Nasal Orbital Ethmoid (NOE) Fractures November, 2014
|
|
|
- Nickolas Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
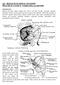
1 TITLE: Nasal Orbital Ethmoid (NOE) Fractures SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Department of Otolaryngology DATE: November 19, 2014 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Samuel Ross Patton, MD FACULTY MENTOR: Michael P. Underbrink, MD, MBA, FACS SERIES EDITOR: Francis B. Quinn, Jr., MD, FACS ARCHIVIST: Melinda Stoner Quinn, MSICS "This material was prepared by resident physicians in partial fulfillment of educational requirements established for the Postgraduate Training Program of the UTMB Department of Otolaryngology/Head and Neck Surgery and was not intended for clinical use in its present form. It was prepared for the purpose of stimulating group discussion in a conference setting. No warranties, either express or implied, are made with respect to its accuracy, completeness, or timeliness. The material does not necessarily reflect the current or past opinions of members of the UTMB faculty and should not be used for purposes of diagnosis or treatment without consulting appropriate literature sources and informed professional opinion." BACKGROUND: Nasal orbital ethmoid fractures (NOE) are widely considered the most difficult facial fracture to manage. Surgical repair is notoriously difficult and fraught with potential complications. As a result, published literature on the topic is quite limited. Treatment principles can be found in textbooks, but published studies in journals are rare. The literature is largely limited to a few case series reported by oral-maxillofacial surgeons. It is likely that the literature is limited because no surgeon wants to be known as an NOE expert. DEFINITION: In its most basic terms, an NOE fracture is a fracture of the facial skeleton in the area of the confluence of the orbits, nasal bones, maxilla, frontal bone, and anterior skull base. The key to defining whether or not a fracture qualifies as an NOE is what happens to the area where the medial canthal tendon attaches to the medial orbital wall (area surrounding the lacrimal fossa). If this area is fractured, the injury is labeled an NOE fracture. NORMAL ANATOMY OF NOE REGION: The normal bony anatomy in the NOE region is comprised by multiple bones. The frontal bone forms the roof of the orbit. The paired nasal bones inter-digitate with the frontal bone superiorly and to each other in the midline. The maxilla forms a large portion of the inferior orbital rim and much of the orbital floor. The nasal process of the maxilla fuses with the nasal bones laterally and the frontal bone superiorly. The lacrimal bone contributes to the medial orbital wall and corresponds to the key area in NOE fracture classification. 1
2 LACRIMAL FOSSA: The lacrimal fossa is demarcated by the anterior and posterior lacrimal crests. The lacrimal sac sits in the lacrimal fossa and collections tears in the medial canthal region. In the cadaver specimen, the opening of the lacrimal duct can be seen as it passes inferiorly toward the nasal cavity. ORBITAL ANATOMY- IMPORTANT DISTANCES TO KNOW: When performing orbital surgery, it is necessary to keep important surgical landmarks in mind. The distance between the anterior lacrimal crest and the anterior ethmoid artery is 24mm. If dissection is carried 12 mm posterior to this landmark, the posterior ethmoid artery is encountered. The optic nerve can be identified 6mm posterior to the posterior ethmoid artery. A commonly use pneumonic for these distances: a case (24 pack), a 12 pack, and a 6 pack. MEDIAL CANTHAL TENDON: The majority of this structure is made up of the tendinous portions of the orbicularis muscle. The tendons of the orbicularis coalesce and insert medially onto the medial orbital wall. Most of the attachment is anteriorly onto the anterior lacrimal crest/frontal process of the maxilla. A small portion of the tendon inserts on the posterior lacrimal crest. The tendon straddles the lacrimal sac and acts as a pump to send excess tears through the lacrimal duct inferiorly. CORONAL ANATOMY OF THE FACIAL SKELETON: Managing NOE fractures requires a working knowledge of the relationship of the ethmiod sinuses, the skull base, and the lamina papyracea. Skull base anatomy is variable. In some individuals, the cribiform plate hangs low, which can have surgical implications (discussed below). BUTTRESS SYSTEM: The mid-face has areas of strength and weakness. The areas of strength are called buttresses. They represent loadpaths for force during chewing and trauma. They resist traumatic impact. Between the buttresses are weaker areas that tend to crumple during blunt trauma. There are two vertical buttresses on either side of the face. NOE fractures involve the medial vertical nasal buttress (nasomaxillary buttress). The lateral vertical buttress is the termed the zygomaticomaxillary buttress. Horizontal buttresses connect the vertical buttresses and are equally important in facial architecture. NOMENCLATURE OF NOE FRACTURES: Multiple acronyms exist to describe fractures of the nasal orbital ethmoid region. Nomenclature over the past ten years is more consistent in referring to these injuries as NOE fractures. Older names include the following: NEC (naso-ethmoid complex fracture), nasoethmoid orbital, naso-orbito ethmoid. Many textbooks group NOE fractures with frontal sinus fractures as concomitant injuries are common. 2
