Malignant Hypertension in a Patient with Primary Aldosteronism with Elevated Active Renin Concentration
|
|
|
- Clinton Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT Malignant Hypertension in a Patient with Primary Aldosteronism with Elevated Active Renin Concentration Kiyoshi Oka, Koichi Hayashi, Tomonori Nakazato, Taichi Suzawa, Keiji Fujiwara and Takao Saruta A 40-year-old male, with a past history of hypertension but receiving no medical treatment, was referred. He manifested malignant hypertension (190/130 mmhg;keith-wagener III), renal dysfunction (serum creatinine, 3.8 mg/dl), and elevated plasma aldosterone (450 pg/ml) and active renin concentration (ARC, 104 pg/ml). His blood pressure was controlled with multiple antihypertensive agents and ARCthus decreased (4.3 pg/ml), but aldosterone remained elevated. Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a right adrenal adenoma, and aldosterone-producing adenomawas confirmed by adrenal venous sampling. Primary aldosteronism very rarely develops to malignant hypertension, and even in that case ARCis suppressed. Therefore this is a rare case of primary aldosteronism complicated with malignant hypertension and high ARC. (Internal Medicine 36: , 1997) Key words: aldosterone, renin, renal injury, adrenal adenoma, hemolytic anemia, hypertension Introduction Primary aldosteronism is one of the most commondisorders that cause secondary forms of hypertension. In this form of hypertension, plasma renin activity is suppressed as a consequence of sodium retention. Previous reports indicate that primary aldosteronism is less likely to cause hypertensioninduced vascular damage (1-6), and is rarely complicated with malignant or accelerated hypertension (7-17). Even evolving into malignant phase, it still presents suppressed renin activity (9, ll, 12, 14, 16, 17). Here, we report a rare case with aldosterone-producing adenoma complicated with malignant hypertension. This case is noteworthy since he initially showed an elevated plasma aldosterone and active renin concentration. After appropriate medical treatment, the renin level declined, but was not suppressed below normal range. For editorial comment, see p 669. Case Report A 40-year-old man had been diagnosed as hypertension (-140/100 mmhg)in 1990, but did not receive medical treatment thereafter. In January 1 996, he noticed headache, dyspnea, and palpitation, and he was admitted to a local hospital for the treatment of hypertension ( 1 90/1 30 mmhg), renal dysfunction (serum creatinine, 3.8 mg/dl; blood urea nitrogen, 51 mg/dl), and hypokalemia (2.3 meq//). Despite an intensive treatment, his blood pressure was uncontrollable. Because of high plasma renin [active renin concentration (ARC), 104 pg/ml (normal range, pg/ml)] and plasma aldosterone concentration (450 pg/ml), he was referred to Keio University Hospital for treatment and full evaluation of intractable hypertension. On admission, physical examination revealed severe hypertension (177/133 mmhg), hypertensive retinopathy (Keith- Wagener III), and cardiomegaly, but abdominal bruit was inaudible. His laboratory data is summarized in Table 1. Serum creatinine was elevated (4.3 mg/dl), but curiously, the serum potassium concentration was reduced (3. 1 meq//). On the basis of the laboratory tests, including anemia (hemoglobin, 10.9 g/ dl), reticulocytosis (35%o), elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH, 681 IU//; isozyme pattern, L{ 30.3%, L2 38.8%), low haptoglobin level (<10 mg/dl), and negative Coomb's test, he was found to suffer from microangiopathic hemolytic anemia due to malignant hypertension. Endocrinological tests revealed high ARC(122 pg/ml) and plasma aldosterone concentration (252 pg/ml). Blood gas analysis indicated metabolic alkalosis (ph ) with a high bicarbonate level (27.2 meq//). Urinary excretion of potassium was increased (65. 1 meq/day) despite decreased serum potassium. His blood pressure was treated with multiple antihyperten- From the Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Keio University, Tokyo Received for publication December 26, 1996; Accepted for publication May 20, 1997 Reprint requests should be addressed to Dr. Takao Saruta, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Keio University, 35 Shinanomachi, Shinjukuku,Tokyo
2 Aldosteronoma and Malignant Hypertension Table 1. Laboratory Data on Admission sive agents including spironolactone, amlodipine, doxazosin, and oc-methyldopa, and it began to decline (Fig. 1). In parallel with changes in blood pressure, serum creatinine (from 4.4 to 2.1 mg/dl) and LDH (from 3,091 to 200 IU//) were decreased, and serum potassium was elevated from 2. 1 to 4.2 meq//. ARC also decreased markedly from 122 to a "normal" level of8.7 pg/ ml. Despite an intensive antihypertensive treatment and amelioration of renal function, his serum aldosterone levels remained elevated (252-1,256 pg/ml). Ultrasound examination revealed concentric left ventricular hypertrophy of the heart, and bilateral renal parenchymal damage with symmetrical renal hypoperfusion. On abdominal computed tomography (CT), right adrenal mass (size, 1.5 cm) was found. Adrenal scintigraphy (13^-cholesterol) also detected a marked accumulation on the right adrenal gland with diminished contralateral accumulation. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of adrenals revealed a nodule in the right adrenal, with isointensity on the Tl-weighted image of the liver and high intensity on the T2-weighted image, a finding compatible with adrenal adenoma (Fig. 2). Both MRI-angiography and Doppler ultrasound showed no stenotic lesion of renal arteries. To clarify the nature of the right adrenal mass, adrenal venous sampling was performed (Table 2). The comparison of the aldosterone/cortisol ratio between left and right adrenal venous blood sampling clearly indicated an aldosterone-producing adenoma in the right adrenal gland. Under the diagnosis of an aldosterone-producing adenoma, an operation (retroperitoneal laparoscopic adrenalectomy) was performed on April 9, The removed adrenal contained a golden-yellow mass (20x15 mm; Fig. 3), and histological examination of the adrenal mass proved to be a clear cell-type adrenocortical adenoma. After the operation, his blood pressure gradually decreased (140/100 mmhg), requiring only smaller doses of antihypertensive agents. The serum aldosterone concentration declined sharply to 77 pg/ml, and serum creatinine was also decreased to 2.1 mg/dl. After the surgery, the serum potassium concentration was maintained constant above 3.8 meq// without potassium supplementation or spironolactone. Discussion Primary aldosteronism is characterized by extracellular volumeexpansion and the subsequent hypertension attributed to increased aldosterone production, and suppressed plasma renin 701
