Neuronal guidance protein semaphorin 7A influences neutrophil arrest and aggravates inflammatory lung injury. Dr. Tiago Granja
|
|
|
- Belinda Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuronal guidance protein semaphorin 7A influences neutrophil arrest and aggravates inflammatory lung injury Dr. Tiago Granja
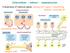
2 Neuronal guidance proteins (NGPs) force cells to move NPGs give axons and dendrites the ability to locate and recognize their appropriate synaptic partners 1 Filopodia filaments are oriented toward the filopodium tip 2 Microtubules stabilize the axon shaft 3 A growth cone drives the filipodia to extend and retract 4 Strong directions stabilise and dilate a single filopodium and following microtubuli
3 Neuronal guidance proteins (NGPs) force cells to move NPGs families and receptors n Semaphorin7A (CDw18) is ligand of: PlexinC1 (CD232) Β1 integrin (CD29) β 1
4 ring The neutrophil recruitment cascade Rolling Adhesion Crawling Transmigration Slow rolling Neutrophil drive: Full arrest Indirect the endothelial leukocyte recruitment signals cascade from tissue involves destruction the fol- (Cytokines, leukotrienes, histamine) Intraluminal crawling Firm Neutrophil adhesion extravasation detection of pathogens that increase expression of adhesi on molecules; within minutes, they upregulate pre- The neutrophil recruitment cascade. In most tissues, stored P-selectin from Weibel Palade bodies. E-selectin, lowing commonly recognized steps: tethering, rolling, which is synthesized de novo, is upregulated within Tethering adhesion, crawling and, finally, carried transmigration by PSGL1,CD62L (FIG. 1). 9 (L-selectin), minutes 2,45. These two selectins have partially overlapping functions and maximize neutrophil recruitment. Neutrophil recruitment is initiated by changes on the Slow surface rolling of endothelium that CD11a/CD18 result from stimulation (LFA1) by (CD62P Once present - P-selectin on the endothelial induced) surface, P-selectin and a Paracellular, inflammatory mediators (including between histamine, cysteinylleukotrienes and cytokines) CD11b/CD18 that endothelial are released cells from (MAC1) tissue- -P-selectin β2 integrins, glycoprotein ligand 1 (PSGL1) 2,46, leading E-selectin bind to their glycosylated ligands, including Adhesion resident sentinel leukocytes when they come into contact Extravasated to the tethering (capturing) of free-flowing neutrophils to Crawling with pathogens 1,2,4. Endothelial MAC1 OR cells can also be activated neutrophil the surface of endothelium and their subsequent rolling directly by pattern-recognition receptor (PRR)-mediated along the vessel in the direction of blood flow (TABLE 1). Direct endothelial signals derived from PPR B oodf o (E-selectin) Transmigration LFA1, MAC1 REVIEWS Rolling Adhesion Crawling Transmigration Extravasated neutrophil Free circulating neutrophil neutrophil Adhering neutrophil Tethering Slow rolling Intraluminal perpendicular crawling Selectin Full arrest b Transcellular via individual cells (potential dome formation a b) Chemokine receptor Firm adhesion Inactive integrin Intraluminal crawling Extravasated neutrophil Integrin ligand Selectin Active Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation Chemokine Rolling neutrophil ligand integrin Kolaczkowska, E. Kubes, P. Nat Rev Immunol; 213 with a tether 1.138/nri3399 Figure 1 The updated classical neutrophil recruitment cascade. Shown are the sequential steps of neutrophil recruitment from the vasculature to the tissue. Two possible methods of transmigration are acknowledged: Nature Reviews Immunology a Paracellular, between endothelial cells OR B oodf o Extravasated neutrophil
5 Lung injury as a model to study Neutrophil recruitment Events during Acute Lung Injury (ALI) Platelet aggregation Endothelial gap formation Neutrophil migration Tissue destruction Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in the injured patient; Magdalena Bakowitz , Brandon Bruns and Maureen McCunn; Scandinavian Journal of Trauma; Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine 212 Release of pro-inflammatory mediators: Fibrin Thrombin MPO TNFα IL6 IL8 IL1β
6 Semaphorin7a is pro-inflammatory NaCl DAPI vwf Sema7a merge NaCl ALI induces the release of proinflammatory cytokines in the lung ALI up-regulates Semaphorin7a in the lung mice have less Platelet-neutrophil complex (PNCs) infiltration
7 Block Sema7a, PlexinC1 and β1 integrin inhibits aggregation Aggregation (Norm. a.u.) Aggregation (AU) Multiplate analysis Whole blood incubated TRAP6 - Thrombin Receptor Activator Peptide 6 - Amino Acid Sequence Ser-Phe-Leu-Leu-Arg-Asn Control CD18 antibody CD29 Antibody PlexinC1 Antibody Semaphorin 7A Antibody - PAR 1 hexapeptide agonist Time (min) TRAP6 Aggregation Inhibition of thrombin derived aggregation by antibody block of: β1 integrin (CD29) Sema7a (CDw18) PlexinC1 (CD232).2 Acquisition of electrical impedance over time. Ctrl CD29 ab CD18 ab SEMA7a ab PLXNC1 ab
8 Neutrophil transmigration (cells/ml) Semaphorin7a slows neutrophils and induce transmigration Primary adhesion with E-Selectin Sema7a ICAM1 ICAM1Sema7a Neutrophils rolling and attach Whole Blood Blood Flow E-selectin E-selectin Semaphorin7a Whole blood from n=5 healthy donors. Capillaries are coated with adhesion molecules PNC transmigration HMEC culture Platelets 1/5 Neutrophils 37 C PNCs E-selectin ICAM-1 E-selectin ICAM-1 Semaphorin7a Semaphorin7a slows Neutrophils in flow Neutrophils isolated from n=5 healthy donors. Platelets isolated and diluted 1/5 Membrane pores of 3µm fmlp as chemoattractant for 9min fmlp 3µm NaCl SEMA7A Semaphorin7a induces Neutrophils to transmigrate
