Is the Peak-to-Mean Pressure Gradient Ratio Useful for Assessment of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Obstruction? Abstract. Introduction
|
|
|
- Randolf Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Is the Peak-to-Mean Pressure Gradient Ratio Useful for Assessment of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Obstruction? Abstract Maryam Esmaeilzadeh, MD, FACC, FCAPSC *, Ahmad Mirdamadi, MD, Mozhgan Parsaee, MD, Anita Sadeghpour, MD, FASE,FACC, Majid Maleki, MD, FACC, FCAPSC, Hooman Bakhshandeh Abkenar, MD Echocardiography Research Center of Shaheed Rajaei Cardiovascular Medical and Research Center, Tehran, Iran. Background: The evaluation of prosthetic valves is very difficult with two-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography alone. Doppler and color flow imaging as well as transesophageal echocardiography are more reliable to detect prosthetic valve dysfunction. However, Doppler study sometimes tends to be misleading due to the load-depending characteristics of peak and mean pressure gradients. The peak-to-mean pressure decrease ratio is a load-independent measure, which was previously used for the detecting and grading of aortic valve stenosis. We assessed the usefulness of this method for the evaluation of aortic valve prosthesis obstruction. Methods: One hundred fifty-four patients with aortic valve prostheses were included in this study. Transthoracic and transesophageal echocardiographic examinations were performed in all the patients. Peak velocity and velocity time integral of the aortic valve and left ventricular outflow tract, peak and mean aortic valve pressure gradients, peak-to-mean pressure gradient ratio, and time velocity integral (TVI) index were measured. Results: There was a significant relation between the TVI index (p value < 0.001) and aortic prosthesis obstruction. A TVI index < 0.2 had a sensitivity of 71% and specificity of 100% for the detection of aortic valve prosthesis obstruction. However, no significant relation was found between the peak-to-mean pressure ratio and aortic valve prosthesis obstruction (p value = 0.09). Conclusion: Although the peak-to-mean pressure gradient (PG/MG) ratio is a simple, quick, and load-independent method which may be useful for the grading of aortic valve stenosis, it is poorly associated with aortic valve prosthesis obstruction. The TVI index is a useful measure for the detection of aortic prosthesis obstruction. J Teh Univ Heart Ctr 2 (2010) Received 11 August 2009; Accepted 28 January 2010 Keywords: Aortic valve Diagnosis Echocardiography, Doppler Introduction The evaluation of prosthetic valves via two-dimensional (2D) transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) alone is very difficult. Doppler and color flow imaging as well as transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) are more reliable to detect prosthetic valve dysfunction. The incidence of prosthetic valve obstruction has been estimated at 0.1% to 0.4% per year, depending on the valve size, type, and location as well as the adequacy of anticoagulation. 1 Whereas the obstruction of a mitral mechanical prosthesis is caused more frequently by thrombus, the obstruction of an aortic mechanical prosthesis is created more frequently by pannus formation. 2 When a * Corresponding Author: Maryam Esmaeilzadeh, Associate Professor of Cardiology, Echocardiography Research Center of Shaheed Rajaei Hospital, Tehran, Iran Tel: Fax: meszadeh@rhc.ac.ir. The Journal of Tehran University Heart Center 69
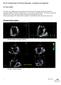
2 The Journal of Tehran University Heart Center Maryam Esmaeilzadeh et al prosthetic valve becomes obstructed, the motion of the disk, ball, or leaflets decreases. Be that as it may, it is difficult to visualize and yet more difficult to quantify the restriction of the excursion with TTE. 3 TEE may be essential in the evaluation of mitral and tricuspid valves, but it is relatively low sensitive for detecting the dysfunction of aortic prostheses. 3 Gross abnormalities such as large thrombi or vegetations can be identified using 2D echocardiography, but assessing the functional significance of such changes is difficult. 4 Thus, most of the diagnostic information related to aortic prostheses depends on a thorough and quantitative Doppler study. 4 The range of normal Doppler values depends primarily on the size of the prosthesis. 4 It is important to remember that increased flow velocity itself does not always indicate prosthetic obstruction. The velocity can be increased without stenosis in a high output state or presence of severe prosthetic regurgitation. The ratio of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) to aortic valve prosthesis (AVP) velocity or time velocity integral (TVI) is helpful in differentiating increased flow velocity across an aortic prosthesis due to prosthetic obstruction (the ratio < 0.2) from increased velocity due to other causes (the ratio remains normal > 0.3). 3 Recently, Chambers et al. reported that the relation of trans aortic peak (PG) and mean gradients (MG), i.e. the PG/MG ratio, is a useful parameter to evaluate the severity of aortic stenosis. 5 The purpose of this study was to evaluate the statistical efficacy (sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and accuracy and probability rates in case of a positive or negative result) of the PG/MG ratio to predict aortic valve prosthesis obstruction and to compare it with the TVI ratio. Methods 2D, M-mode, pulsed Doppler, continuous, and color studies were performed in all the patients in accordance with the recommendations of the American society of echocardiography. Pulsed wave signal of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT) and continuous wave signal of the aortic valve (AV) prosthesis were obtained using the apical 5-chamber view, with the the sample volume placed 5 mm below the aortic annulus. The following echocardiographic variables were measured and calculated from the average of 3-5 consecutive beats: 1. Peak velocity (V max ) 2. Peak gradient (PG) was calculated as 4 (V max ) 2 and mean gradient (MG) with the algorithm incorporated to the ultrasound equipment (Figure 1) 3. Time velocity integral (TVI) 4. TVI index (LVOT TVI / AV TVI ) TEE: aortic valve prosthesis was evaluated on 0, 45, and 120 degrees in the mid esophageal and in deep transgastric view for the detection of the thrombus or pannus formation. From February 2007 to January 2008, we