Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Tabitha Preston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information 1
2 Supplementary information, Figure S1 Establishment of PG-haESCs. (A) Summary of derivation of PG-haESCs. (B) Upper, Flow analysis of DNA content of established PG-haES cell lines. Lower, Images of PG-haESCs derived from parthenogenetic blastocysts. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) Gene expression profiles of PG-haESCs using RNA-seq analysis. Gene expression profiles were clustered using all expressed genes. Two PG-haESC lines (PGH-1 and PGH-2) show similar expression profiles to the AG-haESCs (AGH-OG3 and AGH-EG1). To avoid the influence of diploidized cells on the expression profile, we collected samples after FACS of cells in the G1/G0 phase. (D) Gene expression profiles of PG-haESCs based on imprinting genes. Two PGhaESC lines show similar expression profiles to the AG-haESCs. (E) Bigwig track of maternal imprinted genes (Snrpn, Peg1, Igf2 and Peg3). RNA-seq of PG-haESCs and AG-haESCs reveals similar expression levels of both maternal and paternal imprinted genes in PG-haESCs compared with AG-haESCs. (F) Methylation state of paternally imprinted genes (H19 and Gtl2) in PG-haESCs. (G) Methylation state of maternally imprinted genes (Snrpn and Peg1) in PG-haESCs. PGH-3 and PGH-4 lost maternal imprints at early passages. (H) Methylation profiles of Snrpn and Peg1 in PGH-2 and PGH-5 ES cell lines. PGH- 2 and PGH-5 gradually lost maternal imprints during cell passage. 2
3 3
4 Supplementary information, Figure S2 Establishment of DKO-PG-haESCs. (A) Diagram of generation of DKO-PG-haESCs using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. (B) Summary of establishment of PG-haESCs carrying H19-DMR deletion, IG-DMR deletion or both. (C) Establishment of PG-haESCs carrying H19-DMR deletion, IG-DMR deletion or both. Upper panel, flow analysis of DNA content of established haploid cell lines. Lower panel, represented images of PG-haESCs carrying different mutations. Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) Genotyping analysis of PG-haESCs carrying H19-DMR or IG-DMR deletion. (E) Methylation state of the Snrpn DMR in DKO-PG-haESCs. (F) SC pups from ICPHCI using PGH (left) and IG DMR -PGH (right) cells. Pups and placentas obtained by C-section from pseudopregnant mice at E19.5 are shown. Asterisks indicate growth-retarded SC pups that died shortly after birth. (G) Genotyping analysis of SC pups derived from PG-haESCs carrying H19-DMR or IG-DMR deletion. (H) SC pups from ICPHCI using H19 DMR -IG DMR -PGH cells. Left, newborn SC pups. Right, adult SC mice. (I) Genotyping analysis of SC pups derived from DKO-PG-haESCs. (J) Methylation state of the Snrpn and Peg1 DMRs in adult SC mice. 4
5 Supplementary information, Table S1 Summary of in vivo development of SC mice from PG-haESCs carrying deletions of H19-DMR, IG-DMR or both. Donor cells Haploid ESC lines Passage number No. of embryos transferred No. of growthretarded pups (% of transferred embryos) No. of normal pups (% of transferred embryos) H19-DMR KO PG-haESCs PGH-1 PGH-4 p (1.8) 0 p (1.7) 2 (1.7) p (2.3) 2 (1.5) p (1.7) 7 (6.0) Subtotal p21-p (1.9) 11 (2.6) IG-DMR KO PG-haESCs IG DMR - PGH-1 IG DMR - PGH-2 p (2.0) 0 p (4.9) 1 (1.2) p (4.4) 2 (2.2) Subtotal p (4.1) 3 (1.4) DKO-PGhaESCs IG DMR -PGH -1 IG DMR - PGH-2 IG DMR - PGH-3 p (16.3) p (17.2) p (0.8) 21 (16.8) p (0.8) 24 (20.0) p (14.7) p (12.8) p (12.6) p (13.3) p (17.3) p (15.0) p (12.5) p (2.9) 4 (11.4) p (16.2) Subtotal p12-p (0.3) 158 (15.5) 5
6 WT PGhaESCs PGH-1 p PGH-2 p Subtotal p
7 Materials and Methods Animal use and care All animal procedures were performed under the ethical guidelines of the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology (SIBCB), Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences (SIBS), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Derivation of PG-haESCs For generation of PG-haploid embryos, mature oocytes were obtained from superovulated female mice (C57BL/6 background) and cultured in CZB medium for 1 hr and then activated for 5 6 hr in activation medium containing 10 mm Sr 2+ without CB. Following activation, all of the embryos were cultured in KSOM medium with amino acids at 37 under 5% CO2 in air. The embryos that reached the morula or blastocyst stage by 3.5 days in culture were transferred into ESC medium for derivation of ESC lines. The zona pellucida was removed using acid Tyrode solution. Each embryo was transferred into one well of a 96-well plate seeded with ICR embryonic fibroblast feeders in ESC medium supplemented with 20% knockout serum replacement, 1,500 U/ml LIF, 3 um CHIR99021, and 1 um PD After 4 5 days in culture, the colonies were trypsinized and transferred to a 96-well plate with a fresh feeder layer in fresh medium. Clonal expansion of the ESCs proceeded from 48-well plates to 6-well plates with feeder cells and then in 6-well plates for routine culture. To sort haploid cells, ESCs were trypsinized, washed by DPBS (GIBCO), and then incubated with 15 ug/ml Hoechst33342 in a 37 water bath. Subsequently, the haploid 1C peak was purified using BD FACS AriaII for further culturing. ICPHCI and embryo transfer To generate semi-cloned (SC) embryos, PG-haESCs arrested at M phase by culturing in medium containing 0.05 mg/ml demecolcine for 8 hr were used for intracytoplasmic injection (ICPHCI) as a previous report. Briefly, PG-haESCs were trypsinized and suspended in HEPES-CZB medium with or without 3% (w/v) polyvinylpyrrolidone. Each nucleus from M-phase haploid cells was injected into an 7
