Interleukin 31, a cytokine produced by activated T cells, induces dermatitis in mice
|
|
|
- Warren Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interleukin 31, cytokine produced y ctivted T cells, induces dermtitis in mice Stcey R Dillon 1,8, Cindy Sprecher 2,8, Angel Hmmond 2, Jnine Bilsorough 1, Mrylnd Rosenfeld-Frnklin 3, Scott R Presnell 4, Hrld S Hugen 5, Mrk Murer 1, Brndon Hrder 1, Jnet Johnston 1, Susn Bort 1, Sherri Mudri 1, Joseph L Kuijper 2, Tom Bukowski 6, Pmel She 6, Dennis L Dong 6, Mri Dsovich 2, Frncis J Grnt 4, Lunn Lockwood 5, Steven D Levin 2, Cosette LeCiel 5, Kim Wggie 3, Hether Dy 7, Stvros Topouzis 7, Jnet Krmer 2, Rolf Kuestner 2, Zhi Chen 5, Don Foster 2, Juli Prrish-Novk 2 & Jne A Gross 1 T cell derived cytokines re importnt in the development of n effective immune response, ut when dysregulted they cn promote disese. Here we identify four-helix undle cytokine we hve clled interleukin 31 (IL-31), which is preferentilly produced y T helper type 2 cells. IL-31 signls through receptor composed of IL-31 receptor A nd oncosttin M receptor. Expression of IL-31 receptor A nd oncosttin M receptor mrna ws induced in ctivted monocytes, wheres epithelil cells expressed oth mrnas constitutively. Trnsgenic mice overexpressing IL-31 developed severe pruritis, lopeci nd skin lesions. Furthermore, IL-31 receptor expression ws incresed in disesed tissues derived from n niml model of irwy hypersensitivity. These dt indicte tht IL-31 my e involved in promoting the dermtitis nd epithelil responses tht chrcterize llergic nd non-llergic diseses. The skin is highly specific immune defense orgn, with epithelium composed minly of kertinocytes interspersed with epiderml Lngerhns cells, T lymphocytes nd mcrophges 1. Externl chllenge to the skin is followed y n epiderml response, including relese of chemotctic fctors tht initite the migrtion of vrious inflmmtory cells to the site of injury. T cells re recruited from the loodstrem nd re ctivted in response to foreign ntigens presented y locl ntigen-presenting cells 2. Activted T cells relese cytokines tht interct with cells in the locl environment to further oost the protective immune response. In norml conditions, these infiltrting T cells undergo poptosis or leve the skin once the inflmmtory stimuli re withdrwn. Pthology occurs when T cells persist in the skin nd receive prolonged ntigenic stimultion 2. Thus, the function (nd dysfunction) of T cell is ultimtely tied to its migrtory ctivity nd relese of cytokines into the locl environment 2. These nd other oservtions sustntite the ide tht T cells nd the cytokines they produce re involved in the development of pruritis nd llergic nd non-llergic conditions, including psorisis nd oth topic nd non-topic dermtitis 3,4. Notly, nerly 80% of children with topic dermtitis develop llergic rhinitis or sthm, disese tht involves n llergic response medited y T helper type 2 (T H 2) cells 4. Cytokines comprise lrge fmily of secreted proteins tht regulte diverse cellulr progrms (prolifertion, survivl nd mturtion) nd re essentil for the development nd function of the immune, hemtopoietic nd nervous systems. The ctivities of cytokines re medited through lignd-induced oligomeriztion of dimeric receptor complex. A suset of cytokine receptors, clssified s type 1, shres common structurl fetures within the extrcellulr region, including four conserved cysteines in the N-terminl segment nd tryptophn-serine doulet ner the C-terminl end 5. Further clssifiction shows sufmily of type 1 cytokine receptors composed of gp130-relted chins tht shre either n immunogloulin type C2 like domin t the N terminus or type III fironectin domins t the C terminus, or oth. The receptor chins most closely relted to gp130 in this sufmily include leukemi inhiitory fctor receptor (LIFR), oncosttin M receptor (), gp130-like monocyte receptor (GLMR), interleukin 12 receptor β2 (IL-12Rβ2) nd IL-23R 5. The newest memer of the gp130-relted chins, GLMR 6, lso known s GPL 7, is signling receptor chin possily involved in the development nd function of monocytes nd mcrophges, ut no cognte lignd for this receptor hs een found 6. We hve identified four splice vrints of gp130-like type 1 cytokine receptor, IL-31RAv1 to IL-31RAv4, one of which is highly homologous to GLMR 6. We used functionl cloning pproch, sed on prolifertion of cells ering IL-31RA nd other receptors of the gp130 fmily, to clone the cytokine IL-31. IL-31 ws mde minly y ctivted T cells nd ws produced in lrger mounts in T H 2 thn Deprtments of 1 Immunology, 2 Cytokine Biology, 3 Pre-clinicl Development, 4 Scientific Computing, 5 Genetics, 6 Protein Biochemistry nd 7 In Vitro Biology, ZymoGenetics, 1201 Estlke Avenue Est, Settle, Wshington 98102, USA. 8 These uthors contriuted eqully to this work. Correspondence should e ddressed to J.A.G. (grossj@zgi.com). Pulished online 6 June 2004; doi: /ni VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY 2004 NATURE IMMUNOLOGY
2 in T H 1 cells. IL-31 signled vi the heterodimeric receptor composed of IL-31RA nd tht is expressed constitutively on epithelil cells nd kertinocytes. These cells responded to IL-31 stimultion nd re likely to e involved in the dermtitis nd pruritis of trnsgenic mice overexpressing IL-31. IL-31 receptors lso were upregulted in lung epithelium nd roncholveolr lvge cells derived from n niml model of irwy hypersensitivity. Our chrcteriztion of IL-31 suggests tht this T cell derived cytokine my e involved in promoting skin disorders nd in regulting other llergic diseses such s sthm. RESULTS Receptor identifiction A serch of trnslted humn genomic sequence with known cytokine receptor sequences identified n exon encoding prt of LIFR-like cytokine receptor. Susequent cdna cloning produced four splice vrints of type 1 cytokine receptor, IL-31RAv1 IL- 31RAv4, with sequence nd domin similrity to LIFR, gp130 nd grnulocyte colony-stimulting fctor receptor (Fig. 1). The v1, v3 nd v4 vrints encoded receptors ering cytokine-inding domin with the chrcteristic tryptophn-serine doulet found in ll type 1 cytokine receptors, three fironectin type III domins, trnsmemrne domin, nd cytoplsmic ox 1 nd ox 2 signling motifs 5. The fct tht IL-31RA ws 28% identicl to gp130 nd the presence of the prototypicl fironectin type III domins in its extrcellulr domin mke IL-31RA prt of the gp130-sufmily of type 1 cytokine receptors. The v4 vrint, which we used in our studies, differed from v1 in its signl peptide, wheres the v3 vrint (the vrint most closely relted to GLMR 6 ) ws longer in the cytoplsmic domin, contining three dditionl tyrosine residues. The v2 vrint encoded puttive solule receptor, consisting of the cytokine-inding domin nd one fironectin type III domin. We isolted two c v1 v2 v3 v4 S RLU (10 3 ) CBD FnIII domins TMD 0 Control + IL IL Con.Rec sil-31ra Y Y Box1/2 Y Y Y splice vrints of mouse IL-31RA mrna trnscripts s cdna from mouse testis lirry, one homologous to humn v4 version nd the other solule form consisting of the cytokine-inding domin nd three fironectin type III domins. Full-length mouse IL-31RA shred 61% identity with the humn mino cid sequence. Identifiction of IL-31 A chimeric receptor composed of the extrcellulr domin of c-mpl (proto-oncogene Mpl; the receptor for thromopoietin 8 ) fused with the cytoplsmic domin of humn IL-31RAv4 or IL-31RAv3 signled in response to thromopoietin (dt not shown). However, s memer of the gp130 IL-6 receptor fmily, IL-31RA proly functions s heterodimer. Therefore, we constructed series of BF3 (ref. 9) cell lines expressing humn IL-31RA lone or in comintion with gp130, IL-12Rβ1, IL-12Rβ2, IL-27RA (WSX-1), IL-23R or 5. We ssyed ech cell line for prolifertion in response to known cytokines or to conditioned medi generted from resting nd ctivted cells from different sources. Cells expressing only IL-31RA nd proliferted in response to conditioned medi derived from ctivted humn peripherl T cells nd from n ctivted T cell line, CCRF- CEM. A solule form of IL-31RA, composed of the extrcellulr domin of IL-31RA fused to the Fc portion of humn immunogloulin G1 (IgG1), prtilly locked prolifertion, demonstrting specificity of the stimulus (dt not shown). We identified cdna from n ctivted T cell cdna lirry tht, when trnslted into protein, stimulted prolifertion in the ssy descried ove. We clled the corresponding gene IL31. The cdna encoded previously unknown 164 mino cid precursor nd predicted mture polypeptide of 141 mino cids contining the four helicl undles (representing secondry structure of four α-helices) tht chrcterize this fmily of cytokines (Fig. 1). Bsed on the overll length nd expected helix nd loop extents, IL-31 is proly hil SHTLPVRLLRPSDDVQKIVEELQSLSKMLLKD--VEEEKGV 39 mil TCSLSFGAPISKEDLRTTIDLLKQESQDLYNNYSIKQASGM 42 LVSQNYTLPCLSPDAQPPNNIHSPAIRAYLKTIRQLDNKSVIDEI 84 SADESIQLPCFSLDREALTNISVIIAHLEKVKVLSE-NTVDTSWV 86 IEHLDKLIFQDAPETNISVPTDTHE---CKRFILTISQQFSECMD 127 IRWLTNISCFNPLNLNISVPGNTDESYDCKVFVLTVLKQFSNCMA 131 LALKSLTSGAQQATT 141 ELQAKDNTTC 141 d STAT1 STAT3 STAT5 IL-31RAv3 IL-31RAv4 Counts Fluorescence units Figure 1 IL-31 signls through IL-31RA nd. () Four splice vrints of humn IL-31RA. S, signl peptide; CBD, cytokine-inding domin; FnIII, fironectin type III; TMD, trnsmemrne domin; Box1/2, cytoplsmic ox 1 nd ox 2 signling motifs; Y, loction of tyrosine in the cytoplsmic domin. () Alignment of the humn (h) nd mouse (m) IL-31 mino cid sequences; the four α-helices re in old. (c) Stimultion of luciferse-linked STAT reporter with IL-31 (200 ng/ml; lck rs) or mouse IL-3 (gry rs) in BF3 trnsfectnts expressing oth IL-31RA nd. Dt re presented s reltive light units (RLU; men ± s.d. from three experiments). Bottom, ddition of solule IL-31RA (sil-31ra; 25, 3 nd 0.4 µg/ml) or n irrelevnt control receptor (Con.Rec.; 25 µg/ml). (d) STAT phosphoryltion in BF3 cells trnsfected with plus either IL-31RAv3 or IL-31RAv4, stimulted with IL-31 (solid lines) or left unstimulted (dshed lines), nlyzed y intrcellulr immunofluorescence flow cytometry. NATURE IMMUNOLOGY VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY
3 Brin Hert Kidney Liver Sk muscle Colon Sm intestine Uterus Plcent Testis Adrenl glnd Slivry glnd Thyroid Trche Spleen Thymus Bone mrrow ARTICLES memer of the short-chin cytokine group 5,10 tht hs no pprent homology to other known four helicl undle cytokines. We cloned mouse cdna encoding IL-31 (mouse Il31) from mouse testis lirry; its predicted mture mino cid sequence shred 31% identity with the humn sequence (Fig. 1). Humn IL31 mpped to chromosome 12q24.31, nd the mouse gene ws locted in syntenic region of mouse chromosome 5 (dt not shown). This fct, nd the oservtion tht mouse IL-31 delivered prolifertive signl in BF3 cells ering mouse IL-31RA nd (dt not shown), indictes tht this gene is the mouse ortholog of humn IL31. Humn IL-31 stimulted luciferse reporter contining elements responsive to the trnscriptionl ctivtors STAT1, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5 nd STAT6 in cell lines ering plus either IL-31RAv3 or IL-31RAv4 (Fig. 1c), ut not in cells ering either IL-31RA or lone (dt not shown). This ctivity ws locked in dose-dependent wy with solule IL-31RA protein ut ws not locked y control Fc protein. IL-31 ctivted STAT1, STAT3 nd STAT5 ut not STAT6, s mesured y intrcellulr immunofluorescence stining of phosphorylted STATs 11 in BF3 trnsfectnts expressing plus either IL-31RAv3 or IL-31RAv4 (Fig. 1d). This confirmed tht oth splice vrints of IL-31RA re cple of signling y phosphoryltion of the sme STAT proteins. Expression reltive to GUS Tissue distriution of IL-31 We used quntittive rel-time PCR to chrcterize expression of IL31 in humn tissues nd in resting nd ctivted purified cell popultions (Fig. 2). We detected low expression of IL-31 mrna in testis, one mrrow, skeletl muscle, kidney, colon, thymus, smll intestine nd trche (Fig. 2). Among lymphoid nd myeloid cell susets, ctivted CD4 + T cells expressed IL-31 mrna, with lower expression in ctivted CD8 + cells. Neither resting nor ctivted nturl killer cells or monocytes, or resting B cells, expressed detectle IL-31 mrna (Fig. 2). Short-term kinetic nlysis indicted tht mouse IL-31 mrna ws expressed erly fter mouse T cell ctivtion (within 3 6 h) stimulted with ntiody to CD3 (nti-cd3) nd nti-cd28 or with these ntiodies plus conditions used to skew cell popultions towrd T H 1 or T H 2 (Fig. 2c). Expression of mouse IL-31 mrna ws higher in T cells ctivted in T H 2-skewing conditions. To confirm this, we produced T H 1 nd T H 2 cell popultions from C57BL/6 or DO11.10 TCR-trnsgenic mice nd ctivted the cells for 4 8 d with nti-cd3 nd nti-cd28 or with ovlumin (OVA) ntigen, respectively. In oth cses the T H 2 cell susets hd higher expression of mouse IL-31 mrna (Fig. 2d). We otined similr expression pttern for humn IL-31 mrna with humn T H 1- nd T H 2-skewed cell susets (dt not shown). Therefore, IL-31 represents previously unknown T cell derived cytokine preferentilly ut not exclusively mde y T H 2 cells. Expression reltive to GUS CD19 CD14 CD14 Activ NK NK Activ CD4 Rest CD4 Activ CD8 Rest CD8 Activ c 1.6 d 0.70 Expression reltive to trnsferrinr Expression reltive to trnsferrinr Stim (h) Anti-CD3 nd nti-cd28 T H 1 T H N T H 1 T H 2 N T H 1 T H 2 CD4 D Figure 2 Expression nlysis of IL-31 y rel-time PCR. IL-31 mrna expression ws ssigned units sed on its expression reltive to tht of the housekeeping genes β-glucuronidse (GUS;,) or trnsferrin receptor (trnsferrinr; c,d). RNA smples were prepred from humn tissues () nd from resting (, lck rs; Rest) or ctivted (, gry rs; Activ) peripherl lood derived lymphocyte susets. Sk, skeletl; Sm, smll; NK, nturl killer. (c) Short-term kinetic nlysis of IL-31 mrna expression in BALB/c T cells ctivted with nti-cd3 nd nti-cd28 (lck rs) or with nti-cd3 plus nti-cd28 in comintion with conditions skewing towrd T H 1 (gry rs) or T H 2 (htched rs). Stim, stimultion. (d) Comprison of IL-31 mrna expression in freshly isolted C57BL/6 nive CD4 + T cells (N), C57BL/6 CD4 + T cells skewed towrd T H 1 or T H 2 for 4 d (lck rs), DO11.10 TCR-trnsgenic nive cells (N) or ntigen-ctivted DO11.10 TCR-trnsgenic cells skewed towrd T H 1 or T H 2 for 8 d (gry rs). 754 VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY 2004 NATURE IMMUNOLOGY
4 Skin Thymus Trche Bone mrrow Brin Testis IL-31RA CD4 20 h ct. CD4 4 h ct. CD Mono IFN-γ LPS Mono LPS Mono IFN-γ Mono IL-31RA Expression reltive to GUS Skin Thymus Trche Bone mrrow Brin Testis IL-31RA Expression reltive to HPRT Figure 3 Expression nlysis of IL-31RA nd mrna in humn nd mouse smples y rel-time PCR. IL-31RA mrna expression (gry rs) nd (lck rs) mrna in humn tissues nd cells reltive to GUS mrna expression () or in mouse tissues reltive to hypoxnthine gunine phosphoriosyl trnsferse (HPRT) mrna expression (). Mono, monocyte; ct., ctivted. Tissue distriution of IL-31 receptors We determined the expression pttern of oth humn IL-31RA nd to help elucidte IL-31 trget cell popultions. RNA lot nlysis of vriety of humn nd mouse tissues showed IL-31RA mrna ws present in low undnce nd could e identified only in trche, skeletl muscle, thymus, nd peripherl lood lymphocytes (9.5-k trnscript) nd in plcent, one mrrow nd thyroid (1.2-k trnscript; dt not shown). We lso detected IL-31RA mrna expression y quntittive PCR in testis, rin, one mrrow, trche, thymus nd skin (Fig. 3). expression ws more uiquitous nd could lso e detected in these tissues, with the most mrna in trche, thymus nd skin (Fig. 3). Humn IL-31RA mrna, lthough undetectle in fresh peripherl lood monocytes, ws upregulted sustntilly in monocytes cultured with interferon-γ (IFN-γ). mrna expression ws induced in monocytes treted with lipopolyscchride, nd together lipopolyscchride nd IFN-γ induced expression of oth receptors (Fig. 3). Mouse IL-31RA mrna ws present in skin, testis, one mrrow nd thymus (Fig. 3). Mouse monocytes nd myeloid linege cells otined from peripherl lood lymphocyte, spleen nd peritonel exudtes did not express mouse IL-31RA mrna, even fter stimultion (dt not shown). The expression of humn nd mouse IL-31RA mrna in ctivted humn nd mouse myeloid cell popultions nd in tissue-derived mcrophges remins to e evluted. Biologicl ctivities We nlyzed humn IL-31RA nd expression in RNA smples derived from trnsformed nd primry cell types to determine other potentil trgets of IL-31 ctivity. Severl cell lines derived from humn epithelil, endothelil nd mesenchyml lineges expressed oth receptors. IL-31 induced STAT reporter ctivtion (from 2- to 11-fold over sl mounts) in cell lines expressing oth IL-31RA nd (Supplementry Tle 1 online). The cell lines included lung nd prostte epithelil cells, osteosrcoms, norml humn epiderml kertinocytes (NHEKs; Supplementry Tle 1 online), smll irwy epithelil cells nd humn microvsculr endothelil cells (dt not shown). Anlysis of STAT ctivtion y flow cytometry showed tht STAT3 ws the min STAT ctivted in these primry cells (dt not shown). These dt indicted tht NHEKs nd epithelil cells expressed oth IL-31RA nd nd responded to IL-31 stimultion y ctivting STATs. STAT1, STAT3 nd STAT5 were ctivted in trnsfectnts expressing IL-31RA nd (Fig. 1d), ut cell lines nd primry cells expressing ntive receptors signled minly with STAT3. To determine the genes induced y IL-31 in NHEKs, we used gene rry nlysis surveying expression of pnel of cytokines nd chemokines induced y IL-31. Severl chemokine genes were induced (from 3- to 9.5-fold) in the NHEKs stimulted with humn IL-31 (Supplementry Tle 2 nd Supplementry Note online), including those encoding GRO1α, (CXCL1), TARC, (CCL17), MIP3β, (CCL19), MDC (CCL22), MIP-3 (CCL23), MIP-1β (CCL4) nd I-309, wheres expression of most other interleukins nd cytokines ws not ffected. The induction of chemokines y IL-31 stimultion indictes tht IL-31 my e involved in recruitment of polymorphonucler cells, monocytes nd T cells to site of skin inflmmtion in vivo. IL-31-trnsgenic