3 Oka et al 1-n 1 ; 1 30 Manidipine llo Nifedipine-R 60 ' ' 40 Captopril 1 5QQ ar-methyldopa 750 BP 3?5 L^ Amlodipine i ^ ^ Doxazosin 1 TTN """*»-å!å I SpironolactoneI ^n 1 (mmhg) '-----n. >s^ I rrr ^\Systolic BP/^V^^^ 25^^K LDH 1 1 3,000-i pi (LU.)< II ^^^^m^ Diastolic BP ^^ Cr (mg/dl) f- 5 1,000- ^*^*~*-^-~^^_ K(mEq//) ^ _4 - u II II n n n n rn PI r1 arc arc - S1'256 r600 -M """" \ : -(Pg/ml) (pg/ml)- pi \ Ijl II II fepj-kj Eyd ^iv-h^^^hk-tvxj t -rr;.1 ( (M^ a Jan.a Feb. Mar. a Apr. (b) Operation Figure 1. Clinical course. A: admission to a local hospital, B: admission to our hospital. Figure 2. MRIof the abdomen with Tl-weighted imaging. Arrows indicate the right adrenal tumor. 702
4 Aldosteronoma and Malignant Hypertension Table 2. Adrenal Venous Sampling ALDO:aldosterone, CORTI: cortisol, A: adrenaline, NA: noradrenaline, DA: dopamine. Figure 3. A) Macroscopicfindingsofthe rightadrenal tumor showing a golden-yellow mass (size, 20x15x10 mm). Distance between ticks indicates 5 mmin length. B) Histological examination of the right adrenal tumor showing a clear cell-type adrenocortical adenoma (HE stain, x400). activity. The renin profile is particularly useful for differentiation of the primary form from secondary aldosteronism (e.g., malignant hypertension) that exhibits an elevated plasma renin level. Traditionally, this disorder has been assumed to cause less vascular injury (1-6), probably due to suppressed angiotensin level. Actually it develops relatively less frequently to malignant or accelerated hypertension. Evenin a malignant phase, patients with primary aldosteronism are reported to manifest suppressed renin activity (9, ll, 12, 14, 16, 17). The present case reveals a unique renin profile. Initially, this patient was diagnosed as "secondary aldosteronism" resulting from malignant hypertension; both plasma renin and aldosterone were increased markedly [4-fold greater for ARCand 2- fold for aldosterone]. Despite the appropriate treatment, the serum aldosterone level still remained elevated. Further examination indicated adrenal mass, and adrenal venous blood sampling established the diagnosis as an aldosterone-producing adenomawith malignant hypertension. It has been established that although in patients with primary aldosteronism, the circulating plasma volume is increased, the plasma volume expansion reaches a certain equilibration set point above which natriuresis occurs and consequently peripheral edema does not occur (i.e., escape phenomenon). Thus, the increased extracellular volume inhibits the sodium chloride reabsorption at the proximal tubule. The reduced sodium chloride reabsorption would increase the distal delivery of sodium, and increase the sodium chloride load to the macula densa. This increased load could inhibit renin release from juxtaglomerular cells. In addition, the increased blood pressure would elevate the renal perfusion pressure, resulting in the suppression of renin release. Contrary to the traditional renin profile of primary aldosteronism, the present case manifested markedly elevated plasma renin concentration. It should be noted that the possibility exists that the elevated plasma renin concentration is attributed to renal artery stenosis, leading to renal hypoperfusion. MRIangiography, however, failed to reveal renal artery stenosis. Furthermore, renal Doppler ultrasound did not indicate the stenosis of the renal artery or its large branches, but showed bilateral renal parenchymal damage. Additionally, the present case manifested normocytic anemia, elevated LDHwith dominant L4/L2 isozymes, reduced haptoglobin level, and negative Coomb's test, suggesting microangiopathic hemolytic anemia due to extensive vascular endothelial injury. Finally, the plasma renin concentration fell to the lower limit of the normal range after the medical and surgical treatment. Although the coexistence of renal artery stenosis cannot be excluded completely, it is most likely that the progression of renal injury induced by 703
5 Oka et al malignant/accelerated hypertension and the subsequent glomerular ischemia constitute the pivotal determinant of the markedly elevated renin release. As far as we found in the literature, only three cases have been reported that manifest a similar clinical course (i.e., primary aldosteronism with malignant hypertension, renal failure, and elevated plasma renin activity) to the present case (10, 13, 15), and these cases were confirmed only by postmortem examination. Of note, all of these cases, including our case, presented clinical manifestations of malignant hypertension and progressive deterioration of renal function during relatively short periods. Although renal injury and glomerular ischemia may predispose the renin profile to elevation, this premise does not necessarily apply to primary aldosteronism. Thus, Obanaet al (18) previously reported a case of primary aldosteronism in which preexisting chronic glomerulonephritis developed relatively slowly to a stage of renal insufficiency. In this case, however, plasma renin activity had been suppressed, which increased to a normal level after operation. Furthermore, Inaba et al ( 19) showed a reduced plasmarenin activity in the presence of renal insufficiency in a patient with bilateral adrenal adenoma. Thus, although the renal injury is required