The Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Ureteral Calculi
|
|
|
- Myles Walters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2018; 6(2): doi: /j.ijmi ISSN: (Print); ISSN: X (Online) The Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Ureteral Calculi Fan Weibo Department of Ultrasound, Jingzhou Central Hospital, The Second Clinical Medical College, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China address: To cite this article: Fan Weibo. The Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Ureteral Calculi. International Journal of Medical Imaging. Vol. 6, No. 2, 2018, pp doi: /j.ijmi Received: July 21, 2018; Accepted: August 1, 2018; Published: August 30, 2018 Abstract: Ureteral calculi are one of the most common acute abdomen, most of which are from renal calculi. Color Doppler ultrasound plays a very important role in the diagnosis of ureteral calculi, and has the advantages of simplicity, economy, non-invasive, no radiation, and repeatable examination. The purpose of this study is to investigate the clinical value of color Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of ureteral calculi. To achieve this goal, a retrospective analysis was performed to analyze the clinical symptoms, ultrasonographic appearances and results of 112 patients with ureteral calculi who were treated in author s hospital from March 2016 to March It showed that there were 5 cases of bilateral ureteral calculi, 59 cases of left ureteral calculi, 48 cases of right ureteral calculi, 42 cases of upper ureteral calculi, 11 cases of middle ureteral calculi and 59 cases of lower ureteral calculi in the results of the 112 patients with ureteral calculi. As ultrasound examination can show the location, number and size of the calculi, which can help clinical treatment and can be used as the first choice for ureteral calculi. Therefore, it is concluded that ultrasound diagnosis of ureteral calculi has the advantages of painless, non-invasive, convenient and easy to operate repeatedly, and can be used as the first choice for checking ureteral calculi. Keywords: Color Doppler Ultrasound, Ureteral Calculi, Diagnostic Value 1. Introduction In recent years, with the continuous development of ultrasound equipment and the improvement of the diagnostic level of technicians, the detection rate of ureteral calculi by ultrasound has been relatively improved. At the same time, CT, KUB and IVU are not suitable for repeated inspections because of the high price and radiation. After all, ultrasound is non-invasive, non-radiative, and can be repeatedly tested. The advantage of ultrasonography is that it can clearly show the X-ray negative calculi in the ureter, which compensates for the deficiency of X-ray examination to varying degrees. In the course of ultrasound imaging, the degree of hydro-nephrosis due to ureteral obstruction can be known, so that renal function can be estimated generally, and other diseases of the urinary system coexisting with ureteral calculi can also be found at the same time. Despite this, during the ultrasound imaging process, it is easy to cause missed diagnosis of ureteral calculi due to the physical characteristics of ultrasound and other reasons. The reasons are as follows: 1. The patient's obesity and the interference of intestinal contents can make the sonogram blurred, leading to misdiagnosis. The patients huge body and old age may result in poorer penetrating ultrasound and an unclear strong echo structure of the calculi. The patients poor intestinal condition may influence the penetration of the ultrasound in the ureteral area, which can be solved by allowing the patient to be re-examined after bowel preparation. 2. Due to the small ureteral calculi or short-term obstruction, there is no obvious accumulation of water in the renal pelvis and ureter, ultrasound is not found and easily leads to misdiagnosis. 3. The patients often have an acute onset, poor bladder-filling, and difficulty in cooperating with pain, which is also one of the reasons for misdiagnosis. Therefore, for patients with high suspicion of ureteral calculi and undetectable ultrasound examinations, abdominal plain films, CT or retrograde pyelography can be performed to avoid misdiagnosis of ureteral calculi [1]. Ureteral calculi are one of the most common acute abdomen, most of which are from renal calculi. The stimulation to the ureteral wall from calculi can cause local visceral mucosal
2 13 Fan Weibo: The Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Ureteral Calculi damage, edema and concurrent inflammation, causing ureteral obstruction and spasmodic contraction, leading to dull or paroxysmal abdominal pain, accompanied with gross or microscopic hematuria. Ureteral calculi can cause urinary tract obstruction and different degrees of hydrocele in the affected kidney. In severe cases, the renal cortex becomes thinner, its function is lost or even get uremia. The clinical data of 112 patients who were treated in author s hospital from March 2016 to March 2018 were analyzed and reported as follows. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Clinical Data This clinical study selected 112 patients from March 2016 to March 2018 in author s hospital, which include 70 males and 42 females aged years, mean age (38.2). ±11.3) years old. Those patients are accompanied by sudden, intermittent lumbar pain, radiating along the ipsilateral ureter to the lower abdomen, perineum, external genitalia and inner thighs, and often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, microscopic hematuria or even gross hematuria. They were confirmed by surgery, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy and self-extracting calculi Instruments and Methods The PHILIPS IU22 ultrasound diagnostic instrument is used, and the 3.5-5MHz convex array probe is routinely used. Patients with upper ureteral calculi were placed in the lateral or prone position, and the probe was placed in the lateral lumbar region with the renal hilum or renal pelvis as the sign showing the ureteropelvic junction. Patients with the second stenosis calculi were placed in the supine position. The probe was obliquely cut in the lower abdomen and the iliac artery was found by compression. The dilated ureter was found in front of the iliac artery, and the probe was used to display the long axis of the ureter. Patients with lower ureteral calculi were placed in supine position, whose bladder was moderately filled and the probe was pressurized. Then the lower ureteral opening was scanned in the trigone of the bladder, and the scanning was performed upward. By following a certain examination sequence, combined with a variety of examination methods, multi-position and multi-angle scan, and abdominal ultrasound can be done to patients with ureteral calculi. It can also improve the detection rate of ureteral urinary calculi by some scanning methods like moderate bladder-filling, diuretic pressurization and adding high-frequency probes [2]. 