Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh
|
|
|
- Elmer Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
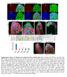
1 Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa Niccoli, and Daniel St Johnston Table S1. Frequency of Cytoplasmic Seething and Streaming at Stage 9 No. oocytes with No. oocytes with cytoplasmic cytoplasmic seething streaming wt 3 0 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ; GFP-Capu 13 0 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ; GFP-CapuΔN 10 0 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ; GFP-SpireD 0 5 spire RP 0 10 spire RP ; GFP-Capu 5 0 spire RP ; GFP-CapuΔN 7 0 spire RP /spire 2F ; GFP-CapuΔN 8 1 spire RP /Df(2L)Exel spire RP /Df(2L)Exel 6046 ; GFP-SpireD 5 0 spire RP /Df(2L)Exel 6046 ; GFP-SpireC 0 3 chic chic 1320 /chic chic 1320 /chic 221 ; GFP-Capu 0 10 chic 1320 /chic 221 ; GFP-CapuΔN 0 12 Table showing the number of egg chambers of various genotypes that show either the slow random movements in the oocyte cytoplasm called seething (See Figure 1I), or unidirectional fast movements of premature streaming (See Figure 1J). UASp Capu and Spire constructs were expressed under the control of noa-gal4-vp16.
2 Table S2. Microtubule Appearance in Stage 9 and 10A Oocytes Stage9 Stage 10A Cortical arrays N Cortical arrays N w 0% 60 0% 17 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 100% % 40 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ; GFP-Capu 0% 58 0% 13 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ; GFP-CapuΔN 0% 65 0% 24 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ; GFP-Spir-D 100% % 12 spire RP 99% % 15 spire RP ; Capu 48% % 17 spire RP ; GFP-Capu 12% % 32 spire RP ; GFP-CapuΔN 1% 69 40% 15 spire RP /spire 2F ; GFP-Spir-D 0% 32 0% 10 capu RK FRT nlsgfp/ capu G7 95% % 8 capu RK khc 17 / capu G7 khc 17 0% 8 0% 2 Table showing the percentage of egg chambers with dense arrays of microtubules along the oocyte cortex (See Figure 1O) instead of the normal anterior to posterior gradient of microtubules (See Figure 1M). N indicates the number of egg chambers analysed for each genotype. UASp Capu and Spire constructs were expressed under the control of noa-gal4-vp16. Table S3. oskar mrna Localisation in Stage 9-10B Egg Chambers Posterior Posterior & Diffuse Diffuse N W 100% 0% 0% 71 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 0% 0% 100% 56 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ; GFP-CapuΔN 100% 0% 0% 106 spire RP 0% 2% 98% 101 spire RP ; GFP-Capu 21% 70% 9% 133 spire RP ; GFP-CapuΔN 53% 21% 25% 255 spire 2F /spire RP ; GFP-Spir-D 100% 0% 0% 26 Table showing the distribution of oskar mrna localisation phenotypes, as visualised by oskar in situ hybridisation, in stage 9-10B egg chambers of various genotypes. The localisation patterns were classified as: Diffuse localisation (See Figure 1N); Posterior and diffuse (See Figure S2B) and Posterior localisation (See Figure 1P). N indicates the number of egg chambers analysed for each genotype. UASp Capu and Spire constructs were expressed under the control of noa-gal4-vp16.
3 Table S4. The Effect of Latrunculin A on Ooplasmic Movement at Stage 9 Without Latrunculin A With Latrunculin A Streaming Seething Streaming Seething w capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ;GFP-Capu capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ;GFP-CapuΔN spire RP /spire 2F ;GFP-Spir-D 7 0 spire RP /spire 2F ;GFP-CapuΔN Table showing the number of control egg chambers or egg chambers treated with Latrunculin A of various genotypes that show either slow random movements of the oocyte cytoplasm (seething (see Figure 1I)), or the fast unidirectional movements of premature streaming (See Figure 1J). UASp Capu and Spire constructs were expressed under the control of noa-gal4-vp16. Table S5. The Effect of Latrunculin A on Microtubule Appearance at Stage 9 Without With Latrunculin A Latrunculin A Cortical N Cortical arrays N arrays w 0% % 55 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ;GFP-Capu 0% 54 97% 65 capu G7 /Df(2l)ed SZ1 ;GFP-CapuΔN 0% 53 0% 54 spire RP /spire 2F ;GFP-Spir-D 0% % 63 spire RP /spire 2F ;GFP-CapuΔN 52% 67 96% 56 Table giving the percentage of control stage 9 egg chambers or stage 9 egg chambers treated with Latrunculin A that contain dense arrays of microtubules along the oocyte cortex (See Figure 1O) instead of the normal anterior to posterior gradient of microtubules (See Figure 1M). N indicates the number of egg chambers analysed for each genotype. UASp Capu and Spire constructs were expressed under the control of noa-gal4-vp16.
