ISSN: TO ELABORATE CONCEPT OF SEVANI WITH THE HELP OF MODERN ANATOMY
|
|
|
- Ralph Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: TO ELABORATE CONCEPT OF SEVANI WITH THE HELP OF MODERN ANATOMY 1 Budruk Pramod Appasaheb 1 M.D. Sharir Rachna, L.L.B.(spl) Principal- Hon.Shri. Annasaheb Dange Ayurved Medical College, Ashta. Tal- Walwa, Dist- Sangli. ABSTRACT : Ayurveda gives new idea about human being in case of Anatomy, Physiology & other subjects also. Ayurvedokth Rachana Sharir describes about various terminology. In fifth chapter of Sharirsthan Susrut described various parts of the body. Not only various parts of the body, but also number of these parts or organs, is nicely given in this Sharir sankhya vyakarana sharir Adhayaya. Anga, Pratyanga, Twacha, Kala, Sira, Snayu, Dhamani are described with it s numbers & distribution of them. Sivani is the one of structure present in the body. There are Sapta-Sevani present in the body. Structure of Sevani & also importance of it is given by Ayurveda. Though Sevani is mentioned in one sloka, Its importance is given by comparative study with modern Science. Division of the skull is done by these sevani, as given in modern science. Sevani word gives two references. First is a sapt Sevani available for the sevani & second in case of sandhi sharir. There is confusion regarding various terms as sevani or Tunnasevani,Sutures. With the help of this article I am trying to clarify these concepts with the help of modern science. Key words: Sevani, Septasevani, Sivani, Tunnasevani,Sutures. INTRODUCTION:We know that structural & functional unit of the body is cell. These cells came together to form tissue. These tissue come together which have same work is called as organ. The chain of organs having same functions forms a system. The various systems come together to form body. Thus body is constituted by various types of cells. In Ayurveda the body is made of various physiological components like body, mind, soul. Susrutachya has nicely described about body. He mentioned various body structures available in the body as given in modern science, these structures we can easily correlate with the structures of modern anatomy. But there are some structures which we can t match with modern anatomy. Sometime these terms are used as per necessity. As these terms came from Ayurveda, the aim of using these terms also mentioned in it, that is meaning should know everyone. To elaborate meaning of the Ayuvedic terminology is necessary for standardization of the subject and to clear concepts of these terms to the students, who are studying Ayurveda. Sapta Sevanya Sirasi Vibhakta Pancha, Jivya shefachasorekeka; ta Parihartavya Shasatrena II. According to Charak, Vaidya who knows all the Sankhya of the body or numberlogy. He can treat all patient without fear & properly. Susrut has explained this numerological anatomy broader than charak. In Sankhya Sharir Adhyaya he given description from shadang sharir to Aparisankheya (numberous) of Parmanu present in the body.
2 Sevani is one of structure which present in head region or shirbhag & also below the tounge & space between bases of penis to anal canal. There are seven sevani, out of 5 are present in the skull called sutures.remaining one is present in the base of tongue called frenulum of tongue, and other is present on scrotal region called raphe of the scrotum. In sanskruit-hindi kosha meaning of the Sevani is structure or line of demarcation or it called as Sandhirekha. It is the part which joints two parts of the body. It looks like sutures taken by needle. Such type of structure is present on the skull. It divides the skull in various regions. Susrut told that these sevani are five in numbers. Also he told that these sevani or sutures should be protected, at the time of surgery. Injury to these structures will be fetal, hence he told that, Ta Pariharatavya Shasataren ll According to V.S. Apate s Sanskrut Shadakosha book meaning of the Pariharatavya is the part which should keep away or to preserve the part from injury by trauma or at the time of surgery. 