3. Results In this group of 112 patients, 36 cases of upper ureteral calculi, 5 cases of middle calculi, and 45 cases of lower ureteral calculi were detected by multi-position and multi-angle scanning of abdominal ultrasound. A total of 86 cases were detected, and the detection rate was 76.8%. Seven cases of ureteral calculi were detected by diuretic pressurization method, and 15 cases of pelvic and intra-ureteral calculi were detected by moderate bladder-filling method. There were 108 cases of ureteral calculi were detected by multiple checking methods in this group, and the detection rate was 96.4%. There were 4 cases of misdiagnosis couldn t be detected because of the patient's obesity and flatulence interference. The diagnosis only indicated the separation of renal sinus echo, but the upper limit of upper ureteral diameter was normal. There were 101 patients (90.2%) who had different degrees of hydronephrosis in this group of patients with ureteral calculi. Eleven patients had normal renal function and had no obvious separation in the collecting system. The diameter of the calculi is 4-14mm, which is more commonly seen in 5-8mm. 4. Discussion Starting from the renal pelvis to the bladder triangle, the ureter is about 20-34cm long that located in the posterior peritoneum. There are three physiological stenosis parts in the ureter, which are separately located at the junction of the renal pelvis and ureter, the site that ureter spans the iliac vessels and the ureteral bladder wall. Calculi can often stay in these stenotic sites. Most ureteral calculi are derived from renal calculi, and primary calculi are rare. The ureteral calculi can cause urinary tract obstruction, and lead to different degrees of hydrocele in the affected renal. The higher the position of ureteral calculi, the more severe the degree of obstruction and hydro-nephrosis. When the sonogram shows the hydro-nephrosis, checking along with the dilated ureter, it can be seen that the dilated ureter is suddenly interrupted, and the strong echo and the wall boundary is clearly defined, followed by an acoustic shadow. Because of the different size, shape, location and composition of ureteral calculi, their sonograms are also displaying differently. For example, the uric acid calculi has a loose texture and rough surface, which presents a round or elliptical high echogenic area and the acoustic shadow behind it is weak or not obvious. The calcium oxalate calculi, possessing hard texture and smooth surface, the sonogram of which can only show that its surface profile presents like an arc-shaped high echogenic area and there is an acoustic shadow at the rear. The small stone with a rough surface has a strong echo of point, and there is no obvious acoustic shadow. The typical sonogram of ureteral calculi appears as a calculus echo at the distal end of the dilated ureter, which is characterized by a curved strong light band, with a acoustic shadow behind the ureter, and a ureteral dilatation above the calculi obstruction (see Figure 1), hydronephrosis, and the inner diameter of the ureter of far end is significantly smaller than the proximal end [3].
3 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2018; 6(2): Figure 1. Upper ureteral calculi on the right side. To detect ureteral calculi quickly and accurately, you must be familiar with the anatomy and characteristics of the ureter, and use reasonable timing and examination sequence to save time and diagnose quickly. The ureteral calculi are best examined during an acute attack of renal colic, because at this time the ureter is mostly accompanied by dilatation, and it is easier to find the obstruction site when the bladder is not full. According to the literature cited [4]: the inner segment of the bladder wall is the narrowest part of the ureter. With its unique dynamic characteristics, 70% of the ureteral stones are located at this site [5]. During the examination, the inner segment of the bladder wall is first found to achieve a rapid diagnosis. If no stone echoes is found in the inner segment of the bladder wall, then the hydronephrosis should be checked. If there is, a hydroureterosis should be confirmed from the hydronephrosis to the pelvic ureter junction, then the multi-faceted scan of the abdomen, the back and the lateral waist will allow for the examination of most of the calculi. If no stones are found in the first and the third stenosis, then the second stenosis should be scanned, during which the supine position is usually taken. The common iliac artery is first found, and the long axis of the ureter is found in front of the common iliac artery. Scanning below and following the hydroureterosis can assure the detection of calculi. The calculi can also be found by firstly being examined by the bladder, which shows the opening of bilateral ureters in the bladder wall, and then scan up. During the examination of ureteral calculi, if the sonographer can master a variety of ultrasound diagnostic techniques for ureteral calculi, the display rate of ureteral calculi can be more effectively improved: 1. The locating scan can be done based on the most painful location of the patient, which can reduce the blind scanning time, especially for patients with no hydronephrosis and no obvious ureteral dilatation, and it is not easy to track each segment of the ureter. 2. For some patients who has no obvious pain symptoms, let them to fill the bladder moderately and increase the degree of dilatation of the ureter as well as appropriately reduce the gain, pressurization, multi-position and multi-section, trying to make the sound beam perpendicular to the ureter that makes it easy to find smaller stones. 