mice develop dermtitis We generted trnsgenic mice overexpressing mouse IL-31, driven y the lymphocyte-specific promoter-enhncer Eµ-Lck or the uiquitous promoter from elongtion fctor-1α (EF1α), to evlute the effects of IL-31 in vivo. The serum of EF1α trnsgenic mice contined ng/ml of mouse IL-31, wheres the serum of Eµ-Lck trnsgenic mice contined ng/ml (dt not shown). Both types of IL-31-trnsgenic mice developed notle skin phenotype round 4 8 weeks of ge consisting of piloerection followed y mild to severe lopeci (Supplementry Tle 3 online). The trnsgenic skin ws lso very pruritic, s evidenced y the scrtching ehvior of the mice, often excessive enough to induce excorition nd skin lesions. We monitored 82 mice over 6-month period to ssess the overll frction of IL-31-trnsgenic founder mice nd their offspring tht develop the skin phenotype (Supplementry Tle 3 online). By 2 months of ge, more thn 25% of the trnsgenic mice hd mild to moderte hir loss nd most of the trnsgenic mice lso hd considerle epiderml thickening of the er pinne, with IL-31-trnsgenic ers mesuring up to 2.5 times thicker thn those of their nontrnsgenic littermtes. As the mice ged, hir loss ws noted over lrger re of the ody, nd 67% of the mice developed conjunctivitis nd swelling round the eye. By 6 months of ge, % of the mice hd developed moderte to severe hir loss ccompnied y severe pruritis. Microscopic nlysis of lesionl nd nonlesionl skin of trnsgenic mice showed mny ltertions, prticulrly in the lesionl skin. These fetures, including hyperkertosis, cnthosis, inflmmtory cell infiltrtion nd n increse in mst cells (Fig. 4), closely resemled those of lesionl skin from ptients with topic dermtitis 4. We noted no ovious pthologicl chnges in the lung, intestine, stomch, prostte or rin of the dult IL-31-trnsgenic mice (dt not shown). In vivo effects of IL-31 To rule out potentil developmentl function of IL-31 overexpression in the trnsgenic mice, we first reconstituted irrdited recomintion ctivting gene 1 deficient (Rg1 / ) mice with one mrrow NATURE IMMUNOLOGY VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY
5 from IL-31trnsgenic mice, nd found tht these mice lso developed similr severe dermtitis (dt not shown). Next we gve purified mouse IL-31 protein (20 µg mouse IL-31 per dy) to dult BALB/c or C57BL/6 mice vi sucutneous insertion of mini-osmotic pumps for 7 or 14 d. Within 3 4 d fter pump implnttion, oth strins of mice developed severe pruritis followed y multiple ptchy regions of lopeci. This phenotype ws induced when mice were given s little s 0.2 µg mouse IL-31 per dy (dt not shown). The pruritis continued for n dditionl 6 9 d fter the pumps were removed ut cesed y out dys 20 23, nd y out dy 40 the mice hd lmost fully regrown hir in res of prior lopeci. Unlike the IL-31-trnsgenic mice, none of the IL-31 protein treted BALB/c or C57BL/6 mice developed skin lesions. This suggests tht development of lesions my rise over time from the excessive scrtching ehvior of the mice, s in ptients with topic dermtitis 4. We lso nlyzed peripherl lymphoid tissues nd one mrrow from oth IL-31-trnsgenic nd IL-31 protein treted mice. Peripherl lymph nodes from IL-31-trnsgenic mice were enlrged generlly two- to fivefold reltive to those of their nontrnsgenic littermtes, even in nonlesionl trnsgenic mice (dt not shown). We consistently found n inverse rtio of B cells to T cells in the trnsgenic lymph nodes nd n incresed proportion of ctivted nd memory T cells reltive to nive T cells, prticulrly in the CD4 + suset (Fig. 5). Effects of IL-31 on T cells in the spleen were more vrile from mouse to mouse nd were much less pronounced c Figure 4 IL-31-trnsgenic lesionl skin is chrcterized y mny hllmrks of topic dermtitis. ( c) Histopthology of prffin-emedded sections of norml nontrnsgenic skin (), IL-31-trnsgenic hirless skin () nd IL-31- trnsgenic lesionl skin (c) stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin. Originl mgnifiction, 20. (d f) For specific visuliztion of infiltrting mst cells, skin sections were stined with toluidine lue: norml nontrnsgenic skin (d), IL-31-trnsgenic hirless skin (e) nd IL-31-trnsgenic lesionl skin (f). Arrows indicte mst cells. Originl mgnifiction, 20. d e f thn effects in the peripherl lymph nodes (dt not shown). We found similr ut less notle results in the peripherl lymph node nd spleens from mice treted with purified IL-31 (dt not shown). We found no overt chnges in the thymus or one mrrow of IL-31-trnsgenic mice. In contrst to other mouse models of dermtitis 12 14, only smll frction of IL-31-trnsgenic mice showed mildly incresed concentrtions of serum IgE nd/or IgG 1, nd these mounts were still within the norml rnge ( ng/ml of IgE nd ng/ml of IgG1; dt not shown). These dt suggest tht IL-31 does not cuse sustntil chnges in the development of lymphoid nd myeloid linege cells or in the ctivtion stte of these cells. The incresed mounts of ctivted nd memory T cells in lymphoid orgns from IL-31-trnsgenic mice my e induced through secondry effects from infection cused y IL-31-induced scrtching. The low concentrtions of serum IgE nd IgG 1 in IL-31-trnsgenic mice suggest tht IL-31 induces lopeci nd pruritis in n IgE-independent wy, s in ptients with non-topic dermtitis 4. CD3 CD62L 62% B220 CD44 NonTg 61% 26% 9% 68% 25% 3% 36% CD4+ 35% IL-31 Tg 34% 48% 16% 45% 45% 7% 63% CD4 + CD8 + Figure 5 IL-31-trnsgenic mice hve enlrged peripherl lymph nodes contining n inverted rtio of T lymphocytes to B lymphocytes nd n incresed numer of ctivted CD4 + nd CD8 + T cells. Cell suspensions were prepred from peripherl (cervicl, inguinl, xillry nd rchil), lymph nodes isolted from nontrnsgenic mice (NonTg; left) nd IL-31- trnsgenic mice (IL-31 Tg; right), then were stined with fluorescenceleled mas to vriety of cell surfce mrkers nd were nlyzed y flow cytometry. () Peripherl lymph node cells stined with phycoerythrinconjugted ma to CD3 nd tricolor-conjugted ma to B220. Numers indicte the percentge of totl live cells in ech gted ox (CD3 + B220 T cells or CD3 B220 + B cells). () Peripherl lymph node cells were stined with nti-cd62l, nti-cd44 nd nti-cd4 or nti-cd8 nd were gted on CD4 + or CD8 + cells. Numers indicte the percentge of totl live cells in ech gted ox. CD62L + CD44 lo T cells re considered nive; CD62L + CD44 int hi re considered ctivted or centrl memory; nd CD62L CD44 hi cells re considered effector memory VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY 2004 NATURE IMMUNOLOGY
6 We dministered mouse IL-31 y osmotic pump to lymphocytedeficient Rg1 / mice to determine whether lymphocytes re required for IL-31-induced dermtitis. Rg1 / mice treted with mouse IL-31 developed pruritis, ut hir loss ws sustntilly reduced nd delyed. C57BL/6 control mice in the sme experiment developed rpid nd severe lopeci (dt not shown). This indictes tht IL-31 cn induce pruritis in the sence of lymphocytes, wheres lymphoid cells nd/or their products re needed to cuse lopeci. We next determined the effects of locl delivery of IL-31 on dult skin physiology. We injected mouse IL-31 directly into the dermis of BALB/c mice once dily (20 µg per dy) for 8 consecutive dys. We killed mice on dy 8 nd did microscopic nlysis of skin iopsies t the site of IL-31 injections compred with contrlterl skin iopsies tht hd een injected with PBS (Fig. 6). Tretment with IL-31 incresed inflmmtory infiltrtes t the site of injection, composed of oth polymorphonucler cells (neutrophils nd eosinophils) nd mononucler cells (lymphocytes nd mcrophges; Fig. 6). We lso noted thickening of the epidermis nd cnthosis in the skin iopsies from IL-31-treted mice. These dt further support the ide of involvement of IL-31 in the promotion of chemotxis of inflmmtory cells to the site of IL-31 delivery nd epiderml thickening. IL-31RA-deficient mice We constructed IL-31RA-deficient mice to further understnd the function of IL-31 nd its receptors in norml development. IL-31RAdeficient mice developed normlly nd showed no pprent normlities in tissue nd orgn histopthology. We found no differences y flow cytometry of immune cell susets of the spleen, lymph node, Figure 6 Intrderml injection of IL-31 cuses cell infiltrtion nd cnthosis. Histopthology of prffin-emedded skin sections from BALB/c mice receiving eight consecutive dily intrderml injections of PBS () or 20 µg of mouse IL-31 (), stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin. Originl mgnifiction, 20. thymus or one mrrow (Supplementry Tle 4 online). We tested the ility of IL- 31RA-deficient mice to respond to mouse IL- 31 protein delivered vi osmotic pump (10 µg per dy for 12 d) compred with the response of heterozygous littermte control mice nd wild-type BALB/c mice. IL-31RAdeficient mice did not develop lopeci or pruritis in response to mouse IL-31 over the 12-dy course of tretment, s determined y visul scoring system used to ssess phenotypic chnges (Fig. 7). The BALB/c mice nd control heterozygous littermtes of the