PATHOLOGY OF GUINEA PIGS, HAMSTERS and GERBILS
|
|
|
- Irene Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PATHOLOGY OF GUINEA PIGS, HAMSTERS and GERBILS Instructor: Bruce H. Williams, DVM, DACVP Dept. of Veterinary Pathology, AFIP (202) PURPOSE The purpose of this 1.5-hour block of instruction is to gain knowledge and experience in the gross diagnosis of diseases of these three rodent species which are actually very rarely used in research today. In most cases, among pathologists, interest in these species generally stems from board preparation. There is extensive overlap in diseases affecting these species (especially infectious disease) and other rodents such as rats and mice, although each species does have one or two unique spontaneous diseases to call their own. When confronted with disease presentation in this species, the observer is well-cautioned to consider the presentation in light of their experience with other rodents and lagomorphs. I have included a brief morphologic diagnosis for each entity. The formulation of concise, accurate morphologic diagnoses is a major pursuit of every good pathologist, especially those who seek certification in this specialty. The formulation of a good morphologic diagnosis is a learned skill; for those seeking additional experience in this endeavor, I would suggest attendance at the annual AFIP Descriptive Pathology Course in Washington, DC. 1
2 Slide Organ Condition Morphologic No. Diagnosis 1 TITLE SLIDE Notes 2 PHOTOGRAPH CREDITS 3 GUINEA PIGS 4 5 Skin, pinna Plantar aspect of feet Acromelanism Albino GP are actually acromelanic, with melanin on pinna and feet. 6 Teats Normal GPs have two paired conical inguinal nipples 7 Vesicular glands Normal Male GPs have extremely large vesicular glands. 8 Penis Normal The end of the penis has to horny styles on either side of the urethra. 9 Vulva Vaginal closure membrane 10 Lung Pulmonary arterial hyperplasia 11 Lung: Perivascular lymphoid nodules Smooth muscle hyperplasia of pulmonary arteries Like other hystricomorphs, females have a vaginal closure membrane which is perforated only at estrus and parturition. This is a normal finding in guinea pigs and should not be construed as evidence of pulmonary hypertension. These are common findings in guinea pigs and do not necessarily 12 Presentation Pregnancy Sows can more than double their weight during pregnancy infants are large and precocious Peripheral blood Spleen Kurloff body Kurloff cells Kurloff cells contain a single PASpositive secretory granule, are more prevalent in females, and may serve anti cancer or immunemodulating functions. They are seen in increased numbers in the 2
3 15 Lung Bordetella bronchiseptica 16 Lung, heart Streptococcus pneumonia 17 Lungs Adenoviral pneumonia Multifocal to coalescing suppurative bronchopneumonia Diffuse severe fibrinosuppurative pleuropneumonia and fibrinous pericarditis Bilaterally symmetrical necrotizing bronchitis and bronchiolitis placenta and spleen, and estrogen administration causes a rise in numbers. B. bronchoseptica is one of the most important GP pathogens. Due to its predilection for ciliated epithelium, it causes classic bronchopneumonia and may be also recovered from the tympanic bulla and uterus. Rabbits may serve as a source of infection. Not as commonly seen today, pneumococcal infections often are triggered by environmental changes. Suppurative lesions in multiple organs and fibrinosuppurative exudates in body cavities are characteristic. High mortality may be seen in outbreaks. Adenoviral pneumonia, characterized by necrosis of airway epithelium and prominent intranuclear inclusions, may have up to 100% in outbreaks. Outbreaks usually occur following experimental manipulation. 18 Heart Rhabdomyoma Focally extensive Cardiac muscle glycogenosis This is a common incidental finding seen in increased prevalence with age. The condition is currently thought to be a glycogen metabolism disorder 19 Aorta Aortic mineralization 20 Heart Metastatic calcification Focally extensive aortic mineralization Metastatic calcification is a common finding in older guinea pigs, and maybe worsened by diets with low magnesium, high calcium, and high phosphorus diets. 21 Cheek teeth Malocclusion Malocclusion of cheek teeth with lingual Normal growth of cheek teeth in guinea pigs results in lingual spur 3
4 entrapment formation in the mandible, and buccal spurs in the maxilla. 22 Facial skin Slobbers Moist facial dermatitis Slobbers is a result of malocclusion in rodents and lagomorphs. 23 Salivary gland, lung Cytomegalovirus Multiple intranuclear inclusions in salivary ductular epithelium Cytomegalovirus is a latent infection in many gp colonies which infects salivary gland, kidney, and liver. Rare cases of systemic CMV have been reported in weanlings, and occasional cases of lymphoproliferative disease may be seen. 24 Stomach Bloat Diffuse gastric dilatation Gastric dilatation and volvulus are occasionally seen as a sporadic finding; predisposing factors have not been identified. 25 Intestine Intussusception Focal jejunal intussusception 26 Cecum Coccidiosis Diffuse chronic necrotizing typhlitis. E. caviae may cause increased severity of a number of other enteric diseases, or weight loss and debilitation in weanlings. 27 Intestine Cryptosporidium wrairi Diffuse catarrhal and hyperplastic enteritis Young guinea pigs less than 6 months manifest disease with ill thrift, weight loss, and diarrheic feces. 28 Anus Fecal impaction Seen in geriatrics due to loss of muscle tone or impaired cecotrophy. 29 Liver Salmonellosis Multifocal to coalescing necrotizing and granulomatous hepatitis 30 Spleen Multifocal to coalescing necrotizing and granulomatous Now uncommon in lab animal colonies, the paratyphoid nodules of Salmonella typhimurium are a rare finding. Outbreaks claim 50% mortality, with weanlings and pregnant sows hardest hit. Zoonotic potential (and potential for human sources) 4
