Table S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample
|
|
|
- Maximillian Stone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3 rep (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3 rep (83.9%) clf28/swn7 H3K27me3 rep (52.85%) clf28/swn7 H3K27me3 rep (55.82%) Col- H2AK121u rep (89.18%) Col- H2AK121u rep (9.25%) atmi1a//c H2AK121u rep (56.84%) atmi1a//c H2AK121u rep (66.72%) Col- H2AK121u rep (87.31%) Col- H2AK121u rep (81.13%) clf28/swn7 H2AK121u rep (85.47%) clf28/swn7 H2AK121u rep (9.2%) Col- H2AK121u rep (72.41%) Col- H2AK121u rep (85.15%) lhp1 H2AK121u rep (79.43%) lhp1 H2AK121u rep (8.35%) Input (71.74%)
2 Tale S2. Primers used for ChIP qpcr ABCG35 Fw ABCG35 Rv TOUCH4 Fw TOUCH4 Rv FBA2 Fw FBA2 Rv FAD3 Fw FAD3 Rv AIL5 Fw AIL5 Rv FLC Fw FLC Rv GA3OX1 Fw GA3OX1 Rv KNU Fw KNU Rv SPL8 Fw SPL8 Rv DPA4 Fw DPA4 Rv SUP Fw SUP Rv CAL Fw CAL Rv SEP3 Fw SEP3 Rv MGP Fw MGP Rv WUS Fw WUS Rv WOX12 Fw WOX12 Rv ChIP primers (5-3 ) GATGGATTACGATCCAGCTCAT CTGCTTGCTTTGCTTACACTAC ACCACAAACCAATCTAACTCAATAC CAGAGGAGGTGATGATAAGAGAAA TTCCTCCTACGCCGATGA AAACACGTGGTAGAGAAGAGA GGAGACCGGAAGAAAGAAGAAA CTTAACCCAACAGTGCTTAGGA GTTGTCTTCTCTTCCGACCTAC CTAGGAAGCTAGCGGCTATTG CGTACTTATCGCCGGAGGAG CATCGAGAAAGCTCGTCAGC GGTGCCTTCCAAATCTCAAAC GAAGAGACTACCGGTGAGAAAC AGTTCTACACATCTCAAGCTCTC GCAAGGGTAAGGACGAAGAA CCAACAGCAACAACCAGTTTC GGATGGTAGATGGGATCGGA GACACGTCATCTTCGGAGAAA TTTGACTGCTGTTCCAGTAAGA CTTTCACAGTCTTAACACCAAAGAG GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGATATAGAGATGAG GCACTCTTTCACATTACCATCATTAG CCTCTTCAATTCAACCCTACCC CCTATGAGGGTCTTTGGTACAC ACATGTCAGCTTCATTACTTGA CTACCGACCAATCAGCGTATC CGATCTCGTGAAGACCGTTATTA CCACAGCATCAGCATCATCA GACACGTGTAACCACCAGAG TGGATCGTCGTCATCTCAAATC GATTCTCCATACCATTGTTGTTCTC
3 H2AK121u WT Rep2 FPKM 1488 Rep2 Rep1 WT Rep1 FPKM H3K27me WT Rep2 FPKM 6843 Rep1 Rep2 WT Rep1 FPKM Figure S1. Comparison of H2AK121u and H3K27me3 ChIP-seq replicates in WT Araidopsis seedlings at 7 DAG. (a) Scatterplot of pairwise comparison etween H2AK121u ChIP-seq replicates (left panel) and Venn diagram showing overlapping H2AK121u marked genes etween replicates (right panel). () Scatterplot of pairwise comparison etween H3K27me3 ChIP-seq replicates (left panel) and Venn diagram showing overlapping H3K27me3 marked genes etween replicates (right panel).
4 Figure S2. Identification of H2AK121u peaks. Two different detection methods, MACS and SICER, were coincident in % of the identified H2AK121u peaks
5 H2AK121u Length H3K27me H2AK121u H3K27me Figure S3. Genome wide localization of H2AK121u and H3K27me3 marks in Araidopsis WT seedlings at 7 DAG. (a) Boxplots representing length distriution of H2AK121u and H3K27me3 peaks. H3K27me3 peaks have an average length of 1.7 K, while H2AK121u peaks were sharper with an average length of.6 K. This difference is significant according to a p-value of 2.2x1-16 otained using the Wilcoxon test. () Representative genome rowser views of H2AK121u and H3K27me3 peaks.
