MUSCULAR SYSTEM. Jhia Anjela D. Rivera Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology, Centro Escolar University
|
|
|
- Ann Andrews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology, Centro Escolar University
2 OUTLINE Overview Major types of muscles Muscle nomenclature Attachments of skeletal muscles Muscle forms Regional study of skeletal muscles Muscles of the thorax Muscles of respiration Muscles of the back Muscles of the anterior abdomen Muscles of the posterior abdomen Muscles of the perineum Muscles of the upper extremity Muscles of the lower extremity Identify origin, insertion, action and nerve supply Clinical considerations
3 OBJECTIVES To describe the properties and functions of the different muscle tissues. To identify the contrast between skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscles. To know the different bases for naming muscles. To differentiate muscular attachments.
4 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Generally regarded as consisting of one type of muscle found in the body skeletal muscle
5 FUNCTIONS OF THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Muscle tissue is highly specialized to contract, or shorten, forcefully. The process of metabolism extracts energy from nutrient molecules. Part of that energy is used for muscle contraction, and the remainder is used for other cell processes or is released as heat. Body movement Maintenance of posture Respiration Production of body heat Communication Constriction of organs and vessels Heart beat
6 PROPERTIES OF MUSCLES Muscle has four major functional properties: Contractility is the ability of muscle to shorten forcefully Excitability is the capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Extensibility means that muscle can be stretched beyond its normal resting length and is still able to contract Elasticity is the ability of muscle to recoil to its original resting length after it has been stretched
7 TYPES OF MUSCLE TISSUES Forms the majority of the muscle tissue in the body Consists of parallel bundles of long, multinucleated fibers with transverse stripes Capable of powerful contractions, innervated by somatic and branchial motor nerves Used to move bones and other structures, provides support and gives form to the body Striated muscle found only in the walls of the heart (myocardium) and in some of the large vessels close to where they join the heart Consists of a branching network of individual cells linked electrically and mechanically Less powerful contractions, resistant to fatigue Innervated by visceral motor nerves Absence of stripes Consists of elongated or spindle shaped fibers capable of slow and sustained contractions Found in the walls of blood vessels (tunica media), associated with hair follicles in the skin, in the eyeballs, GIT, urinary system Innervated by visceral motor nerves Skeletal Cardiac Smooth
8 MUSCLE NOMENCLATURE Muscles are named according to: Location Size Shape Orientation of fasciculi Origin and insertion Number of heads Function
9 LOCATION A pectoralis (chest) muscle is located in the chest, a gluteus (buttock) muscle is located in the buttock, and a brachial (arm) muscle is located in the arm.
10 SIZE The gluteus maximus (large) is the largest muscle of the buttock, and the gluteus minimus (small) is the smallest. A longus (long) muscle is longer than a brevis (short) muscle.
11 SHAPE The deltoid (triangular) muscle is triangular, a quadratus (quadrate) muscle is rectangular, and a teres (round) muscle is round.
12 ORIENTATION OF FASCICULI. A rectus (straight) muscle has muscle fasciculi running straight with the axis of the structure to which the muscle is associated, whereas the fasciculi of an oblique muscle lie oblique to the longitudinal axis of the structure.
13 ORIGIN AND INSERTION The sternocleidomastoid originates on the sternum and clavicle and inserts onto the mastoid process of the temporal bone. The brachioradialis originates in the arm (brachium) and inserts onto the radius.
