Life Science Unit I. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
- Austen Alexander
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: ate: 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells. are much smaller. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. ell iagram. have permeable membranes.. have a higher rate of reproduction.. have nuclei. 2. Which statement about plant and animal cells is true?. Plant cells have a nucleus and a cell wall; animal cells do not have either of these structures.. Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts; animal cells do not have either of these structures. Which arrow indicates the location of the cell membrane?. arrow. arrow. arrow. arrow. Plant cells have a cell wall and a cell membrane; animal cells have a cell wall but not a cell membrane.. Plant cells have chloroplasts and mitochondria; animal cells have chloroplasts but do not have mitochondria. 5. What are the basic structural units of living organisms? 3. Which structure is responsible for allowing materials into and out of an animal cell?. cells. nuclei. organs. tissues. Nucleus. ell wall. Mitochondrion. ell membrane page 1
2 6. Some cells, such as human nerve and muscle cells, contain many more mitochondria than do other cells, such as skin cells. Why do some cells have more mitochondria than others?. The cells use more energy.. The cells store more nutrients.. The cells degrade more proteins.. The cells divide more frequently. 9. Which of the following describes N replication in eukaryotic cells?. copy of the N is made in the nucleus.. molecule of RN is produced from the N.. Each strand of N is combined with a strand of RN.. Each strand of N is separated into a new chromosome. 7. Which of the following is a main function of the cell wall?. to store carbohydrates for later use 10. diagram of a plant cell is shown below.. to give the cell a rigid structure. to package proteins for export. to carry out photosynthesis 8. Which of the following statements correctly matches a cell part with its function?. The cell membrane packages lipids for export.. The mitochondria perform photosynthesis.. The lysosome digests molecules. Which number identifies the organelle that functions to store water and dissolved salts? The nucleus produces energy page 2
3 11. The illustration below represents two protists. 13. Which cell part is correctly matched to its function?. chloroplast controls cell division. mitochondrion releases energy. cell membrane contains genetic code. ribosome makes sugar Euglena Paramecium What do these two organisms have in common?. They are unicellular.. They cause diseases.. They live underground.. They are photosynthetic. 14. Refer to the diagram below of the single-celled, eukaryotic organisms to answer the following question(s). 12. Which of these is the site where proteins are made in all cells?. the nuclei. the ribosomes. the chloroplasts. the mitochondria Euglena uses which of these to move?. cilia. a vacuole. a flagellum. pseudopodia page 3
4 15. Use the information below to answer the following question(s). Scientists have recently discovered a new species that lives attached to the side of a tree. n organism from this new species is multicellular has cell walls has vascular tissues makes its own food has structures that absorb moisture from the air Which of these is not true about cells in the new organism?. They contain nuclei. 17. Use the information and the diagrams below to answer the following question(s). student observed different types of cells under a microscope. Four of the cells he observed are shown below. ell 4 has many hair-like structures that it uses for movement. What are these structures called?. cilia. flagella. vacuoles. pseudopodia. They use vacuoles for storage.. They contain mitochondria.. They use pseudopodia to move. 16. Maryland white oak trees make their own food. Their cells contain structures that capture energy from the sun. What are these structures?. chloroplasts. nuclei. mitochondria. ribosomes page 4
5 18. Use the information and the figure below to answer the following question(s). uring a trip to the beach, llen finds a colony of sea anemones on a rock. These sea anemones are green and get their color from tiny single-celled algae that live in their tissues. The algae produce food for the anemones while the anemones provide a place for the algae to live. 19. Organisms that have physical features common to both plants and animals are difficult to classify. The diagram below shows physical features of a euglena. drawing of a mobile form of the single-celled green algae is shown below. Which euglena feature caused some scientists to classify the euglena as a plant? Which of these structures help this algae move?. chloroplast. eyespot. flagellum. nucleus. flagella. cilia. pseudopodia. vacuoles page 5
