The Efficacy of Thoracic Ultrasonography in Postoperative Newborn Patients after Cardiac Surgery
|
|
|
- Bennett Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Efficacy of Thoracic Ultrasonography in Postoperative Newborn Patients after Cardiac Surgery Erkut Ozturk 1,2, MD; Ibrahim Cansaran Tanidir 1, MD; Okan Yildiz 3, MD; Yakup Ergul 1, MD; Alper Guzeltas 1, MD DOI: / Abstract Objective: In this study, the efficacy of thoracic ultrasonography during echocardiography was evaluated in newborns. Methods: Sixty newborns who had undergone pediatric cardiac surgery were successively evaluated between March 1, 2015, and September 1, Patients were evaluated for effusion, pulmonary atelectasis, and pneumothorax by ultrasonography, and results were compared with X-ray findings. Results: Sixty percent (n=42) of the cases were male, the median age was 14 days (2-30 days), and the median body weight was 3.3 kg ( kg). The median RACHS-1 score was 4 (2-6). Atelectasis was demonstrated in 66% (n=40) of the cases. Five of them were determined solely by X-ray, 10 of them only by ultrasonography, and 25 of them by both ultrasonography and X-ray. Pneumothorax was determined in 20% (n=12) of the cases. Excluding one case determined by both methods, all of the 11 cases were diagnosed by X-ray. Pleural effusion was diagnosed in 26% (n=16) of the cases. Four of the cases were demonstrated solely by ultrasonography, three of them solely by X-ray, and nine of the cases by both methods. Pericardial effusion was demonstrated in 10% (n=6) of the cases. Except for one of the cases determined by both methods, five of the cases were diagnosed by ultrasonography. There was a moderate correlation when all pathologies evaluated together (k=0.51). Conclusion: Thoracic ultrasonography might be a beneficial non-invasive method to evaluate postoperative respiratory problems in newborns who had congenital cardiac surgery. Keywords: Pulmonary Atelectasis. Cardiac Surgical Procedures. Infant, Newborn. Postoperative Care. Ultrasonography. Abbreviations, acronyms & symbols CT ICU NPV PPV RACHS-1 USG INTRODUCTION = Computerized tomography = Intensive care unit = Negative predictive value = Positive predictive value = Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery-1 = Ultrasonography The diagnosis of respiratory complications such as pleural effusion, pulmonary atelectasis, and pneumothorax are important in postoperative management of neonates after cardiac surgery. Imaging techniques are as well used verification of correct positions of chest tubes, central venous lines, and endotracheal tubes. X-ray is the most frequently used method in differential diagnosis of these intrathoracic pathologies, but radiation exposure due to repetitive examination might have hazardous effect for neonates [1-3]. Radiation dose reduction is especially important for newborns, as they are more sensitive to harmful effects of ionizing radiation. Considering the long-life expectancy of newborns risk for development of immune dysfunction, cataract and malignancy increased after radiation exposure. Therefore, every effort should be made to minimize radiation exposure whenever possible, especially in neonatal period [4]. Thorax ultrasonography (USG) is fast, repeatable, and harmless. The use of thorax USG in cardiac intensive care units (ICU) is steadily increasing. However, little data is available concerning the pediatric and neonatal populations [4,5]. 1 Department of Pediatric Cardiology, Istanbul Saglik Bilimleri University Istanbul Mehmet Akif Ersoy Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Education and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey. 2 Istanbul Gelisim University, Istanbul, Turkey. 3 Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Istanbul Saglik Bilimleri University Istanbul Mehmet Akif Ersoy Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Education and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey. This study was carried out at the Department of Pediatric Cardiology, Istanbul Saglik Bilimleri University Mehmet Akif Ersoy Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Education and Research Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey. No financial support. No conflict of interest. Correspondence Address: Erkut Ozturk İstanbul Sağlık Bilimleri Universitesi Mehmet Akif Ersoy Eğitim Araştırma Hastanesi, İstasyon Mahallesi İstanbul Caddesi Bezirganbahçe Mevki Küçükçekmece- İstanbul cansaran@yahoo.com Article received on January 24 th, Article accepted on April 2 nd,
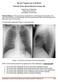
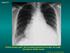
