ANGIOLOGY: HEART AND ARTERIES
|
|
|
- Alban Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 "APPROVED" Head of the Normal Anatomy Department Associate professor D. Volchkevich Discussed at a meeting of the department "03" january 2014, protocol 10 TESTS ON HUMAN ANATOMY FOR PRE-EXAM TESTING OF STUDENTS ANGIOLOGY: HEART AND ARTERIES 1. What are the surfaces of heart can be distinguished? 1. Diaphragmatic; 2. Mediastinal; 3. Pulmonalis; 4. Sternocostal; 2. Specify the elements belonging to blood microcirculatory channel: 1. Venula; 2. Capillaries; 3. Arteriola; 4. Arteriolovenular anastomosis; 3. Where does the fossa ovalis localize? 1. On the interventricular septum; 2. Between aorta and pulmonary trunk at the place of their exit; 3. In interatrial septum at the left; 4. In interatrial septum at the right; 4. Specify the anatomic structures available on an internal surface of the right atrium: 1. Mm. papillares; 2. Mm. pectinati; 3. Trabeculae carneae; 4. Chordae tendineae; 5. Specify anatomic structures, which are part of interventricular septum: 1. Myocardium; 2. Epicardium; 3. Endocardium; 4. Fibrous tissue;
2 6. Specify apertures of vessels, which are available for the right atrium: 1. Aperture of pulmonary trunk; 2. Apertures of pulmonary veins; 3. Aperture of coronal sinus; 4. Apertures of cava veins; 7. Specify the apertures of vessels available for the right ventricle: 1. Aperture of inferior cava vein; 2. Aperture of pulmonary trunk; 3. Apertures of minimus veins; 4. Aperture of an aorta; 8. Specify the apertures of vessels available for the left ventricle: 1. Aperture of coronal sinus; 2. Apertures pulmonary veins; 3. Aperture of an aorta; 4. Aperture of pulmonary trunk; 9. Specify apertures of the vessels belonging to the left atrium: 1. Apertures of pulmonary veins; 2. Apertures of cava veins; 3. Aperture of pulmonary trunk; 4. Aperture of coronal sinus; 10. Specify parts of the heart: 1. Body (corpus); 2. Basis (basis); 3. Isthmus; 4. Apex; 11. Which parts of the heart attach to the tendinous center of the diaphragm? 1. Posterior (inferior) wall of the right atrium; 2. Posterior (inferior) wall of the right ventricle; 3. Anterior wall of the right atrium; 4. Anterior wall of the right ventricle; 12. Specify direction of longitudinal axis of heart: 1. From right to left; 2. From front to back; 3. From top to down; 4. From back to front; 13. Specify coats of heart: 1. Epicardium; 2. Myocardium; 3. Mesocardium; 4. Endocardium; 2
3 14. Specify place of fibrous rings localization: 1. Around of right atrioventricular osthium; 2. Around of left atrioventricular osthium; 3. Around of osthium of inferior cava vein; 4. Around of osthium of pulmonary veins; 15. Specify the location of sinoatrial node of conducting system of heart: 1. Wall of the left atrium; 2. Interatrial septum; 3. Wall of the right atrium; 4. Interventricular septum; 16. What is belong to the conducting system of heart? 1. Crura of atrioventrical bundle; 2. Sinoatrial nodus; 3. Atrioventrical nodus; 4. Vortex of heart; 17. Specify the shape of right ventricle: 1. The shape of cube; 2. The shape of trihedral pyramid; 3. The shape of prism; 4. The shape of the cylinder; 18. Specify the anatomic structures available on internal walls of left ventricle of the heart: 1. Chordae tendinea; 2. Septal papillary muscles; 3. Trabeculae carneae; 4. Posterior papillary muscle; 19. Specify layers of myocardium, which are common for both ventricle of the heart: 1. External layer of longitudinal fibers; 2. Middle layer of circular fibers; 3. Superficial layer of transversal fibers; 4. Internal layer of longitudinal fibers; 20. What is the name of valve closing the right atrioventricular osthium? 1. Valva atrioventricularis dextra; 2. Valva mitralis; 3. Valva tricuspidalis; 4. Valva bicuspidalis; 21. Specify cuspises of left atrioventrical valve of heart: 1. Back; 2. Septal; 3. Lateral; 4. Anterior; 3
