COURSE SYLLABUS AND INSTRUCTOR PLAN
|
|
|
- Sharlene Mae Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 WACO, TEXAS COURSE SYLLABUS AND INSTRUCTOR PLAN BIOL Anatomy & Physiology Specialized 1 Semester Course Heather Mattingly AN EQUAL OPPORTUNITY INSTITUTION Spring
2 Course Description: Study of the structure and function of human anatomy, including the neuroendocrine, integumentary, musculoskeletal, digestive, urinary, reproductive, respiratory, and circulatory systems. Content may be either integrated or specialized. This course is designed to introduce the integrative processes within cells, tissues, organs and body systems associated with human anatomy and physiology. Lecture in combination with laboratory exercises will be utilized to provide a basis for anatomical and physiological processes. This knowledge base will provide a background for selected programs in health careers. Semester Hours 4 (3 lec/3 lab) Prerequisites and/or Corequisites: None Course Notes and Instructor Recommendations: Course Notes will be available on Blackboard. Instructor Information: Instructor Name: Heather Mattingly hmattingly@mclennan.edu Office: CSC C200 Office/Teacher Conference Hours: M/W 9:00-10: 30 and by appointment Phone: Required Text & Materials: Title: Hole s essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Author: Shier Edition: 11th Publisher: McGraw- Hill ISBN: Title: A & P Applications Manual Author: Martini Edition: 9 th Publisher: Benjamin- Cummings Publishing Company ISBN: MCC Bookstore Website 2
3 Methods of Teaching and Learning: The course material will be presented in lecture / lab format. Lecture and discussion in combination with laboratory exercises will provide a basic for anatomical and physiological processes. Lecture power points and other course materials will be posted on blackboard. Course Objectives and/or Competencies: The student will identify the structure of each of the major body systems; describe the functions of each of the major body systems; discuss the interrelationship of systems in maintaining homeostasis. In addition the student will apply the knowledge of selected basic concepts of microbiology and chemistry and related principles of homeostasis in the body with possible variation that result in disease processes. General Objectives: BIOL 2404 is an introductory course designed to introduce the student to the processes and systems of the human body. 1. To be able to read and analyze various printed materials. 2. To demonstrate knowledge of the major issues and problems facing modern science, including issues that touch upon ethics, values, and public policies. 3. To demonstrate critical thinking by using both qualitative and quantitative analysis to evaluate strategies and recognize alternative strategies. Specific course objectives: At the end of the course the learner should be able to: 1. Describe the basic organization of the human body and how homeostasis is maintained via feedback systems. 2. Know basic atomic structure and bonding. Know the structure and function of water and classes of organic compounds as they relate to the human body. 3. Know the basic structure and function of the cell membrane, cell transport process, and cell organelles. 4. Know major tissue types and their functions. Be able to identify tissue types 5. Know the structure and functions of the systems of the human body. Be able to identify specific structures of these systems. 6. Know the basic concepts of heredity and fetal development. Content objectives: A. Body as a Whole After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Review the levels of organization 2- Discuss feedback 3- Define the terms related to body parts 4- Identify the major body regions, cavities, and planes 5- Define anatomy and physiology. 3
4 6- Define homeostasis and explain its importance. B. Chemistry as Metabolism - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Briefly discuss atomic structure and bonding 2- Describe types of bonds and the importance of each 3- Explain the ph scale, acids and bases 4- Discuss properties of water 5- Discuss classes of organic compounds and their importance 6- Define chemical element and list the six elements that form the bulk of body matter. 7- Explain how elements and atoms are related. 8- Define electrolytes. 9- Distinguish between catabolism and anabolism C. The Cell - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Describe structure of the cell membrane 2- Discuss passive and active transport 3- List the cell organelles and functions 4- Explain the importance of mitosis and meiosis 5- Describe the basic sequence of events involved in protein synthesis. 6- Explain the basic concept of DNA replication. 7- List the major events that occur in each stage of mitosis. D. Tissues - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Describe the four categories of tissue, what type of specific tissues are in each type, and their function 2- Identify tissue types (list attached) Adipose Areolar Blood Bone Cardiac muscle Dense connective Elastic cartilage Elastic connective Fibrocartilage Hyaline cartilage Nervous tissue Pseudostratified columnar Simple columnar Simple cuboidal Simple squamous Skeletal muscle Smooth muscle Stratified squamous Transitional epithelium 4
