Link full download:
|
|
|
- Malcolm Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
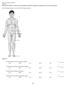
1 Link full download: Human Anatomy, 7e (Marieb/Mitchell/Smith) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1.1 Multiple Choice Questions Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure 1.1 1) Which letter indicates the mental region? B) B C) C 1
2 D) D E) E 2) Which letter indicates the umbilical region? B) B C) C D) D E) E 3) Which letter indicates the hallux? B) B C) C D) D E) E Answer: E 4) Which letter indicates the inguinal region? B) B C) C D) D E) E 5) Which letter indicates the femoral region? B) B C) C D) D E) E 2
3 Figure 1.2 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 6) Which letter indicates the lumbar region? B) B C) C D) D E) E 3
4 7) Which letter indicates the acromial region? B) B C) C D) D E) E Diff: 3 Page Ref: 7 8) Which letter indicates the scapular region? B) B C) C D) D E) E 9) Which letter indicates the popliteal region? B) B C) C D) D E) E Answer: E 10) Which letter indicates the occipital region? B) B C) C D) D E) E Diff: 3 Page Ref: 7 11) The chest is to the abdomen. Page Ref: 7-8 4
5 Diff: 2 12) The sternal region is to the scapular region ) The knee is to the foot. Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) The brain is to the skull. Answer: E -8 15) The thumb is to the index finger. Page Ref: 7-8 5
6 Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Muscles are to the skin. Answer: E Diff: 1 17) The axillary region is to the sternum ) The lip is to the chin ) The eye is to the occipital region. -8 Page Ref: 7-8 6
7 20) The acromial region is to the scapular region ) The gluteal region is to the popliteal region. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 7-8 7
8 22) The femoral region is to the plantar region ) The heart is to the sternum. Answer: E -8 24) The pubic area is to the gluteal region ) The umbilical region is to the lumbar region ) The smallest living unit is A) a cell. B) an organ. C) a human being. D) a molecule. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 3 8
9 27) Which branch of anatomy studies the structural changes that occur as one ages? A) developmental anatomy B) pathological anatomy C) regional anatomy D) surface anatomy Diff: 2 Page Ref: 2 28) Which organ system includes the pancreas, thymus, testes, and pituitary gland? A) integumentary B) endocrine C) reproductive D) lymphatic Diff: 2 Page Ref: 3 &5 29) A coronal section through the human body can A) pass through both the nose and the occipital region. B) pass through both ears. C) provide mirror right and left images. D) lie in a horizontal plane., 9 30) During the process of, noncellular artifacts can be introduced into histology samples. A) time B) observation C) staining D) photography Diff: 2 Page Ref: 14 31) The cervical region is the A) thigh. B) calf. C) neck. D) head. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 7 9
10 32) The "CT" in "CT scanning" stands for A) cut transversely. B) Charles Thorgaard, the inventor's name. C) correlated thickness. D) computed tomography. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 16 33) What is the function of serous membranes? A) They act like wrapping paper to hold visceral organs together. B) They contain gland cells that secrete mucus. C) They halt the spread of infection. D) They reduce friction so that viscera move freely. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12 34) The dorsal hollow nerve cord A) develops into the brain and spinal cord. B) is a primitive supporting rod. C) contains the notochord. D) is the same as the human backbone. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 10 35) The main purpose of fixation is A) to preserve the tissue. B) to mend breaks in tissue sections. C) to make an organ easier to section. D) to stick tissue sections to a glass slide. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 14 36) A histologist examines a specimen that has an epithelium overlying some smooth muscle. This specimen is part of A) a molecule. B) a cell. C) a tissue. D) an organ. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 5 37) An example of a tissue in the body is A) the stomach. B) a muscle cell. 10
11 C) epithelium. D) a macromolecule. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 4 38) An example of an organ is A) a fat cell. B) the intestine. C) epithelium. D) the cardiovascular system (but not the circulatory system). Diff: 1 Page Ref: 5 39) Which organ system consists of vessels that do not carry blood, but pick up fluids (and some cells) that are leaked from the blood? A) urinary B) endocrine C) integumentary D) lymphatic Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Large molecules such as proteins are called A) cells. B) macromolecules. C) multi-atom units. D) cellular organelles. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 4 41) Which organ system covers the external surface of the body, but not the internal surface of the mouth? A) lymphatic B) digestive C) integumentary D) cutaneous Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which organ system includes the spinal cord? A) skeletal B) muscular C) nervous D) integumentary 11