4 22. Between which anatomical structures does the transverse sinus of pericardium localize? 1. Anterior surface of the left atrium; 2. Anterior surface of the right ventricle; 3. Initial department of the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk; 4. Superior vena cava; 23. Specify anatomical structures, which limit the oblique sinus of pericardium: 1. Vv. pulmonales sin. 2. Vv. pulmonales dext. 3. V. cava superior; 4. V. cava inferior; 24. Which anatomic structures does the epicardium cover? 1. Initial departments of ascending aorta; 2. Initial departments of pulmonary trunk; 3. Final departments of cava veins; 4. Final departments of pulmonary veins; 25. Specify skeletotopy of the apex of heart in adult person: 1. Cartilage of IV left rib; 2. Left IV rib, 6-7 cm from sternum; 3. Left V intercostals space, 1-1,5 cm to the right from midclavian line; 4. Left V rib on midclavian line; 26. What is the position of heart in asthenic people? 1. Vertical; 2. Oblique; 3. Sagittal; 4. Horizontal (transversal); 27. What is the position of heart in normosthenic people? 1. Vertical; 2. Horizontal (transversal); 3. Oblique; 4. Horizontal (sagittal); 28. Specify skeletotopy of the superior border of heart in adult person: 1. The line connecting the upper edges of cartilages of V ribs; 2. The line connecting the upper edges of cartilages of II ribs; 3. The line connecting the upper edges of cartilages of III ribs; 4. The line connecting the upper edges of cartilages of IV ribs; 29. Where do the coronal arteries of heart begin? 1. Arcus aortae; 2. Truncus pulmonalis; 3. Ventriculus sinister; 4. Bulbus aortae; 4
5 30. What are the largest branches of the right coronal artery? 1. R. interventricularis anterior; 2. R. circumflexus; 3. R. interventricularis posterior; 4. R. septalis anterior; 31. Which structures of heart does the right coronary artery blood supply? 1. Posterior part of interventrical septum; 2. Anterior part of interventrical septum; 3. Posterior papillary muscle of right ventricle; 4. Posterior papillary muscle of left ventricle; 32. Name the largest branches of the left coronal artery: 1. R. circumflexus; 2. R. interventricularis anterior; 3. R. interventricularis posterior; 4. R. septalis posterior; 33. Which structures of heart does the left coronary artery blood supply? 1. Interventricular septum; 2. Anterior wall of right ventricle; 3. Walls of the left atrium; 4. Posterior wall of left ventricle; 34. Specify types of blood supply of heart: 1. Dextracoronal; 2. Sinistrocoronal; 3. Mixed; 4. Main; 35. Specify a place of projection of the aortic valve: 1. Level of left II costal cartilage; 2. Sternum at level of III ribs; 3. Level of right II costal cartilage; 4. Level of IV left costal cartilage; 36. Specify branches of the arch of aorta: 1. A. subclavia sinistra; 2. A. subclavia dextra; 3. A. carotis communis sinistra; 4. Truncus brachiocephalicus; 37. Specify branches of the thoracic part of aorta: 1. Aa. intercostales anteriores; 2. Aa. intercostales posteriores; 3. Rr. bronchiales; 4. Aa. phrenicae inferiores; 5
