Biology 218 Human Anatomy
|
|
|
- Cassandra Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Picture 1. This image represents a whole mount (NOT a section ) of mesentery (the tissue which binds together the loops of intestine within the peritoneal cavity. This view looks through the entire mesentery, which is a sandwich of mesothelium on front and back surfaces with loose connective tissue and blood vessels in between. The two most common cell types are mesothelial cells and fibroblasts. Picture 2. In this image indicates the Connective Fibrous Loose Areolar collagen, mast cells and elastic fibers. Picture 3. The thick bands are the protein collogen and the thin dark thread like are the protein elastin. Picture 4. Another image of blood/lymp vessels, pointer 1 - bundle of collagen fibres circled and pointer 2 - each elastic fibers are shown. Picture 5. Image of mucous membrane between tissue of body organs which has collagenous and elastic fibers. Body Parts / Organs Mesentery (loops of intestine) Skin Blood Vessels Blood/Lymph Vessels Mucous Membrane kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/.../lb4pg6.htm kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.ca/.../lb4pg6.htm Picture 1 is a picture of tissue taken from the umbilical cord (Wharton's jelly) of a newborn. The cell size is 50um. Picture 2 image shows connective tissue deep in skin.subcutaneous adipose tissue occupies the lower left portion of the image. Fibrous connective tissue of the dermis occupies the remaining regions and includes a conspicuous artery, a small nerve, and a cluster of lymphocytes. Several smaller blood vessels may also be seen. Adipose Numerous capillaries in this area cannot be reliably recognized in this specimen. Picture 3 image is from venule mesentery (close image), the cell size is 20um. Picture 4 image can be found in the subcutaneous layer behind the eyes, you can see the adipocyte and adipocyte nucleus. Picture 5 this is a tissue sample from parathyroid gland where the adipocytes are labeled Body Parts / Organs Umbilical cord (Wharton's jelly) Skin, dermis and hypodermis Venule, Mesentery Subcutaneous Layer behind the Eyes Parathyroid Gland Reticular Picture 1. This tissue image taken from the lymph nodes consist of very dark thread like fibers called reticular fibers, fibroblast and the small dark circular cells called lymphocyte, forms the internal stroma of the soft organs. Picture 2. This image form network or lattice in this spleen tissue. Picture 3. Tissue Image taken from the lymph node shows a more detailed view. Picture 4. Another tissue sample of spleen from a different angle and shows more reticular fibers. Body Parts / Organs Lymph node Spleen Lymph node Spleen Page.htm Dense Regular Picture 1. This tissue image is a tendon, it shows the regular pattern or arrangements of the collagen fibers. Picture 2. This is an image of a ligament tissue which shows us the fibroblasts that are making the collagen bundles. The blue arrows points to the collagen bundles while the green arrows points to the fibroblast nuclei. Picture 3. Another image of tendon tissue that shows the regular pattern of the collagen fibers, a great sample of dense regular connective tissue. Picture 4. This is a sample tissue of joint capsules which shows the regular pattern of collagen fibers. Body Parts / Organs Tendon Ligament tendon Joint Capsules nse_connective_tissue.htm Irregular Picture 1. This is a dermis tissue image under the epithelium. This is a good example of dense irregular connective tissue because the arrangement of fibers are in an irregular pattern or in different direction. Picture 2. Another tissue sample of the dermis but more detailed view. The yellow line shows the collagen fibers and the green arrow points to the long elastic fibers and again looks dense but runs in different direction. Picture 3. Found in Lip between the hair follicles, there's the collagen fibers (blueish gray) and the elastin fibers (red/brown). Picture 4. This is a tissue found in the dermis of the skin in breast. The arrows pointing to collagen fibers, blood vessels, connective tissue nuclei. Body Parts / Organs Dermis Dermis Lip between hair follicles Non-lactating Breast nse_connective_tissue.htm onnective.htm Elastic Picture 1. This is a tissue sample from the wall of aorta, a good example of elastic dense connective tissue. The arrows are pointing to the elastic fibers and fibroblasts. Picture 2. This image is from the walls of arteries and shows the elastic fibers in more detailed view, and the internal elastic lamina. Picture 3. This is a tissue from the dermis of the skin, again shows elastic fibers (black). Picture 4. Another tissue from the artery, see the elastic fibers in the adventitia section and in the media section there's the internal elastic lamina and intima. Body Parts / Organs Wall of Aorta Wall of elastic arteries Dermis Artery GIF Page 1 of
2 Picture 1. An image of the Trachea, a sample of hyaline cartilage, indicated by the arrow. Picture 2. This is a tissue sample of human nose, a sample of hyaline cartilage, pointed by the arrow are the matrix, chondrocyte, lacuna, chondroblast, perichondrium. Picture 3. Another image of the Trachea in more focused view. This organ is supported by C-shape rings of hyaline cartilage, also the cells are grouped into small clusters or cell nests called Supportive Cartilage Hyaline isogenous groups. Picture 4. An image of Aortic Valve, microscopically, it showed extensive degenerative changes, which included multiple foci of calcification, bone metaplasia, and formation of hyaline cartilages. The largest focus of mature hyaline cartilage measures 2.1x0.2 cm, which was composed of unilacunated chondrocytes with small, but distinct nuclei embedded in semitranslucent matrix There were no nuclear atypia or Body Parts / Organs Trachea Nose Trachea Aortic