6 Browser view only-h2ak121u marked active genes 2. ChIP qpcr ABCG35; FPKM WT mock WT IP TOUCH4; FPKM % INPUT FBA2; FPKM FAD3; FPKM only-h3k27me3 marked genes Browser view WT mock WT IP ChIP qpcr CAL %INPUT SUP.4 SEP3 Figure S4. ChIP-qPCR validations of H2AK121u levels in WT at 7 DAG. (a) H2AK121u levels at only-h2ak121u marked active genes. The expression levels of the genes are indicated in FPKM. () H2AK121u levels at only-h3k27me3 marked genes. Structure of the genes and location of the region amplified y qpcr (green line) are shown in the Browser views. For each locus, the amount of immunoprecipitated DNA using H2AK121u antiody (IP) or no antiody (mock) is indicated as % of input. Error ars represent SD etween replicates.
7 12 only-h2ak121u H2AK121u/H3K27me3 12 only-h2ak121u repressed only-h2ak121u active RPKM TSS 33% 66% TES 2-2 TSS 33% 66% TES 2 RPKM Figure S5. Genomic distriution of H2AK121u marks at different categories of marked genes. (a) Metagene plot showing the distriution of H2AK121u marks at only-h2ak121u and H2AK121u/H3K27me3 marked genes. () Metagene plot showing the distriution of H2AK121u marks at only-h2ak121u active and repressed genes.
8 Sample Total Numer of Reads Concurrent Pair Alignment Rate WT rep (88.7%) WT rep (86.8%) atmi1a//c rep (88.6%) atmi1a//c rep (87.%) Figure S6. RNA-seq analysis of WT and atmi1a//c at 7 DAG. (a) Numer of reads and concurrent pair alignment rate per sequencing sample. The numers indicate a high read sequencing quality and the lack of sample contamination. () Scatterplots of pairwise comparison etween RNA-seq replicates of WT (Col-, left panel) and atmi1a//c (right panel).
9 H2AK121u/H3K27me3 only-h3k27me3 -log(p-value) Figure S7. Different families of Transcription Factors (TFs) are enriched in H2AK121u/H3K27me3 and only-h3k27me3 marked genes. While H2AK121u/H3K27me3 marked genes showed enrichment for different TF families, only-h3k27me3 marked genes were significantly enriched for MADSox transcription factors of the MIKC type, which are mostly involved in the control of flowering time, flower, seed, and fruit development. A p-value of.5 was used as a cut-off to determine significance (indicated as dashed line). X- axis of the plot represents the significance level using -log(p-value). The p-value was computing using Fisher s Exact test.
10 clf28/swn7 Rep2 FPKM WT Rep1 FPKM clf28/swn 7Rep1 FPKM WT Rep2 FPKM lhp1 Rep2 FPKM WT Rep2 FPKM WT Rep1 FPKM lhp1 Rep1 FPKM Figure S8. Comparison of clf28/swn7 and lhp1 H2AK121u ChIP-seq replicates at 7 DAG. (a) Scatterplots of pairwise comparison etween H2AK121u ChIP-seq replicates of WT (left panel) and clf28/swn7 (right panel). () Scatterplots of pairwise comparison etween H2AK121u ChIP-seq replicates of WT (left panel) and lhp1 (right panel).
11 H2AK121u WT clf28/swn7 WT H2AK121u lhp TSS TSS TSS TSS 1 2 WT clf28/swn7 Figure S9. The gloal levels of H2AK121u marks are increased in clf28/swn7 mutants. (a) ChIP-seq density heatmaps of H2AK121u marks in WT and clf28/swn7 (left panel) and WT and lhp1 (right panel) mutants at genomic regions surrounding the TSS of target genes. () Western lot (WB) analysis showing gloal H2AK121u levels in WT and clf28/swn7 mutants at 7 DAG. A two fold dilution series of extracted chromatin efore immunoprecipitation was proed with the indicated antiodies to ensure quantitative results.
12 Rep 1 Rep 2 Rep 1 Rep 2 Figure S1. H2AK121u levels at H2AK121u peaks in clf28/swn7 and lhp1 mutants compared to WT after normalization with a modified MAnorm protocol. (a,) Fold-change (M) and average intensity (A) for common H2AK121u peaks efore normalization and for all peaks after normalization in the comparison etween (a) clf28/swn7 and WT and () lhp1 and WT. Common peaks used to uild the rescaling model are highlighted in lack. Peaks with increased levels of H2AK121u were indicated in red and with decreased levels in lue.
13 1,5,8,4 % INPUT,6,4,2 WT mock WT IP clf28/swn7 mock clf28/swn7 IP % INPUT,3,2,1 WUS WOX12 2,5 1,6 2 1,4 1,2 % INPUT 1,5 1,5 % INPUT 1,8,6,4,2 AIL5 FLC Figure S11. ChIP-qPCR validations of H2AK121u levels in clf28/swn7 at 7 DAG. (a) Genes showing unaltered or increased levels of H2AK121u marks in clf28/swn7. () Genes showing decreased levels of H2AK121u marks in clf28/swn7. Structure of the genes and location of the region amplified y qpcr (green line) are shown in the Browser views. For each locus, the amount of immunoprecipitated DNA using H2AK121u antiody (IP) or no antiody (mock) is indicated as % of input. Error ars represent SD etween replicates.
