Embryology and Anatomy of the Facial Nerve: Correlates of Misdirected Reinnervation and Poor Recovery of Function after Lesions
|
|
|
- Heather Watts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Videos Foreword Eugene N. Myers Foreword Johannes J. Manni Preface Dedication and Acknowledgments Contributors xv xvii xviii xix xx xxi Part I: Embryology, Anatomy, Physiology, and Applied Basic Sciences Embryology and Anatomy of the Facial Nerve: Correlates of Misdirected Reinnervation and Poor Recovery of Function after Lesions 2 Doychin N. Angelov 1.1 Introduction. 1.2 Neural Plate, Neural Crest, Ectodermal Placodes Neural Folds, Neural Tube, Rhombomeres, Roof and Floor Plates First Differentiation into Motor and Sensory Cells Development of Facial Nerve Branches 6 Development of Intratemporal Communications 7 Development of Extratemporal Communications Relationships to Developing Facial Muscles Primordial Tissues of the Facial Nerve Occur at the End of the 3rd Week The Second Pharyngeal Arch Development of the Intraparenchymal Portion of the Facial Nerve Development of the Extramedullar Portion of the Facial Nerve Development of the Pars Intratemporalis Axonal Growth and Guidance 8 Postnatal Development 8 Intracranial Portion of the Facial Nerve 9 Surgical Anatomy of the Facial Nerve Trunk and its Branches Key Points 12 Physiology of the Facial Motor System 14 Andrey Irintchev 2.1 Introduction Muscles Motoneurons and Glial Cells 15 Proprioception 17 Reflex Responses and Automatic Motor Behaviors 18
2 2.6 Central Pattern Generators Voluntary Motor Control Emotional Motor Control Key Points Applied Bask Science: Improvement c Andrey Irintchev and Doychin N. Angelov 3.1 Introduction Clinical Relevance of Animal Models Factors Limiting Recovery Therapeutic Approaches Targeting Axonal Misdirection Electrical Stimulation to Counteract Denervation Atrophy and Accelerate Reinnervation 27 yierve Regeneration Manual Stimulation Reduces Polyinnervation of Muscle Fibers Growth Factors to Promote Axonal Growth Mimetic Peptides Improve Diameters and Myelination of Regenerated Axons Cell-Based Approaches for Axonal Growth Enhancement across a Nerve Prosthesis Key Points 28 Part II: Diagnostics 4. Clinical Examination 32 Cerd Fabian VoIk, Orlando Cuntinas-Lichius, and Barry M. Schaitkin 4.1 Introduction Patient History Time Course Recurrence Recurrent Alternating Palsy Bilateral Simultaneous Palsy Conditions Associated with Facial Nerve Palsy Family History and Congenital Facial Palsy Pregnancy Systemic Illnesses Drugs Immunizations Malignancies Idiopathic (Bell's) Palsy Clinical Examination Facial Muscle Weakness and Facial Palsy Gross Neurological Examination Cranial Nerve Survey Corneal Sensation Keratitis Palate Symmetry Tongue Deviation Loss of Taste and Taste Papillae Signs of Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome Pain or Numbness Vesicles Ear Dizziness Topodiagnostics Stapedial Reflex (Acoustic Reflex) Other Hearing Tests and Balance Tests Schirmer's Test Taste Test Extended Diagnostics Imaging Electrodiagnostics Psychological Exploration Follow-up Key Points Imaging 57 Cerd Fabian Volk, Hartmut Peter Burmeister, and Orlando Cuntinas-Lichius 5.1 Introduction Indications for Imaging Studies 57 vi
3 5.3 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Computed Tomography Ultrasonography 64 Key Points Electrophysiology Hans-Christoph Scholle, Nikolaus-Peter Schumann, and Gerd Fabian Volk Introduction Definition Physiology behind Electrophysiologic Diagnostics Pathology and its Electrophysiologic Correlates Supranuclear Lesions Infranuclear Lesions Synaptic Lesions Muscular Lesions Electrophysiologic Diagnostic Work-Up Needle Electromyography Electroneurography Blink Reflex Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and Magnetic Evoked Potentials Surface Electromyography Key Points Grading Orlando Cuntinas-Lichius and Mira Finkensieper 7.1 Introduction Definition Subjective Grading House-Brackmann Facial Grading System Yanagihara's Facial Grading Scale Stennert's Index May Facial Nerve Grading Scale Sunnybrook (Toronto) Facial Grading System Facial Nerve Grading System Objective Grading Systems Burres-Fisch Linear Measurement Index and the Nottingham System Neely's Facial Analysis Computerized Evaluation system Facial Landmark-Based Computer Systems and Programs Three-Dimensional Video Analysis and Surface Analysis Glasgow Facial Palsy Scale Facial Assessment by Computer Evaluation Facial Action Coding System Assessment of Nonmimic Motor Function and Nonmotor Facial Nerve Functions 105 Assessment of the Communicative and Emotional Function 105 Facial Disability Index 106 Facial Clinimetric Evaluation Scale Instrument 106 Assessment of Psychological Distress, Anxiety, and Depression Key Points 107 Part III: Management of Acute Peripheral Facial Palsy 8. Bell's Palsy 112 Eric Smouha and Elizabeth Toh Clinical Features Diagnostic Work-Up Treatment 118
4 8.6.1 Eye Care Outcomes and Prognosis Medical Treatment of Bell's Palsy Surgical Decompression 120 Key Points Medical Treatment of Bell's Palsy Facial Nerve Trauma 124 Peter L. Santa Maria, Mira Finkensieper, Orlando Guntinas-Lichius, and Robert K. Jackler 9.1 Introduction Definition Epidemiology and Etiology Clinical Features Intracranial Trauma lntratemporal Trauma Extratemporal Trauma Diagnostic Work-Up Examination Electrophysiology Imaging Facial Nerve and Facial Muscle Biopsies Treatment Nonsurgical Treatment Surgical Treatment Outcome and Prognosis Key Points Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Claus Wittekindt 10.1 Introduction Definition Epidemiology and Etiology Clinical Features Diagnostic Work-Up Virology Testing Imaging Studies Electrodiagnostic Tests of Facial Nerve Lumbar Puncture Treatment Medical Treatment Treatment for Disequilibrium Treatment for Facial Paralysis Treatment for Pain Treatment for Postherpetic Neuralgia Topical Antiviral Cream Treatment for the Eye Surgical Treatment Outcome and Prognosis Complications Prevention Key Points Lyme Disease Howard S. Moskowitz and Barry M. Schaitkin 11.1 Introduction Definition Epidemiology and Etiology Clinical Features Diagnostic Work-Up Outcomes and Prognosis Lyme Facial Palsy versus Bell's Palsy Studies on Lyme Facial Palsy Studies on Lyme Facial Palsy Focusing on Children Overview of Lyme Facial Palsy Studies Key Points Treatment 159 viii
