Supporting Information
|
|
|
- Roderick Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supporting Information Gorgun et al /pnas SI Text Animals, Disease Detection and Infusion of CLL Cells. Mice were examined for lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly and at specific ages or when visibly ill, mice were killed and hematopoietic tissues including spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, peripheral blood, and liver were extracted. Splenic mononuclear cells were separated by ficoll-hypaque centrifugation and cells were labeled with anti-mouse CD5 PE, CD19 CYT, IgM FITC, and IgD FITC, Ig FITC, and Ig FITC monoclonal antibodies. Three-monthold E -TCL1 mice that had not developed CLL were infused (i.v. injection) with splenic mononuclear cells ( 98% CD5 CD19 Ig or Ig ) in 0.5 ml PBS into the tail vein on days 0 and 3, and spleens removed at day 8. CLL cells were obtained from E -TCL1 mice over 12 months of age with disease. Antibodies and Reagents. Rhodamine Phalloidin, CellTracker Blue CMAC, and Alexa Fluor 488-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG antibodies were all purchased from Invitrogen. Anti-Cdc42 and anti-lck were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Anti-phosphotyrosine, clone 4G10 (FITC conjugate) was purchased from Millipore. All other reagents were purchased from Sigma unless otherwise stated. Gene-Chip Array and Expression-Data Analysis. Quality control of the RNA samples was performed by spectrophotometric analysis and size fractionation (Agilent Technologies). RNA conversion of cdna and subsequent hybridization to gene arrays was performed in the Core Facility at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, according to the manufacturer s protocols (Affymetrix). CEL files have been deposited into the Gene Expression Omnibus and are available with accession numbers GSE8835 for human data ( GSE8836 for murine data ( Data were normalized using DNA-Chip Analyzer (dchip) to obtain perfect-match-only model-based expression intensities. An array with a median overall intensity was chosen as the baseline array against which other arrays were normalized at probe-intensity level. dchip was used to perform unsupervised analysis by gene filtering, excluding genes that lacked sufficient variability across groups, and hierarchical clustering of genes and samples. The filtering criteria required that a gene s coefficient of variation across all samples (after pooling replicate arrays) be between 0.9 and 2.0 and that a gene be called present in more than 20% of the arrays. Hierarchical clustering was performed using the distant metric 1-correlation (Pearson): that is, the distance between 2 genes is defined as 1 r, where r is the Pearson correlation coefficient between the standardized expression values (mean 0 and SD 1) of the 2 genes across the samples and centroid linkage. The expression levels for each gene was standardized to mean 0 and SD 1, with the standardized expression values falling within [ 3, 3]. To identify the genes whose expression patterns best distinguished groups, the permutation distribution of the maximum t-statistic was analyzed using Permax. The custom program written for R software by Robert Gray calculates Permax values and is available free on-line ( gray/permax.html). For CD4 and CD8 T-cell groups, we compared gene-expression profiles using the Permax test according to cell purity ( 85% vs. 85%), age ( 12 months old vs. 12 months old), CLL cell content ( 40% vs. 40%) and gender (female vs. male). In these supervised analyses, to control the overall error rate, the Permax P-value was calculated by comparing the observed t-statistics for each gene from their log values to the permutation distribution of the largest t-statistic obtained over the 45,037 genes. For each gene, the P-value is the proportion of permutations with the maximum t-statistics over all genes greater or equal to the observed value for a particular gene. Differentially