3 Shata Sirasiti ll 4. According to Susrut six bones are present in the head.these bones separate in intrauterine life & the movement of these bones is helpful at the time of delivery. Afterward these bones attach with each other keeping mark on it & these are called as sevani. Actually there are four bones in adult but in early age there are six bones. Hence susrut has decribed as six bones are present in the skull. There are frontal or purakapalasthi, parietal or Pashvakapalasthi, Paschakapalasthi orocciptal & Sankhasthi or temporal bone. Sevani word is also mentioned at the time of description of the sandhi, Type of sandhi is given as Tunna Sevani, Ta Atha Sandhayoshthavidha Kor halasamudaga Pratara Tunnasevani vayasatunda Mandal Shankhavarta.ll 5 Ayurveda divides all joints of the body in above eight types.these types of joint are given as kor, Udukhal, samudga, Pratara, Tunnasevani, vayastunda, mandal & Shankhavarta. Tunna Sevani is a suture type of joint. Tunnasevani is a sevani type joint which is present in the skull. It divides skull into various parts. There are five joints present in it. Shirakati Kapaleshu Tunnasevanya.ll 6 Mainly the Tunnasevani type of joint is present in case of skull bone. The bones which are flat means scapula and hip bone has or in case of skull or skull cap. In case of skull or skull cap stitch like joints are available. Especially the Joint when two flat bones meet together having serrate edges is called as Tunnasevani Joint. Chinnanalpasevanam Tunnasevani Tunnasevanyo nam paraspar Pedicinedanturdharabhi Nirmita Kanatarala Sandhayall 7 The edges of the Joining edges are denticulate appearance. These denticulate process meet each other to form uniform Joint such type of joint is named as Tunnasevani. This is sthir joint or immovable joint. Tunna means tailor or stich like mark of wound. A structure which appears like stitches of tailor or mark on the IJAAR VOLUME II ISSUE 7 MAY-JUNE 2016
3 clothes or mark remains after wound. This mark we can see on the skull not on the skin. Simanta sevanicha bahitwacha sirashi na drushate.ll 8 Sevanya are not seen on the surface of the body or exterior of the head. It present below the skin. It is present only on the bone or exterior of skull. MATERIALS AND METHODS: In the dissection hall of ADAMC Ashta skull and dead body used for observed and for dissection purpose. Instruments like scalp and blade, tooth forceps and plain forceps is used for dissection of scalp and to see sevani of the skull, as well as frenulum of tongue and rape of the scrotum is observed. Firstly various references regarding sevani are collected, also references regarding skull sutures and importance of sutures are collected. After observation and discussion regarding sevani future conclusion is drawn. DISCUSSION:Skull has 22 bones, it is divided into calvaria which surrounds cranial cavity containing brain and lower anterior part is facial skeleton. The bones forming calvaria are paired temporal bones & parietal bones unpaired frontal & occipital bones and small bones like sphenoid & ethmoid bones. 9 Suture is process of joining two surfaces or edges & afterword line or stitch so formed. Anatomically it is line of junction or an immovable joint between two bones especially of the skull. The frontal bone, parietal bone, occipital bone are seen in a superior view of the skull. These bones make up the superior part of the calvaria or the calva (skull cap) 10 Following sutures are found in the skull. 1-Coronal suture- the unpaired frontal bone articulates with the parietal bones at the coronal suture 11. This sutures divides skull into anterior and posterior parts. The lateral portion of the calvaria begins anteriorly with the frontal bone. In upper regions the frontal bone articulate with parietal bones by coronal suture. 2-Sagital suture- the two parietal bones articulate with each other in the midline at the sagittal suture. This sutures divides skull into right and left halves. This suture generally present in the midline of the body. 3-Lambdoid suture- the parietal bones articulate with unpaired occipital bone at the lambdoid suture. This suture present on posterior view of the skull Squamous suture-this suture starts from pterion point. It is present in between temporal and parietal bones and ends at the point asterion. Temporal bone is a major contributor to lower portion of lateral wall of the cranium 13 Frontal bone articulates with greater wing of sphenoid bone and also with parietal bone at the sphenoparietal suture. At the end of temporal bone articulate with sphenosquamous suture. Temporal bone articulates with sphnoid bone at sphenosquamous suture & with parital bone superiorly at the squamous suture & mastoid bone attached with occipital bone by ooccipitomastoid suture.parietal bone attaches with mastoid bone parietomastoid suture. Thus sphenosquamous suture, squamaus suture, parietomastoid suture and occipitomastoid suture forms along suture 14 This suture forms one of the sivani of skull.next part of sevani is present below tongue. The under surface of oral part of IJAAR VOLUME II ISSUE 7 MAY-JUNE 2016