3 MECHANISM OF INJURY: In the mid twentieth century, the most common cause of an NOE fracture was an MVC in which the patient s face struck the dashboard/steering wheel. While airbags have significantly decreased the incidence of this injury, MVC accidents remain the most common cause. Any high velocity blunt force trauma to the face can cause an NOE fracture. DEMOGRAPHICS: NOE fractures represent only 5% adult fractures and 16% of pediatric facial fractures. These fractures don t usually occur in isolation. Patients frequently have severe injuries to the facial skeleton, brain, and rest of the body in a polytrauma setting. There is a high rate of concomitant le fort fracture and frontal sinus fracture. 60% of NOE fractures are associated with an orbital or ZMC fracture. Soft tissue injuries are also common. Traumatic brain injury and CSF leaks are also possible comorbidities. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE FRACTURE: By definition an NOE fracture involves disruption of: the inferior orbital rim, lateral nasal bones, medial orbital wall, and the frontal process of the maxilla. A high velocity force is necessary to produce these fractures. The bones in the nasion/glabellar region are very strong. Once a force strong enough to break them proceeds posteriorly, the resistance is much less. A telescoping injury can occur as the underlying lacrimal/ethmoid bones are much more fragile. The fractured segments of bone (comprised of the nasal bones and the nasal process of the frontal bone) can be driven posteriorly. The thin-walled ethmoid sinus walls are fractured and the nasal bones can get lodged superiorly under the frontal bone. The lacrimal bone gets fractured and displaced laterally. The medial canthal tendon can be disrupted, resulting in telecanthus. The medial canthal tendon and globe get displaced laterally because of the traction of the orbicularis muscle. NOE FRACTURE CLASSIFICATION: Multiple classification systems exist for NOE fractures, but only the Markowitz Classification is routinely cited in the literature. This system is favored because it separates fractures based on surgical repair. Sorting fractures into categories based on the central bony fragment attached to the medial canthal tendon (MCT), the Markowitz Classification has 3 types. Type I fractures involve a single, non-comminuted bony fragment with the MCT still attached. In Type II fractures, there is comminution of the central bony fragment, but the MCT is still attached. Type III fractures involve severe central fragment comminution with disruption of the MCT attachment. WHAT MAKES NOE FRACTURES SO DIFFICULT TO MANAGE?: A high degree of suspicion is required to diagnose NOE fractures. The exam is difficult in the acute setting because of the severity of the facial injury and other associated injuries. Management of 3
4 NOE fractures is somewhat controversial as no universally accepted method of repair or surgical approach is described. Furthermore, the NOE region is a delicate area of the face. Both bone and soft tissue structures are injured that require reconstruction for good and aesthetic and functional outcomes. For the bony portion, the fractured segments are technically difficult to reduce and plate. The soft tissue deformity is also challenging to restore to the proper, natural contour. NOE fractures are sustained in the setting of major trauma with high velocity forces. Making a diagnosis is based on physical exam alone is challenging due to the facial edema. The examiner must rely on a combination of exam and imaging. PHYSICAL EXAM: NOE fractures display a number of characteristic physical exam findings. Notably, these patients have telecanthus. Disruption of medial canthal tendon results in this traumatic telecanthus. Normal inter-canthal distance is roughly half the inter-pupillary distance. One should suspect an NOE fracture if the inter-canthal distance is 35mm. An inter-canthal distance greater than 40mm is diagnostic of an NOE fracture. The bowstring sign is a described physical exam maneuver to diagnose medial canthal disruption. The examiner places an instrument in the nose and palpates the medial canthal region. Lateral traction is placed on the the lateral canthus. Normally there is palpable resistance. In NOE fractures, the examiner s finger might