12 Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) The height of an average person's trunk, from neck to perineum, is about A) 5 meters. B) 10 centimeters. C) 1000 μm. D) 1 meter. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 3 44) Which statement concerning the anatomical position is FALSE? A) The palms face anteriorly. B) The toes point anteriorly, but the fingers point inferiorly. C) The knees, elbow, and neck are straight (not bent). D) The person is lying down, as straight as possible. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 6 45) Bilateral symmetry can apply to objects as well as to animal bodies. Which of the following capital letters of the alphabet is not bilaterally symmetrical? B) M C) L D) O Diff: 2 Page Ref: 10 46) Which structure is not covered by visceral serosa? A) lungs B) ribs C) stomach D) uterus Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12 47) The femoral region is the A) buttocks. B) hip. C) thigh. D) toes. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 7 12
13 48) The inguinal region lies A) anterior to the elbow joint. B) on the anterior neck. C) where the thigh joins the trunk. D) on the external genitals. 49) The perineal region is the A) side of the leg. B) region between the external genitals and the anus. C) point of the shoulder. D) superior part of the gluteal region. 50) Which structure is not present in the mediastinum? A) esophagus B) heart C) lung D) trachea Diff: 2 Page Ref: 11 51) A frontal plane is the same as a plane. A) midsagittal B) transverse C) coronal D) sagittal, 9 52) Another name for the midsagittal plane is A) parasagittal. B) oblique. C) coronal. D) median. 53) What point or structure in the body is located farthest laterally? (Hint: Questions always refer to the body in the anatomical position.) A) the coxal region B) ear C) little toe 13
14 D) tip of thumb Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) Although transmission electron microscopy is usually used for high-magnification viewing, it is certainly possible to use it at low magnification as well. That is, one can produce similar micrographs of tissues taken by light microscopy and electron microscopy at the same magnification. Even at the same magnification, however, you can easily tell the two kinds of micrographs apart. How? A) The image in the electron micrograph is still sharper. B) Tissue viewed by electron microscopy is colored, whereas light micrographs are always black and white (and shades of gray). C) Tissue for light microscopy cannot be fixed (no fixation). D) Tissue for electron microscopy cannot be sectioned. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 14 55) What is the main advantage of MRI as a medical imaging technique? A) It is safe. B) The patient feels less pain during the procedure than with any other imaging technique. C) It is very inexpensive. D) It shows soft tissues very clearly. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 18 56) The extremities are the same as A) the ears. B) the fingers and toes. C) the limbs. D) all structures in the head. 57) Which of the following pairs of organs/structures is located ipsilateral? A) cecum : sigmoid colon B) descending colon : spleen C) mouth : navel D) right lung : left lung Diff: 3 Page Ref: 8 58) A physician viewing an injury to the back would look at the patient's side. A) lateral 14
15 B) posterior C) cranial D) ventral Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8 59) The body cavity contains the brain. A) dorsal B) ventral C) serous D) lateral Diff: 2 Page Ref: 11 60) The roots of anatomical terminology lie mainly in A) German and French. B) Latin and Greek. C) Esperanto. D) Russian and Old English. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 6 61) The cavity contains the heart and lungs. A) abdominopelvic B) dorsal C) thoracic D) lateral Diff: 2 Page Ref: 11 62) Hormones are regulatory proteins that are secreted by the system. A) urinary B) endocrine C) integumentary D) lymphatic Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) Which organ system keeps blood constantly supplied with oxygen, removes carbon dioxide, and contains many air tubes? A) urinary B) endocrine C) circulatory D) respiratory 15
16 Diff: 2 Page Ref: ) The elimination of nitrogenous wastes from body fluids is regulated by the system. A) urinary B) endocrine C) integumentary D) lymphatic Diff: 1 Page Ref: ) Which structures are evidence of the vertebrate characteristic of segmentation? A) branches of the blood vessels B) multiple joints of fingers C) subdivisions of the gastrointestinal tract D) vertebral column Diff: 2 Page Ref: 11 66) Which statement about visceral serosa is false? A) It clings to the surface of organs. B) It is continuous with the membrane that covers the outer body wall. C) It is deep to the parietal serosa. D) It lines the internal surface of hollow organs. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12 67) How many centimeters are there in a meter? A) 10 B) 100 C) 1,000 D) 1,000,000 Diff: 3 Page Ref: 6 68) Which organ is not found in the ventral body cavity? A) heart B) liver C) spinal cord D) urinary bladder Diff: 2 Page Ref: 11 16