4 tongue lacks papillae, but has number of linear mucosal folds. A single median fold called frenulum of tongue is continuous with mucosa covering the floor of oral cavity overlies midline sagittal septum. On the each side of frenulum there is lingual vein and lateral to vein fimbriated fold is present. 15 The remnant of the line of fusion between labioscrotal swelling in the embryo visible on the skin of scrotum as longitudinal midline raphe that extends from anus, around the scrotal sac & on the inferior aspect of the body of the penis called raphe of penis. The base of the raphe is continuants with frenulum of the glans to more loosely attached skin proximal to the glans. 16 In case of female the labia minora each bifurcate forming a medial & lateral fold, the medial folds unites to form a frenulum of clitoris & that joins the glans clitoris. Also labia minora unite forming a small transverse fold, to the frenulum of the labia minora, it is also called as fourchette. 17 Skull is most important part of the body. Brain is vital part of the body and it is placed in the skull. It is well protected by various covering as well as skull. Skull is the bony part which protects the brain from various impacts or shocks.when we observe skull, there are various types of sutures are present on it. It has 5 surfaces and upper part of the skull is called Norma Superioris. This part has the sutures on it. These sutures or marks are denticulate, serrate or squamous type. When there are saw like edges of meeting surfaces then it is called as serrate joint. When there is one surface overlaps another surface at the time of joint then it is called as sutura squamosa. When plain edges meet together then it is called as plain sutures. Sevanya are not seen on the surface of the body or extension of the head. Hence it is present only on the bone or skull. According to paribhasha koasha sevani means mark remains after wound. Hence Tunnasevani is mark on the skull, or mark like sutures or stitch marks like structure. This mark we can see on the skull. Susruta told that Sevani is also called as sivani. Sometime it is called as simant. We can observe the sivani s on the skull. There are coronal suture, sagittal suture, lambdoid & squamous suture present on the skull. Comparative structures against is given in following table. Second meaning of the sevani is said to be folds of skin or mucus folds. This has been seen in case of tongue.the fold present in the midline of tongue then it is called frenulum of the tongue. This is very important structure because in case of any injury to this structure can hamper work tongue and this also creates difficulty in the pronunciation or speaking. If there is congenital shorting of frenulum then there may be sometime protrusion of the tongue. Hence Susruta has suggested preserving this structure. Also in case of the raphe of scrotum of male or frenulum of the clitoris and frenulum of the labia minora are structure resembles to structure mentioned in the sevani. These structures also clinical importance as well surgical important. Second importance of the skull is that if there are no sutures, at the time of birth it will create problem in the birth of child. The bones of skull are flexible and overlaps each IJAAR VOLUME II ISSUE 7 MAY-JUNE 2016
5 other for easy delivery. If certain bones of skull grow fast, then also create deformity in the skull,due to this symmetry of skull will not maintained. Also frenulum of the tongue connects gums to lips. Sublingual papilla & lingual veins are present near this structure. Injury to this structure create bleeding & Injury to salivary glands. Hence this structure also preserved from injury at the time of surgery. Figure 18 Table Sevani Structures Structures present on sevani Important points Sevani-1 Sagittal suture In between two parietal bones. 1 From Bregma to Lambda point Sevani-2 Coronal suture In between frontal & parietal From right pterion to 1 bone. left pterion Sevani-3 Lambdoid In between parietal & occipital From right Asterion 1 suture bone. to left Asterion point Sevani-4 and5, Sevani-6 Sevani-7 Squamous suture frenulum tongue raphe scrotum male frenulum clitoris female of of in of in In between frontal long temp - parietal & occipital bone. floor of oral cavity. 1 anus, around the scrotal sac. 1 frenulum of the labia minora. 1 2 From Pterion &Asterion point sagittal septum and fimbriated fold frenulum of the glans penis and scrotum Frenulum of glans clitoris IJAAR VOLUME II ISSUE 7 MAY-JUNE 2016