for the elevated renin activity, it does not fully explain the increase in plasma renin activity. Additional factors would act in concert with renal injury to cause the enhanced renin activity in primary aldosteronism; the rate of the progression of renal injury may participate in the enhanced renin profile. Alternatively, the acute exacerbation of renal function could be a precipitating factor for the development of malignant hypertension. In summary, we have described a rare case of primary aldosteronism with malignant hypertension and rapidly progressive renal dysfunction. The present case is of particular note since active renin concentration is markedly elevated rather than suppressed. This paradoxical rise in renin activity would veil the original hormonal characteristics observed in primary aldosteronism, and should therefore be born in mind when hypertension develops to a malignant phase. The diagnosis of this curable hypertension would offer better quality of life and prognosis for these patients. References 1) Conn JWPart I, Painting background Part II, Primary aldosteronism, a new clinical syndrome. J Lab Clm Med 43: 3, ) Conn JW. Aldosteronism in man; Some clinical and climatological aspects, Part II. JAMA 183: 871, ) Conn JW, Knopf RF, Nesbit RM. Clinical characteristics of primary aldosteronism from an analysis of 145 cases. AmJ Surg 107: 159, ) Conn JW, Cohen ED, Rovner DRSuppression of plasma renin activity in primary aldosteronism. Distinguishing primary from secondary aldosteronism in hypertensive disease. JAMA190: 213, ) Conn JW, Cohen ED, Rovner DR, Nesbit RM. Normokalemic primary aldosteronism A detectable cause of curable "essential" hypertension. JAMA 193: 200, ) Laragh JH. Vasoconstnction-volume analysis for understanding and treating hypertension* the use ofremn and aldosterone profiles AmJ Med 55: 261, ) Kaplan NM. Primary aldosteronism with malignant hypertension. N Engl J Med269:1282, ) Del Greco F, Dolkart R, Skom J, Method H. Association of accelerated (malignant) hypertension in a patient with primary aldosteronism. J Clin Endocnnol Metab 26: 808, ) McAllister RG Jr, Van Way CW, Dayani K, et al. Malignant hypertension: Effect of therapy on renm and aldosterone. Circ Res 28: Suppl 2: 160, ) Baglin A, Weiss Y, Safar M, Milhez P. Hyperaldosteronisme pnmaire avec hypertension maligne. La Nouvelle Presse medicale 2: 295, 1973 (in French). 1 1) Aloia JF, Beutow G. Malignant hypertension with aldosteronoma producing adenoma. Am J Med Sci 268: 241, ) Baxter RH, Wang I. Malignant hypertension in a patient with Conn's syndrome. Scott Med J 19: 161, ) Iyon S, Saruta T, Kondo K, Ozawa Y, Hata J, Shimizu K. Renin and juxtaglomerular apparatus in a patient with primary aldosteronism complicated by chronic renal failure. South Med J 69: 951, ) Murphy BF, Whitworth JA, Kincaid-Smith P. Malignant hypertension due to an aldosterone producing adrenal adenoma. Clm Exp Hypertens [A] 7: 939, ) Iwaoka T, Umeda T, Sato T, Katsuragi S, Takeuchi T. High plasmarenin activities in primary aldosteronism with malignant hypertension. A case report. Jpn Heart J 21: 423, ) Bravo EL, Fouad-Tarazi FM, Tarazi RC, Pohl M, Gifford RW, Vidt DG. Clinical implications of primary aldosteronism with resistant hypertension. Hypertension ll: 1207, ) Sunman W, Rothwell M, Sever PS. Conn's syndrome can cause malignant hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 6: 75, ) Obana M, Hayakawa Y, Higashi F, et al. A case of primary aldosteronism with chronic renal failure (author's transl). Nippon Jmzo Gakkai Shi 22: 51, 1980 (in Japanese). 19) Inaba M, Nakamura K, Isogai S, et al A case report of primary aldosteronism with bilateral multiple adrenal adenoma Nippon Naika Gakkaishi 66: 128, 1977 (Abstract in Japanese). 704 Internal Medicine Vol. 36, No 10 (October 1997)
High Plasma Renin Activities in Primary Aldosteronism with Malignant Hypertension. A Case Report
 High Plasma Renin Activities in Primary Aldosteronism with Malignant Hypertension A Case Report Taisuke IWAOKA, M.D., Teruhisa UMEDA, M.D., Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Shoichi KATSURAGI, M.D.,* and Tadao TAKEUCHI,
High Plasma Renin Activities in Primary Aldosteronism with Malignant Hypertension A Case Report Taisuke IWAOKA, M.D., Teruhisa UMEDA, M.D., Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Shoichi KATSURAGI, M.D.,* and Tadao TAKEUCHI,
Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1
 Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1 QUESTION 96 A 32yo woman if found to have high blood pressure (180/105mmHg) at an insurance medical examination. She is asymptomatic. Clinical examination
Year 2004 Paper two: Questions supplied by Megan 1 QUESTION 96 A 32yo woman if found to have high blood pressure (180/105mmHg) at an insurance medical examination. She is asymptomatic. Clinical examination
Endocrine. Endocrine as it relates to the kidney. Sarah Elfering, MD University of Minnesota
 Endocrine Sarah Elfering, MD University of Minnesota Endocrine as it relates to the kidney Parathyroid gland Vitamin D Endocrine causes of HTN Adrenal adenoma PTH Bone Kidney Intestine 1, 25 OH Vitamin
Endocrine Sarah Elfering, MD University of Minnesota Endocrine as it relates to the kidney Parathyroid gland Vitamin D Endocrine causes of HTN Adrenal adenoma PTH Bone Kidney Intestine 1, 25 OH Vitamin
Primary Aldosteronism
 Primary Aldosteronism Odelia Cooper, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Cedars-Sinai Medical Center HYPERTENSION CENTER Barriers to diagnosing primary
Primary Aldosteronism Odelia Cooper, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism Cedars-Sinai Medical Center HYPERTENSION CENTER Barriers to diagnosing primary
Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome
 RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Indications for Surgical Removal of Adrenal Glands
 The adrenal glands are orange-colored endocrine glands which are located on the top of both kidneys. The adrenal glands are triangular shaped and measure about one-half inch in height and 3 inches in length.