17 69) The ankle lies to the thigh. A) distal B) proximal C) lateral D) inferior Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8 70) The axillary artery is found in the region of the A) posterior surface of the knee. B) vertebral column. C) armpit. D) long axis of any limb. 71) As an anatomical region, lumbar refers to A) the infero-medial aspect of the back. B) part of the lower limb. C) the wrist. D) the breast. 72) The buccal region is the A) cheeks. B) waist. C) calf of the leg. D) underside of the foot. 73) The popliteal region is A) the side of the leg. B) in the cervical region. C) the posterior surface of the knee. D) the inferior part of the gluteal region. 74) The coxal region is A) the same as the inguinal region. B) the skin over the "tailbone." 17
18 C) the hip. D) the posterior surface of the wrist. 75) Which structure is located entirely within the right upper quadrant? A) appendix B) gallbladder C) spleen D) stomach Diff: 2 Page Ref: True/False Questions 1) Serous cavities include the pleural cavity. Answer: TRUE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 12 2) Serous cavities contain air. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12 3) The peritoneal cavity is a serous cavity. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 12 4) EM has much greater resolution than LM. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 14 5) The dorsal body cavity is subdivided into a cranial cavity and a vertebral cavity. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 11 6) Pathological anatomy deals with structural changes caused by disease. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 2 7) A CT scan produces an image of a transverse section of the body. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref:
19 8) MRI techniques can show only images that are hard and deflect the X-rays. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 18 9) Ultrasound techniques are used to image a fetus because they are less damaging than other techniques. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 18 10) Angiography imaging is used primarily in the study of blood supply to the heart wall and brain. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 17 11) Most adults are between 1.5 and 2 meters tall. Answer: TRUE Diff: 3 Page Ref: 6 12) All vertebrate embryos have a dorsal hollow nerve cord. Answer: TRUE Diff: 2 Page Ref: 10 13) A transverse plane could cut the head off the body! Answer: TRUE, 9 14) In anatomical position, the palms of the hands face medially toward the thighs. Answer: FALSE Diff: 1 Page Ref: 6 15) The mediastinum contains the trachea and lungs. Answer: FALSE Diff: 2 Page Ref: Short Answer Questions 1) Describe the terms proximal and distal. Answer: Proximal means closer to the point of attachment to the main part of the body; distal is farther from the point of attachment. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8 2) Describe the location of the femoral region in relation to the crural region. Answer: The femoral region is proximal to the crural region. 19
20 -8 3) Describe the location of the brachial region in relation to the pollex. Answer: The brachial region is proximal to the pollex. -8 4) In humans, what term is synonymous with posterior? Answer: dorsal Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8 5) Clinicians refer to anatomy when locating blood vessels to draw blood, feeling pulses, and avoiding nerves while giving injections. Answer: surface Diff: 1 Page Ref: 2 6) In humans, the region between the anus and the external genitals is the region. Answer: perineal 7) The olecranal region is posterior to what region? Answer: antecubital 8) The head, neck, and trunk comprise the region. Answer: axial 9) What is the anatomical term for the thumb? Answer: pollex 10) One could say that the forearm is to the brachial region. Answer: distal Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8 11) Cutting the body along the median plane produces a section Answer: midsagittal Diff: 1 Page Ref: 7, 9 12) One could describe the scalp as being to the skull. Answer: superficial Diff: 2 Page Ref: 8 20
21 13) A plane separates the body into equal left and right halves. Answer: midsagittal (or median), 9 14) The measurement typically used for structures within a cell is the. Answer: micrometer Diff: 3 Page Ref: 6 15) The system is involved in immunity. Answer: lymphatic Diff: 3 Page Ref: Essay Questions 1) Identify each of the systems that are found in the arm. Answer: The arm contains elements of the skeletal, nervous, cardiovascular, muscular, lymphatic, and integumentary systems. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 4-5 2) Which of the organ systems found in the arm are not found in the leg? Answer: None Diff: 3 Page Ref: 4-5 3) List the six unique features found in all vertebrates at some stage of their life. Answer: Tube-within-a-tube body plan, bilateral symmetry, dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord and vertebrae, segmentation, and pharyngeal pouches. Diff: 3 Page Ref: ) In adult humans, what remnants of segmentation remain? Answer: The ribs and the vertebrae, with their segmental spinal nerves, are remnants of segmentation. Diff: 3 Page Ref: 11 5) Select from the following techniques the best method for assessing brain function in a stroke patient: X-ray imaging, sonography, MRI. Explain why the other choices are not the best choice. Answer: MRI is the best method of assessing brain function. X-rays do not image soft tissues well or with high resolution. They also produce only two-dimensional images of a structure. Sonography cannot be used to study the brain because sound waves cannot pass through the body skull. Diff: 3 Page Ref:
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
Human Anatomy 8th edition Chapter 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Use the diagram below to answer the following questions. Figure
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
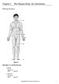 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Matching Questions Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, match the following: 1) Mental 2) Umbilical 1 2 Test Bank for Human Anatomy 3) Hallux Answer: E 4) Inguinal 5) Femoral
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
9. Which term refers to the back? A. Inferior B. Lateral C. Posterior D. Peripheral 10. The heart is to the lungs. A. dorsal B. superior C.
 1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
1 Student: 1. Which term refers to the study of how an organ functions? A. Anatomy B. Physiology C. Ecology D. Homeostasis 2. Observing the parts of the brain would be part of the study of A. homeostasis.
Bio 5/6
 Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Name: THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Study Guide Period: Most of us have a natural curiosity about our bodies, and a study of anatomy and physiology elaborates
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Pearson Education, Inc.
 Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Welcome to ANAT 10A! What is Anatomy? Different levels of Anatomy The Language of Anatomy Introduction Anatomy means to dissect: (ANAT 10A) The study of internal & external body structures The study of
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
Anatomy & Physiology Ch 1: The Human Body Worksheet 1. The structures of the body are organized in successively larger and more complex structures. Fill in the blanks with the correct terms for these increasingly
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
2) The level of organization when different multiple types of tissues join together is called the
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: IHB10e Chapter Number: 1 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) The science dealing with body functions is called a) physiology. b) cytology. c) anatomy. d) histology.
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter One: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy is the scientific study of structure or form (morphology) Physiology is the scientific study of function Functional role of a body part
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Introduction: The early students of anatomy and physiology
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
A&P 1. Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist
 A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
A&P 1 Intro to A&P Terminology Direction Correct Anatomical Position and the Cavities Study Guide Studying the Wordlist Do these exercises before trying the on-line quiz. Read Me Step 1. Demonstrate the
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of the body and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy (visible structures)
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Scanlon Sanders Test Bank Link full download: http://testbankcollection.com/download/essentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology- 6th-edition-scanlon-sanders-test-bank
The Human Body: An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. Anatomy - Study of internal and external body structures
 C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function Anatomy - Study of internal and external
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders
 Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
Test Bank for Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th edition by Valerie C. Scanlon and Tina Sanders Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-foressentials-of-anatomy-and-physiology-6th-edition-by-scanlon-and-sanders/
If time is limited, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment.
 EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
EXERCISE 1 Download FULL Solution Manual for Human Anatomy Laboratory Manual with Cat Dissections 8th Edition by Marieb & Smith https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-legal-environment-of-business-7e-nancy-k-kubase-bartley-abrennan-m-neil-browne
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ANSWERS TO Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. b 2. a. 3 b. 7 c. 5 d. 6 e. 4 f. 1 g. 8 h. 2 i. 10 j. 9 3. a. frontal b. cervical c. antecubital d.