9 s CD11b function is controlled by Semaphorin7a CD66b - FITC CD66b - FITC ICAM1 PerCp (Norm. Freq. of parent) TNFα TNFα Rolling Neutrophils Inactive Neutrophil integrin CD18/CD11b Active Neutrophil integrin CD18/CD11b 85% PMNs Alive % PMNs Dead CD11b block Semaphorin7a ICAM-1 DRAQ7-APC FSC ICAM1 - PerCp Neutrophils were isolated from n=5 healthy donors. 1 Proper controls set for CD11b block Reactions take min TNFα induces ICAM1 adhesion in neutrophils 4 2. Semaphorin7a Alone induces max. ICAM-1 adhesion through CD11b 2 3. Semaphorin7a TNFα inhibits CD11b function Semaphorin7a has different functions during haemostasis and inflammation CD11b Block TNFa Sema7a Sema7a TNFa
10 25min Neutrophil interaction (stationary cells over 1µm) Platelet sedimentation (Norm. a.u.) 2min min Tramsmigration distance (mm) cell transmigration (cell/mm 2 ) 1min 5min Cell speed (mm/sec) Stationary cells (cells/mm 2 ) min i.v. Neutrophils Platelets neutrophils do not adhere Sham Sham Neutrophil rolling Stationary cells Time (min) Time (min) 4 3 Transmigration distance PNC transmigration Time (min) Time (min) 4 3 Neutrophil contact Platelet sedimentation Time (min) Time (min)
11 Neutrophil survey time (sec) Rolling cells after min i.v. PNC buildup aftermin (Platelet fluo. a.u.) PNC buildup after min (Platelet fluo. norm. a.u.) neutrophils do not crosstalk min i.v. min PNC cross section (µm) 2 1 and Semaphorin7a -/- mice are equally able to build PNCs after i.v. Semaphorin7a -/- neutrophils in flow do not crosstalk
12 CD42b -FITC CD42b FITC Platelet Activity Ly6G-/ CD42b High PLTs Ly6G-/ CD42b/ CD62P SSC SSC Platelet Activity Ly6G-/ CD42b High PLTs Ly6G-/ CD42b/ CD62P Ab cocktail incubation (min) Semaphorin7a inhibits Platelet CD62P Scanning for Platelet function Par-4 Whole blood 1 withdrawn from n=5 healthy 25 8 mice per group Platelets were 2 focused by invert gate of 5 FSC 1 CD42 HIgh - FITC FSC CD42b /Ly6G Ly6G - BV421 Ly6G - BV421 CD62P - APC and both hold their platelet reactivity (CD42b-GPIbα) CD62P is not active in mice after thrombin stimulation CD42b - FITC CD42b -FITC
13 CD42b -FITC CD42b FITC SSC SSC Ab cocktail incubation (min) PNC adhesion is inhibited in Understand PNC function Par-4 Whole blood withdrawn from n=5 healthy mice per group PNCs were focused as CD42b /Ly6G FSC FSC Ly6G - PC7 Ly6G - PC7 Ly6G - PC7 Ly6G - PC7
14 PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b PNCs PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b (Med. (Med. Fluo. Fluo. Units) Units) PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 (Med. Fluo. Fluo. Units) PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P PNCs PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Med. (Med. Fluo. Fluo. Units) Units) PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Med. Fluo. Fluo. Units) PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/CD62L PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/CD62L PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/CD62L PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b/CD62L (Med. Fluo. Fluo. Units) PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b Freq. of Parent PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b Freq. of Parent PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b Freq. of Parent PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b Freq. of Parent PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b Freq. of Parent Ab cocktail incubation (min) PNC adhesion is inhibited in Understand PNC function CD62P - APC PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b High PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b High CD42B - FITC CD62L - PerCp PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b High PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b High PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b High Sema7a -/- - mice form less PNCs after stimulation - PNCs from mice have impaired adhesion through: CD62P CD11b LFA1 (CD11a/CD18) CD11b - BV LFA1 -PE
15 SSC CD42b -FITC SSC PNCs Ly6G/ CD42b Freq. of Parent PlexinC1 and β1 integrin control aggregation in vivo Understand PNC function Inhalation (45min) Ab cocktail incubation (min) 8 6 CD18 block CD232 block CD29 block After inhalation blood was withdrawn Samples were separately blocked and stained PNCs were focused as Ly6G /CD42 FSC 4 2 inhalation - PlexinC1 (CD232) blocks - β1 integrin (CD29) blocks - β2 integrin (CD18) Ly6G - BV421 Ly6G - BV421