6 20. The diagram below shows an amoeba performing a function necessary for life. 21. Which statement explains why the nucleus can be referred to as the brain of plant and animal cells?. It releases energy to the cell.. It controls the activities of the cell.. It stores food, water, and wastes of the cell.. It controls the materials that go into and out of the cell. 22. Which function is shown in the diagram?. collecting food. excreting wastes. making food. destroying wastes The part of the cell marked by the arrow is the. cytoplasm.. chloroplast.. mitochondrion.. chlorophyll. page 6
7 23. The illustrations below are of a euglena, a paramecium, and an amoeba. 26. The digestion process begins in which of the following?. large intestine. mouth. small intestine. stomach How do these organisms compare?. They use different structures for movement.. They use different structures to control cell activity. 27. patient suffering from a sore throat goes to a doctor in a hospital to get a check-up. uring the exam the doctor collects the following information:. They all make their own food by photosynthesis.. They all have eyespots to sense sunlight. 24. Which two systems primarily function to rid the human body of the wastes resulting from cellular energy production? The doctor strikes the patient s knee with a small rubber hammer and observes the reaction. The doctor is checking the.. excretory and skeletal systems. nervous and endocrine systems. nervous system. muscular system. circulatory system. skeletal system. circulatory and digestive systems. respiratory and circulatory systems 25. Which of the following is a harmful waste material that leaves the blood and travels through the lungs before leaving the body?. O 2. O 2. H 2 O. Nal 28. The doctor strikes the patient s knee with a small rubber hammer and observes the reaction. The doctor is checking the.. nervous system. muscular system. circulatory system. skeletal system page 7
8 29. Which graph could represent a child s growth from kindergarten through the fourth grade? 30. Which graph could represent a child s growth from kindergarten through the fourth grade? page 8
9 31. Which is a primary function that kidneys perform for the excretory system? 34. Which of the following offers the human body initial protection from disease-causing organisms?. They control sensory input using nerve cells.. They conduct chemical digestion using hormones.. The stomach. The brain. The skin. The intestines. They remove waste from blood using filtration structures.. They exchange oxygen for carbon dioxide using capillaries. 35. Use the diagram below to answer the question. IGESTIVE SYSTEM 32. Which of the following pairs provides structural support for a human?. skin and blood. bones and muscles. spine and heart. brain and nerves Which part of the digestive system gets nutrients from food?. part. part. part. part 33. The respiratory system depends on the nervous system for signals to. enhance the amount of available oxygen in the lungs.. coordinate muscles controlling breathing.. release enzymes to increase the exchange of gases.. exchange gases with the circulatory system. 36. Which body system s primary function is the continuation of the species?. digestive. nervous. excretory. reproductive page 9
10 37. The terms gas exchange, diaphragm, and inhale are most closely associated with which system in the human body?. circulatory. digestive. excretory. respiratory 40. When Lance goes jogging, his heart rate increases to pump blood faster and supply his muscles with more oxygen. Which of the following helps to maintain homeostasis in response to this increase in heart rate?. an increase in digestion. an increase in respiration. a decrease in perspiration. a decrease in bone growth 38. What is the primary function of the large intestine?. to digest proteins. to absorb nutrients. to break down complex carbohydrates. to remove water from undigested waste 41. therosclerosis is a condition in which substances such as fats and cholesterol are deposited on the inside walls of arteries, resulting in a decrease in the internal diameter of the arteries. This directly interferes with which of the following processes in the body?. the production of red blood cells. the delivery of oxygen to body tissues. the release of insulin to regulate blood sugar. the transmission of nerve impulses to the heart 39. Which of the following is a correct order in which air moves through the human respiratory system when a person inhales?. nose, larynx, trachea, pharynx, bronchi, lungs. nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs. pharynx, bronchi, nose, larynx, trachea, lungs. pharynx, nose, trachea, bronchi, larynx, lungs 42. In which of the following ways does perspiring help the body to maintain homeostasis?. by decreasing body temperature. by increasing blood sugar levels. by increasing the amount of fluid in the body. by reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in cells page 10