2 In this study, the efficiency of thorax USG during echocardiography was evaluated in postoperative neonates. METHODS Sixty neonates operated on between March 1, 2015, and September 1, 2015, were included in the study. The study was approved by the local ethics committee. A routine chest X-ray was performed on each of the patients every morning after the operation during their ICU stay, along with echocardiography and thorax USG for the evaluation of pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, atelectasis, and pneumothorax. USG and X-ray findings were compared. Antero-posterior bedside chest radiographs were obtained using portable X-ray equipment. Atelectasis was identified as an essentially homogenous opacity with loss of normal radiolucency. Pleural effusion in the supine position was considered as an increased homogenous density superimposed over lung fields. Pneumothorax was identified by an increased radiolucency without lung markings in the costophrenic angle. Pericardial effusion was suspected when the X-ray showed an enlarged cardiac silhouette with or without an epicardial fat-pad sign and with lungs typically clear (Figure 1A). Thorax USG was performed by a single pediatric cardiac intensivist (EO) skilled in echocardiographic examinations, using a Vivid S5 (GE, Vivid S5, Norway) with 7-MHz transducers. Examination was performed according to the literature (Figure 1B). Exclusion criteria included congenital pulmonary problems, premature birth, and neurological problems causing respiratory distress. The data were collected from the medical records of the pediatric cardiovascular surgery ICU. The data reviewed included age, sex, weight, and the type and diagnosis of congenital anomalies. The operative data included lesion and type of repair by Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery-1 (RACHS-1) risk category [6]. Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS, Chicago, Il, USA) version 15.0 for Windows. The descriptive analysis (frequency, median and range) was used to identify the general and specific features of the studied sample. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. To assess the agreements of thorax ultrasound with chest X-ray, Cohen s kappa coefficient ( k ) statistics were used, with k values 0 as indicating no agreement and as none to slight, as fair, as moderate, as substantial, and as almost perfect agreement [7]. RESULTS The majority, 60% (n=36) of the patients were male. Median age was 14 days (2-30 days), and median weight was 3.3 kg ( kg). Median RACHS-1 score was 4 (2-6). The demographic features are listed in Table 1. Atelectasis was demonstrated in 66% (n=40) of the cases. Five of the atelectasis cases were demonstrated only by X-ray, 10 of them by USG, and 25 of them both by X-ray and USG. Pneumothorax was observed in 20% (n=12) of the cases. While 11 of them were demonstrated only by X-ray, one of them was discerned both by X-ray and USG. Pleural effusion was demonstrated in 26% (n=16) of the cases. Four of these were demonstrated only by USG, three of them by X-ray, and nine of them both by X-ray and USG. Pericardial effusion was demonstrated in 10% (n=6) of the cases. While one of the pericardial effusion cases was demonstrated both by X-ray and USG, the remaining five were diagnosed by USG. Fig. 1 - A 19-day old patient, operated for coarctation of aorta, on the 5 th postoperative day. A) Chest X-ray revealed increased opacity on the left lung and B) Thorax USG showed lung consolidation with clearly demarcated borders. 284
3 Table 1. General clinical characteristics of the cases. Characteristic Total (n=60) Age, day, median (range) 14 (2-30) Male, n (%) 36 (60) BMI (kg/m 2 ) 0.2 ( ) Weight, kg, median (range) 3.3 ( ) Cardiac Pathology HLHS 12 TOF 3 PDA 2 TGA 11 Aortic coarctation 8 TAPVR 5 Truncus arteriosus 3 Pulmonary atresia 7 Complex cardiac pathology 9 RACHS-1 Undefined HLHS=hypoplastic left heart syndrome, PDA=patent ductus arteriosus; TGA=transposition of the great arteries; TOF=Tetralogy of Fallot; TAPVD=total abnormal pulmonary venous drainage, RACHS-1=risk adjustment for congenital heart surgery Three lung pathologic changes and pericardial effusion were found. There was a moderate correlation between abnormalities detected by thorax USG and X-ray (k=0.51). When thorax USG and X-ray were compared separately for different pathologies, the k was 0.64 for atelectasis, 0.22 for pneumothorax, 0.68 for pleural effusion and 0.28 for pericardial effusion. The evaluation of the presence of atelectasis, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, and pericardial effusion are listed in Table 2. DISCUSSION The benefits of utilizing thorax USG in emergency departments and ICU was supported by multiple studies [4,8-10]. In contrast, there is limited data about using thorax USG after congenital heart surgery in newborns. In this study, the efficacy of thorax USG in determining respiratory complications after congenital heart surgery in newborns was compared with that of a chest X-ray. This study s results indicate that thorax USG is both efficient and useful in this condition. This is the first comprehensive study about this topic in the literature to our knowledge. Atelectasis is a clinical condition, particularly observed frequently in neonates and children who underwent congenital heart surgery. This morbidity can be associated with excessive and viscous pulmonary secretions, and it presents with associated respiratory symptoms. Accumulation of mucus causes susceptibility to pulmonary and systemic infections, causing prolonged need for mechanical ventilation and hospitalization [11,12]. The sensitivity and accuracy of USG in determining consolidation or atelectasis is reported as % and %, respectively [8,13]. Atelectasis was the most common respiratory complication and was determined in 66% of the cases in the study. Atelectasis was shown in 88% of patients by USG and in 75% by X-ray. Although atelectasis was more frequently diagnosed by USG, imaging of right and left upper lobe atelectasis were Table 2. The evaluation of chest X-ray and USG of the pathologies. Observed problem Only X-ray Only USG USG and X-ray Atelectasis Right apical Right basal Left apical Left basal Pneumothorax 11-1 Right 8-0 Left 3-1 Pleural Effusion Right Left Pericardial effusion