retrospectively analyzed the Doppler echocardiograms of 154 consecutive patients (mean age: 49 years, range: years, 52% male) with aortic valve prosthesis evaluated for several clinical indications. The exclusion criteria were inadequate echocardiographic images, rhythm other than sinus rhythm, paravalvular regurgitation, aortic bioprosthesis, and significant mitral valve disease. Echocardiographic examinations were performed with the subject in the left lateral decubitus position. Commercially available ultrasonography instruments equipped with 2.0 to 3.5-MHZ transthoracic probes and 2.0 MHz non-imaging (Pedoff) transducers were utilized from the left and right parasternal, apical, suprasternal, and sub-xyphoid windows (GE Medical Systems, Vivid 3). TEE was performed using a commercial 5.0-/3.5-MHz multi-plane probe. Complete Figure 1. Deep transgastric view of an obstructed aortic prosthesis. Continuous Doppler echocardiography showed significant increase in peak and mean pressure gradient through the aortic prosthesis AV peak V, Aortic valve peak velocity; Peak PG, Peak pressure gradient; Mean PG, Mean pressure gradient; AV VTI, Aortic valve velocity time integral Cinefluoroscopy was done in all the patients to assess the valve leaflet (s) motion. Cinefluoroscopy is superior to echocardiography in identifying disc motion, whilst Doppler study allowed the measurement of gradients and areas. A significant increase in trans-prosthesis pressure gradient along with a decreased TVI index through Doppler echocardiography and decreased leaflet (s) motion (more than 25 ± 5 degrees) 6 using cinefluoroscopy was defined as prosthetic valve obstruction. All the data are expressed as mean ± SD. Crude associations 70
3 Is the Peak-to-Mean Pressure Gradient Ratio Useful for Assessment... between the PG/MG ratio and the other variables were determined via the independent sample t-test and Mann- Whitney U test for the categorical data and bivariate linear regression models for the interval data. Multivariate analysis was performed using a multiple linear regression model to determine adjusted associations. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. SPSS 15 (SPSS Corporation, Chicago, Illinois, USA) was used for statistical analysis. Results The clinical and echocardiographic characteristics of the patients are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Time to valve replacement surgery was 10±8 years (range from 1 to 36 Table 1. Patients characteristics and their comparisons in two groups of patients (n=154) years). TEE showed thrombus, pannus, and mixed thrombus with pannus in 26.7%, 31%, and 12% of the patients, respectively. Nonetheless, cinefluoroscopy revealed decreased leaflet motion only in 7.8% of the patients. There was an inverse correlation between the PG/MG ratio and MG (β = 0.010, r = 0.54, p value < 0.001), but there was no correlation between the PG/MG ratio and the TVI index (β = 0.09, r = 0.053; p value = 0.52). Additionally, there was a significant negative correlation between the PG/ MG ratio and the V max. (β = 0.03, r = 0.165, p value = 0.04). The logistic regression analysis showed no significant relation between the peak-to-mean pressure ratio and aortic valve prosthesis obstruction (B = 1.25, p value = 0.09, OR = 0.29, 95% CI: , but a significant relation was AVP Obstruction Total p value (n=154) Yes No (n=71) (n=83) Age (y) (mean±sd) 49± ± ± Female/Male 75/79 42/29 33/ Time from operation (y) (mean±sd) 10± ±7.2 7±6.8 <0.001 Type of mechanical valve (%) Mono-leaflet 41 (26.6) 21 (29.6) 12 (14.5) Bi-leaflets 113 (73.4) 37 (70.4) 60 (85.5) Referral reason (%) AVR 63 (40.9) 22 (31) 41 (49.4) AVP malfunction 52 (33.8) 29 (40.8) 23 (27.7) Infective endocarditis 13 (8.4) 3 (4.2) 10 (12.1) Cardiac source of systemic emboli 22 (14.2) 15 (21.2) 7 (8.4) Syncope 4 (2.7) 2 (2.8) 2 (2.4) LVEF (%) (mean±sd) 45± ±9.8 43± AVR, Aortic valve replacement; AVP, Aortic valve prosthesis; LVEF, Left ventricular ejection fraction Table 2. Patients> Doppler echocardiographic findings * AVP Obstruction Total p value (n=154) Yes No (n=71) (n=83) AV peak velocity (m/s) 2.90± ±2 2.50±0.60 <0.001 AV peak PG (mmhg) 35± ± ±12.70 <0.001 AV mean PG (mmhg) 20± ± ±13 <0.001 AV TVI (cm) 50.70± ± ±13.70 <0.001 LVOT TVI (cm) 20±7 20± ± LVOT TVI / AV TVI 0.43± ± ±0.15 <0.001 Normally functioning AV 0.44± ± ±0.15 <0.001 Abnormal motion of AV 0.33± ± ± PG/MG ratio 1.80± ± ± Normally functioning AV 1.80± ± ± Abnormal motion of AV 1.80± ± ± * Data are presented as mean±sd AV, Aortic valve; PG, Pressure gradient; TVI, Time velocity integral; LVOT, Left ventricular outflow tract; PG/MG ratio, The ratio of peak gradient to mean gradient; AVP, Aortic valve prosthesis The Journal of Tehran University Heart Center71
4 The Journal of Tehran University Heart Center Maryam Esmaeilzadeh et al Table 3. Logistic regression analysis between PG/MG ratio and multiple variables found between the TVI index and aortic valve prosthesis obstruction (B = 5.69, p value < 0.001, OR = 0.003, 95% CI: The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve showed that the TVI index was an accurate (AUC = 0.73 ± 0.041, 95% CI: ) method for the evaluation of AVP obstruction (Figure 2). The VTI index<0.2 had a sensitivity of 71%, specificity of 100%, positive likelihood ratio of 100%, and negative likelihood ratio of 54.5% for the prediction of AVP obstruction. Figure 2. ROC curve of the TVI index for the diagnosis of aortic valve prosthesis obstruction according to fluoroscopy The probability of obstruction was twice higher in the monoleaflet prosthesis in comparison with the bileaflet prosthesis (OR: 2.8, 95% CI: ). Furthermore, aortic valve prosthesis obstruction was more frequent in the female gender (OR: 2.1, 95% CI: ); it was not, however, affected by the patient s age and time duration from valve surgery (table 3). Coefficient SE PV Odds Ratio 95% CI for OR Sex Age Time to surgery Valve Type Valve Size PG/MG ratio TVI index Constant PG, Peak pressure gradient; MG, Mean pressure gradient; TVI, Time velocity integral; SE, Standard error; PV, Probability value; CI, Confidence interval; OR, Odds ratio Discussion Obstruction of the AV prosthesis is an important clinical entity. It can occur by thrombus formation, pannus ingrowths, or infective endocarditis. TTE has limited value for the evaluation of AVP obstruction 3 and has a low sensitivity for the detection of its dysfunction. 