4 Figure S1. oskar mrna Localises to the Posterior of Late Stage spire Mutant Oocytes (A-C ) Fluorescent in situ hybridisations to oskar mrna in spire RP /Df(2L)Exel 6046 egg chambers. (A-C) Shows the fluorescent signal from an in situ hybridization to oskar mrna, while (A -C ) show DIC images of the oocytes. (A and A ) Stage 9; (B and B ) Stage 10A; (C and C ) Stage 13. As oogenesis progresses, more oskar mrna accumulates at the posterior of the oocyte. (D) Table showing the distribution of oskar mrna at different stages of oogenesis in spire RP /Df(2L)Exel 6046 oocytes. The localisation patterns are classified as diffuse localisation as seen in (A); posterior and diffuse as in (B) and posterior as in (C).N indicates the number of egg chambers analysed at each stage.
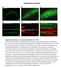
5 Figure S2. Comparisons of the Actin Mesh in a Range of chic and capu Alleles (A-D, F-J ) Stage 9 egg chambers stained with TRITC-Phalloidin. (A -D ) show magnifications of the oocyte cytoplasm imaged 10 µm below the cortex. (A-D ) and (F-J ) show egg chambers stained, imaged and processed in parallel under identical conditions. The vertical lines show the standard deviations in mean pixel intensities. The F-actin forms a dense actin mesh in wildtype oocytes (A). The actin mesh appears slightly less dense in chic 1320 /+ (B), is almost gone in chic 1320 oocytes, (C), and is completely absent in chic 1320 /chic 221 oocytes (D).
6 (E) Bar diagram showing the relative average of mean pixel intensity of the F-actin staining in 30 µm by 30 µm regions of 3-5 stage 9 egg chambers of different chic genotypes. (F-J ) A similar graded effect on the actin mesh is observed in capu mutant combinations of increasing strength. (F) Wildtype; (G) Df(2L)ed SZ1 /+ ; (H) capu 2F ; (I) capu 2F /Df(2L)ed SZ1 ; (J) capu G7 /Df(2L)ed SZ1. (J ) shows the bright dots of residual F-actin staining in the oocyte cytoplasm in the absence of Capu.
7 Figure S3. The chic Mutant Phenotype Is Not Rescued by GFP-Capu, GFP- CapuΔN, or GFP-SpireD (A-E) Confocal images of s7age 8-9 egg chambers stained with TRITC-Phalloidin to label F-actin. (A - E ) show a magnification of the oocyte cytoplasm imaged 10 µm from the cortex. (A) wildtype egg chamber, (B) chic 1320 /chic 221, (C) chic 1320 /chic 221 ; GFP-Capu, (D) chic 1320 /chic 221 ; GFP-CapuΔN, (E) chic 1320 /chic 221 ; GFP-Spir-D.
8 Figure S4. The Actin Mesh in Untreated and Latrunculin A Treated Egg Chambers (A-J) Confocal images of stage 9 egg chambers stained with TRITC-Phalloidin to label F-actin, (Grey scale bar, 30 µm). (A -J ) show a magnification of the F-actin stained oocyte cytoplasm imaged 10 µm from the cortex (White scale bar, 10µm). (A,C,E,G, I) are images of untreated egg chambers, while (B,D,F,H) are images of egg chambers after 8 hours of treatment. (A-D) were processed in parallel as were (E) and (F), (G) and (H), and (I) and (J). (A-B ) wildtype; (C-D ) capu G7 /Df(2L)ed SZ1 ; GFP-Capu; (E-F ) capu G7 /Df(2L)ed SZ1 ; GFP-CapuΔN; (G-H ) spire 2F /spire RP ; GFP-Spir-D; (I-J ) spire 2F /spire RP ; GFP- CapuΔN.