sink into the orbit. A flat nasal bridge (loss of nasal dorsal height) may also be found in NOE fractures. Injury to the nasal bones and nasal septum results in a loss of nasal support. This gives rise to the characteristic pigsnout deformity seen in some NOE fractures. By definition NOE fractures result in a disruption of the orbital wall. It is necessary to examine the eye for visual acuity and entrapment. Ophthalmology consultation is required to rule out corneal laceration, injury to the globe, dislocated lens, and detached retina. IMAGING: CT scans provide the best detail of bony anatomy in the setting of suspected NOE fracture. In the axial view it is often possible to identify the status of the central bony fragment. A normal lacrimal fossa can be seen as an indentation in the anterior aspect of the medial orbital wall. Alternatively, one can trace the lacrimal duct after it is identified inferiorly up to the lacrimal fossa to more easily identify the area. This may not be possible in type III injuries as the entire area may be blown out. MANAGEMENT-ACUTE STABILIZATION: Epistaxis is very common in all forms of nasal trauma. Severity may range from minor or extreme. Nasal packing is frequently required. The planum sphenoidale refers to an area of the floor of the anterior cranial fossa which lies between the sella turcica and the cribiform plate. It is comprised largely of the lesser wing of the sphenoid (which forms the roofs of the optic foramina). In very severe facial trauma, the optic nerves can be damaged by a fracture of this area. The fracture may extend through the superior orbital fissure and damage structures that run through the fissure: (CN III/IV/V1/VI, ophthalmic vein, sympathetic fibers). 4
5 MANAGEMENT-LACRIMAL SYSTEM: 50% of NOE fractures will present with epiphora at the time of injury. Obstruction of the lacrimal system can be secondary to injury to the duct, obstruction of duct by bone fragments, and swelling. Only 5-10% will have persistent swelling TIMING OF OPERATION: Optimally, surgery takes place immediately after the swelling has subsided. This is general days after the injury. With Type III fractures, locating the medial canthal ligament is difficult in the delayed setting. Timing of the operation is also influenced by the patient s overall general condition. Frequently, the operation is delayed by management of intra-cranial injury. PICKING A SURGICAL APPROACH: Multiple options exist for surgical approaches to repair NOE fractures. Three approaches predominate the literature (open sky, midface degloving, and coronal approach). Each surgeon must pick the approach he is most comfortable performing safely that affords the exposure needed. NOE fractures rarely occur in isolation and the surgeon may need to address multiple fractures by performing multiple approaches. OPEN SKY/EXISTING LACERATION: The open sky approach is essentially bilateral lynch incisions connected with a transverse incision just below the glabella. This provides excellent exposure of the NOE region. Downsides include significant scarring. This approach is generally avoided unless a pre-existing laceration provides direct access. MID-FACE DE-GLOVING: The main benefit of a mid-face de-gloving is avoiding skin incisions. In addition, addressing other associated mid-face fractures (e.g.: Le Forte, ZMC) can be accomplished easily. Drawbacks include difficulty exposing the medial canthal region. BI-CORONAL FLAP/APPROACH: The coronal flap is the most popular approach described in the literature. This approach provides access to frontal sinus area as well as the medial canthal regions. Harvesting parietal bone for grafting is also possible in the coronal approach. Additional approaches to repair the orbital floor and frontal process of the maxilla are required (eg. trans-conjunctival or sub-cilliary). In addition, it is difficult to gain access to associated mid-face fractures. 5
6 BI-CORONAL TECHNIQUE: A skin incision is traditionally made from helix to helix across the scalp. Dissection is carried down to the periostium and the flap is elevated between the frontalis muscle/galea and the periostium of the frontal bone. The periostium can be incised and lifted with the flap, or it can be incised over the forehead region when dissection transitions to sub-perioistial.. The supra-orbital neuro-vascular bundles are identified in the area of the medial superior orbital rim. In some cases, ligation is necessary to gain exposure. Dissection on the medial orbital wall must proceed with caution to avoid inadvertently avulsing the medial canthal tendon insertion. This results in turning a type I fracture into a type III fracture. Ligation of the anterior ethmoid artery may be necessary for exposure as well when retracting the globe. SURGICAL REPAIR- GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS: Repair of NOE fractures is very difficult and the type