14 NUMBER OF HEADS A biceps muscle has two heads, and a triceps muscle has three heads.
15 FUNCTION An abductor moves a structure away from the midline, and an adductor moves a structure toward the midline. The masseter (a chewer) is a chewing muscle
16 ATTACHMENTS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Tendon muscle to bone Aponeuroses muscle to muscle Origin (head) stationary end of the muscle Insertion end of the muscle attached to the bone Belly part of the muscle between the origin and insertion
17 REGIONAL STUDY OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Thorax Respiration Back Anterior abdomen Posterior abdomen Perineum Upper extremity Lower extremity
18 MUSCLE OF THE THORAX AND RESPIRATION MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION External intercostal (11 muscles) Internal intercostal (11 muscles) Lower border of a rib Upper border of the rib below Within intercostal space, each extends from the tubercle of the rib dorsally to the cartilage of the rib ventrally Ridge on the inner surface near lower border of the rib Upper border of the rib below Within intercostal space, each extends from the sternum ventrally to the angle of the rib dorsally Intercostal nerves Intercostal nerves Elevate the ribs; active during normal inspiration Elevate the ribs; active during inspiration and expiration
19 MUSCLE OF THE THORAX AND RESPIRATION MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Transversus thoracis Subclavius Inner surface of body; xiphoid process, posterior surface of the sternum 1 st rib and its cartilage at their junction Costal cartilages of ribs 2-6, inner surfaces of costal cartilages 2-6 Groove on the lower surface of the middle 1/3 rd of clavicle Subcostalis angle of ribs angle of a rib 2-3 ribs above origin Diaphragm xiphoid process, costal margin, fascia over the quadratus lumborum and psoas major mm.(lateral & medial arcuate ligaments), vertebral bodies L1-L3 central tendon of the diaphragm Intercostal nerves Nerve to subclavius from upper trunk of brachial plexus Intercostal nerves phrenic nerve (C3-C5) compresses the thorax for forced expiration Depresses and pulls clavicle forward compresses the intercostal spaces pushes the abdominal viscera inferiorly, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity (inspiration)
20 MUSCLES OF THE THORAX AND RESPIRATION
21 MUSCLE OF THE BACK MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Erector spinae iliac crest, sacrum, transverse and spinous processes of vertebrae and supraspinal ligament Iliocostalis iliac crest and sacrum Interspinales Intertransversarii upper border of spinous process upper border of transverse process angles of the ribs, transverse and spinous processes of vertebrae, posterior aspect of the skull angles of the ribs lower border of spinous process above lower border of transverse process above segmentally innervated by dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C1-S5 dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C4-S5 dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C1-L5 dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C1-L5 extends and laterally bends the trunk, neck and head extends and laterally bends the trunk and neck extend trunk and neck laterally bend trunk and neck
22 MUSCLE OF THE BACK MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Longissimus transverse process at inferior vertebral levels Multifidus sacrum, transverse processes of C3-L5 Obliquus capitis inferior Obliquus capitis superior spinous process of the axis transverse process of atlas transverse process at superior vertebral levels and mastoid process spinous processes 2-4 vertebral levels superior to their origin transverse process of atlas occipital bone above inferior nuchal line dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C1-S1 dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C1-L5 suboccipital nerve (DPR of C1) suboccipital nerve (DPR of C1) extends and laterally bends the trunk, neck and head extend and laterally bend trunk and neck, rotate to opposite side rotates the head to the same side extends the head, rotates the head to the same side
23 MUSCLE OF THE BACK MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Rectus capitis posterior major Rectus capitis posterior minor spinous process of axis posterior tubercle of atlas inferior nuchal line inferior nuchal line medially Rotatores transverse processes long rotatores: spines 2 vertebrae above origin; short rotatores: spines 1 vertebrae above origin Semispinalis transverse processes of C7-T12 capitis: back of skull between nuchal lines; cervicis & thoracis: spines 4-6 vertebrae above origin suboccipital nerve (DPR of C1) suboccipital nerve (DPR of C1) dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C1-L5 dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C1-T12 extends the head, rotate to same side extends the head rotates the vertebral column to the opposite side extends the trunk and laterally bends the trunk, rotates the trunk to the opposite side