6 38. Specify visceral branches of the thoracic part of aorta: 1. Rr. bronchiales; 2. Rr. esophageales; 3. Rr. pericardiaci; 4. Rr. mediastinales; 39. Specify parts of the descending aorta: 1. Bulbus aortae; 2. Pars cervicalis; 3. Pars thoracica; 4. Pars abdominalis; 40. At which level does the aorta bifurcate? 1. L-III; 2. L-IV; 3. L-V; 4. L-I; 41. Specify the location of ligamentum arteriosum: 1. Between right and left pulmonary arteries; 2. Between aorta and superior vena cava; 3. Between descending aorta and left pulmonary vein; 4. Between aorta and bifurcation of pulmonary trunk; 42. Which blood vessels supply walls of the pharynx? 1. Branches of the inferior thyroid artery; 2. Branches of maxillary artery; 3. Branches of lingual artery; 4. Branches of facial artery; 43. Specify anterior branches of the external carotid artery: 1. A. facialis; 2. A. lingualis; 3. A. maxillaries; 4. A. thyroidea superior; 44. Which anatomical structures does the posterior auricular artery supply? 1. Bony and membranous labyrinths; 2. Skin of the auricle; 3. Mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity; 4. Cells of the mastoid process; 45. Specify terminal branches of the external carotid artery: 1. A. temporalis superficialis; 2. A. maxillaries; 3. A. supraorbitalis; 4. A. infraorbitalis; 6
7 46. From which artery does the middle meningeal artery begin? 1. A. infraorbitalis; 2. A. carotis interna; 3. A. maxillaris; 4. A. occipitalis; 47. Specify branches of maxillary artery in its second department: 1. A. masseterica; 2. Rr. pterygoidei; 3. A. temporalis profunda; 4. A. buccalis; 48. Specify branches of maxillary artery in its third department: 1. A. sphenopalatina; 2. A. meningea media; 3. A. palatina descendens; 4. A. infraorbitalis; 49. Which arteries supply blood to the medial and lateral pterigoid muscles? 1. A. maxillaris; 2. A. lingualis; 3. A. thyroidea superior; 4. A. temporalis superficialis; 50. Where does the superior alveolar artery begin? 1. A. maxillaris; 2. A. facialis; 3. A. ophthalmica; 4. A. infraorbitalis; 51. Specify branches of the superior thyroid artery: 1. A. laryngea superior; 2. A. laryngea inferior; 3. A. laryngea anterior; 4. A. laryngea posterior; 52. Specify branches of the thyrocervical trunk: 1. A. suprascapularis; 2. A. cervicalis profunda; 3. A. thyroidea inferior; 4. A. cervicalis ascendens; 53. Specify sources of blood supply of esophagus: 1. Branches of the left gastric artery; 2. Branches of the inferior thyroid artery; 3. Branches of the superior thyroid artery; 4. Visceral branches of the thoracic part of aorta; 7
8 54. Specify anatomical structures, through which the internal carotid artery pass: 1. Trigonum caroticum; 2. Canalis caroticus; 3. Spatium caroticum; 4. Sulcus caroticus; 55. Which branches of ophthalmic artery participate in blood supply of the nasal cavity? 1. A. supratrochlearis; 2. A. ethmoidalis anterior; 3. A. lacrimalis; 4. A. ethmoidalis posterior; 56. Specify branches of the ophthalmic artery: 1. A. lacrimalis; 2. A. centralis retinae; 3. A. supratrochlearis; 4. A. infraorbitalis; 57. Which arteries does the anterior communicans artery connect? 1. Aa. cerebri anterior et media; 2. Aa. cerebri media et posterior; 3. Aa. cerebri anteriores dextra et sinistra; 4. Aa. carotis internae dextra et sinistra; 58. Specify the branches arising from the first portion of subclavian artery: 1. A. transversa colli; 2. A. thoracica interna; 3. Truncus thyrocervicalis; 4. A. cervicalis profunda; 59. Specify structures through which the vertebral artery passes: 1. Jugular foramen; 2. Foramen of transverse processes; 3. Atlanto-occipital membrane; 4. Foramen rotundum; 60. Specify branches of the intracranial part of vertebral artery: 1. A. spinalis anterior; 2. A. cerebri posterior; 3. A. cerebelli posterior inferior; 4. Aa. cerebellares superiores; 61. Specify terminal branches of the basilar artery: 1. Aa. cerebri mediae; 2. Aa. cerebri posteriores; 3. Aa. cerebellares; 4. Aa. insulae; 8