5 splenitis must be considered. 31 Liver Idiopathic hepatic necrosis Multifocal to coalescing hepatic coagulative necrosis An occasional finding in guinea pigs, terminal blood flow changes in the liver are postulated to be the cause. 32 Liver Pregnancy toxemia Diffuse hepatic lipidosis Two forms, the metabolic and circulatory forms are identified in gps. The metabolic form is seen in obese sows during last 2 3 weeks of pregnancy is the result of caloric deprivation due to changes in diet or environment. The circulatory form results in uteroplacental ischemia due to compression of the aorta caudal to the renal vessels by the gravid uterus, and is also associated with uterine and placental hemorrhage and necrosis. 33 Cervical lymph node Cervical lymphadenitis Focally extensive suppurative cervical lymphadenitis Cervical lymph nodes are a characteristic location for abscesses due to S. zooepidemicus (Lancefield Group C). Inoculation is usually the result of oral abrasions with contamination. Most guinea pigs harbor the organism in the nasopharynx. 34 Cervical lymph nodes Cavian leukemia Cervical node lymphoma 35 Liver Hepatic lymphoma 36 Liver Cavian leukemia is a leukemic form of lymphoma (as the name suggests) with massive numbers of lymphoblasts within circulating blood and infiltrating numerous organs. Both type C retrovirus particles have been seen in the disease, and it has been transmitted by transplanted cells and cell free extracts. 37 Stifles Hypovitaminosis C Bilateral periarticular Vitamin C is a cofactor for lysyl and 5
6 38 Costochondral junction (scurvy) hemorrhage proline hydroxylases, a Diffuse costochondral osteodystrophy requirement of the proper crosslinking of Type I and IV collagen. Deficiency results in mineralized abnormal cartilage that cannot be remodeled and converted to bone. Deficient type IV collagen results in increased capillary fragility. Other lesions include odontoblastic defects, decreased cholesterol metabolism, decreased resistance to bacterial infections, and aberrations in amino acids. 39 Hind feet Ulcerative pododermatitis Bilateral chronic suppurative pododermatitis Ulcerative pododermatitis (also known as bumblefoot, is a common problem in guinea pigs associated with wire cages, poor sanitation, and obesity. The infection is often due to coagulasepositive S. aureus and severe cases may be associated with systemic amyloidosis. 40 Face Sarcoptic mange Focally extensive ulcerative and eosinophilic dermatitis 41 Hair Pediculosis Diffuse pelagic peiculosis 42 Face Dermatophytosis Focally extensive proliferative and hyperkeratotic dermatitis Trixacarus caviae, the sarcoptid mite of the guinea pig causes intense pruritus and crusting excoriations over the body. Hematologic signs may be seen, and severe pruritus may result in seizures. Affected animals may lose boy condition and die. Gliricola porcelli and G. ovalis are large common lice that are often seen in guinea pigs. Usually due to T. mentagrophytes, dermatophytosis is common in guinea pig colonies (although most animals are asymptomatic. Environmental condition may predispose to outbreaks. 6
7 43 Abdomen Telogen effluvium Diffuse alopecia Telogen effluvium can occur in a number of conditions, especially pregnancy, weaning, or other stressful conditions. 44 Haired skin Trichofolliculoma Trichofolliculoma is the most common skin neoplasm of gps, is invariable benign, and differentiates toward all three segments of the hair follicle. 45 Perineum Urine scald Focally extensive perineal exfoliative dermatitis Urine scald in any pet rodents or lagomorphs suggests poor husbandry/sanitation. 46 Eye Guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis Focally extensive suppurative conjunctivitis Usually seen in gps from 4 8 weeks, GPIC (due to C. psittaci )is usually a self limiting disease. Other syndromes, such as pneumonia or abortions have been reported. 47 Eye Pea eye Unilateral prolapse of the third eyelid The third eyelid is prolapsed as a result of swelling of the lachrymal gland and/or local fatty tissue. 48 Presentation Lethal white Multiple defects 25% of the offspring of roan or Dalmatian guinea pigs are homozygous for the roan allele, resulting in a constellation of birth defects including white coloration, microopthalmia, deafness, malocclusion, malabsorption, and a poor immune system. 49 Uterus Bordetella bronchiseptica Diffuse chronic and suppurative endometritis B. bronchiseptica is occasionally isolated from the uterine tract, and during outbreak, pregnant sows may abort or deliver stillborn. 50 Ovaries Cystic rete ovarii Bilateral ovarian cysts Cystic rete ovarii are associated with decreased reproductive performance in sows aged 1.5 years or older. 7