14 WT Rep2 FPKM atmi1a//c Rep2 FPKM WT Rep1 FPKM atmi1a//c Rep1 FPKM WT Rep2 FPKM atmi1a//c Rep2 FPKM WT Rep1 FPKM atmi1a//c Rep1 FPKM Figure S12. Comparison of atmi1a//c ChIP-seq replicates at 7 DAG. (a) Scatterplots of pairwise comparison etween H2AK121u ChIP-seq replicates of WT (left panel) and atmi1a//c (right panel). () Scatterplots of pairwise comparison etween H3K27me3 ChIP-seq replicates of WT (left panel) and atmi1a//c (right panel).
15 WT atmi1a//c WT atmi1a//c c WT atmi1a//c Figure S13. The gloal levels of H2AK121u marks are reduced in atmi1a//c mutants. (a, ) ChIP-seq density heatmaps of H2AK121u marks in WT and atmi1a//c mutants at genomic regions surrounding the TSS of target genes. (a) reads per kiloase and million mapped reads (RPKM) and () total lirary size (reads per million reads sequenced (RPM)) normalizations produced similar results with a sharper apparent decrease in the case of total lirary size normalization when comparing atmi1a//c to WT. (c) WB analysis showing gloal levels of H2AK121u in atmi1a//c mutants compared to WT. A two fold dilution series of extracted chromatin efore immunoprecipitation was proed with the indicated antiodies.
16 DPA4 SPL8 GA3OX1 3 2,5 % INPUT 2 1,5 1 WT mock WT IP atmi1a//c mock atmi1a//c IP,5 DPA4 SPL8 GA3OX1 Figure S14. H2AK121u levels at selected genes in WT and atmi1a//c. ChIP qpcr analysis of H2AK121u levels at genes in WT and atmi1a//c mutants. Structure of the genes and location of the region amplified y qpcr (green line) are shown in the Browser views. For each locus, the amount of immunoprecipitated DNA using H2AK121u antiody (IP) or no antiody (mock) is indicated as % of input. Error ars represent SD etween replicates.
17 Rep 1 Rep 2 Figure S15. H2AK121u levels at H2AK121u peaks in atmi1a//c mutant compared to WT after normalization with a modified MAnorm protocol. Foldchange (M) and average intensity (A) for common H2AK121u peaks efore normalization and for all peaks after normalization in the comparison etween atmi1a//c and WT. Common peaks used to uild the rescaling model are highlighted in lack. Peaks with increased levels of H2AK121u were indicated in red and with decreased levels in lue.
18 WT atmi1a//c % INPUT 1,8,6,4,2 WUS % INPUT 1,2 1,8,6,4,2 MGP WT mock WT IP atmi1a//c mock atmi1a//c IP % INPUT,45,4,35,3,25,2,15,1,5 WOX12 % INPUT KNU c Figure S16. Genes displaying reduced levels of H2AK121u marks were significantly enriched in genes that are transcriptionally upregulated in atmi1a//c mutants. (a) ChIP qpcr analysis of H2AK121u levels at selected genes in WT and atmi1a//c mutants. Structure of the genes and location of the region amplified y qpcr (green line) are shown in the Browser views. For each locus, the amount of immunoprecipitated DNA using H2AK121u antiody (IP) or no antiody (mock) is indicated as % of input. Error ars represent SD etween replicates. () Enrichment score of upregulated genes in the different gene categories according to their level of change in H2AK121u etween WT and atmi1a//c mutants. Genes displaying a reduction of H2AK121u levels equal or igger than 2% were significantly enriched in genes that ecame activated in atmi1a//c mutants, indicating that a reduction of 2% may already have an impact on gene expression. (c) Fraction of genes in the different categories according to their levels of H2AK121u marks in atmi1a//c mutants that were statistically significant (p<.5 computed y MAnorm ased on a Bayesian model [42]).
19 H2AK121u levels in atmi1a//c Reduced Levels (<8% of WT levels) 1171 No change (8-12% of WT levles) Increased levels (>12% of WT levels) Figure S17. Loss of AtBMI1 function impacts H2AK121u levels. Pie chart showing the total numer of genes with altered levels of H2AK121u in atmi1a//c mutants at 7 DAG. 78% of H2AK121u marked genes displayed reduced levels of these marks in atmi1a//c mutants, ranging from to 8% of WT levels.