A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm
 Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Supporting Information for A Precise Bicoid Gradient is Nonessential During Cycles 11-13 for Precise Patterning in the Drosophila Blastoderm Elena M. Lucchetta, Meghan E. Vincent and Rustem F. Ismagilov*
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Gilberti et al. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Figure S1: The effect of pharmacological inhibitors on particle uptake. The data presented in Figure 1
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplemental Information. Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo
 Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Chapter 5 A Dose Dependent Screen for Modifiers of Kek5
 Chapter 5 A Dose Dependent Screen for Modifiers of Kek5 "#$ ABSTRACT Modifier screens in Drosophila have proven to be a powerful tool for uncovering gene interaction and elucidating molecular pathways.
Chapter 5 A Dose Dependent Screen for Modifiers of Kek5 "#$ ABSTRACT Modifier screens in Drosophila have proven to be a powerful tool for uncovering gene interaction and elucidating molecular pathways.
Supplementary Figures
 J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Direct observation of regulated RNP transport across the nurse cell/oocyte boundary
 Direct observation of regulated RNP transport across the nurse cell/oocyte boundary Sarah Mische, Mingang Li, Madeline Serr, Thomas S. Hays University of Minnesota, Department of Genetics, Cell Biology,
Direct observation of regulated RNP transport across the nurse cell/oocyte boundary Sarah Mische, Mingang Li, Madeline Serr, Thomas S. Hays University of Minnesota, Department of Genetics, Cell Biology,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Loss of Ena/VASP proteins inhibits filopodia and neuritogenesis. (a) Bar graph of filopodia number per stage 1 control and mmvvee (Mena/ VASP/EVL-null) neurons at 40hrs in culture. Loss of all
Figure S1. Loss of Ena/VASP proteins inhibits filopodia and neuritogenesis. (a) Bar graph of filopodia number per stage 1 control and mmvvee (Mena/ VASP/EVL-null) neurons at 40hrs in culture. Loss of all
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by
 The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
The subcortical maternal complex controls symmetric division of mouse zygotes by regulating F-actin dynamics Xing-Jiang Yu 1,2, Zhaohong Yi 1, Zheng Gao 1,2, Dan-dan Qin 1,2, Yanhua Zhai 1, Xue Chen 1,
Supplements. Figure S1. B Phalloidin Alexa488
 Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
Supplements A, DMSO, PP2, PP3 Crk-myc Figure S1. (A) Src kinase activity is necessary for recruitment of Crk to Nephrin cytoplasmic domain. Human podocytes expressing /7-NephrinCD () were treated with
J. Cell Sci. 129: doi: /jcs : Supplementary information
 Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Patterning of the follicle cell epithelium along the anterior-posterior axis during Drosophila oogenesis
 Development 125, 2837-2846 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV7654 2837 Patterning of the follicle cell epithelium along the anterior-posterior axis during Drosophila
Development 125, 2837-2846 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV7654 2837 Patterning of the follicle cell epithelium along the anterior-posterior axis during Drosophila
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures. for. pirna-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional
 Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Karen L.P. McNally, Amy S. Fabritius, Marina L. Ellefson, Jonathan R. Flynn, Jennifer A. Milan, and Francis J. McNally
 Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Kinesin-1 Prevents Capture of the Oocyte Meiotic Spindle by the Sperm Aster Karen L.P. McNally, Amy S. Fabritius, Marina L. Ellefson, Jonathan R.
Developmental Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Kinesin-1 Prevents Capture of the Oocyte Meiotic Spindle by the Sperm Aster Karen L.P. McNally, Amy S. Fabritius, Marina L. Ellefson, Jonathan R.
Inhibition of patterned cell shape change and cell invasion by Discs large during Drosophila oogenesis
 Inhibition of patterned cell shape change and cell invasion by Discs large during Drosophila oogenesis Scott Goode 1 and Norbert Perrimon 2 Department of Genetics, 2 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard
Inhibition of patterned cell shape change and cell invasion by Discs large during Drosophila oogenesis Scott Goode 1 and Norbert Perrimon 2 Department of Genetics, 2 Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity Chris Church, Lee Moir, Fiona McMurray, Christophe Girard, Gareth T Banks, Lydia Teboul, Sara Wells,
Supplementary Information Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity Chris Church, Lee Moir, Fiona McMurray, Christophe Girard, Gareth T Banks, Lydia Teboul, Sara Wells,
El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc.
 Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
Supplementary Figure S1: TIPF reporter validation in the wing disc. a,b, Test of put RNAi. a, In wildtype discs the Dpp target gene Sal (red) is expressed in a broad stripe in the centre of the ventral
sfigure 1: Detection of L-fucose in normal mouse renal cortex using the plant lectin LTL
 sfigure 1: Detection of L-fucose in normal mouse renal cortex using the plant lectin LTL LTL staining Negative control Fluorescence microscopy of normal (CL-11 +/+ ) mouse renal tissue after staining with
sfigure 1: Detection of L-fucose in normal mouse renal cortex using the plant lectin LTL LTL staining Negative control Fluorescence microscopy of normal (CL-11 +/+ ) mouse renal tissue after staining with
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines
 Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
mrna cis Elements Located in Non-Protein-Coding Regions
 mrna cis Elements Located in Non-Protein-Coding Regions IRP Repressor mirnas Bcd/4EHP Repressor cap 5 Leader ORF 3 UTR (A) n eif4e/4e-bp 2 o structure uorf eif2α kinases Localization Transcript-independent
mrna cis Elements Located in Non-Protein-Coding Regions IRP Repressor mirnas Bcd/4EHP Repressor cap 5 Leader ORF 3 UTR (A) n eif4e/4e-bp 2 o structure uorf eif2α kinases Localization Transcript-independent
CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES FIGURE S1. Detection of MCs. A, Schematic representation of T cells stimulated on anti- CD3 coated cover slips indicating stimulatory contact site, F-actin polymerization and microclusters.
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: Luminal localization of CCM-3. (a) The CCM-3::GFP fusion protein localizes along the apical (luminal) surface of the pharynx (b) as well as the lumen of
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Midterm 1. Number of students Score. Mean: 73 Median: 75 Top Score: 98
 Midterm 1 14 12 Number of students 10 8 6 4 2 0 35-40 41-45 Mean: 73 Median: 75 Top Score: 98 46-50 51-55 56-60 61-65 66-70 71-75 Score 76-80 81-85 86-90 91-95 96-100 Write your name and student ID# on
Midterm 1 14 12 Number of students 10 8 6 4 2 0 35-40 41-45 Mean: 73 Median: 75 Top Score: 98 46-50 51-55 56-60 61-65 66-70 71-75 Score 76-80 81-85 86-90 91-95 96-100 Write your name and student ID# on
Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration
 Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration Alison A. Staton, Holger Knaut, and Antonio J. Giraldez Supplementary Note Materials and
Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration Alison A. Staton, Holger Knaut, and Antonio J. Giraldez Supplementary Note Materials and
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
a 10 4 Link et al. Supplementary Figure 1 Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.1842 Cells per mouse ( 10 5 ) TRPV2KO anti-gr1 anti-gr anti-f4/80
 a 10 4 WT 10 4 TRPV2KO 10 3 10 3 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 42.3 45.2 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 10 4 10 4 40 42.5 anti-cd11b 10 3 10 2
a 10 4 WT 10 4 TRPV2KO 10 3 10 3 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 anti-gr1 10 2 10 1 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 42.3 45.2 10 0 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 anti-f4/80 10 4 10 4 40 42.5 anti-cd11b 10 3 10 2
Supplemental Information. Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes. Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain. and Regulates Ventricular Development
 Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Supplemental data Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Supplemental Figure 2.