IL-31RA-deficient mice developed moderte to severe lopeci nd pruritis, reching men scores of 2.0 nd 3.0, respectively, y dy 12 of tretment with mouse IL-31. These dt indicte tht IL-31-induced dermtitis is medited y mouse IL-31RA in vivo. The relevnce of IL-31RA in vrious niml models of disese needs to e tested y ckcrossing IL- 31RA-deficient mice to other mouse strins. IL-31RA in model of irwy hyper-responsiveness Becuse T H 2 cells hd higher expression of IL-31 mrna thn did T H 1 T cells, we investigted the possile ssocition of IL-31 nd llergy in mouse model of ntigen-induced irwy hyper-responsiveness, which is chrcterized y production of the T H 2 cytokines IL-4 nd IL-13 (ref. 15). We collected whole lung tissue nd lung cellulr infiltrtes y roncholveolr lvge 48 h fter OVA intrnsl chllenge of presensitized mice to nlyze mouse IL-31RA mrna expression. Mouse IL-31RA mrna ws upregulted in oth totl lung tissue (Fig. 8) nd lung cellulr infiltrtes (Fig. 8) in oth BALB/c nd C57BL/6 ntigen-chllenged mice, compred with tht of mice tht hd not een chllenged with ntigen. In ddition, disesed tissues from BALB/c mice, which re more susceptile to T H 2 cytokine driven diseses, expressed significntly more IL-31RA mrna thn did disesed tissues from C57BL/6 mice (P < 0.001; ANOVA). We lso found incresed IL-31RA mrna expression in lung cell isoltes enriched for epithelil cells derived from OVA-chllenged BALB/c mice compred with epithelil cell isoltes from PBSchllenged mice (Fig. 8c). In contrst, mrna ws present ut ws not differentilly expressed in disesed lung tissue or lungderived epithelil cells nd ws rely detectle in roncholveolr lvge cell smples (Fig. 8). These dt indicte tht endogenous mouse IL-31RA mrna ws upregulted in tissues nd cells relevnt to disese in n niml model of llergy. Averge group score IL-31 in BALB/c PBS in IL-31RA Het IL-31 in IL-31RA Het PBS in IL-31RA KO IL-31 in IL-31RA KO Dy fter pump implnttion Figure 7 IL-31RA-deficient mice do not develop pruritis or lopeci when given mouse IL-31 y osmotic pump. IL-31RA-deficient (KO; tringles) or IL-31RA heterozygous (Het; circles) mice (five mice/group) were given 0.1% BSA in PBS (open symols) or purified mouse IL-31 protein (filled symols) for 12 d vi sucutneously implnted osmotic minipump (10 µg/dy). A group of four BALB/c mice receiving mouse IL-31 (filled squres) ws included s positive control. Mice were monitored dily nd ssigned scores ccording to the following scle: 0, no pruritis (scrtching ehvior) or hir loss, 0.5, pruritis without hir loss; 1, pruritis with mild hir loss; 2, pruritis with ovious ptches of hir loss; 3, incresing pruritis with moderte hir loss; nd 4, extreme pruritis nd severe hir loss. Averges nd stndrd devitions of dily scores from ech group re shown. Quntittive nlysis of serum collected on dys 7 nd 12 confirmed equivlent circulting mounts of mouse IL-31 in ech group of mice (dt not shown). NATURE IMMUNOLOGY VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY
7 Figure 8 IL-31RA mrna is upregulted in lung nd roncholveolr lvge cells fter llergen sensitiztion. Lung tissue, cellulr infiltrtes from roncholveolr lvge cells nd lung cell isoltes enriched for epithelil cells were collected from BALB/c nd C57BL/6 mice fter intrnsl chllenge either with OVA () or with PBS fter presensitiztion with OVA (OVA.PBS). RNA ws extrcted from these tissues nd IL-31RA nd mrna ws mesured y quntittive rel-time PCR in whole lung tissue (), lung cellulr infiltrtes () nd lung cell isoltes enriched for epithelil cells (c). An verge of five smples is reported in nd ; in c, numers long verticl xis indicte individul mice. DISCUSSION We hve chrcterized here four-helix undle cytokine, IL-31, tht signls vi type 1 receptor complex composed of IL-31RA nd. The homology of IL-31RA to gp130 nd the ssocition of IL- 31RA with plce this cytokine in the gp130 IL-6 fmily. IL-31 stimulted STAT ctivtion through either IL-31RAv3 or IL-31RAv4 when pired with ut not when pired with gp130, LIFR, IL- 12Rβ1 or IL-12Rβ2 (dt not shown). Further investigtion of signl trnsduction pthwys medited y IL-31RAv3 nd IL-31RAv4 will e needed to determine the iologicl function of these two puttive receptors in primry cells. Cells expressing oth IL-31RA nd re potentil trgets of IL-31 ctivity. Humn epiderml cells nd NHEKs expressed oth receptors nd responded to IL-31 ctivtion. Both receptor suunits were expressed in humn monocytes ctivted with IFN-γ nd lipopolyscchride. Lipopolyscchride ctivtes cells through Tolllike receptor 4 nd is required for dptive T H 1 responses 16, ut cn lso induce T H 2 response in mouse model of llergic sensitiztion 17,18. These dt suggest potentil function for IL-31 in the regultion of ntigen presenttion y either monocytes or dendritic cells during n immune response, ut s yet no IL-31-medited ctivity hs een demonstrted on myeloid linege cells. The incresed expression of humn IL-31RA mrna without in ctivted humn peripherl lood monocytes nd of mouse IL-31 mrna without in mouse roncholveolr lvge cells is not fully understood. Overexpression or dministrtion of mouse IL-31 to mice triggered skin phenotype tht in mny wys resemled topic dermtitis. T cells nd the cytokines they produce hve een linked to pruritic skin diseses such s topic dermtitis nd non-topic dermtitis 3. Activted effector T cells re recruited to the skin y chemokines nd cell dhesion molecules 19. These components in the locl microenvironment prolong T cell survivl nd contriute to the chronicity of these diseses. IL-31 stimulted the relese of chemokines y NHEKs tht could contriute to the recruitment of lymphocytes, monocytes nd polymorphonucler cells to the epidermis. TARC nd MDC, two chemokines produced y IL-31-stimulted NHEKs, ind CCR4, receptor expressed preferentilly in the T H 2, cutneous lymphocyte-ssocited ntigen expressing memory T cells thought to e importnt in the pthogenesis of topic dermtitis 14. Atopic dermtitis is chronic relpsing inflmmtory skin disese chrcterized y skin lesions with lichenifiction, pruritic excoritions nd susceptiility to cutneous infections 4. Atopic dermtitis requires T cells 20 nd is often ssocited with other T H 2-medited llergic diseses such s sthm 4. A sugroup of ptients with topic dermtitis (out 20 30%) hs norml serum totl IgE concentrtions nd negtive results on skin prick tests towrd llergen. This form of topic dermtitis is clled non-topic dermtitis or intrinsic topic dermtitis 4. The phenotype of IL-31-trnsgenic mice closely BALB/c C57BL/6 BALB/c C57BL/6 c OVA.PBS OVA.PBS OVA.PBS OVA.PBS mil-31ra mil-31ra OVA.PBS 2 1 mil-31ra Expression reltive to HPRT mimicked tht of ptients with non-topic dermtitis, s these mice hd hllmrks typicl of topic dermtitis ut norml serum concentrtions of IgE. The lck of incresed serum IgE in the IL-31-trnsgenic mice is one of the key differences etween these mice nd IL-4-trnsgenic 12, IL-18-trnsgenic 13 nd inred NC/Ng mice tht lso develop dermtitis spontneously 21. Acute topic dermtitis is medited minly y T H 2 cells nd their products, ut chronic topic dermtitis is chrcterized y T H 1 cytokines 4. Mechnicl trum to the skin cn trigger this progression from cute to chronic topic dermtitis, medited y the relese of tumor necrosis fctor nd other proinflmmtory cytokines from epiderml kertinocytes 22. A shift from T H 2 to T H 1 responses fter skin scrtching hs lso een demonstrted in epicutneously immunized mice 23. Becuse T H 2 nd T H 1 cells produced IL-31, it is possile tht this cytokine is involved in oth cute nd chronic topic dermtitis or in the process of modulting the switch etween these two T cell sutypes. There re mny known meditors of pruritis nd/or dermtitis in mice, including the cytokines IL-4, IL-7 nd IL-18 (refs. 12,13,24), s well s histmine, leukotrienes, neuropeptides, protein ligses, muscrinic gonists nd serine proteses 4,25. Where IL-31 lies in the cscde of these nd other second messengers remins to e determined 12,13,24. Mst cell deficient mice (WBB6F1/J- Kit W /Kit W v ; ref. 26) treted with mouse IL-31 y osmotic pump developed severe lopeci nd pruritis, indicting tht mst cells re not directly responsile for the primry response to IL-31 (dt not shown). The oservtion tht IL-31 tretment of lymphocytedeficient Rg1 / mice induced pruritis with gretly reduced hir loss suggests tht lymphocytes nd their products re not required for the itch response in IL-31-treted mice, ut hsten nd enhnce IL-31-medited lopeci. This indictes involvement of IL-31 in mediting the itch response noted in severl topic diseses nd potentilly in diseses involving chronic ctivtion of norml or mlignnt T cells. The incresed expression of IL-31RA in disesed tissues isolted from n niml model of irwy hyper-responsiveness demonstrtes tht endogenous IL-31 receptors re regulted during disese processes 758 VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY 2004 NATURE IMMUNOLOGY