20 WT atmi1a//c WT atmi1a//c c WT Figure S18. ChIP-seq density heatmaps of H3K27me3 marks in WT and atmi1a//c mutants at genomic regions surrounding the TSS of target genes. (a) reads per kiloase and million mapped reads (RPKM) and () total lirary size (reads per million reads sequenced (RPM)) normalizations produced similar results with a sharper apparent decrease in the case of total lirary size normalization when comparing atmi1a//c to WT. (c) WB analysis showing gloal levels of H3K27me3 in atmi1a//c mutants compared to WT. A two fold dilution series of extracted chromatin efore immunoprecipitation was proed with the indicated antiodies.
21 Rep 1 Rep 2 Figure S19. H3K27me3 levels at H3K27me3 peaks in atmi1a//c mutant compared to WT after normalization with a modified MAnorm protocol. Foldchange (M) and average intensity (A) for common H3K27me3 peaks efore normalization and for all peaks after normalization in the comparison etween atmi1a//c and WT. Common peaks used to uild the rescaling model are highlighted in lack. Peaks with increased levels of H3K27me3 were indicated in red and with decreased levels in lue.
22 H3K27me3 levels in atmi1a//c Reduced Levels (<8% of WT levels) No change (8-12% of WT levles) Increased levels (>12% of WT levles) Figure 2. Loss of AtBMI1 function impacts H3K27me3 levels. Pie chart showing the total numer of genes with altered levels of H3K27me3 in atmi1a//c mutants at 7 DAG. 44% of H2AK121u marked genes displayed reduced levels of these marks in atmi1a//c mutants, ranging from to 8% of WT levels, ut there were also a 18.3% of the genes that gained H3K27me3 marks.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes
 Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Sirt1 Hmg20b Gm (0.17) 24 (17.3) 877 (857)
 3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
Supplementary Table S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort. Chr. # of Gene 2. Chr. # of Gene 1
 Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
H2A monoubiquitination in Arabidopsis thaliana is generally independent of LHP1 and PRC2 activity
 Zhou et al. Genome Biology (2017) 18:69 DOI 10.1186/s13059-017-1197-z RESEARCH H2A monoubiquitination in Arabidopsis thaliana is generally independent of LHP1 and PRC2 activity Open Access Yue Zhou 1,
Zhou et al. Genome Biology (2017) 18:69 DOI 10.1186/s13059-017-1197-z RESEARCH H2A monoubiquitination in Arabidopsis thaliana is generally independent of LHP1 and PRC2 activity Open Access Yue Zhou 1,
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary text Collectively, we were able to detect ~14,000 expressed genes with RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) > 1 or ~16,000 with RPKM > 0.1 in at least one cell type from oocyte to the morula
Supplementary text Collectively, we were able to detect ~14,000 expressed genes with RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) > 1 or ~16,000 with RPKM > 0.1 in at least one cell type from oocyte to the morula
Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data
 Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data Bioinformatics methods, models and applications to disease Alex Essebier ChIP-seq experiment To
Processing, integrating and analysing chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) data Bioinformatics methods, models and applications to disease Alex Essebier ChIP-seq experiment To
H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells
 Nucleic Acids Research, 2017 1 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx251 H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells Runsheng He 1,2 and
Nucleic Acids Research, 2017 1 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx251 H3K4 demethylase KDM5B regulates global dynamics of transcription elongation and alternative splicing in embryonic stem cells Runsheng He 1,2 and
Computational aspects of ChIP-seq. John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory
 Computational aspects of ChIP-seq John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory ChIP-seq Using highthroughput sequencing to investigate DNA
Computational aspects of ChIP-seq John Marioni Research Group Leader European Bioinformatics Institute European Molecular Biology Laboratory ChIP-seq Using highthroughput sequencing to investigate DNA
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
ChIP-seq hands-on. Iros Barozzi, Campus IFOM-IEO (Milan) Saverio Minucci, Gioacchino Natoli Labs
 ChIP-seq hands-on Iros Barozzi, Campus IFOM-IEO (Milan) Saverio Minucci, Gioacchino Natoli Labs Main goals Becoming familiar with essential tools and formats Visualizing and contextualizing raw data Understand
ChIP-seq hands-on Iros Barozzi, Campus IFOM-IEO (Milan) Saverio Minucci, Gioacchino Natoli Labs Main goals Becoming familiar with essential tools and formats Visualizing and contextualizing raw data Understand
Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder Labs August 30, 2012
 Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
Elucidating Transcriptional Regulation at Multiple Scales Using High-Throughput Sequencing, Data Integration, and Computational Methods Raymond Auerbach PhD Candidate, Yale University Gerstein and Snyder
ddm1a (PFG_3A-51065) ATG ddm1b (PFG_2B-60109) ATG osdrm2 (PFG_3A-04110) osdrm2 osdrm2 osdrm2
 Relative expression.6.5.4.3.2.1 OsDDM1a OsDDM1b OsDRM2 TG TG TG ddm1a (PFG_3-5165) P1 P3 ddm1b (PFG_2-619) P2 531bp 5233bp P1 P4 P3 P2 F1 R1 F1 TG TG TG F1 R1 C ddm1a -/- -/- ddm1b -/- +/- +/- -/- D (PFG_3-411)
Relative expression.6.5.4.3.2.1 OsDDM1a OsDDM1b OsDRM2 TG TG TG ddm1a (PFG_3-5165) P1 P3 ddm1b (PFG_2-619) P2 531bp 5233bp P1 P4 P3 P2 F1 R1 F1 TG TG TG F1 R1 C ddm1a -/- -/- ddm1b -/- +/- +/- -/- D (PFG_3-411)
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1 33,312. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2 # 44,325 # 44,055. Aire rep 1. Aire rep 2.