16 Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 (Mean Fluo. PE) Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 (Mean Fluo. PE) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b (Mean Fluo. Pac. Blue) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b (Mean Fluo. Pac. Blue) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Mean Fluo. APC) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62L (Mean Fluo. PerCp) SSC Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Mean Fluo. APC) SSC Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Mean Fluo. APC) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62L (Mean Fluo. PerCp) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62L (Mean Fluo. PerCp) Ly6G/ CD42b (Freq. of Parent) Ly6G/ CD42b/ JON/A (Mean Fluo. PE) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD42b (Mean Fluo. FITC) Ly6G/ CD42b (Freq. of Parent) Ly6G/ CD42b (Freq. of Parent) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD42b (Mean Fluo. FITC) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD42b (Mean Fluo. FITC) Platelets from Sema7a-/- mice have impaired function Scanning for Platelet function Inhalation (45min) Ab cocktail incubation (min) untreated FSC CD42b - FITC 1 5 JON/A - PE /- - and are able to build PNCs 2 - PNCs from 1 mice have 5 impaired function of Platelet: JON/A (active GPIIb/IIIa) CD62P d 25 2 Ly6G - BV d CD62P - APC d d Reconstitution 1 with induces injury (gain 5 of function)
17 Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 (Mean Fluo. PE) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b (Mean Fluo. Pac. Blue) SSC SSC Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 (Mean Fluo. PE) Ly6G/ CD42b/ LFA1 (Mean Fluo. PE) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b (Mean Fluo. Pac. Blue) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Mean Fluo. APC) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD11b (Mean Fluo. Pac. Blue) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62L (Mean Fluo. PerCp) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Mean Fluo. APC) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62P (Mean Fluo. APC) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62L (Mean Fluo. PerCp) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD62L Ly6G/ (Mean CD42b Fluo. (Freq. PerCp) of Parent) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD42b (Mean Fluo. FITC) Ly6G/ CD42b (Freq. of Parent) Ly6G/ CD42b (Freq. of Parent) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD42b (Mean Fluo. FITC) Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD42b (Mean Fluo. FITC) Sema7a induces PNC adhesion -/- 2 1 Understand PNC function Inhalation (45min) CD62L - PerCp Ab cocktail incubation (min) 2 untreated 1 5 CD62L 1 CD11b - PNCs from mice have impaired adhesion through neutrophil: 5 LFA1 (CD11a/CD18) FSC CD11b - BV Reconstitution with induces injury (gain of function) Ly6G - BV421 LFA-1 - PE 5 1
18 Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD29 (Mean Fluo. PE) PlexinC1 is chemorepulsive, β1 integrin is chemoattactive Understand PNC function Inhalation (45min) Ab cocktail incubation (min) untreated 1 Integrin ß1 (CD29) Relative transcript expression Ly6G/ CD42b/ CD232 (Mean Fluo. PE) Plexin C1 (CD232) Relative transcript expression CD232 - PE Whole Blood Lung CD29 - PE Whole Blood Lung PlexinC1 is not regulated during inhalation in and mice β1 integrin (CD29) expression increases in the blood and is maximum in the lung Reconstitution with in induces PlexinC1 expression after 45min inhalation
19 Summary Semaphorin7a controls cell communication during haemostasis and inflammation Neutrophil Platelet Blood Flow Neutrophils from Semaphorin7a -/- mice ( i.v.) Keep Rolling speed Have no stationary cells Do not trans-migrate Do not cross-talk PlexinC1 Semaphorin7a α1β1 Inactive α1β1 active Neutrophil Free Cells Platelet Activated PNC formation Semaphorin7a-/- mice under inflammation have impaired - Platelet adhesion, CD62P, JON/A (active GPIIb/IIIa), - neutrophil adhesion, CD62L, CD11b, CD11a, CD18 PNC Arrest Sema7a PlexinC1 is chemorepulsive between PMNs and PLTs (haemostasis) Sema7a β1 integrin is a chemoattractant between PMNs and PLTs (inflammation)
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Supplementary Information
 Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Nature Immunology doi:1.138/ni.2477 Supplementary Information Capillary and arteriolar pericytes attract innate leukocytes exiting through venules and instruct them with pattern recognition and motility
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Intercellular indirect communication
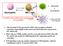
 Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Inflammation I. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Inflammation I Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD http://library.med.utah.edu/webpath/exam/m ULTGEN/examidx.htm 2 ILOs Distinguish between acute and chronic inflammation with respect to causes, nature of the inflammatory
Inflammation I Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD http://library.med.utah.edu/webpath/exam/m ULTGEN/examidx.htm 2 ILOs Distinguish between acute and chronic inflammation with respect to causes, nature of the inflammatory
Brain barriers control immune cell trafficking to the CNS. Britta Engelhardt Theodor Kocher Institute University of Bern - Switzerland
 Brain barriers control immune cell trafficking to the CNS Britta Engelhardt Theodor Kocher Institute University of Bern - Switzerland The brain barriers 2 The BBB establishes a physical and metabolic barrier
Brain barriers control immune cell trafficking to the CNS Britta Engelhardt Theodor Kocher Institute University of Bern - Switzerland The brain barriers 2 The BBB establishes a physical and metabolic barrier
Homing and Inflammation!
 Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
The Immune Response in Time and Space
 The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
Fisher et al. Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A TNF IL-1 IL-6 CCL2 CCL5 CXCL10 pg/mg total protein 50 30 10 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000 n.d. 1 1 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 6,000,000 CT26 5,000 16,000 B16 4,000 12,000
Supplemental Figure 1 A TNF IL-1 IL-6 CCL2 CCL5 CXCL10 pg/mg total protein 50 30 10 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000 n.d. 1 1 14,000 12,000 10,000 8,000 6,000 4,000 2,000 6,000,000 CT26 5,000 16,000 B16 4,000 12,000
1) Mononuclear phagocytes : 2) Regarding acute inflammation : 3) The epithelioid cells of follicular granulomas are :
 Pathology Second 1) Mononuclear phagocytes : - Are the predominant cells in three day old wounds - Are common in liver, spleen and pancreasd - Produce fibroblast growth factor - Secrete interferon-g -
Pathology Second 1) Mononuclear phagocytes : - Are the predominant cells in three day old wounds - Are common in liver, spleen and pancreasd - Produce fibroblast growth factor - Secrete interferon-g -
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Homing and Inflammation!
 Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Homing and Inflammation! Micro 204. Molecular and Cellular Immunology! Lecturer: Jason Cyster! jason.cyster@ucsf.edu! How do cells migrate from blood into tissue?! the four step model! role of selectins,
Loss of HS1 inhibits neutrophil extravasation during. inflammation via disturbed PKA signaling. IV. Immunology Summit, Houston,
 Loss of HS1 inhibits neutrophil extravasation during inflammation via disturbed PKA signaling IV. Immunology Summit, Houston, 29.09.2015 Michael Schnoor, PhD Center for Research and Advanced Studies, (Cinvestav-IPN),
Loss of HS1 inhibits neutrophil extravasation during inflammation via disturbed PKA signaling IV. Immunology Summit, Houston, 29.09.2015 Michael Schnoor, PhD Center for Research and Advanced Studies, (Cinvestav-IPN),
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Table 1
 Supplementary Table 1 Flow Cytometry Antibodies Antibody Fluorochrome Clone Vendor CD45 PE-cyanine 7 30-F11 D ioscience CD3 Pacific lue 17A2 iolegend (San Diego, CA) CD11b APC M1/70 iolegend (San Diego,
Supplementary Table 1 Flow Cytometry Antibodies Antibody Fluorochrome Clone Vendor CD45 PE-cyanine 7 30-F11 D ioscience CD3 Pacific lue 17A2 iolegend (San Diego, CA) CD11b APC M1/70 iolegend (San Diego,
Monocytes must also leave the circulation in response to inflammatory signals, and neutrophils and other granulocytes must be able to do so as well.
 Immunology Dr. John J. Haddad Chapter 15 Leukocyte Migration and inflammation Lymphocytes must recirculate in the body in search of antigens. Since antigens are brought to lymph nodes and the spleen, the
Immunology Dr. John J. Haddad Chapter 15 Leukocyte Migration and inflammation Lymphocytes must recirculate in the body in search of antigens. Since antigens are brought to lymph nodes and the spleen, the
Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Endogenous TNFα orchestrates the trafficking of neutrophils into and within lymphatic vessels during acute inflammation Samantha Arokiasamy 1,2, Christian Zakian 1, Jessica Dilliway
Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions
 INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions Sequence of Vascular Events 1. Vasodilation (increased blood flow) CALOR & RUBOR 2. Increased microvascular permeability: fluids into tissues TUMOR 3. Blood flow slows
INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions Sequence of Vascular Events 1. Vasodilation (increased blood flow) CALOR & RUBOR 2. Increased microvascular permeability: fluids into tissues TUMOR 3. Blood flow slows
CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay
 Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 215 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 215 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
PHM142 Lecture 3: Phagocytes + Granulocytes
 PHM142 Lecture 3: Phagocytes + Granulocytes 1 Constituents of Blood (erythrocytes) Cellular Elements (leukocytes) (~35-55%) (thrombocytes) 2 White Blood Cells: Division of Labour (60%) (1-4%) (2-9%) (20-40%)
PHM142 Lecture 3: Phagocytes + Granulocytes 1 Constituents of Blood (erythrocytes) Cellular Elements (leukocytes) (~35-55%) (thrombocytes) 2 White Blood Cells: Division of Labour (60%) (1-4%) (2-9%) (20-40%)
Homing properties of mesenchymal stromal cells
 Homing properties of mesenchymal stromal cells Karlien Kallmeyer and Michael S. Pepper Corresponding Author Prof. Michael S. Pepper Department of Immunology Faculty of Health Sciences University of Pretoria
Homing properties of mesenchymal stromal cells Karlien Kallmeyer and Michael S. Pepper Corresponding Author Prof. Michael S. Pepper Department of Immunology Faculty of Health Sciences University of Pretoria
Platelet function in diabetes
 Platelet function in diabetes Agneta Siegbahn, MD, PhD, FESC Professor Clinical Coagulation Science Department of Medical Sciences and Uppsala Clinical Research Center Uppsala University Disclosures: None
Platelet function in diabetes Agneta Siegbahn, MD, PhD, FESC Professor Clinical Coagulation Science Department of Medical Sciences and Uppsala Clinical Research Center Uppsala University Disclosures: None
Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer?
 Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer? Małgorzata Lipinska-Gediga Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Medical University Wroclaw,
Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer? Małgorzata Lipinska-Gediga Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Medical University Wroclaw,
Cell Mediated Immunity CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY. Basic Elements of Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI) Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
 Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Chapter 16 CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY Cell Mediated Immunity Also known as Cellular Immunity or CMI The effector phase T cells Specificity for immune recognition reactions TH provide cytokines CTLs do the
Novel model for in vivo imaging of large arteries in steady state and atherosclerosis using 2 photon microscopy
 Fakultät für Medizin Klinikum rechts der Isar Novel model for in vivo imaging of large arteries in steady state and atherosclerosis using 2 photon microscopy A comparison of the role of Mac-1 integrin
Fakultät für Medizin Klinikum rechts der Isar Novel model for in vivo imaging of large arteries in steady state and atherosclerosis using 2 photon microscopy A comparison of the role of Mac-1 integrin
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
The Expression of Adhesion Molecule and ARDS. Asrar B. Malik and Masashi Bando
 The Expression of Adhesion Molecule and ARDS Asrar B. Malik and Masashi Bando Introduction The acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a process of nonhydrostatic pulmonary edema and hypoxemia associated
The Expression of Adhesion Molecule and ARDS Asrar B. Malik and Masashi Bando Introduction The acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), a process of nonhydrostatic pulmonary edema and hypoxemia associated
Disturbance of leucocyte circulation and adhesion to the endothelium as factors in circulatory pathology
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 1996; 77: 17 31 Disturbance of leucocyte circulation and adhesion to the endothelium as factors in circulatory pathology D. H. ADAMS AND G. B. NASH Advances in molecular
British Journal of Anaesthesia 1996; 77: 17 31 Disturbance of leucocyte circulation and adhesion to the endothelium as factors in circulatory pathology D. H. ADAMS AND G. B. NASH Advances in molecular
Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15)
 Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15) I. General types of immunity (Chapter 15 introduction) a. Innate i. inborn ii. pattern recognition b. Adaptive i. "learned" through exposure
Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15) I. General types of immunity (Chapter 15 introduction) a. Innate i. inborn ii. pattern recognition b. Adaptive i. "learned" through exposure
De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 2nd partie
 De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 2nd partie Christophe Dubois INSERM UMR-S1076, Faculté de Pharmacie,
De l'utilisation de la microscopie intravitale pour étudier la thrombose in vivo et tester de nouveaux médicaments antithrombotiques- 2nd partie Christophe Dubois INSERM UMR-S1076, Faculté de Pharmacie,
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology For The First Class 2 nd Semester Thrombocytes = Platelets Thrombocytes = Platelets Blood platelets are non-nucleated disc like cell fragments 2-4 µm in diameter. Platelets are not
Anatomy and Physiology For The First Class 2 nd Semester Thrombocytes = Platelets Thrombocytes = Platelets Blood platelets are non-nucleated disc like cell fragments 2-4 µm in diameter. Platelets are not
20.GEM GEM4 Summer School: Cell and Molecular Biomechanics in Medicine: Cancer Summer 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 20.GEM GEM4 Summer School: Cell and Molecular Biomechanics in Medicine: Cancer Summer 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 20.GEM GEM4 Summer School: Cell and Molecular Biomechanics in Medicine: Cancer Summer 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Hemostasis and Thrombosis
 Hemostasis Hemostasis and Thrombosis Normal hemostasis is a consequence of tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid state in normal vessels, yet also permit the rapid formation of a hemostatic
Hemostasis Hemostasis and Thrombosis Normal hemostasis is a consequence of tightly regulated processes that maintain blood in a fluid state in normal vessels, yet also permit the rapid formation of a hemostatic
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties
 Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Innate immune cells---- one time migration preprogrammed homing properties neutrophils---acute inflammation monocytes---subacute/chronic inflammation eosinophils---parasitic or allergic inflammation natural
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Effect of Toll-like Receptor agonists. on platelet activation in Acute Coronary. Syndromes
 Effect of Toll-like Receptor agonists on platelet activation in Acute Coronary Syndromes Michael Chen-Xu 2012 University of Otago, Wellington Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree
Effect of Toll-like Receptor agonists on platelet activation in Acute Coronary Syndromes Michael Chen-Xu 2012 University of Otago, Wellington Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Targeting neuroinflammation in the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer s disease
 Drugs of the Future 2017, 42(1): 21-42 Copyright 2017 Clarivate Analytics CCC: 0377-8282/2017 DOI: 10.1358/dof.2017.042.01.2564104 Review Article Targeting neuroinflammation in the treatment and prevention
Drugs of the Future 2017, 42(1): 21-42 Copyright 2017 Clarivate Analytics CCC: 0377-8282/2017 DOI: 10.1358/dof.2017.042.01.2564104 Review Article Targeting neuroinflammation in the treatment and prevention
NEUTROPHIL-PLATELET INTERACTION
 NEUTROPHIL-PLATELET INTERACTION Johnny Nijm, MD; PhD Specialist in Internal medicine, Cardiology & Clinical Physiology Department of Medicine Diagnostic, Division of Clinical Physiology, County Hospital
NEUTROPHIL-PLATELET INTERACTION Johnny Nijm, MD; PhD Specialist in Internal medicine, Cardiology & Clinical Physiology Department of Medicine Diagnostic, Division of Clinical Physiology, County Hospital
VWF other roles than hemostasis. Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis 11/4/16. Structure/function relationship & functions kDa.