5 12. Pediatric Facial Nerve Palsies Kristen M. Davidge, J. Michael Hendry, Ronald Zuker, and Gregory H. Borschel Introduction 167 Definition 167 Epidemiology Etiology Mobius Syndrome Hemifacial Microsomia and Goldenhar's Syndrome Hereditary Congenital Facial Nerve Paralysis History Physical Examination Investigations Treatment Addressing the Lower Face Neonatal Asymmetric Crying Fades Acquired Facial Paralysis in the Pediatric Population Key Points Diagnostic Work-Up 171 Part IV: Importance of the Facial Nerve for Communication and Emotion 13. Psychological Exploration of Emotional, Communicative, and Social Impairments in Patients with Facial Impairments 184 Christian Dobel and Orlando Guntinas-Lichius 13.1 Introduction Psychological Changes After Facial 13.2 Emotions as a Core of Human Palsy 187 Interactions Key Points Understanding Own and Others' Emotions Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Emotional and Social Impairments in Patients with Facial Paresis 192 Christian Dobel and Orlando Guntinas-Lichius 14.1 Introduction Guidance for Clinicians Diagnosis of Emotional and Social Symptoms Assessment of General Anxiety, Social Assessment of Quality of Life and Social 14.3 Assessment of Emotional Functions Therapeutic Approaches to Address 192 Emotional and Social Changes Key Points Part V: Surgery around the Facial Nerve 15. Intraoperative Facial Nerve Monitoring 200 Brent ]. Benscoter and Jack M. Kartush 15.1 Introduction History. 200 ix
6 15.3 Clinical Application Physiology Training Technical Setup Troubleshooting/Pitfalls Further Study Key Points Tumors Affecting the Facial Nerve John P. Leonetti, Sam J. Marzo, and Matthew L Kircher 16.1 Introduction Surgical Anatomy Clinical Features Presenting Symptoms Presenting Signs Diagnostic Work-Up Surgical Approaches Facial Nerve Management Primary Neurorrhaphy Interposition Graft Hypoglossal-Facial Anastomosis Microvascular Free Flap Cross-Facial Graft Facial Schwannoma Adjuvant Procedures Key Points The Facial Nerve in Otologic Infection and Iatrogenic Injury Jacob S. McAfee and Barry E. Hirsch introduction Structural Considerations Acute Otitis Media Pathophysiology Electrophysiologic Diagnostics Treatment Prognosis Chronic Otitis Media Pathophysiology Treatment Necrotizing Otitis Externa Pathophysiology Diagnostic Work-Up Treatment Perioperative Management of Acute Facial Palsy during Middle Ear and Mastoid Surgery Immediate, Complete Paralysis Delayed-Onset, Incomplete Palsy Key Points Facial Nerve and Vestibular Schwannoma John C. Coddard, Courtney C. J. Voelker, and Derald E. Brackmann Introduction General Considerations in Vestibular Schwannoma Surgery Indications and Patient Selection Patient Information and Consent: Surgical Patient Information and Consent: Stereotactic Radiation Stereotactic Radiation Patient Selection Treatment Steps Microsurgery Retrosigmoid Approach Middle Fossa Approach Translabryinthine Approach Postoperative Considerations Complications Measures for Specific Complications Key Points 248 x
7 19. The Facial Nerve and Parotid Surgery Orlando Guntinas-Lichius and Mira Finkensieper 19.1 Introduction Definition Epidemiology and Etiology Risk Factors for Postoperative Facial Palsy After Parotid Surgery Preoperative Assessment and Measures to Avoid Postoperative Facial Palsy Intraoperative Measures to Prevent a Facial Nerve Lesion Identification of the Extratemporai Portion of the Facial Nerve and its End Branches Management of the Facial Nerve Depending on the Type of Surgery Management of Intraoperative Facial Nerve Lesions Management of Postoperative Facial Palsy A Facial Nerve Lesion Occurs During Parotid Surgery and is Recognized The Patient Wakes Up After Parotid Surgery and has a Complete Facial Palsy on the Side of Surgery The Patient Wakes Up After Parotid Surgery and has an Incomplete Facial Palsy The Patient Develops a Delayed Facial Palsy Key Points 260 Part VI: Rehabilitation Techniques for Chronic Facial Palsy 20. Facial Nerve Reconstruction Orlando Guntinas-Lichius and Mira Finkensieper Introduction Definition Direct Facial-Facial Nerve Reconstruction Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes Facial-Facial Nerve Interposition Craft Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes 271 Hypoglossal-Facial Nerve Suture and Hypoglossal-Facial Jump Nerve Suture Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes Cross-Face Facial Nerve Suture Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes Other Cross-Nerve Sutures Combined Approach Key Points 280 xi
8 21. Muscle Flaps and Static Procedures... Markus Jungehulsing and Orlando Cuntinas-Lichius 21.1 Introduction Definition Temporalis Muscle Transfer Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes Masseter Muscle Transfer Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes Digastric Muscle Transfer Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes Sling Techniques Indications Patient Information, Consent Anesthesia and Positioning Surgical Steps Complications Postoperative Care Outcomes Combining Procedures Key Points Free Flaps Caroline A. Banks and Tessa A. Hadlock 22.1 Introduction Two-Stage Procedures One-Stage Procedures Indications Gracilis Free Muscle Transfer in Special Populations Patient Information and Consent Anesthesia and Positioning First-Stage Cross-Face Preparation of the Face and Neck for Free Flap Gracilis Harvest Gracilis Preparation and Inset Complications Postoperative Care Key Points Surgical Steps Functional Outcomes of Facial Nerve Repair following Face Transplantation 306 Maria Z. Siemionow and Bahar Bassiri Gharb 23.1 Introduction Current Clinical Experience with c. A U * c IM Facial Nerve R ep air in Face 23.2 Surgical Approach to Facial Nerve Transplantation 311 Repair in Face Transplantation 307 _, Functional Outcomes of Facial Nerve 23.3 Rehabilitation Following Facial Nerve Repair In Face Transplantation 311 Repair in Face Transplantation Key Points 311