5 E. Integumentary System - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- List the major functions of the skin. 2- Describe the layers of the integument, their major structures and function of the structures. F. Skeletal System - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Describe the functions of the skeletal system 2- Describe the general structure of the bone from a macroscopic and microscopic perspective 3- Define the two main types of bone formation 4- Explain long bone growth 5- List the parts of the axial and appendicular skeleton 6- Describe the major types of joints 7- Describe the four main classifications of bone based upon shape. 8- Identify the major bone markings 9- Identify the major bones and their markings (list attached) Acetabulum Acromion process of scapula Carpals Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Coccyx Coracoid process Coronal suture of skull Costa Cranium Epiphyseal line External auditory meatus Facial bones False ribs Femur Fibula Foramen magnum of occipital bone Frontal bone Frontal sinus Humerus Iliac crest Ilium Ischium Lumbar vertebrae Mandible Manubrium of sternum Mastoid process of temporal bone Maxilla Metacarpals Metatarsals Nasal Occipital bone Parietal bone Patella Phalanges Pubic symphysis Pubis Radius Sacrum Scapula Sphenoid bone Sphenoid sinus Spine of scapula Sternum Styloid process of temporal bone Tarsal Temporal bone Thoracic vertebrae 5
6 Tibia True ribs Ulna Xiphoid process of sternum Zygomatic bone Zygomatic arch G. Muscular System - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Describe the functions of the muscular system 2- List the three types of muscles and their characteristics and functions 3- Define origin, insertion, agonist, and antagonist 4- Explain the importance of nerve impulse for a muscle contraction 5- Briefly explain the sliding filament mechanism 6- Identify the major muscles (list attached) Biceps brachii Biceps femoris Deltoid External intercostals External oblique Forearm muscles -extensors Forearm muscles -flexors Frontal portion of occipitofrontalis Gastrocnemius Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gracilis Latissimus dorsi Masseter Occipital portion of occipitofrontalis Orbicularis oculi Orbicularis oris Pectoralis major Platysma Rectus abdominis Rectus femoris Sartorius Semimembranosis Semitendinosus Serratus anterior Soleus Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis Tibialis anterior Trapezius Triceps brachii Vastus lateralis Vastus medialis H. Nervous System - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- List the functions of the nervous system 2- Describe the major divisions of the nervous system and the parts of each 3- Describe the basic structure of the nerve cell 4- Explain the importance of neurotransmitters 5- Describe the simple reflex 6- Identify the structures of the central nervous system 7- Describe the divisions of the peripheral nervous system 8- Identify the major parts of the brain and their functions 9- Name the three meningeal layers 10- Identify the major structures of the brain (list included) 6
7 Central sulcus Cerebellum Cerebrum Corpus callosum Frontal lobe Hypothalamus Lateral sulcus Longitudinal fissure Midbrain Occipital lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Thalamus Transverse fissure I. Senses - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Briefly describe the structures and functions of the five special senses J. Endocrine System - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- List the functions of the endocrine system 2- Describe how hormones are regulated 3- Identify the major endocrine glands, their hormones, and their functions 4- Define negative feedback and describe its role in regulating hormone concentration and secretion 5- Explain the function of tropic hormones. 6- Identify major endocrine glands (list included) Adrenal glands Ovaries Pancreas Parathyroid gland Pineal gland Pituitary gland Testes Thymus Thyroid gland 7