of repair is dictated by fracture classification. Almost all NOE fractures require surgical repair. Select type I injuries with non-mobile medial canthal regions are candidates for observation. Goals of surgery include restoring the face to pre injury function/appearance, reconstructing the medial orbital wall (if necessary), resetting the nasal dorsum (if necessary), and re-attaching the medial canthal tendons (if necessary). Over- correction of telecanthus is preferred as the canthi will tend to drift apart in the post-operative period. The patient may have multiple facial fractures that require repair. It is preferable to fix other fractures first and then repair the NOE fracture. This maximizes facial landmarks used for reconstruction. TYPE I SURGICAL REPAIR: Type I fractures involve a large central bony fragment in the NOE region with the MCT attached. After adequate exposure, microplates are used to secure the frontal process of maxilla to central bone fragment. The frontal bone is also plated to the central bone fragment. TYPE II SURGICAL REPAIR: Type II fractures require more extensive techniques. Because the central bony fragment is comminuted, these fractures require microplating and transnasal wiring (trans-nasal canthopexy). More extensive exposure is required, including retraction of the orbit. It is preferable to perform trans-nasal wiring first and then plate the fracture second. Trans-nasal wiring involves passing a 26 gauge wire from lateral to medial through the central fragment. Holes are drilled in the bony fragment posterior to the to the lacrimal fossa before passing the wire. The wire is passed through the ethmoids/septum and secured to the contralateral orbital wall. The wire may be secured either to a plate/screw on the contralateral side or to the trans-nasal wire from the contralateral side if the fracture is bilateral. When drilling holes in the medial orbital wall it is necessary to drill posterior to the lacrimal fossa. This avoids an unfavorable vector which would result in telecanthus. One must avoid the pitfall of drilling above the fronto-ethmoid suture line on the medial orbital wall to avoid hitting the cribiform plate. 6
7 TYPE III FRACTURE REPAIR: Type III NOE fractures the most challenging and are also the least common (1-5% of all NOE fractures). Repair is similar to type II fractures in that the exposure required is extensive. Type III fractures also require trans-nasal wiring and plating. In addition, severe comminution may require reconstruction of the medial orbital wall in the area of the lacrimal fossa. This can be achieved with bone grafting or placing a titanium mesh plate. Reconstruction of the medial orbital wall is needed if 2 drill holes 4mm apart vertically cannot be placed with sufficient surrounding bone for microplating. If the avulsed medial canthal tendon can be identified, it can be re-attached to the bone graft/titanium plate used in orbital wall reconstruction. A modified kessler stitch may be used to secure the tendon to bone fragment. Reconstructing the nasal dorsum can be accomplished, if needed, with calvarial bone grafts. A cantilevered bone graft can be plated or screwed to the radix. DERMAL CONTOURING- TYPE II/III FRACTURES Type II/III injuries require wide exposure around the medial canthal tendon region. The subperiostial dissection often results in hematoma/chronic edema which may lead to scarring. Scaring in the NOE region can cause excessive tension on the medial canthal tendon resulting a loss of adherence of the soft tissue to the underlying bone. This phenomenon, known as pseudo-telecanthus, gives the appearance of a widened nasal bridge despite proper reduction of the bony skeleton. Pseudotelecanthus can be mitigated by placing soft tissue bolsters. Several authors describe using 2mm thick lead plates lined with ortho felt. These bolsters are secured with 28 gauge wire passed through the nasal bones to help in soft tissue compression for the first week after surgery. REFERENCES AO Foundation. Nasal/NOE. Kellman RM. Maxillofacial Trauma. Cummings Otolaryngology 5 th Edition. Ch 23 Bailey BJ. Nasal Fractures. Head & Neck Surgery- Otolaryngology 4 th Edition. Ch 71 Papel ID. Frontal Sinus and Nasoorbitoethmoid Complex Fractures. Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2 nd edition. Donald PJ. Frontal sinus and nasofrontoethmoidal complex fractures. SIPAC Shibuya TY. Chen VY. Oh YS. Naso-orbito-ethmoid fracture management. Operative Techniques in Otolaryngology. 2008;19: Naso-orbital ethmoid fractures. Medscape Reference. 2/1/
8 Nguyen M. Koshy JC. Hollier LH. Pearls of Nasoorbitoethmoid trauma Management. Seminars in Plastic Surgery. 24:4:2010. Papadopoulos H. Salib NK. Management of Naso-Orbital-Ethmoidal Fractures. Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 21(2009)
Technique Guide. Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Prodecures.