4 difficult. Atelectasis could not be demonstrated in 60% (n=5) of the cases with right upper lobe atelectasis and 40% (n=5) of the cases with left upper lobe atelectasis. Pneumothorax is defined as the presence of air within the pleural space that prevents full expansion of the lung. Pneumothorax may progress and cause hemodynamic instability, especially in patients receiving positive pressure ventilation [4,14]. In the literature, comparing the efficiency of X-ray and USG in determining pneumothorax was found 98% sensitivity, 99% specificity, 98% positive predictive value (PPV), and 99% negative predictive value (NPV) for USG, whereas the results were 75%, 100%, 100%, and 90% for X-ray, respectively [13]. In a study including 126 patients with pneumothorax due to different etiologies (range 2 months-88 years) efficiency of USG in determining pneumothorax was compared with thorax computerized tomography (CT). The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, PPV, and NPV of chest USG was 89%, 88.5%, 88.9%, 96.7%, and 67.6%, respectively [15]. X-ray was more diagnostic than USG for the demonstration of pneumothorax. Only 8% of the cases with pneumothorax (n=12) could be diagnosed by USG. The lack of experience in determining, localizing, and classifying pneumothorax might be the underlying reason in this study. The other most common pathology after cardiac surgery is pleural effusion [3,16]. The compression effect of the effusion leads to different degrees of aeration, even complete loss of alveolar aeration of that particular lung area. Out of the fluid collection, the gradual restoration of the aeration in concordance with gradual manifestation of this consolidative process is often seen. This feature may lead to differentiate the compressive atelectasis from pneumonia [17]. Vezzani et al. [13] demonstrated 100% sensitivity and 99% diagnostic accuracy of chest ultrasound in their series. The false positive result was probably due to the presence of a small pleural effusion not identified by chest X-ray. In this study, pleural effusion was demonstrated in 16 patients; 82% of them were diagnosed by USG and 75% by X-ray. USG was better than X-ray for the diagnosis of pericardial effusion [1,4,17]. Only 16% of the cases (n=1) could be diagnosed by X-ray. Results were similar for both methods for the diagnosis of pleural effusion. Cost analysis of X-ray and ultrasonography also were compared, resulting in slightly lower costs for ultrasonography, but with a considerable advantage in terms of reduction of ionizing radiation exposure for both patients and staff [10,17]. X- ray has certain limitations including risks of radiation exposure, high inter-observer and intra-observer variations. USG is a relatively smaller device that makes point of care more feasible. USG is easy, rapid, portable and repeatable. The USG has also shown less inter and intra-observer variations. Learning curve of techniques and interpretations of USG is simple and fast [18]. The sensitivity, specificity, inter and intra-observer variability were found different in a small number of pediatric studies that compare USG and X-ray to determine the lung pathologies [5,18]. Yadav et al. [19] evaluated 118 community-acquired pneumonia cases age between 2-59 months old with X-ray and USG. Abnormal X-ray were found in 101 (85.6%) and abnormal USG in 105 (89%) children. In diagnosing the specific radiological type of pneumonia, very good concordance (Kappa=0.7) was found between X-ray and USG. Kappa was found 0.9 especially in diagnosis of pleural effusion. In the present study, there was a moderate relation (k=0.51) between USG and X-ray in evaluation of all of the pathologies. The concordance relation was much higher in pleural effusion (k=0.68) and atelectasis (k=0.64) than pneumothorax (k=0.22) and pericardial effusion (k=0.28). Limitation The current study was conducted at a single center with a limited number of cases. It would be more valuable to study this topic in a prospective randomized protocol with a larger patient population. Although computerized tomography (CT) is more accurate and almost a gold standard method in evaluation of thorax pathologies technical difficulties in practice, financial cost and radiation exposure prevent its routine use. Thorax CT might be evaluated in addition to these two modalities. CONCLUSION Thorax USG might be a useful non-invasive method to evaluate the postoperative respiratory problems of neonates after congenital heart