8 K. Blood - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Explain the functions of blood 2- Describe the composition of blood and the functions of the formed elements 3- Describe clotting 4- Explain blood types L. Heart - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- List the functions of the heart 2- Describe the pericardium 3- Identify the parts of the heart 4- Trace blood flow through the heart 5- Explain conduction in the heart M. Vessels - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Define blood pressure and pulse. Identify several pulse points.. 2- Explain the functions of the circulatory system 3- Describe the features of arteries, veins, and capillaries 4- Compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary circulation 5- Identify the major blood vessels (list attached) Abdominal aorta Aortic arch Ascending aorta Axillary A Axillary V Brachial A Brachiocephalic A Brachiocephalic V Common carotid A Common Iliac A Common Iliac V Coronary Arteries External Carotid A External Iliac A External Iliac V External Jugular V Femoral A Femoral V Great Saphenous V Inferior Vena Cava Internal Carotid A Internal Jugular V Popliteal A Popliteal V Pulmonary A Pulmonary V Radial A Renal A Renal V Subclavian A Subclavian V Superior Vena Cava Thoracic Aorta Ulnar A 8
9 N. Lymphatic and Immunity - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Describe the functions of the lymphatic system 2- Identify the structures of the lymphatic system and their functions O. Respiratory - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- List the functions of the respiratory system 2- Identify the structures of the respiratory system and their functions 3- Trace the flow of air through the respiratory system and name the structures it passes through in order 4- Describe negative pressure breathing 5- Describe how oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the blood. 6- Identify areas of the brain involved in control of respiration. 7- Identify several physical factors that influence respiratory rate. P. Digestive - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- List the functions of the digestive system 2- Identify the structures of the digestive system and their functions 3- Trace the flow of food through the digestive system and name the structures it passes through in order 4- Briefly describe where each class of compound is digested. Q. Urinary - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Describe the functions of the urinary system 2- Identify the major structures of the kidney R. Reproduction - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1- Describe the functions of the reproductive system 2- Identify the structures and functions of the male reproductive system 3- Identify the structures and functions of the female reproductive system S. Development and Heredity - After successful completion of this unit the student will be able to: 1. Explain fertilization? 2. Describe the zygote and explain its significance? 3. Describe the role of implantation and the structure and function of the placenta? 4. Define: a. Ectopic pregnancy
10 BIOL b. Abortion c. Gestation d. Embryo e. Fetus 5. Explain how is the circulatory system of the fetus different from that of an adult. 6. Describe dominant and recessive genes? 7. Explain the difference between Genotype and Phenotype? 8. Explain how Homologous Chromosomes are related to the Diploid Number and the Haploid Number? 9. Explain how the gender of a child determined? 10. Describe a Mutation and how often it is a good thing or beneficial? 11. Identify the two causes of Congenital Defects? Course Schedule: Date Topic Chapters 1/13 Introduction to the course 1/15 Terms, Chemistry 1,2 1/20 Holiday 1/22 The cell 3,4 1/27 Tissues 5 1/29 Integumentary system 6 2/3 Skeletal System 7 2/5 Muscular system 8 2/10 Review 2/12 EXAM 1 Units 1-2 2/17 Nervous system 9 2/19 LAB EXAM /24 Senses 11 10
11 BIOL /26 Endocrine system 11 3/3 Blood 12 3/5 Cardiovascular system 13 3/10-3/16 SPRING BREAK woo hoo 3/17 Lymphatic system 14 3/19 Review 3/24 EXAM 2 Units 3-4 3/26 Digestion and Nutrition 15 3/31 Respiratory system 16 4/2 Urinary system 17 4/7 Water 18 4/9 Reproductive system 19 4/14 Pregnancy & development 20 4/16 EXAM 3 Units 5-6 4/21 Lab review day 4/23 LAB EXAM 2 4/28 Review for final exam 5/5 COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAM *course schedule is tentative and subject to change as needed 11
12 BIOL Course Grading Information: Grade Compilation: Total 100% Written Exams (3) 30% Written Final 20% Lab Exam (2) 30% Quizzes 10% Assignments 10% Total 100% *Note: Grades will NOT be rounded in this course* Make-up exams, written and lab as well as quizzes will be considered only with proper documentation of reason for excused absence and instructor approval. Assignments: Assignments will be given roughly weekly and are designed to enhance learning of material being covered. Quizzes: Quizzes will be given on a weekly or bi-weekly status. Students are expected to review materials prior to meeting for lecture and lab to enhance his/her learning. Quizzes will be totaled at the conclusion of the semester. Late Work, Attendance, and Make Up Work Policies: Attendance: Attendance is essential for attainment of course objectives. A