 Technique Guide Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Prodecures. Indications/Features Indications The Synthes Titanium Wire with Barb and straight Needle is
Technique Guide Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Prodecures. Indications/Features Indications The Synthes Titanium Wire with Barb and straight Needle is
Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Procedures.
 Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Procedures. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Titanium Wire with Barb and Needle. Surgical Technique Guide for Canthal Tendon Procedures. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Titanium Wire With Barb and Needle
 For Canthal Tendon Procedures Titanium Wire With Barb and Needle Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Wire With Barb and Needle 2 Indications 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning
For Canthal Tendon Procedures Titanium Wire With Barb and Needle Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Titanium Wire With Barb and Needle 2 Indications 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning
Epidemiology 3002). Epidemiology and Pathophysiology
 Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
Epidemiology Maxillofacial trauma or injuries are commonly encountered in the practice of emergency medicine and are presenting one of the most challenging problems to the attending surgeons or physicians
CT of Maxillofacial Injuries
 CT of Maxillofacial Injuries Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology changes the diagnosis Technologic Evolution
CT of Maxillofacial Injuries Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology changes the diagnosis Technologic Evolution
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery FACIAL FRACTURES
 Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
Core Curriculum Syllabus Emergencies in Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery A. General Considerations FACIAL FRACTURES Look for other fractures like skull and/or cervical spine fractures Test function
CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns. CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns
 CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology
CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns CT of Maxillofacial Fracture Patterns Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Viking 1 1976 MGS 2001 Technology
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury
 Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Imaging Orbit/Periorbital Injury 9 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2016 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology University of Maryland School of Medicine Fireworks Topics to Cover Struts
Maxillofacial Injuries Practical Tips
 Saturday, October 29, 2016 Maxillofacial Injuries Practical Tips Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC THE ROOTS OF PENN RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL Assistant Professor of Radiology Assistant Professor of Neurosurgery Neuroradiology
Saturday, October 29, 2016 Maxillofacial Injuries Practical Tips Suyash Mohan MD, PDCC THE ROOTS OF PENN RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL Assistant Professor of Radiology Assistant Professor of Neurosurgery Neuroradiology
MAXILLOFACIAL TRAUMA. The on-call maxillofacial surgeons can be contacted through the switchboard at the Southern General Hospital
 MAXILLOFACIAL TRAUMA The on-call maxillofacial surgeons can be contacted through the switchboard at the Southern General Hospital Mandibular Injuries Mechanism of injury Assault, falls, RTA-Direct trauma
MAXILLOFACIAL TRAUMA The on-call maxillofacial surgeons can be contacted through the switchboard at the Southern General Hospital Mandibular Injuries Mechanism of injury Assault, falls, RTA-Direct trauma
Thickened and thinner parts of the skull = important base for understanding of the functional structure of the skull - the transmission of masticatory
 Functional structure of the skull and Fractures of the skull Thickened and thinner parts of the skull = important base for understanding of the functional structure of the skull - the transmission of masticatory
Functional structure of the skull and Fractures of the skull Thickened and thinner parts of the skull = important base for understanding of the functional structure of the skull - the transmission of masticatory
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 + Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
+ Evaluation and Management of Facial Trauma D Antoni Dennis, MD North Oaks ENT an Allergy November 3, 2017 + Financial Disclosure I do not have any conflicts of interest or financial interest to disclose
Diagnosis of Midface Fractures with CT: What the Surgeon Needs to Know 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. EDUCATION EXHIBIT
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. EDUCATION EXHIBIT
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
FRONTAL SINUS FRACTURES February 1995
 TITLE: FRONTAL SINUS FRACTURES SOURCE: Dept. of Otolaryngology, UTMB, Grand Rounds DATE: February 22, 1995 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Kelly D. Sweeney, M.D. FACULTY: Brian P. Driscoll, M.D. SERIES EDITOR: Francis
TITLE: FRONTAL SINUS FRACTURES SOURCE: Dept. of Otolaryngology, UTMB, Grand Rounds DATE: February 22, 1995 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Kelly D. Sweeney, M.D. FACULTY: Brian P. Driscoll, M.D. SERIES EDITOR: Francis
Facial Trauma ASHNR. Disclosures: Acknowledgments: None. Edward P. Quigley, III, MD PhD University of Utah
 Disclosures: Facial Trauma ASHNR Edward P. Quigley, III, MD PhD University of Utah None Acknowledgments: Dr. Rebecca Cornelius Dr. Ilona M. Schmalfuss Dr. Richard Wiggins III Dr. Yoshimi Anzai Dr. Lindell
Disclosures: Facial Trauma ASHNR Edward P. Quigley, III, MD PhD University of Utah None Acknowledgments: Dr. Rebecca Cornelius Dr. Ilona M. Schmalfuss Dr. Richard Wiggins III Dr. Yoshimi Anzai Dr. Lindell
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy of. External NOSE. By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC
 Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Anatomy of External NOSE By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 24 th Nov. 2017 The External Nose Descriptions of the nose always begin with that part of it which is covered by the skin, i.e., the EXPOSED PART
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #1 Facial Trauma The face is vital to human appearance and function. Facial injuries can impair a patient
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Dr. Esam Ahmad Z. Omar BDS, MSc-OMFS, FFDRCSI. Monitor the vital signs. Monitor the vital signs. Complications of Facial Traumas.