8 MII-arrested oocyte (B6D2F1 background) using a Piezo-drill micromanipulator. The SC embryos were activated and cultured in vitro for 24 hr to reach the two-cell stage two-cell SC embryos were transferred into each oviduct of pseudo-pregnant ICR females at 0.5 days postcoitum (dpc). 8
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL SUPPORTING ONLINE TEXT Efficiency of SCNT Alive fetuses at mid-gestation The rate of viable (beating heart) embryos at day 12.5-14.5 dpc was assessed after sacrifice of foster
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL SUPPORTING ONLINE TEXT Efficiency of SCNT Alive fetuses at mid-gestation The rate of viable (beating heart) embryos at day 12.5-14.5 dpc was assessed after sacrifice of foster
Development of normal mice from metaphase I oocytes fertilized with primary spermatocytes
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 5611 5615, May 1998 Developmental Biology Development of normal mice from metaphase I oocytes fertilized with primary spermatocytes ATSUO OGURA*, OSAMU SUZUKI*,
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 5611 5615, May 1998 Developmental Biology Development of normal mice from metaphase I oocytes fertilized with primary spermatocytes ATSUO OGURA*, OSAMU SUZUKI*,
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
Dissecting gene regulation network in human early embryos. at single-cell and single-base resolution
 Dissecting gene regulation network in human early embryos at single-cell and single-base resolution Fuchou Tang BIOPIC, College of Life Sciences Peking University 07/10/2015 Cockburn and Rossant, 2010
Dissecting gene regulation network in human early embryos at single-cell and single-base resolution Fuchou Tang BIOPIC, College of Life Sciences Peking University 07/10/2015 Cockburn and Rossant, 2010
oocytes were pooled for RT-PCR analysis. The number of PCR cycles was 35. Two
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a Kdm3a Kdm4b β-actin Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis b 1.8 Relative expression.6.4.2 Kdm3a Kdm4b RT-PCR analysis of Kdm3a and Kdm4b expression in oocytes and testes. Twenty
Supplementary Fig. 1 a Kdm3a Kdm4b β-actin Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis b 1.8 Relative expression.6.4.2 Kdm3a Kdm4b RT-PCR analysis of Kdm3a and Kdm4b expression in oocytes and testes. Twenty
To describe the procedure used for piezo-activated mouse intracellular sperm injection (ICSI) in mice.
 1.0 Purpose: To describe the procedure used for piezo-activated mouse intracellular sperm injection (ICSI) in mice. Useful References: Kimura, Y & Yanagimuach1 R (1995) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
1.0 Purpose: To describe the procedure used for piezo-activated mouse intracellular sperm injection (ICSI) in mice. Useful References: Kimura, Y & Yanagimuach1 R (1995) Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
Today. Genomic Imprinting & X-Inactivation
 Today 1. Quiz (~12 min) 2. Genomic imprinting in mammals 3. X-chromosome inactivation in mammals Note that readings on Dosage Compensation and Genomic Imprinting in Mammals are on our web site. Genomic
Today 1. Quiz (~12 min) 2. Genomic imprinting in mammals 3. X-chromosome inactivation in mammals Note that readings on Dosage Compensation and Genomic Imprinting in Mammals are on our web site. Genomic
Ellen Anckaert, Sergio Romero, Tom Adriaenssens, Johan Smitz Follicle Biology Laboratory UZ Brussel, Brussels
 Effects of low methyl donor levels during mouse follicle culture on follicle development, oocyte maturation and oocyte imprinting establishment. Ellen Anckaert, Sergio Romero, Tom Adriaenssens, Johan Smitz
Effects of low methyl donor levels during mouse follicle culture on follicle development, oocyte maturation and oocyte imprinting establishment. Ellen Anckaert, Sergio Romero, Tom Adriaenssens, Johan Smitz
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
EMMA Cryopreservation Workshop Novel concepts in mouse production and preservation
 EMMA Cryopreservation Workshop Novel concepts in mouse production and preservation Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas Madrid, Espagna May 7-8, 2012 K. C. Kent Lloyd, DVM, PhD University of
EMMA Cryopreservation Workshop Novel concepts in mouse production and preservation Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientificas Madrid, Espagna May 7-8, 2012 K. C. Kent Lloyd, DVM, PhD University of
Supplementary tables and figure legends
 Supplementary tables and figure legends Suzuki et al., Mitotic Reprogramming of Sperm, Supplementary Information, 5/7/16, page 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of mouse preimplantation development
Supplementary tables and figure legends Suzuki et al., Mitotic Reprogramming of Sperm, Supplementary Information, 5/7/16, page 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of mouse preimplantation development