9 24. Surgery of the Periorbital Region Kris S. Moe and Farhad Ardeshirpour 24.1 Introduction Forehead and Brow Browlift Eyelids Upper Lid Correction of Lower Lid Malposition Midface Lift Adjuvant Measures Botulinum Toxin Fillers and Fat Key Points Adjuvant Treatment with Botulinum Toxin and Fillers Claus Wittekindt Introduction Mechanism of Action and Recovery of Hyperlacrimation 333 Gustatory Sweating (Frey's Syndrome). 334 Facial Asymmetry 335 Fillers 337 Types of Fillers 337 Complications 338 Choosing the Right Filler 338 Injection Technique 338 Key Points Feedback Training and Other Training Programs Wolfgang H. R. Miltner, Thomas Weiss, and Eva Maria Miltner Introduction Neuromuscular Biofeedback Training 342 Technique 342 Efficacy Rehabilitation of Facial Paralysis following Different Treatment Concepts of Physical Therapy without Concurrent Biofeedback Methods Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation Mime Therapy Mixed Home Training Neuromuscular Re-Education Versus Conventional Therapeutic Measures General Status of Current Rehabilitation Outcome Methodological Problems Assessment of Motor Dysfunction Evaluation of Stability of Treatment Effects Beyond the Termination of Rehabilitation Sequencing of Treatment Components, Manualization Intensity of Daily Training and Total Duration of Training Key Points 354 xiii
10 Part VII: Diseases Other Than Peripheral Facial Palsy 27. Central Facial Palsy Carsten M. Klingner and Otto W. Witte 27.1 Introduction Definition Epidemiology and Etiology Causes of a Central Facial Palsy Anatomy of the Central Facial Pathway Voluntary Facial Movements Emotional Facial Movements The Facial Nucleus Clinical Features Diagnostic Work-Up Medical Interview Imaging Electrophysiology Treatment Key Points Facial Dystonia and Facial Spasms Claus Wittekindt 28.1 Introduction Definition Dystonia Classification Blepharospasm Epidemiology and Etiology Clinical Features Diagnostic Work-Up Treatment Outcome and Prognosis Meige's Syndrome Otomandibular Dystonia Hemifacial Spasm Epidemiology and Etiology Clinical Features Diagnostic Work-Up Treatment Outcome and Prognosis Key Points Other Dystonias Affecting the Face. 373 Part VIII: Miscellaneous 29. Medicolegal Aspects of Iatrogenic Facial Nerve Palsy Eric L Slattery and Jack M. Kartush Introduction Epidemiology of iatrogenic Facial Nerve Injury Oral Surgery Head and Neck Surgery Otologic Surgery Neurotologic Surgery Plastic Surgery Avoiding Error in Surgery near the Facial Nerve Intraoperative Monitoring Management of Facial Nerve injury Initial Assessment Surgical Exploration and Repair Key Points Malpractice Claims, Litigation, and Facial Nerve Injury 382 Index 393
ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY. Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan
 ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan FACIAL PARALYSIS - ETIOLOGY Bells Palsy Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Infection (Acute/Chronic)
ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT OF FACIAL PALSY Michael J. LaRouere, M.D. Michigan Ear Institute Farmington Hills, Michigan FACIAL PARALYSIS - ETIOLOGY Bells Palsy Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Infection (Acute/Chronic)
REHABILITATION AND REANIMATION. Facial Plastic Surgery. University of Missouri Columbia, Missouri
 FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS: REHABILITATION AND REANIMATION Matthew A. Kienstra, MD, FACS Facial Plastic Surgery Mercy Health Care Springfield, Missouri University of Missouri Columbia, Missouri Incidence and
FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS: REHABILITATION AND REANIMATION Matthew A. Kienstra, MD, FACS Facial Plastic Surgery Mercy Health Care Springfield, Missouri University of Missouri Columbia, Missouri Incidence and
4/30/2009 FN PARALYSIS HEMIFACIAL SPASM
 FN PARALYSIS HEMIFACIAL SPASM 1 Hemifacial spasm (Involuntary twitches) Etiology: Vascular loop compressing the FN at the root exit zone in the CPA = Neuro-vascular conflict Diagnosis: CT & MRI, Electrophysiology
FN PARALYSIS HEMIFACIAL SPASM 1 Hemifacial spasm (Involuntary twitches) Etiology: Vascular loop compressing the FN at the root exit zone in the CPA = Neuro-vascular conflict Diagnosis: CT & MRI, Electrophysiology
Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face
 Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Karen H. Calhoun, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30,
Rehabilitation of the Paralyzed Face Elizabeth J. Rosen, MD Faculty Advisor: Karen H. Calhoun, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 30,
Grading Facial Nerve Function Following Combined Static and Mimetic Surgical Techniques
 416 Original Article Grading Facial Nerve Function Following Combined Static and Mimetic Surgical Techniques John P. Leonetti 1 Sam J. Marzo 1 Douglas A. Anderson 2 Joshua M. Sappington 1 1 Department
416 Original Article Grading Facial Nerve Function Following Combined Static and Mimetic Surgical Techniques John P. Leonetti 1 Sam J. Marzo 1 Douglas A. Anderson 2 Joshua M. Sappington 1 1 Department
Preface... Contributors... 1 Embryology... 3
 Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS
 CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS Introduction Facial nerve paralysis, whilst not a disease of the ear itself, commonly arises within the ear due to its anatomical course, and often as a result of ear
CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS Introduction Facial nerve paralysis, whilst not a disease of the ear itself, commonly arises within the ear due to its anatomical course, and often as a result of ear
BMJ Open. Prognostication of recovery time after acute peripheral facial palsy
 Prognostication of recovery time after acute peripheral facial palsy Journal: Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-000 Article Type: Research Date Submitted by the Author: 0-Apr-0 Complete List of Authors: Volk, Gerd;
Prognostication of recovery time after acute peripheral facial palsy Journal: Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-000 Article Type: Research Date Submitted by the Author: 0-Apr-0 Complete List of Authors: Volk, Gerd;
CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS. Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD
 CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD The facial nerve innervates a total of 23 paired muscles and the orbicularis oris muscle. The majority of muscles innervated by the
CHAPTER 11 FACIAL PARALYSIS Shailesh Agarwal, MD and Arash Momeni, MD The facial nerve innervates a total of 23 paired muscles and the orbicularis oris muscle. The majority of muscles innervated by the
OTOLOGY. 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training.
 OTOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training. Longwood Rotation PGY-2 through PGY-5 years o Clinic experience
OTOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF OTOLOGIC TRAINING Rotations that include otologic training are a component of each of the four years of training. Longwood Rotation PGY-2 through PGY-5 years o Clinic experience
Facial Paralysis Facial Nerve Subcommittee of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery
 Facial Paralysis Facial Nerve Subcommittee of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery Editor: Peter S Roland MD Contributors: Peter S Roland MD, Larry Lundy MD, Jacques Herzog MD, Fred
Facial Paralysis Facial Nerve Subcommittee of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery Editor: Peter S Roland MD Contributors: Peter S Roland MD, Larry Lundy MD, Jacques Herzog MD, Fred
Via Transmastoid Approach. Mitul Chaitan Bhatt. Maharashtra University Miraj India
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 6 Issue 1 2016 Evaluation Of Patients Of Traumatic Facial Palsy Treated By Facial Nerve Decompression Via Transmastoid Approach Mitul Chaitan Bhatt Maharashtra University Miraj India
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 6 Issue 1 2016 Evaluation Of Patients Of Traumatic Facial Palsy Treated By Facial Nerve Decompression Via Transmastoid Approach Mitul Chaitan Bhatt Maharashtra University Miraj India
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Facial Paralysis. A Comprehensive Rehabilitative Approach. Mark K. Wax, MD
 Facial Paralysis A Comprehensive Rehabilitative Approach Mark K. Wax, MD Contents Introduction Acknowledgments Contributors vii viii ix 1 Facial Nerve Anatomy and Mastoid Surgery in the Management 1 of
Facial Paralysis A Comprehensive Rehabilitative Approach Mark K. Wax, MD Contents Introduction Acknowledgments Contributors vii viii ix 1 Facial Nerve Anatomy and Mastoid Surgery in the Management 1 of
Nonmotor Disabilities in Patients With Facial Palsy Measured by Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
 The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Nonmotor Disabilities in Patients With Facial Palsy Measured by Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Gerd Fabian
The Laryngoscope VC 2015 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Nonmotor Disabilities in Patients With Facial Palsy Measured by Patient-Reported Outcome Measures Gerd Fabian
The Role of Botulinum Toxin A in the Establishment of Symmetry in Pediatric Paralysis of the Lower Lip
 Research Original Investigation The Role of Botulinum Toxin A in the Establishment of Symmetry in Pediatric Paralysis of the Lower Lip Siba Haykal, MD, PhD; Ehud Arad, MD; Shaghayegh Bagher, MSc; Carolyn
Research Original Investigation The Role of Botulinum Toxin A in the Establishment of Symmetry in Pediatric Paralysis of the Lower Lip Siba Haykal, MD, PhD; Ehud Arad, MD; Shaghayegh Bagher, MSc; Carolyn
Series Preface. Preface. Acknowledgments. Abbreviations
 Contents Series Preface Preface Acknowledgments Abbreviations vii ix xiii xxv Introduction xxxi Definition...xxxi Normal Hearing...xxxi Deafness...xxxi Overall Concept of the Bionic Ear...xxxii Training
Contents Series Preface Preface Acknowledgments Abbreviations vii ix xiii xxv Introduction xxxi Definition...xxxi Normal Hearing...xxxi Deafness...xxxi Overall Concept of the Bionic Ear...xxxii Training
Examination and Diseases of Cranial Nerves
 Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Bell's Palsy
 Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Bell's Palsy Number: 0745 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. I. Aetna considers blink reflex testing medically necessary for the diagnosis
Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Bell's Palsy Number: 0745 Policy *Pleasesee amendment forpennsylvaniamedicaidattheendofthiscpb. I. Aetna considers blink reflex testing medically necessary for the diagnosis
3D-Ultrasonography for evaluation of facial muscles in patients with chronic facial palsy or defective healing: a pilot study
 Volk et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2014, 14:4 TECHNICAL ADVANCE 3D-Ultrasonography for evaluation of facial muscles in patients with chronic facial palsy or defective healing: a pilot study
Volk et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2014, 14:4 TECHNICAL ADVANCE 3D-Ultrasonography for evaluation of facial muscles in patients with chronic facial palsy or defective healing: a pilot study
Medical Policy Manual
 Medical Policy Manual Policy Number: 0013 Effective Date: Reviewed Date: Next Review: August 2019 CLINICAL BACKGROUND INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROMONITORING BACKGROUND Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring
Medical Policy Manual Policy Number: 0013 Effective Date: Reviewed Date: Next Review: August 2019 CLINICAL BACKGROUND INTRAOPERATIVE NEUROMONITORING BACKGROUND Intraoperative neurophysiologic monitoring
Chorley and South Ribble Clinical Commissioning Group and Greater Preston Clinical Commissioning Group. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare
 Chorley and South Ribble Clinical Commissioning Group and Greater Preston Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for Rehabilitation after Damage to the Facial
Chorley and South Ribble Clinical Commissioning Group and Greater Preston Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for Rehabilitation after Damage to the Facial
Hemifacial spasm. Parkinson's Disease Center and Movement Disorders Clinic
 Parkinson's Disease Center and Movement Disorders Clinic 7200 Cambridge Street, 9th Floor, Suite 9A Houston, Texas 77030 713-798-2273 phone www.jankovic.org Hemifacial spasm Diagnosis Hemifacial spasm
Parkinson's Disease Center and Movement Disorders Clinic 7200 Cambridge Street, 9th Floor, Suite 9A Houston, Texas 77030 713-798-2273 phone www.jankovic.org Hemifacial spasm Diagnosis Hemifacial spasm
Lower motor cranial nerve dysfunction has an. Reconstructive
 Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Volumetry of Facial Muscles in Healthy Patients with Facial Palsy Gerd F. Volk, MD* Inna Karamyan, MD* Carsten M. Klingner, MD Jürgen R. Reichenbach, PhD Orlando
Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Volumetry of Facial Muscles in Healthy Patients with Facial Palsy Gerd F. Volk, MD* Inna Karamyan, MD* Carsten M. Klingner, MD Jürgen R. Reichenbach, PhD Orlando
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences DYNAMIC REANIMATION FOR FACIAL PARALYSIS A REVIEW ABSTRACT
 Review Article Allied Sciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 DYNAMIC REANIMATION FOR FACIAL PARALYSIS A REVIEW RATHISHREE 1 AND DR. M.P.SANTHOSH KUMAR *2 1 Intern, saveetha
Review Article Allied Sciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 DYNAMIC REANIMATION FOR FACIAL PARALYSIS A REVIEW RATHISHREE 1 AND DR. M.P.SANTHOSH KUMAR *2 1 Intern, saveetha