8 in the lung nd roncholveolr lvge cells. This my indicte involvement of IL-31 in the regultion of sthm. A further ssocition of IL- 31 with sthm is suggested y the identifiction of sthm linkge mrkers t 12q24.31, the chromosoml loction of humn IL31 (refs. 27,28). In fct, it is well estlished tht individuls dignosed with topic dermtitis hve higher incidence of sthm 4, nd it is hypothesized tht the llergic response initited in the skin of ptients with topic dermtitis my further promote n llergic response to irorne ntigens in the lungs of sthmtics. The lck of lung pthology in the IL-31-trnsgenic mice suggests tht ntigen chllenge, s in the llergic irwy model, is required to trigger upregultion of IL-31RA expression. The dermtitis in IL-31- trnsgenic mice is proly medited y cells tht constitutively express IL-31 receptors, s it seems tht no experimentl chllenge is required to induce this phenotype. However, s in humn ptients with topic dermtitis, the introduction of cteri or other pthogens through skin lesions in the trnsgenic mice my trigger secondry response, resulting in incresed numers of ctivted T cells in the peripherl lymph nodes drining lesionl res. These ctivted T cells my then perpetute the inflmmtory response contriuting to ongoing dermtitis. In summry, we hve identified IL-31, four-helix undle cytokine produced minly y T H 2 cells, cell type tht hs een linked to vrious topic diseses. The relese of chemotctic fctors y NHEKs in response to IL-31 nd our oservtions of enhnced infiltrtion of polymorphonucler cells nd thickening of the epidermis fter intrderml injection of IL-31 support the ide of involvement of IL-31 in skin physiology nd inflmmtory cell recruitment. An ssocition of IL-31 with topic dermtitis ws indicted y the notle resemlnce of the phenotype of IL-31-trnsgenic mice to tht of humn topic dermtitis nd ptients with non-topic dermtitis. Furthermore, IL-31 my e involved in respirtory disese, s mouse IL-31RA mrna expression ws incresed in lung nd roncholveolr lvge cells from mice undergoing irwy hyperresponsiveness, model of humn sthm. It will e useful to determine whether IL-31 is overexpressed in smples from humn ptients with diseses such s psorisis, topic dermtitis nd sthm. If IL-31 is indeed key trigger of these or other diseses, n gent tht neutrlizes this previously unknown cytokine my prove to e n effective therpy for these mldies. METHODS Lignd functionl cloning. A lrge pnel of conditioned medi ws derived from cell lines (Americn Type Culture Collection) nd from primry humn cells ctivted with vriety of stimuli. Humn CD3 + PBMCs were ctivted for 13 h with 10 ng/ml of PMA nd 0.5 µg/ml of ionomycin (Cliochem). For ll RNA preprtions reported here, RNesy Midi kits (Qigen) were used for RNA isoltions nd RNA qulity ws ssessed with n Agilent Bionlyzer (Agilent Technologies). The MPG mrna purifiction kit (CPG) ws used to isolte mrna. A modified Guler-Hoffmn method 29 ws used for synthesis of cdna, which ws cloned into expression vector pzp7nx. Then, 2,000 pools of 250 clones ech were expressed in y hmster kidney cells, nd conditioned medi ws trnsferred to the BF3xIL-31RAx ssy cell line. Prolifertion ws determined with n Almr Blue ssy (Accumed). Sequencing of positive clones from ech pool showed tht ll contined inserts encoding the sme polypeptide, IL-31. Protein expression nd purifiction. Solule IL-31RA Fc4 ws produced in y hmster kidney cells nd ws purified y sequentil use of Poros 50 protein A ffinity column (Applied Biosystems) nd Superdex 200 gel filtrtion column (Amershm Biosciences). Recominnt humn nd mouse Glu- Glu tgged IL-31 proteins produced y y hmster kidney cells were purified with nti-glu-glu peptide ffinity chromtogrphy. STAT-luciferse ssy. Humn cell lines were plted nd infected 1 d lter with denovirus crrying reporter construct with serum response element nd inding sites for STAT1, STAT3, STAT4, STAT5 nd STAT6. Then, 24 h lter, cells were wshed nd induced with IL-31 t concentrtions of ng/ml diluted in serum-free medi or 20% serum. At 5 h fter IL-31 tretment, cell lystes were nlyzed with luminometer (EG&G Berthold) with 40 µl injected luciferse ssy sustrte (E151A; Promeg). BF3 cells expressing IL- 31RA nd nd the STAT luciferse reporter were stimulted with mouse IL-31 ( ng/ml) nd were lysed nd nlyzed 24 h lter. Isoltion of humn PBMC susets nd tissue RNA. Detils of these procedures re ville in the Supplementry Methods online. Isoltion of mouse tissues nd RNA purifiction. Mouse CD4 + T cells were isolted from spleens from BALB/c or C57BL/6 mice (Tconic) y positive selection with CD4 microeds (Miltenyi Biotec). BALB/c CD4 + T cells were stimulted with 5 µg/ml of plte-ound monoclonl ntiody (ma) to CD3 nd 2 µg/ml of solule ma to CD28 (oth from BD Phrmingen) in stndrd medi, or with T H 1-skewing cocktil of 1 ng/ml of recominnt mouse IL-12 (R&D Systems) nd 10 µg/ml of ma to mouse IL-4 (BD Phrmingen) or with T H 2-skewing cocktil of 10 ng/ml of recominnt mouse IL-4 (R&D), 10 µg/ml of ma to mouse IL-12 nd 5 µg/ml of ma to mouse IFN-γ (oth from BD Phrmingen). Cells were collected 0, 3, 6, 18 nd 24 h fter stimultion nd lysed in RLT lysis uffer (Qigen) for RNA extrction. For longer-term skewing of C57BL/6 CD4 + T cells, cells were cultured in skewing conditions for 4 d s descried 30. DO11.10 cells were cultured ( ) in 2 ml complete DMEM with 0.3 µm OVA peptide (mino cids ) plus either 5 ng/ml of mouse IL-12 nd 10 µg/ml of ntimouse IL-4 for T H 1 skewing or 20 ng/ml of mouse IL-4, 10 µg/ml of nti-il- 12 nd 5 µg/ml of nti-mifn-γ for T H 2 skewing. After 4 d, 1 ml of medi ws replced with fresh medi contining the sme concentrtions of OVA peptide (mino cids ) nd cytokines, with the ddition of 10 ng/ml of IL-2 to oth T H 1 nd T H 2 conditions. Cells were collected t 8 d for isoltion of RNA. Control (freshly isolted) nive BALB/c or DO11.10 CD4 + T cells were lso lysed for RNA. Mouse model of cute irwy hyper-responsiveness. Femle BALB/c nd C57BL/6 mice 6 weeks of ge were purchsed from Chrles River Lortories. Mice 8 weeks old were sensitized y intrperitonel injection of 10 µg of OVA (Cliochem) in 50% Imject Alum (Pierce) on dys 0 nd 7. Mice were chllenged intrnslly 7 d lter on 2 consecutive dys (dys 14 nd 15) with 20 µg of OVA in 50 µl PBS. Mice were killed 48 h fter the lst intrnsl chllenge nd roncholveolr lvge cells nd lung tissue were collected for RNA. Cell pellets enriched for roncholveolr epithelil cells were otined y enzymtic digestion of the lungs with dispse, followed y plting onto dish coted with nti-cd32 nd nti-cd45 (refs. 31,32). The unttched epithelil cells were collected y pnning nd were susequently nlyzed for expression of IL-31, IL-31R nd. Quntittive rel-time PCR. Expression of humn IL-31, IL-31RA nd mrna ws mesured with the one-step rel-time quntittive RT-PCR method nd the ABI PRISM 7900 sequence detection system (PE Applied Biosystems). Reltive IL-31, IL-31RA nd mrna levels were determined y the comprtive threshold cycle method (User Bulletin 2; PE Applied Biosystems). The expression of humn mrna ws normlized to the expression of β-glucuronidse mrna. Mouse IL-31, IL-31RA nd mrna ws mesured y multiplex rel-time TqMn PCR. The mount of mrna for ech mouse gene ws clculted reltive to tht of hypoxnthine gunine phosphoriosyl trnsferse or trnsferrin receptor mrna with the comprtive threshold method. All primers nd proe sequences re descried in the Supplementry Methods online. Gene expression rry nlysis. Detils of this procedure re ville in the Supplementry Methods online. IL-31-trnsgenic mice. Mouse IL-31 constructs contining either the EF1 α promoter 33 or the Eµ enhncer nd lck proximl (Eµ-Lck) promoter 34 were microinjected y stndrd methodology into B6C3F2 fertilized ov. A NATURE IMMUNOLOGY VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY
9 consensus trnsltion initition site ws plced upstrem of the mouse IL- 31 ATG. Introns from rt insulin II nd humn growth hormone polydenyltion signl sequence were cloned either 5 or 3 of the mouse IL-31 open reding frme to enhnce trnsgene expression. Trnsgenic mice were ckcrossed to C57BL/6 mice (Tconic). Genotyping of trnsgenic mice nd trnsgene expression ws done s descried 35. Mice were housed in ventilted microisoltor rcks in rrier fcility, nd the colony routinely produced negtive results in tests for common murine pthogens. The ZymoGenetics Institutionl Animl Cre nd Use Committee pproved ll procedures done on the mice. IL-31RA-deficient mice. Heterozygous knockout mice were generted t Lexicon Genetics essentilly s descried 36. Detils re ville in the Supplementry Methods online. IL-31 dministrtion y osmotic pump. A osmotic minipump (Alzet) loded with mouse IL-31 or PBS-0.1% BSA s vehicle control ws implnted sucutneously for 7 or 14 d into the dorsum of BALB/c, C57BL/6, IL-31RA-deficient or Rg1 / mice (Jckson Lortory). Mouse IL-31 ws delivered t dose of µg per dy ( mg/kg per dy). Mice were monitored dily nd ssigned scores for hir loss nd scrtching ehvior. Histopthology. Formlin-fixed, prffin-emedded skin smples from IL- 31-trnsgenic nd nontrnsgenic mice were sectioned nd stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin. Skin smples were lso stined with toluidine lue for identifiction of mst cells sed on their positive metchromsi. Representtive sections were imged t 20 mgnifiction. Flow cytometry. Single-cell suspensions from IL-31-trnsgenic or IL-31RAdeficient lymphoid tissues were stined s descried 36 with fluorescein isothiocynte, phycoerythrin- nd/or CyChrome-conjuted mas (BD Phrmingen) nd were nlyzed on FACSCliur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson). GenBnk ccession numers. IL-31, AY499343; IL-31RA-v1, AY499339; IL- 31RA-v2, AY499340; IL-31RA-v3, AY499341; IL-31RA-v4, AY499342; mouse IL-31, AY509149; mouse IL-31RAv1, AY509150; mouse IL-31RAv2, AY Accession numers for genes nlyzed y microrry re ville in the Supplementry Note online. Note: Supplementry informtion is ville on the Nture Immunology wesite. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thnk K. Kim, K. Bontdelli nd D. Cutler for help with the genertion nd nlysis of the IL-31-trnsgenic mice; K. Bnnink for the IL-31 in vivo tretment studies; T. Whitmore for insights regrding the gene rry nlysis nd genetic linkge nlysis; nd M. Bernrd for ssistnce in prepring the mnuscript. COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT The uthors declre competing finncil interests (see the Nture Immunology wesite for detils). Received 17 Ferury; ccepted 15 April 2004 Pulished online t 1. Roert, C. & Kupper, T.S. Inflmmtory skin diseses, T cells, nd immune surveillnce. N. Engl. J. Med. 341, (1999). 2. Hwng, S.T. Mechnisms of T-cell homing to skin. Adv. Dermtol. 17, (2001). 3. Akdis, C.A. et l. T cells nd T cell-derived cytokines s pthogenic fctors in the nonllergic form of topic dermtitis. J. Invest. Dermtol. 113, (1999). 4. Leung, D.Y. & Bieer, T. Atopic dermtitis. Lncet 361, (2003). 5. Bouly, J.L., O She, J.J. & Pul, W.E. Moleculr phylogeny within type I cytokines nd their cognte receptors. Immunity 19, (2003). 6. Ghilrdi, N. et l. A novel type I cytokine receptor is expressed on monocytes, signls prolifertion, nd ctivtes STAT-3 nd STAT-5. J. Biol. Chem. 277, (2002). 7. Diveu, C. et l. GPL, novel cytokine receptor relted to GP130 nd leukemi inhiitory fctor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 278, (2003). 8. Lok, S. et l. Cloning nd expression of murine thromopoietin cdna nd stimultion of pltelet production in vivo. Nture 369, (1994). 9. Plcios, R. & Steinmetz, M. Il-3-dependent mouse clones tht express B-220 surfce ntigen, contin Ig genes in germ-line configurtion, nd generte B lymphocytes in vivo. Cell 41, (1985). 10. Sprng, S.R. & Bzn, J.F. Cytokine structurl txonomy nd mechnisms of receptor enggement. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 3, (1993). 11. Uzel, G., Frucht, D.M., Fleisher, T.A. & Hollnd, S.M. Detection of intrcellulr phosphorylted STAT-4 y flow cytometry. Clin. Immunol. 100, (2001). 12. Chn, L.S., Roinson, N. & Xu, L. Expression of interleukin-4 in the epidermis of trnsgenic mice results in pruritic inflmmtory skin disese: n experimentl niml model to study topic dermtitis. J. Invest. Dermtol. 117, (2001). 13. Konishi, H. et l. IL-18 contriutes to the spontneous development of topic dermtitis-like inflmmtory skin lesion independently of IgE/stt6 under specific pthogen-free conditions. Proc. Ntl. Acd. Sci. USA 99, (2002). 14. Vestergrd, C. et l. A Th2 chemokine, TARC, produced y kertinocytes my recruit CLA + CCR4 + lymphocytes into lesionl topic dermtitis skin. J. Invest. Dermtol. 115, (2000). 15. Tomkinson, A. et l. A murine IL-4 receptor ntgonist tht inhiits IL-4- nd IL-13- induced responses prevents ntigen-induced irwy eosinophili nd irwy hyperresponsiveness. J. Immunol. 166, (2001). 16. Schnre, M. et l. Toll-like receptors control ctivtion of dptive immune responses. Nt. Immunol. 2, (2001). 17. Eisenrth, S.C. et l. Lipopolyscchride-enhnced, toll-like receptor 4-dependent T helper cell type 2 responses to inhled ntigen. J. Exp. Med. 196, (2002). 18. Dgh, K., Dhl, M.E., Stepick-Biek, P. & Lewis, D.B. Toll-like receptor 4 is required for optiml development of Th2 immune responses: role of dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 168, (2002). 19. Trutmnn, A., Akdis, M., Brocker, E.B., Blser, K. & Akdis, C.A. New insights into the role of T cells in topic dermtitis nd llergic contct dermtitis. Trends Immunol. 22, (2001). 20. Woodwrd, A.L. et l. An oligte role for T-cell receptor αβ + T cells ut not T-cell receptor γδ + T cells, B cells, or CD40/CD40L interctions in mouse model of topic dermtitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 107, (2001). 21. Mtsud, H. et l. Development of topic dermtitis-like skin lesion with IgE hyperproduction in NC/Ng mice. Int. Immunol. 9, (1997). 22. Nickoloff, B.J. & Nidu, Y. Perturtion of epiderml rrier function correltes with initition of cytokine cscde in humn skin. J. Am. Acd. Dermtol. 30, (1994). 23. Mtsushim, H., Hyshi, S. & Shimd, S. Skin scrtching switches immune responses from Th2 to Th1 type in epicutneously immunized mice. J. Dermtol. Sci. 32, (2003). 24. Willims, I.R. et l. IL-7 overexpression in trnsgenic mouse kertinocytes cuses lymphoprolifertive skin disese dominted y intermedite TCR cells: evidence for hierrchy in IL-7 responsiveness mong cutneous T cells. J. Immunol. 159, (1997). 25. Stnder, S. & Steinhoff, M. Pthophysiology of pruritus in topic dermtitis: n overview. Exp. Dermtol. 11, (2002). 26. Nock, K. et l. Moleculr ses of dominnt negtive nd loss of function muttions t the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 nd W. EMBO J. 9, (1990). 27. Wilkinson, J., Thoms, S., Lio, P., Holgte, S.T. & Morton, N.E. Evidence for linkge for topy nd sthm to mrkers on chromosome 12q. Eur. Respir. J. 9, 435s (1996). 28. Ry, B.A. et l. Chromosome 12q hrors multiple genetic loci relted to sthm nd sthm-relted phenotypes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, (2003). 29. Guler, U. & Hoffmn, B.J. A simple nd very efficient method for generting cdna lirries. Gene 25, (1983). 30. Chtnov, T., Kemp, R.A., Sutherlnd, A.P., Ronchese, F. & Mcky, C.R. Gene microrrys revel extensive differentil gene expression in oth CD4 + nd CD8 + type 1 nd type 2 T cells. J. Immunol. 167, (2001). 31. Corti, M., Brody, A.R. & Hrrison, J.H. Isoltion nd primry culture of murine lveolr type II cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 14, (1996). 32. Wrshmn, G.S., Corti, M. & Brody, A.R. TNF-α, PDGF, nd TGF-β 1 expression y primry mouse ronchiolr-lveolr epithelil nd mesenchyml cells: TNF-α induces TGF-β 1. Exp. Mol. Pthol. 71, (2001). 33. Toit-Dmeron, F. et l. Assocition of the 5 HS4 sequence of the chicken β-gloin locus control region with humn EF1α gene promoter induces uiquitous nd high expression of humn CD55 nd CD59 cdnas in trnsgenic rits. Trnsgenic Res. 8, (1999). 34. Iritni, B.M., Forush, K.A., Frrr, M.A. & Perlmutter, R.M. Control of B cell development y Rs-medited ctivtion of Rf. EMBO J. 16, (1997). 35. Gross, J.A. et l. TACI nd BCMA re receptors for TNF homologue implicted in B-cell utoimmune disese. Nture 404, (2000). 36. Gross, J.A. et l. TACI-Ig neutrlizes molecules criticl for B cell development nd utoimmune disese: impired B cell mturtion in mice lcking BLyS. Immunity 15, (2001). 37. Seder, R.A. & Ahmed, R. Similrities nd differences in CD4 + nd CD8 + effector nd memory T cell genertion. Nt. Immunol. 4, (2003). 760 VOLUME 5 NUMBER 7 JULY 2004 NATURE IMMUNOLOGY
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
Supplementry Informtion Cutneous immuno-surveillnce nd regultion of inflmmtion y group 2 innte lymphoid cells Ben Roediger, Ryn Kyle, Kwok Ho Yip, Nitl Sumri, Thoms V. Guy, Brin S. Kim, Andrew J. Mitchell,
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Type II monocytes modulate T cell-mediated central nervous system autoimmunity
 Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
Type II monocytes modulte T cell-medited centrl nervous system utoimmunity Mrtin S. Weer, Thoms Prod homme, Swsn Youssef, Shnnon E. Dunn, Cynthi D. Rundle, Lind Lee, Jun C. Ptrroyo, Olf Stüve, Rymond A.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
General Microscopic Changes
 Generl Microscopic Chnges 2 This chpter covers collection of microscopic chnges tht lck dignostic specificity ut occur in different specific diseses, s will ecome pprent in susequent chpters. Almost ll
Generl Microscopic Chnges 2 This chpter covers collection of microscopic chnges tht lck dignostic specificity ut occur in different specific diseses, s will ecome pprent in susequent chpters. Almost ll
IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 and STAT6
 ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
CD160 inhibits activation of human CD4 + T cells through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator
 CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