3. It has been reported that intracavity ultrasound has obvious advantages in the examination of lower ureteral calculi, especially for patients with acute abdomen and less bladder filling [6]. Because of the obvious bladder irritation, not easy to urinate, small calculi and ureter without dilatation, obesity, intestinal contents and gas interference, etc., patients who have lower ureteral calculi can affect the diagnosis of lower ureteral calculi by abdominal ultrasound, while intracavity ultrasound requires less filling of the bladder, and the diagnosis of calculi is more sensitive than the abdomen. However, patients with renal calculi often appear in the emergency department at night, so it is not convenient to carry out intracavity ultrasound. Therefore, intracavity ultrasound has not been used in author s hospital to diagnose ureteral calculi. 4. Ultrasonic diagnosis of ureteral calculi with diuretic compression method is convenient and quick to check. The patient has no noticable discomfort and adverse reactions and is easy to accept. Check again by using the diuretic abdominal compression method (use the sandbag to compress the second stenosis of the ureter closest to the abdominal wall), cleaning the enema, using the diuretic and filling the bladder, forming a good urine-stone acoustic interface, which helps to improve the calculi detection rate. 5. On the basis of two-dimensional ultrasound examination, color Doppler imaging can be used to identify
4 15 Fan Weibo: The Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Ureteral Calculi the dilated ureter and surrounding blood vessels, and the "twinkling artifact" of color Doppler ultrasound can be used to diagnose ureteral calculi [7-8]. Twinkling artifact" refers to the appearance of a flashing blood flow signal (similar to the "tail of a comet" sign) behind the ureteral calculi (see Figures 2 and 3). Figure 2. Inner bladder wall ureteral calculi on the left side. Figure 3. The twinkling artifact of inner bladder wall ureteral calculi on the left side. This feature can be used as a basis for the presence of ureteral calculi. Based on the mechanism of twinkling artifact, a variety of hyperechoic structures can show twinkling artifact, such as ureteral calcification, foreign body, ureteral stent, double "J" tube and intestinal gas, so doctors should also pay attention to identify these flashes during the examination. The interference of artifacts on the diagnosis of calculi. 6. Try to use a higher frequency probe scanning (except for obesity). The local enlargement can clearly show the ureteral lumen and display 2mm tiny calculi in the ureter to improve the display
5 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2018; 6(2): rate of ureteral calculi. 7. Perirenal fluid collection (see Figure 4) is an indirect sign of acute urinary tract obstruction caused by partial ureteral calculi [9-10], the side of the perirenal fluid collection that has water accumulation or renal sinus echo separation is more obvious than the contralateral side. Figure 4. Mild hydronephrosis of the left renal with perirenal fluid collection. The clinical symptoms are typical and there are red blood cells in the urine test. The urinary calculi should be highly suspected and the bladder should be properly filled if necessary. For those who don t have hydronephrosis, ureteral calculi are easily overlooked and further missed. 8. Add tissue harmonic, which can darken the ureteral lumen and enhance the echo of the wall, and not only can it clearly show the ureteral calculi echo, boundary and posterior acoustic shadow, but also clearly show the ureteral lumen with different degrees of expansion. If the ultrasound doctors have mastered the examination sequence of ureteral calculi, combined with a variety of examination methods, the location, size, shape and number of ureteral calculi can quickly and accurately found, providing a strong basis for clinical treatment, which is a safe, fast, effective, high-rate diagnostic inspection. 5. Conclusion The Previous literature reported that multi-slice spiral CT diagnosis of calculus sensitivity and specificity was close to 100% [11], and the sensitivity of ultrasound diagnosis of ureteral calculi was 19% to 93% [12], higher than KUB. The sensitivity of B-ultrasound diagnosis of hydro-nephrosis was 72.6% and the specificity was 73.3% [13]. The study concluded that the sensitivity of ultrasound diagnosis of hydro-nephrosis was 93.5%, which was higher than the sensitivity of detected calculi. In the presence of hydrocele, the sensitivity of B-ultrasound was increased from 72.0% to 91.2%. As an important indicator of post-renal obstruction, hydro-nephrosis helps emergency doctors to find ureteral calculi [14]. It is clear that the risk factors associated with the degree of hydrocele can help to predict calculi information and guide the next treatment decision. In summary, color Doppler ultrasound plays a very important role in the diagnosis of ureteral calculi, and has the advantages of simplicity, economy, non-invasive, no radiation, and repeatable examination. Ultrasound examination can show the location, number and size of the calculi, which can help clinical treatment and can be used as the first choice for ureteral calculi. References [1] Shen Long. Comparison of the Value of Ultrasound and CT in the Diagnosis of Ureteral Calculi [J]. Contemporary Medicine Forum, 2017, 15 (8): [2] Yang Xiaoxia, Zhou Xiaoying. Value Analysis of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Ureteral Calculi [J]. Clinical Medicine & Engineering, 2015, 22 (11): [3] Lu Ming, Luo Mei, Sun Yu. Diagnostic Value of Ultrasound for Ureteral Calculi [J]. Xinjiang Medical Journal, 2015, 45 (10): [4] Jing Fengjie, Li Jinyan. Clinical Value of Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Ureteral Calculi [J]. Chinese Medical Journal of Metallurgical Industry, 2016, 33 (2):