Chapter Overview. Chapter 1. Anatomy. Physiology
 Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Chapter Overview Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Define Anatomy and Physiology Levels of Organization Characteristics of Living Things Homeostasis Anatomical Terminology 1 2 Anatomy Describes
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation. Short Answer. Figure 1.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Short Answer Figure 1.1 Using Figure 1.1, identify the following: 1) Label A points to the cavity. 2) Label B
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body
 Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
Testbank Chapter 1. An Introduction to the Human Body Multiple Choice 1. This is the study of the functions of body structures. a. Anatomy b. Physiology c. Dissection d. Histology e. Immunology Ans: B
A&P 1. Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities. Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology
 Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Overview of A&P and Anatomical Terminology Anatomy The Study of Structure Based on observation Gross anatomy is what is visible with naked eye - dissection Histology is examination of cell populations
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics
 Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Anatomy & Physiology Names:, Period date: Textbook Reference: See Chapter 1 Lab Exercise 1. Getting Started with the Basics Measurement Body Organization Body Systems What you need to be able to do to
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition
 Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 8 th Edition Chapter 01-A: Organization of the Body Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1 A scientific theory is a fact ANS: F DIF: Application TOP: Science and Society REF: Page 4 2 A
1 PART 8/24/13. The Human Body: An Orientation. An Overview of Anatomy. Anatomy. Physiology. An Overview of Anatomy. An Overview of Anatomy
 1 PART 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Leslie
1 PART 1 The Human Body: An Orientation An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy The study of the structure of the human body Physiology The study of body function PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Leslie
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
The Human Body An Overview
 The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Human Body An Overview An Overview of Anatomy OAnatomy - The study of the structure of the human body OPhysiology - The study of body function The Hierarchy of Structural Organization O Chemical level
The Language of Anatomy
 The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
The Language of Anatomy Notes Booklet Name: Period: I Can Objectives *Check off once you have mastered each of these objectives. 1. I can describe the anatomical position and can stand in it myself. 2.
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Anatomy Definition - anatome = up (ana) + cutting (tome) Disciplines of anatomy Macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Neuroanatomy Approach to study of gross anatomy Upper
Introduction in human anatomy Anatomy Definition - anatome = up (ana) + cutting (tome) Disciplines of anatomy Macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Neuroanatomy Approach to study of gross anatomy Upper
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static)
 Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another (static) Word anatomy comes from the Greek words that mean to cut apart Physiology the study of the function of the
https://testbanksolution.net/
 Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Structure and Function of the Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which word is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up? A. dissection C. pathology B. physiology
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Lab Activity 1. Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 1 Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1 Portland Community College BI 231 Anatomy Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) Microscopic anatomy:
Lab Activity 1 Language of Anatomy Martini Chapter 1 Portland Community College BI 231 Anatomy Gross anatomy: the study of body structures visible to the naked eye (without a microscope) Microscopic anatomy:
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide
 Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Name Pd Date Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 1 Study Guide AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1. Match the terms in Column B to the appropriate descriptions provided in Column A. Enter the correct letter
Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body
 Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Name Date Physiology & Anatomy Chapter 1 Organization of the Human Body Checkpoint 1. What is the basic difference between anatomy and physiology? 2. Provide your own example of how the structure of a
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
8/27/2017. The Human Body: An Orientation. Homeostasis BODY SYSTEMS WORK TOGETHER TO MAINTIN HOMEOSTASIS. Chapter 1 Part B
 Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Chapter Part B The Human Body: An Orientation Homeostasis The organism s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is constantly changing. Dynamic State
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy Introduction Anatomy The study of external structures The study of internal structures The study of the relationship
What is Anatomy & Physiology?
 What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
What is Anatomy & Physiology? Big Ideas: 1. How does the body maintain homeostasis? 2. How are structure and function interdependent? anatomy - structure of body parts and how they are organized anatomy
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy. General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position
 #1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
#1 - Chapter 1 - Anatomy General Anatomical Terms The Anatomical Position The anatomical position is a stance in which a person stands erect with the feet flat on the floor and close together, arms at
Human Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction (Ch. 1)
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Human Anatomy & Physiology Introduction (Ch. 1) Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic
Organization of the Body Chapter 1. Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden
 Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
Organization of the Body Chapter 1 Anatomy & Physiology Ms. Roden 1 The Scientific Method Andreas Vesalius founder of modern anatomy Woodcut of a gross dissection In world s first anatomy textbook in 1543
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
**Confirm accuracy of above with your instructor.** Revised 8/22/2017 1
 AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
AP1 Lab 1 Cavities, Organs, Serous Membranes, Quadrants, Regions, and Directional Terms, Planes & Sections Project 1 Directional Terminology Step 1: Define/Describe what is known as the "ANATOMICAL POSITION."