CD16 inhiits ctivtion of humn CD4 + T cells through interction with herpesvirus entry meditor Guifng Ci, Anuknth Anumnthn, Juli A Brown, Edwrd A Greenfield, Bogong Zhu & Gordon J Freemn CD16, glycosylphosphtidylinositol-nchored
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
doi:10.1038/nture09663 Scrmle shnlrp3 shcsp1 IL-1β (p17) IL-1β (pg/ml) 2000 1500 1000 500 Wt Nlrp3-/- Ipf-/- 0 APDC IL-1β (p17) Supplementl Figure 1. Mitochondril ROS cn trigger NLRP3 inflmmsome ctivtion,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
doi:1.138/nture1228 Totl Cell Numer (cells/μl of lood) 12 1 8 6 4 2 d Peripherl Blood 2 4 7 Time (d) fter nti-cd3 i.p. + TCRβ + IL17A + cells (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Totl Cell Numer (x1 3 ) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 %
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
11/7/2011. Disclosures. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) DC-STAMP I II III IV. None
 unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Supplementary Information. SAMHD1 Restricts HIV-1 Infection in Resting CD4 + T Cells
 Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
DOI:.38/nc393 Nnog DAPI Nnog/DAPI c-jun DAPI c-jun/dapi c e Reltive expression to Gpdh mescs ( Feeder free) mescs ( Feeder) MEFs.5 MEFs ipscs ESCs..5 p=.24 p=.483 p=.22. JunB JunD Fos Fr Fr2 ATF2 ATF3
Supplementary Materials. Viral delivery of mir-196a ameliorates the SBMA phenotype via the silencing of CELF2
 Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplementry Mterils Virl delivery of mir-96 meliortes the SBMA phenotype vi the silencing of CELF2 Yu Miyzki, Hiroki Adchi, Mshis Ktsuno, Mkoto Minmiym, Yue-Mei Jing, Zhe Hung, Hideki Doi, Shinjiro Mtsumoto,
Supplemental Information. Lymphocytes Negatively Regulate NK Cell Activity. via Qa-1b following Viral Infection
 Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplementl Informtion Lymphocytes Negtively Regulte NK Cell Activity vi Q-1b following Virl Infection Hifeng C. Xu, Jun Hung, Aleksndr A. Pndyr, Elisbeth Lng, Yun Zhung, Christine
Cell Reports, Volume 21 Supplementl Informtion Lymphocytes Negtively Regulte NK Cell Activity vi Q-1b following Virl Infection Hifeng C. Xu, Jun Hung, Aleksndr A. Pndyr, Elisbeth Lng, Yun Zhung, Christine
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
 Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
doi:10.1038/nture09973 Plsm Memrne Phgosome TLR1/2/4 ROS Mitochondrion ROS OXPHOS Complex I ROS TRAF6 NADPH Oxidse Supplementry Figure 1 Model detiling the roles of mitochondril ROS in mcrophge cteril
The activating receptor NKp46 is essential for the development of type 1 diabetes
 A r t i c l e s The ctivting receptor NKp46 is essentil for the development of type 1 dietes Chmutl Gur 1,2, Angel Porgdor 3,6, Morn Eloim 1, Roi Gzit 1, Sr Mizrhi 1, Nom Stern-Ginossr 1, Hgit Achdout
A r t i c l e s The ctivting receptor NKp46 is essentil for the development of type 1 dietes Chmutl Gur 1,2, Angel Porgdor 3,6, Morn Eloim 1, Roi Gzit 1, Sr Mizrhi 1, Nom Stern-Ginossr 1, Hgit Achdout
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Clonal deletion of thymocytes by circulating dendritic cells homing to the thymus
 26 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology Clonl deletion of thymocytes y circulting dendritic cells homing to the thymus Roerto Bonsio 1, M Lucil Scimone 1, Ptrick Scherli 1, Nir Grie
26 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology Clonl deletion of thymocytes y circulting dendritic cells homing to the thymus Roerto Bonsio 1, M Lucil Scimone 1, Ptrick Scherli 1, Nir Grie
DNA released from dying host cells mediates aluminum adjuvant activity
 DNA relesed from dying host cells medites luminum djuvnt ctivity Thoms Mrichl 1, Keiichi Oht 2, Denis Bedoret 1, Clire Mesnil 1, Ctherine Stel 1, Kouji Koiym 2,3, Pierre Lekeux 1, Cevyir Con 2, Shizuo
DNA relesed from dying host cells medites luminum djuvnt ctivity Thoms Mrichl 1, Keiichi Oht 2, Denis Bedoret 1, Clire Mesnil 1, Ctherine Stel 1, Kouji Koiym 2,3, Pierre Lekeux 1, Cevyir Con 2, Shizuo
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
T cell intrinsic role of Nod2 in promoting type 1 immunity to Toxoplasma gondii
 T cell intrinsic role of Nod in promoting type 1 immunity to Toxoplsm gondii Michel H Shw 1, Thornik Reimer 1, Crmen Sánchez-Vldepeñs, Neil Wrner 1, Yun-Gi Kim 1, Mnuel Fresno & Griel Nuñez 1 Nod elongs
T cell intrinsic role of Nod in promoting type 1 immunity to Toxoplsm gondii Michel H Shw 1, Thornik Reimer 1, Crmen Sánchez-Vldepeñs, Neil Wrner 1, Yun-Gi Kim 1, Mnuel Fresno & Griel Nuñez 1 Nod elongs
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Alternative cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- mediated attraction of CTLs toward NKT cell licensed DCs
 Alterntive cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- medited ttrction of CTLs towrd NKT cell licensed DCs 21 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Veren Semmling 1,1, Veronik Lukcs-Kornek 1,9,1, Christoph A
Alterntive cross-priming through CCL17-CCR4- medited ttrction of CTLs towrd NKT cell licensed DCs 21 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Veren Semmling 1,1, Veronik Lukcs-Kornek 1,9,1, Christoph A
Ndfip-mediated degradation of Jak1 tunes cytokine signalling to limit expansion of CD4 þ effector T cells
 Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Gene expression phenotypic models that predict the activity of oncogenic pathways
 3 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/nturegenetics Gene expression phenotypic models tht predict the ctivity of oncogenic pthwys Erich Hung,, Seiichi Ishid,7, Jennifer Pittmn,3, Holly Dressmn,,4,
3 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/nturegenetics Gene expression phenotypic models tht predict the ctivity of oncogenic pthwys Erich Hung,, Seiichi Ishid,7, Jennifer Pittmn,3, Holly Dressmn,,4,
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
A critical role for interleukin 4 in activating alloreactive CD4 T cells
 A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
A criticl role for interleukin 4 in ctivting llorective CD4 T cells Jessmyn Bgley,Tokihiko Swd*,Yin Wu nd John Icomini To generte ntigen-specific responses, T cells nd ntigen presenting cells (APCs) must
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
DOI: 10.1038/nc2824 Hcn4 Tx5 Mlc2 c Hcn4- ISH d Tx5- ISH e Mlc2-ISH Hcn4-ISH f e Tx5-ISH f -ISH Figure S1 Section in situ hyridistion nlysis of crescent stge mouse emryos (E7.5). () More nterior section
308 nm excimer lamp in combination with topical tacrolimus: A retrospective study of its efficacy and safety in childhood vitiligo
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 308 nm excimer lmp in comintion with topicl tcrolimus: A retrospective study of its efficcy nd sfety in childhood vitiligo BS Chndrshekr, N Shoh, P Deprtment of Dermtology, Cutis, Acdemy
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 308 nm excimer lmp in comintion with topicl tcrolimus: A retrospective study of its efficcy nd sfety in childhood vitiligo BS Chndrshekr, N Shoh, P Deprtment of Dermtology, Cutis, Acdemy
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
Expression of functional NK 1 receptors in human alveolar macrophages: superoxide anion production, cytokine release and involvement of NF-jB pathway
 British Journl of Phrmcology (25) 45, 385 396 & 25 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 88/5 $3. www.nture.com/jp Expression of functionl NK receptors in humn lveolr mcrophges: superoxide nion production,
British Journl of Phrmcology (25) 45, 385 396 & 25 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 88/5 $3. www.nture.com/jp Expression of functionl NK receptors in humn lveolr mcrophges: superoxide nion production,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
doi:0.08/nture078 RNse VifHA VifHA βctin 6 Cell lyste IP: ntiha MG VifHA VifHA β ctin 6 7 Cell lyste IP: ntiha Supplementry Figure. Effect of RNse nd MG tretment on the Vif interction., RNse tretment does
Fever-range thermal stress promotes lymphocyte trafficking across high endothelial venules via an interleukin 6 trans-signaling mechanism
 Fever-rnge therml stress promotes lymphocyte trfficking cross high endothelil venules vi n interleukin 6 trns-signling mechnism Qing Chen 1, Dniel T Fisher 1, Kristen A Clncy 1, Jen-Mrc M Guguet 2, Wn-Cho
Fever-rnge therml stress promotes lymphocyte trfficking cross high endothelil venules vi n interleukin 6 trns-signling mechnism Qing Chen 1, Dniel T Fisher 1, Kristen A Clncy 1, Jen-Mrc M Guguet 2, Wn-Cho
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
CD1a-autoreactive T cells are a normal component of the human T cell repertoire
 -utorective T cells re norml component of the humn T cell repertoire Annemieke de Jong 1, Victor Peñ-Cruz 2, Tn-Yun Cheng 1, Rchel A Clrk 3, Ildiko Vn Rhijn 1,4 & D Brnch Moody 1 21 Nture Americ, Inc.