8 52 Uterus Mucometra Mucometra Mucometra, hydrometra, and cystic endometrial hyperplasia have all been reported in association with cystic rete ovarii. 53 Kidney, adrenal gland Segmental nephrosclerosis Multifocal to coalescing fibrosing interstitial nephritis GPs have a characteristic pattern of segmental fibrosis which parallels chronic progressive renal disease in other species. Note the very large size of the adrenal gland in the GP. 54 Kidney Segmental nephrosclerosis 55 Kidney Polycystic kidney Multiple renal cortical cysts In segmental nephrosclerosis, the glomeruli are largely spared. It happens in guinea pigs just like in other species. 56 Urinary bladder Urolithiasis Multiple cystic calculi Cystic calculi are seen in older sows, and chronic bacterial UTIs are considered a major predisposing cause. 57 Fetus, presentation Anasarca Dystocia is a common problem in gps due to the large size at births. 58 HANSTERS 59 Presentation Syrian or Golden Hamster Most Golden Hamsters today originated from the same litter captured in Syria in 1930, resulting in a low number of MHC genes due to extensive inbreeding. 60 Presentation Chinese or gray hamster 61 Cheek pouches Normal Cheek pouches are highly distensible and an anatomically privileged site. 62 Hip glands Normal Sebaceous glands used for scent marking. 63 Presentation Diarrhea Wet tail is a commonly abused term for a variety of bacterial causes of enteritis in this species. 8
9 64 Ileum Lawsonia intracellulare Diffuse proliferative ileitis The classic cause of wet tail in this species, L. intracellulare results is epizootics in younger animals, primarily weanlings, with resistance occurring about weeks. Environmental changes can result in disease in older animals. In outbreaks, morbidity of 60% and mortality of 90% is expected. 65 Small intestine Helicobacter pylori Diffuse proliferative ileitis 66 Cecum Giardia muris Chronic lymphoplasmacytic typhlocolitis 67 Intestine Clostridium difficile Focally extensive transmural necrotizing enteritis A range of Helicobacter species have been identified in hamsters, and they can also be infected with H. pylori. Gastritis and intestinal metaplasia have been identified in hamsters infected with H. aurati. Giardiasis in hamsters are usually asymptomatic, but some animals develop marked distention, both acute and gaseous and chronic with marked mural thickening. Infections may be associated with wasting and hepatic amyloidosis in this species. Clostridial infections in this species are associated with antibiotic administration. The most common bacteria in the hamster enteron are Lactobacillus and Bacteroides. Administration of mycins and cillins will precipitate overgrowth with C. difficile, toxin production, and death. Even non treated animals in the same room may result in fatal typhlocolitis. 68 Liver Clostridium piliforme Multifocal to coalescing necrotizing hepatitis Epizootics of Tyzzer disease, primarily in weanlings, may occur following environmental changes. Clostridial spores persist for up to 2 years in the environment. 9
10 69 Small intestine Rodentolepis nana Segmental catarrhal enteritis 70 Rectum Rectal prolapse Focally extensive rectal prolapsed and exenteration 71 Liver Hepatocellular inclusions R. nana infections are common but asymptomatic, and the life cycle is a direct one. There is zoonotic potential for a related tapeworm, Hymenolepis diminuta, in man. This sequel to the multiple forms of wet tail in this species is not uncommon. Pick one. Non specific inclusions are comon n the liver of the hamster. IC may be lysosomes and represent liver injury, IN may represent nuclear membrane invaginations. 72 Liver, accessory sex glands Polycystic disease Multiple hepatic, intestinal, and peritesticular cysts Considered to be on congenital origin, liver cysts (generally of biliary origin) are often accompanied by cysts in the gonads, accessory sex glands, and pancreas. They are considered incidental findings at necropsy.. 73 Liver Amyloidosis Diffuse hepatic amyloidosis 74 Kidney Diffuse renal amyloidosis 75 Left atrium Atrial thrombosis Focally extensive atrial 76 thrombosis Amyloidosis is a common cause of renal insufficiency and mortality in older hamsters, but may be seen as early as 5 mos. Affected livers have a prominent lobular pattern, and in the kidney, deposition being in the glomerulus. Atrial thrombosis is often associated with amyloidosis, although cardiac insufficiency may also play a role. Changes also occur in coag and fibrinolytic parameters in affected animals. May be seen in up to 33% in some colonies. 77 Pancreas Diabetes mellitus Focally extensive pancreatic islet degeneration and Diabetes mellitus is autosomal recessive in some lines of Chinese hamsters. Unlike traditional diabetes, islet cells involute and 10
11 necrosis 78 Kidneys Nephrosclerosis Diffuse bilateral chronic progressive nephropathy. become necrotic, rather than accumulate glycogen. Very similar to that seen in rats, it is a common cause of disease in mortality in older hamsters, and may confound chronic renal research protocols in this species. 79 Ovary Paraovarian cysts This finding is occasionally seen in hamsters. 80 Meninges, choroid Lymphocytic choriomeningitis 71 Brain Spontaneous hemorrhagic necrosis of the CNS Diffuse lymphoplasmacytic meningitis and choroiditis Focally extensive liquefactive cerebral necrosis This arenavirus has zoonotic potential, especially for immunosuppressed owners. Most hamsters are asymptomatic, and the virus is spread through saliva or urine. Serology is the recognized method for diagnosis. This condition has been seen in third trimester fetuses and newborn hamsters and is reproduced by feeding dams a vitamin E deficient diet. Most affected pups are cannibalized. 82 Liver, mesenteric lymph nodes Hamster papovavirusassociated lymphoma Hepatic lymphoma Hamster papovavirus is the agent of transmissible lymphoma, which primarily causes epizootics within naïve colonies. Tumors do not have detectible virus. It is spread in the urine. Enzootic infections of colonies require slaughter to rid the colony of the virus. 83 Haired skin Hamster papovavirusassociated trichoepithelioma Cutaneous trichoepitheliomas Caused by the same virus as transmissible lymphoma, this form is more commonly seen in infected adults, and tumors do contain infectious virus (although it is likely not necessary for transmission.) These tumors are only seen in association with virus. 11