6 17 Fan Weibo: The Diagnostic Value of Color Doppler Ultrasound in Ureteral Calculi [5] WOLF J S Jr. Treatment selection and outcomes:ureteral calculi [J]. Urol Clin North Am, 2007, 34: [6] Jiang Ju, Gao Jicheng, Zhou Chunyan, et. al. Comparative Analysis of Intracavitary Ultrasound and Transabdominal Ultrasound in the diagnosis of Ureteral Calculi [J]. Journal of Hebei Medical University, 2014, 35 (3): [7] Cui Chuanxiang. The Application Value of Color Doppler Flash Artifact in the Diagnosis of Ureteral Calculi [J]. Huaihai Medicine, 2015, 33 (6): [8] Wu Jianhui, Meng Hongzhou, He Yi. The Value of Color Doppler Ultrasound Scintillation Artifacts in Ultrasonic Localization of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy [J]. China Modern Doctro, 2016, 54 (25): [9] Wen Xingyue. Ultrasound Observation and Analysis of Ureteral Calculi with Acute Perirenal Effusion. Journal of Clinical Medical Literature, 2014, 1 (7): [10] Yang Yanzhen. Value of Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Acute Ureteral Calculi Associated with Perirenal Effusion [J]. Clinical Journal of Chinese Medicine, 2017, 9 (8): [11] Na Yanqun, Ye Zhangqun, Sun Yinghao, Sun Guang. Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urological Diseases in China. People s Medical Publishing House (PMPH), [12] D P Viprakasit, M D Sawyer, S D Herrell, et a1. Limitations of ultrasonography in the evaluation of urolithiasis:a correlation with computed tomography. JEndourol, 2012, 26 (3):209~ 213. [13] M K Herbst, G Rosenberg, B Daniels, et a1. Effect of provider experience on clinician performed ultrasonography for hydronephrosis in patients with suspected renal colic. Ann Emerg Med, 2014, 64 (3): [14] B Daniels, CP Gross, A Molinaro, et a1. STONE PLUS:Evaluation of Emergency Department Patients With Suspected Renal Colic, Using a Clinical Prediction Tool Combined With Point-of- Care Limited Ultrasonography. Ann Emerg Med, 2015.
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان
 4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
4th stage Lec-8 جراحة بولية د.نعمان 11/10/2015 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ureteric, Vesical, & urethral stones Ureteric Calculus Epidemiology like renal stones Etiology like renal stones Risk factors like
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol
 FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
An overview of Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and the role of Radiographers in ESWL. Tse Ka Wai, Sam (Rad II, TMH)
 An overview of Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and the role of Radiographers in ESWL Tse Ka Wai, Sam (Rad II, TMH) What is ESWL? ESWL Machine Body Stone Renal Stone Incidence rate in HK population
An overview of Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and the role of Radiographers in ESWL Tse Ka Wai, Sam (Rad II, TMH) What is ESWL? ESWL Machine Body Stone Renal Stone Incidence rate in HK population
Outline. Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system. Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract
 Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning
Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning
Outline. Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system. Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract
 Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Diagnostic Investigations in Urinary System PLAIN KUB EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY RETROGRADE
Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Diagnostic Investigations in Urinary System PLAIN KUB EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY RETROGRADE
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
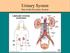 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Basic of Ultrasound Physics E FAST & Renal Examination. Dr Muhammad Umer Ihsan MBBS,MD, DCH CCPU,DDU1,FACEM
 Basic of Ultrasound Physics E FAST & Renal Examination Dr Muhammad Umer Ihsan MBBS,MD, DCH CCPU,DDU1,FACEM What is Sound? Sound is Mechanical pressure waves What is Ultrasound? Ultrasounds are sound waves
Basic of Ultrasound Physics E FAST & Renal Examination Dr Muhammad Umer Ihsan MBBS,MD, DCH CCPU,DDU1,FACEM What is Sound? Sound is Mechanical pressure waves What is Ultrasound? Ultrasounds are sound waves
Ultrasonographic diagnosis and typing of renal tuberculosis
 International Journal of Urology (2008) 15, 135 139 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2007.01962.x, Original Article: Clinical Investigation Ultrasonographic diagnosis and typing of renal tuberculosis Xuefang Rui,
International Journal of Urology (2008) 15, 135 139 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2007.01962.x, Original Article: Clinical Investigation Ultrasonographic diagnosis and typing of renal tuberculosis Xuefang Rui,
Urologic Stone Disease. Urologic Stone Disease. Urologic Stone Disease. Urologic Stone Disease. Urologic Stone Disease 5/7/2010
 Diagnosis and Treatment Stephen E. Strup MD William Farish Professor and Chief of Urology Director of Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery University of Kentucky I will not cut, even for the stone, but
Diagnosis and Treatment Stephen E. Strup MD William Farish Professor and Chief of Urology Director of Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery University of Kentucky I will not cut, even for the stone, but
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic
 Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
Abdominal Ultrasound
 Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging Control Buttons Depth The organ imaged should take up 3/4 of the screen Frequency = Penetration Use high frequencies (harmonics) for fluid filled and superficial structures
Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging Control Buttons Depth The organ imaged should take up 3/4 of the screen Frequency = Penetration Use high frequencies (harmonics) for fluid filled and superficial structures
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Principles of Ultrasound. Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012
 Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
Principles of Ultrasound Cara C. Prideaux, M.D. University of Utah PM&R Sports Medicine Fellow March 14, 2012 None Disclosures Outline Introduction Benefits and Limitations of US Ultrasound (US) Physics
Background & Indications Probe Selection
 Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Bladder Schistosomes. Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection.
 Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that can become toxic if they accumulate Functions the urinary system
Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that can become toxic if they accumulate Functions the urinary system
Certification Review. Module 28. Medical Coding. Radiology
 Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
Module 28 is the study of x-rays, using radiant energy and other imaging techniques, such as resonance imaging or ultrasound, to diagnose illnesses and diseases. Vocabulary Barium enema (BE): lower gastrointestinal
R adio logical investigations of urinary system
 R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
R adio logical investigations of urinary system There are 4 main radiological Ix: 1 IVU: Intravenous urography. 2- U/S 3-CT scan 4-Radioisotope scan. Others (not frequently used): MRI, arteriography, antegrade
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Shlomi Albert, M.D., Inc Warner Avenue, Suite 423 Fountain Valley, Ca Tel (714) Fax (714) Kidney Stone Disease in Adults
 Shlomi Albert, M.D., Inc. 11160 Warner Avenue, Suite 423 Fountain Valley, Ca 92708 Tel (714)549-3333 Fax (714)549-3334 Kidney Stone Disease in Adults Overview Kidney stones are one of the most painful
Shlomi Albert, M.D., Inc. 11160 Warner Avenue, Suite 423 Fountain Valley, Ca 92708 Tel (714)549-3333 Fax (714)549-3334 Kidney Stone Disease in Adults Overview Kidney stones are one of the most painful
이학종분당서울대학교병원. Ultrasound in Urinary Colic
 이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
이학종분당서울대학교병원 Ultrasound in Urinary Colic U l t r a s o u n d i n U r i n a US: Normal Kidney r y C o l i c Contents 1. 1. Definition and clinical consideration 2. 2. Pathophysiology 3. 3. US in in obstructive
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
URINARY SYSTEM. Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3
 URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Urinary System. Dr. Thorson
 Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder
 Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder Nilam J. Soni, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Divisions of Hospital Medicine and Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine University
Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder Nilam J. Soni, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Divisions of Hospital Medicine and Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine University
The Kidneys. (L., ren; Gk, nephros; hence the adjectives renal and nephric) & Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MBChB
 The Kidneys (L., ren; Gk, nephros; hence the adjectives renal and nephric) & Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MBChB Functions of Urinary System Regulate electrolytes (K+, Na+, etc) Regulate
The Kidneys (L., ren; Gk, nephros; hence the adjectives renal and nephric) & Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MBChB Functions of Urinary System Regulate electrolytes (K+, Na+, etc) Regulate
AUA Guidelines for Imaging Known or Suspected Ureteral Calculi. Michael Ferrandino, MD Assoc Professor of Urology Duke University Medical Center
 AUA Guidelines for Imaging Known or Suspected Ureteral Calculi Michael Ferrandino, MD Assoc Professor of Urology Duke University Medical Center Imaging for Urolithiasis Justification for the Guidelines
AUA Guidelines for Imaging Known or Suspected Ureteral Calculi Michael Ferrandino, MD Assoc Professor of Urology Duke University Medical Center Imaging for Urolithiasis Justification for the Guidelines
Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
 Scan for mobile link. Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is an x-ray exam that uses an injection of contrast material to evaluate your kidneys, ureters and bladder and help diagnose
Scan for mobile link. Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is an x-ray exam that uses an injection of contrast material to evaluate your kidneys, ureters and bladder and help diagnose
The Urinary System. Chapter 17
 The Urinary System Chapter 17 Quick Overview of the Urinary System Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that
The Urinary System Chapter 17 Quick Overview of the Urinary System Bladder Schistosomes Normally, urine is sterile. Presence of blood may indicate an infection. 17.1 Introduction -Cells produce waste that
US Applications. Case Based Wrap-Up 1. Case 1 E-FAST. Case presentations E-FAST Abdominal. Pearls for each indication
 Case Based Wrap-Up 1 Stephanie J. Doniger MD RDMS FAAP FACEP Associate Director, Pediatric Emergency Ultrasound Stanford University Medical Center US Applications Case presentations E-FAST Abdominal Aorta
Case Based Wrap-Up 1 Stephanie J. Doniger MD RDMS FAAP FACEP Associate Director, Pediatric Emergency Ultrasound Stanford University Medical Center US Applications Case presentations E-FAST Abdominal Aorta
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 4: Cystography & Urethrography - Part 2 American Urological Association Review Cystography is useful in evaluating the bladder, the urethra and the competence of
Abdominal Ultrasonography
 Abdominal Ultrasonography David A. Masneri, DO, FACEP, FAAEM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Director, Emergency Medicine Residency Medical Director, Operational Medicine Division Center