The adrenal glands are orange-colored endocrine glands which are located on the top of both kidneys. The adrenal glands are triangular shaped and measure about one-half inch in height and 3 inches in length.
Diseases of the Adrenal gland
 Diseases of the Adrenal gland Adrenal insufficiency Cushing disease vs syndrome Pheochromocytoma Hyperaldostronism What are the layers of the adrenal gland?? And what does each layer produce?? What are
Diseases of the Adrenal gland Adrenal insufficiency Cushing disease vs syndrome Pheochromocytoma Hyperaldostronism What are the layers of the adrenal gland?? And what does each layer produce?? What are
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Blood Pressure Regulation 2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the intermediate term and long term regulators of ABP. Describe the role of Epinephrine, Antidiuretic hormone (ADH), Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone
Urinary Kallikrein Excretion in Hypertensive Man
 Urinary Kallikrein Excretion in Hypertensive Man RELATIONSHIPS TO SODIUM INTAKE AND SODIUM-RETAINING STEROIDS By Harry S. Margolius, David Horwttz, John J. Pisano, and Harry R. Kelser ABSTRACT Urinary
Urinary Kallikrein Excretion in Hypertensive Man RELATIONSHIPS TO SODIUM INTAKE AND SODIUM-RETAINING STEROIDS By Harry S. Margolius, David Horwttz, John J. Pisano, and Harry R. Kelser ABSTRACT Urinary
BODY FLUID. Outline. Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid. Regulation of fluid homeostasis
 BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
Endocrine MR. Jan 30, 2015 Michael LaFata, MD
 Endocrine MR Jan 30, 2015 Michael LaFata, MD Brief case 55-year-old female in ED PMH: HTN, DM2, HLD, GERD CC: Epigastric/LUQ abdominal pain, N/V x2 days AF, HR 103, BP 155/85, room air CMP: Na 133, K 3.6,
Endocrine MR Jan 30, 2015 Michael LaFata, MD Brief case 55-year-old female in ED PMH: HTN, DM2, HLD, GERD CC: Epigastric/LUQ abdominal pain, N/V x2 days AF, HR 103, BP 155/85, room air CMP: Na 133, K 3.6,
Renal artery stenosis
 Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
Renal artery stenosis Dr. Alexander Woywodt Consultant Renal Physician, Royal Preston Hospital Preston, 31.10.2007 Menu anatomy of the renal arteries diseases of the large renal arteries atherosclerotic
ADRENAL INCIDENTALOMA. Jamii St. Julien
 ADRENAL INCIDENTALOMA Jamii St. Julien Outline Definition Differential Evaluation Treatment Follow up Questions Case Definition The phenomenon of detecting an otherwise unsuspected adrenal mass on radiologic
ADRENAL INCIDENTALOMA Jamii St. Julien Outline Definition Differential Evaluation Treatment Follow up Questions Case Definition The phenomenon of detecting an otherwise unsuspected adrenal mass on radiologic
ADRENAL GLAND. Introduction 4/21/2009. Among most important and vital endocrine organ. Small bilateral yellowish retroperitoneal organ
 Introduction Among most important and vital endocrine organ ADRENAL GLAND D.Hammoudi.MD Small bilateral yellowish retroperitoneal organ Lies just above kidney in gerota s fascia 2 1 The Adrenal Gland Anatomy
Introduction Among most important and vital endocrine organ ADRENAL GLAND D.Hammoudi.MD Small bilateral yellowish retroperitoneal organ Lies just above kidney in gerota s fascia 2 1 The Adrenal Gland Anatomy
About 20% of the Canadian population
 Mineralocorticoid Hypertension: Common and Treatable Hypertension is the most common chronic disease treated by the primary-care physician. It is now evident that mineralocorticoid hypertension, which
Mineralocorticoid Hypertension: Common and Treatable Hypertension is the most common chronic disease treated by the primary-care physician. It is now evident that mineralocorticoid hypertension, which
Agenda. Management of Accelerated Hypertension (Updated in 2017) Salwa Roshdy Prof. of Cardiology Assiut University CardioEgypt 23/2/2017 2/27/2017
 Management of Accelerated Hypertension (Updated in 2017) By Salwa Roshdy Prof. of Cardiology Assiut University CardioEgypt 23/2/2017 Agenda Definition of Accelerated HTN Pathophysiology & Etiology Prognosis
Management of Accelerated Hypertension (Updated in 2017) By Salwa Roshdy Prof. of Cardiology Assiut University CardioEgypt 23/2/2017 Agenda Definition of Accelerated HTN Pathophysiology & Etiology Prognosis
AVS and IPSS: The Basics and the Pearls William F. Young, Jr., MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, MN, USA
 AVS and IPSS: The Basics and the Pearls William F. Young, Jr., MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, MN, USA 2016 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
AVS and IPSS: The Basics and the Pearls William F. Young, Jr., MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, MN, USA 2016 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
Functional vascular disorders
 Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
Functional vascular disorders Raynaud s phenomenon Raynaud s phenomenon Refers to Intermittent,bilateral attacks of ischemia of the fingers or toes, and sometimes ears or nose. It clinically manifests
SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HYPERTENSION
 SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HYPERTENSION 1. Systolic blood pressure is elevated when it is over: 1. 120mmHg. 2. 130mmHg. 3. 160mmHg. 4. 140mmHg. 5. 150mmHg. 2. Diastolic blood pressure is elevated when it
SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY HYPERTENSION 1. Systolic blood pressure is elevated when it is over: 1. 120mmHg. 2. 130mmHg. 3. 160mmHg. 4. 140mmHg. 5. 150mmHg. 2. Diastolic blood pressure is elevated when it
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Resistant hypertension is defined as blood. Primary Hyperaldosteronism Decoded: A Case of Curable Resistant Hypertension.