12 84 Haired skin Demodicosis Diffuse hyperkeratotic and proliferative dermatitis D. auratus and D. criceti occur naturally in the Syrian hamsters. Infection is common, and lesions are rarely seen except in older animals. 85 Presentation D aurati is a long, slender parasite that lives in hair follicles, while D. criceti are stubbier mites which live in epidermal pits. 86 Presentation Diffuse hyperkeratotic and proliferative dermatitis An alternate location for D. aurati is within the ostia of sebaceous glands. 87 Haired skin T cell epitheliotropic lymphoma Cutaneous lymphoma GERBILS T cell epitheliotropic lymphoma, also referred to as mycosis fungoides is a spontaneous lymphoma of older hamsters. 88 Presentation Mongolian gerbil Mongolian gerbils are the most common type of gerbil used in research today. Additional types include jirds, sand rats, and antelope rats. Gerbils are diurnal and won t bite you like hamsters. 89 Presentation Gerbils All sorts of pretty colors. The agouti pattern is the standard color. 90 Presentation Fat sand rat Psamommys obesus, the fat sand rat is gaining in popularity due to a predilection to develop diabetes mellitus on normal rodent chows, and its extremely efficient kidney function. 91 Ventral abdomen Ventral making gland The ventral marking gland of male gerbils is a modified sebaceous gland, and a site for cutaneous neoplasia. 12
13 92 Adrenal glands Gerbils have extremely large adrenal glands (up to 4x that of other species.) 93 Presentation Gerbil pups Pups are not precocious, and eyes do not open until around 3 weeks at which time they may be weaned. Distressed mothers will cannibalize young.. 94 Nasal planum Sorenose Focally extensive ulcerative nasal dermatitis Sorenose is a common problem in gerbils. When not groomed, porphyrin pigments from the nasolacrimal duct accumulate and irritate the nasal skin. This area is commonly infected by S. aureus as a sequel. 95 Tail Tail slip Gerbils should not be picked up by the tail. Tail slip is a degloving injury which is used to escape predators. 96 Presentation Epilepsy Epileptiform seizures are common among Mongolian gerbils under stress. Up to 40% are afflicted with the condition, and lines with high incidence are sought after for research purposes. No histologic lesions have been reported. 97 Cerebrum Incomplete circle of Willis 98 Middle ear Aural cholesteatoma Aural cholesterol granuloma Gerbils have an incomplete circle of Willis. Ligation of the common carotid artery results in cerebral ischemia, which makes them a good model for stroke research. Up to 50% of gerbils over 2 years of age have aural cholesteatomas. These are masses of keratinizing epithelium which arise from the external surface of the eardrum and external auditory canal. Compression can result in destruction of the temporal bone 13
14 and inner ear structures. 99 Presentation Head tilt is a common presenting sign of aural cholesteatoma. 100 Liver Clostridium piliforme 101 Liver Salmonella enteritidis Multifocal to coalescing necrotizing hepatitis Multifocal to coalescing pyogranulomatous hepatitis Mongolian gerbils are very susceptible to the disease, and are often used as a sentinel to detect the presence of C. piliforme in the research facility. Fatal salmonellosis may be seen as epizootic in weanlings with evidence of paratyphoid nodules, enteritis, and septicemia. 102 Intestine Rodentolepis nana Very similar situation to that seen in hamsters. R. nana may be cause debilitation in severely affected gerbils. 103 Colon Dentostomella translucida 105 Kidney Chronic progressive nephropathy Diffuse chronic interstitial nephritis The flattened eggs are unusual, but pinworms don t really cause any problems in this species. Syphacia obvelata has been reported in gerbils. This common lesion of aging gerbils results in thickening of glomerular and tubular basements membranes and abundant protein tubular casts. 106 Mite Demodex meriones It is unknown whether this actually may be one of the hamster mites. These are usually not a problem in healthy gerbils 107 Haired skin Ventral marking gland carcinoma 108 Ovary Granulosa cell tumor 109 Adrenal gland Adrenocortical adenoma Ventral marking gland carcinoma Ovarian granulose cell tumor Adrenocortical adenoma These neoplasms are consistent with squamous cell carcinomas. This is one of the most common neoplasms in gerbils Another commonly recognized neoplasm in gerbils. 14
15 110 Heart Focal Myocardial degeneration Multifocal to coalescing myocardial fibrosis with myocyte loss This is a common finding in older gerbils with up to 50% of male breeders affected. It is considered an incidental finding in the majority of cases. A linkage to hyperadrenocorticism has been proposed. 111 Eye Cataracts Yeah, they get them. 15
Mammary glands 8/15/2012. Photograph Credits. Coloring. Guinea Pigs. Pathology of Guinea Pigs, Hamsters and Gerbils
 Pathology of Guinea Pigs, Hamsters and Gerbils Bruce H. Williams, DVM, DACVP Email: williamsb@afip.osd.mil Dr. Paul Stromberg Dr. Dean Percy Dr. Charles Clifford Dr. John King Dr. Marti Hanes Dr. Michael
Pathology of Guinea Pigs, Hamsters and Gerbils Bruce H. Williams, DVM, DACVP Email: williamsb@afip.osd.mil Dr. Paul Stromberg Dr. Dean Percy Dr. Charles Clifford Dr. John King Dr. Marti Hanes Dr. Michael
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY
 AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
AFIP MINIBOARD EXAMINATION MAY 2008 LAB ANIMAL PATHOLOGY 1. Hallmark lesions of infection with polytropic strains of mouse hepatitis virus include: A. Lymphocytic syncytia in mesenteric lymph nodes B.