student who is not present at the scheduled start time of class is considered tardy, and three (3) tardies constitute one absence. A student that is more than 30 minutes late will be considered absent. It is the student s responsibility to get any missed class information due to absence or tardiness. Assignments will be accepted late with a 10 point deduction for each day late. MCC Attendance Policy: Regular and punctual attendance is expected of all students, and each instructor will maintain a complete record of attendance for the entire length of each course, including online and hybrid courses. Students will be counted absent from class meetings missed, beginning with the first official day of classes. Students, whether present or absent, are responsible for all material presented or assigned for a course and will be held accountable for such materials in the determination of course grades. Please refer to the Highlander Guide for the complete policy. 12
13 BIOL cellular telephones, and personal telephone calls Students are NOT to receive or place telephone calls during class. Cellular telephones are to be turned off or set to vibrate before entering the classroom. Student Behavioral Expectations or Conduct Policy: Students are expected to maintain professional classroom decorum that includes respect for other students and the instructor, prompt and regular attendance, and an attitude that seeks to take full advantage of the education opportunity. Food/Drink, LAB: Food and drink will ONLY be allowed in the classroom. Students are required to clean up after themselves. If this becomes an issue, food and drink will no longer be allowed. NO FOOD OR DRINK allowed in the lab at any time. Academic Integrity Statement: Students are expected to refrain from academic dishonesty. This includes any conduct aimed at misrepresentation with respect to a student s academic performance. Examples of academic dishonesty include: cheating, plagiarism, collaborating with others if contrary to stated guidelines for assignment, providing students who have not completed exams with information related to the exam, and intentionally assisting another student in any dishonest action. Violations of this policy will be brought to the attention of the student by the instructor. If there is suspicion of wrongdoing without corroborating evidence, the matter will be discussed with the student, and a verbal warning will be issued if warranted. If there is clear evidence that a violation has taken place, the instructor may impose a sanction ranging from a written warning to expulsion from the course with a failing grade. If the student does not feel that the issue is satisfactorily resolved, the student should contact the Math and Science Division Chair. If the issue is not satisfactorily resolved at the end of this process, the student may initiate a formal grievance procedure. The Student Grievance Procedure is outlined in the Highlander Guide: MCC Student Handbook. ADA Statement: In accordance with the requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), and the regulations published by the United States Department of Justice 28 C.F.R (a), MCC s designated ADA coordinators, Dr. Drew Canham Vice President, Student Success and Mr. Gene Gooch - Vice President, Finance and Administration shall be responsible for coordinating 13
14 BIOL the College s efforts to comply with and carry out its responsibilities under ADA. Students with disabilities requiring physical, classroom, or testing accommodations should contact Ms. Renee Jacinto, Disabilities Specialist, Student Services Center, Student Development Department, Room 227 or at or rrjacinto@mclennan.edu TITLE IX No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any education program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance. Legal Citation: Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972, and its implementing regulation at 34 C. F. R. Part 106 (Title IX) In accordance with the requirements of the Title IX Education Amendments of 1972 MCC s designated Title IX Coordinator, Al Pollard Vice President, Program Development/EEO Officer and Deputy Coordinator, Phyllis Blackwood Director of Human Resources shall be responsible for coordinating the College s effort to comply with and carry out its responsibilities under Title IX. Contact information Al Pollard, Title IX Coordinator Vice President, Program Development McLennan Community College Administration Building, Room 417 Administration Building, Room College Drive 1400 College Drive FAX FAX apollard@mclennan.edu pblackwood@mclennan.edu Phyllis Blackwood, Title IX Deputy Coordinator Director, Human Resources McLennan Community College 14
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Nervous & Skeletal Systems. Virtual Science University
 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