 Case Review Primary Hyperaldosteronism Decoded: A Case of Curable Resistant Hypertension Timothy R. Larsen, DO, Wadie David, Susan Steigerwalt, MD, Shukri David, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Section
Case Review Primary Hyperaldosteronism Decoded: A Case of Curable Resistant Hypertension Timothy R. Larsen, DO, Wadie David, Susan Steigerwalt, MD, Shukri David, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Section
Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic
![Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic Heart Failure. Acute. Plasma [NE] (pg/ml) 24 Hours. Chronic](/thumbs/90/103241154.jpg) Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
Heart Failure Heart failure is the inability of the heart to deliver sufficient blood to the tissues to ensure adequate oxygen supply. Clinically it is characterized by signs of volume overload or symptoms
A case of hypokalemia MIHO TAGAWA FIRST DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE NARA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
 A case of hypokalemia MIHO TAGAWA FIRST DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE NARA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Case 57 y.o. male CC: Weakness HPI: About 20 years ago, he developed bilateral lower extremity weakness. Laboratory
A case of hypokalemia MIHO TAGAWA FIRST DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE NARA MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Case 57 y.o. male CC: Weakness HPI: About 20 years ago, he developed bilateral lower extremity weakness. Laboratory
The Work-up and Treatment of Adrenal Nodules
 The Work-up and Treatment of Adrenal Nodules Lawrence Andrew Drew Shirley, MD, MS, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgical-Clinical Department of Surgery Division of Surgical Oncology The Ohio State University
The Work-up and Treatment of Adrenal Nodules Lawrence Andrew Drew Shirley, MD, MS, FACS Assistant Professor of Surgical-Clinical Department of Surgery Division of Surgical Oncology The Ohio State University
had no effect on the production of aldosterone, corticosterone, or cortisol after
 INHIBITION OF THE EFFECTS OF ANGIOTENSIN II ON ADRENAL STEROID PRODUCTION BY DIETARY SODIUM BY WARREN W. DAVIS,* LAWRENCE R. BURWELL,t AND FREDERIC C. BARTTERt ENDOCRINOLOGY BRANCH, NATIONAL HEART INSTITUTE,
INHIBITION OF THE EFFECTS OF ANGIOTENSIN II ON ADRENAL STEROID PRODUCTION BY DIETARY SODIUM BY WARREN W. DAVIS,* LAWRENCE R. BURWELL,t AND FREDERIC C. BARTTERt ENDOCRINOLOGY BRANCH, NATIONAL HEART INSTITUTE,
Malignant Hypertension in North West India. A Hospital Based Study. Bal K. SHARMA, M.D., Gurpreet SINGH, M.D., and Sushil SAGAR, M.D.