2015 Lab Animal 8/22/ Mouse. 2. Rat. 3. Mouse. Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse
 1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
1. Mouse 2015 Lab Animal 2. Rat Tissue from an Mouse: Morphologic Diagnosis: Rectal prolapse Causes: 1. Syphacia obveluta 2. Citrobacter rodentum 3. Heicobacter sp 3. Mouse 2. Tissue from a Rat: Morphologic
-1- Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks).
 -1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
-1- BENHA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF MEDICINE Pathology Department (code: 0605) Final Exam for Third year students Date: 28-5-2011 Time allowed: 2 hours. Paper II (75 marks). Please note that this question
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract
 Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION. Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta
 DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
S2 File. Clinical Classifications Software (CCS). The CCS is a
 S2 File. Clinical Classifications Software (CCS). The CCS is a diagnosis categorization scheme based on the ICD-9-CM that aggregates all diagnosis codes into 262 mutually exclusive, clinically homogeneous
S2 File. Clinical Classifications Software (CCS). The CCS is a diagnosis categorization scheme based on the ICD-9-CM that aggregates all diagnosis codes into 262 mutually exclusive, clinically homogeneous
Disclaimer. The Laboratory Guinea Pig. Not ACLAM-sanctioned No specific knowledge of material on the 2009 ACLAM exam
 The Laboratory Guinea Pig Stephen B. Harvey, DVM, MS, DACLAM University of Georgia May 2009 Disclaimer Not ACLAM-sanctioned No specific knowledge of material on the 2009 ACLAM exam Many thanks to these
The Laboratory Guinea Pig Stephen B. Harvey, DVM, MS, DACLAM University of Georgia May 2009 Disclaimer Not ACLAM-sanctioned No specific knowledge of material on the 2009 ACLAM exam Many thanks to these
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Gross Exam #2 KEY
 2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Gross Exam #2 KEY 2014 DESCRIPTIVE VETERINARY PATHOLOGY COURSE GROSS EXAM #2 1. Tissue from a chicken. Morphologic Diagnosis: Multifocal proliferative and ulcerative facial
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Gross Exam #2 KEY 2014 DESCRIPTIVE VETERINARY PATHOLOGY COURSE GROSS EXAM #2 1. Tissue from a chicken. Morphologic Diagnosis: Multifocal proliferative and ulcerative facial
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
RHODOCOCCUS EQUI. Post-mortem Environmental Persistence Specific Control Measures Release of Animals from Isolation
 RHODOCOCCUS EQUI Definition Clinical Signs Transmission Diagnostic Sampling, Testing and Handling Post-mortem Environmental Persistence Specific Control Measures Release of Animals from Isolation Biosecurity
RHODOCOCCUS EQUI Definition Clinical Signs Transmission Diagnostic Sampling, Testing and Handling Post-mortem Environmental Persistence Specific Control Measures Release of Animals from Isolation Biosecurity
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1)
 2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1) Tuskegee University College of Veterinary Medicine Dr. Ebony Gilbreath Tissues submitted to TUSVM diagnostic services for histopathology Puppies 4 weeks of age From
2014 SEVPAC Case #63 (Slide ID: #1) Tuskegee University College of Veterinary Medicine Dr. Ebony Gilbreath Tissues submitted to TUSVM diagnostic services for histopathology Puppies 4 weeks of age From
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Principles of Infectious Disease Lecture #13 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Terminology Pathology study of disease Etiology cause of disease Pathogenesis disease process Infection colonization by microbes Disease illness
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: April 2013
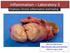 Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome.
 Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Disorders of the kidney. Urine analysis. Nephrotic and nephritic syndrome. Azotemia and Urinary Abnormalities Disturbances in urine volume oliguria, anuria, polyuria Abnormalities of urine sediment red
Gastrointestinal Pathology of Pigs. Jerome C. Nietfeld, DVM, MS, PhD Kansas State Veterinary Diagnostic Lab Department DMP Kansas State University
 Gastrointestinal Pathology of Pigs Jerome C. Nietfeld, DVM, MS, PhD Kansas State Veterinary Diagnostic Lab Department DMP Kansas State University Neonatal Diarrhea Likely the number 1 killer of neonatal
Gastrointestinal Pathology of Pigs Jerome C. Nietfeld, DVM, MS, PhD Kansas State Veterinary Diagnostic Lab Department DMP Kansas State University Neonatal Diarrhea Likely the number 1 killer of neonatal
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury. VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016
 Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results
 SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
SHN-1 Human Digestive Panel Test results HN-30 tongue HN-24 salivary gland HN-12 larynx HN-28 esophagus HN-29 stomach HN-20 pancreas HN-13 liver HN-14 gall bladder HN-27-1 duodenum HN-27-2 ileum HN-27-3
Attending Physician s Statement
 ( Form A A This form is used for claiming the social insurance benefit. This form should be completed and signed by the attending physician outpatient and One form for each month, one form for hospitalization
( Form A A This form is used for claiming the social insurance benefit. This form should be completed and signed by the attending physician outpatient and One form for each month, one form for hospitalization
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION
 DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
DEGENERATION NECROSIS AND INFILTRATION Cellular Degenerations and Infiltrations 1. Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration Cloudy swelling and hydropic degeneration occur when the regulatory mechanisms
0301 Anemia Others. Endocrine nutritional and metabolic disorders Others Vascular dementia and unspecified dementia
 Certain infectious and parasitic diseases 0101 Intestinal infectious diseases 0102 Tuberculosis 0103 Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission 0104 Viral infections characterized by skin
Certain infectious and parasitic diseases 0101 Intestinal infectious diseases 0102 Tuberculosis 0103 Infections with a predominantly sexual mode of transmission 0104 Viral infections characterized by skin
Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals.
 Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals. For the purposes of this presentation, "zoonotic disease" will be defined as a disease that is caused
Zoonosis = an infection or infestation which is shared in nature by man and lower vertebrate animals. For the purposes of this presentation, "zoonotic disease" will be defined as a disease that is caused
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Inflammation Laboratory 2. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: March 2012
 Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Crosswalk File of ICD9 Diagnosis Codes to Risk Group Assignment 1-Apr-15
 1 1500 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF CERVICAL ESOPHAGUS 1 1501 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF THORACIC ESOPHAGUS 1 1502 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF ABDOMINAL ESOPHAGUS 1 1503 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF UPPER THIRD OF ESOPHAGUS 1
1 1500 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF CERVICAL ESOPHAGUS 1 1501 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF THORACIC ESOPHAGUS 1 1502 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF ABDOMINAL ESOPHAGUS 1 1503 MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF UPPER THIRD OF ESOPHAGUS 1
Pancreas composed of 2 parts: 1- exocrine gland 2- endocrine gland
 pancreas Pancreas composed of 2 parts: 1- exocrine gland 2- endocrine gland Acute pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas associated with acinar cell injury Clinical features: 1-abdominal pain cardinal
pancreas Pancreas composed of 2 parts: 1- exocrine gland 2- endocrine gland Acute pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas associated with acinar cell injury Clinical features: 1-abdominal pain cardinal
Extracellular degeneration
 Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Schistosome life cycle.
 Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs
 Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW A change in the frequency, consistency, and volume of bowel movement (feces) for more than 3 weeks Can be either small bowel (small intestine) diarrhea, large bowel
Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs Basics OVERVIEW A change in the frequency, consistency, and volume of bowel movement (feces) for more than 3 weeks Can be either small bowel (small intestine) diarrhea, large bowel
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Digestive System. Digestion Myths
 Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY. PgC & GPCert (DERM) SYLLABUS
 POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (DERM) 2018 SYLLABUS POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE IN DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (Derm) 2018 SYLLABUS This syllabus is designed as a guideline to the key areas
POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (DERM) 2018 SYLLABUS POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE IN DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (Derm) 2018 SYLLABUS This syllabus is designed as a guideline to the key areas
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
DATA REQUEST RESPONSE- XRT AND BRACHYTHERAPY
 Date: 10 th April 2018 DATA REQUEST RESPONSE- XRT AND BRACHYTHERAPY Request: 1. Utilization Data of Overseas Beam Therapy and Brachytherapy 2. Diagnoses Data of Overseas Claims for Beam Therapy and Brachytherapy
Date: 10 th April 2018 DATA REQUEST RESPONSE- XRT AND BRACHYTHERAPY Request: 1. Utilization Data of Overseas Beam Therapy and Brachytherapy 2. Diagnoses Data of Overseas Claims for Beam Therapy and Brachytherapy
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
APPENDIX A. Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2
 APPENDIX A Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2 The comparability ratio is an adjustment factor that is applied to the number of deaths coded
APPENDIX A Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2 The comparability ratio is an adjustment factor that is applied to the number of deaths coded
Overview of Anatomy and Physiology
 1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
1 The Human Body: An Orientation Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental
Normal Flora. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Normal Flora CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Relationships between Organisms Symbiosis Permanent association between two different organisms. Neutralism Two organisms living together, and neither is affected
Normal Flora CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Relationships between Organisms Symbiosis Permanent association between two different organisms. Neutralism Two organisms living together, and neither is affected
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Endocrine Lab. Heather Fenton VPM 222 November
 Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
WLH Tumor Frequencies between cohort enrollment and 31-Dec Below the Women Lifestyle and Health tumor frequencies are tabulated according to:
 DESCRIPTION Below the Women Lifestyle and Health tumor frequencies are tabulated according to: Benign =171 (Cervix uteri) treated as not recorded =191 (non-melanoma skin cancer) treated as not recorded
DESCRIPTION Below the Women Lifestyle and Health tumor frequencies are tabulated according to: Benign =171 (Cervix uteri) treated as not recorded =191 (non-melanoma skin cancer) treated as not recorded
8. POST- MORTEM PROTOCOL (John Trupkiewicz)
 8. POST- MORTEM PROTOCOL (John Trupkiewicz) 8.1. GENERAL COMMENTS Those individuals who may be charged with performing a necropsy examination should formulate a plan of action in the case of the sudden,
8. POST- MORTEM PROTOCOL (John Trupkiewicz) 8.1. GENERAL COMMENTS Those individuals who may be charged with performing a necropsy examination should formulate a plan of action in the case of the sudden,
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
PATHOLOGY MCQs. The Pancreas
 PATHOLOGY MCQs The Pancreas A patient with cystic fibrosis is characteristically: A. more than 45 years of age B. subject to recurring pulmonary infections C. obese D. subject to spontaneous fractures
PATHOLOGY MCQs The Pancreas A patient with cystic fibrosis is characteristically: A. more than 45 years of age B. subject to recurring pulmonary infections C. obese D. subject to spontaneous fractures
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
WLH Tumor Frequencies between cohort enrollment and 31-Dec Below the Women Lifestyle and Health tumor frequencies are tabulated according to:
 WLH Tumor Frequencies between cohort enrollment and 31-Dec 2012 DESCRIPTION Below the Women Lifestyle and Health tumor frequencies are tabulated according to: Benign =171 (Cervix uteri) treated as not
WLH Tumor Frequencies between cohort enrollment and 31-Dec 2012 DESCRIPTION Below the Women Lifestyle and Health tumor frequencies are tabulated according to: Benign =171 (Cervix uteri) treated as not
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
HCPCS Codes (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) ICD-9-CM Codes Covered by Medicare Program
 HCPCS s (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal neoplasm screening ICD-9-CM
HCPCS s (Alphanumeric, CPT AMA) 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal neoplasm screening ICD-9-CM
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Clinical History. 29 yo woman with polyhydramnios Cardiac mass at fetal ultrasound At 35 weeks, newborn died 30 minutes after delivery
 CASE 1 a Clinical History 29 yo woman with polyhydramnios Cardiac mass at fetal ultrasound At 35 weeks, newborn died 30 minutes after delivery Interface between tumor and normal myocardium Smaller well-demarcated
CASE 1 a Clinical History 29 yo woman with polyhydramnios Cardiac mass at fetal ultrasound At 35 weeks, newborn died 30 minutes after delivery Interface between tumor and normal myocardium Smaller well-demarcated
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Pathophysiology lab 2. Cellular injury and adaptation
 Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
Pathophysiology lab 2 Cellular injury and adaptation Adaptation Cellular changes that aim to preserve cell viability and prevent cell injury. The adaptive responses include: 1. Atrophy 2. Hypertrophy 3.