24 MUSCLE OF THE BACK MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Spinalis spinous processes at inferior vertebral levels spinous processes at superior vertebral levels and base of the skull dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C2-L3 extends and laterally bends trunk and neck Splenius ligamentum nuchae and spines C7-T6 capitis: mastoid process & superior nuchal line laterally; cervicis: posterior tubercles of C1-C3 vertebrae dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C2-C6 extends and laterally bends neck and head; rotates head to same side Splenius capitis ligamentum nuchae and spines of C7-T6 vertebrae mastoid process and lateral end of the superior nuchal line dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C2-C6 extends and laterally bends the neck and head, rotates head to the same side Splenius cervicis ligamentum nuchae and spines of C7-T6 vertebrae posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of C1-C3 vertebrae dorsal primary rami of spinal nerves C2-C6 extends and laterally bends neck and head, rotates head to the same side
25 MUSCLE OF THE BACK
26 MUSCLE OF THE BACK
27 MUSCLE OF THE BACK
28 MUSCLE OF THE BACK
29 MUSCLE OF THE ABDOMEN MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Cremaster inguinal ligament forms thin network of muscle fascicles around the spermatic cord and testis (or around the distal portion of the round ligament of the uterus) Dartos External abdominal oblique Interfoveolar subcutaneous connective tissue of the scrotum and the penis (or labium majus and clitoris) lower 8 ribs transversus abdominis fibers that lie superficial to the inferior epigastric vessels skin of the scrotum and penis (or labium majus and clitoris) linea alba, pubic crest & tubercle, anterior superior iliac spine & anterior half of iliac crest anterior lamina of femoral sheath, immediately distal to origin of inferior epigastric vessels genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve postganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers arriving via the ilioinguinal nerve and the posterior scrotal nerve intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves elevates testis (not well developed in females) elevates testis (tenses the skin of the pudendal region in the female) flexes and laterally bends the trunk compresses abdominal contents
30 MUSCLE OF THE ABDOMEN MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Internal abdominal oblique Oblique, external abdominal Oblique, internal abdominal Psoas major thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest, lateral 2/3 of the inguinal ligament lower 8 ribs thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest, lateral 2/3 of the inguinal ligament bodies and transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae lower 3 or 4 ribs, linea alba, pubic crest linea alba, pubic crest & tubercle, anterior superior iliac spine & anterior half of iliac crest lower 3 or 4 ribs, linea alba, pubic crest lesser trochanter of femur (with iliacus) via iliopsoas tendon intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves L2-L4 flexes and laterally bends the trunk flexes and laterally bends the trunk flexes and laterally bends the trunk flexes the thigh; flexes & laterally bends the lumbar vertebral column
31 MUSCLE OF THE ABDOMEN MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Psoas minor Pyramidalis Quadratus lumborum Rectus abdominis Transversus abdominis bodies of the T12 & L1 vertebrae pubis, anterior to the rectus abdominis posterior part of the iliac crest and the iliolumbar ligament pubis and the pubic symphysis lower 6 ribs, thoracolumbar fascia, anterior 3/4 of the iliac crest, lateral 1/3 of inguinal ligament iliopubic eminence at the line of junction of the ilium and the superior pubic ramus branches of the ventral primary rams of spinal nerves L1-L2 flexes & laterally bends the lumbar vertebral column linea alba subcostal nerve draws the linea alba inferiorly transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae 1-4 and the 12th rib xiphoid process of the sternum and costal cartilages 5-7 linea alba, pubic crest and pecten of the pubis subcostal nerve and ventral primary rami of spinal nerves L1-L4 intercostal nerves 7-11 and subcostal nerve intercostal nerves 7-11, subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves laterally bends the trunk, fixes the 12th rib flexes the trunk compresses the abdomen
32 MUSCLE OF THE ANTERIOR ABDOMEN
33 MUSCLE OF THE ANTERIOR ABDOMEN
34 MUSCLE OF THE ANTERIOR ABDOMEN
35 MUSCLE OF THE ANTERIOR ABDOMEN
36 MUSCLE OF THE ANTERIOR ABDOMEN
37 MUSCLE OF THE ANTERIOR ABDOMEN
38 NEXT MEETING Muscles of Perineum Muscles of the upper and lower extremities Clinical Considerations
39 MUSCLES OF THE PELVIC WALLS MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Obturator internus flat, fan-shaped muscle Piriformis triangular Anterolateral wall of true pelvis (deep surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bone) Anterior surface of sacrum between anterior sacral foramina Medial surface of greater trochanter of femur Medial side of superior border of greater trochanter of femur Nerve to obturator internus L5, S1 Branches from L5, S1 and S2 Lateral rotation of the extended hip joint; abduction of flexed hip Lateral rotation of the extended hip joint; abduction of flexed hip
40