Abdominal Ultrasonography David A. Masneri, DO, FACEP, FAAEM Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine Assistant Director, Emergency Medicine Residency Medical Director, Operational Medicine Division Center
La calcolosi urinaria :patologia di interesse multidisciplinare
 La calcolosi urinaria :patologia di interesse multidisciplinare Nuovi standard radiologici e di medicina nucleare nello studio della litiasi urinaria CT Dott. PAOLO BRESCIANI U.O.C. RADIOLOGIA Azienda
La calcolosi urinaria :patologia di interesse multidisciplinare Nuovi standard radiologici e di medicina nucleare nello studio della litiasi urinaria CT Dott. PAOLO BRESCIANI U.O.C. RADIOLOGIA Azienda
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS. Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital
 URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital URETERAL OBSTRUCTION Vague history and clinical signs Difficult diagnosis
URETERAL OBSTRUCTION IN SMALL ANIMALS Courtney Ikuta, DVM Department of Surgery VCA West Coast Specialty and Emergency Animal Hospital URETERAL OBSTRUCTION Vague history and clinical signs Difficult diagnosis
Hydronephrosis. Nephrosis. Refers to the kidney
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
Transvaginal sonography in the assessment of distal ureteral calculi
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 658 662 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2610 Transvaginal sonography in the assessment of distal ureteral calculi
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 658 662 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2610 Transvaginal sonography in the assessment of distal ureteral calculi
Abdominal Ultrasound
 Abdominal Ultrasound What is Ultrasound Imaging of the Abdomen? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is
Abdominal Ultrasound What is Ultrasound Imaging of the Abdomen? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is
ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA
 1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System
 Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
Accuracy of ultrasonography for renal stone detection and size determination: is it good enough for management decisions?
 Upper Urinary Tract Accuracy of ultrasonography for renal stone detection and size determination: is it good enough for management decisions? Vishnu Ganesan*,, Shubha De*, Daniel Greene*, Fabio Cesar Miranda
Upper Urinary Tract Accuracy of ultrasonography for renal stone detection and size determination: is it good enough for management decisions? Vishnu Ganesan*,, Shubha De*, Daniel Greene*, Fabio Cesar Miranda
WELCOME! Introduction to Bedside Ultrasound
 WELCOME! Introduction to Bedside Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
WELCOME! Introduction to Bedside Ultrasound TEACHERS University of California-Irvine School of Medicine Nathan Molina nathan.d.molina@gmail.com Trevor Plescia taplescia90@gmail.com Jack Silva jpsilva42@gmail.com
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist
 The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, 2017 Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist Disclosures Outline Index case Introduction Etiology Risk factors Acute stone event Conservative
The 82 nd UWI/BAMP CME Conference November 18, 2017 Jeetu Nebhnani MBBS D.M. Urology Consultant Urologist Disclosures Outline Index case Introduction Etiology Risk factors Acute stone event Conservative
RETROGRADE URETEROSCOPIC HOLMIUM: YAG LASER LITHOTRIPSY FOR URETERAL AND RENAL STONES
 1110-5712 Vol. 20, No. 3, 2014 Egyptian Journal of Urology 121-125 RETROGRADE URETEROSCOPIC HOLMIUM: YAG LASER LITHOTRIPSY FOR URETERAL AND RENAL STONES AHMED EL-FEEL, AHMED SAMIR, HESHAM FATHY, OMAR M
1110-5712 Vol. 20, No. 3, 2014 Egyptian Journal of Urology 121-125 RETROGRADE URETEROSCOPIC HOLMIUM: YAG LASER LITHOTRIPSY FOR URETERAL AND RENAL STONES AHMED EL-FEEL, AHMED SAMIR, HESHAM FATHY, OMAR M
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder)
 Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy
 CASE REPORT Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy Bowei Yang 1, Jiongming Li 1, Jianhe Liu 1, Yuepan Bao 2, Prashant Mishra 1, Haixiang
CASE REPORT Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy Bowei Yang 1, Jiongming Li 1, Jianhe Liu 1, Yuepan Bao 2, Prashant Mishra 1, Haixiang
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is a stone? right kidney left kidney A stone is a hard, solid mass that
Patient Information English Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is a stone? right kidney left kidney A stone is a hard, solid mass that
Paediatric surgical emergencies. Mani Thyagarajan BWCH
 Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology What is Laparoscopy? Minimally invasive surgical alternative to standard surgery How is Laparoscopy Performed? A laparoscope and video camera are used to visualize internal organs
Kaiser Oakland Urology What is Laparoscopy? Minimally invasive surgical alternative to standard surgery How is Laparoscopy Performed? A laparoscope and video camera are used to visualize internal organs
The Urinary System. Maintenance Systems Unit 5
 The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
w This information leaflet contains basic information Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones What is a stone? Patient Information Go Online