4 Whereas the detection of obstruction and assessment of the functional significance of obstruction is difficult by 2D echocardiography, Doppler study can help to evaluate AVP abnormality. 4 Doppler study can help to diagnose AVP obstruction by measuring peak velocity, peak and mean pressure gradients, and TVI index, but load dependency can sometimes misguide physicians. The peak-to-mean pressure ratio was previously used to evaluate aortic valve stenosis. This parameter is flow independent. 7 Opinions about this variable is controversial. For example, Volbery et al. reported a weak correlation between the PG/MG ratio and aortic valve area. 5 They found marked overlap in the PG/MG ratio values in patients with aortic stenosis of variable severity. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the PG/MG ratio for the diagnosis of severe stenosis in their study were fair. In a study by Chambers et al., this variable was shown to be related to the aortic valve area (1.75 in mild stenosis, 1.66 in moderate stenosis, 1.56 in severe stenosis and 1.57 in severe aortic stenosis with left ventricular ejection fraction less than 40%). 5 In the present study, we assessed the usefulness of the PG/ MG ratio as a parameter proposed for the diagnosis of AVP obstruction. This parameter has the advantage, compared to the other available ones, of being independent of flows such as V max, and MG, which represents and advantage over the indices that require flow correction. We compared the PG/MG ratio with V max MG and TVI index, which are the three criteria most often used for the diagnosis of AVP obstruction. Using multiple statistical analysis methods, we did not find a significant relation between the PG/MG ratio and AVP obstruction; although the logistic regression method 72
5 Is the Peak-to-Mean Pressure Gradient Ratio Useful for Assessment... did not rule out this association strongly (p value = 0.09). We presumed that it might be secondary to the triangular shape of the CW Doppler flow profile in the aortic valve prosthesis, which would cause the prosthetic valve mean pressure gradient to not follow the classic formula (mean PG = 2.4 V 2 ). We, therefore, calculated the mean gradient mathematically by applying this formula and compared them with the previous automatically measured mean gradients. There was an insignificant difference between the automatically and mathematically derived measurements (16.5 versus mmhg, respectively); nevertheless, the linear regression analysis showed a significant correlation between the two methods (correlation coefficient = 0.96, regression coefficient of mean pressure gradient = 0.918, p value < 0.001). This study showed that the TVI index had a strong relation with AVP obstruction. Using several analysis methods, we found that the TVI index < 0.2 had a specificity of 100% for the prediction of significant obstruction. The PG/MG ratio had a low clinical impact for the diagnosis of AVP obstruction; be that as it may, further studies are required to evaluate the PG/MG ratio as a parameter for the diagnosis of AVP obstruction. The greatest limitation of this study is that the criteria for AVP obstruction, considered to be standard, V max, MG, and TVI index, are all parts of the PG/MG ratio; consequently, there is contamination between the parameters. This limitation is also shared by Chambers and Volberg et al. Another limitation is the lack of direct anatomic confirmation at surgery or post-mortem examinations of abnormalities such as thrombus or pannus. Furthermore, we did not follow the patients during a long-term period, so the clinical relevance of the non-invasive abnormalities needs to be established. Conclusion Acknowledgments This study was supported by Iran University of Medical Sciences. We wish to thank all the nursing staff involved in the echocardiography and angiography departments at Shaheed Rajaei Cardiovascular, Medical and Research Center. References Cannegieter SC, Torn M, Rosendual FR. Oral anticoagulant treatment in patients with mechanical heart valves: how to reduce the risk of thromboembolic and bleeding complications. J Inter Med 1999;245: Girad SE, Miller FA Jr, Orszulak TA, Mullany CJ, Montgomery S, Edwards WD, Tazelaar HD, Malouf JF, Tajik AJ. Reoperation for prosthetic aortic valve obstruction in the era of echocardiography: trends in diagnostic testing and comparison with surgical findings. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;37: OH Jk, Seward JB, Tajik AJ. Prosthetic valve evaluation. In: OH Jk, Seward JB, Tajik AJ, eds. The Echo Manual. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Baltimore, New york, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p Feigenbaum H, Armstrong W, Ryan T. Prosthetic valves. In: Feigenbaum H, Armstrong W, Ryan T, eds. Feigenbaum s Echocardiography. 6th ed. Philadelphia, Baltimore, New york, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p Chambers J, Rajani R, Hankins M, Cook R. The peak to mean pressure decrease ratio: a new method of assessing aortic stenosis. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2005;18: Cianciulli TE, Lax JA, Beck MA, Cerruti FE, Gigena GE, Saccheri MC, Fernández E, Dorelle AN, Leguizamón JH, Prezioso HA. Cinefluoroscopic assessment of mechanical disc prostheses: its value as a complementary method to echocardiography. J Heart Valve Dis 2005;14: Volberg VI, Berensztein CS, Ber MG, Lanosa G, Lerman J, Pineiro DJ. Efficacy of the peak to mean pressure decrease ratio for the assessment of aortic stenosis severity. Rev Argent Cardiol 2006;74: The PG/MG ratio is a simple, quick, and load-independent method, but the present study showed that the PG/MG ratio correlated weakly with the AVP obstruction. Although this correlation was insignificant, it was not ruled out strongly. There was also a marked overlap between the PG/MG ratio values among patients with AVP obstruction of variable severities. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the PG/MG ratio for the diagnosis of AVP obstruction were fair. In the population studied, the predictive values of the PG/ MG ratio for the diagnosis of AVP obstruction were modest (0.09). Moreover, the analysis of the probability rates in the case of a positive or negative result showed that the PG/ MG ratio had a low clinical impact for the diagnosis of AVP obstruction. Finally, we found the TVI index a useful measure for detecting aortic prosthesis obstruction. The Journal of Tehran University Heart Center73
Prosthesis-Patient Mismatch or Prosthetic Valve Stenosis?