41 MUSCLES OF THE PELVIC DIAPHRAGM MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Levator ani Posterior pubis and ischial spine (In a line around the pelvic wall beginning on the posterior aspect of the pubic bone and extending across the obturator internus muscle as a tendinous arch (thickening of the obturator internus fascia) to the ischial spine) Sacrum and Coccyx The anterior part is attached to the superior surface of the perineal membrane; the posterior part meets its partner on the other side at the perineal body, around the anal canal, and along the anococcygeal ligament Branches direct from the ventral ramus of S4, and by the inferior rectal branch of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Elavates anus, supports pelvic viscera, contributes to the formation of the pelvic floor, reinforces the external anal sphincter and in women, functions as a vaginal sphincter Coccygeus Ischial spine and pelvic surface of the sacrospinous ligament Lateral margin of coccyx, and related border of sacrum Branches from the anterior rami of S3 and S4 Contributes to the formation of the pelvic floor, which supports the pelvic
42
43 MUSCLES WITHIN THE DEEP PERINEAL POUCH MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Deep transverse perineal Compressor urethrae (in women only) Sphincter urethrovaginalis (in women only) Medial aspect of ischial ramus Ischiopubic ramus on each side Perineal body Perineal body Blends with partner on other side anterior to the urethra Passes forward lateral to the vagina to blend with partner on other side anterior to the urethra Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Stabilizes the position of the perineal body Functions as an accessory sphincter of the urethra Functions as an accessory sphincter of the urethra (also may facilitate closing the vagina)
44 MUSCLES WITHIN THE DEEP PERINEAL POUCH MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION External urethral sphincter Deep transverse perineal Compressor urethrae (in women only) Sphincter urethrovaginalis (in women only) From the inferior ramus of the pubis on each side and adjacent walls of the deep perineal pouch Medial aspect of ischial ramus Ischiopubic ramus on each side Perineal body Surrounds membranous part of urethra Perineal body Blends with partner on other side anterior to the urethra Passes forward lateral to the vagina to blend with partner on other side anterior to the urethra Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Perineal branches of the pudendal nerve (S2 to S4) Compresses the membranous urethra; relaxes during micturition Stabilizes the position of the perineal body Functions as an accessory sphincter of the urethra Functions as an accessory sphincter of the urethra (also may facilitate closing the vagina)
45
46 MUSCLES IN GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION External anal sphincter Coccyx Central tendon of perineum Puborectalis Internal anal sphincter Iliococcygeus posterior aspect of the body of the pubis unites with the puborectalis m. of other side posterior to the rectum inferior rectal nerves (from the pudendal nerve) branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 encircles the anal canal encircles the anal canal parasympathetic fibers from S4 arcus tendineus levator ani and the ischial spine anococcygeal raphe and the coccyx branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves S3-S4 Keeps orifice of anal canal closed draws the distal rectum forward and superiorly; aids in voluntary retention of feces constricts the anal canal elevates the pelvic floor
47
48 MUSCLES OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Trapezius Deltoid Levator scapulae Rhomboid minor Rhomboid major Superior nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, medial margin of the ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of CVII to TXII and the related supraspinous ligaments Inferior edge of the crest of the spine of the scapula, lateral margin of the acromion, anterior border of lateral onethird of clavicle Transverse processes of CI and CII vertebrae and posterior tubercles of transverse processes of CIII and CIV vertebrae Lower end of ligamentum nuchae and spinous processes of CVII and TI vertebrae Spinous processes of TII TV vertebrae and intervening supraspinous ligaments Superior edge of the crest of the spine of the scapula, acromion, posterior border of lateral one-third of clavicle Motor spinal part of accessory nerve (XI). Sensory (proprioception) anterior rami of C3 and C4 Powerful elevator of the scapula; rotates the scapula during abduction of humerus above horizontal; middle fibers retract scapula; lower fibers depress scapula Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Axillary nerve (C5, C6) Major abductor of arm (abducts arm beyond initial 15 done by supraspinatus); clavicular fibers assist in flexing the arm; posterior fibers assist in extending the arm Posterior surface of medial border of scapula from superior angle to root of spine of the scapula Posterior surface of medial border of scapula at the root of the spine of the scapula Posterior surface of medial border of scapula from the root of the spine of the scapula to the inferior angle Branches directly from anterior rami ofc3 and C4spinal nerves and by branches (C5) from the dorsal scapular nerve Dorsal scapular nerve (C4, C5) Dorsal scapular nerve (C4, C5) Elevates the scapula Elevates and retracts the scapula Elevates and retracts the scapula
49