surgery. These findings should be supported by further studies. Authors roles & responsibilities EO ICT OY YE AG REFERENCES Conception or design of the work; drafting the work; any part of the work appropriately investigated and resolved; final approval of the version to be published Drafting the work; any part of the work appropriately investigated and resolved; final approval of the version to be published Acquisition and analysis; any part of the work appropriately investigated and resolved; final approval of the version to be published Revision of the work; any part of the work appropriately investigated and resolved; final approval of the version to be published Conception or design of the work; revising the work; any part of the work appropriately investigated and resolved; final approval of the version to be published 1. Bouhemad B, Zhang M, Lu Q, Rouby JJ. Clinical review: bedside lung ultrasound in critical care practice. Crit Care. 2007;11(1): Lobo V, Weingrow D, Perera P, Williams SR, Gharahbaghian L. Thoracic ultrasonography. Crit Care Clin. 2014;30(1): Mayo P, Volpicelli G, Lerolle N, Schreiber A, Doelken P, Vieillard-Baron 286
5 A. Ultrasonography evaluation during the weaning process: the heart, the diaphragm, the pleura and the lung. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42(7): Gargani L. Lung ultrasound: a new tool for the cardiologist. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2011;9:6. 5. Riu B, Ruiz J, Mari A, Silva S. Chest ultrasonography in pediatric critical care practice. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2013;32(12):e Jenkins KJ, Gauvreau K, Newburger JW, Spray TL, Moller JH, Iezzoni LI. Consensus-based method for risk adjustment for surgery for congenital heart disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002;123(1): Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1): Tomà P, Owens CM. Chest ultrasound in children: critical appraisal. Pediatr Radiol. 2013;43(11): Trinavarat P, Riccabona M. Potential of ultrasound in the pediatric chest. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83(9): Vezzani A, Brusasco C, Palermo S, Launo C, Mergoni M, Corradi F. Ultrasound localization of central vein catheter and detection of postprocedural pneumothorax: an alternative to chest radiography. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(2): Ozturk E, Tanidir IC, Haydin S, Onan IS, Odemis E, Bakir I. The use of dornase alpha for post-operative pulmonary atelectasis after congenital heart surgery. Cardiol Young. 2014;24(5): Peroni DG, Boner AL. Atelectasis: mechanisms, diagnosis and management. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2000;1(3): Vezzani A, Manca T, Brusasco C, Santori G, Valentino M, Nicolini F, et al. Diagnostic value of chest ultrasound after cardiac surgery: a comparison with chest X-ray and auscultation. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2014;28(6): Irwin Z, Cook JO. Advances in point-of-care thoracic ultrasound. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2016;34(1): Balesa J, Rathi V, Kumar S, Tandon A. Chest sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2015;57(1): Grimberg A, Shigueoka DC, Atallah AN, Ajzen S, Iared W. Diagnostic accuracy of sonography for pleural effusion: systematic review. Sao Paulo Med J. 2010;128(2): Cantinotti M, Giordano R, Volpicelli G, Kutty S, Murzi B, Assanta N, et al. Lung ultrasound in adult and paediatric cardiac surgery: is it time for routine use? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016;22(2): Copetti R, Cattarossi L. Ultrasound diagnosis of pneumonia in children. Radiol Med. 2008;113(2): Yadav KK, Awasthi S, Parihar A. Lung ultrasound is comparable with chest roentgenogram for diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia in hospitalised children. Indian J Pediatr. 2017;84(7):
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
 Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Cardiac Catheterization in the Early Post-Operative Period after Congenital Heart Surgery
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2018;34:481 487 doi: 10.6515/ACS.201811_34(6).20180524B Cardiovascular Surgery Cardiac Catheterization in the Early Post-Operative Period after Congenital Heart Surgery
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2018;34:481 487 doi: 10.6515/ACS.201811_34(6).20180524B Cardiovascular Surgery Cardiac Catheterization in the Early Post-Operative Period after Congenital Heart Surgery
The Intensive Care Unit
 Imaging of the ADRS patient: Risk of transportation and alternative to repetitive radiation exposure Jean-Jacques Rouby Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital The Intensive Care Unit The Intensive Care Unit Multidisciplinary
Imaging of the ADRS patient: Risk of transportation and alternative to repetitive radiation exposure Jean-Jacques Rouby Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital The Intensive Care Unit The Intensive Care Unit Multidisciplinary
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
9/8/2009 < 1 1,2 3,4 5,6 7,8 9,10 11,12 13,14 15,16 17,18 > 18. Tetralogy of Fallot. Complex Congenital Heart Disease.
 Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, June: 307-314, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients FARES AUF, M.D.; AHMED ABO-NAGLH,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, June: 307-314, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients FARES AUF, M.D.; AHMED ABO-NAGLH,
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by
 24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of Pneumothorax in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
Ultrasound. FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma
 Ultrasound FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Ultrasound FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
ASSESSMENT OF LUNG PARENCHYMAL ABNORMALITIES
 2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph
 Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph Poster No.: C-1008 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad ; Hyderabad/IN, 1 2 1 1 2 HYDERABAD, ANDHRA PRADESH/IN
Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph Poster No.: C-1008 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad ; Hyderabad/IN, 1 2 1 1 2 HYDERABAD, ANDHRA PRADESH/IN
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Index. cardiology.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACHD. See Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) Adult congenital heart disease (ACHD), 503 512 across life span prevalence of, 504 506
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
Incidence and treatment of chylothorax after cardiac surgery in children: analysis of a large multi-institutional database. Carlos M.
 Incidence and treatment of chylothorax after cardiac surgery in children: analysis of a large multi-institutional database Carlos M. Mery, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, and Pediatrics Congenital Heart Texas
Incidence and treatment of chylothorax after cardiac surgery in children: analysis of a large multi-institutional database Carlos M. Mery, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, and Pediatrics Congenital Heart Texas
disease, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, pulmonary hypoplasia and congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
 Neonatal Chest Imaging - What the Nurse Should Know Expires Monday, April 30, 2018 Nursing Michael J. Diament, M.D. Objectives 1. Describe a good technique for positioning a neonate for the purpose of
Neonatal Chest Imaging - What the Nurse Should Know Expires Monday, April 30, 2018 Nursing Michael J. Diament, M.D. Objectives 1. Describe a good technique for positioning a neonate for the purpose of
Ultrasound in the ICU
 Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings
 Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Respiratory complications are a major contributing factor to postoperative morbidity and mortality in pediatric liver transplantation.
 Real-time ultrasound-guided pigtail catheter placement in supine position for drainage of symptomatic pleural effusions in paediatric patients who underwent liver transplantation Poster No.: B-0163 Congress:
Real-time ultrasound-guided pigtail catheter placement in supine position for drainage of symptomatic pleural effusions in paediatric patients who underwent liver transplantation Poster No.: B-0163 Congress:
Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects
 Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects Wanda C. Miller-Hance, M.D. Objective: At the conclusion of this workshop the participant should
Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects Wanda C. Miller-Hance, M.D. Objective: At the conclusion of this workshop the participant should
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions
 Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Original Article. Double Aortic Arch in Infants and Children CH XIE, FQ GONG, GP JIANG, SL FU. Key words. Background
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:233-238 Original Article Double Aortic Arch in Infants and Children CH XIE, FQ GONG, GP JIANG, SL FU Abstract Key words Background: This study aimed to report the diagnosis,
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:233-238 Original Article Double Aortic Arch in Infants and Children CH XIE, FQ GONG, GP JIANG, SL FU Abstract Key words Background: This study aimed to report the diagnosis,
RSV infection and lung ultrasound
 RSV infection and lung ultrasound Neonatology Clinic, University Hospital, Krakow Joanna Hurkała Joanna Pietras Agnieszka Ochoda-Mazur Poznań, 28.09.2018 1 Disclosure In relations to this presentation,
RSV infection and lung ultrasound Neonatology Clinic, University Hospital, Krakow Joanna Hurkała Joanna Pietras Agnieszka Ochoda-Mazur Poznań, 28.09.2018 1 Disclosure In relations to this presentation,
A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
Unilateral pulmonary oedema, a forgotten presentation.
 Unilateral pulmonary oedema, a forgotten presentation. Poster No.: C-2146 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. A. Arboleda Vallejo, M. I. carvajal, M. Perez ; Medellin, 1 2 1 1 2 Antioquia/CO,
Unilateral pulmonary oedema, a forgotten presentation. Poster No.: C-2146 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. A. Arboleda Vallejo, M. I. carvajal, M. Perez ; Medellin, 1 2 1 1 2 Antioquia/CO,
Accuracy of Lung Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia as Compared to Chest X-Ray in Pediatric Age Group
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (8), Page 4977-4983 Accuracy of Lung Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia as Compared to Chest X-Ray in Pediatric Age
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (8), Page 4977-4983 Accuracy of Lung Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia as Compared to Chest X-Ray in Pediatric Age
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP. October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18
 Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1).
 PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome
 Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
PULMONARY VENOLOBAR SYNDROME. Dr.C.Anandhi DNB Resident, Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital.
 PULMONARY VENOLOBAR SYNDROME Dr.C.Anandhi DNB Resident, Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital. Presenting complaint: 10 yrs old girl with recurrent episodes of lower respiratory tract infection from infancy.
PULMONARY VENOLOBAR SYNDROME Dr.C.Anandhi DNB Resident, Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital. Presenting complaint: 10 yrs old girl with recurrent episodes of lower respiratory tract infection from infancy.