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology (Spring 2013)
 DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology (Spring 2013) Director: 651 Ilalo Street, BSB163-3 e-mail: yyamazak@hawaii.edu Phone: (808) 692-1416 Instructors (e-mail): Steve Ward Yusuke Marikawa
DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology (Spring 2013) Director: 651 Ilalo Street, BSB163-3 e-mail: yyamazak@hawaii.edu Phone: (808) 692-1416 Instructors (e-mail): Steve Ward Yusuke Marikawa
Development Supplementary information. Supplementary Figures * * +/+ +/- -/- +/+ +/- -/-
 Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology Spring Semester, 2011
 DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology Spring Semester, 2011 Director: 651 Ilalo Street, BSB163-3 e-mail: yyamazak@hawaii.edu Phone: (808) 692-1416 Instructors (e-mail): Steve Ward Yusuke
DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology Spring Semester, 2011 Director: 651 Ilalo Street, BSB163-3 e-mail: yyamazak@hawaii.edu Phone: (808) 692-1416 Instructors (e-mail): Steve Ward Yusuke
Supplemental Information. Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo
 Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Supplemental Information Fluorescence-based visualization of autophagic activity predicts mouse embryo viability Satoshi Tsukamoto*, Taichi Hara, Atsushi Yamamoto, Seiji Kito, Naojiro Minami, Toshiro Kubota,
Methylation reprogramming dynamics and defects in gametogenesis and embryogenesis: implications for reproductive medicine
 Univ.-Prof. Dr. Thomas Haaf Methylation reprogramming dynamics and defects in gametogenesis and embryogenesis: implications for reproductive medicine Epigenetics and DNA methylation Heritable change of
Univ.-Prof. Dr. Thomas Haaf Methylation reprogramming dynamics and defects in gametogenesis and embryogenesis: implications for reproductive medicine Epigenetics and DNA methylation Heritable change of
DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology Spring Semester, 2018
 DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology Spring Semester, 2018 Director:, DVM, Ph.D. 651 Ilalo Street, BSB163-3 e-mail: yyamazak@hawaii.edu Phone: (808) 692-1416 Instructors (e-mail): Steve
DRB666 Applied Developmental and Reproductive Biology Spring Semester, 2018 Director:, DVM, Ph.D. 651 Ilalo Street, BSB163-3 e-mail: yyamazak@hawaii.edu Phone: (808) 692-1416 Instructors (e-mail): Steve
Transcriptional repression of Xi
 Transcriptional repression of Xi Xist Transcription of Xist Xist RNA Spreading of Xist Recruitment of repression factors. Stable repression Translocated Xic cannot efficiently silence autosome regions.
Transcriptional repression of Xi Xist Transcription of Xist Xist RNA Spreading of Xist Recruitment of repression factors. Stable repression Translocated Xic cannot efficiently silence autosome regions.
INFRAFRONTIER-I3 - Cryopreservation training course. Hosted by the Frozen Embryo and Sperm Archive, MRC - Harwell
 Hosted by the Frozen Embryo and Sperm Archive, MRC - Harwell IVF recovery procedure incorporting methyl-β-cyclodextrin and reduced glutathione This protocol is based on the work published by Takeo et al.,
Hosted by the Frozen Embryo and Sperm Archive, MRC - Harwell IVF recovery procedure incorporting methyl-β-cyclodextrin and reduced glutathione This protocol is based on the work published by Takeo et al.,
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: polar body and embryo biopsy
 Human Reproduction, Vol. 15, (Suppl. 4), pp. 69-75, 2000 Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: polar body and embryo biopsy Luca Gianaroli SISMER, Via Mazzini 12, 40138 Bologna, Italy Scientific Director
Human Reproduction, Vol. 15, (Suppl. 4), pp. 69-75, 2000 Preimplantation genetic diagnosis: polar body and embryo biopsy Luca Gianaroli SISMER, Via Mazzini 12, 40138 Bologna, Italy Scientific Director
3. What law of heredity explains that traits, like texture and color, are inherited independently of each other?
 Section 2: Genetics Chapter 11 pg. 308-329 Part 1: Refer to the table of pea plant traits on the right. Then complete the table on the left by filling in the missing information for each cross. 6. What
Section 2: Genetics Chapter 11 pg. 308-329 Part 1: Refer to the table of pea plant traits on the right. Then complete the table on the left by filling in the missing information for each cross. 6. What
Understanding eggs, sperm and embryos. Marta Jansa Perez Wolfson Fertility Centre
 Understanding eggs, sperm and embryos Marta Jansa Perez Wolfson Fertility Centre What does embryology involve? Aims of the embryology laboratory Creation of a large number of embryos and supporting their
Understanding eggs, sperm and embryos Marta Jansa Perez Wolfson Fertility Centre What does embryology involve? Aims of the embryology laboratory Creation of a large number of embryos and supporting their
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
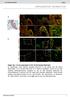 Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Suppl. Fig. 1 in vivo expression of ISL1 in the human fetal heart. a, Hematoxylin eosin staining showing structures of left atrium and left atrium appendage (*) of a human fetal heart at 11 weeks of gestation.