 EuroValves 2015, Nice Prosthesis-Patient Mismatch or Prosthetic Valve Stenosis? Philippe Pibarot, DVM, PhD, FACC, FAHA, FASE FESC Canada Research Chair in Valvular Heart Diseases Université LAVAL Disclosure
EuroValves 2015, Nice Prosthesis-Patient Mismatch or Prosthetic Valve Stenosis? Philippe Pibarot, DVM, PhD, FACC, FAHA, FASE FESC Canada Research Chair in Valvular Heart Diseases Université LAVAL Disclosure
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Co-Director, Echocardiography, Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Co-Director, Echocardiography, Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System
Prosthetic valve dysfunction: stenosis or regurgitation
 Prosthetic valve dysfunction: stenosis or regurgitation Jean G. Dumesnil MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE(Hon) Quebec Heart and Lung Institute, Québec, Québec No disclosures Possible Causes of High Gradients in
Prosthetic valve dysfunction: stenosis or regurgitation Jean G. Dumesnil MD, FRCP(C), FACC, FASE(Hon) Quebec Heart and Lung Institute, Québec, Québec No disclosures Possible Causes of High Gradients in
TAVR: Echo Measurements Pre, Post And Intra Procedure
 2017 ASE Florida, Orlando, FL October 10, 2017 8:00 8:25 AM 25 min TAVR: Echo Measurements Pre, Post And Intra Procedure Muhamed Sarić MD, PhD, MPA Director of Noninvasive Cardiology Echo Lab Associate
2017 ASE Florida, Orlando, FL October 10, 2017 8:00 8:25 AM 25 min TAVR: Echo Measurements Pre, Post And Intra Procedure Muhamed Sarić MD, PhD, MPA Director of Noninvasive Cardiology Echo Lab Associate
Hemodynamic Assessment. Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics
 Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
Hemodynamic Assessment Matt M. Umland, RDCS, FASE Aurora Medical Group Milwaukee, WI Assessment of Systolic Function Doppler Hemodynamics Stroke Volume Cardiac Output Cardiac Index Tei Index/Index of myocardial
25 different brand names >44 different models Sizes mm
 Types of Prosthetic Valves BIOLOGIC STENTED Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft STENTLESS Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft Homograft (allograft) Autograft PERCUTANEOUS MECHANICAL Bileaflet Single
Types of Prosthetic Valves BIOLOGIC STENTED Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft STENTLESS Porcine xenograft Pericardial xenograft Homograft (allograft) Autograft PERCUTANEOUS MECHANICAL Bileaflet Single
A Practical Approach to Prosthetic Valves
 A Practical Approach to Prosthetic Valves Bonita Anderson DMU (Cardiac), MApplSc (Med Ultrasound), ACS, AMS, FASE https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.108.778886 Disclosures None 1 Know the Product Know
A Practical Approach to Prosthetic Valves Bonita Anderson DMU (Cardiac), MApplSc (Med Ultrasound), ACS, AMS, FASE https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.108.778886 Disclosures None 1 Know the Product Know
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Co Director, Echocardiography, Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Co Director, Echocardiography, Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Valve Prostheses
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Valve Prostheses Dennis A. Tighe, M.D., FACC, FACP, FASE Cardiovascular Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School Worcester, MA www.asecho.org 1 Nishimura
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Mitral Valve Prostheses Dennis A. Tighe, M.D., FACC, FACP, FASE Cardiovascular Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School Worcester, MA www.asecho.org 1 Nishimura
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
The correlation of AVA measured by transthoracic, transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac CT
 The correlation of AVA measured by transthoracic, transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac CT R.Petr, H.Linkova, J.Knot, E.Paskova, J.Daniel, M.Labos Cardiocenter of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady
The correlation of AVA measured by transthoracic, transesophageal echocardiography and cardiac CT R.Petr, H.Linkova, J.Knot, E.Paskova, J.Daniel, M.Labos Cardiocenter of University Hospital Kralovske Vinohrady
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Doppler echocardiography is currently the
 Doppler Echocardiography of 119 Normal-functioning St Jude Medical Mitral Valve Prostheses: A Comprehensive Assessment Including Time-velocity Integral Ratio and Prosthesis Performance Index* Joseph F.
Doppler Echocardiography of 119 Normal-functioning St Jude Medical Mitral Valve Prostheses: A Comprehensive Assessment Including Time-velocity Integral Ratio and Prosthesis Performance Index* Joseph F.
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System Associate Professor of Medicine,
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Aortic Valve Prosthesis Amr E Abbas, MD, FACC, FASE, FSCAI, FSVM, RPVI Director, Interventional Cardiology Research, Beaumont Health System Associate Professor of Medicine,
Affecting the elderly Requiring new approaches. Echocardiographic Evaluation of Hemodynamic Severity. Increasing prevalence Mostly degenerative
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of Hemodynamic Severity Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None A re-emerging public-health
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Hemodynamic Severity Steven J. Lester MD, FACC, FRCP(C), FASE Mayo Clinic, Arizona Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None A re-emerging public-health
Congenital. Unicuspid Bicuspid Quadricuspid
 David Letterman s Top 10 Aortic Stenosis The victim can be anyone: Echo is the question and the answer!!!! Hilton Head Island Echocardiography Conference 2012 Timothy E. Paterick, MD, JD, MBA Christopher
David Letterman s Top 10 Aortic Stenosis The victim can be anyone: Echo is the question and the answer!!!! Hilton Head Island Echocardiography Conference 2012 Timothy E. Paterick, MD, JD, MBA Christopher
New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor. Cardiothoracic Radiology
 New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor Cardiothoracic Radiology Disclosure I have no disclosure pertinent to this presentation.
New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor Cardiothoracic Radiology Disclosure I have no disclosure pertinent to this presentation.
Patient/prosthesis mismatch: how to evaluate and when to act?
 Patient/prosthesis mismatch: how to evaluate and when to act? Svend Aakhus, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Disclosures: No conflict of interest Types of aortic valve prostheses (AVR) Mechanical
Patient/prosthesis mismatch: how to evaluate and when to act? Svend Aakhus, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Disclosures: No conflict of interest Types of aortic valve prostheses (AVR) Mechanical
The Normal Echocardiogram
 The Normal Echocardiogram Pravin V. Patil, MD FACC Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Acknowledgments Dr. Susan Wiegers Dr. Martin Keane Temple Cardiac Sonographers Disclosures No relevant
The Normal Echocardiogram Pravin V. Patil, MD FACC Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Acknowledgments Dr. Susan Wiegers Dr. Martin Keane Temple Cardiac Sonographers Disclosures No relevant
Dobutamine Stress testing In Low Flow, Low EF, Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Case Studies
 Dobutamine Stress testing In Low Flow, Low EF, Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Case Studies Mitral Regurgitation The New ASE Guidelines: Role of 2D/3D and CMR William A. Zoghbi MD, FASE, MACC Professor and
Dobutamine Stress testing In Low Flow, Low EF, Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Case Studies Mitral Regurgitation The New ASE Guidelines: Role of 2D/3D and CMR William A. Zoghbi MD, FASE, MACC Professor and
Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants
 Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Basic root structure Parasternal
Aortic Stenosis: Spectrum of Disease, Low Flow/Low Gradient and Variants Martin G. Keane, MD, FASE Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Basic root structure Parasternal
Back to Basics: Common Errors In Quantitation In Everyday Practice
 Back to Basics: Common Errors In Quantitation In Everyday Practice Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE October 9, 2017 ASE: Echo Florida Rebecca T. Hahn, MD Director of Interventional Echocardiography Professor
Back to Basics: Common Errors In Quantitation In Everyday Practice Deborah Agler, ACS, RDCS, FASE October 9, 2017 ASE: Echo Florida Rebecca T. Hahn, MD Director of Interventional Echocardiography Professor
Evaluation of St. Jude Medical Valve s Long-term Function by Doppler Echocardiography
 Evaluation of St. Jude Medical Valve s Long-term Function by Doppler Echocardiography Akira Sezai, MD, Motomi Shiono, MD, Kenji Akiyama, MD, Yukihiko Orime, MD, Hiroaki Hata, MD, Shinya Yagi, MD, Tomonori
Evaluation of St. Jude Medical Valve s Long-term Function by Doppler Echocardiography Akira Sezai, MD, Motomi Shiono, MD, Kenji Akiyama, MD, Yukihiko Orime, MD, Hiroaki Hata, MD, Shinya Yagi, MD, Tomonori
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations
 Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Doppler Basic & Hemodynamic Calculations August 19, 2017 Smonporn Boonyaratavej MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
Echo Assessment Pre-TAVI
 Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the past 12 months, I or my spouse/partner have had a financial Interest /arrangement or affiliation with the organization(s) listed below Echocardiographic
Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest Within the past 12 months, I or my spouse/partner have had a financial Interest /arrangement or affiliation with the organization(s) listed below Echocardiographic
Ultrasound 10/1/2014. Basic Echocardiography for the Internist. Mechanical (sector) transducer Piezoelectric crystal moved through a sector sweep
 Ultrasound Basic Echocardiography for the Internist Carol Gruver, MD, FACC UT Erlanger Cardiology Mechanical wave of compression and rarefaction Requires a medium for transmission Ultrasound frequency
Ultrasound Basic Echocardiography for the Internist Carol Gruver, MD, FACC UT Erlanger Cardiology Mechanical wave of compression and rarefaction Requires a medium for transmission Ultrasound frequency
When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference?