Team Members: System:
 Team Members: System: Your team s job is to prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Team Members: System: Your team s job is to prepare a presentation to educate your classmates about one of the body systems that makes up the human body. Your presentation must include the following requirements:
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
The Musculoskeletal system
 Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions
 BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017
 IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
Name: Class: IB SEHS (SL) Teacher: Mrs. Rowe IB SEHS Anatomy Handbook
 Name: Class: IB SEHS (SL) Teacher: Mrs. Rowe strowe@crec.org www.gomlc.com IB SEHS Anatomy Handbook Topic Table of Contents Page Number Intro and Note to Students 3 Anatomical Position - Diagram 4 Anatomical
Name: Class: IB SEHS (SL) Teacher: Mrs. Rowe strowe@crec.org www.gomlc.com IB SEHS Anatomy Handbook Topic Table of Contents Page Number Intro and Note to Students 3 Anatomical Position - Diagram 4 Anatomical
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation
 Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
Chapter 1 - The Human Body: An Orientation A. Terminology I. AN OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 1. Anatomy: To Cut. No analyzing involved. - where things are, how connect to each other - Gross vs. microscopic
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
2. Be able to define and give examples of each of the following planes:
 Anatomy Skeletal and Muscular Systems Part 1: Directional terms, Planes, Body Cavities Lab Materials: male & female surface landmarks models various models, textbook Lab Activities: Use models and charts
Anatomy Skeletal and Muscular Systems Part 1: Directional terms, Planes, Body Cavities Lab Materials: male & female surface landmarks models various models, textbook Lab Activities: Use models and charts
Updated: 3/15/2018 Page 1 of 7
 A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Science MASTER SYLLABUS 2017-2018 C. Course Number and Title: BIOL1730 Basic Anatomy & Physiology D. Course Coordinator: Jeff Taylor Assistant Dean:
A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Science MASTER SYLLABUS 2017-2018 C. Course Number and Title: BIOL1730 Basic Anatomy & Physiology D. Course Coordinator: Jeff Taylor Assistant Dean:
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Exam 3 Self Quiz. Muscle
 Exam 3 Self Quiz Muscle ***Disclaimer- ALL lectured material is fair game for the exam. The instructor DOES NOT guarantee in any way that these questions will be on the exam. The instructor DOES guarantee
Exam 3 Self Quiz Muscle ***Disclaimer- ALL lectured material is fair game for the exam. The instructor DOES NOT guarantee in any way that these questions will be on the exam. The instructor DOES guarantee
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY
 SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
SKELETAL MUSCLE ANATOMY OUTLINE I. Anatomical Terms of Motion II. Head, Face & Neck Muscles III. Anterior Torso Muscles IV. Posterior Torso Muscles V. Arm & Shoulder Muscles VI. Leg & Hip Muscles 2 ANATOMICAL
Anatomy Midterm. 1- In gametogenesis, diploid primary Oocyte cell inter the process of meiosis to produce? b. Haploid egg cell*
 Anatomy Midterm 1- In gametogenesis, diploid primary Oocyte cell inter the process of meiosis to produce? b. Haploid egg cell* 2- Spermatogenesis is a process in which? d. Spermatogonial cells produces
Anatomy Midterm 1- In gametogenesis, diploid primary Oocyte cell inter the process of meiosis to produce? b. Haploid egg cell* 2- Spermatogenesis is a process in which? d. Spermatogonial cells produces
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Bell Work. How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive
 Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Name this muscle. Name this muscle
 this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
this muscle this muscle Pectoralis Major Pectoralis Minor Serratus anterior Pectoralis minor Serratus anterior this muscle Deltoid: The major abductor of the upper limb this muscle this muscle this muscle
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
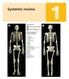 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401
 Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Monday, November 13, 2017 A & P 2401 Today you will complete the following handouts. Study the last part of the handout for this will be on your quiz, which will be on Wednesday. It is titled steps of
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Deborah Allen. Revised date: July, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 120 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Division Chair, Math, Science & Business Ms.