 Supplemental data Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Analysis of deletion of AMPK!2 in POMC and AgRP neurons in control and POMC!2KO and AgRP!2KO mice. (A) mmunofluorescence analysis for
Supplemental data Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Analysis of deletion of AMPK!2 in POMC and AgRP neurons in control and POMC!2KO and AgRP!2KO mice. (A) mmunofluorescence analysis for
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 5 microns C7 B6 unclassified H19 C7 signal H19 guide signal H19 B6 signal C7 SNP spots H19 RNA spots B6 SNP spots colocalization H19 RNA classification Supplementary Figure 1. Allele-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 5 microns C7 B6 unclassified H19 C7 signal H19 guide signal H19 B6 signal C7 SNP spots H19 RNA spots B6 SNP spots colocalization H19 RNA classification Supplementary Figure 1. Allele-specific
Merlin, the Drosophila homologue of neurofibromatosis-2, is specifically required in posterior follicle cells for axis formation in the oocyte
 Development 128, 665-673 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV7846 665 Merlin, the Drosophila homologue of neurofibromatosis-2, is specifically required in posterior
Development 128, 665-673 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV7846 665 Merlin, the Drosophila homologue of neurofibromatosis-2, is specifically required in posterior
Supplemental Data. Hao et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Confocal Images and VA-TIRFM Analysis of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis Seedlings. (A) RbohD expression in whole Arabidopsis seedlings. RbohD was expressed in the leaves, hypocotyl, and
Supplemental Figure 1. Confocal Images and VA-TIRFM Analysis of GFP-RbohD in Arabidopsis Seedlings. (A) RbohD expression in whole Arabidopsis seedlings. RbohD was expressed in the leaves, hypocotyl, and
Problem Set 5 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2294 Figure S1 Localization and function of cell wall polysaccharides in root hair cells. (a) Spinning-disk confocal sections of seven day-old A. thaliana seedlings stained with 0.1% S4B
IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia
 Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2860
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Amelio et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203134/dc1 Figure S1. mir-24 regulates proliferation and by itself induces
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
genome edited transient transfection, CMV promoter
 Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
50mM D-Glucose. Percentage PI. L-Glucose
 Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figure 1: Characterisation of phospho-fgfr-y463 antibody. (A)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Characterisation of phospho-fgfr-y463 antibody. (A) Cells over-expressing hfgfr1-pcdna3 (+) or pcdna3 (-) were stimulated for 10 minutes with 50ng/ml FGF2 and lysates immunoblotted
Supplementary Figure 1: Characterisation of phospho-fgfr-y463 antibody. (A) Cells over-expressing hfgfr1-pcdna3 (+) or pcdna3 (-) were stimulated for 10 minutes with 50ng/ml FGF2 and lysates immunoblotted
Yasunaga et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Yasunaga et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201502043 /DC1 THE JOU RNAL OF CELL BIO LOGY Figure S1. Spatial and temporal expression of nphp4, and localization
Supplemental material JCB Yasunaga et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201502043 /DC1 THE JOU RNAL OF CELL BIO LOGY Figure S1. Spatial and temporal expression of nphp4, and localization
Supplementary information. The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic. Spindle Orientation
 Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Article. Transport of Germ Plasm on Astral Microtubules Directs Germ Cell Development in Drosophila
 Current Biology 21, 439 448, March 22, 2011 ª2011 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2011.01.073 Transport of Germ Plasm on Astral Microtubules Directs Germ Cell Development in Drosophila
Current Biology 21, 439 448, March 22, 2011 ª2011 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2011.01.073 Transport of Germ Plasm on Astral Microtubules Directs Germ Cell Development in Drosophila
Distributions of Mitochondria and the Cytoskeleton in Hamster Embryos Developed In Vivo and In Vitro
 J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 23, 128 134, 2006 128 Original Distributions of Mitochondria and the Cytoskeleton in Hamster Embryos Developed In Vivo and In Vitro Hiroyuki Suzuki 1 *, Manabu Satoh 1 ** and Katsuya
J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 23, 128 134, 2006 128 Original Distributions of Mitochondria and the Cytoskeleton in Hamster Embryos Developed In Vivo and In Vitro Hiroyuki Suzuki 1 *, Manabu Satoh 1 ** and Katsuya
A central role for microtubules in the differentiation of Drosophila oocytes
 Development 118, 1169-1180 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 1169 A central role for microtubules in the differentiation of Drosophila oocytes William E. Theurkauf
Development 118, 1169-1180 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 1169 A central role for microtubules in the differentiation of Drosophila oocytes William E. Theurkauf
Supplemental Information. Proprioceptive Opsin Functions. in Drosophila Larval Locomotion
 Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Affecting Rhomboid-3 Function Causes a Dilated Heart in Adult Drosophila
 Affecting Rhomboid-3 Function Causes a Dilated Heart in Adult Drosophila Lin Yu 1, Teresa Lee 2, Na Lin 3, Matthew J. Wolf 1 * 1 Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Duke University Medical