VI. Head and Neck and aesthetics.
 UEMS ENT SECTION SUBSPECIALTY LOG BOOK IN HEAD AND NECK SURGERY VI. Head and Neck and aesthetics. A. Diagnostic Procedures and multidisciplinary approach a) CLINICAL EXAMINATION 1 investigation of the
UEMS ENT SECTION SUBSPECIALTY LOG BOOK IN HEAD AND NECK SURGERY VI. Head and Neck and aesthetics. A. Diagnostic Procedures and multidisciplinary approach a) CLINICAL EXAMINATION 1 investigation of the
Features of Facial Asymmetry Following Incomplete Recovery from Facial Paralysis
 Original Article DOI.49/ymj..5.6.94 pissn: 5-5796, eissn: 976-47 Yonsei Med J 5(6):94-948, Features of Facial Asymmetry Following Incomplete Recovery from Facial Paralysis Jin Kim, Hyung Rok Lee, Jun Hui
Original Article DOI.49/ymj..5.6.94 pissn: 5-5796, eissn: 976-47 Yonsei Med J 5(6):94-948, Features of Facial Asymmetry Following Incomplete Recovery from Facial Paralysis Jin Kim, Hyung Rok Lee, Jun Hui
CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST
 CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST Hannah Shinoda, OD Caroline Ooley, OD, FAAO Assistant Professors Pacific University College of Optometry The authors have no financial interest in
CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST Hannah Shinoda, OD Caroline Ooley, OD, FAAO Assistant Professors Pacific University College of Optometry The authors have no financial interest in
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
Facial Paralysis: Objectives: Discuss the anatomy of the facial nerve. Look at common patterns of facial nerve palsy
 Facial Paralysis: Objectives: Discuss the anatomy of the facial nerve Look at common patterns of facial nerve palsy Discuss imaging appearance of lesions that lead to facial paralysis. Lindell R. Gentry,
Facial Paralysis: Objectives: Discuss the anatomy of the facial nerve Look at common patterns of facial nerve palsy Discuss imaging appearance of lesions that lead to facial paralysis. Lindell R. Gentry,
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
International Journal of Research and Review E-ISSN: ; P-ISSN:
 International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Effectiveness of Facial Nerve Stimulation with Kabat Technique in Bell s
International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Original Research Article Effectiveness of Facial Nerve Stimulation with Kabat Technique in Bell s
Facial nerve, more than any other cranial nerves, Intratemporal Facial Nerve Paralysis- A Three Year Study. Case Series
 Case Series Intratemporal Facial Nerve Paralysis- A Three Year Study Anirban Ghosh, 1 Sankar Prasad Bera, 2 Somnath Saha 3 ABSTRACT Introduction This study on intratemporal facial paralysis is an attempt
Case Series Intratemporal Facial Nerve Paralysis- A Three Year Study Anirban Ghosh, 1 Sankar Prasad Bera, 2 Somnath Saha 3 ABSTRACT Introduction This study on intratemporal facial paralysis is an attempt
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II. Nerves covered in other lectures. A reminder about embryology. Prof. Stuart Bunt
 Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Tanta University. Faculty of Medicine. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Department. Doctorate Degree in Plastic Surgery
 Componenets : Tanta University Faculty of Medicine Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Department Doctorate Degree in Plastic Surgery Students should fulfill the designated number of credit hours, including
Componenets : Tanta University Faculty of Medicine Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Department Doctorate Degree in Plastic Surgery Students should fulfill the designated number of credit hours, including
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
POST TRAUMATIC FACIAL PARALYSIS - A REVIEW
 POST TRAUMATIC FACIAL PARALYSIS - A REVIEW Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Naresh K. Panda, Y. N. Mehra, S.B.S. Mann, Satish K. Mehta ( Deptt. of Otolaryngology, Postgraduate Institute of
POST TRAUMATIC FACIAL PARALYSIS - A REVIEW Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Naresh K. Panda, Y. N. Mehra, S.B.S. Mann, Satish K. Mehta ( Deptt. of Otolaryngology, Postgraduate Institute of
A Study of Etiopathology and Management of Facial Palsy at a Tertiary Care Institute
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver.VII (July 2016), PP 71-75 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Etiopathology and Management
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver.VII (July 2016), PP 71-75 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of Etiopathology and Management
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Partial Lesions on Intratemporal Segment of the Facial Nerve. Total Graft or Partial Reconstruction?
 Original Article Partial Lesions on Intratemporal Segment of the Facial Nerve. Total Graft or Partial Reconstruction? Ricardo Ferreira Bento*, Raquel Salomone**, Rubens Brito Neto***, Robinson Koiji Tsuji****,
Original Article Partial Lesions on Intratemporal Segment of the Facial Nerve. Total Graft or Partial Reconstruction? Ricardo Ferreira Bento*, Raquel Salomone**, Rubens Brito Neto***, Robinson Koiji Tsuji****,
Laith Sorour. Facial nerve (vii):
 Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Table of Contents. Preface... xi. Part I: Introduction to Movement Disorders
 Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Table of Contents Visit www.healthreferenceseries.com to view A Contents Guide to the Health Reference Series, a listing of more than 14,000 topics and the volumes in which they are covered. Preface...
