali Pal With its flashy sequences and high-speed protocols, there's no shortage of razzle-dazzle in MRI. But learning to
Susceptibility-weighted MRI ups contrast, offers minute detail 9/15/04 By: Shalmali Pal With its flashy sequences and high-speed protocols, there's no shortage of razzle-dazzle in MRI. But learning to
Computed Tomography of Normal Adrenal Glands in Indian Population
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. V January. (2018), PP 26-30 www.iosrjournals.org Computed Tomography of Normal Adrenal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. V January. (2018), PP 26-30 www.iosrjournals.org Computed Tomography of Normal Adrenal
Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES
 DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
A Method of Connectivity Analysis of Epileptiform Discharges during Epileptic Seizure
 International Journal of Bioelectromagnetism Vol. 19, No.1, pp. 6-10, 2017 www.ijbem.org A Method of Connectivity Analysis of Epileptiform Discharges during Epileptic Seizure Hisashi Yoshida a, Yasuto
International Journal of Bioelectromagnetism Vol. 19, No.1, pp. 6-10, 2017 www.ijbem.org A Method of Connectivity Analysis of Epileptiform Discharges during Epileptic Seizure Hisashi Yoshida a, Yasuto
P2 Visual - Perception
 P2 Visual - Perception 2014 SOSE Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions gyula.kovacs@uni-jena.de 11/09/06 Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) The very basics What is fmri? What is MRI? The
P2 Visual - Perception 2014 SOSE Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions gyula.kovacs@uni-jena.de 11/09/06 Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) The very basics What is fmri? What is MRI? The
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
 Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo
 Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears ABSTRACT
 1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