6 CONCLUSION: 1)Sivani is surgically important structure which is preserved at the time of surgery or any injury to it. 2) There are seven number of sivani. Out of five present in the skull. These structures are resembles to coronal suture, sagital suture, Lambdoid suture and squamous sutures. 3) Structure of sivani is like stich mark or like frenulum. Structure of sivani in tongue is mucus membrane of frenulum of tongue. 4) Second meaning of sevani is structure resembles to frenulum and it is like raphe of scrotum in male & fold of frenulum of clitoris and frenulum of labia minora in female. 5) Thus the structures of the sevani are found on skull, skin or mucus membrane.whatever may be but Susrut told to preserve these structures. REFERENCES: 1)Sushrut samhita sharirsthanam.-dr B.G. samhita sharirsthana Chapter 5\14 Page )Sanskruita-hindi Koash.- By V.S.Apte- ChaukhambaSanskruita Bhavan. Chitra Theatre samor, Near Bank of Baroda Buliding, Post Box No Varanashi (India).ISBL Reprint 2012 Page )Sanskruita-hindi Koash.- By V.S.Apte- ChaukhambaSanskruita Bhavan. Chitra Theatre samor, Near Bank of Baroda Buliding, Post Box No Varanashi (India).ISBL Reprint 2012 Page592. 4)Sushrut samhita sharirsthanam.-dr B.G. samhita sharirsthana Chapter 5\21 Page )Sushrut samhita sharirsthanam.-dr B.G. samhita sharirsthana Chapter 5\32 Page )Sushrut samhita sharirsthanam.-dr B.G. samhita sharirsthana Chapter 5\32 Page )Sushrut samhita sharirsthanam.-dr B.G. samhita sharirsthana-haranchand- Chapter 5\32 Page )Sushrut samhita sharirsthanam.-dr B.G. samhita sharirsthana-indutika- Chapter 5\14 Page )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no IJAAR VOLUME II ISSUE 7 MAY-JUNE 2016
7 11)Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no )Grey s anatomy for students- by Richard edition ISBN page no ) by image. Anatomy of the Female pelvic & fetal skull. Corresponding Author: Dr.Budruk Pramod Appasaheb,M.D. Sharir Rachna, L.L.B.(spl) Principal- Hon.Shri. Annasaheb Dange Ayurved,Medical College, Ashta. Tal- Walwa, Dist- Sangli. pramodbudruk@rediffmail.com Source of support: Nil Conflict of Interest: None Declared IJAAR VOLUME II ISSUE 7 MAY-JUNE 2016
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Anatomy Made Easy MSS
 Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
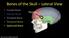 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
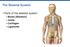 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
the study of the body s physical structures
 Chapter 1: Page 10 anatomy anterior (ventral) coronal (frontal) plane distal the study of the body s physical structures directional term meaning "toward the front" plane of reference which divides the
Chapter 1: Page 10 anatomy anterior (ventral) coronal (frontal) plane distal the study of the body s physical structures directional term meaning "toward the front" plane of reference which divides the
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted from the text book
The Skeletal System. Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab. Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly adopted
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton
 The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
Neurosurgical Techniques
 Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Neurosurgical Techniques EBEN ALEXANDER, JR., M.D., EDITOR Supratentorial Skull Flaps GuY L. ODOM, M.D., AND BARNES WOODHALL,!V[.D. Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, Duke University Medical
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions
 Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
Anatomy & Physiology Autopsy of a Banana Planes / Anatomical Directions Purpose: During this lab you will demonstrate your knowledge of directional terms by performing an autopsy on a banana. It is important
The University Hospital/ 90! Twenty-Third.Street, N.IV./ Washington, D.C Representatives Select Committee on Assassinations Staff Member
 222 ADDENDUM D REPORT OF DAVID O. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION OF THE AUTOPSY X-RAYS OF PRESIDENT JOHN F. KENNEDY, DATED AUGUST 23, 1975 REPORT OF DAVID 0. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION
222 ADDENDUM D REPORT OF DAVID O. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION OF THE AUTOPSY X-RAYS OF PRESIDENT JOHN F. KENNEDY, DATED AUGUST 23, 1975 REPORT OF DAVID 0. DAVIS, M.D., CONCERNING THE EXAMINATION
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
* Articular system I
 *Articular system I *Articular system=syndesmology (Systema articulare) System of joints Joint occurs, where 2 bones meet Combine bones of skeleton into a single unit Provide mobility *Classification
*Articular system I *Articular system=syndesmology (Systema articulare) System of joints Joint occurs, where 2 bones meet Combine bones of skeleton into a single unit Provide mobility *Classification
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