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives
 Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Case Report Bilateral Facial Paralysis Caused by Bilateral Temporal Bone Fracture: A Case Report and a Literature Review
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 306950, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/306950 Case Report Bilateral Facial Paralysis Caused by Bilateral Temporal Bone Fracture: A Case Report
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 306950, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/306950 Case Report Bilateral Facial Paralysis Caused by Bilateral Temporal Bone Fracture: A Case Report
The 12 Cranial Nerves. Edited by Sterling Precision Nelson
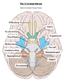 The 12 Cranial Nerves Edited by Sterling Precision Nelson Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory Nerve Type of Nerve: Sensory Function of Nerve: Sense of Smell Brief description: The Olfactory Nerve is the first of
The 12 Cranial Nerves Edited by Sterling Precision Nelson Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory Nerve Type of Nerve: Sensory Function of Nerve: Sense of Smell Brief description: The Olfactory Nerve is the first of
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF IDIOPATHIC FACIAL PALSY. All children under 16 presenting to UHW or CHfW with IFP. Dr P Jeffrey Morgan ST8
 GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF IDIOPATHIC FACIAL PALSY Reference: IFP Version No: 1 Applicable to All children under 16 presenting to UHW or CHfW with IFP Classification of document: Area for Circulation:
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF IDIOPATHIC FACIAL PALSY Reference: IFP Version No: 1 Applicable to All children under 16 presenting to UHW or CHfW with IFP Classification of document: Area for Circulation:
Michigan Ear Institute
 Michigan Ear Institute Facial Nerve Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-110 BOOK Facial Nerve Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:09 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
Michigan Ear Institute Facial Nerve Problems www.michiganear.com 15-56111-110 BOOK Facial Nerve Problems.indd 1 2/13/18 10:09 A DOCTORS Dennis I. Bojrab, MD Seilesh C. Babu, MD John J. Zappia, MD, FACS
A Clinical Analysis of Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Inflammatory Diseases of the Middle Ear and the Role of Early Decompression
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/311 A Clinical Analysis of Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Inflammatory Diseases of the Middle Ear and the Role of Early
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/311 A Clinical Analysis of Facial Nerve Paralysis due to Inflammatory Diseases of the Middle Ear and the Role of Early
7. Anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system. Harmonic and disharmonic vestibular syndrome.
 7. Anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system. Harmonic and disharmonic vestibular syndrome. 8. Fundamental examination tools of otoneurology. 20. Ménière s syndrome and Ménière s disease. Therapeutic
7. Anatomy and physiology of the vestibular system. Harmonic and disharmonic vestibular syndrome. 8. Fundamental examination tools of otoneurology. 20. Ménière s syndrome and Ménière s disease. Therapeutic
SELECTIVE NEURECTOMIES TO ACHIEVE SYMMETRY IN PARTIAL AND COMPLETE FACIAL PARALYSIS
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (I976), 29, 43-52 SELECTIVE NEURECTOMIES TO ACHIEVE SYMMETRY IN PARTIAL AND COMPLETE FACIAL PARALYSIS By L. CLODIVS, M.D. Plastic Surgery Section, Second Surgical Department,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (I976), 29, 43-52 SELECTIVE NEURECTOMIES TO ACHIEVE SYMMETRY IN PARTIAL AND COMPLETE FACIAL PARALYSIS By L. CLODIVS, M.D. Plastic Surgery Section, Second Surgical Department,
Schwannoma of the intermediate nerve
 J Neurosurg 109:144 148, 2008 Schwannoma of the intermediate nerve Case report CHRISTIAN SCHELLER, M.D., 1 JENS RACHINGER, M.D., 1 JULIAN PRELL, M.D., 1 MALTE KORNHUBER, M.D., 2 AND CHRISTIAN STRAUSS,
J Neurosurg 109:144 148, 2008 Schwannoma of the intermediate nerve Case report CHRISTIAN SCHELLER, M.D., 1 JENS RACHINGER, M.D., 1 JULIAN PRELL, M.D., 1 MALTE KORNHUBER, M.D., 2 AND CHRISTIAN STRAUSS,
Management of Facial Synkinesis with a Combination of BTX-A and Biofeedback: A Randomized Trial
 Original Article Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.27(6), Serial No.83, Nov 2015 Management of Facial Synkinesis with a Combination of BTX-A and Biofeedback: A Randomized Trial Abstract * Abbas
Original Article Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Vol.27(6), Serial No.83, Nov 2015 Management of Facial Synkinesis with a Combination of BTX-A and Biofeedback: A Randomized Trial Abstract * Abbas
CONTENTS. Foreword George H. Kraft. Henry L. Lew
 EVOKED POTENTIALS Foreword George H. Kraft xi Preface Henry L. Lew xiii Overview of Artifact Reduction and Removal in Evoked Potential and Event-Related Potential Recordings 1 Martin R. Ford, Stephen Sands,
EVOKED POTENTIALS Foreword George H. Kraft xi Preface Henry L. Lew xiii Overview of Artifact Reduction and Removal in Evoked Potential and Event-Related Potential Recordings 1 Martin R. Ford, Stephen Sands,
Evaluation and Management of Bell's Palsy January 2002
 TITLE: Evaluation and Management of Bell s Palsy SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: January 29, 2002 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Russell D. Briggs, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Byron
TITLE: Evaluation and Management of Bell s Palsy SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: January 29, 2002 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Russell D. Briggs, MD FACULTY PHYSICIAN: Byron
What cranial nerves can we monitor?
 What cranial nerves can we monitor? Laura Hemmer, M.D. SNACC Neuromonitoring Subcommittee Linda Aglio, M.D., M.S. Laura Hemmer, M.D. Antoun Koht, M.D. David L. Schreibman, M.D. What cranial nerve (CN)
What cranial nerves can we monitor? Laura Hemmer, M.D. SNACC Neuromonitoring Subcommittee Linda Aglio, M.D., M.S. Laura Hemmer, M.D. Antoun Koht, M.D. David L. Schreibman, M.D. What cranial nerve (CN)
Cranial Nerves. Study slides
 Cranial Nerves Study slides What is the name of cranial nerve V? ANSWER What is the name of cranial nerve V? Trigeminal nerve What number is the trigeminal nerve? ANSWER What number is the trigeminal nerve?
Cranial Nerves Study slides What is the name of cranial nerve V? ANSWER What is the name of cranial nerve V? Trigeminal nerve What number is the trigeminal nerve? ANSWER What number is the trigeminal nerve?
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII
 Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
TOTAL Head and Neck Congenital Defects 50
 Operative Minimums Effective July 1, 2014 Review Committee for Plastic Surgery NOTE: The index procedure number for Laser is tracked by Total Laser and not by the subcategories of Aesthetic Laser and Reconstructive
Operative Minimums Effective July 1, 2014 Review Committee for Plastic Surgery NOTE: The index procedure number for Laser is tracked by Total Laser and not by the subcategories of Aesthetic Laser and Reconstructive
VII NERVE PALSY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT
 VII NERVE PALSY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT The eye cannot close and constantly weeps. The mouth dribbles, the speech is interfered with and mastication impaired. The delicate shades of continence are lost.
VII NERVE PALSY EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT The eye cannot close and constantly weeps. The mouth dribbles, the speech is interfered with and mastication impaired. The delicate shades of continence are lost.