9 62. Which arteries take part in formation of Willi s circle of brain? 1. A. communicans anterior; 2. Aa. cerebri anteriores; 3. Aa. cerebri posteriores; 4. Aa. chorioideae anteriores; 63. Specify branches of the third portion of subclavian artery: 1. A. transversa colli; 2. Truncus costocervicalis; 3. A. supraclavicularis; 4. A. cervicalis superficialis; 64. Specify branches of the second portion of subclavian artery: 1. A. cervicalis superficialis; 2. A. supraclavicularis; 3. Truncus costocervicalis; 4. Truncus thyrocervicalis; 65. Specify vessels, which supply blood to the deltoid muscle: 1. A. subscapularis; 2. A. thoracoacromialis; 3. A. circumflexa humeri posterior; 4. A. transversa colli; 66. Specify branches of the axillary artery in the pectoral triangle: 1. A. subscapularis; 2. A. thoracoacromialis; 3. A. thoracica lateralis; 4. A. thoracica superior; 67. Specify branches of the axillary artery in the subpectoral triangle: 1. A. circumflexa humeri posterior; 2. A. circumflexa humeri anterior; 3. A. subscapularis; 4. A. thoracoacromialis; 68. Which blood vessels supply a shoulder joint? 1. A. thoracoacromialis; 2. Trunсus costocervicalis; 3. A. subscapularis; 4. A. circumflexa humeri posterior; 69. Specify branches of the a. profunda brachii: 1. A. collateralis media; 2. A. recurrens radialis; 3. A. collateralis ulnaris inferior; 4. A. collateralis radialis; 9
10 70. Specify branches of the brachial artery: 1. A. circumflexa humeri posterior; 2. A. circumflexa humeri anterior; 3. A. collateralis ulnaris superior; 4. A. profunda brachii; 71. Which branch of the radial artery participate in formation of arterial network of elbow joint? 1. A. collateralis radialis; 2. A. recurrens radialis; 3. A. collateralis media; 4. A. interossea communis; 72. Which branch of the ulnar artery participate in formation of arterial network of elbow joint? 1. A. collateralis ulnaris inferior; 2. A. collateralis media; 3. A. collateralis ulnaris superior; 4. A. recurrens ulnaris; 73. Specify branches of the ulnar artery: 1. A. collateralis media; 2. A. interossea communis; 3. R. carpeus palmaris; 4. A. collateralis ulnaris inferior; 74. Which arteries participate in formation of deep palmar arch? 1. A. radialis; 2. R. palmaris a. radialis; 3. A. ulnaris; 4. R. palmaris profundus a. ulnaris; 75. Specify branches of the radial artery in the radiocarpal joint region: 1. R. palmaris superficialis; 2. R. palmaris profundus; 3. A. interossea; 4. A. collateralis radialis; 76. Through which opening does the a. circumflexa scapula pass? 1. Foramen quadrilaterum; 2. Foramen ovale; 3. Foramen trilaterum; 4. Foramen spinosum; 10