50 MUSCLES OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Supraspinatus Medial two-thirds of the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and the deep fascia that covers the muscle Most superior facet on the greater tubercle of the humerus Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6) Rotator cuff muscle; initiation of abduction of arm to 15 at glenohumeral joint Infraspinatus Medial two-thirds of the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and the deep fascia that covers the muscle Middle facet on posterior surface of the greater tubercle of the humerus Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6) Rotator cuff muscle; lateral rotation of arm at the glenohumeral joint Teres minor Upper two-thirds of a flattened strip of bone on the posterior surface of the scapula immediately adjacent to the lateral border of the scapula Inferior facet on the posterior surface of the greater tubercle of the humerus Axillary nerve (C5, C6) Rotator cuff muscle; lateral rotation of arm at the glenohumeral joint Teres major Elongate oval area on the posterior surface of the inferior angle of the scapula Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus on the anterior surface of the humerus Inferior subscapular nerve (C5, C6,C7) Medial rotation and extension of the arm at the glenohumeral joint Long head of triceps brachii Infraglenoid tubercle on scapula Common tendon of insertion with medial and lateral heads on the olecranon process of ulna Radial nerve (C6, C7, C8) Extension of the forearm at the elbow joint; accessory adductor and extensor of the arm at the glenohumeral joint
51
52 MUSCLES OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Pectoralis major Clavicular head anterior surface of medial half of clavicle; sternocostal head anterior surface of sternum; first seven costal cartilages; sternal end of sixth rib; aponeurosis of external oblique Lateral lip of intertubercular sulcus of humerus Medial and lateral pectoral nerves; clavicular head (C5, C6); sternocostal head (C6, C7, C8, T1) Flexion, adduction, and medial rotation of arm at glenohumeral joint; clavicular head flexion of extended arm; sternocostal head extension of flexed arm Subclavius First rib at junction between rib and costal cartilage Groove on inferior surface of middle one-third of clavicle Nerve to subclavius (C5, C6) Pulls tip of shoulder down; pulls clavicle medially to stabilize sternoclavicular joint Pectoralis minor Anterior surfaces and superior borders of ribs III to V; and from deep fascia overlying the related intercostal spaces Coracoid process of scapula (medial border and upper surface) Medial pectoral nerve (C5, C6,C7, C8, T1) Pulls tip of shoulder down; protracts scapula Serratus anterior Lateral surfaces of upper 8 9 ribs and deep fascia overlying the related intercostal spaces Costal surface of medial border of scapula Long thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7) Protraction and rotation of the scapula; keeps medial border and inferior angle of scapula opposed to thoracic wall
53
54
55
56 MUSCLES OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Subscapularis Medial two-thirds of subscapular fossa Lesser tubercle of humerus Upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5, C6, (C7)) Rotator cuff muscle; medial rotation of the arm at the glenohumeral joint Teres major Elongate oval area on the posterior surface of the inferior angle of the scapula Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus on the anterior surface of the humerus Lower subscapular nerve (C5, C6, C7) Medial rotation and extension of the arm at the glenohumeral joint Latissimus dorsi Spinous processes of lower six thoracic vertebrae and related interspinous ligaments; via the thoracolumbar fascia to the spinous processes of the lumbar vertebrae, related interspinous ligaments, and iliac crest; lower 3 4 ribs Floor of intertubercular sulcus Thoracodorsal nerve (C6, C7, C8) Adduction, medial rotation, and extension of the arm at the glenohumeral joint Long head of triceps brachii Infraglenoid tubercle on scapula Common tendon of insertion with medial and lateral heads on the olecranon process of ulna Radial nerve (C6, C7, C8) Extension of the forearm at the elbow joint; accessory adductor and extensor of the arm at the
57
58
59 MUSCLES OF THE UPPER EXTREMITY MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Biceps brachii Long head supraglenoid tubercle of scapula; short head apex of coracoid process Tuberosity of radius Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6) Powerful flexor of the forearm at the elbow joint and supinator of the forearm; accessory flexor of the arm at the glenohumeral joint Coracobrachialis Apex of coracoid process Linear roughening on midshaft of humerus on medial side Musculocutaneous nerve ( C5, C6, C7) Flexor of the arm at the glenohumeral joint; adducts arm
60
61 Quadrate tubercle on the MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY (GLUTEAL REGION) MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Piriformis Anterior surface of sacrum between anterior sacral foramina Medial side of superior border of greater trochanter of femur Branches from S1 ands2 Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint Obturator internus Anterolateral wall of true pelvis; deep surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bone Medial side of greater trochanter of femur Nerve to obturator internus (L5,S1) Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint Gemellus superior External surface of ischial spine Along length of superior surface of the obturator internus tendon and into the medial side of greater trochanter of femur with obturator internus tendon Nerve to obturator internus (L5,S1) Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint Gemellus inferior Upper aspect of ischial tuberosity Along length of inferior surface of the obturator internus tendon and into the medial side of greater trochanter of femur with obturator internus tendon Nerve to quadratus femoris (L5, S1) Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint
62 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY (GLUTEAL REGION) MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Gemellus inferior Upper aspect of ischial tuberosity Along length of inferior surface of the obturator internus tendon and into the medial side of greater trochanter of femur with obturator internus tendon Nerve to quadratus femoris (L5, S1) Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint Quadratus femoris Lateral aspect of the ischium just anterior to the ischial tuberosity Quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest of the proximal femur Nerve to quadratus femoris (L5, S1) Laterally rotates femur at hip joint Gluteus minimus External surface of ilium between inferior and anterior gluteal lines Linear facet on the anterolateral aspect of the greater trochanter Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1) Abducts femur at hip joint; holds pelvis secure over stance leg and prevents pelvic drop on the opposite swing side during walking; medially rotates thigh Gluteus medius External surface of ilium between anterior and posterior gluteal lines Elongate facet on the lateral surface of the greater trochanter Superior gluteal nerve (L4, L5, S1) Abducts femur at hip joint; holds pelvis secure over stance leg and prevents pelvic drop on the opposite swing side during walking; medially rotates thigh
63
64
65 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY (ANTERIOR COMP. THIGH) MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Psoas major Posterior abdominal wall (lumbar transverse processes, intervertebral discs, and adjacent bodies from TXII to LV and tendinous arches between these points) Lesser trochanter of femur Anterior rami (L1, L2, L3) Flexes the thigh at the hip joint Iliacus Posterior abdominal wall (iliac fossa) Lesser trochanter of femur Femoral nerve (L2, L3) Flexes the thigh at the hip joint Vastus medialis Femur medial part of intertrochanteric line, pectineal line, medial lip of the linea aspera, medial supracondylar line Quadriceps femoris tendon and medial border of patella Femoral nerve (L2,L3, L4) Extends the leg at the knee joint Vastus intermedius Femur upper two-thirds of anterior and lateral surfaces Quadriceps femoris tendon, lateral margin of patella, and lateral condyle of tibia Femoral nerve (L2,L3, L4) Extends the leg at the knee joint Vastus lateralis Femur lateral part of intertrochanteric line, margin of greater trochanter, lateral margin of gluteal tuberosity, lateral lip of the linea aspera Quadriceps femoris tendon and lateral margin of patella Femoral nerve (L2,L3, L4) Extends the leg at the knee joint Rectus femoris Straight head originates from the anterior inferior iliac spine; reflected head originates from the ilium just superior to the acetabulum Quadriceps femoris tendon Femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4) Flexes the thigh at the hip joint and extends the leg at the knee joint Medial surface of tibia just Flexes the thigh at the hip
66
67
68
69 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY (MEDIAL COMP. THIGH) MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Gracilis Pectineus Adductor longus Adductor brevis A line on the external surfaces of the body of the pubis, the inferior pubic ramus, and the ramus of the ischium Pectineal line (pecten pubis) and adjacent bone of pelvis External surface of body of pubis (triangular depression inferior to pubic crest and lateral to pubic symphysis) External surface of body of pubis and inferior pubic ramus Adductor part Medial surface of proximal shaft of tibia Oblique line extending from base of lesser trochanter to linea aspera on posterior surface of proximal femur Linea aspera on middle one-third of shaft of femur Posterior surface of proximal femur and upper one-third of linea aspera Obturator nerve (L2, L3) Femoral nerve (L2, L3) Obturator nerve (anterior division) (L2, L3, L4) Obturator nerve (L2, L3) Posterior surface of proximal femur, linea Obturator nerve (L2, Adducts thigh at hip joint and flexes leg at knee joint Adducts and flexes thigh at hip joint Adducts and medially rotates thigh at hip joint Adducts and medially rotates thigh at hip joint Adducts and medially rotates thigh at hip
70
71
72
73 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER EXTREMITY (MEDIAL COMP. THIGH) MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION INNERVATION ACTION Biceps Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Long head inferomedial part of the upper area of the ischial tuberosity; short head lateral lip of linea aspera Inferomedial part of the upper area of the ischial tuberosity Superolateral impression on the ischial tuberosity Head of fibula Sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2] Medial surface of proximal tibia Groove and adjacent bone on medial and posterior surface of medial tibial condyle Sciatic nerve (L5,S1,S2) Sciatic nerve (L5, S1,S2) Flexes leg at knee joint; extends and laterally rotates thigh at hip joint and laterally rotates leg at knee joint Flexes leg at knee joint and extends thigh at hip joint; medially rotates thigh at hip joint and leg at knee joint Flexes leg at knee joint and extends thigh at hip joint; medially rotates thigh at hip joint and leg at knee joint