Table of Contents: Neligan Plastic Surgery 4e. Volume 1: Principles. 1. Plastic Surgery and Innovation in Medicine
 Table of Contents: Neligan Plastic Surgery 4e Volume 1: Principles 1. Plastic Surgery and Innovation in Medicine 2. History of Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery 3. Psychological Aspects of Plastic Surgery
Table of Contents: Neligan Plastic Surgery 4e Volume 1: Principles 1. Plastic Surgery and Innovation in Medicine 2. History of Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery 3. Psychological Aspects of Plastic Surgery
Neurology Goals: Knowledge:
 Neurology Goals: A solid understanding of normal neurological development, anatomy and neurophysiology is imperative to the treatment of neurological pathology. The goal is to sensitize the family medicine
Neurology Goals: A solid understanding of normal neurological development, anatomy and neurophysiology is imperative to the treatment of neurological pathology. The goal is to sensitize the family medicine
Clinical teaching/experi ence. Lectures/semina rs/conferences Self-directed. learning. Clinical teaching/experi ence
 Regional Medical Center (The MED) Plastic Surgery PGY-3 By the end of the Plastic Surgery at the MED, the PGY-3 residents are expected to expand and cultivate knowledge and skills developed during previous
Regional Medical Center (The MED) Plastic Surgery PGY-3 By the end of the Plastic Surgery at the MED, the PGY-3 residents are expected to expand and cultivate knowledge and skills developed during previous
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
THE CLINICAL USE OF BOTULINUM TOXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF MOVEMENT DISORDERS, SPASTICITY, AND SOFT TISSUE PAIN
 THE CLINICAL USE OF BOTULINUM TOXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF MOVEMENT DISORDERS, SPASTICITY, AND SOFT TISSUE PAIN Spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), blepharospasm, and writer s cramp are specific types
THE CLINICAL USE OF BOTULINUM TOXIN IN THE TREATMENT OF MOVEMENT DISORDERS, SPASTICITY, AND SOFT TISSUE PAIN Spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia), blepharospasm, and writer s cramp are specific types
Accepted 22 January 2013 Published online 1 June 2013 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: /hed.23276
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of postoperative brachytherapy and external beam radiotherapy on functional outcomes of immediate facial nerve repair after radical parotidectomy Bernardo Hontanilla, MD, PhD,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of postoperative brachytherapy and external beam radiotherapy on functional outcomes of immediate facial nerve repair after radical parotidectomy Bernardo Hontanilla, MD, PhD,*
Schriftenreihe Neurologie
 Schriftenreihe Neurologie 18 Neurology Series Herausgeber H.I Bauer, Gottingen. H. Ganshirt, Heidelberg P. Vogel, Heidelberg Beirat H.Caspers, Munster H.Hager, GieBen M.Mumenthaler, Bern A. Pentschew,
Schriftenreihe Neurologie 18 Neurology Series Herausgeber H.I Bauer, Gottingen. H. Ganshirt, Heidelberg P. Vogel, Heidelberg Beirat H.Caspers, Munster H.Hager, GieBen M.Mumenthaler, Bern A. Pentschew,
READYTALK. Moderator: Melissa Baumbick June 6, :00 p.m. ET
 Page!1 READYTALK June 6, 2016 2:00 p.m. ET Operator: This is Conference # 39166216. Melissa Baumbick: Welcome to the first Webinar in ANA's 2016 Summer Series. We are honored to welcome Dr. Babak Azizzadeh
Page!1 READYTALK June 6, 2016 2:00 p.m. ET Operator: This is Conference # 39166216. Melissa Baumbick: Welcome to the first Webinar in ANA's 2016 Summer Series. We are honored to welcome Dr. Babak Azizzadeh
Facial Palsy Management by the Multidisciplinary Team
 Facial Palsy Management by the Multidisciplinary Team Catriona Neville and Vanessa Venables Extended Scope Practitioner Therapists in Facial Palsy Queen Victoria Hospital East Grinstead 2013 MDT members
Facial Palsy Management by the Multidisciplinary Team Catriona Neville and Vanessa Venables Extended Scope Practitioner Therapists in Facial Palsy Queen Victoria Hospital East Grinstead 2013 MDT members
ORIGINAL RESEARCH FACIAL PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2008) 138, 468-472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH FACIAL PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY Novel 3-D video for quantification of facial movement Ritvik P. Mehta, MD, Song Zhang,
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2008) 138, 468-472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH FACIAL PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY Novel 3-D video for quantification of facial movement Ritvik P. Mehta, MD, Song Zhang,
Ramsay Hunt syndrome a case report and review of literature
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan January 1, 2013 Ramsay Hunt syndrome a case report and review of literature Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/27/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan January 1, 2013 Ramsay Hunt syndrome a case report and review of literature Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/27/
Medicine I: Part 1: Medical Physical Examination. Kanchan Ganda, MD. Physical Examination: Detailed Discussion
 1. Kanchan Ganda, MD 2. Physical Examination: Detailed Discussion Page - 1 3. Physical Examination 4. Physical Examination (P.E): Steps Page - 2 5. General Appearance 6. Left Parotid Enlargement Page -
1. Kanchan Ganda, MD 2. Physical Examination: Detailed Discussion Page - 1 3. Physical Examination 4. Physical Examination (P.E): Steps Page - 2 5. General Appearance 6. Left Parotid Enlargement Page -
Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 21, No.2, August 2007. pp. 63-70 Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 21, No.2, August 2007. pp. 63-70 Comparison of one-stage free gracilis muscle flap with two-stage method in chronic facial palsy*
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull. Emphasis on Amniota
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull Emphasis on Amniota Initial introduction to components parts of a vertebrate head. This lecture
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Embryology of the Vertebrate Skull Emphasis on Amniota Initial introduction to components parts of a vertebrate head. This lecture
Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy
 Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy Session objectives List the four functions of the cranial nerves (CNs).
Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy Session objectives List the four functions of the cranial nerves (CNs).