 a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
a 33,312 b rep 1 rep 1 # 44,325 rep 2 # 44,055 [0-84] rep 2 [0-84] 1810043G02Rik Pfkl Dnmt3l Icosl rep 1 [0-165] rep 2 [0-165] Rps14 Cd74 Mir5107 Tcof1 rep 1 [0-69] rep 2 [0-68] Id3 E2f2 Asap3 rep 1 [0-141]
Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis
 Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis Due date: Friday, 2/24 10am. Note: no late assignments will be accepted. Introduction CpG islands (CGIs) are important regulatory regions in the genome. What
Assignment 5: Integrative epigenomics analysis Due date: Friday, 2/24 10am. Note: no late assignments will be accepted. Introduction CpG islands (CGIs) are important regulatory regions in the genome. What
BIMM 143. RNA sequencing overview. Genome Informatics II. Barry Grant. Lecture In vivo. In vitro.
 RNA sequencing overview BIMM 143 Genome Informatics II Lecture 14 Barry Grant http://thegrantlab.org/bimm143 In vivo In vitro In silico ( control) Goal: RNA quantification, transcript discovery, variant
RNA sequencing overview BIMM 143 Genome Informatics II Lecture 14 Barry Grant http://thegrantlab.org/bimm143 In vivo In vitro In silico ( control) Goal: RNA quantification, transcript discovery, variant
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf. Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016
 Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
Patterns of Histone Methylation and Chromatin Organization in Grapevine Leaf Rachel Schwope EPIGEN May 24-27, 2016 What does H3K4 methylation do? Plant of interest: Vitis vinifera Culturally important
Accessing and Using ENCODE Data Dr. Peggy J. Farnham
 1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
Peak-calling for ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq
 Peak-calling for ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq Shamith Samarajiwa CRUK Autumn School in Bioinformatics 2017 University of Cambridge Overview Peak-calling: identify enriched (signal) regions in ChIP-seq or ATAC-seq
Peak-calling for ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq Shamith Samarajiwa CRUK Autumn School in Bioinformatics 2017 University of Cambridge Overview Peak-calling: identify enriched (signal) regions in ChIP-seq or ATAC-seq
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging By Keith E. Szulwach 1,8, Xuekun Li 1,8, Yujing Li 1, Chun-Xiao Song 2, Hao Wu
Supplementary Information 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging By Keith E. Szulwach 1,8, Xuekun Li 1,8, Yujing Li 1, Chun-Xiao Song 2, Hao Wu
A Practical Guide to Integrative Genomics by RNA-seq and ChIP-seq Analysis
 A Practical Guide to Integrative Genomics by RNA-seq and ChIP-seq Analysis Jian Xu, Ph.D. Children s Research Institute, UTSW Introduction Outline Overview of genomic and next-gen sequencing technologies
A Practical Guide to Integrative Genomics by RNA-seq and ChIP-seq Analysis Jian Xu, Ph.D. Children s Research Institute, UTSW Introduction Outline Overview of genomic and next-gen sequencing technologies
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
CTCF-Mediated Functional Chromatin Interactome in Pluripotent Cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CTCF-Mediated Functional Chromatin Interactome in Pluripotent Cells Lusy Handoko 1,*, Han Xu 1,*, Guoliang Li 1,*, Chew Yee Ngan 1, Elaine Chew 1, Marie Schnapp 1, Charlie Wah
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CTCF-Mediated Functional Chromatin Interactome in Pluripotent Cells Lusy Handoko 1,*, Han Xu 1,*, Guoliang Li 1,*, Chew Yee Ngan 1, Elaine Chew 1, Marie Schnapp 1, Charlie Wah
MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome
 Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region
 Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis. Lei Zhou
 High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis Lei Zhou (leizhou@ufl.edu) High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis 1. Representation of HTS data. 2. Visualization of HTS data. 3. Discovering genomic
High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis Lei Zhou (leizhou@ufl.edu) High Throughput Sequence (HTS) data analysis 1. Representation of HTS data. 2. Visualization of HTS data. 3. Discovering genomic
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table.