 VWF other roles than hemostasis Len$ng PJ, Casari C et al JTH 2012 Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis Structure/function relationship & functions (HMWM) 20.000kDa multimerization propeptide FVIII GPIb
VWF other roles than hemostasis Len$ng PJ, Casari C et al JTH 2012 Summary 1: VWF & hemostasis synthesis Structure/function relationship & functions (HMWM) 20.000kDa multimerization propeptide FVIII GPIb
Micro 204. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier
 Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
Micro 204 Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes (CTL) Lewis Lanier Lewis.Lanier@ucsf.edu Lymphocyte-mediated Cytotoxicity CD8 + αβ-tcr + T cells CD4 + αβ-tcr + T cells γδ-tcr + T cells Natural Killer cells CD8 + αβ-tcr
IL-6: a regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation
 Opinion TRENDS in Immunology Vol.24 No.1 January 2003 25 IL-6: a regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation Gilles Kaplanski 1, Valérie Marin 1,Félix Montero-Julian
Opinion TRENDS in Immunology Vol.24 No.1 January 2003 25 IL-6: a regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation Gilles Kaplanski 1, Valérie Marin 1,Félix Montero-Julian
Supplementary Figure 1. mtor LysM and Rictor LysM mice have normal cellularity and percentages of hematopoe>c cells. a. Cell numbers of lung, liver,
 a. b. c. Supplementary Figure 1. mtor LysM and Rictor LysM mice have normal cellularity and percentages of hematopoe>c cells. a. Cell numbers of lung, liver, and spleen. b. Cell numbers of bone marrow
a. b. c. Supplementary Figure 1. mtor LysM and Rictor LysM mice have normal cellularity and percentages of hematopoe>c cells. a. Cell numbers of lung, liver, and spleen. b. Cell numbers of bone marrow
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Dept. Immunology, RPCI Jan. 29 & Feb 3, 2015
 Adhesion Molecules And Lymphocyte Homing Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Dept. Immunology, RPCI Jan. 29 & Feb 3, 2015 Outline General introduction to lymphocyte trafficking homeostatic recirculation vs active recruitment.
Adhesion Molecules And Lymphocyte Homing Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Dept. Immunology, RPCI Jan. 29 & Feb 3, 2015 Outline General introduction to lymphocyte trafficking homeostatic recirculation vs active recruitment.
The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD
 The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body Aird WC. Circ Res 2007 Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body The endothelium should be viewed for what it is:
The Study of Endothelial Function in CKD and ESRD Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body Aird WC. Circ Res 2007 Endothelial Diversity in the Human Body The endothelium should be viewed for what it is:
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Acute and Chronic Inflammation Pathology 1 - Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Injurious stimuli cause a protective vascular connective tissue reaction called inflammation Acute and chronic forms o Inflame
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Pathologic Stage. Lymph node Stage
 ASC ASC a c Patient ID BMI Age Gleason score Non-obese PBMC 1 22.1 81 6 (3+3) PBMC 2 21.9 6 6 (3+3) PBMC 3 22 84 8 (4+4) PBMC 4 24.6 68 7 (3+4) PBMC 24. 6 (3+3) PBMC 6 24.7 73 7 (3+4) PBMC 7 23. 67 7 (3+4)
ASC ASC a c Patient ID BMI Age Gleason score Non-obese PBMC 1 22.1 81 6 (3+3) PBMC 2 21.9 6 6 (3+3) PBMC 3 22 84 8 (4+4) PBMC 4 24.6 68 7 (3+4) PBMC 24. 6 (3+3) PBMC 6 24.7 73 7 (3+4) PBMC 7 23. 67 7 (3+4)
Chapter 2 Leukocyte Kinetics and Migration in the Lungs
 Chapter 2 Leukocyte Kinetics and Migration in the Lungs Prithu Sundd and Margaret F. Bennewitz Introduction The primary function of the lungs is to enable the oxygenation of venous blood [1]. The blood
Chapter 2 Leukocyte Kinetics and Migration in the Lungs Prithu Sundd and Margaret F. Bennewitz Introduction The primary function of the lungs is to enable the oxygenation of venous blood [1]. The blood
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
CytoSelect Leukocyte- Endothelium Adhesion Assay
 Product Manual CytoSelect Leukocyte- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 210 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leukocyte extravasation into perivascular
Product Manual CytoSelect Leukocyte- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 210 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leukocyte extravasation into perivascular
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Microparticles- Signaling in Atherothrombosis Agneta Siegbahn, MD, PhD, FESC Professor in Coagulation Science
 Microparticles- Signaling in Atherothrombosis Agneta Siegbahn, MD, PhD, FESC Professor in Coagulation Science Department of Medical Sciences and Uppsala Clinical Research Center, Uppsala University Uppsala,
Microparticles- Signaling in Atherothrombosis Agneta Siegbahn, MD, PhD, FESC Professor in Coagulation Science Department of Medical Sciences and Uppsala Clinical Research Center, Uppsala University Uppsala,
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy
 Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Review Questions: Janeway s Immunobiology 8th Edition by Kenneth Murphy Chapter 11 (pages 429-460): Dynamics of Adaptive Immunity prepared by Kelly von Elten, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center,
Trauma Resuscitation: more than just blood products
 Trauma Resuscitation: more than just blood products Benjamin T. Houseman, MD, PhD Assistant Professor in Residence Department of Anesthesia University of California San Francisco Traumatic injury Leading
Trauma Resuscitation: more than just blood products Benjamin T. Houseman, MD, PhD Assistant Professor in Residence Department of Anesthesia University of California San Francisco Traumatic injury Leading
Disabled-2 regulates platelet heterotypic and homotypic aggregation through sulfatide binding
 Disabled-2 regulates platelet heterotypic and homotypic aggregation through sulfatide binding John Douglas Welsh Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Disabled-2 regulates platelet heterotypic and homotypic aggregation through sulfatide binding John Douglas Welsh Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
LECTURE: 13 Title: MACROPHAGE "MONOCYTES" SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Describe the blood monocytes (size, and shape of nucleus). Enumerate some of the monocytes
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Ann Biomed Eng. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 May 5.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ann Biomed Eng. 2008 April ; 36(4): 661 671. doi:10.1007/s10439-008-9445-8. Hydrodynamic Shear Rate Regulates Melanoma-Leukocyte Aggregation,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Ann Biomed Eng. 2008 April ; 36(4): 661 671. doi:10.1007/s10439-008-9445-8. Hydrodynamic Shear Rate Regulates Melanoma-Leukocyte Aggregation,
Control of leukocyte rolling velocity in TNF- induced inflammation by LFA-1 and Mac-1
 PHAGOCYTES Control of leukocyte rolling velocity in TNF- induced inflammation by LFA-1 and Mac-1 Jessica L. Dunne, Christie M. Ballantyne, Arthur L. Beaudet, and Klaus Ley Introduction Previously it was
PHAGOCYTES Control of leukocyte rolling velocity in TNF- induced inflammation by LFA-1 and Mac-1 Jessica L. Dunne, Christie M. Ballantyne, Arthur L. Beaudet, and Klaus Ley Introduction Previously it was
La Trombosi Arteriosa
 La Trombosi Arteriosa Prof. Giovanni Davì Medicina Interna Chieti Platelet activation and thrombosis Harrison 19 edizione Platelets are essential for primary hemostasis and repair of the endothelium They
La Trombosi Arteriosa Prof. Giovanni Davì Medicina Interna Chieti Platelet activation and thrombosis Harrison 19 edizione Platelets are essential for primary hemostasis and repair of the endothelium They
Macrophages and Exosomes Employ Brain Inflammation for CNS Delivery of Therapeutics A. Kabanov
 Macrophages and Exosomes Employ Brain Inflammation for CNS Delivery of Therapeutics A. Kabanov Targeting Brain Inflammation in Disease Biochemical studies of brains from individuals with many neurologic
Macrophages and Exosomes Employ Brain Inflammation for CNS Delivery of Therapeutics A. Kabanov Targeting Brain Inflammation in Disease Biochemical studies of brains from individuals with many neurologic
Cell Signaling (part 1)
 15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
Hydrodynamic Shear Rate Regulates Melanoma-Leukocyte Aggregation, Melanoma Adhesion to the Endothelium, and Subsequent Extravasation
 Annals of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 36, No. 4, April 2008 (Ó 2008) pp. 661 671 DOI: 10.1007/s10439-008-9445-8 Hydrodynamic Shear Rate Regulates Melanoma-Leukocyte Aggregation, Melanoma Adhesion to the
Annals of Biomedical Engineering, Vol. 36, No. 4, April 2008 (Ó 2008) pp. 661 671 DOI: 10.1007/s10439-008-9445-8 Hydrodynamic Shear Rate Regulates Melanoma-Leukocyte Aggregation, Melanoma Adhesion to the
Basis of Immunology and
 Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Innate vs Adaptive Response
 General Immunology Innate vs Adaptive Response Innate- non-specific (4 types of barriers) anatomic- ato mechanical ca (skin), ph, mucous, normal flora Physiologic- temperature, ph, chemicals (lysozyme,
General Immunology Innate vs Adaptive Response Innate- non-specific (4 types of barriers) anatomic- ato mechanical ca (skin), ph, mucous, normal flora Physiologic- temperature, ph, chemicals (lysozyme,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Application Information Bulletin: Human NK Cells Phenotypic characterizing of human Natural Killer (NK) cell populations in peripheral blood
 Application Information Bulletin: Human NK Cells Phenotypic characterizing of human Natural Killer (NK) cell populations in peripheral blood Christopher A Fraker, Ph.D., University of Miami - Miami, Florida
Application Information Bulletin: Human NK Cells Phenotypic characterizing of human Natural Killer (NK) cell populations in peripheral blood Christopher A Fraker, Ph.D., University of Miami - Miami, Florida
Vulnerable Plaque. Atherothrombosis
 Vulnerable Plaque Nuove acquisizioni sull'aterosclerosi: placca vulnerabile Marina Camera Dip. Scienze Farmacologiche, Facoltà di Farmacia, Università degli Studi di Milano & Laboratorio di Biologia Cellulare