 Complications of Facial Traumas 1) Immediate Complications 2) Late Complications Dr. Esam Ahmad Z. Omar BDS, MSc-OMFS, FFDRCSI Assistant Professor Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Taibah University Monitor
Complications of Facial Traumas 1) Immediate Complications 2) Late Complications Dr. Esam Ahmad Z. Omar BDS, MSc-OMFS, FFDRCSI Assistant Professor Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Taibah University Monitor
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Intranasal location of lacrimal sac in Thai cadavers
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries
 Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to: Identify the key anatomical structures of the face and eye and the impact of force on
Maxillofacial and Ocular Injuries Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to: Identify the key anatomical structures of the face and eye and the impact of force on
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient. Barts and The London NHS Trust
 Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons and the seriously injured patient Barts and The London NHS Trust How do you assess this? Primary Survey A B C D E Airway & Cervical Spine Breathing & Ventilation Circulation
Fracture frontal bone and its management
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan March 1, 2013 Fracture frontal bone and its management Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/14/ ISSN: 2250-0359
Maxillary and Periorbital Fractures January 2004
 TITLE: Maxillary and Periorbital Fractures SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: January 7, 2004 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Gordon Shields, MD FACULTY ADVISOR: Francis B. Quinn,
TITLE: Maxillary and Periorbital Fractures SOURCE: Grand Rounds Presentation, UTMB, Dept. of Otolaryngology DATE: January 7, 2004 RESIDENT PHYSICIAN: Gordon Shields, MD FACULTY ADVISOR: Francis B. Quinn,
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Nasal region. cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?
 Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
Nasal region skull bones: nasal and frontal processes of maxilla cartilages: septal cartilage (l); lateral nasal cartilage (2); greater alar cartilages (2); lesser alar cartilages (?) 1 Nasal cavity Roof
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Transnasal Endoscopic Sinonasal Surgery
 Reda kamel, Cadaveric dissection 1 Transnasal Endoscopic Sinonasal Surgery Cadaver Dissection Guide For Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Cairo University Egypt Reda Kamel Professor of Rhinology Cairo University
Reda kamel, Cadaveric dissection 1 Transnasal Endoscopic Sinonasal Surgery Cadaver Dissection Guide For Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Cairo University Egypt Reda Kamel Professor of Rhinology Cairo University
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Anatomy Made Easy MSS
 Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
By JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, M.D., and DAUBERT TELSEY, D.D.S.
 THE TRIPARTITE OSTEOTOMY OF THE MID-FACE FOR ORBITAL EXPANSION AND CORRECTION OF THE DEFORMITY IN CRANIOSTENOSIS By JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, M.D., and DAUBERT TELSEY, D.D.S. Center for Craniofacial Anomalies
THE TRIPARTITE OSTEOTOMY OF THE MID-FACE FOR ORBITAL EXPANSION AND CORRECTION OF THE DEFORMITY IN CRANIOSTENOSIS By JOHN MARQUIS CONVERSE, M.D., and DAUBERT TELSEY, D.D.S. Center for Craniofacial Anomalies
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Chapter(2):the lid page (1) THE LID
 Chapter(2):the lid page (1) THE LID Anatomy of the lid: * Check movie anatomy of the lid model The eyelids are two movable muco-cutaneous folds which protect the eye on closure. The are joined temporary
Chapter(2):the lid page (1) THE LID Anatomy of the lid: * Check movie anatomy of the lid model The eyelids are two movable muco-cutaneous folds which protect the eye on closure. The are joined temporary
Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience
 80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
80 Original Article THIEME Management Strategies for Communited Fractures of Frontal Skull Base: An Institutional Experience V. Velho 1 Hrushikesh U. Kharosekar 1 Jasmeet S. Thukral 1 Shonali Valsangkar
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line.
 Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line. After reading the article, the staff will be able to: Define facial trauma
Lesson Plans and Objectives: Review material for article Prep work for article Picture recovery Review for placement on-line. After reading the article, the staff will be able to: Define facial trauma
Facial Trauma. Facial Trauma. Facial Trauma
 Facial Trauma Facial Trauma Brian Bast DMD, MD Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University of California, San Francisco School of Dentistry Brian Bast DMD, MD Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
Facial Trauma Facial Trauma Brian Bast DMD, MD Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University of California, San Francisco School of Dentistry Brian Bast DMD, MD Department of Oral and Maxillofacial
Facial skeletal fractures are common,
 CE This symbol indicates that there is more content in the online version of this article. Computed Tomography of Facial Fractures Bryant Furlow, BA Facial skeletal fractures are common, potentially serious,
CE This symbol indicates that there is more content in the online version of this article. Computed Tomography of Facial Fractures Bryant Furlow, BA Facial skeletal fractures are common, potentially serious,
PROBLEM RECOMMENDATION
 PREVENTION (MINIMIZING) IN ENDOSCOPIC Steven D. Schaefer, MD Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology PREVENTION AND Intraoperative Hemorrhage Loss of Orientation Inability to Identify/Preserve
PREVENTION (MINIMIZING) IN ENDOSCOPIC Steven D. Schaefer, MD Professor and Chair Department of Otolaryngology PREVENTION AND Intraoperative Hemorrhage Loss of Orientation Inability to Identify/Preserve
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
1 Eyelids. Lacrimal Apparatus. Orbital Region. 3 The Orbit. The Eye
 1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
The cribriform plate. ethmoid bone. Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths.
 ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
ethmoid bone Ethmoid bone consists from: 1) A horizontal cribriform plate. 2) A perpendicular plate. 3) Two lateral labyrinths. The cribriform plate 1) Connect the two labyrinths to the perpendicular plate.
Management of Craniofacial injuries
 Management of Craniofacial injuries Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Cirujanos PlástiKos Mundi Cranio-Facial Trauma 1. Introduction Cranio-facial trauma is as old as the human race. What has changed
Management of Craniofacial injuries Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Cirujanos PlástiKos Mundi Cranio-Facial Trauma 1. Introduction Cranio-facial trauma is as old as the human race. What has changed
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
Neurosurgical Techniques
 Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
NASAL FRACTURES. Andrew H. Murr, MD FACS Professor Chief of Service Department of Otolaryngology/ Head and Neck Surgery San Francisco General Hospital
 NASAL FRACTURES Andrew H. Murr, MD FACS Professor Chief of Service Department of Otolaryngology/ Head and Neck Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Roger Boles, M.D. Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education
NASAL FRACTURES Andrew H. Murr, MD FACS Professor Chief of Service Department of Otolaryngology/ Head and Neck Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Roger Boles, M.D. Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE
 REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
Facial Trauma. Rural Emergency Services and Trauma Symposium 2008
 Rural Emergency Services and Trauma Symposium 2008 Facial Trauma Mitchell Stotland, MD Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Children s Hospital of Dartmouth
Rural Emergency Services and Trauma Symposium 2008 Facial Trauma Mitchell Stotland, MD Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Children s Hospital of Dartmouth
Clues of a Ruptured Globe
 Definition any eye that has sustained a full thickness traumatic disruption of the cornea or sclera Overwhelmingly, rupture accidents occur in young men, small children and the elderly Corneal laceration
Definition any eye that has sustained a full thickness traumatic disruption of the cornea or sclera Overwhelmingly, rupture accidents occur in young men, small children and the elderly Corneal laceration
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
The diagnostic value of Computed Tomography in evaluation of maxillofacial Trauma
 The diagnostic value of Computed Tomography in evaluation of maxillofacial Trauma Qais H. Muassa FICMS College of Dentistry, Babylon University Ibrahim S. Gataa, BDS, FICMS College of Dentistry, Sulaimania
The diagnostic value of Computed Tomography in evaluation of maxillofacial Trauma Qais H. Muassa FICMS College of Dentistry, Babylon University Ibrahim S. Gataa, BDS, FICMS College of Dentistry, Sulaimania
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
TOTAL MAXILLECTOMY, ORBITAL EXENTERATION
 TOTAL MAXILLECTOMY, ORBITAL EXENTERATION CC-BY-NC 3.0 Johan Fagan Total maxillectomy refers to surgical resection of the entire maxilla. Resection includes the floor and medial wall of the orbit and the
TOTAL MAXILLECTOMY, ORBITAL EXENTERATION CC-BY-NC 3.0 Johan Fagan Total maxillectomy refers to surgical resection of the entire maxilla. Resection includes the floor and medial wall of the orbit and the
Midface fractures; what the radiologist should know.