11 77. Specify branches of the abdominal part of aorta: 1. Aa. lumbales; 2. Aa. epigastricae inferiores; 3. Aa. suprareniales mediae; 4. Aa. phrenicae superiores; 78. Where do the arteries to adrenal glands begin? 1. Aa. pancreaticoduodenales; 2. Aa. phrenicae inferiores; 3. Aa. renales; 4. Pars abdominalis aortae; 79. Specify unpaired visceral branches of the abdominal part of aorta: 1. Truncus celiacus; 2. A. rectalis superior; 3. A.mesenterica inferior; 4. A. colica media; 80. Specify branches of coeliac trunk: 1. A. gastrica sinistra; 2. A. gastrica dextra; 3. A.mesenterica superior; 4. A. lienalis; 81. Which anatomical structures does the lienalis artery blood supply? 1. Omentum majus; 2. Ventriculus; 3. Omentum minus; 4. Pancreas; 82. Specify branches of the common hepatic artery: 1. A. gastroepiploica dextra; 2. A. gastroepiploica sinistra; 3. A. gastroduodenalis; 4. A. gastrica sinistra; 83. Specify branches of gastroduodenal artery: 1. A. gastroepiploica sinistra; 2. A. suprarenalis media; 3. A. gastroepiploica dextra; 4. A. gastrica dextra; 84. Specify the position of a. hepatica propria in the hepatoduodenal ligament: 1. Extreme right position; 2. Extreme left position; 3. Middle position; 4. Extreme inferior position; 11
12 85. Specify organs, which the superior mesenteric artery blood supplies: 1. Duodenum; 2. Pancreas; 3. Jejunum; 4. Cecum; 86. Which anatomical structures does the a. colica media blood supply? 1. Descending colon; 2. Sigmoid colon; 3. Ascending colon; 4. Transverse colon; 87. Which anatomical structures does the inferior mesenteric artery blood supply? 1. Rectum; 2. Sigmoid colon; 3. Descending colon; 4. Omentum majus; 88. Where do the rectal arteries begin? 1. Pars abdominalis aortae; 2. A. iliaca communis; 3. A. iliaca interna; 4. A. mesenterica inferior; 89. Specify anatomic structures, which the a. sacralis lateralis blood supplies: 1. Articulatio coxae; 2. Mm. obturatorii; 3. M. levator ani; 4. M. piriformis; 90. Where do the ovarian arteries begin? 1. Pars abdominalis aortae; 2. A. iliaca interna; 3. A. iliaca externa; 4. A. umbilicalis; 91. Which organs are supplied by the inferior vesical artery in male? 1. Rectum; 2. Prostata; 3. Vesiculae seminales; 4. Ureter; 92. Specify anatomical structures, which are supplied by the internal pudendal artery: 1. Rectum; 2. Perineum; 3. Penis; 4. Hip joint; 12
13 93. Through which anatomical structures does the superior gluteal artery pass? 1. Foramen infrapiriforme; 2. Foramen ischiadicum minus; 3. Foramen suprapiriforme; 4. Trigonum lumbale; 94. Specify anatomical structures through which the femoral artery passes: 1. Femoral canal; 2. Femoral triangle; 3. Adductorius canal; 4. Vascular lacuna; 95. Which anatomical structures does the obturatory artery blood supply? 1. External obturatory muscle; 2. Adductorius muscles of hip; 3. Hip joint; 4. Sartorius muscle; 96. Specify anatomical structures through which the a. tibialis posterior passes: 1. Superior musculoperoneal canal; 2. Cruropopliteal canal; 3. Adductorius canal; 4. Plantar canal; 97. Which anatomical structures does the a. tibialis anterior blood supply? 1. Knee joint; 2. Long extensor of the fingers of foot; 3. Distal interfibular connection; 4. Anterior tibial muscle; 98. Specify the arteries participating in formation of the articulate network of knee: 1. A. genus superior lateralis; 2. A. genus anterior; 3. A. genus superior medialis; 4. A. recurrens tibialis anterior; 99. Where does the fibular artery begin? 1. A. tibialis anterior; 2. A. poplitea; 3. A. tibialis posterior; 4. A. recurrens tibialis posterior; 100. Specify arteries, which participate in formation of the vertical arch on foot: 1. A. arcuata; 2. A. plantaris profundus; 3. A. plantaris medialis; 4. Arcus plantaris; 13
14 Key to the test on Angiology: heart and arteries
15 15
16 16
Latin. VASA REGIONIS PELVINAE 72 A. et V. iliaca communis 73 A. et V. iliaca externa 74 A. sacralis mediana 75 A. et V.