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells
 Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 5 microns C7 B6 unclassified H19 C7 signal H19 guide signal H19 B6 signal C7 SNP spots H19 RNA spots B6 SNP spots colocalization H19 RNA classification Supplementary Figure 1. Allele-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 5 microns C7 B6 unclassified H19 C7 signal H19 guide signal H19 B6 signal C7 SNP spots H19 RNA spots B6 SNP spots colocalization H19 RNA classification Supplementary Figure 1. Allele-specific
Harmful or Not: Trichostatin A treatment of embryos generated by ICSI or ROSI
 DOI: 10.2478/s11535-006-0023-5 Research article CEJB 1(3) 2006 376 385 Harmful or Not: Trichostatin A treatment of embryos generated by ICSI or ROSI Satoshi Kishigami, Hiroshi Ohta, Eiji Mizutani, Sayaka
DOI: 10.2478/s11535-006-0023-5 Research article CEJB 1(3) 2006 376 385 Harmful or Not: Trichostatin A treatment of embryos generated by ICSI or ROSI Satoshi Kishigami, Hiroshi Ohta, Eiji Mizutani, Sayaka
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Effects of Centrifugation and Lipid Removal on the Cryopreservation of in Vitro Produced Bovine Embryos at the Eight-Cell Stage
 CRYOBIOLOGY 36, 206 212 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CY982077 Effects of Centrifugation and Lipid Removal on the Cryopreservation of in Vitro Produced Bovine Embryos at the Eight-Cell Stage M. Murakami,* T. Otoi,
CRYOBIOLOGY 36, 206 212 (1998) ARTICLE NO. CY982077 Effects of Centrifugation and Lipid Removal on the Cryopreservation of in Vitro Produced Bovine Embryos at the Eight-Cell Stage M. Murakami,* T. Otoi,
ICSI with sperm derived from cultured testes (Nature 2011) Establishment of rabbit ips cells (J Biol Chem 2010)
 Efficient production of offspring in wild-derived strains of mice (Biol Reprod in press) (Presented by Keiji Mochida) Birth of offspring from ectopically transplanted PGCs (Biol Reprod 211) ICSI with sperm
Efficient production of offspring in wild-derived strains of mice (Biol Reprod in press) (Presented by Keiji Mochida) Birth of offspring from ectopically transplanted PGCs (Biol Reprod 211) ICSI with sperm
Manipulating the Mouse Embryo
 Manipulating the Mouse Embryo A LABORATORY MANUAL Second Edition Brigid Hogan Rosa Beddington Frank Costantini Elizabeth La~y Preface to First Edition, v Preface to Second Edition, vii Developmental Genetics
Manipulating the Mouse Embryo A LABORATORY MANUAL Second Edition Brigid Hogan Rosa Beddington Frank Costantini Elizabeth La~y Preface to First Edition, v Preface to Second Edition, vii Developmental Genetics
Mouse sperm extraction:
 Mouse sperm extraction: This method of extraction is used for acrosome reaction assays, immunocytochemistry and biochemical assays. Collect two cauda epidydimus from one male, cut them 5 times and place
Mouse sperm extraction: This method of extraction is used for acrosome reaction assays, immunocytochemistry and biochemical assays. Collect two cauda epidydimus from one male, cut them 5 times and place
Lecture 27. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development
 Lecture 27 Epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development Development of a multicellular organism is not only determined by the DNA sequence but also epigenetically through DNA methylation
Lecture 27 Epigenetic regulation of gene expression during development Development of a multicellular organism is not only determined by the DNA sequence but also epigenetically through DNA methylation
Fertilization depends on mechanisms that help sperm meet eggs of the same species.