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Practical #1 Checklist Spring 2010
 External Features Caudal fin Clasper Dorsal fins External nares Gill slits Pectoral fin Rostrum Spiracle SHARK CHECK LIST STRUCTURE CHECK Internal Anatomy Digestive system Bile Duct Gall Bladder Rectal
External Features Caudal fin Clasper Dorsal fins External nares Gill slits Pectoral fin Rostrum Spiracle SHARK CHECK LIST STRUCTURE CHECK Internal Anatomy Digestive system Bile Duct Gall Bladder Rectal
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Chapter 6 General Anatomy & Physiology
 Chapter 6 General Anatomy & Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of body structures that can be seen with the eye is called. a. anatomy b. physiology c. kinesiology d. histology ANS: A PTS: 1 REF: Page
Chapter 6 General Anatomy & Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of body structures that can be seen with the eye is called. a. anatomy b. physiology c. kinesiology d. histology ANS: A PTS: 1 REF: Page
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED
 Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
Anatomy and Physiology Workbook LEARN - INSPIRE - SUCCEED Label The Skeletal System Fibula Lumbar vertebrae Patella Sternum Ilium Femur Scapula Phalanges Sacrum Ischium Tarsals Cranium Clavicle Pubis Ribs
1. Define Anatomy and Physiology-
 Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Name Date Anatomy and Physiology Midterm Study Guide Directions: This packet contains an extensive study guide that will help you prepare for the upcoming Midterm Exam. Pace yourself and be prepared to
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
Reason Examine the relationship between homeostasis and stress. Differentiate between negative and positive mechanisms
 Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Learning Objective 1: BODY PLAN AND ORGANIZATION-Students will explore and describe the body plan, organization, and homeostasis. Describe the six levels of structural organization of the human body and
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy
 Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Body System: Team Members: Body System Project
 Body System: Team Members: Body System Project Working with your team, you will research an assigned body system, create a slide presentation, draw a diagram of the system, and present to the class. You
Body System: Team Members: Body System Project Working with your team, you will research an assigned body system, create a slide presentation, draw a diagram of the system, and present to the class. You
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Anatomy & Physiology Semester A EXAM Review
 Anatomy & Physiology Semester A EXAM Review Material from the following chapters / topics will be covered: Prefixes & Suffixes Anatomical & Positional Terminology (Chapter 1) Cells (Chapter 3) Tissues
Anatomy & Physiology Semester A EXAM Review Material from the following chapters / topics will be covered: Prefixes & Suffixes Anatomical & Positional Terminology (Chapter 1) Cells (Chapter 3) Tissues
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Anatomy and physiology for sport
 Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
Human Body System Research Project
 Names: Period: Human Body System Research Project Body System: Research this body system using the following guided research questions. You will use this information to complete your project. You must
Names: Period: Human Body System Research Project Body System: Research this body system using the following guided research questions. You will use this information to complete your project. You must
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Control center! (set point)! (Change is compared! to the set point.)!
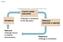 Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
NATURAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT HOSTOS COMMUNITY COLLEGE of THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK
 NATURAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT HOSTOS COMMUNITY COLLEGE of THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK BIO 230 (formerly BIO 3906), ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Section: 4 credits. 3-hr. lecture/3-hr. lab (syllabus: Fall
NATURAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT HOSTOS COMMUNITY COLLEGE of THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK BIO 230 (formerly BIO 3906), ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Section: 4 credits. 3-hr. lecture/3-hr. lab (syllabus: Fall
Anatomy and Physiology 2016
 Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Masseter- in front of ear Temporalis Mandible
 Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Frontal Belly (Epicranius) Occipital Belly (Epicranius) Orbicularis Oculi Orbicularis Oris Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Facial Expression Origin- stays still Raises eyebrows Galea aponeurotica
Lassen Community College Course Outline. I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body.