SD School Anatomy Program 1: Bones QuikNotes. Student Notes
 QuikNotes The transverse plane runs from right to left and divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections. Student Notes The frontal plane lies vertically along the body from head
QuikNotes The transverse plane runs from right to left and divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections. Student Notes The frontal plane lies vertically along the body from head
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Ayurved, Pune-43.India. 2 Assistant professor (Kriya Sharir) 2. Bharati Vidyapeeth (Deemed to be University), College of
 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 INTERPRETATION OF PESHI ON THE BASIS OF LITERARY AND CADAVERIC STUDY 1 Kadam Rupaji J. 2 Kadam Manisha R. 1 Associate professor(rachana
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 INTERPRETATION OF PESHI ON THE BASIS OF LITERARY AND CADAVERIC STUDY 1 Kadam Rupaji J. 2 Kadam Manisha R. 1 Associate professor(rachana
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES. At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions:
 HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES CHAPTER ONE The Special Senses Learning objectives At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions: 1. What is the gross and histological
HUMAN ANATOMY II STUDY NOTES CHAPTER ONE The Special Senses Learning objectives At the end of this chapter the student should be able to answer the following questions: 1. What is the gross and histological
Oral cavity landmarks
 By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Dorsal surface-the upper area or top of the foot. Terminology
 It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial Skeleton
 A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
The SCALP. Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
The SCALP By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The SCALP includes FIVE layers external to the Calvaria. These are: S: Skin & Superficial Fascia C: Connective Tissue A: Aponeurosis (Epicranial) L: Loose
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology. Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity
 Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Chapter 8A. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. Types of Bones. Types of Bones
 Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Rachana Sareeram. : Classes for 6 months, including examination & result. Study leave + Universrity Exam for 2 months
 Rachana Sareeram It is proposed to divide the 1-½ years of professional course into three terms as envisaged by DAME. The three terms, study leave & periodical exams can be as follows: TTerm 1 Term 2 Term
Rachana Sareeram It is proposed to divide the 1-½ years of professional course into three terms as envisaged by DAME. The three terms, study leave & periodical exams can be as follows: TTerm 1 Term 2 Term
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Pichayen Duangthongpon MD*, Chaiwit Thanapaisal MD*, Amnat Kitkhuandee MD*, Kowit Chaiciwamongkol MD**, Vilaiwan Morthong MD**
 The Relationships between Asterion, the Transverse-Sigmoid Junction, the Superior Nuchal Line and the Transverse Sinus in Thai Cadavers: Surgical Relevance Pichayen Duangthongpon MD*, Chaiwit Thanapaisal
The Relationships between Asterion, the Transverse-Sigmoid Junction, the Superior Nuchal Line and the Transverse Sinus in Thai Cadavers: Surgical Relevance Pichayen Duangthongpon MD*, Chaiwit Thanapaisal
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Fibrous Joints * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46403 1 Fibrous Joints * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m46403 1 Fibrous Joints * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology. ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations
 Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Forensic Archaeology & Forensic Anthropology ADJ14 Advanced Criminal Investigations Anthropology & Archaeology Anthropology is the study of the biological and cultural aspects of all humans in all places
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
 CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints
 Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections )
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections 8.1-8.3) I. Divisions of the skeletal system a) An adult human skeleton has 206 named bones b) Most are paired
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections 8.1-8.3) I. Divisions of the skeletal system a) An adult human skeleton has 206 named bones b) Most are paired
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