11 43. The circulatory system is directly responsible for which of the following? 45. What is the primary role of the stomach in the human digestive system?. breaking down food. transmitting nerve impulses. transporting nutrients to cells. controlling movement of muscles. producing specialized salts that absorb fats. absorbing water and minerals from undigested food. using muscle movements and enzymes to break down food. transferring nutrients from digested food to the bloodstream 44. The diagram below shows one response pathway the human body uses to control blood pressure. 46. Human bodies have complex structures that support growth and survival. What is the most basic structure of the human body that supports growth and survival?. a cell. a tissue. an organ. an organ system Which body systems work together in this response pathway to control blood pressure?. digestive and nervous. nervous and circulatory. respiratory and digestive. circulatory and excretory 47. The ability of the human body to regulate the level of blood glucose is an example of. osmosis. homeostasis. binary fission. aerobic respiration page 11
12 48. Use the information below to answer the following question(s). Most organisms need oxygen for their cells to function normally. In mammals, two organ systems work together to move oxygen throughout the body. The respiratory system brings oxygen into the body from the environment. Which of these body systems is directly involved in the delivery of oxygen to the major organs of the human body? 50. single-celled organism, such as the amoeba, uses its cell membrane to take in oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. Which organ system in humans has the same function as the cell membrane of the amoeba?. circulatory. digestive. nervous. respiratory. the nervous system. the digestive system. the endocrine system. the circulatory system 51. This chart compares the levels of organisms to the way a school is organized. 49. Use the information below to answer the following question(s). Hummingbirds need large amounts of energy to flap their wings between 60 and 200 times per second. Their wings beat so rapidly that it is difficult to see them move. They often appear suspended in air for extended periods of time without changing their location. Hummingbirds have long bills and grooved tongues to reach into flowers to feed on flower nectar. They also feed on insects. The body system most directly interacting with the skeletal system to enable hummingbirds to beat their wings between 60 and 200 times per second is the ells? Tissues Organs Organ Systems Whole Organism Ecosystem lassroom Grade Level School School System ity Using the chart, which is the best comparison to cells?. State. Home. ountry. Students. digestive system. muscular system. endocrine system. circulatory system page 12
13 52. Look at the picture below. What human body system does this organ belong to?. Nervous system. igestive system. irculatory system. Respiratory system page 13
14 Problem-ttic format version c Educide Software Licensed for use by MJ Wharton Terms of Use at 05/16/
15 Teacher s Key Page
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes
 Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
Science 8 - Cells & Cell Organization Notes 1.1 - Characteristics of Living Things Composed of cells Reproduce, grow & repair themselves Require energy o Plants usually from sun o Animals from plants or
Cell Organelles, Communication and Transport. A. A gametes; B zygote. B. A zygote; B gametes. C. A organs; B organelles. D. A organelles; B organs
 ell Organelles, ommunication and Transport Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a cell of a green plant. 3. Some levels of organization in a multicellular organism are shown in the sequence below.
ell Organelles, ommunication and Transport Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a cell of a green plant. 3. Some levels of organization in a multicellular organism are shown in the sequence below.
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p.
 NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
NOTES Inv. 2 Supporting Cells / / p. Food (energy) Delivery System into our Bodies Excretory System digestive breaks down food into molecules that cells can use nutrient molecules pass into the bloodstream
C) amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the animal B) rate of respiration of the animal
 Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
Cell Processes Review
 1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions. Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18
 Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18 1. Which of the following would be least affected by defective receptor proteins on a cell membrane? a. Homeostasis b. Muscle activity
Cells and Osmosis BCT Questions Questions taken from 2-12 to 2-18 1. Which of the following would be least affected by defective receptor proteins on a cell membrane? a. Homeostasis b. Muscle activity
Topic 1: Chemistry of Living Things
 1. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below.1 utilize energy 2 detect changes in the environment 3 rearrange and synthesize chemical compounds 4. The diagram below represents a sequence of
1. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below.1 utilize energy 2 detect changes in the environment 3 rearrange and synthesize chemical compounds 4. The diagram below represents a sequence of
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Unit 3 - Homeostasis in the Human Body
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers
 Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Cellular Organelles EOC Quiz
 Cellular Organelles EOC Quiz This quiz is composed of 10 EOC type questions Each question is followed by the same question with the correct answer highlighted Therefore, Read the questions and the choices,
Cellular Organelles EOC Quiz This quiz is composed of 10 EOC type questions Each question is followed by the same question with the correct answer highlighted Therefore, Read the questions and the choices,
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
Review for Regular Test - H2O, ph, Macromolecules, Enzymes, ATP, Photo, CR A. A B. F C. C D. D
 Macromolecules, Enzymes, TP, Photo, R Name: ate: 1. The accompanying diagram represents some chemical events that take place in one type of autotrophic nutrition. 3. The dark reactions in the stroma are
Macromolecules, Enzymes, TP, Photo, R Name: ate: 1. The accompanying diagram represents some chemical events that take place in one type of autotrophic nutrition. 3. The dark reactions in the stroma are
Name: Class: Date: Question #1. Question #2. What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels.
 9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Cell Structure and Function
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Chemistry Regents Review A. A B. B C. C D. D
 hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
Name 9 weeks exam Study Guide: Nature of Biology
 1. I can analyze an experiment and identify the major parts. This means that I know the difference between an independent variable, dependent variable, constant, experimental group, and control group.
1. I can analyze an experiment and identify the major parts. This means that I know the difference between an independent variable, dependent variable, constant, experimental group, and control group.
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Cell Basics. Basic Unit of Life. Prokaryotic. Eukaryotic. Plant Cell. Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Bacteria. Very Complex.
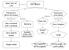 Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Basic Unit of Life It is Cell Basics Type Type Prokaryotic (before the nucleus) Examples Eukaryotic (true nucleus) Characteristics Has a nucleoid (not a nucleus) Examples Bacteria Plant Cell Characteristics
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes
 Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Name: BLK. Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :)
 Name: BLK Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :) 1) A boy jumps into a cold swimming pool and his body temperature goes down. His muscles, blood vessels, and nervous system work together to restore his body temperature.which
Name: BLK Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :) 1) A boy jumps into a cold swimming pool and his body temperature goes down. His muscles, blood vessels, and nervous system work together to restore his body temperature.which
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Homeostasis Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome
 Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key. Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions
 Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
Cells and Homeostasis Vocabulary Key Unicellular organism: An organism having only one cell but carries out all life functions Multicellular: An organism with many cells, each of which is specialized to
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
Name Class Date. What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon
 UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2014-2015 Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon Experiment: an orderly procedure
UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2014-2015 Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon Experiment: an orderly procedure
Science 8. Unit 2. Body Systems
 Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions)
 Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions) Major topics include: 1) Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (energy and matter) 2) Role of enzymes 3) Animal systems* 4) Plant
Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions) Major topics include: 1) Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (energy and matter) 2) Role of enzymes 3) Animal systems* 4) Plant