 When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference? Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network 1 Practical Applications of 3D Echocardiography Recommended
When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference? Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network 1 Practical Applications of 3D Echocardiography Recommended
The Ross Procedure: Outcomes at 20 Years
 The Ross Procedure: Outcomes at 20 Years Tirone David Carolyn David Anna Woo Cedric Manlhiot University of Toronto Conflict of Interest None The Ross Procedure 1990 to 2004 212 patients: 66% 34% Mean age:
The Ross Procedure: Outcomes at 20 Years Tirone David Carolyn David Anna Woo Cedric Manlhiot University of Toronto Conflict of Interest None The Ross Procedure 1990 to 2004 212 patients: 66% 34% Mean age:
Bogdan A. Popescu. University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania. EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010
 Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010 This is how it started Mitral stenosis at a glance 2D echo narrow diastolic opening of MV leaflets
Bogdan A. Popescu University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, Romania EAE Course, Bucharest, April 2010 This is how it started Mitral stenosis at a glance 2D echo narrow diastolic opening of MV leaflets
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Stage of Valvular AS. Outline 10/14/16. Low-flow and Other Challenges to the Assessment of Aortic Stenosis. Severe AS
 Low-flow and Other Challenges to the Assessment of Aortic Stenosis Nithima Ratanasit, MD, FACC, FASE Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University Bangkok, Thailand Outline Types of low-flow aortic stenosis Assessment
Low-flow and Other Challenges to the Assessment of Aortic Stenosis Nithima Ratanasit, MD, FACC, FASE Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University Bangkok, Thailand Outline Types of low-flow aortic stenosis Assessment
Cardiology Fellowship Manual. Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e
 Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
Cardiology Fellowship Manual Goals & Objectives -Cardiac Imaging- 1 P a g e UNIV. OF NEBRASKA CHILDREN S HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENTER DIVISION OF CARDIOLOGY FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM CARDIAC IMAGING ROTATION GOALS
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
 Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Echocardiography in Intensive Care: The Basics. Part I
 Clinical practice review Echocardiography in Intensive Care: The Basics. Part I K. D. DONOVAN, F. COLREAVY Intensive Care Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, WESTERN AUSTRALIA ABSTRACT Objective: To review
Clinical practice review Echocardiography in Intensive Care: The Basics. Part I K. D. DONOVAN, F. COLREAVY Intensive Care Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, WESTERN AUSTRALIA ABSTRACT Objective: To review
ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF
 APPENDIX 1 ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF Study #: - Pt Initials: 1. Date of study: / / D D M M M Y Y Y Y 2. Type of Study: TTE TEE 3. Quality of Study: Poor Moderate Excellent Ejection Fraction 4. Ejection Fraction
APPENDIX 1 ICE: Echo Core Lab-CRF Study #: - Pt Initials: 1. Date of study: / / D D M M M Y Y Y Y 2. Type of Study: TTE TEE 3. Quality of Study: Poor Moderate Excellent Ejection Fraction 4. Ejection Fraction
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Valve Quantification
 Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
Echocardiography: Guidelines for Echocardiography: Guidelines for Chamber Quantification British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee Richard Steeds (Chair), Gill Wharton (Lead Author), Jane
Cases of Abnormal Prosthetic Valves
 Cases of Abnormal Prosthetic Valves Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echcoardiography Associate Director, Cardiology
Cases of Abnormal Prosthetic Valves Sunil Mankad, MD, FACC, FCCP, FASE Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Director, Transesophageal Echcoardiography Associate Director, Cardiology
Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics.
 Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP Northwell, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York Professor of Cardiology Hofstra University
Echo Doppler Assessment of Right and Left Ventricular Hemodynamics. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP Northwell, Lenox Hill Hospital, New York Professor of Cardiology Hofstra University
Effect of Heart Rate on Tissue Doppler Measures of E/E
 Cardiology Department of Bangkok Metropolitan Administration Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract Background: Our aim was to study the independent effect of heart rate (HR) on
Cardiology Department of Bangkok Metropolitan Administration Medical College and Vajira Hospital, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract Background: Our aim was to study the independent effect of heart rate (HR) on
Aortic Stenosis: LVOT Obstruction
 Aortic Stenosis: LVOT Obstruction Raymond Stainback, MD 7 th annual Houston Echo Review 2016: Boot Camp for the Echo Board Murmur: Additional heart or vascular sound due to normal or abnormal turbulent
Aortic Stenosis: LVOT Obstruction Raymond Stainback, MD 7 th annual Houston Echo Review 2016: Boot Camp for the Echo Board Murmur: Additional heart or vascular sound due to normal or abnormal turbulent
Index. K Knobology, TTE artifact, image resolution, ultrasound, 14
 A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
Echocardiographic evaluation of mitral stenosis
 Echocardiographic evaluation of mitral stenosis Euroecho 2011 Philippe Unger, MD, FESC Erasme Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium I have nothing to declare EuroHeart Survey Etiology of single native left-sided
Echocardiographic evaluation of mitral stenosis Euroecho 2011 Philippe Unger, MD, FESC Erasme Hospital, ULB, Brussels, Belgium I have nothing to declare EuroHeart Survey Etiology of single native left-sided
A pregnant patient with a prosthetic valve Giacomo Boccuzzi, MD, FESC
 A pregnant patient with a prosthetic valve Giacomo Boccuzzi, MD, FESC Department of Invasive Cardiology, Ospedale San Giovanni Bosco, Turin, Italy *C.V. was born the 24th May 1980 Rheumatic fever during
A pregnant patient with a prosthetic valve Giacomo Boccuzzi, MD, FESC Department of Invasive Cardiology, Ospedale San Giovanni Bosco, Turin, Italy *C.V. was born the 24th May 1980 Rheumatic fever during
ECHO HAWAII. Role of Stress Echo in Valvular Heart Disease. Not only ischemia! Cardiomyopathy. Prosthetic Valve. Diastolic Dysfunction
 Role of Stress Echo in Valvular Heart Disease ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan Not only ischemia! Cardiomyopathy Prosthetic Valve Diastolic
Role of Stress Echo in Valvular Heart Disease ECHO HAWAII January 15 19, 2018 Kenya Kusunose, MD, PhD, FASE Tokushima University Hospital Japan Not only ischemia! Cardiomyopathy Prosthetic Valve Diastolic
Comprehensive Hemodynamics By Doppler Echocardiography. The Echocardiographic Swan-Ganz Catheter.