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Chapter 1 Introductory Anatomical Terminology and Physiological Concepts Most of the terms used in anatomy and physiology are of either Greek or Latin origin. (In fact, the term anatomy is derived from
Introduction. Chapter 1. Structure and Function. Introduction. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated. Anatomy and Physiology Integrated Anatomy
 Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Introduction Chapter 1 An Introduction to A&P Study strategies crucial for success Attend all lectures, labs, and study sessions Read your lecture and laboratory assignments before going to class or lab
Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m47807 1 Anatomical Terms * Tonye A. Ogele This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract By the end of this section,
Station 2: Torso Model Practical
 Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
Station 2: Torso Model Practical Label # Organ System Cavity 1 Spinal cord Nervous Spinal or vertebral 2 Liver Digestive Abdominal 3 Large Intestine Digestive Abdominal 4 Small Intestine Digestive Abdominal
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 1 The Human Body: An Orientation: Part A Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: The study of structure Subdivisions:
Anatomy Physiology. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Introduction to Anatomy Physiology Danil Hammoudi.MD "Dispel from your mind the thought that t an understanding di of the human body in every aspect of its structure can be given in words; the more thoroughly
Introduction to Anatomy Physiology Danil Hammoudi.MD "Dispel from your mind the thought that t an understanding di of the human body in every aspect of its structure can be given in words; the more thoroughly
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy
 Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter 3 General Anatomy and Radiographic Positioning Terminology General Anatomy Definition of Terms Anatomy- term applied to the science of the structure of the body Physiology- study of the function
Chapter 1: The Human Organism
 Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Chapter 1: The Human Organism I. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy - study of structure 1. Studying structural changes from conception to adulthood is called: 2. Embryology is the study of 3. The study
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
topographical anatomy
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 Anatomy Study of the body Structure what something looks like where something is located how big or small it is Ex- what the heart looks like Gross Anatomy structures
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology
 is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
is the study of the body s structure. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology is the study of the body s function. a. Histology b. Anatomy c. Embryology d. Physiology When the anatomy of a
Medical Terminology. Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements
 Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Medical Terminology Anatomical Position, Directional Terms and Movements What we will cover... Content Objectives Students will be able to gain a better understanding and application of medical terminology
Chapter 1. An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington
 Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
Chapter 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to Studying the Human Body Learning Outcomes 1-1 Explain the
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I. Laboratory Manual. Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems
 BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
BIO 137 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Laboratory Manual Laboratory #1: Measurements, Body Organization and Anatomical Systems Lab Exercise 1 Measurements Body Organization Body Systems What you need to
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Learners who thrive in an environment with visual stimulation, such as looking at diagrams
"Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Name(s): Period: Date: "Anatomy is the foundation of medicine and should be based on the form of the human body." Hippocrates http://www.skyscanner.net/news/x_ray_full.jpg
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1)
 Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
Name Date Period Introduction to Human Anatomy (Chapter 1) 1. Anatomy is the study of structures making up an organism. 2. Physiology is the study of how an organism functions. 3. The major organ systems
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 1 2 SECTION vs. PLANE SECTION = a cut PLANE: when the section is made through the body wall or through an organ, it is made along an imaginary
Anatomy & Physiology. Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
Anatomy & Physiology Introduction Anatomy: The study of the structure of an organism and the relationship to its parts Anatomy is derived from the Greek word meaning cutting up which is still how we learn
SYSTEMS PROCEDURE B-4RGAN. ovafles testes thymus cardiovascular
 Figure 2.7 Label the major body cavities' (cavity (cavity Diaphragm (cavity (canalor c.avity '{ (cavity (cavity PROCEDURE B-4RGAN SYSTEMS 1. Review the section entitled "Organ Systems"in chapter 1 of the
Figure 2.7 Label the major body cavities' (cavity (cavity Diaphragm (cavity (canalor c.avity '{ (cavity (cavity PROCEDURE B-4RGAN SYSTEMS 1. Review the section entitled "Organ Systems"in chapter 1 of the
2. Draw or define ANTERIOR/VENTRAL and POSTERIOR/DORSAL. Give an example.
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 01a Internet Activity Anatomical Terminology: Relative Position Go to the following site: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=ap15305 1. Draw or define
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Introduction Anatomy Deals with the structures (morphology) of body parts Physiology Deals with the functions of body parts. What they do and how they do it. Structure