 Malignant Hypertension in North West India A Hospital Based Study Bal K. SHARMA, M.D., Gurpreet SINGH, M.D., and Sushil SAGAR, M.D. SUMMARY One hundred and thirty-five patients with malignant hypertension
Malignant Hypertension in North West India A Hospital Based Study Bal K. SHARMA, M.D., Gurpreet SINGH, M.D., and Sushil SAGAR, M.D. SUMMARY One hundred and thirty-five patients with malignant hypertension
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Upon completion, participants should be able to:
 Learning Objectives Upon completion, participants should be able to: Describe the causes of secondary hypertension and the prevalence of primary aldosteronism Discuss the diagnostic approach to primary
Learning Objectives Upon completion, participants should be able to: Describe the causes of secondary hypertension and the prevalence of primary aldosteronism Discuss the diagnostic approach to primary
27 F with new onset hypertension and weight gain. Rajesh Jain Endorama 10/01/2015
 27 F with new onset hypertension and weight gain Rajesh Jain Endorama 10/01/2015 HPI 27 F with hypertension x 1 year BP 130-140/90 while on amlodipine 5 mg daily She also reports weight gain, 7 LB, mainly
27 F with new onset hypertension and weight gain Rajesh Jain Endorama 10/01/2015 HPI 27 F with hypertension x 1 year BP 130-140/90 while on amlodipine 5 mg daily She also reports weight gain, 7 LB, mainly
Approach to patient with hypertension. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal
 Approach to patient with hypertension Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Definition A systolic blood pressure ( SBP) >139 mmhg and/or A diastolic (DBP) >89 mmhg. Based on the average of two or more properly measured,
Approach to patient with hypertension Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Definition A systolic blood pressure ( SBP) >139 mmhg and/or A diastolic (DBP) >89 mmhg. Based on the average of two or more properly measured,
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the rule
 Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College of Medicine and NF/SGVHS The 20-50
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College of Medicine and NF/SGVHS The 20-50
How to Recognize Adrenal Disease
 How to Recognize Adrenal Disease CME Away India & Sri Lanka March 23 - April 7, 2018 Richard A. Bebb MD, ABIM, FRCPC Consultant Endocrinologist Medical Subspecialty Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi
How to Recognize Adrenal Disease CME Away India & Sri Lanka March 23 - April 7, 2018 Richard A. Bebb MD, ABIM, FRCPC Consultant Endocrinologist Medical Subspecialty Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi
Doppler ultrasound, see Ultrasonography. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), kidney oxygenation assessment 75
 Subject Index Acidemia, cardiorenal syndrome type 3 146 Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) acute kidney injury biomarkers, see Acute kidney injury; specific biomarkers cardiorenal syndrome, see specific
Subject Index Acidemia, cardiorenal syndrome type 3 146 Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) acute kidney injury biomarkers, see Acute kidney injury; specific biomarkers cardiorenal syndrome, see specific
Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis
 Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Etiology Fibromuscular
Current Role of Renal Artery Stenting in Patients with Renal Artery Stenosis Young-Guk Ko, M.D. Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Etiology Fibromuscular
Pancreatic Insulinoma Presenting. with Episodes of Hypoinsulinemic. Hypoglycemia in Elderly ---- A Case Report
 2008 19 432-436 Pancreatic Insulinoma Presenting with Episodes of Hypoinsulinemic Hypoglycemia in Elderly ---- A Case Report Chieh-Hsiang Lu 1, Shih-Che Hua 1, and Chung-Jung Wu 2,3 1 Division of Endocrinology
2008 19 432-436 Pancreatic Insulinoma Presenting with Episodes of Hypoinsulinemic Hypoglycemia in Elderly ---- A Case Report Chieh-Hsiang Lu 1, Shih-Che Hua 1, and Chung-Jung Wu 2,3 1 Division of Endocrinology
LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF SURGICAL MENAGEMENT OF PRIMARY ALDOSTERONISM ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SISTEM
 LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF SURGICAL MENAGEMENT OF PRIMARY ALDOSTERONISM ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SISTEM Riccardo Marsili, Pietro Iacconi, Massimo Chiarugi, Giampaolo Bernini*, Alessandra Bacca*, Paolo Miccoli Department
LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF SURGICAL MENAGEMENT OF PRIMARY ALDOSTERONISM ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SISTEM Riccardo Marsili, Pietro Iacconi, Massimo Chiarugi, Giampaolo Bernini*, Alessandra Bacca*, Paolo Miccoli Department
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Transplant Proc. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 July 14.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1990 February ; 22(1): 17 20. The Effects of FK 506 on Renal Function After Liver Transplantation J. McCauley, J.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1990 February ; 22(1): 17 20. The Effects of FK 506 on Renal Function After Liver Transplantation J. McCauley, J.
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA. Anita Chiu, MD Kings County Hospital Center January 13, 2011
 PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA Anita Chiu, MD Kings County Hospital Center January 13, 2011 Case Presentation 62 year old female from Grenada with longstanding HTN, DM, CRI Complaints of palpitations for years Abdominal
PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA Anita Chiu, MD Kings County Hospital Center January 13, 2011 Case Presentation 62 year old female from Grenada with longstanding HTN, DM, CRI Complaints of palpitations for years Abdominal
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE
 LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
LXIV: DRUGS: 4. RAS BLOCKADE ACE Inhibitors Components of RAS Actions of Angiotensin i II Indications for ACEIs Contraindications RAS blockade in hypertension RAS blockade in CAD RAS blockade in HF Limitations
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Secondary Hypertension: A Real World Approach
 Secondary Hypertension: A Real World Approach Evan Brittain, MD December 7, 2012 Kingston, Jamaica Disclosures None Real World Causes Renovascular Hypertension Endocrine Obstructive Sleep Apnea Pseudosecondary
Secondary Hypertension: A Real World Approach Evan Brittain, MD December 7, 2012 Kingston, Jamaica Disclosures None Real World Causes Renovascular Hypertension Endocrine Obstructive Sleep Apnea Pseudosecondary
Mineralocorticoids: aldosterone Angiotensin II/renin regulation by sympathetic tone; High potassium will stimulate and ACTH Increase in aldosterone
 Disease of the Adrenals 1 Zona Glomerulosa Mineralocorticoids: aldosterone Angiotensin II/renin regulation by sympathetic tone; High potassium will stimulate and ACTH Increase in aldosterone leads to salt