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
ChIP-seq analysis. J. van Helden, M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, N. Servant, M. Thomas-Chollier, O.Sand
 ChIP-seq analysis J. van Helden, M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, N. Servant, M. Thomas-Chollier, O.Sand Tuesday : quick introduction to ChIP-seq and peak-calling (Presentation + Practical session)
ChIP-seq analysis J. van Helden, M. Defrance, C. Herrmann, D. Puthier, N. Servant, M. Thomas-Chollier, O.Sand Tuesday : quick introduction to ChIP-seq and peak-calling (Presentation + Practical session)
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material HLA-DM Captures Partially Empty HLA-DR Molecules for Catalyzed Peptide Removal Anne-Kathrin Anders, Melissa J. Call, Monika-Sarah E. D. Schulze, Kevin D. Fowler, David A. Schuert,
Supplementary Material HLA-DM Captures Partially Empty HLA-DR Molecules for Catalyzed Peptide Removal Anne-Kathrin Anders, Melissa J. Call, Monika-Sarah E. D. Schulze, Kevin D. Fowler, David A. Schuert,
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic diagram of o2n-seq. Double-stranded DNA was sheared, end-repaired, and underwent A-tailing by standard protocols.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic diagram of o2n-seq. Double-stranded DNA was sheared, end-repaired, and underwent A-tailing by standard protocols. A-tailed DNA was ligated to T-tailed dutp adapters, circularized
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic diagram of o2n-seq. Double-stranded DNA was sheared, end-repaired, and underwent A-tailing by standard protocols. A-tailed DNA was ligated to T-tailed dutp adapters, circularized
Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples.
 Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Supplemental Data. Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature
 Supplemental Data Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature Jianfu Jiang 1, Xinna Liu 1, Guotian Liu, Chonghuih Liu*, Shaohuah Li*, and Lijun
Supplemental Data Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature Jianfu Jiang 1, Xinna Liu 1, Guotian Liu, Chonghuih Liu*, Shaohuah Li*, and Lijun
Genome-Wide Localization of Protein-DNA Binding and Histone Modification by a Bayesian Change-Point Method with ChIP-seq Data
 Genome-Wide Localization of Protein-DNA Binding and Histone Modification by a Bayesian Change-Point Method with ChIP-seq Data Haipeng Xing, Yifan Mo, Will Liao, Michael Q. Zhang Clayton Davis and Geoffrey
Genome-Wide Localization of Protein-DNA Binding and Histone Modification by a Bayesian Change-Point Method with ChIP-seq Data Haipeng Xing, Yifan Mo, Will Liao, Michael Q. Zhang Clayton Davis and Geoffrey
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
GeneOverlap: An R package to test and visualize
 GeneOverlap: An R package to test and visualize gene overlaps Li Shen Contact: li.shen@mssm.edu or shenli.sam@gmail.com Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, New York http://shenlab-sinai.github.io/shenlab-sinai/
GeneOverlap: An R package to test and visualize gene overlaps Li Shen Contact: li.shen@mssm.edu or shenli.sam@gmail.com Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, New York http://shenlab-sinai.github.io/shenlab-sinai/
Supplemental Information. Genomic Characterization of Murine. Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription. Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells
 Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Implication of Long noncoding RNAs in the endothelial cell response to hypoxia revealed y RNAsequencing. Voellenkle C., Garcia-Manteiga J. M., Pedrotti S., Perfetti A., De Toma
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Implication of Long noncoding RNAs in the endothelial cell response to hypoxia revealed y RNAsequencing. Voellenkle C., Garcia-Manteiga J. M., Pedrotti S., Perfetti A., De Toma
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
Expanded View Figures
 EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures. for. pirna-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional
 Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Supplemental Figures Legends and Supplemental Figures for pirn-guided slicing of transposon transcripts enforces their transcriptional silencing via specifying the nuclear pirn repertoire Kirsten-ndré
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
Comprehensive nucleosome mapping of the human genome in cancer progression
 /, Vol. 7, No. 12 Comprehensive nucleosome mapping of the human genome in cancer progression Brooke R. Druliner 1,5, Daniel Vera 1,6, Ruth Johnson 2, Xiaoyang Ruan 3, Lynn M. Apone 4, Eileen T. Dimalanta
/, Vol. 7, No. 12 Comprehensive nucleosome mapping of the human genome in cancer progression Brooke R. Druliner 1,5, Daniel Vera 1,6, Ruth Johnson 2, Xiaoyang Ruan 3, Lynn M. Apone 4, Eileen T. Dimalanta
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Dynamic reprogramming of DNA methylation in SETD2- deregulated renal cell carcinoma
 /, Vol. 7, No. 2 Dynamic reprogramming of DNA methylation in SETD2- deregulated renal cell carcinoma Rochelle L. Tiedemann 1, Ryan A. Hlady 2, Paul D. Hanavan 3, Douglas F. Lake 3, Raoul Tibes 4,5, Jeong-Heon