 Comprehensive Hemodynamics By Doppler Echocardiography. The Echocardiographic Swan-Ganz Catheter. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP North Shore HS, LIJ/Lenox Hill Hospital, New York
Comprehensive Hemodynamics By Doppler Echocardiography. The Echocardiographic Swan-Ganz Catheter. Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, FACC, FESC, FAHA, FACP, FCCP North Shore HS, LIJ/Lenox Hill Hospital, New York
Adopted by Council March 2006, Revised March 2012, September 2015
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements E4 Education Protocol: Competences Required Of Cardiac Sonographers Who Practice Adult Transthoracic Cardiac Ultrasound Examinations Adopted by Council March 2006, Revised
Guidelines, Policies and Statements E4 Education Protocol: Competences Required Of Cardiac Sonographers Who Practice Adult Transthoracic Cardiac Ultrasound Examinations Adopted by Council March 2006, Revised
Severity of AS Degree of AV calcification (? Bicuspid AV), annulus size, & aortic root
 The role of Cardiac Imaging modalities in evaluation & selection of patients for Trans-catheter Aortic Valve Implantation Dr.Saeed AL Ahmari Consultant Cardiologist Prince Sultan Cardaic Center, Riyadh
The role of Cardiac Imaging modalities in evaluation & selection of patients for Trans-catheter Aortic Valve Implantation Dr.Saeed AL Ahmari Consultant Cardiologist Prince Sultan Cardaic Center, Riyadh
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY. MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C.
 AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C. Roy February 2016 Montreal Heart Institute HF Research Aude Turgeon,
AIMI-HF PROCEDURE MANUAL TECHNICAL GUIDE FOR ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY MHI Core Laboratory E. O Meara - J.C. Tardif J. Vincent, G. Grenier, C. Roy February 2016 Montreal Heart Institute HF Research Aude Turgeon,
TAVR TTE INTERROGATION BY ALAN MATTHEWS
 TAVR TTE INTERROGATION BY ALAN MATTHEWS KEYS TO ACCURATE ASSESSMENT EDWARDS SAPIEN VALVE 3 PHASES OF TAVR TTE Evaluation (Qualifying) Placement (Intraoperative) Follow-up (Post-Op) GOALS High quality TTE
TAVR TTE INTERROGATION BY ALAN MATTHEWS KEYS TO ACCURATE ASSESSMENT EDWARDS SAPIEN VALVE 3 PHASES OF TAVR TTE Evaluation (Qualifying) Placement (Intraoperative) Follow-up (Post-Op) GOALS High quality TTE
Clinical material and methods. Departments of 1 Cardiology and 2 Anatomy, Gaziantep University, School of Medicine, Gaziantep, Turkey
 Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
Interatrial Block and P-Terminal Force: A Reflection of Mitral Stenosis Severity on Electrocardiography Murat Yuce 1, Vedat Davutoglu 1, Cayan Akkoyun 1, Nese Kizilkan 2, Suleyman Ercan 1, Murat Akcay
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Imaging in TAVI. Jeroen J Bax Dept of Cardiology Leiden Univ Medical Center The Netherlands Davos, feb 2013
 Imaging in TAVI Jeroen J Bax Dept of Cardiology Leiden Univ Medical Center The Netherlands Davos, feb 2013 Research grants: Medtronic, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, St Jude, BMS imaging, GE Healthcare,
Imaging in TAVI Jeroen J Bax Dept of Cardiology Leiden Univ Medical Center The Netherlands Davos, feb 2013 Research grants: Medtronic, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, St Jude, BMS imaging, GE Healthcare,
Course Learning Objectives Sunday, February 17 Friday, February 22
 Course Learning Objectives Sunday, February 17 Friday, February 22 1. Define the physical principles of ultrasound technology and its applications for two and threedimensional (2D, 3D) imaging and use
Course Learning Objectives Sunday, February 17 Friday, February 22 1. Define the physical principles of ultrasound technology and its applications for two and threedimensional (2D, 3D) imaging and use
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY. Patient Care. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Patient Care Be able to: Perform and interpret basic TTE and X cardiac Doppler examinations Perform and interpret a comprehensive X TTE and cardiac Doppler examination Perform and interpret a comprehensive
Patient Care Be able to: Perform and interpret basic TTE and X cardiac Doppler examinations Perform and interpret a comprehensive X TTE and cardiac Doppler examination Perform and interpret a comprehensive
TEE Zebras. Case Cardiac Anesthesia Group
 TEE Zebras Edwin G. Avery, IV, M.D., C.P.I. Chief, Division of Cardiac Anesthesia University Hospitals Case Medical Center Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Case Western Reserve University School of
TEE Zebras Edwin G. Avery, IV, M.D., C.P.I. Chief, Division of Cardiac Anesthesia University Hospitals Case Medical Center Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Case Western Reserve University School of
Echocardiography. Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification. In partnership with
 Echocardiography Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification In partnership with Explanatory note & references These guidelines have been developed by the Education Committee of the British Society
Echocardiography Guidelines for Valve and Chamber Quantification In partnership with Explanatory note & references These guidelines have been developed by the Education Committee of the British Society
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis
 JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
Effect of Valve Suture Technique on Incidence of Paraprosthetic Regurgitation and 10-Year Survival
 Effect of Valve Suture Technique on Incidence of Paraprosthetic Regurgitation and 10-Year Survival Sukumaran K. Nair, FRCS (C Th), Gauraang Bhatnagar, MBBS, Oswaldo Valencia, MD, and Venkatachalam Chandrasekaran,
Effect of Valve Suture Technique on Incidence of Paraprosthetic Regurgitation and 10-Year Survival Sukumaran K. Nair, FRCS (C Th), Gauraang Bhatnagar, MBBS, Oswaldo Valencia, MD, and Venkatachalam Chandrasekaran,
ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the Management of Valvular Heart Disease
 ES/EATS Guidelines for the Management of Valvular Heart Disease European Journal of ardio-thoracic Surgery 2012 - Why do we need new guidelines on the management of valvular disease? New evidence has been
ES/EATS Guidelines for the Management of Valvular Heart Disease European Journal of ardio-thoracic Surgery 2012 - Why do we need new guidelines on the management of valvular disease? New evidence has been
TEE Outside of the Cardiac OR
 TEE Outside of the Cardiac OR STEVE GIBSON MD PHD OU DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHEIOLOGY I have no financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY Basic principles