 Patient Information English Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is a stone? right kidney left kidney A stone is a hard, solid mass that
Patient Information English Basic Information on Kidney and Ureteral Stones The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is a stone? right kidney left kidney A stone is a hard, solid mass that
ISSN East Cent. Afr. J. surg. (Online)
 87 Ureteroscopy in a Resource Limited Setting: The Tikur Anbessa General Specialized Hospital Experience in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. D. Andualem, L. Be-ede, T. Mulat, L. Samodi Addis Ababa University-School
87 Ureteroscopy in a Resource Limited Setting: The Tikur Anbessa General Specialized Hospital Experience in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. D. Andualem, L. Be-ede, T. Mulat, L. Samodi Addis Ababa University-School
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students
 Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
Uroradiology Tutorial For Medical Students Lesson 3: Cystography & Urethrography Part 1 American Urological Association Introduction Conventional radiography of the urinary tract includes several diagnostic
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research
 Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Masch et al. Genitourinary Imaging Original Research William R. Masch 1 Richard H. Cohan 1,2 James H. Ellis 1,2 Jonathan R. Dillman 1,3 Jonathan M. Rubin 1,2 Matthew
Genitourinary Imaging Original Research Masch et al. Genitourinary Imaging Original Research William R. Masch 1 Richard H. Cohan 1,2 James H. Ellis 1,2 Jonathan R. Dillman 1,3 Jonathan M. Rubin 1,2 Matthew
ULTRASOUND NOMENCLATURE
 Chapter 1: Ultrasound Nomenclature, Image Orientation, and Basic Instrumentation CYNTHIA SIKOWSKI Ultrasound waves are sound waves that have a frequency exceeding 20,000 Hz. When sound waves are transmitted
Chapter 1: Ultrasound Nomenclature, Image Orientation, and Basic Instrumentation CYNTHIA SIKOWSKI Ultrasound waves are sound waves that have a frequency exceeding 20,000 Hz. When sound waves are transmitted
Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Terminology Tissue Appearance
 By Marc Nielsen, MD Advantages/Disadvantages Generation of Image Ultrasound Machine/Transducer selection Modes of Ultrasound Terminology Tissue Appearance Scanning Technique Real-time Portable No ionizing
By Marc Nielsen, MD Advantages/Disadvantages Generation of Image Ultrasound Machine/Transducer selection Modes of Ultrasound Terminology Tissue Appearance Scanning Technique Real-time Portable No ionizing
Duplex ultrasound is first-line imaging for all
 Our Protocol for Transabdominal Pelvic Vein Duplex Ultrasound A summary of s protocol for pelvic vein duplex ultrasonography, including equipment, patient positioning, ultrasound settings, and technique.
Our Protocol for Transabdominal Pelvic Vein Duplex Ultrasound A summary of s protocol for pelvic vein duplex ultrasonography, including equipment, patient positioning, ultrasound settings, and technique.
Abdominal Ultrasound. Diane Hallinen, MD. Bloodroot
 Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Clinical Application and Value of Ultrasound in Diagnosis of. Acute Abdomen A Single Center Experience
 Original Paper Research in Health Science ISSN 2470-6205 (Print) ISSN 2470-6213 (Online) Vol. 3, No. 1, 2018 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/rhs Clinical Application and Value of Ultrasound in Diagnosis
Original Paper Research in Health Science ISSN 2470-6205 (Print) ISSN 2470-6213 (Online) Vol. 3, No. 1, 2018 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/rhs Clinical Application and Value of Ultrasound in Diagnosis
Haematuria Clinic. Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST
 Haematuria Clinic Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST The Haematuria Clinic You have been referred to the Haematuria Clinic as
Haematuria Clinic Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST The Haematuria Clinic You have been referred to the Haematuria Clinic as
Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1
 Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22
 Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
A single center experience with a lithotripsy machine Modulith SLX-F2 : Evaluation of dual focus system and clinical results
 A single center experience with a lithotripsy machine Modulith SLX-F2 : Evaluation of dual focus system and clinical results Kotaro Suzuki, Yuzo Yamashita, Minoru Yoshida and Junichi Matsuzaki The department
A single center experience with a lithotripsy machine Modulith SLX-F2 : Evaluation of dual focus system and clinical results Kotaro Suzuki, Yuzo Yamashita, Minoru Yoshida and Junichi Matsuzaki The department
Abstract Submission Form
 Abstract Submission Form All abstracts must be submitted to the AOCR by September 15 th. All information included must be the original work of the author(s) and be in typed form. Incomplete or handwritten
Abstract Submission Form All abstracts must be submitted to the AOCR by September 15 th. All information included must be the original work of the author(s) and be in typed form. Incomplete or handwritten
Pancreatic Stone Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy-A New Concern for Urologists?