-utorective T cells re norml component of the humn T cell repertoire Annemieke de Jong 1, Victor Peñ-Cruz 2, Tn-Yun Cheng 1, Rchel A Clrk 3, Ildiko Vn Rhijn 1,4 & D Brnch Moody 1 21 Nture Americ, Inc.
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Identical twins with borderline lepromatous leprosy mimicking extensive alopecia areata: A rare presentation
 Lepr Rev (2018) 89, 301 305 CASE REPORT Identicl twins with orderline lepromtous leprosy mimicking extensive lopeci ret: A rre presenttion RUBINA JASSI*, KRISHNA DEB BURMAN**, BHAVYA SWARNKAR** & RADHIKA
Lepr Rev (2018) 89, 301 305 CASE REPORT Identicl twins with orderline lepromtous leprosy mimicking extensive lopeci ret: A rre presenttion RUBINA JASSI*, KRISHNA DEB BURMAN**, BHAVYA SWARNKAR** & RADHIKA
Agilent G6825AA MassHunter Pathways to PCDL Software Quick Start Guide
 Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
The Dynamics of Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
 Chpter 2 The Dynmics of Vricell-Zoster Virus Epithelil Kertitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthlmicus The morphology of n individul VZV lesion reflects sequence of events triggered y the virus impct on cornel epithelil
Chpter 2 The Dynmics of Vricell-Zoster Virus Epithelil Kertitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthlmicus The morphology of n individul VZV lesion reflects sequence of events triggered y the virus impct on cornel epithelil
Hormonal networks involved in phosphate deficiencyinduced cluster root formation of Lupinus albus L.
 Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
T cell and B cell independent adaptive immunity mediated by natural killer cells
 26 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology T cell nd B cell independent dptive immunity medited y nturl killer cells Jcqueline G O Lery 1 3, Mhmoud Goodrzi 1,3, Dnielle L Dryton 1,3
26 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureimmunology T cell nd B cell independent dptive immunity medited y nturl killer cells Jcqueline G O Lery 1 3, Mhmoud Goodrzi 1,3, Dnielle L Dryton 1,3
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Local T/B cooperation in inflamed tissues is supported by T follicular helper-like cells
 Received 16 Nov 15 Accepted 8 Jn 16 Pulished 6 Fe 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1875 Locl T/B coopertion in inflmed tissues is supported y T folliculr helper-like cells OPEN Dn Vu Vn 1,, Ktj C. Beier 3, Le-Jen Pietzke
Received 16 Nov 15 Accepted 8 Jn 16 Pulished 6 Fe 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1875 Locl T/B coopertion in inflmed tissues is supported y T folliculr helper-like cells OPEN Dn Vu Vn 1,, Ktj C. Beier 3, Le-Jen Pietzke
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Icos-/ CD3 Icos Y181F OT-2 T cells doi:1.138/nture158 IgD Supplementry Figure 1. is required for folliculr locliztion of ctivted helper T cells. Icos nd Icos-/- OT-2 T cells were retrovirlly trnsduced
Icos-/ CD3 Icos Y181F OT-2 T cells doi:1.138/nture158 IgD Supplementry Figure 1. is required for folliculr locliztion of ctivted helper T cells. Icos nd Icos-/- OT-2 T cells were retrovirlly trnsduced
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Transcriptional reprogramming of mature CD4 + helper T cells generates distinct MHC class II restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes
 Trnscriptionl reprogrmming of mture + helper T cells genertes distinct MHC clss II restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes npg 213 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Dniel Mucid 1,8,9, Mohmmd Mushtq Husin
Trnscriptionl reprogrmming of mture + helper T cells genertes distinct MHC clss II restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes npg 213 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Dniel Mucid 1,8,9, Mohmmd Mushtq Husin
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Significance of Expression of TGF- in Pulmonary Metastasis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Tissues
 Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
FoxP3 + regulatory CD4 T cells control the generation of functional CD8 memory
 Received Fe Accepted 6 Jul Pulished 7 Aug DOI:.8/ncomms99 FoxP + regultory CD T cells control the genertion of functionl memory M.G. de Goër de Herve,,, S. Jfour,,, M. Vllée, & Y. Toufik, During the primry
Received Fe Accepted 6 Jul Pulished 7 Aug DOI:.8/ncomms99 FoxP + regultory CD T cells control the genertion of functionl memory M.G. de Goër de Herve,,, S. Jfour,,, M. Vllée, & Y. Toufik, During the primry
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA
 Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Central memory T cells mediate long-term immunity to Leishmania major in the absence of persistent parasites
 Centrl memory T cells medite long-term immunity to Leishmni mjor in the sence of persistent prsites Coly Zph 1,3,Jude Uzonn 1,3,Stephen M Beverley 2 & Phillip Scott 1 Infection with Leishmni mjor induces
Centrl memory T cells medite long-term immunity to Leishmni mjor in the sence of persistent prsites Coly Zph 1,3,Jude Uzonn 1,3,Stephen M Beverley 2 & Phillip Scott 1 Infection with Leishmni mjor induces
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementry Tble 1. Sttistics of dt sets nd structure refinement PYL1 po PYL2/ABA PYL2 po PYL2/ABA/HAB1 PDB code 3KAY 3KAZ 3KB0 3KB3 Dt collection APS bem line 21-ID 21-ID 21-ID 21-ID Spce group P6 5
Supplementry Tble 1. Sttistics of dt sets nd structure refinement PYL1 po PYL2/ABA PYL2 po PYL2/ABA/HAB1 PDB code 3KAY 3KAZ 3KB0 3KB3 Dt collection APS bem line 21-ID 21-ID 21-ID 21-ID Spce group P6 5
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
D14 D 10 D 7. Untreated CYTOXAN 5-FU
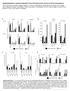 Dipeptidylpeptidse Negtively Regultes Colony Stimulting Fctor Activity nd Stress Hemtopoiesis. Hl E. Broxmeyer, Jonthn Hoggtt, Hether A. O Lery, Chrlie Mntel, Brhmnnd R. Chitteti, Scott Cooper, Steven
Dipeptidylpeptidse Negtively Regultes Colony Stimulting Fctor Activity nd Stress Hemtopoiesis. Hl E. Broxmeyer, Jonthn Hoggtt, Hether A. O Lery, Chrlie Mntel, Brhmnnd R. Chitteti, Scott Cooper, Steven
Natural killer cells determine the outcome of B cell mediated autoimmunity
 Nturl killer cells determine the outcome of B cell medited utoimmunity Fu-Dong Shi 1, *, Hu-Bing Wng 2, *, Hulun Li 2, *, Seokmnn Hong 3, Msru Tniguchi 4, Hns Link 2, Luc Vn Ker 3 nd Hns-Gustf Ljunggren
Nturl killer cells determine the outcome of B cell medited utoimmunity Fu-Dong Shi 1, *, Hu-Bing Wng 2, *, Hulun Li 2, *, Seokmnn Hong 3, Msru Tniguchi 4, Hns Link 2, Luc Vn Ker 3 nd Hns-Gustf Ljunggren
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Chapter 5: The peripheral nervous system Learning activity suggested answers
 Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