Disease of the Adrenals 1 Zona Glomerulosa Mineralocorticoids: aldosterone Angiotensin II/renin regulation by sympathetic tone; High potassium will stimulate and ACTH Increase in aldosterone leads to salt
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
AJH 1998;11: by the American Journal of Hypertension, Ltd /98/$19.00
 AJH 1998;11:8 13 Acute Effects of Intravenous Sodium Chloride Load on Calcium Metabolism and on Parathyroid Function in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism Compared With Subjects With Essential Hypertension
AJH 1998;11:8 13 Acute Effects of Intravenous Sodium Chloride Load on Calcium Metabolism and on Parathyroid Function in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism Compared With Subjects With Essential Hypertension
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Received for Publication: August 7, 2006
 447 Case Report St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 34, pp. 447 453, 2006 Analysis of Interleukin 2 Receptor IL-2R and Type III Procollagen-N-peptide P-III-P in a Case of Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Haruyuki Takama
447 Case Report St. Marianna Med. J. Vol. 34, pp. 447 453, 2006 Analysis of Interleukin 2 Receptor IL-2R and Type III Procollagen-N-peptide P-III-P in a Case of Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Haruyuki Takama
Approach to Adrenal Incidentaloma. Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCP
 Approach to Adrenal Incidentaloma Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCP Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form
Approach to Adrenal Incidentaloma Alice Y.Y. Cheng, MD, FRCP Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted in any form
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Adrenal Mass. Cynthia Kwong SUNY Downstate Medical Center Grand Rounds October 13, 2016
 Adrenal Mass Cynthia Kwong SUNY Downstate Medical Center Grand Rounds October 13, 2016 Case Presentation 65F found to have a 4cm left adrenal mass in 2012 now presents with 6.7cm left adrenal mass PMHx:
Adrenal Mass Cynthia Kwong SUNY Downstate Medical Center Grand Rounds October 13, 2016 Case Presentation 65F found to have a 4cm left adrenal mass in 2012 now presents with 6.7cm left adrenal mass PMHx:
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Endocrine hypertensionmolecules. Marie Freel Caledonian Endocrine Society Meeting 29 th November 2015
 Endocrine hypertensionmolecules and genes Marie Freel Caledonian Endocrine Society Meeting 29 th November 2015 Plan Mineralocorticoid hypertension Myths surrounding Primary Aldosteronism (PA) New developments
Endocrine hypertensionmolecules and genes Marie Freel Caledonian Endocrine Society Meeting 29 th November 2015 Plan Mineralocorticoid hypertension Myths surrounding Primary Aldosteronism (PA) New developments
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
** TMP mean page 340 in 12 th edition. Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2:
 QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
AVS and IPSS: The Basics and the Pearls
 AVS and IPSS: The Basics and the Pearls William F. Young, Jr., MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, MN, USA 2018 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
AVS and IPSS: The Basics and the Pearls William F. Young, Jr., MD, MSc Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, MN, USA 2018 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.
Renal Artery Stenosis With Severe Hypertension: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Renal Artery Stenosis With Severe Hypertension: A Case Report Suwaid MA ABSTRACT Background: Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is found in 77% of hypertensive patients and is responsible for 1-2%
CASE REPORT Renal Artery Stenosis With Severe Hypertension: A Case Report Suwaid MA ABSTRACT Background: Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is found in 77% of hypertensive patients and is responsible for 1-2%
Mannitol-induced Metabolic Alkalosis
 Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
A Closer Look: Renal Artery Stenosis. Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is defined as a TOPICS FROM CHEP. Shawn s stenosis
 TOPICS FROM CHEP A Closer Look: Renal Artery Stenosis On behalf of the Canadian Hypertension Education Program (CHEP), Dr. Tobe gives an overview of renal artery stenosis, including the prevalence, screening
TOPICS FROM CHEP A Closer Look: Renal Artery Stenosis On behalf of the Canadian Hypertension Education Program (CHEP), Dr. Tobe gives an overview of renal artery stenosis, including the prevalence, screening
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the rule
 Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of
Updates in primary hyperaldosteronism and the 20-50 rule I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of
Role of Minerals in Hypertension
 Role of Minerals in Hypertension Lecture objectives By the end of the lecture students will be able to Define primary and secondary hypertention and their risk factors. Relate role of minerals with hypertention.
Role of Minerals in Hypertension Lecture objectives By the end of the lecture students will be able to Define primary and secondary hypertention and their risk factors. Relate role of minerals with hypertention.
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Pharmacologic Management of Hypertension
 Current Concepts In Management of Fernando Vega, MD Secondary - Definition Renovascular Disease (The kidney doesn t get impressed by blood pressure) Renovascular stenosis Renal artery stenosis Fibromuscular
Current Concepts In Management of Fernando Vega, MD Secondary - Definition Renovascular Disease (The kidney doesn t get impressed by blood pressure) Renovascular stenosis Renal artery stenosis Fibromuscular
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency
 Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency Budi Yuli Setianto Cardiology Divisision Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine UGM Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta Background USA: Hypertension is 30% of
Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency Budi Yuli Setianto Cardiology Divisision Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine UGM Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta Background USA: Hypertension is 30% of
Primary Aldosteronism: screening, diagnosis and therapy
 Primary Aldosteronism: screening, diagnosis and therapy Jacques W.M. Lenders, internist DEPT. OF INTERNAL MEDICINE, RADBOUD UNIVERSITY NIJMEGEN MEDICAL CENTER, NIJMEGEN,THE NETHERLANDS DEPT. OF INTERNAL
Primary Aldosteronism: screening, diagnosis and therapy Jacques W.M. Lenders, internist DEPT. OF INTERNAL MEDICINE, RADBOUD UNIVERSITY NIJMEGEN MEDICAL CENTER, NIJMEGEN,THE NETHERLANDS DEPT. OF INTERNAL
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE. Jules B. Puschett, M.D.