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page. Deltoid. Trapezius. Latissimus Dorsi
 Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop)
 Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop) www.oluwadiya.com Bony Anatomy Shoulder Complex: Sternum(manubrium) Clavicle Scapula Proximal humerus Manubrium Sterni Upper part of
Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop) www.oluwadiya.com Bony Anatomy Shoulder Complex: Sternum(manubrium) Clavicle Scapula Proximal humerus Manubrium Sterni Upper part of
Muscles of the Upper Limb that are dissected in the Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes
 Muscles of Upper Limb that are dissected in Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes floor of thoraco thoraco inserting spines from intertubercular arm nerve (C7,8) a. tendon
Muscles of Upper Limb that are dissected in Back Region Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes floor of thoraco thoraco inserting spines from intertubercular arm nerve (C7,8) a. tendon
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Sports Medicine Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part II : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan & A. Eastlake, 2008 Muscles of the Upper Limbs In this
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back
 Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column
 Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES
 ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
ACTIVITIES 5 & 6: APPENDICULAR AND AXIAL MUSCLES Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 11 & 12, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Begin identifying
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter Elevates mandible. Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion. Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders
 Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Anterior Posterior Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible Masseter Elevates mandible Sternocleidomastoid Neck flexion Trapezius Elevates & depresses shoulders Masseter Elevates mandible Temporalis Elevates
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Muscles Built on the Maniken
 Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Muscles Built on the Maniken Facial Muscle Group 1. Temporalis O temporal fossa I anterior border of the ramus of the mandible A elevates the mandible (bite muscle) and holds jaw while at rest 2. Procerus
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS
 TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla
 Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
Upper limb Pectoral region & Axilla 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 1 Pectoral region Intercostal nerve Anterior branch of lateral cutaneous branch Lateral cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous branch Anterior cutaneous
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]
![_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come] _CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1. [Half-Title to come]](/thumbs/81/84146690.jpg) 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 1 [Half-Title to come] 10752-01_CH01redo.qxd 9/24/07 3:07 PM Page 2 THE BACK Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of ANATOMY CHAPTER 1 Plate 1-01 Palpable Structures
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration-
 This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R A L ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumeral joint) = scapula and humerus Lippert, p115
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck.
 Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Pectoral region. Lecture 2
 Pectoral region Lecture 2 Muscle Action Each muscle has: Origin Beginning. Insertion End. Body (belly). Law: When a muscle performs its action, its insertion, moves towards its origin. Spring 2016 Dr.
Pectoral region Lecture 2 Muscle Action Each muscle has: Origin Beginning. Insertion End. Body (belly). Law: When a muscle performs its action, its insertion, moves towards its origin. Spring 2016 Dr.
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
7/31/2012 THE SHOULDER JOINT CLARIFICATION OF TERMS OSTEOLOGY OF THE GH JOINT(BONES)
 THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R AL ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumerual joint) = scapula and Lippert, p115 OSTEOLOGY
THE SHOULDER JOINT T H E G L E N O H U M E R AL ( G H ) J O I N T CLARIFICATION OF TERMS Shoulder girdle = scapula and clavicle Shoulder joint (glenohumerual joint) = scapula and Lippert, p115 OSTEOLOGY
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only. Side lye or prone.25 x 30-50mm Inferior to ilium
 LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
LUMBAR SPINE LEVEL II MUSCLE CHART NB: Needle length varies with tissue depth, this chart acts as a guide only Muscle/ Innervation Comments Position Quadratus Lumborum T12-L3/4 segmentally PSIS Comments.