Agreement between the Facial Nerve Grading System 2.0 and the House-Brackmann Grading System in Patients with Bell Palsy
 Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 6, No. 3: 135-139, September 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2013.6.3.135 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Agreement between the Facial
Original Article Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology Vol. 6, No. 3: 135-139, September 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2013.6.3.135 pissn 1976-8710 eissn 2005-0720 Agreement between the Facial
List the tumours that may arise in CPA:
 List the tumours that may arise in CPA: 1. Vestibular schwannoma: 75-90% 2. Meningioma: 5-10% 3. Epidermoid 5% 4. Cholesteatoma: 5% 5. Other schwannomas 2-5%: trigeminal is the most common (0.3% of intracranial
List the tumours that may arise in CPA: 1. Vestibular schwannoma: 75-90% 2. Meningioma: 5-10% 3. Epidermoid 5% 4. Cholesteatoma: 5% 5. Other schwannomas 2-5%: trigeminal is the most common (0.3% of intracranial
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Rehabilitation Institute of Neuromuscular Disease, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):381-387 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.381 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Diagnostic Value of Facial Nerve Antidromic
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):381-387 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.381 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Diagnostic Value of Facial Nerve Antidromic
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Audit and Compliance Department 1
 Introduction to Intraoperative Neuromonitoring An intro to those squiggly lines Kunal Patel MS, CNIM None Disclosures Learning Objectives History of Intraoperative Monitoring What is Intraoperative Monitoring
Introduction to Intraoperative Neuromonitoring An intro to those squiggly lines Kunal Patel MS, CNIM None Disclosures Learning Objectives History of Intraoperative Monitoring What is Intraoperative Monitoring
Treatment of gustatory hyperlacrimation (crocodile tears) with injection of botulinum toxin into the lacrimal gland
 (2002) 16, 705 709 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye Treatment of gustatory hyperlacrimation (crocodile tears) with injection of botulinum toxin into
(2002) 16, 705 709 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/eye Treatment of gustatory hyperlacrimation (crocodile tears) with injection of botulinum toxin into
Clare Gaduzo BSc RMN Registered Aesthetics Practitioner (qualified with Medics Direct)
 Clare Gaduzo BSc RMN Registered Aesthetics Practitioner (qualified with Medics Direct) 07935567067 cjg.aesthetics@yahoo.co.uk www.cjgaesthetics.co.uk http://www.facebook.com/cjgaesthetics @CJGAesthetics
Clare Gaduzo BSc RMN Registered Aesthetics Practitioner (qualified with Medics Direct) 07935567067 cjg.aesthetics@yahoo.co.uk www.cjgaesthetics.co.uk http://www.facebook.com/cjgaesthetics @CJGAesthetics
Facial Asymmetry Correction in Facial Palsy Patients with Silhouette Sutures
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2012, 3, 55-59 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijcm.2012.31012 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Facial Asymmetry Correction in Facial
International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2012, 3, 55-59 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ijcm.2012.31012 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcm) Facial Asymmetry Correction in Facial
DR SHRENIK M SHAH SHREY HOSPITAL AHMEDABAD
 DR SHRENIK M SHAH SHREY HOSPITAL AHMEDABAD Surgical anatomy Physiology of healing Classification Pre-operative evaluation OVERVIEW Ultrastructure of the nerve Fragile handle with care Damaged by pressure,
DR SHRENIK M SHAH SHREY HOSPITAL AHMEDABAD Surgical anatomy Physiology of healing Classification Pre-operative evaluation OVERVIEW Ultrastructure of the nerve Fragile handle with care Damaged by pressure,
Unilateral Trigeminal Mandibular Motor Neuropathy Caused by Tumor in the Foramen Ovale
 Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / September, 2006 Unilateral Trigeminal Mandibular Motor Neuropathy Caused by Tumor in the Foramen Ovale Kyung Seok Park, M.D., Jae-Myun Chung, M.D., Beom S. Jeon,
Journal of Clinical Neurology / Volume 2 / September, 2006 Unilateral Trigeminal Mandibular Motor Neuropathy Caused by Tumor in the Foramen Ovale Kyung Seok Park, M.D., Jae-Myun Chung, M.D., Beom S. Jeon,
Management of Ear, Hearing and Balance Disorders: Fact, Fiction, and Future
 Management of Ear, Hearing and Balance Disorders: Fact, Fiction, and Future George W. Hicks, M,D. 7440 N. Shadeland Avenue, Suite 150 Indianapolis, IN 46250 904 N. Samuel Moore Parkway Mooresville, IN
Management of Ear, Hearing and Balance Disorders: Fact, Fiction, and Future George W. Hicks, M,D. 7440 N. Shadeland Avenue, Suite 150 Indianapolis, IN 46250 904 N. Samuel Moore Parkway Mooresville, IN
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Novel 3-D Video for Quantification of Facial Movement
 Novel 3-D Video for Quantification of Facial Movement Ritvik P. Mehta MD*, Song Zhang PhD, and Tessa A. Hadlock MD * Division of Otolaryngology, University of California San Diego, San Diego CA Harvard
Novel 3-D Video for Quantification of Facial Movement Ritvik P. Mehta MD*, Song Zhang PhD, and Tessa A. Hadlock MD * Division of Otolaryngology, University of California San Diego, San Diego CA Harvard
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Bell Work What s your reaction time? Go to this website and check it out: https://www.justpark.com/creative/reaction-timetest/ Read the following brief article and summarize
The Best Candidates for Nerve-Sparing Stripping Surgery for Facial Nerve Schwannoma
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Best Candidates for Nerve-Sparing Stripping Surgery for Facial Nerve Schwannoma Soon H. Park, MD; Jin
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Best Candidates for Nerve-Sparing Stripping Surgery for Facial Nerve Schwannoma Soon H. Park, MD; Jin
Cranial Nerves Exam. 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
 Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
Course specification of Plastic surgery & Burn. (MD degree) Year: 2015 / 2016
 University Faculty : Al-Azhar University : Faculty of Medicine (Boys) Department : Plastic surgery & Burn Department Course specification of Plastic surgery & Burn. (MD degree) Year: 2015 / 2016 1. Course
University Faculty : Al-Azhar University : Faculty of Medicine (Boys) Department : Plastic surgery & Burn Department Course specification of Plastic surgery & Burn. (MD degree) Year: 2015 / 2016 1. Course
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS. To cite this article: W Alviandi et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic utility of Freyss motor examination, House Brackmann grading, topognostic tests, and electrophysiological assessments for unilateral peripheral
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic utility of Freyss motor examination, House Brackmann grading, topognostic tests, and electrophysiological assessments for unilateral peripheral
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination
 The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
Unit Six The Nervous System
 Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
Unit Six The Nervous System I. Introduction A. Definition a coordinating system of the body, composed of highly specialized cells that conduct nerve impulses to a center so responses can be made. The nervous
A Patient s Guide to Intraoperative Monitoring
 A Patient s Guide to Intraoperative Monitoring 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Intraoperative Monitoring 228 West Main, Suite C Missoula, MT 59802 Phone: info@spineuniversity.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