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE Jules B. Puschett, M.D. Diuretic Resistance A clinical circumstance in which patients do not respond to a combination of salt restriction and even large
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE Jules B. Puschett, M.D. Diuretic Resistance A clinical circumstance in which patients do not respond to a combination of salt restriction and even large
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
How do I investigate suspected secondary hypertension? Marie Freel RCP Update in Medicine 23 rd November 2016
 How do I investigate suspected secondary hypertension? Marie Freel RCP Update in Medicine 23 rd November 2016 World beaters..! Michel Joffres et al. BMJ Open 2013;3:e003423 Hypertension often poorly controlled
How do I investigate suspected secondary hypertension? Marie Freel RCP Update in Medicine 23 rd November 2016 World beaters..! Michel Joffres et al. BMJ Open 2013;3:e003423 Hypertension often poorly controlled
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries. Duplex Ultrasound. In the Beginning
 Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Duplex Ultrasound of the Renal Arteries DIMENSIONS IN HEART AND VASCULAR CARE 2013 PENN STATE HEART AND VASCULAR INSTITUTE ROBERT G. ATNIP MD PROFESSOR OF SURGERY AND RADIOLOGY Duplex Ultrasound Developed
Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal. Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S.
 1156 Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S. Alpert The purpose of this study was to examine Na + handling and regulation
1156 Patterns of Sodium Excretion During Sympathetic Nervous System Arousal Gregory A. Harshfield, Derrick A. Pulliam, and Bruce S. Alpert The purpose of this study was to examine Na + handling and regulation
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY
 CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma. patients. Supplemental data. First author: Baojun Wang
 Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma patients Supplemental data First author: Baojun Wang Patients and tumor samples A total of 87 patients with
Prevalence and characterization of somatic mutations in Chinese aldosterone-producing adenoma patients Supplemental data First author: Baojun Wang Patients and tumor samples A total of 87 patients with
Oral Calcium Treatment Lowers Blood Pressure in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System
 Hypertension Laboratory Studies Oral Calcium Treatment Lowers Blood Pressure in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System Yo KAGEYAMA, HIROMICHI SUZUKI, KOICHIRO ARIMA,
Hypertension Laboratory Studies Oral Calcium Treatment Lowers Blood Pressure in Renovascular Hypertensive Rats by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System Yo KAGEYAMA, HIROMICHI SUZUKI, KOICHIRO ARIMA,
Karim Said. 41 year old farmer. Referred from the Uro-surgery Department because of uncontrolled hypertension prior to Lt. partial nephrectomy
 Case Presentation Karim Said Cardiology Departement Cairo University 41 year old farmer Referred from the Uro-surgery Department because of uncontrolled hypertension prior to Lt. partial nephrectomy ١
Case Presentation Karim Said Cardiology Departement Cairo University 41 year old farmer Referred from the Uro-surgery Department because of uncontrolled hypertension prior to Lt. partial nephrectomy ١
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 4 CBULP 2010 004 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 4 CBULP 2010 004 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
USMLE PREP LECTURE SERIES Lecture 2.2
 USMLE PREP LECTURE SERIES Lecture 2.2 Elite Medical Prep Guide for Ben Gurion Students from Day 1 to Test day Last Updated: January 17, 2019. Delivered: January 17, 2019 Objectives 5 month planning Flashcards:
USMLE PREP LECTURE SERIES Lecture 2.2 Elite Medical Prep Guide for Ben Gurion Students from Day 1 to Test day Last Updated: January 17, 2019. Delivered: January 17, 2019 Objectives 5 month planning Flashcards:
Tiny Jaarsma Linköping University No conflict of interest
 Detrimental effects of sodium in heart failure - Tiny Jaarsma Linköping University No conflict of interest Sodium restriction in Heart Failure Why? Prevention of heart failure Blood pressure treatment
Detrimental effects of sodium in heart failure - Tiny Jaarsma Linköping University No conflict of interest Sodium restriction in Heart Failure Why? Prevention of heart failure Blood pressure treatment
RESISTENT HYPERTENSION. Dr. Helmy Bakr Professor and Head of Cardiology Dept. Mansoura University
 RESISTENT HYPERTENSION Dr. Helmy Bakr Professor and Head of Cardiology Dept. Mansoura University Resistant Hypertension Blood pressure remaining above goal in spite of concurrent use of 3 antihypertensive
RESISTENT HYPERTENSION Dr. Helmy Bakr Professor and Head of Cardiology Dept. Mansoura University Resistant Hypertension Blood pressure remaining above goal in spite of concurrent use of 3 antihypertensive
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Secondary hypertension is defined as being
 Canadian Coalation for High Blood Pressure Prevention and Control Coalition Canadienne pour la Prévention et le Contrôle de l Hypertension Artérielle Secondary Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management Options
Canadian Coalation for High Blood Pressure Prevention and Control Coalition Canadienne pour la Prévention et le Contrôle de l Hypertension Artérielle Secondary Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management Options
Incidental Findings; Management of patients presenting with high BP. Phil Swales
 Incidental Findings; Management of patients presenting with high BP Phil Swales Consultant Physician Acute & General Medicine University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust Objectives The approach to an incidental
Incidental Findings; Management of patients presenting with high BP Phil Swales Consultant Physician Acute & General Medicine University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust Objectives The approach to an incidental
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management
 AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
AKI Definition : Stages : ( RIFLE vs. AKIN ) Causes and classification : Pre-renal Renal Post- renal Clinical manifestations and Complication Management and indications for RRT Etiology prerenal causes
Urinary system. Urinary system
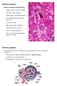 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