 Fertilization depends on mechanisms that help sperm meet eggs of the same species. www.uchsc.edu/ltc/fertilization.html Fertilization union of sperm and egg Is a chain of events. Interruption of any step
Fertilization depends on mechanisms that help sperm meet eggs of the same species. www.uchsc.edu/ltc/fertilization.html Fertilization union of sperm and egg Is a chain of events. Interruption of any step
Generation of Bimaternal and Bipaternal Mice from Hypomethylated Haploid ESCs with Imprinting Region Deletions
 Article Generation of Bimaternal and Bipaternal Mice from Hypomethylated Haploid ESCs with Imprinting Region Deletions Graphical Abstract Authors Zhi-Kun Li, Le-Yun Wang, Li-Bin Wang,..., Wei Li, Qi Zhou,
Article Generation of Bimaternal and Bipaternal Mice from Hypomethylated Haploid ESCs with Imprinting Region Deletions Graphical Abstract Authors Zhi-Kun Li, Le-Yun Wang, Li-Bin Wang,..., Wei Li, Qi Zhou,
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology. October 11, Multiple choice (one point each)
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 October 11, 2005 Name: ID#: Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Sertoli cells a. surround spermatocytes b. are the structural components of the seminiferous tubules
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 October 11, 2005 Name: ID#: Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Sertoli cells a. surround spermatocytes b. are the structural components of the seminiferous tubules
OVERVIEW OF EPIGENETICS
 OVERVIEW OF EIENETICS Date: * Time: 9:00 am - 9:50 am * Room: Berryhill 103 Lecturer: Terry Magnuson 4312 MBRB trm4@med.unc.edu 843-6475 *lease consult the online schedule for this course for the definitive
OVERVIEW OF EIENETICS Date: * Time: 9:00 am - 9:50 am * Room: Berryhill 103 Lecturer: Terry Magnuson 4312 MBRB trm4@med.unc.edu 843-6475 *lease consult the online schedule for this course for the definitive
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a,
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of Gli1-lacZ in E17.5 ovary and mesonephros. a, Transverse sections of E17.5 ovary and mesonephros from Gli1-LacZ reporter embryos (n=3) after LacZ staining (blue). The
Novel Technologies for Selecting the Best Sperm for IVF and ICSI
 Novel Technologies for Selecting the Best Sperm for IVF and ICSI Denny Sakkas, Ph.D. Scientific Director, Boston IVF Waltham, MA, USA Testing The Sperm Population NOW Sperm DNA testing Although we are
Novel Technologies for Selecting the Best Sperm for IVF and ICSI Denny Sakkas, Ph.D. Scientific Director, Boston IVF Waltham, MA, USA Testing The Sperm Population NOW Sperm DNA testing Although we are
Animal Development. Lecture 3. Germ Cells and Sex
 Animal Development Lecture 3 Germ Cells and Sex 1 The ovary of sow. The ovary of mare. The ovary of cow. The ovary of ewe. 2 3 The ovary. A generalized vertebrate ovary. (Wilt and Hake, Ch 2, 2004) 4 The
Animal Development Lecture 3 Germ Cells and Sex 1 The ovary of sow. The ovary of mare. The ovary of cow. The ovary of ewe. 2 3 The ovary. A generalized vertebrate ovary. (Wilt and Hake, Ch 2, 2004) 4 The
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Towards an automated procedure for annotation of gene products through SAS Methods. Henrik Tveit Norwegian University of Science and Technology
 Towards an automated procedure for annotation of gene products through SAS Methods Henrik Tveit Norwegian University of Science and Technology Overview! Biology: the Structure of Life! Functional genomics!
Towards an automated procedure for annotation of gene products through SAS Methods Henrik Tveit Norwegian University of Science and Technology Overview! Biology: the Structure of Life! Functional genomics!
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Imprinting. Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821
 Imprinting Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the basic concepts of genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that causes
Imprinting Joyce Ohm Cancer Genetics and Genomics CGP-L2-319 x8821 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the basic concepts of genomic imprinting Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon that causes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary text Collectively, we were able to detect ~14,000 expressed genes with RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) > 1 or ~16,000 with RPKM > 0.1 in at least one cell type from oocyte to the morula
Supplementary text Collectively, we were able to detect ~14,000 expressed genes with RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) > 1 or ~16,000 with RPKM > 0.1 in at least one cell type from oocyte to the morula
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development
 Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Thawing MEFs (Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts (MEFs)
 1 FEEDER CULTURES The function of feeder cultures is to support the undifferentiated growth of hpsc. Typically primary fibroblasts are used for this purpose. We prepare our mouse feeder cells from ICR
1 FEEDER CULTURES The function of feeder cultures is to support the undifferentiated growth of hpsc. Typically primary fibroblasts are used for this purpose. We prepare our mouse feeder cells from ICR
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
a. Smo+/+ b. Smo+/+ 5.63 5.48 c. Lin- d. e. 6 5 4 3 Ter119 Mac B T Sca1 Smo+/+ 25 15 2 o BMT 2 1 5 * Supplementary Figure 1: Deletion of Smoothened does not alter the frequency of hematopoietic lineages
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature11463 %Sox17(+) 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %Sox17(+) #Sox17(+) d2 d4 d6 d8 d1 d12 d14 d18 25 2 15 1 5 Number of Sox17(+) cells X 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
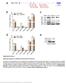 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
SHORT COMMUNICATION CHICAGO, ILLINOIS. Visualization of Chromosomes in Single Human Blastomeres
 Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, Vol. 16, No. 3, 1999 SHORT COMMUNICATION CHICAGO, ILLINOIS Visualization of Chromosomes in Single Human Blastomeres The present work describes our results