/, Vol. 7, No. 2 Dynamic reprogramming of DNA methylation in SETD2- deregulated renal cell carcinoma Rochelle L. Tiedemann 1, Ryan A. Hlady 2, Paul D. Hanavan 3, Douglas F. Lake 3, Raoul Tibes 4,5, Jeong-Heon
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
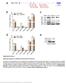 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
ChIP-seq data analysis
 ChIP-seq data analysis Harri Lähdesmäki Department of Computer Science Aalto University November 24, 2017 Contents Background ChIP-seq protocol ChIP-seq data analysis Transcriptional regulation Transcriptional
ChIP-seq data analysis Harri Lähdesmäki Department of Computer Science Aalto University November 24, 2017 Contents Background ChIP-seq protocol ChIP-seq data analysis Transcriptional regulation Transcriptional
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES
 EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1701143/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Impaired DNA replication derepresses chromatin and generates a transgenerationally inherited epigenetic memory Adam
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/8/e1701143/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Impaired DNA replication derepresses chromatin and generates a transgenerationally inherited epigenetic memory Adam
pirna pathway targets active LINE1 elements to establish the repressive H3K9me3markingermcells
 pirna pathway targets active LINE1 elements to establish the repressive H3K9me3markingermcells Dubravka Pezic, 1,3 Sergei A. Manakov, 1,3 Ravi Sachidanandam, 2 and Alexei A. Aravin 1,4 1 Division of Biology
pirna pathway targets active LINE1 elements to establish the repressive H3K9me3markingermcells Dubravka Pezic, 1,3 Sergei A. Manakov, 1,3 Ravi Sachidanandam, 2 and Alexei A. Aravin 1,4 1 Division of Biology
The Epigenome Tools 2: ChIP-Seq and Data Analysis
 The Epigenome Tools 2: ChIP-Seq and Data Analysis Chongzhi Zang zang@virginia.edu http://zanglab.com PHS5705: Public Health Genomics March 20, 2017 1 Outline Epigenome: basics review ChIP-seq overview
The Epigenome Tools 2: ChIP-Seq and Data Analysis Chongzhi Zang zang@virginia.edu http://zanglab.com PHS5705: Public Health Genomics March 20, 2017 1 Outline Epigenome: basics review ChIP-seq overview
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
User Guide. Association analysis. Input
 User Guide TFEA.ChIP is a tool to estimate transcription factor enrichment in a set of differentially expressed genes using data from ChIP-Seq experiments performed in different tissues and conditions.
User Guide TFEA.ChIP is a tool to estimate transcription factor enrichment in a set of differentially expressed genes using data from ChIP-Seq experiments performed in different tissues and conditions.
Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos 3, Hui Yang 1, and Guillermo Garcia-Manero 1
 Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
Genome-wide CHIP-Seq Analysis of Histone Methylation Reveals Modulators of NF- B Signaling And the Histone Demethylase JMJD3 Implicated in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Yue Wei 1, Rui Chen 2, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Figure S1 Expression of AHL gene family members in diploid (Ler Col) and triploid (Ler
 Supplemental material Supplemental figure legends Figure S Expression of AHL gene family members in diploid (Ler ) and triploid (Ler osd) seeds. AHLs from clade B are labelled with (I), and AHLs from clade
Supplemental material Supplemental figure legends Figure S Expression of AHL gene family members in diploid (Ler ) and triploid (Ler osd) seeds. AHLs from clade B are labelled with (I), and AHLs from clade
Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection
 Resource Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection Highlights d Examined chromatin accessibility in endogenous CD8 + T cells during viral infection
Resource Dynamic Changes in Chromatin Accessibility Occur in CD8 + T Cells Responding to Viral Infection Highlights d Examined chromatin accessibility in endogenous CD8 + T cells during viral infection
Supplemental Data. Müller-Xing et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypes of iclf (clf-28 swn-7 CLF pro :CLF-GR) plants. A, Late rescue of iclf plants by renewed DEX treatment; senescent inflorescence with elongated siliques (arrow; 90 DAG,
Cluster Dendrogram. dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:10, 24, 27, 30, 48:50, dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:99, 103, 104, 109, 110,
 A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen
 Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
Xenoestrogen-induced Regulation of EZH2 and Histone Methylation via Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor Signaling to PI3K/AKT Tiffany G. Bredfeldt, Kristen L. Greathouse, Stephen H. Safe, Mien-Chie Hung, Mark
The corrected Figure S1J is shown below. The text changes are as follows, with additions in bold and deletions in bracketed italics:
 Correction H3K4me3 readth Is Linked to Cell Identity and Transcriptional Consistency érénice A. enayoun, Elizabeth A. Pollina, Duygu Ucar, Salah Mahmoudi, Kalpana Karra, Edith D. Wong, Keerthana Devarajan,
Correction H3K4me3 readth Is Linked to Cell Identity and Transcriptional Consistency érénice A. enayoun, Elizabeth A. Pollina, Duygu Ucar, Salah Mahmoudi, Kalpana Karra, Edith D. Wong, Keerthana Devarajan,
sirna count per 50 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand Repeat length (bp) per 50 kb repeats in the chromosome
 Qi et al. 26-3-2564C Qi et al., Figure S1 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats
Qi et al. 26-3-2564C Qi et al., Figure S1 sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the direct strand sirna count per 5 kb small RNAs matching the complementary strand Repeat length (bp) per 5 kb repeats
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
A -GLS Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii
 -GLS Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii internal standard 4MS Wildtype Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii base Cuscuta gronovii apex 3MSP internal standard MSP 4MT 8MSO 4MO 1MO Figure S1. Representative HPLC-DAD chromatograms
-GLS Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii internal standard 4MS Wildtype Arabidopsis Cuscuta gronovii base Cuscuta gronovii apex 3MSP internal standard MSP 4MT 8MSO 4MO 1MO Figure S1. Representative HPLC-DAD chromatograms
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance.! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014
 Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Not IN Our Genes - A Different Kind of Inheritance! Christopher Phiel, Ph.D. University of Colorado Denver Mini-STEM School February 4, 2014 Epigenetics in Mainstream Media Epigenetics *Current definition:
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD,
 Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
Supplemental Material for:
 Supplemental Material for: Transcriptional silencing of γ-globin by BCL11A involves long-range interactions and cooperation with SOX6 Jian Xu, Vijay G. Sankaran, Min Ni, Tobias F. Menne, Rishi V. Puram,
Supplemental Material for: Transcriptional silencing of γ-globin by BCL11A involves long-range interactions and cooperation with SOX6 Jian Xu, Vijay G. Sankaran, Min Ni, Tobias F. Menne, Rishi V. Puram,
An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression
 www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
Results. Abstract. Introduc4on. Conclusions. Methods. Funding
 . expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
. expression that plays a role in many cellular processes affecting a variety of traits. In this study DNA methylation was assessed in neuronal tissue from three pigs (frontal lobe) and one great tit (whole
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition
 In the format provided y the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 217.15 Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition Chloé
In the format provided y the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 217.15 Light triggers PILS-dependent reduction in nuclear auxin signalling for growth transition Chloé
High-Throughput Sequencing Course
 High-Throughput Sequencing Course Introduction Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Summer 2017 From Raw Unaligned Reads To Aligned Reads To Counts Differential Expression Differential Expression 3 2 1 0 1
High-Throughput Sequencing Course Introduction Biostatistics and Bioinformatics Summer 2017 From Raw Unaligned Reads To Aligned Reads To Counts Differential Expression Differential Expression 3 2 1 0 1
Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis. Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford
 Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford 1 Lecture 8 RNA-seq Analysis RNA-seq principles How can we characterize mrna isoform
Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford 1 Lecture 8 RNA-seq Analysis RNA-seq principles How can we characterize mrna isoform
Global Epigenetic and Transcriptional Trends among Two Rice Subspecies and Their Reciprocal Hybrids W
 The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 17 33, January 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists RESEARCH ARTICLES Global Epigenetic and Transcriptional Trends among Two Rice Subspecies and
The Plant Cell, Vol. 22: 17 33, January 2010, www.plantcell.org ã 2010 American Society of Plant Biologists RESEARCH ARTICLES Global Epigenetic and Transcriptional Trends among Two Rice Subspecies and
Supplemental Figure S1. A. Venn diagram depicting overlap between anti-correlated genes of
 Supplemental Figure S1. A. Venn diagram depicting overlap between anti-correlated genes of 1,000 most differentially expressed genes with NKX2-1 amplification in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and anti-correlated
Supplemental Figure S1. A. Venn diagram depicting overlap between anti-correlated genes of 1,000 most differentially expressed genes with NKX2-1 amplification in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines and anti-correlated
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB
 RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