TEE Outside of the Cardiac OR STEVE GIBSON MD PHD OU DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHEIOLOGY I have no financial relationships or conflicts of interest to disclose TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY Basic principles
Conflict of interest: none declared
 The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
The value of left ventricular global longitudinal strain assessed by three-dimensional strain imaging in the early detection of anthracycline-mediated cardiotoxicity C. Mornoş, A. Ionac, D. Cozma, S. Pescariu,
Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies
 Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
Department of cardiac, thoracic and vascular sciences University of Padua, School of Medicine Padua, Italy Right Heart Hemodynamics: Echo-Cath Discrepancies Luigi P. Badano, MD, PhD, FESC, FACC **Dr. Badano
G. AORTIC STENOSIS (AS)
 G. AORTIC STENOSIS (AS) DEFINITION THE FACTS Aortic stenosis (AS) is a narrowing/thickening/obstruction of the aortic valve (AOV) that impedes systolic flow traveling from the left ventricle, through the
G. AORTIC STENOSIS (AS) DEFINITION THE FACTS Aortic stenosis (AS) is a narrowing/thickening/obstruction of the aortic valve (AOV) that impedes systolic flow traveling from the left ventricle, through the
2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Performance Measures
 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Performance Measures Description: This document contains the 18 performance measures approved by CMS for inclusion in the 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry
2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Performance Measures Description: This document contains the 18 performance measures approved by CMS for inclusion in the 2019 Qualified Clinical Data Registry
좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function
 Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
Basic Echo Review Course 좌심실수축기능평가 Cardiac Function Seonghoon Choi Cardiology Hallym university LV systolic function Systolic function 좌심실수축기능 - 심근의수축으로심실에서혈액을대동맥으로박출하는기능 실제임상에서 LV function 의의미 1Diagnosis
TAVR Cases. Disclosures 2/17/2018. February 17, :15 3:30 PM 15 min
 31 st Annual State of the Art Echocardiography San Diego, CA February 17, 2018 3:15 3:30 PM 15 min TAVR Cases Muhamed Sarić MD, PhD, MPA Director of Noninvasive Cardiology Echo Lab Associate Professor
31 st Annual State of the Art Echocardiography San Diego, CA February 17, 2018 3:15 3:30 PM 15 min TAVR Cases Muhamed Sarić MD, PhD, MPA Director of Noninvasive Cardiology Echo Lab Associate Professor
Revealing new insights. irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging. Ultrasound cardiology. irotate and xplane
 Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Successful Transfemoral Edwards Sapien Aortic. Valve Implantation in a Patient with Previous. Mitral Valve Replacement
 Advanced Studies in Medical Sciences, Vol. 2, 2014, no. 1, 37-45 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/asms.2014.31213 Successful Transfemoral Edwards Sapien Aortic Valve Implantation
Advanced Studies in Medical Sciences, Vol. 2, 2014, no. 1, 37-45 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/asms.2014.31213 Successful Transfemoral Edwards Sapien Aortic Valve Implantation
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
How Do I Evaluate a Patient Being Considered for TAVR? Sunday, February 14, :00 11:25 PM 25 min
 2016 ASE State of the Art Echocardiography Course Tucson, AZ How Do I Evaluate a Patient Being Considered for TAVR? Sunday, February 14, 2016 11:00 11:25 PM 25 min 1 M U H A M E D S A R I Ć, M D, P H D
2016 ASE State of the Art Echocardiography Course Tucson, AZ How Do I Evaluate a Patient Being Considered for TAVR? Sunday, February 14, 2016 11:00 11:25 PM 25 min 1 M U H A M E D S A R I Ć, M D, P H D
P = 4V 2. IVC Dimensions 10/20/2014. Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography. The Simplified Bernoulli Equation
 Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography Itzhak Kronzon, MD North Shore LIJ/ Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Disclosure: Philips Healthcare St. Jude Medical The Simplified Bernoulli
Comprehensive Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Echocardiography Itzhak Kronzon, MD North Shore LIJ/ Lenox Hill Hospital New York, NY Disclosure: Philips Healthcare St. Jude Medical The Simplified Bernoulli
M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec 2D: 30 / sec
 M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE Honoraria: Philips Classical M-mode Echocardiography M-Mode offers better time and image resolution. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec
M-Mode Echocardiography Is it still Alive? Itzhak Kronzon, MD,FASE Honoraria: Philips Classical M-mode Echocardiography M-Mode offers better time and image resolution. Sampling Rate M-Mode: 1800 / sec
Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index in Patients With Regional Wall Motion Abnormalities
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2010.40.3.114 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2010 The Korean Society of Cardiology Open Access Segmental Tissue Doppler Image-Derived Tei Index
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency
 Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Uncommon Doppler Echocardiographic Findings of Severe Pulmonic Insufficiency Rahul R. Jhaveri, MD, Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD, FASE, and Itzhak Kronzon, MD, FASE, New York, New York Background: Two-dimensional
Case # 1. Page: 8. DUKE: Adams
 Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
MR echo case. N.Koutsogiannis Department of Cardiology University Hospital Of Patras
 MR echo case N.Koutsogiannis Department of Cardiology University Hospital Of Patras Case A 35 years old male came to the echo lab for a third opinion for his valvulopathy. He reports a long standing MR
MR echo case N.Koutsogiannis Department of Cardiology University Hospital Of Patras Case A 35 years old male came to the echo lab for a third opinion for his valvulopathy. He reports a long standing MR
Exercise Pulmonary Hypertension predicts the Occurrence of Symptoms in Asymptomatic Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation
 Exercise Pulmonary Hypertension predicts the Occurrence of Symptoms in Asymptomatic Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation Julien Magne, PhD, Kim O Connor, MD, Giuseppe Romano, MD, Marie Moonen, MD, Luc A.
Exercise Pulmonary Hypertension predicts the Occurrence of Symptoms in Asymptomatic Degenerative Mitral Regurgitation Julien Magne, PhD, Kim O Connor, MD, Giuseppe Romano, MD, Marie Moonen, MD, Luc A.