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics, Vol. 16, No. 3, 1999 SHORT COMMUNICATION CHICAGO, ILLINOIS Visualization of Chromosomes in Single Human Blastomeres The present work describes our results
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Biopsy of Blastomeres from Cleavage-stage Mouse Embryos with Eppendorf PiezoXpert
 APPLICATION NOTE No. 270 Biopsy of Blastomeres from Cleavage-stage Mouse Embryos with Eppendorf PiezoXpert Norhazlin Jusoh Mohd. Yusoff and Nor Ashikin Mohamed Noor Khan, Institute of Medical Molecular
APPLICATION NOTE No. 270 Biopsy of Blastomeres from Cleavage-stage Mouse Embryos with Eppendorf PiezoXpert Norhazlin Jusoh Mohd. Yusoff and Nor Ashikin Mohamed Noor Khan, Institute of Medical Molecular
Bisphenol A Exposure Disrupts Genomic Imprinting in the Mouse
 Bisphenol A Exposure Disrupts Genomic Imprinting in the Mouse Martha Susiarjo 1,2, Isaac Sasson 3, Clementina Mesaros 4, Marisa S. Bartolomei 1,2 * 1 Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, University
Bisphenol A Exposure Disrupts Genomic Imprinting in the Mouse Martha Susiarjo 1,2, Isaac Sasson 3, Clementina Mesaros 4, Marisa S. Bartolomei 1,2 * 1 Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, University
REPRODUCTIVE BIOTECHNOLOGY IN SWINE
 REPRODUCTIVE BIOTECHNOLOGY IN SWINE References * Animal breeding and infertility by M. J. Meredith * Controlled reproduction in pigs by I. Gordon * Reproduction in farm animals by E.S.E. Hafez * Progress
REPRODUCTIVE BIOTECHNOLOGY IN SWINE References * Animal breeding and infertility by M. J. Meredith * Controlled reproduction in pigs by I. Gordon * Reproduction in farm animals by E.S.E. Hafez * Progress
Patrick Quinn IVF PROTOKOL FOR SINGLE EMBRYO CULTURE
 1. With cumulus-free oocytes and embryos up to Day (D) 3, use 275-300 um diameter pipette tips to minimize medium transfer between drops; transfer volume should be < 1 ul. DAY -1 2. At ~ 4.00 pm on the
1. With cumulus-free oocytes and embryos up to Day (D) 3, use 275-300 um diameter pipette tips to minimize medium transfer between drops; transfer volume should be < 1 ul. DAY -1 2. At ~ 4.00 pm on the
Rejuvenation of Gamete Cells; Past, Present and Future
 Rejuvenation of Gamete Cells; Past, Present and Future Denny Sakkas PhD Scientific Director, Boston IVF Waltham, MA, USA Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest related to this presentation.
Rejuvenation of Gamete Cells; Past, Present and Future Denny Sakkas PhD Scientific Director, Boston IVF Waltham, MA, USA Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest related to this presentation.
MEGA Assay. Modernizing quality control in IVF.
 MEGA Assay Modernizing quality control in IVF MEGA assures product consistency through: Analysis of pre-implantation embryo development and health by gene expression in addition to morphology Increased
MEGA Assay Modernizing quality control in IVF MEGA assures product consistency through: Analysis of pre-implantation embryo development and health by gene expression in addition to morphology Increased
Rescue IVF protocol for legacy stock
 Rescue IVF protocol for legacy stock Sperm thawing/ivf protocol for MTG sperm samples (80ul per straw) from straw and conventional CPA from Vial (100ml per vial) This protocol is based on methods developed
Rescue IVF protocol for legacy stock Sperm thawing/ivf protocol for MTG sperm samples (80ul per straw) from straw and conventional CPA from Vial (100ml per vial) This protocol is based on methods developed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Influence ovarian stimulation on oocyte and embryo quality. Prof.Dr. Bart CJM Fauser
 Influence ovarian stimulation on oocyte and embryo quality Prof.Dr. Bart CJM Fauser How to balance too much vs too little? Lecture Outline Context ovarian stimulation Impact ovarian stimulation on oocyte
Influence ovarian stimulation on oocyte and embryo quality Prof.Dr. Bart CJM Fauser How to balance too much vs too little? Lecture Outline Context ovarian stimulation Impact ovarian stimulation on oocyte
Joanna Hillman Michael Higgins Lab Oncology for Scientists I 10/29/2015
 Joanna Hillman Michael Higgins Lab Oncology for Scientists I 10/29/2015 ! Define Epigenetics & Genomic Imprinting! Discovery! What is the imprint! Lifecycle of an Imprint DMRs and ICEs! 2 main mechanisms
Joanna Hillman Michael Higgins Lab Oncology for Scientists I 10/29/2015 ! Define Epigenetics & Genomic Imprinting! Discovery! What is the imprint! Lifecycle of an Imprint DMRs and ICEs! 2 main mechanisms
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Title. Author(s)TEKELI, Tevfik; KWEON, Oh Kyeong; KANAGAWA, Hiroshi. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 35(4): 283-
 Title THE VIABILITY OF DEEP-FROZEN AGGREGATED MOUSE EMBRYO Author(s)TEKELI, Tevfik; KWEON, Oh Kyeong; KANAGAWA, Hiroshi CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 35(4): 283- Issue Date 1987-10-30
Title THE VIABILITY OF DEEP-FROZEN AGGREGATED MOUSE EMBRYO Author(s)TEKELI, Tevfik; KWEON, Oh Kyeong; KANAGAWA, Hiroshi CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 35(4): 283- Issue Date 1987-10-30
Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Microinsemination schedule. 1. Preparation of mediums
 Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Masumi Hirabayashi Section of Mammalian Transgenesis, Center for Genetic Analysis of Behavior, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, National
Microinsemination (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) Masumi Hirabayashi Section of Mammalian Transgenesis, Center for Genetic Analysis of Behavior, National Institute for Physiological Sciences, National
The storage of cow eggs at room temperature and at low temperatures
 The storage of cow eggs at room temperature and at low temperatures A. O. Trounson, S. M. Willadsen, L. E. A. Rowson and R. Newcomb A.R.C. Unit of Reproductive Physiology and Biochemistry, Cambridge, U.K.*
The storage of cow eggs at room temperature and at low temperatures A. O. Trounson, S. M. Willadsen, L. E. A. Rowson and R. Newcomb A.R.C. Unit of Reproductive Physiology and Biochemistry, Cambridge, U.K.*
4. Which of the following cell parts can be found in human cells, but not plant cells? A. mitochondria B. chloroplast C. centrioles D.