expressed genes (filtered by P 0.05 and 1.2 fold 1.2) from supervised analyses by their involvement in specific cellular pathways were determined using gene microarray pathway profiler 2.0 (GenMapp) software. Fisher t-test analysis was used to determine over-represented cellular pathways (P 0.05). The comparison of overlapping genes obtained by supervised analyses between our human gene-expression profiles (Affymetrix) hu133a and mouse gene-expression profiles (Affymetrix moe430.2) was performed using RESOURCERER, a database for annotating and linking microarray resources within and cross species. Quantitative RT-PCR and Western Immunoblot. Total cell protein was extracted from 99% pure splenic CD4 T or CD8 T cells and protein blots performed with primary antibodies against rabbit mouse polyclonal antibodies Lyn and PI3K (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and then labeled with secondary antibody HRPconjugated goat anti rabbit Ig and detected by Western blot chemiluminescence reagents (Perkin Elmer). Expression levels normalized with -Actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and measured using Kodak Digital Science Image Station-440CF luminometer (Eastman Kodak). Immune Assessment. For CTL effector assays, CD8 cells from WT and E -TCL1 mice with and without CLL (6 animals per group) were stimulated in vitro with monocyte derived dendritic cells pulsed with Ig heavy chain- (IgVH) derived peptide GSAINY- APSI weekly for 4 weeks. Killing of CLL cells expressing this IgVH by the resulting T-cell lines was assessed at the effector- :target ratios shown from WT and E -TCL1 mice with and without CLL. For in vivo antigen-specific T-cell activation assays, WT and E -TCL1 mice with and without CLL were immunized with gp33 peptide KAVYNFATM. On day 8 spleen cells from immunized mice (9 in each group) were stimulated with indicated concentrations of KAVYNFATM peptide in 96-well plates in triplicates. Proliferation was assayed after 3 days of treatment by [ 3 H]-Thymidine incorporation, measured by -scintillation counter. For proliferation assays, mononuclear cells from E -TCL1 mice with and without CLL were stimulated in triplicate with 100-ng/ml phorbol myristate acetate and 4- g/ml ionomycin for 3 days. Next, 1 Ci per well [ 3 H]- Thymidine was added to each triplicate 18 h before harvesting and proliferation measured by -scintillation counter. Cell Conjugation Assays. Healthy or malignant B cells ( healthy WT B cells or CLL cells) were stained with CellTracker Blue CMAC (7-amino-4-chloromethylcoumarin) following the manufacturer s instructions and pulsed with or without 2 g/ml of a mixture of staphylococcal superantigens (SEA and SEB; Sigma) for 30 min at 37 C. B cells were centrifuged (200 g for 5 min) with an equal number of T cells, incubated at 37 C for 10 min (CD8 T cells) or 15 min (CD4 T cells). Phosphotyrosine and Lck were assessed at 5-min conjugation times, then plated (centrifuged) onto polyl-lysine-coated coverslips and fixed for 15 min at room temperature with 3% methanol-free formaldehyde in PBS. 1of9
2 Immunofluorescence and Confocal Microscopy Image Acquisition. F-actin was stained with rhodamine phalloidin (Invitrogen). CD8 T-cell conjugates formed during 5 min were stained for Lck. CD4 T-cell conjugates formed during 15 min were stained for Cdc42. Medial optical section images were captured with a Zeiss 510 confocal laser-scanning microscope using a 63 objective. Detectors were set to detect an optimal signal below the saturation limits. Image sets to be compared were acquired during the same session and using the same acquisition settings. 2of9
3 Fig. S1. Phenotypic characteristics of CLL cells in E -TCL1 mice. (A) Development of CLL disease was demonstrated by increased CD5 CD19 Ig ( or ) coexpression B cells in 12-month-old E -TCL1 mice. Data represents phenotypic characteristics of 12 E -TCL1 mice. (B) Enlargement in spleen from 12-month-old E -TCL1 mouse with CLL compared to 12-month-old E -TCL1 mouse without CLL. 3of9