Affecting Rhomboid-3 Function Causes a Dilated Heart in Adult Drosophila Lin Yu 1, Teresa Lee 2, Na Lin 3, Matthew J. Wolf 1 * 1 Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, Duke University Medical
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment
 Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
Supplementary Data Dll4-containing exosomes induce capillary sprout retraction ina 3D microenvironment Soheila Sharghi-Namini 1, Evan Tan 1,2, Lee-Ling Sharon Ong 1, Ruowen Ge 2 * and H. Harry Asada 1,3
The microtubule motor cytoplasmic dynein is required for spindle orientation during germline cell divisions and oocyte differentiation in Drosophila
 Development 124, 2409-2419 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 DEV8417 2409 The microtubule motor cytoplasmic dynein is required for spindle orientation during germline
Development 124, 2409-2419 (1997) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1997 DEV8417 2409 The microtubule motor cytoplasmic dynein is required for spindle orientation during germline
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material. Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN
 SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN Jana Husse, Xunlei Zhou, Anton Shostak, Henrik Oster and Gregor Eichele SOM Husse et al.,
SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN Jana Husse, Xunlei Zhou, Anton Shostak, Henrik Oster and Gregor Eichele SOM Husse et al.,
Edited by J. Richard McIntosh, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, and approved June 17, 2016 (received for review November 13, 2015) Results
 Role of kinesin-1 based microtubule sliding in Drosophila nervous system development Michael Winding a, Michael T. Kelliher b,c, Wen Lu a, Jill Wildonger b, and Vladimir I. Gelfand a,1 a Department of
Role of kinesin-1 based microtubule sliding in Drosophila nervous system development Michael Winding a, Michael T. Kelliher b,c, Wen Lu a, Jill Wildonger b, and Vladimir I. Gelfand a,1 a Department of
Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
 open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
open reading frame 1565 (segment 5) 47 (-) 3 5 (+) 76 101 125 149 173 197 221 246 287 open reading frame 890 (segment 8) 60 (-) 3 5 (+) 172 Supplementary Fig. S1. Schematic diagram of minigenome segments.
Interaction with eif5b is essential for Vasa function during development
 4167 Interaction with eif5b is essential for Vasa function during development Oona Johnstone and Paul Lasko* Department of Biology, McGill University, 1205 Avenue Docteur Penfield, Montréal, Québec H3A
4167 Interaction with eif5b is essential for Vasa function during development Oona Johnstone and Paul Lasko* Department of Biology, McGill University, 1205 Avenue Docteur Penfield, Montréal, Québec H3A
Irf1 fold changes (D) 24h 48h. p-p65. t-p65. p-irf3. t-irf3. β-actin SKO TKO 100% 80% 60% 40% 20%
 Irf7 Fold changes 3 1 Irf1 fold changes 3 1 8h h 8h 8h h 8h p-p6 p-p6 t-p6 p-irf3 β-actin p-irf3 t-irf3 β-actin TKO TKO STKO (E) (F) TKO TKO % of p6 nuclear translocation % % 1% 1% % % p6 TKO % of IRF3
Irf7 Fold changes 3 1 Irf1 fold changes 3 1 8h h 8h 8h h 8h p-p6 p-p6 t-p6 p-irf3 β-actin p-irf3 t-irf3 β-actin TKO TKO STKO (E) (F) TKO TKO % of p6 nuclear translocation % % 1% 1% % % p6 TKO % of IRF3
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.4257
 Supplementary Figure 1 Screen for polypeptides that affect cellular actin filaments. (a) Table summarizing results from all polypeptides tested. Source shows organism, gene, and amino acid numbers used.
Supplementary Figure 1 Screen for polypeptides that affect cellular actin filaments. (a) Table summarizing results from all polypeptides tested. Source shows organism, gene, and amino acid numbers used.
Supplementary Figure 1: Co-localization of reconstituted L-PTC and dendritic cells
 a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
McWilliams et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
Supplemental material JCB McWilliams et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201603039 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. In vitro characterization of mito-qc. (A and B) Analysis
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Courtheoux et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200902093/dc1 S1 Figure S2. Visualization of multiple merotelic attachments.
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Courtheoux et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200902093/dc1 S1 Figure S2. Visualization of multiple merotelic attachments.
Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
Supplementary Figure 1 Quantification of myelin fragments in the aging brain (a) Electron microscopy on corpus callosum is shown for a 18-month-old wild type mice. Myelin fragments (arrows) were detected
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified
 Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Distinct mechanisms for mrna localization during embryonic axis specification in the wasp Nasonia
 Developmental Biology 306 (2007) 134 142 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio Distinct mechanisms for mrna localization during embryonic axis specification in the wasp Nasonia Eugenia C. Olesnicky, Claude Desplan
Developmental Biology 306 (2007) 134 142 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio Distinct mechanisms for mrna localization during embryonic axis specification in the wasp Nasonia Eugenia C. Olesnicky, Claude Desplan
1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization
 Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
Supplementary figures: 1. Microfluidic device characteristics and cell compartmentalization Microfluidic channels were molded in PDMS (Fig. S1 A and B) over silicon masters, which were structured with