MANAGEMENT OF LATE PRESENTATION OF CONGENITAL HEART DESEASE
 MANAGEMENT OF LATE PRESENTATION OF CONGENITAL HEART DESEASE Guillermo E. Moreno Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (UCI35) Hospital de Pediatría Dr. Juan P. Garrahan Buenos Aires - Argentina Non financial
MANAGEMENT OF LATE PRESENTATION OF CONGENITAL HEART DESEASE Guillermo E. Moreno Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (UCI35) Hospital de Pediatría Dr. Juan P. Garrahan Buenos Aires - Argentina Non financial
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax.
 Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017
 Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Chapter 21. Flail Chest. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Flail Chest 1 Figure 21-1. Flail chest. Double fractures of three or more adjacent ribs produce instability of the chest wall and paradoxical motion of the thorax. Inset, Atelectasis, a common
Chapter 21 Flail Chest 1 Figure 21-1. Flail chest. Double fractures of three or more adjacent ribs produce instability of the chest wall and paradoxical motion of the thorax. Inset, Atelectasis, a common
Debate: Should Ductal Stent Implantation be Considered for All Newborn Infants with Reduced Pulmonary Blood Flow?_Pros
 Debate: Should Ductal Stent Implantation be Considered for All Newborn Infants with Reduced Pulmonary Blood Flow?_Pros Mazeni Alwi Institut Jantung Negara Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 5 th Asia Pacific Congenital
Debate: Should Ductal Stent Implantation be Considered for All Newborn Infants with Reduced Pulmonary Blood Flow?_Pros Mazeni Alwi Institut Jantung Negara Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 5 th Asia Pacific Congenital
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Case Report. Stent Placement in a Neonate with Sano Modification of the Norwood using Semi-Elective Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation.
 Stent Placement in a Neonate with Sano Modification of the Norwood using Semi-Elective Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Mustafa Gulgun and Michael Slack Associated Profesor Children National Medical
Stent Placement in a Neonate with Sano Modification of the Norwood using Semi-Elective Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Mustafa Gulgun and Michael Slack Associated Profesor Children National Medical
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Stabilization and Transportation guidelines for Neonates and infants with Heart disease:
 Stabilization and Transportation guidelines for Neonates and infants with Heart disease: Background: Referral Pediatric Cardiac Units, frequently receive neonates and infants referred and transported from
Stabilization and Transportation guidelines for Neonates and infants with Heart disease: Background: Referral Pediatric Cardiac Units, frequently receive neonates and infants referred and transported from
Most infants and children admitted to
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 January NUMBER 1 Original Article Correlation between chest x-ray findings and outcomes of patients with mechanical ventilation Indah Nurhayati 1, Muhammad Supriatna 1,
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 53 January NUMBER 1 Original Article Correlation between chest x-ray findings and outcomes of patients with mechanical ventilation Indah Nurhayati 1, Muhammad Supriatna 1,
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영
 When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month. Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA
 May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA Clinical History: A 32-year-old man presented for routine
May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA Clinical History: A 32-year-old man presented for routine
Accuracy of lung ultrasonography in diagnosis of community acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children as compared to chest x-ray
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Tirdia PR et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2016 Aug;3(3):1026-1031 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20162385
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Tirdia PR et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2016 Aug;3(3):1026-1031 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20162385
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience
 Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
Low-dose prospective ECG-triggering dual-source CT angiography in infants and children with complex congenital heart disease: first experience Ximing Wang, M.D., Zhaoping Cheng, M.D., Dawei Wu, M.D., Lebin
DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME OF HEART DISEASE IN SUDANESE PATIENTS
 434 E AST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL September 2007 East African Medical Journal Vol. 84 No. 9 September 2007 DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE IN SUDANESE PATIENTS K.M.A. Sulafa,
434 E AST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL September 2007 East African Medical Journal Vol. 84 No. 9 September 2007 DIAGNOSIS, MANAGEMENT AND OUTCOME OF CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE IN SUDANESE PATIENTS K.M.A. Sulafa,
TTC Catalog - Respiratory Care (RES)
 2018-2019 TTC Catalog - Respiratory Care (RES) RES 110 - Cardiopulmonary Science I This course focuses on assessment, treatment evaluation of patients with cardiopulmonary disease. RES 121 Restrictions:
2018-2019 TTC Catalog - Respiratory Care (RES) RES 110 - Cardiopulmonary Science I This course focuses on assessment, treatment evaluation of patients with cardiopulmonary disease. RES 121 Restrictions:
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Recent technical advances and increasing experience