 ARC Journal of Urology Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018, PP 1-5 ISSN No. (Online):2456-060X http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2456-060x.0301001 www.arcjournals.org Pancreatic Stone Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy-A
ARC Journal of Urology Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018, PP 1-5 ISSN No. (Online):2456-060X http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2456-060x.0301001 www.arcjournals.org Pancreatic Stone Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy-A
Urolithiasis. Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery
 Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
Urolithiasis Ali Kasraeian, MD, FACS Kasraeian Urology Advanced Laparoscopic, Robotic & Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Urolithiasis: Why should we care? Affects 5% of US men and women Men twice as
Bedside Ultrasound in the Emergency Department to Detect Hydronephrosis for the Evaluation of Suspected Ureteric Colic
 Bedside Ultrasound in the Emergency Department to Detect Hydronephrosis for the Evaluation of Suspected Ureteric Colic Shrestha R, Shakya RM, Khan A ABSTRACT Background Department of Emergency Medicine
Bedside Ultrasound in the Emergency Department to Detect Hydronephrosis for the Evaluation of Suspected Ureteric Colic Shrestha R, Shakya RM, Khan A ABSTRACT Background Department of Emergency Medicine
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation
 Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked
 Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked 10-20% of all injured patients Long term morbidity Impotence Incontinence Life-threatening injuries first Urethral Injury Plan Bladder Injury Kidney
Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked 10-20% of all injured patients Long term morbidity Impotence Incontinence Life-threatening injuries first Urethral Injury Plan Bladder Injury Kidney
MA HOSSAIN. Summary: Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 29, No. 2, April 2011
 Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 29, No. 2, April 2011 Comparative Study of Stone Pulverization and Clearance Rate between Patients Treated by ESWL Under Spinal Anesthesia
Journal of Bangladesh College of Physicians and Surgeons Vol. 29, No. 2, April 2011 Comparative Study of Stone Pulverization and Clearance Rate between Patients Treated by ESWL Under Spinal Anesthesia
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines. Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination
 Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination Approved by Council Feb 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination Approved by Council Feb 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to
The Evaluation of not Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy: A Randomized Prospective Study
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.26, No. 1, Mach 2004 The Evaluation of not Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy: A Randomized Prospective Study Waleed Ali, FRCS* Mohammed Al-Durazi, FRCS** Reem Al-Bareeq,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.26, No. 1, Mach 2004 The Evaluation of not Stenting after Uncomplicated Ureteroscopy: A Randomized Prospective Study Waleed Ali, FRCS* Mohammed Al-Durazi, FRCS** Reem Al-Bareeq,
Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy to distal ureteric stones: the transgluteal approach significantly increases stone-free rates
 Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy to distal ureteric stones: the transgluteal approach significantly increases stone-free rates Simon Phipps, Carolann Stephenson and David Tolley Scottish Lithotriptor
Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy to distal ureteric stones: the transgluteal approach significantly increases stone-free rates Simon Phipps, Carolann Stephenson and David Tolley Scottish Lithotriptor
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases
 HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
The 2 nd Cambridge Advanced Emergency Ultrasound Course
 The 2 nd Cambridge Advanced Emergency Ultrasound Course Addenbrooke s Hospital Cambridge Sept 2008 1 2 Faculty! UK! USA! Australia! Toshiba! Emergency Medicine! Radiology 3 Programme! Day 1 Introduction
The 2 nd Cambridge Advanced Emergency Ultrasound Course Addenbrooke s Hospital Cambridge Sept 2008 1 2 Faculty! UK! USA! Australia! Toshiba! Emergency Medicine! Radiology 3 Programme! Day 1 Introduction
Ultrasound Physics & Terminology
 Ultrasound Physics & Terminology This module includes the following: Basic physics terms Basic principles of ultrasound Ultrasound terminology and terms Common artifacts seen Doppler principles Terms for
Ultrasound Physics & Terminology This module includes the following: Basic physics terms Basic principles of ultrasound Ultrasound terminology and terms Common artifacts seen Doppler principles Terms for
Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 203-208 203 Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma TZE-YU LEE SHEUNG-FAT KO CHUNG-CHENG HUANG YU-FENG CHENG Department of Radiology, Chang Gung
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 203-208 203 Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma TZE-YU LEE SHEUNG-FAT KO CHUNG-CHENG HUANG YU-FENG CHENG Department of Radiology, Chang Gung
Ultrasound - Prostate
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Prostate Ultrasound of the prostate uses sound waves to produce pictures of a man s prostate gland and to help diagnose symptoms such as difficulty urinating or an elevated
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Prostate Ultrasound of the prostate uses sound waves to produce pictures of a man s prostate gland and to help diagnose symptoms such as difficulty urinating or an elevated
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION
 CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
Ultrasound Applied Physics
 Ultrasound Applied Physics University of Toronto Department of Medical Imaging Applied Physics Mini-Course #3 2016 Ultrasound Laboratory Manual and Examination Booklet 1/21/2016 Ultrasound Applied Physics
Ultrasound Applied Physics University of Toronto Department of Medical Imaging Applied Physics Mini-Course #3 2016 Ultrasound Laboratory Manual and Examination Booklet 1/21/2016 Ultrasound Applied Physics
URINARY SYSTEM. MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Chapter Six HIT #141. Anatomy
 URINARY SYSTEM MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Chapter Six HIT #141 Anatomy Kidneys = bean-shaped organs, located on each side of the spinal column, removal of waste from the blood. Nephron = microscopic located in
URINARY SYSTEM MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Chapter Six HIT #141 Anatomy Kidneys = bean-shaped organs, located on each side of the spinal column, removal of waste from the blood. Nephron = microscopic located in