 Midface fractures; what the radiologist should know. Poster No.: C-1056 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Garcia Villanego, E.-M. Heursen, A. Rodriguez Piñero; Cadiz/ES Keywords:
Midface fractures; what the radiologist should know. Poster No.: C-1056 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Garcia Villanego, E.-M. Heursen, A. Rodriguez Piñero; Cadiz/ES Keywords:
Learn Connect Succeed. JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017
 Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017 Financial Disclosure Evaluation and Treatment of Orbital Cellulitis Thomas E. Johnson, M.D. Bascom Palmer Eye Institute University of Miami School of
Learn Connect Succeed JCAHPO Regional Meetings 2017 Financial Disclosure Evaluation and Treatment of Orbital Cellulitis Thomas E. Johnson, M.D. Bascom Palmer Eye Institute University of Miami School of
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball
 Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Computed-Tomography of maxillofacial fractures: What do surgeons want to know?
 Computed-Tomography of maxillofacial fractures: What do surgeons want to know? Poster No.: C-0968 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Ammar, M. Jrad, I. KASRAOUI, A. Zoubli, H. Mizouni
Computed-Tomography of maxillofacial fractures: What do surgeons want to know? Poster No.: C-0968 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Ammar, M. Jrad, I. KASRAOUI, A. Zoubli, H. Mizouni
Case Report Mid Facial Degloving Procedure: Managing A Case of Multiple Mid Face Fractures with Significant External Deformity
 55 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(1): 51-56 Case Report Mid Facial Degloving Procedure: Managing A Case of Multiple Mid Face Fractures with Significant External Deformity Akhil Chndra Biswas 1,
55 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(1): 51-56 Case Report Mid Facial Degloving Procedure: Managing A Case of Multiple Mid Face Fractures with Significant External Deformity Akhil Chndra Biswas 1,
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Case Presentation: Indications for orbital decompression in TED: Modern surgical techniques for orbital decompression in TED: Inferomedial
 Case Presentation: Jonathan W. Kim, MD Director, Oculoplastic Surgery Stanford Medical Center 61 year old man with active Graves orbitopathy Visual acuity 20/30 OD 20/50 OS Left RAPD Bilateral optic disc
Case Presentation: Jonathan W. Kim, MD Director, Oculoplastic Surgery Stanford Medical Center 61 year old man with active Graves orbitopathy Visual acuity 20/30 OD 20/50 OS Left RAPD Bilateral optic disc
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
SINUS ANATOMY AND FUNCTION
 EMBRYOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT SINUS ANATOMY AND FUNCTION -4 th week gestation: -frontonasal process identified, arises over developing forebrain -ectodermal -contributes to nasal capsule -9 th and 10 th week
EMBRYOLOGY AND DEVELOPMENT SINUS ANATOMY AND FUNCTION -4 th week gestation: -frontonasal process identified, arises over developing forebrain -ectodermal -contributes to nasal capsule -9 th and 10 th week
Pediatric Craniofacial Injuries: Concept of Treatment
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, March: 217-224, 201 5 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Pediatric Craniofacial Injuries: Concept of Treatment FAWZY T. AL-SAYED, Ph.D.* and MOHAMAD A. SHOEIB,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, March: 217-224, 201 5 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Pediatric Craniofacial Injuries: Concept of Treatment FAWZY T. AL-SAYED, Ph.D.* and MOHAMAD A. SHOEIB,
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