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
Body Regions Review. Anatomical Position. Anatomical Planes. Supine versus Prone 9/9/2009
 Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
Body Regions Review The fundamental divisions of the human body Christine Sparks Anatomy / Physiology I Sept. 9, 2009 Anatomical Position Universal terms are used to describe the body accurately and result
NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test
 NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test Applicable CPT Code(s): 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal
NCD for Fecal Occult Blood Test Applicable CPT Code(s): 82272 Blood, occult, by peroxidase activity (e.g., guaiac), qualitative, feces, 1-3 simultaneous determinations, performed for other than colorectal
What you will learn in this section:
 DISEASE DIAGNOSIS What you will learn in this section: Best practice for undertaking necropsies in pigs. How to euthanase pigs safely and humanely. How monitoring pigs post-mortem during processing can
DISEASE DIAGNOSIS What you will learn in this section: Best practice for undertaking necropsies in pigs. How to euthanase pigs safely and humanely. How monitoring pigs post-mortem during processing can
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Pathology of the Respiratory System 4: Pneumonia
 Pathology of the Respiratory System 4: Pneumonia Shannon Martinson, March 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 222 Systemic Pathology LUNG PNEUMONIA Review Classification of Pneumonia Diffuse LUNG
Pathology of the Respiratory System 4: Pneumonia Shannon Martinson, March 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ VPM 222 Systemic Pathology LUNG PNEUMONIA Review Classification of Pneumonia Diffuse LUNG
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Genito Urinary Pathology
 Duration: 5 Weeks (25 days) Genito Urinary Pathology Concepts Objectives Time T/L Activity Dept. Comments 3/SBM-5/01 Kidneys and the urinary tract a. Auto regulation of renal blood flow b. The basic functional
Duration: 5 Weeks (25 days) Genito Urinary Pathology Concepts Objectives Time T/L Activity Dept. Comments 3/SBM-5/01 Kidneys and the urinary tract a. Auto regulation of renal blood flow b. The basic functional
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics
 Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
BIOLOGY 2290 Pathophysiology I (Health Sciences III ) Sept 2010 Instructor : Dr. Paul S. Sunga, Rm A359a, , Introduction
 BIOLOGY 2290 Pathophysiology I (Health Sciences III ) Sept 2010 Instructor : Dr. Paul S. Sunga, Rm A359a, 323-5251, psunga@langara.bc.ca Introduction This course is designed to provide students with insights
BIOLOGY 2290 Pathophysiology I (Health Sciences III ) Sept 2010 Instructor : Dr. Paul S. Sunga, Rm A359a, 323-5251, psunga@langara.bc.ca Introduction This course is designed to provide students with insights
Tumors of the Spleen
 Tumors of the Spleen 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
Tumors of the Spleen 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
7/4/2018. Key Objectives. A and P 2401 Lecture 2 TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS. Negative Feedback Examples. Review of Homeostasis
 Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
Key Objectives Review of Homeostasis Negative Feedback Mechanisms Positive Feedback Mechanisms Body Systems and Function A and P 2401 Lecture 2 HOMEOSTASIS TWO MECHANISMS USED TO MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS The
The basis of Disease
 General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
General Curriculum The basis of Disease ZHOU REN 周韧 Prof., M.D., Ph.D. Institute of Pathology & Forensic Medicine Department of Pathology & Patho-physiology Zhenjiang University Judicial Evidence & Evaluation
Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / /
 Fall 2015 22TBio 142 22THuman Anatomy and Physiology II Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Semester/Year 22TBio 142
Fall 2015 22TBio 142 22THuman Anatomy and Physiology II Faculty Name: Virginia Garden Program Head: Virginia Garden Dean s Review: Dean s Signature: Date Reviewed: / / Revised: Semester/Year 22TBio 142
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Chronic inflammation. 07-Dec-15. Macrophage Tissue destruction
 Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
Chronic inflammation DR. M. TARIQ JAVED PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY FACULTY OF VETERINARY SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF AGRICULTURE, FAISALABAD. Other types of cells present B & T lymphocytes (antibody and
5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176)
 Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
Hexythiazox 225 5.15 HEXYTHIAZOX (176) TOXICOLOGY Hexythiazox is the ISO approved name for (trans-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-n-cyclohexyl-4-methyl-2-oxo- 3-thiazolidine-carboxamide (CAS No. 78587-05-0). Hexythiazox
Review for Lecture 2016
 Review for Lecture 2016 Final exam About 2/3 will be on new material Look for repetition and interconnections. What affects reproduction? Husbandry Nutrition Hormones Breeding management Genetics Sanitation
Review for Lecture 2016 Final exam About 2/3 will be on new material Look for repetition and interconnections. What affects reproduction? Husbandry Nutrition Hormones Breeding management Genetics Sanitation
Vascular Related Torsion Venous compression Hemorrhagic infarct Young men At night Very painful Can be reduced Scrotal Masses Testicular Tumors (solid
 Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Vascular Lung Diseases
 Vascular Lung Diseases SESSION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES List the major types of vascular lung disease Recognize and describe the pathology of vascular lung disease: Pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, hypertension,
Vascular Lung Diseases SESSION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES List the major types of vascular lung disease Recognize and describe the pathology of vascular lung disease: Pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, hypertension,
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 6 PURPOSE To establish basic understanding of indications and contraindications for transplantation of various organs. POLICY The N.C. Department of Correction, Division of Prisons, Health Services
PAGE 1 of 6 PURPOSE To establish basic understanding of indications and contraindications for transplantation of various organs. POLICY The N.C. Department of Correction, Division of Prisons, Health Services
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics
 Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
Proteinuria (Protein in the Urine) Basics OVERVIEW Proteinuria is the medical term for protein in the urine Urinary protein is detected by urine dipstick analysis, urinary protein: creatinine ratio (UP:C
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
Chapter Outline. Structural defects. Obstructive disorders. Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 98. Cleft lip and cleft palate
 Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Structural defects Chapter Outline Cleft lip and cleft palate Page 3 of 98 Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Hernias Obstructive disorders Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis Intussusception Anorectal
Semester I 2013/2014. Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316
 Semester I 2013/2014 Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 Course Content Outline/Lecture Details & Timetable: 1. Introduction to Pathology Part I: Sunday* 01/09/13 (MD)*** a. Course introduction. b. Pathology
Semester I 2013/2014 Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 Course Content Outline/Lecture Details & Timetable: 1. Introduction to Pathology Part I: Sunday* 01/09/13 (MD)*** a. Course introduction. b. Pathology
Function Alimentary Canal
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Function: to help convert food into simpler molecules that can be absorbed and used by the cells of the body. Alimentary Canala one way tube that passes through the body. (found in
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