 http://chss.sd57.bc.ca/~spearce/science_9/practice%20tests/reproductionpracticetest.htm Sc.9 Biology Practise Test 1. Single-celled organisms use cell division for growth. 2. Chromosomes are made of two
http://chss.sd57.bc.ca/~spearce/science_9/practice%20tests/reproductionpracticetest.htm Sc.9 Biology Practise Test 1. Single-celled organisms use cell division for growth. 2. Chromosomes are made of two
Mouse oocytes injected with testicular spermatozoa or round spermatids can develop into normal offspring
 Development 121, 2397-2405 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 2397 Mouse oocytes injected with testicular spermatozoa or round spermatids can develop into normal offspring
Development 121, 2397-2405 (1995) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1995 2397 Mouse oocytes injected with testicular spermatozoa or round spermatids can develop into normal offspring
Imagine Innovate Integrate. Using the NSET for embryo transfer and artificial insemination in mice and rats Kendra Steele, Ph.D.
 Imagine Innovate Integrate Using the NSET for embryo transfer and artificial insemination in mice and rats Kendra Steele, Ph.D. Outline- Here to make your life easier Non-surgical embryo transfer in mice
Imagine Innovate Integrate Using the NSET for embryo transfer and artificial insemination in mice and rats Kendra Steele, Ph.D. Outline- Here to make your life easier Non-surgical embryo transfer in mice
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
DNA methylation Dots(+) CxxC EGFP DAP
 a 1.2 b 5mC PI Merge n level Relativ ve expressio 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 a b c Wildtype Gadd45 Gadd4 45b KO Figure S1. Gadd45b-deficiency does not affect paternal DNA demethylation (a) Relative expression
a 1.2 b 5mC PI Merge n level Relativ ve expressio 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 a b c Wildtype Gadd45 Gadd4 45b KO Figure S1. Gadd45b-deficiency does not affect paternal DNA demethylation (a) Relative expression
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.
 Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
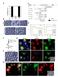 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
FERTIUP PM 1 ml / 0.5 ml - CARD MEDIUM Set
 Product manual FERTIUP PM 1 ml / 0.5 ml - CARD MEDIUM Set Cat. No. KYD-004-EX Size: 1 SET KYD-005-EX 1 SET Department of Reproductive Engineering, Center for Animal Resources and Development, Kumamoto
Product manual FERTIUP PM 1 ml / 0.5 ml - CARD MEDIUM Set Cat. No. KYD-004-EX Size: 1 SET KYD-005-EX 1 SET Department of Reproductive Engineering, Center for Animal Resources and Development, Kumamoto
Maintenance of Paternal Methylation and Repression of the Imprinted H19 Gene Requires MBD3
 Maintenance of Paternal Methylation and Repression of the Imprinted H19 Gene Requires MBD3 Kimberly J. Reese 1, Shu Lin 1, Raluca I. Verona 1, Richard M. Schultz 2, Marisa S. Bartolomei 1* 1 Department
Maintenance of Paternal Methylation and Repression of the Imprinted H19 Gene Requires MBD3 Kimberly J. Reese 1, Shu Lin 1, Raluca I. Verona 1, Richard M. Schultz 2, Marisa S. Bartolomei 1* 1 Department
Fig. S1. Weight of embryos during development. Embryos are collected at different time points (E12.5, E14.5, E16.5 and E18.5) from matings between
 Fig. S1. Weight of embryos during development. Embryos are collected at different time points (E12.5, E14.5, E16.5 and E18.5) from matings between Myod +/ or Myod / females and Myod +/ ;Igf2 +/ males and
Fig. S1. Weight of embryos during development. Embryos are collected at different time points (E12.5, E14.5, E16.5 and E18.5) from matings between Myod +/ or Myod / females and Myod +/ ;Igf2 +/ males and
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 ID#: October 11, 2005
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Name: Key Exam 1 ID#: October 11, 2005 Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Primordial germ cells a. are immortal b. produce polar bodies c. are haploid d. are somatic
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Name: Key Exam 1 ID#: October 11, 2005 Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Primordial germ cells a. are immortal b. produce polar bodies c. are haploid d. are somatic
Articles Somatic cell haploidization: an update
 RBMOnline - Vol 6. No 1. 60 65 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/717 on web 4 November 2002 Articles Somatic cell haploidization: an update Jan Tesarik obtained his MD degree in
RBMOnline - Vol 6. No 1. 60 65 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/717 on web 4 November 2002 Articles Somatic cell haploidization: an update Jan Tesarik obtained his MD degree in
Genetic Assessment and Counseling
 Genetic Assessment and Counseling Genetic counseling is the communication of information and advice about inherited conditions and a person seeking such advice is called a consultand. This process includes