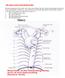
 G30 Latin VASA CAPITIS et CERVICIS 1 V. frontalis 2 V. temporalis superficialis 3 A. temporalis superficialis 3 a A. maxillaris 4 A. occipitalis 5 A. supratrochlearis 6 A. et V. angularis 7 A. et V. facialis
G30 Latin VASA CAPITIS et CERVICIS 1 V. frontalis 2 V. temporalis superficialis 3 A. temporalis superficialis 3 a A. maxillaris 4 A. occipitalis 5 A. supratrochlearis 6 A. et V. angularis 7 A. et V. facialis
Arteriae Venulae Tunica intima Arteriolae Venae Tunica media. (sinusoids) Vasa vasorum Collaterals Anastomoses
 ARTERIES Arteriae Venulae Tunica intima Arteriolae Venae Tunica media Vasa capillaria Tunica adventitia (sinusoids) Vasa vasorum Collaterals Anastomoses Collaterals Anastomosis TRUNCUS PULMONALIS a. pulmonalis
ARTERIES Arteriae Venulae Tunica intima Arteriolae Venae Tunica media Vasa capillaria Tunica adventitia (sinusoids) Vasa vasorum Collaterals Anastomoses Collaterals Anastomosis TRUNCUS PULMONALIS a. pulmonalis
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Structural plan of blood vessels
 The blood vessels 1. The structure of the blood vessels arteries, capillaries, veins 2. Vessels of the pulmonary circuit the pulmonary trunk 3. Aorta an overview 4. Arteries of the head and neck 5. Arteries
The blood vessels 1. The structure of the blood vessels arteries, capillaries, veins 2. Vessels of the pulmonary circuit the pulmonary trunk 3. Aorta an overview 4. Arteries of the head and neck 5. Arteries
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
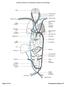
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
Anuli fibrosi Cartilago cordis (eq, ca, su) Ossa cordis (bo) Myocardium Nodus sinuatrialis Nodus atrioventricularis Fasciculus atrioventricularis
 ANGIOLOGIA PERICARDIUM Pericardium fibrosum Lig. sternopericardiacum (eq, bo) Lig. phrenicopericardiacum (ca, su) Pericardium serosum Lamina parietalis Lamina visceralis [=Epicardium] Cavum pericardii
ANGIOLOGIA PERICARDIUM Pericardium fibrosum Lig. sternopericardiacum (eq, bo) Lig. phrenicopericardiacum (ca, su) Pericardium serosum Lamina parietalis Lamina visceralis [=Epicardium] Cavum pericardii
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Lab 6: Blood. BIO104 Laboratory Handouts 147. Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics. 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition -
 147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
MODUL 3 TASK 1. Systemic (greater) and pulmonary (lesser) circulation. The Heart: topography of the heart, chambers and valves of the heart.
 MODUL 3 TASK 1. Systemic (greater) and pulmonary (lesser) circulation. The Heart: topography of the heart, chambers and valves of the heart. 1. During the percussion of the patient s chest the doctor examines
MODUL 3 TASK 1. Systemic (greater) and pulmonary (lesser) circulation. The Heart: topography of the heart, chambers and valves of the heart. 1. During the percussion of the patient s chest the doctor examines
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Cardiovascular System. Chapter 22
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART BLOOD
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector. Section I
 Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium. Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying
 Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Middle mediastinum---- heart & pericardium Dep. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Subdivisions of the mediastinum Contents of Middle mediastinum Heart Pericardium: a serous sac enclosing
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE
 TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system
 Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Surface anatomy of Cardiovascular system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The lines cover the front, side, and back of the thorax Midsternal
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
ANATDMY. lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi
 ANATDMY 27 lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Pericardium A double-walled fibroserous conical-shaped sac, within middle mediastinum. Enclose the heart and roots of its large vessels. Vagus nerves
ANATDMY 27 lecture # : Date : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Pericardium A double-walled fibroserous conical-shaped sac, within middle mediastinum. Enclose the heart and roots of its large vessels. Vagus nerves
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES. The theme of the lesson The vessels of the upper limb.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 The theme of the lesson The vessels of the upper limb. Course Faculties І Medical
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 The theme of the lesson The vessels of the upper limb. Course Faculties І Medical
The Cardiovascular System
 C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES. The theme of the lesson The vessels of the lower limb.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 The theme of the lesson The vessels of the lower limb. Course Faculties І Medical
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of Human Anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 The theme of the lesson The vessels of the lower limb. Course Faculties І Medical