 Lassen Community College Course Outline HO-54 Basic Structure and Function of the Human Body 3.0 Units I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body. Recommended
Lassen Community College Course Outline HO-54 Basic Structure and Function of the Human Body 3.0 Units I. Catalog Description Basic course focusing on the structure and function of the human body. Recommended
General Anatomy & Physiology
 Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
Wisconsin Indianhead Technical College 10806177 General Anatomy & Physiology Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Instructional Level Total Credits 4.00 Total Hours 80.00 Examines basic
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
ATMORE: BIO201 AN THURSDAY, 12:50-5:20PM ROOM 107
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I REID STATE TECHNICAL COLLEGE SPRING SEMESTER 2017 I. BIO201 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Theory 3 credit hours Lab 1 credit hour Clinical 0 credit hours Total 4 credit hours
Human Anatomy & Physiology I REID STATE TECHNICAL COLLEGE SPRING SEMESTER 2017 I. BIO201 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I Theory 3 credit hours Lab 1 credit hour Clinical 0 credit hours Total 4 credit hours
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Updated: Page 1 of 6
 A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Science MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 C. Course Number and Title: BIOL2751 Human Anatomy & Physiology I D. Course Coordinator: Jeff Taylor, MS Assistant
A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Science MASTER SYLLABUS 2019-2020 C. Course Number and Title: BIOL2751 Human Anatomy & Physiology I D. Course Coordinator: Jeff Taylor, MS Assistant
COWLEY COLLEGE. & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR. HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY I BIO Credit Hours
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore year. Catalog Description:
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore year. Catalog Description:
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES
 UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
the Skeletal System provided by Academic Web Services Grand Canyon University
 Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
List of Muscles and Function. Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows
 List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
List of Muscles and Function Region View Muscle Function Facial Anterior/Oblique Occipitofrontalis front belly Raises eyebrows Orbicularis oculi Closes eye Orbicularis oris Purses lips Zygomaticus minor/major
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
Interactive Notebooks. PowerPoint. Printables. Human. Body. Systems. By: The Discovery Apple
 PowerPoint Interactive Notebooks Printables Human Body Systems By: The Discovery Apple Name: The Human Body PowerPoint Review 1. Food provides us with,, and that our body needs. 2. What is stage four of
PowerPoint Interactive Notebooks Printables Human Body Systems By: The Discovery Apple Name: The Human Body PowerPoint Review 1. Food provides us with,, and that our body needs. 2. What is stage four of
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
The Muscular System. - composed of mostly skeletal muscle tissue, nervous tissue, blood and connective tissue
 The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
The Muscular System Every action the body takes utilizes a muscular activity. Some of the muscles of the body are under voluntary control (skeletal muscles), and by using these muscle, you are able to
Intro Anatomy and Physiology
 Main Arts and Sciences Science Department Intro Anatomy and Physiology BIOL-145 201330 2013 Section All 4 Credits 06/06/2013 to 08/04/2013 Modified 05/22/2013 Description An introductory course in human
Main Arts and Sciences Science Department Intro Anatomy and Physiology BIOL-145 201330 2013 Section All 4 Credits 06/06/2013 to 08/04/2013 Modified 05/22/2013 Description An introductory course in human
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 8 : Appendicular Skeleton 8-1 Appendicular Skeleton Includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs. The girdles of bones that attach the upper
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 8 : Appendicular Skeleton 8-1 Appendicular Skeleton Includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs. The girdles of bones that attach the upper
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE
 HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
HIBBING COMMUNITY COLLEGE COURSE OUTLINE COURSE NUMBER & TITLE: BIOL 2151: Human Physiology CREDITS: 4 (Lecture 3 / Lab 1) PREREQUISITES: Human Anatomy or Integrated Science recommended CATALOG DESCRIPTION:
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