Genetic Assessment and Counseling Genetic counseling is the communication of information and advice about inherited conditions and a person seeking such advice is called a consultand. This process includes
A. One to three months of age. Anterior Lens (Mean ± SEM) Posterior Lens (Mean ± SEM) Mid Lens (Mean ± SEM) Cornea (Mean ± SEM) Genotype
 Supplementary Table 1. Location of lens opacification in Aldh1a1(-/-), Aldh3a1(-/-) single and Aldh1a1(-/-)/Aldh3a1(-/-) double knockout mice (DKO) at different ages. A. One to three months of age Genotype
Supplementary Table 1. Location of lens opacification in Aldh1a1(-/-), Aldh3a1(-/-) single and Aldh1a1(-/-)/Aldh3a1(-/-) double knockout mice (DKO) at different ages. A. One to three months of age Genotype
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS
 TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Differential Developmental Ability of Cloned from Tissue- Specific Stem Cells KIMIKO INOUE, SHINICHI NODA, NARUMI OGONUKI, HIROMI MIKI, SHINICHI INOUE, KAZUFUMI KATAYAMA, KAZUYUKI
TISSUE-SPECIFIC STEM CELLS Differential Developmental Ability of Cloned from Tissue- Specific Stem Cells KIMIKO INOUE, SHINICHI NODA, NARUMI OGONUKI, HIROMI MIKI, SHINICHI INOUE, KAZUFUMI KATAYAMA, KAZUYUKI
Supplementary. presence of the. (c) mrna expression. Error. in naive or
 Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Figure 1. (a) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated in the presence of the indicated cytokines for 3 days. Enpp2 mrna expression was measured by qrt-pcrhr, infected with (b, c) Naive CD4 + T cells were activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Mouse Parthenogenetic Embryos with Monoallelic H19 Expression Can Develop to Day 17.5 of Gestation
 Developmental Biology 243, 294 300 (2002) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0561, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Mouse Parthenogenetic Embryos with Monoallelic H19 Expression Can Develop to Day
Developmental Biology 243, 294 300 (2002) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0561, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Mouse Parthenogenetic Embryos with Monoallelic H19 Expression Can Develop to Day
The placenta: phenotypic and epigenetic modifications induced by Assisted Reproductive Technologies throughout pregnancy
 Choux et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2015) 7:87 DOI 10.1186/s13148-015-0120-2 REVIEW Open Access The placenta: phenotypic and epigenetic modifications induced by Assisted Reproductive Technologies throughout
Choux et al. Clinical Epigenetics (2015) 7:87 DOI 10.1186/s13148-015-0120-2 REVIEW Open Access The placenta: phenotypic and epigenetic modifications induced by Assisted Reproductive Technologies throughout
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Introduction Kit Components Cat. # # of vials Reagent Quantity Storage
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Analysis of Aneuploidy in First-Cleavage
 Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 31, pp. 141-149, 1979 Analysis of Aneuploidy in First-Cleavage Mouse Embryos Fertilized in Vitro and in Vivo by Lynn R. Fraser* and Ian Maudlint First-cleavage mouse
Environmental Health Perspectives Vol. 31, pp. 141-149, 1979 Analysis of Aneuploidy in First-Cleavage Mouse Embryos Fertilized in Vitro and in Vivo by Lynn R. Fraser* and Ian Maudlint First-cleavage mouse
Committee Paper SCAAC(05/09)01. ICSI guidance. Hannah Darby and Rachel Fowler
 Committee Paper Committee: Scientific and Clinical Advances Advisory Committee Meeting Date: 12 May 2009 Agenda Item: 4 Paper Number: SCAAC(05/09)01 Paper Title: ICSI guidance Author: Hannah Darby and
Committee Paper Committee: Scientific and Clinical Advances Advisory Committee Meeting Date: 12 May 2009 Agenda Item: 4 Paper Number: SCAAC(05/09)01 Paper Title: ICSI guidance Author: Hannah Darby and
CARD HyperOva (Superovulation Reagent for mouse)
 Product manual (Superovulation Reagent for mouse) Cat. No. KYD-010-EX -X5 Size: 5 1 ML Origin Serum of goat, Horse-derived villus gonatropin. Composition 1. Inhibin antiserum (Goat). 2. Equine chorionic
Product manual (Superovulation Reagent for mouse) Cat. No. KYD-010-EX -X5 Size: 5 1 ML Origin Serum of goat, Horse-derived villus gonatropin. Composition 1. Inhibin antiserum (Goat). 2. Equine chorionic
CRYOTOP SAFETY KIT Protocol. Cryotop Method
 CRYOTOP SAFETY KIT Protocol Cryotop Method R Vitrification PART Materials Required Cryotop Safety Kit-Vitrification No.0 Basic Solution (BS): 1 X 1.5ml vial (Only for Oocyte Vitrification) No.1 Equilibration
CRYOTOP SAFETY KIT Protocol Cryotop Method R Vitrification PART Materials Required Cryotop Safety Kit-Vitrification No.0 Basic Solution (BS): 1 X 1.5ml vial (Only for Oocyte Vitrification) No.1 Equilibration
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