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Biology 105 Human Biology QZM CVS. Cardiovascular System. Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers
 Cardiovascular System Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers 1. The heart and pericardium are located within the and medial to the A) pleural cavities B) peritoneal cavity C) cardiac skeleton D) mediastinum
Cardiovascular System Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers 1. The heart and pericardium are located within the and medial to the A) pleural cavities B) peritoneal cavity C) cardiac skeleton D) mediastinum
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Misc Anatomy. Upper Limb! 2. Lower Limb! 5. Venous Drainage! Head & neck! 8
 Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
2) Gas exchange occurs in all the below EXCEPT: A) alveolar sac B) respiratory bronchioles C) alveolar ducts D) terminal bronchioles
 Exam 2 Version A Anatomy 125 Spring 2011 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The median cubital vein connects the and veins. A)
Exam 2 Version A Anatomy 125 Spring 2011 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The median cubital vein connects the and veins. A)
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI
 IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Bogomolets National Medical University. Department of Human Anatomy GUIDLINES
 Bogomolets National Medical University Department of Human Anatomy GUIDLINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Modul 2 Content module 2 Topic of the lesson The abdominal aorta. The arteries of the pelvis.
Bogomolets National Medical University Department of Human Anatomy GUIDLINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Modul 2 Content module 2 Topic of the lesson The abdominal aorta. The arteries of the pelvis.
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Read Me. covering the Heart Anatomy. Labs. textbook. use. car: you
 Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
A closed system of the heart/blood. Function: The heart pumps blood. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body
 A closed system of the heart/blood The heart pumps blood It is no more than a transportation pump Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body MILES of blood vessels intricate network At
A closed system of the heart/blood The heart pumps blood It is no more than a transportation pump Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body MILES of blood vessels intricate network At
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements
 Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: papillary muscle Trabeculae Carneae chordae tendineae
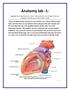 Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Anatomy lab -1- Imp note: the arrangement of this sheet is different than the lab recording, it has been arranged in a certain way to make it easier to study. When you open the left ventricle you can see
Heart & Pericardium. December, 2015
 Heart & Pericardium December, 2015 2 Pericardium Definition Fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and the roots of great vessels Function Restrict excessive movements of the heart as a whole Serve as
Heart & Pericardium December, 2015 2 Pericardium Definition Fibro-serous sac that encloses the heart and the roots of great vessels Function Restrict excessive movements of the heart as a whole Serve as
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
BIOL 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam IV FA 2018 page 1 of 8
 BIOL 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam IV FA 2018 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then you
BIOL 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam IV FA 2018 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then you
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Anatomy Midterm. 1- In gametogenesis, diploid primary Oocyte cell inter the process of meiosis to produce? b. Haploid egg cell*
 Anatomy Midterm 1- In gametogenesis, diploid primary Oocyte cell inter the process of meiosis to produce? b. Haploid egg cell* 2- Spermatogenesis is a process in which? d. Spermatogonial cells produces
Anatomy Midterm 1- In gametogenesis, diploid primary Oocyte cell inter the process of meiosis to produce? b. Haploid egg cell* 2- Spermatogenesis is a process in which? d. Spermatogonial cells produces
Chapter 13. Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs. Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament
 Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament Plan: 1. Variations of the branching pattern of the aortic arch 2. Arterial
Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament Plan: 1. Variations of the branching pattern of the aortic arch 2. Arterial
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
The Cardiovascular System The Manila Times College of Subic Prepared by: Stevens B. Badar, RN, MANc THE HEART Anatomy of the Heart Location and Size approx. the size of a person s fist, hollow and cone-shaped,
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
The Cardiovascular System
 11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