Vulnerable Plaque Nuove acquisizioni sull'aterosclerosi: placca vulnerabile Marina Camera Dip. Scienze Farmacologiche, Facoltà di Farmacia, Università degli Studi di Milano & Laboratorio di Biologia Cellulare
Leukocyte Rolling Velocities and Migration Are Optimized by Cooperative L-Selectin and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Functions
 This information is current as of November 24, 2018. Leukocyte Rolling Velocities and Migration Are Optimized by Cooperative L-Selectin and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Functions Takafumi Kadono,
This information is current as of November 24, 2018. Leukocyte Rolling Velocities and Migration Are Optimized by Cooperative L-Selectin and Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 Functions Takafumi Kadono,
Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Med. doi:10.1038/nm.3547; corrected online 25 August 2014 Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines Christine Schauer, Christina
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Med. doi:10.1038/nm.3547; corrected online 25 August 2014 Aggregated neutrophil extracellular traps limit inflammation by degrading cytokines and chemokines Christine Schauer, Christina
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
CD40L TCR IL-12 TLR-L
 CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
CD40L B cells plasmacells Neutrophils TCR inkt cells IL-12 Ab production Can inkt cells modulate the cytokine profile of neutrophils? TLR-L CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses 1. The invariant TCR expressed
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Postarrest stalling rather than crawling favors CD8 + over CD4 + T-cell migration across the blood brain barrier under flow in vitro
 Eur. J. Immunol. 2016. 46: 2187 2203 DOI: 10.1002/eji.201546251 Henriette Rudolph et al. 2187 Tissue immunology and leukocyte trafficking Research Article Postarrest stalling rather than crawling favors
Eur. J. Immunol. 2016. 46: 2187 2203 DOI: 10.1002/eji.201546251 Henriette Rudolph et al. 2187 Tissue immunology and leukocyte trafficking Research Article Postarrest stalling rather than crawling favors
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection. All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention. Infusates/ drugs. hub/lines Dressing
 Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
Dissertation. zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades. der Naturwissenschaften. vorgelegt beim Fachbereich 14. der Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität
 Investigations into the influence of pretubulysin and other microtubule-targeting agents on the interaction of endothelial cells with tumor cells and leukocytes Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades
Investigations into the influence of pretubulysin and other microtubule-targeting agents on the interaction of endothelial cells with tumor cells and leukocytes Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW
 MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
Ex vivo modelling of the formation of inflammatory platelet leucocyte aggregates and their adhesion on endothelial cells, an early event in sepsis
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-018-0526-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ex vivo modelling of the formation of inflammatory platelet leucocyte aggregates and their adhesion on endothelial cells, an early event in sepsis
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-018-0526-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ex vivo modelling of the formation of inflammatory platelet leucocyte aggregates and their adhesion on endothelial cells, an early event in sepsis
Platelet Neutrophil crosstalk in thrombotic disorders Dimitrios A. Stakos
 Platelet Neutrophil crosstalk in thrombotic disorders Dimitrios A. Stakos Assistant professor of Cardiology Cardiology Dept. & Laboratory of Molecular Hematology DUTH, Alexandroupolis Aspects of the common
Platelet Neutrophil crosstalk in thrombotic disorders Dimitrios A. Stakos Assistant professor of Cardiology Cardiology Dept. & Laboratory of Molecular Hematology DUTH, Alexandroupolis Aspects of the common
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Ch 12. Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses
 Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
Ch 12 Host Defenses I: Nonspecific Defenses SLOs Differentiate between innate and adaptive immunity. Define and explain PRRs and PAMPs Differentiate physical from chemical factors, and list examples of
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments
 02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
Impedance whole blood electrical aggregometry:
 Impedance whole blood electrical aggregometry: Measurements, evaluation and interpretation of aggregometry outcomes Cezary Watała Department of Haemostatic Disorders Medical University of Lodz cwatala@csk.umed.lodz.pl
Impedance whole blood electrical aggregometry: Measurements, evaluation and interpretation of aggregometry outcomes Cezary Watała Department of Haemostatic Disorders Medical University of Lodz cwatala@csk.umed.lodz.pl