 Pediatric Open Heart Operations Without Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization Jean-Pierre Pfammatter, MD, Pascal A. Berdat, MD, Thierry P. Carrel, MD, and Franco P. Stocker, MD Division of Pediatric Cardiology,
Pediatric Open Heart Operations Without Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization Jean-Pierre Pfammatter, MD, Pascal A. Berdat, MD, Thierry P. Carrel, MD, and Franco P. Stocker, MD Division of Pediatric Cardiology,
Children with Single Ventricle Physiology: The Possibilities
 Children with Single Ventricle Physiology: The Possibilities William I. Douglas, M.D. Pediatric Cardiovascular Surgery Children s Memorial Hermann Hospital The University of Texas Health Science Center
Children with Single Ventricle Physiology: The Possibilities William I. Douglas, M.D. Pediatric Cardiovascular Surgery Children s Memorial Hermann Hospital The University of Texas Health Science Center
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS
 Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS ABSTRACT Background: The congenital heart disease occurs in 0,8% of live births and they have a wide spectrum
Pattern of Congenital Heart Disease A Hospital-Based Study *Sadiq Mohammed Al-Hamash MBChB, FICMS ABSTRACT Background: The congenital heart disease occurs in 0,8% of live births and they have a wide spectrum
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
Ultrasound Assessment of Pulmonary Embolism in Patients Receiving CT Pulmonary Angiography
 CHEST Ultrasound Assessment of Pulmonary Embolism in Patients Receiving CT Pulmonary Angiography Seth Koenig, MD, FCCP ; Subani Chandra, MD ; Artur Alaverdian, MD ; Christopher Dibello, MD ; Paul H. Mayo,
CHEST Ultrasound Assessment of Pulmonary Embolism in Patients Receiving CT Pulmonary Angiography Seth Koenig, MD, FCCP ; Subani Chandra, MD ; Artur Alaverdian, MD ; Christopher Dibello, MD ; Paul H. Mayo,
Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2)
 Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Methods ORIGINAL ARTICLES ABSTRACT
 Bedside lung ultrasound, mobile radiography and physical examination: a comparative analysis of diagnostic tools in the critically ill Andrew J Inglis, Marek Nalos, Kwan-Hing Sue, Jan Hruby, Daniel M Campbell,
Bedside lung ultrasound, mobile radiography and physical examination: a comparative analysis of diagnostic tools in the critically ill Andrew J Inglis, Marek Nalos, Kwan-Hing Sue, Jan Hruby, Daniel M Campbell,
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings
 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
PAEDIATRIC EMQs. Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info.
 PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
PAEDIATRIC EMQs Andrew A Mallick Paediatrics.info www.paediatrics.info Paediatric EMQs Paediatrics.info First published in the United Kingdom in 2012. While the advice and information in this book is believed
Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.1, March 2000 Two Cases Report of Scimitar Syndrome: The Classical one with Subaortic Membrane and the Scimitar Variant F Hakim, MD* A Madani, MD* A Abu Haweleh, MD,MRCP*
Signs in Chest Radiology
 Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT
 Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
X-Rays. Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady
 X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
Sports cardiology: Pre-competition screening
 Sports cardiology: Pre-competition screening Dr. med Andreas E. Brauchlin Division of cardiology, University Hospital, Zurich andreas.brauchlin@usz.ch Content Interactive case presentation Background and
Sports cardiology: Pre-competition screening Dr. med Andreas E. Brauchlin Division of cardiology, University Hospital, Zurich andreas.brauchlin@usz.ch Content Interactive case presentation Background and
Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications
 No disclosures But Heavy accent Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in
No disclosures But Heavy accent Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in
Cost Containment in the Intensive Care Unit: Chest Roentgenograms
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 5 Number 2 Cost Containment in the Intensive Care Unit: Chest Roentgenograms G Diaz-Fuentes, R Rosen, L Menon Citation G Diaz-Fuentes, R Rosen,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 5 Number 2 Cost Containment in the Intensive Care Unit: Chest Roentgenograms G Diaz-Fuentes, R Rosen, L Menon Citation G Diaz-Fuentes, R Rosen,
Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery Shunt Narrowing
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology. Outline. Technique. Technique. Principles of interpretation. Case Examples. Optimize image quality
 A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology Kacie Schmitt Felber, DVM, DACVIM Cardiology Thursday, May 17 th, 2018 Mid Atlantic States Veterinary Clinic Conference Outline Technique Principles of interpretation
A Cardiologist s Approach to Thoracic Radiology Kacie Schmitt Felber, DVM, DACVIM Cardiology Thursday, May 17 th, 2018 Mid Atlantic States Veterinary Clinic Conference Outline Technique Principles of interpretation
Intravascular ultrasound catheter for transesophageal echocardiography in congenital heart surgery -A case report-
 Case Report Korean J Anesthesiol 2010 May 58(5): 480-484 DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.5.480 Intravascular ultrasound catheter for transesophageal echocardiography in congenital heart surgery -A case report-
Case Report Korean J Anesthesiol 2010 May 58(5): 480-484 DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.5.480 Intravascular ultrasound catheter for transesophageal echocardiography in congenital heart surgery -A case report-
Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations
 Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations Poster No.: C-1724 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper
Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations Poster No.: C-1724 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper
PEDIATRIC CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY SERVICE. Referral Center for Pediatric Cardiovascular Surgery
 PEDIATRIC CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY SERVICE Referral Center for Pediatric Cardiovascular Surgery INTRODUCTION Each year 133 million children are born worldwide from a population of 6.6 billion people; one
PEDIATRIC CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY SERVICE Referral Center for Pediatric Cardiovascular Surgery INTRODUCTION Each year 133 million children are born worldwide from a population of 6.6 billion people; one
Differentiation of Pleural Effusions From Parenchymal Opacities: Accuracy of Bedside Chest Radiography
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Kitazono et al. Chest Radiography of Pleural Effusions Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Mary T. Kitazono 1 Charles T. Lau Andrea N. Parada Pooja Renjen
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Kitazono et al. Chest Radiography of Pleural Effusions Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Mary T. Kitazono 1 Charles T. Lau Andrea N. Parada Pooja Renjen
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES. PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU
 CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
Transthoracic Echocardiography:
 Transthoracic Echocardiography: An essential tool for the obstetric anaesthetist? Brendan Carvalho MBBCh, FRCA Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University, California Focused TTE Stethoscope of the
Transthoracic Echocardiography: An essential tool for the obstetric anaesthetist? Brendan Carvalho MBBCh, FRCA Department of Anesthesiology Stanford University, California Focused TTE Stethoscope of the
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
The incidence and risk factors of arrhythmias in the early period after cardiac surgery in pediatric patients
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2008; 50: 549-553 Original The incidence and risk factors of arrhythmias in the early period after cardiac surgery in pediatric patients Selman Vefa Yıldırım 1, Kürşad
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2008; 50: 549-553 Original The incidence and risk factors of arrhythmias in the early period after cardiac surgery in pediatric patients Selman Vefa Yıldırım 1, Kürşad
The Heart Center. Quality Counts: Cardiothoracic Surgery and Interventional Cardiology
 The Heart Center Quality Counts: Cardiothoracic Surgery and Interventional Cardiology The Cardiothoracic Surgery Program at Nationwide Children s Hospital is dedicated to the treatment of all patients,
The Heart Center Quality Counts: Cardiothoracic Surgery and Interventional Cardiology The Cardiothoracic Surgery Program at Nationwide Children s Hospital is dedicated to the treatment of all patients,
Clinical Study Lung Ultrasound Diagnostic Accuracy in Neonatal Pneumothorax
 Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 6515069, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6515069 Clinical Study Lung Ultrasound Diagnostic Accuracy in Neonatal Pneumothorax Luigi Cattarossi,
Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 6515069, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6515069 Clinical Study Lung Ultrasound Diagnostic Accuracy in Neonatal Pneumothorax Luigi Cattarossi,
Alper Toker, MD. VATS decortication. Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery
 VATS decortication Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery Pleural space infection is a common pathology causing morbidity and mortality. It is a collection
VATS decortication Alper Toker, MD Istanbul University, Istanbul Medical School Department of Thoracic Surgery Pleural space infection is a common pathology causing morbidity and mortality. It is a collection
OVERVIEW. Need for USG. Weaning assessment. Mechanics of USG. Pneumonia / VAP. Principles of lung USG. Prone position ventilation assessment
 OVERVIEW Need for USG Mechanics of USG Principles of lung USG BLUE protocol Alveolar syndrome Interstitial syndrome Weaning assessment Pneumonia / VAP Prone position ventilation assessment ETT positioning
OVERVIEW Need for USG Mechanics of USG Principles of lung USG BLUE protocol Alveolar syndrome Interstitial syndrome Weaning assessment Pneumonia / VAP Prone position ventilation assessment ETT positioning
Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation
 CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
Case N 1. Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds. Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania
 Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
DR. DO NGUYEN TIN CHILDREN HOSPITAL 1
 DR. DO NGUYEN TIN CHILDREN HOSPITAL 1 BACKGROUND Congenital extrahepatic porto-systemic shunt (CEPS), known as Abernethy malformation, is a rare malformation. Intestinal and/or splenic venous blood bypasses
DR. DO NGUYEN TIN CHILDREN HOSPITAL 1 BACKGROUND Congenital extrahepatic porto-systemic shunt (CEPS), known as Abernethy malformation, is a rare malformation. Intestinal and/or splenic venous blood bypasses
S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
 S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences No financial disclosures Aorta Congenital aortic stenosis/insufficiency
S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences No financial disclosures Aorta Congenital aortic stenosis/insufficiency