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES:
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES: Pages 2-11 Week 1 Head and Neck Pages 12-39 Week 2 Trunk Pages 40-52 Week 3 Hip Joint Pages 53-60 Week 4 Knee Joint Pages 61-70 Week 5 Ankle Joint Pages 71-82 Week 6 Foot
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY WEEKLY NOTES: Pages 2-11 Week 1 Head and Neck Pages 12-39 Week 2 Trunk Pages 40-52 Week 3 Hip Joint Pages 53-60 Week 4 Knee Joint Pages 61-70 Week 5 Ankle Joint Pages 71-82 Week 6 Foot
Internship Questions. PP 1 Anatomical Planes & Directions
 Internship Questions PP 1 Anatomical Planes & Directions 1. Which of the following is not a plane of motion a. Sagittal b. Vertical c. Frontal d. Transverse 2. Which of the following terms are related
Internship Questions PP 1 Anatomical Planes & Directions 1. Which of the following is not a plane of motion a. Sagittal b. Vertical c. Frontal d. Transverse 2. Which of the following terms are related
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical
 Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Cadaver Muscular System Practice Practical Station 1 Station 1 1. Specific structure 1. Rectus sheath 2. Red line 2. Linea alba Station 2 Station 2 3. Red muscle 1. Rectus abdominis 4. Red muscle actions
Abdomen: Introduction. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Main Menu. Trunk and Spinal Column click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
Scapular and Deltoid Regions
 M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy Scapular and Deltoid Regions Dr. Peters 1 Outline I. Skeleton of the Shoulder and Attachment of the Upper Extremity to Trunk II. Positions and Movements of the Scapula
M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy Scapular and Deltoid Regions Dr. Peters 1 Outline I. Skeleton of the Shoulder and Attachment of the Upper Extremity to Trunk II. Positions and Movements of the Scapula
Appendix. Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance
 Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
Appendix Useful Anatomical Data of Clinical Significance Appendix Outline Respiratory System 426 Table I. Important Airway Distances (Adult) 426 Table II. Important Data Concerning the Trachea 426 Musculoskeletal
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
3 Movements of the Trunk. Flexion Rotation Extension
 3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes. border of the superior ramus. inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis
 Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles.
 L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Chapter 11: The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions
 BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Pectoral region. Lecture 2
 Pectoral region Lecture 2 Muscle Action Each muscle has: Origin Beginning. Insertion End. Body (belly). Law: When a muscle performs its action, its insertion, moves towards its origin. Spring 2016 Dr.
Pectoral region Lecture 2 Muscle Action Each muscle has: Origin Beginning. Insertion End. Body (belly). Law: When a muscle performs its action, its insertion, moves towards its origin. Spring 2016 Dr.
First practical session. Bones of the gluteal region
 First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT. Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Dated:
 Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy
 Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
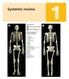 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Locomotor system - Part 6
 Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Healing Hands School of Holistic Health. Advanced Circulatory & Sports Massage Class Handouts
 Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Electrode Placement. Skin Preparation. Frontalis (FRL) (Specific) Temporalis Anterior (TA) (Specific) Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) (Specific)
 Electrode Placement Skin Preparation 1) Removing the hair: Shave if necessary 2) Clean the skin: Use a towel or abrasive pad with conductive cleaning paste or alcohol to remove dead skin cells (high impedance)
Electrode Placement Skin Preparation 1) Removing the hair: Shave if necessary 2) Clean the skin: Use a towel or abrasive pad with conductive cleaning paste or alcohol to remove dead skin cells (high impedance)
LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED
 Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
The Anterolateral Abdominal Wall By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 1 P age The Anterolateral Abdominal Wall By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Introduction The abdomen is the region of the trunk located between the thorax and the pelvis. It includes the anterolateral
1 P age The Anterolateral Abdominal Wall By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Introduction The abdomen is the region of the trunk located between the thorax and the pelvis. It includes the anterolateral