Non-invasive estimation of the mean pressure
 Br Heart J 1986;56:45-4 Non-invasive estimation of the mean pressure difference in aortic stenosis by Doppler ultrasound DAG TEIEN, KJELL KARP, PETER ERIKSSON From the Departments of Clinical Physiology
Br Heart J 1986;56:45-4 Non-invasive estimation of the mean pressure difference in aortic stenosis by Doppler ultrasound DAG TEIEN, KJELL KARP, PETER ERIKSSON From the Departments of Clinical Physiology
Aortic stenosis aetiology: morphology of calcific AS,
 How to improve patient selection in aortic stenosis? Fausto J. Pinto, FESC Aortic stenosis aetiology: morphology of calcific AS, bicuspid valve, and rheumatic AS (Adapted from C. Otto, Principles of
How to improve patient selection in aortic stenosis? Fausto J. Pinto, FESC Aortic stenosis aetiology: morphology of calcific AS, bicuspid valve, and rheumatic AS (Adapted from C. Otto, Principles of
PISA Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation. Raymond Graber, MD Cardiac Anesthesia Group University Hospitals Case Medical Center 4/07/2011
 PISA Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation Raymond Graber, MD Cardiac Anesthesia Group University Hospitals Case Medical Center 4/07/2011 Introduction Evaluation of MR. What is PISA? Physiologic basis Issues
PISA Evaluation of Mitral Regurgitation Raymond Graber, MD Cardiac Anesthesia Group University Hospitals Case Medical Center 4/07/2011 Introduction Evaluation of MR. What is PISA? Physiologic basis Issues
Echocardiographic variables associated with mitral regurgitation after aortic valve replacement for aortic valve stenosis
 The Egyptian Heart Journal (2013) 65, 135 139 Egyptian Society of Cardiology The Egyptian Heart Journal www.elsevier.com/locate/ehj www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Echocardiographic variables associated
The Egyptian Heart Journal (2013) 65, 135 139 Egyptian Society of Cardiology The Egyptian Heart Journal www.elsevier.com/locate/ehj www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Echocardiographic variables associated
ENVIRONMENT Operating Room, Simulation Suite, Echo Lab. Operating Room, Simulation Suite. Simulation Suite, Echo Lab.
 Goals and Objectives, Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography, CA-3 year UCSD DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY PERIOPERATIVE TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES, CA-3 YEAR PATIENT
Goals and Objectives, Perioperative Transesophageal Echocardiography, CA-3 year UCSD DEPARTMENT OF ANESTHESIOLOGY PERIOPERATIVE TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES, CA-3 YEAR PATIENT
Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application
 Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application Dr. Bruce Bollen 3D matrix array TEE probes provide options for both 2D and 3D imaging. Indeed, their utility in obtaining multiple
Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application Dr. Bruce Bollen 3D matrix array TEE probes provide options for both 2D and 3D imaging. Indeed, their utility in obtaining multiple
HOW IMPORTANT ARE THESE ECHO MEASUREMENTS ANYWAY?
 HOW IMPORTANT ARE THESE ECHO MEASUREMENTS ANYWAY? John D. Carroll, MD Professor, Director of Interventional Cardiology and Co-Medical Director of the Cardiac and Vascular Center, University of Colorado
HOW IMPORTANT ARE THESE ECHO MEASUREMENTS ANYWAY? John D. Carroll, MD Professor, Director of Interventional Cardiology and Co-Medical Director of the Cardiac and Vascular Center, University of Colorado
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
HEMODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT
 HEMODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT INTRODUCTION Conventionally hemodynamics were obtained by cardiac catheterization. It is possible to determine the same by echocardiography. Methods M-mode & 2D echo alone can provide
HEMODYNAMIC ASSESSMENT INTRODUCTION Conventionally hemodynamics were obtained by cardiac catheterization. It is possible to determine the same by echocardiography. Methods M-mode & 2D echo alone can provide
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease
 Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Tissue Doppler Imaging in Congenital Heart Disease L. Youngmin Eun, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Cardiology, Kwandong University College of Medicine The potential advantage of ultrasound
Prosthetic Mitral Valve Thrombosis: Can Fluoroscopy Predict the Efficacy of Thrombolytic Treatment?
 Prosthetic Mitral Valve Thrombosis: Can Fluoroscopy Predict the Efficacy of Thrombolytic Treatment? Piero Montorsi, MD; Dario Cavoretto, MD; Marina Alimento, MD; Manuela Muratori, MD; Mauro Pepi, MD Background
Prosthetic Mitral Valve Thrombosis: Can Fluoroscopy Predict the Efficacy of Thrombolytic Treatment? Piero Montorsi, MD; Dario Cavoretto, MD; Marina Alimento, MD; Manuela Muratori, MD; Mauro Pepi, MD Background
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure
 Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Introduction to Biomedical Imaging
 Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu Basic principles. Comparison to X-rays Ultrasound > 20kHz
Alejandro Frangi, PhD Computational Imaging Lab Department of Information & Communication Technology Pompeu Fabra University www.cilab.upf.edu Basic principles. Comparison to X-rays Ultrasound > 20kHz
Characteristic Doppler Echocardiographic Pattern of Mitral Inflow Velocity in Severe Aortic Regurgitation
 1712 JACC Vol. 14, No. 7 December 1989: 1712-7 Characteristic Doppler Echocardiographic Pattern of Mitral Inflow Velocity in Severe Aortic Regurgitation JAE K. OH, MD, FACC, LIV K. HATLE, MD, LAWRENCE
1712 JACC Vol. 14, No. 7 December 1989: 1712-7 Characteristic Doppler Echocardiographic Pattern of Mitral Inflow Velocity in Severe Aortic Regurgitation JAE K. OH, MD, FACC, LIV K. HATLE, MD, LAWRENCE
MITRAL STENOSIS. Joanne Cusack
 MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
MITRAL STENOSIS Joanne Cusack BSE Breakdown Recognition of rheumatic mitral stenosis Qualitative description of valve and sub-valve calcification and fibrosis Measurement of orifice area by planimetry
Doppler-Echocardiographic Assessment of Carbomedics Prosthetic Valves in the Mitral Position
 Doppler-Echocardiographic Assessment of Carbomedics Prosthetic Valves in the Mitral Position Chee-Siong Soo, MRCP, Mestres Ca, MD, Monica Tay, Joon-Kuan Yeoh, MRCP, Eugene Sim, FRCS, and M. Choo, FRCP,
Doppler-Echocardiographic Assessment of Carbomedics Prosthetic Valves in the Mitral Position Chee-Siong Soo, MRCP, Mestres Ca, MD, Monica Tay, Joon-Kuan Yeoh, MRCP, Eugene Sim, FRCS, and M. Choo, FRCP,
Title of image and video article Sub-Acute Leaflet Thrombosis: A Reversible Cause of Aortic Stenosis
 Page 1 of 5 Title of image and video article Sub-Acute Leaflet Thrombosis: A Reversible Cause of Aortic Stenosis Authors Athina Chasapi, Adam Hobbs, Theodore Velissaris & Benoy N Shah. Wessex Cardiac &
Page 1 of 5 Title of image and video article Sub-Acute Leaflet Thrombosis: A Reversible Cause of Aortic Stenosis Authors Athina Chasapi, Adam Hobbs, Theodore Velissaris & Benoy N Shah. Wessex Cardiac &
The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation
 Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
Assessment of Diastolic Function The Patient with Atrial Fibrilation Assoc. Prof. Adriana Ilieşiu, FESC University of Medicine Carol Davila Bucharest, Romania Associated Conditions with Atrial Fibrillation