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. Chapter 7
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Chapter 7 WARM UP EXERCISE Please complete the pretest that you picked up as you came in. LIFE IS CELLULAR Robert Hooke- coined the term cells The Cell Theory All living things
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
HOMEOSTASIS & IMMUNITY Week Two Packet
 Ms. Scott HOMEOSTASIS & IMMUNITY Week Two Packet Packet Grade: / 9 Completed notes / 30 Completed Classwork / 30 Completed Homework / 10 Packet turned in on time / 1 Name and Class are filled in / 80 Total
Ms. Scott HOMEOSTASIS & IMMUNITY Week Two Packet Packet Grade: / 9 Completed notes / 30 Completed Classwork / 30 Completed Homework / 10 Packet turned in on time / 1 Name and Class are filled in / 80 Total
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Biochemistry Regents Practice
 iochemistry Regents Practice Name: Date: 1. The diagram below represents a sequence of events that occurs in living things. 3. Which statement describes a similarity between all enzymes, antibodies, and
iochemistry Regents Practice Name: Date: 1. The diagram below represents a sequence of events that occurs in living things. 3. Which statement describes a similarity between all enzymes, antibodies, and
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Standard 2 Exam Biology. 2. This macromolecule is responsible for short term energy storage and structural support in plants
 1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
Living Environment. Scientific Inquiry Exam
 Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus
 )ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
)ur Digestive System ibel the parts pf your digestive system. Name pancreas stomach esophagus salivary glands WORD BANK liver mouth teeth anus gall bladder large intestine small intestine Topic 3.1 Digestive
Topic 1: Living Things
 Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Name # Class Date Human Body Systems Take Home Test
 Name # Class Date Human Body Systems Take Home Test 1. In the knee, the ends of the leg bones are held together primarily by A) ligaments B) smooth muscle C) tendons D) cardiac muscle 2. Which two structures
Name # Class Date Human Body Systems Take Home Test 1. In the knee, the ends of the leg bones are held together primarily by A) ligaments B) smooth muscle C) tendons D) cardiac muscle 2. Which two structures
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
2. Eukaryote plant, animal, protozoa and fungal cells; complex and organized; organelles; true nucleus
 BIOLOGY TERMS AND CONCEPTS TO KNOW: 2010-2011. Prokaryote unicellular organism; bacteria; lacks a true nucleus but does contain dna; cell membrane and often a flage 2. Eukaryote plant, animal, protozoa
BIOLOGY TERMS AND CONCEPTS TO KNOW: 2010-2011. Prokaryote unicellular organism; bacteria; lacks a true nucleus but does contain dna; cell membrane and often a flage 2. Eukaryote plant, animal, protozoa
Day 1 Essential Questions:
 Day 1 Essential Questions: ~What are the different body systems? ~What are the parts of the systems? ~How is this system connected to other body systems? ~How do you keep this system working properly?
Day 1 Essential Questions: ~What are the different body systems? ~What are the parts of the systems? ~How is this system connected to other body systems? ~How do you keep this system working properly?
Cells and Systems Unit Test
 Cells and Systems Unit Test Student Name Student N Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow
Cells and Systems Unit Test Student Name Student N Class 1. Characteristics of living organisms include all of the following, EXCEPT... A. they need energy and produce wastes B. they reproduce and grow
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Cells and Cell Transport
 Cells and Cell Transport Use the list below to answer question 1. Functions of a Cell Structure 1. The functions of which cell structure are described in this list? A. a lysosome B. a mitochondrion C.
Cells and Cell Transport Use the list below to answer question 1. Functions of a Cell Structure 1. The functions of which cell structure are described in this list? A. a lysosome B. a mitochondrion C.
Directions: Use Aim # 7-13 (Unit 2) to complete this study guide. Part I. Aim # 7 Inorganic and Organic Molecules. Building Blocks (monomers)
 Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 2 Biochemistry and The Cell Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 2 Important Topics: Aim # 7: Inorganic and Organic Molecules Aim # 8: Organic Macromolecules
Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 2 Biochemistry and The Cell Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 2 Important Topics: Aim # 7: Inorganic and Organic Molecules Aim # 8: Organic Macromolecules
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20
 Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Animal & Plant Cells Biology 20 Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Overview of Cell Structures
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
S7L Which part of the body receives messages transmitted by nerve cells located throughout the body?
 S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Review Page 94 UNIT SUMMARY. Review Key Ideas and Vocabulary Suggested Answers. Time. Skills and Processes. Program Resources.
 Review Page 94 Time 45 60 min Skills and Processes The Unit Review provides an opportunity for students to demonstrate their understanding of and their ability to apply the key ideas, vocabulary, and skills
Review Page 94 Time 45 60 min Skills and Processes The Unit Review provides an opportunity for students to demonstrate their understanding of and their ability to apply the key ideas, vocabulary, and skills
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per:
 Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER
 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