4 Fig. S2. CLL induces changes in gene-expression profiles in T cells from E -TCL1 mice. Hierarchical clusters of (A) CD4 T cells and (B) CD8 T cells from WT mice (n 6), E -TCL1 mice with CLL (n 12), or young mice infused with CLL cells (n 6) compared to E -TCL1 mice without CLL (n 4) using dchip to perform an unsupervised statistical analysis as described in Materials and Methods. 4of9
5 Fig. S3. CLL cells induce in vivo molecular and protein expression changes in CD4 and CD8 T cells from E -TCL1 mice with CLL and after infusion (i.v. injection, IV) of CLL cells in young mice. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis confirmed gene-expression changes seen on the microarrays, represented here by decreased expression of Il12 in both CD4 and CD8 T cells from mice with CLL (CLL) and young mice infused with CLL cells (IV-CLL) compared to WT mice. The results represent fold-difference of the mean of triplicates relative to mean GAPDH expression and is representative of 3 experiments performed. (B) Western blot analysis confirmed changes in protein expression were consistent with the altered gene-expression profiles, as shown here with decreased expression of PI3K and Lyn proteins in CD4 T cells. The figure is representative of 3 independent experiments performed. (C) Immunophenotypic changes in protein expression confirmed changes in gene-expression profiling. Shown here is decreased expression of CD28 and BTLA and increased expression of CD25 and CTLA-4 in CD4 T cells from mice with CLL (Middle) or young mice infused with CLL (Right). Age-matched WT mice were used as comparative controls (Left). The expression levels were measured using flow cytometry as % cells/10,000 cell count. Figure plots shown are representative of 3 independent experiments. 5of9
6 Fig. S3. continued. 6of9
7 Table S1. Classification of differentially expressed genes in CD4 T cells by their involvement in specific signaling pathways Pathway Probe set ID Gene name Gene symbol Fold (CLL vs. healthy) A. MAPK-dependent cell proliferation pathway Ras-dependent Th cell differentiation pathway Cytokine/chemokine response pathway _a_at Myb proto-oncogene protein Myb _at Cytotoxic T lymphocyte associated protein 4 CTLA _a_at Lymphocyte protein tyrosine kinase Lck _at CD28 antigen CD _at B and T lymphocyte attenuator BTLA _s_at Vav3 oncogene Vav _s_at Protein kinase C, epsilon Pkce _at Reticuloendotheliosis oncogene Rel _s_at Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible 45 beta Gadd45b _a_at Yamaguchi sarcoma viral (v-yes-1) oncogene homolog Lyn _at Mitogen activated protein kinase kinase 1 Map2k _at Kirsten rat sarcoma oncogene 2 Kras _at Related RAS viral (r-ras) oncogene homolog 2 Rras _at Mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 3 Map3k _a_at Interferon (alpha and beta) receptor 2 Ifnar _at mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 Mapk _at FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene B Fosb _x_at B-cell leukemia/lymphoma10 Bcl _at Jun oncogene Jun _a_at Nuclear factor kappa-b1 Nfkb _at Transforming growth factor, beta receptor I Tgfbr _at Transforming growth factor, beta receptor II Tgfbr _a_at Transforming growth factor B induced factor Tgif _at Sloan-Kettering viral oncogene homolog Ski _a_at SKI-like Skil _at CREB binding protein Crebbp _at Mad homolog 7(Madh7) Smad _at Interferon gamma receptor 2 Ifngr _at Interleukin 12b Il12b _at Interleukin enhancer binding factor 3 Ilf _s_at Interferon alpha responsive gene Ifrg _at Interferon regulatory factor 4 Irf _x_at Granulin Grn _at Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 Tnfsf _at Chemokine (C-X-C) motif receptor 4 Cxcr4 2.3 Differentially expressed genes involved in MAPK-dependent cell proliferation and actin cytoskeletal formation, ras-dependent (Th cell differentiation) and cytokine/chemokine response pathways in CD4 T cells from E -TCL1 mice with CLL or young mice infused with CLL cells compared to E -TCL1 mice without CLL are represented by selected genes. Increased gene expression ( Fold) and decreased gene expression ( Fold) in T cells from CLL compared to healthy mice. 7of9
8 Table S2. Classification of differentially expressed genes in CD8 T cells by their involvement in specific signaling pathways Pathway Probe set ID Gene name Gene symbol Fold (CLL vs healthy) Vesicle-trafficking, cytoskeleton organization, intracellular transport and cell motility pathways Cytokine-Chemokine regulation pathways _a_at Rac GTPase-activating protein 1 Racgap _at Member of RAS oncogene family Rab27a _at Member of RAS oncogene family Rab3d _s_at Adaptor protein complex AP-1, Ap1 g2 1.9 gamma 2 subunit _at Adaptor-related protein complex Ap3 s , sigma 1 subunit _at Golgi phosphoprotein 2 Golph _a_at Vesicle-associated membrane Vamp5 1.4 protein _at Member of RAS oncogene family Rab _at Member of RAS oncogene family Rab33b _at Solute carrier 12 member 2 Slc12a _a_at Vesicle-associated membrane Vapa 1.5 protein-associated protein A _at Kirsten rat sarcoma oncogene 2 Kras _at Cell division cycle 42 Cdc _a_at Protein kinase C, beta Pkcb _at Interleukin 18 receptor accessory Il18rap 1.9 protein _at Chemokine (C-C) receptor 2 Ccr _at Intercellular adhesion molecule Icam _at Interleukin 18 Il _at Guanine nucleotide binding protein Gnaq 2.1 alpha q polypeptide _s_at Guanine nucleotide binding protein, Gna alpha _at IQ motif containing GTPase activating Iqgap1 1.4 protein _s_at Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase, regulatory Pik3r4 1.9 subunit, polypeptide 4, p _at Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, C2 domain Pik3c2a 1.8 containing, alpha polypeptide _at Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase, Pip5k2a 1.5 type II, alpha _at Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, Tnfrsf13b 2.3 member 13b _at Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 Vcam _at Integrin alpha X Itgax _at Interleukin 12b Il12b _at Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 Cxcl _at Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 Cxcl9 2.3 Differentially expressed genes involved in cytoskeleton organization, vesicle trafficking, intracellular transport, cell motility and cytokine-chemokine regulation pathways in CD8 T cells from E -TCL1 mice with CLL or young mice infused with CLL cells compared to E -TCL1 mice without CLL are represented by selected genes. Comparison of expression levels between E -TCL1 mice with CLL, young mice infused with CLL cells, and E -TCL1 mice without CLL were detected using a supervised analysis (P 0.05). Increased gene expression ( Fold) and decreased gene expression ( Fold) in T cells from CLL compared to healthy mice. 8of9
9 Table S3. Characteristics of mice used for the gene-expression profiling studies Mice Gender Wild type E -TCL1 E -TCL1 injected with CLL cells Male Female Age, month Tumor cells, % T cell purity, % TCL1 gene transgenic B6C3 mice (E -TCL1)(n 16) were examined for lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly to detect for CLL development. At different ages ( months old) and visibly ill, mice were killed to obtain hematopoietic tissues, including spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow, peripheral blood, and liver. To analyze the in vivo impact of CLL cells on T cells, E -TCL1 mice without CLL (n 6) were infused (intravenous injection) with splenic mononuclear cells with a high number of CLL cells ( 98% CD5 CD19 Ig light chain B cells). Confirmation that no CLL was seen in young mice was assessed by immunophenotyping of peripheral blood samples. Age-matched WT (B6C3) mice (n 6) were used as controls. 9of9
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
Supplemental Figure 1. Furin is efficiently deleted in CD4 + and CD8 + T cells. a, Western blot for furin and actin proteins in CD4cre-fur f/f and fur f/f Th1 cells. Wild-type and furin-deficient CD4 +
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum...1. Trademarks: HiLyte Fluor (AnaSpec, Inc.)
 Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion
 Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs;
 regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs; p.vandersluijs@umcutrecht.nl cytotoxic T cell recognizes complex of viral peptide with MHC class I and kills infected cell
regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs; p.vandersluijs@umcutrecht.nl cytotoxic T cell recognizes complex of viral peptide with MHC class I and kills infected cell
To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Supporting Information Table of Contents
 Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of Contents Supporting Information Figure 1 Page 2 Supporting Information Figure 2 Page 4 Supporting Information Figure 3 Page 5 Supporting Information Figure 4 Page 6 Supporting
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
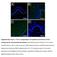 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
B220 CD4 CD8. Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN
 B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
B220 CD4 CD8 Natarajan et al., unpublished data Figure 1. Confocal Image of Sensitized HLN. Representative image of a sensitized HLN showing B cell follicles and T cell areas. 20 µm thick. Image of magnification
Figure S1. A Non-lesional Lesional
 Figure S1 Non-lesional Lesional GEN1 Non-lesional GEN1 Lesional C Normal Negative control Figure S1. Dermal Populations of + cells are found in human skin. Immunohistochemistry for on fixed, frozen skin
Figure S1 Non-lesional Lesional GEN1 Non-lesional GEN1 Lesional C Normal Negative control Figure S1. Dermal Populations of + cells are found in human skin. Immunohistochemistry for on fixed, frozen skin
MCB 4211 Basic Immunology 2nd Exam; 10/26/17 Peoplesoft #:
 For this first section, circle the letter that precedes the best answer for each of the following multiple-choice questions. LOOK AT ALL ALTERNATIVES BEFORE CHOOSING YOUR ANSWER. 1. The TcR (T cell receptor)
For this first section, circle the letter that precedes the best answer for each of the following multiple-choice questions. LOOK AT ALL ALTERNATIVES BEFORE CHOOSING YOUR ANSWER. 1. The TcR (T cell receptor)
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or
 Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
Figure S1. Western blot analysis of clathrin RNA interference in human DCs Human immature DCs were transfected with 100 nm Clathrin SMARTpool or control nontargeting sirnas. At 90 hr after transfection,
activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1 compares CXCR4 expression in untreated CD8 + T cells, following activation with anti-cd3/cd28 beads and 3d following transduction. Supplemental Figure 2 shows the
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
 Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens
 1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
Supplementary Materials for
 immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. b-galactosidase staining of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Clinical significance of ZNF322A overexpression in Caucasian lung cancer patients. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of ZNF322A protein expression in tissue
Eosinophils are required. for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow
 Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
Supplementary Figure 1 Lymphocytes can be tracked for at least 4 weeks after
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lymphocytes can be tracked for at least 4 weeks after photoconversion by using H2B-Dendra2. 4-5 PPs of H2B-Dendra2 BM chimeras were photoconverted and analyzed 7 days (upper panel)
Supplementary Figure 1 Lymphocytes can be tracked for at least 4 weeks after photoconversion by using H2B-Dendra2. 4-5 PPs of H2B-Dendra2 BM chimeras were photoconverted and analyzed 7 days (upper panel)
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs
 Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
T cell Receptor. Chapter 9. Comparison of TCR αβ T cells
 Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
Supporting Information lpek et al. 1.173/pnas.1121217 SI Materials and Methods Mice. cell knockout, inos / (Taconic arms), Rag1 /, INγR /, and IL-12p4 / mice (The Jackson Laboratory) were maintained and/or
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to
 Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
Class II tetramer staining Commercially available HLA Class II tetramers (Beckman Coulter) conjugated to PE were combined with dominant HIV epitopes (DRB1*0101-DRFYKTLRAEQASQEV, DRB1*0301- PEKEVLVWKFDSRLAFHH,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3957
 Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplemental Materials for. Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to. FTY720 during neuroinflammation
 Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS BMP6 treatment compensates for the molecular defect and ameliorates hemochromatosis in Hfe knockout mice Elena Corradini, Paul J. Schmidt, Delphine Meynard, Cinzia Garuti, Giuliana
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Supplementary Figure 1 a Percent of body weight! (%) 4! 3! 1! Epididymal fat Subcutaneous fat Liver SD Percent of body weight! (%) ** 3! 1! SD Percent of body weight! (%) 6! 4! SD ** b Blood glucose (mg/dl)!
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Supplementary Figure 1: Co-localization of reconstituted L-PTC and dendritic cells
 a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
a CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-y CD11c Na + K + ATPase Na + K + ATPase CD11c x-z c b x-y view BoNT NAPs CD11c BoNT CD11c NAPs BoNT NAPs CD11c 90 x-z view Apical Basolateral Supplementary
Serafino et al. Thymosin α1 activates complement receptor-mediated phagocytosis in human monocyte-derived macrophages. SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Supplementary Fig. S1. Evaluation of the purity and maturation of macrophage cultures tested by flow cytometry. The lymphocytic/monocytic cellular fraction was isolated from buffy coats of healthy donors
Chapter 11. B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation. Pro-B cells. - B cells mature in the bone marrow.
 Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Chapter B cell generation, Activation, and Differentiation - B cells mature in the bone marrow. - B cells proceed through a number of distinct maturational stages: ) Pro-B cell ) Pre-B cell ) Immature
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the
 Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Supplementary Figure 1. LAG3 + Treg-mediated regulation of germinal center B cells and follicular helper T cells is Egr2-dependent. (a) Diagrammatic representation of the experimental protocol for the
Protein SD Units (P-value) Cluster order
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE AND FIGURES Table S1. Signature Phosphoproteome of CD22 E12 Transgenic Mouse BPL Cells. T-test vs. Other Protein SD Units (P-value) Cluster order ATPase (Ab-16) 1.41 0.000880 1 mtor
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE AND FIGURES Table S1. Signature Phosphoproteome of CD22 E12 Transgenic Mouse BPL Cells. T-test vs. Other Protein SD Units (P-value) Cluster order ATPase (Ab-16) 1.41 0.000880 1 mtor
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. NKT ligand-loaded tumour antigen-presenting B cell- and monocyte-based vaccine induces NKT, NK and CD8 T cell responses. (A) The cytokine profiles of liver
Live cell imaging of trafficking of the chaperone complex vaccine to the ER. BMDCs were incubated with ER-Tracker Red (1 M) in staining solution for
 Live cell imaging of trafficking of the chaperone complex vaccine to the ER. BMDCs were incubated with ER-Tracker Red (1 M) in staining solution for 15 min at 37 C and replaced with fresh complete medium.
Live cell imaging of trafficking of the chaperone complex vaccine to the ER. BMDCs were incubated with ER-Tracker Red (1 M) in staining solution for 15 min at 37 C and replaced with fresh complete medium.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice
 Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (a) CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (tg) were treated with 8 ng/g body weight (b.w.) diphtheria toxin (DT) i.p. on day -1 and every
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficient DC depletion in CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (a) CD11c.DOG transgenic mice (tg) were treated with 8 ng/g body weight (b.w.) diphtheria toxin (DT) i.p. on day -1 and every
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Mon, Wed, Fri 11:00 AM-12:00 PM. Owen, Judy, Jenni Punt, and Sharon Stranford Kuby-Immunology, 7th. Edition. W.H. Freeman and Co., New York.
 Course Title: Course Number: Immunology Biol-341/541 Semester: Fall 2013 Location: HS 268 Time: Instructor: 8:00-9:30 AM Tue/Thur Dr. Colleen M. McDermott Office: Nursing Ed 101 (424-1217) E-mail*: mcdermot@uwosh.edu
Course Title: Course Number: Immunology Biol-341/541 Semester: Fall 2013 Location: HS 268 Time: Instructor: 8:00-9:30 AM Tue/Thur Dr. Colleen M. McDermott Office: Nursing Ed 101 (424-1217) E-mail*: mcdermot@uwosh.edu
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3631
 Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Supplementary Figure 1 SPT analyses of Zap70 at the T cell plasma membrane. (a) Total internal reflection fluorescent (TIRF) excitation at 64-68 degrees limits single molecule detection to 100-150 nm above
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/83/LAP/#2.006 B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/86/LAP/#2.016 CD11C B6/COLODR/SPL/11C/80/LAP/#2.011 CD11C
 CD3-specific antibody-induced immune tolerance and suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis involves TGF-β production through phagocytes digesting apoptotic T cells Sylvain Perruche 1,3, Pin Zhang 1,
CD3-specific antibody-induced immune tolerance and suppression of autoimmune encephalomyelitis involves TGF-β production through phagocytes digesting apoptotic T cells Sylvain Perruche 1,3, Pin Zhang 1,