Valve education.vetmed.vt.edu/.../labs/lab7/lab7.htm g y therefore called elastic cartilage and can be distinguished by the stain for elastin that brings out the dense bundles. Picture 2. This is an image of the Epiglottis. The main support of this organ is a plate of elastic cartilage surrounded by perichondrium. The cell size is 100um. Picture 3. Another image of Epiglottis, the pointer arrow points to the heterogenous matrix with Elastic elastic fibers and the chondrocytes in lacunae. Picture 4. An image of the external Ear, this is a more focused view and stained to easily see the elastic fibers. Body Parts / Organs Ear Epiglottis Epiglottis External Ear cellbio.utmb.edu/microanatomy/bone/cartilage.htm w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/cartilage.html virtual.yosemite.cc.ca.us/.../slides.htm Picture 1. This is an image of Intervetebral disk, sample of fibrocartilage tissue. The arrows points to the collagen fibers and to the chondrocytes in the lacunael. It has a similar appearance to dense collagenous CT than to the traditional cartilage, also they have similarities as well. Picture 2. This is a tissue sample from the pubis symphysis. There is no recognisable perichondrium. The cells are squeezed into rows by thick bundles of Fibro collagen fibres in the matrix. The collagen is orientated in the direction of stress. The gel component of the matrix is reduced. Picture 3. This is an image of the menisci of the knee, you can still see the collagen fibers and the lacunae. Picture 4. Another sample tissue of Pubis symphysis, this is the higher magnification of the fibrocartilage. The red arrows are pointing to the collagen fibers and the blue arrow are pointing to the chondrocytes in the Body Parts / Organs Intervetebral Disk Pubis symphysis Menisci of the knee Pubis symphysis education.vetmed.vt.edu/.../labs/lab7/lab7.htm www3.umdnj.edu/.../lab4fibrocartilage.html Bone Compact Picture 1. This is an image of the Humerus, sample tissue of compact bone. In this image, in the center is the osteon inside is the haverisian canal, the concentric ring is the lamellae and the dark spots called the lacuna and the threadlike structures are the canaliculi. Picture 2. Another image of Femur in a different view, it is clearly labeled where the compat bone is beside tha bone is the periosteum. Picture 3. This is a different slide of the femur, the arrows pointing to the periosteum and the endosteum. Picture 4. In this image of the scapula, the dark circular center is the osteon and the not so clear concentric rings is the lamellae. Body Parts / Organs Humerus Femur Femur Scapula w3.ouhsc.edu/histology/text%20sections/bone.html isto.life.uiuc.edu/histo/atlas/image.php?sname=m11&iname=350a1&w=500 Spongy Picture 1. This is an image of the Humerus at high power, the bone matrix is lined with osteoblasts and within the matrix are osteocytes. Picture 2. This is an image of the Femur with trabeculae (pink color) it contians osteocytes in the lacunae and the periosteum. Picture 3. This is an image of spongy bone tissue in the epiphyses of either the Femur or Humerus, the ossified trabeculae are thin and surrounded by bone marrow and blood vessels. Osteons are mostly absent, and the spaces between spicules are filled with hemopoietic tissue. Picture 4. Another image of spongy bone in the head of a long bone, marrow space is labeled also have the trabeculae, osteocytes, cancellous cavity and red marrow. Body Parts / Organs Humerus Femur with trabeculae Epiphyses (Femur or Humerus) Head of a long Bone commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/image:spongy_bone_... faculty.ircc.edu/.../histology_flash_cards.htm Page 2 of
3 Platelets.jpg commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/image:platelets.jpg xambm41.jpg g name=licha_iv.a.018.jpg gans/8-lymph%20node.jpg g Biology 218 Human Anatomy Fluid Blood Cells Erythrocytes Picture 1. This is an image of human red blood cells (erythrocytes), they are the most abundant elements and the easiest to identify. There are no nucleus and uniform in size. Picture 2. Another image of just one erythrocyte and its measurement which is mm. Picture 3. This is an image of blood in urine. The arrow is pointing to the erythrocytes, often appear as regular, dark cells. Picture 4. An image of erythrocytes in Bone marrow where they are mostly made. Again, no nucleus and have almost the same size. Body Parts / Organs Erythrocytes Erythrocytes Blood in Urine (erythrocytes) Erythrocytes in Bone Marrow user.gru.net/clawrence/vccl/chpt7/erythro.htm flickr.com/photos/ @n00/ Leukocytes Basophil Picture 1. This is an image of Basophil in human white blood cells (leukocytes, color purple), and microns in diameter. Picture 2. Another image of the basophil found in the Bone Marrow, on this image basophilic granules are visible and it is colored dark purple. Picture 3. In this image is a more detailed and enlarge view of the basophil leukocyte, its nucleus is not lobulated and the granules are visible and it is 10 to 15 um in diameter. Picture 4. This is an image of an immature basophil pointed by the arrow, in which basophilic specific granules are present but other phenotypic features of the mature form is lacking. Body Parts / Organs Human Blood Bone Marrow Human Blood Human Blood / Immature education.vetmed.vt.edu/.../labs/lab6/lab6.htm faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/histolab3a.htm Picture 1. This is an image of Eosinophil found in human white blood cells. It shows the distinct large eosinophilic granules (bright pink) and the nucleus is bilobed. Picture 2. In this image of Eosinophil found in human blood, the cell indicated by the arrow is an eosinophilic myelocyte and immature eosinophil. Picture 3. This is an image of Eosinophils in the Gall Bladder Eosinophil which in this specific image you will see an ulcerated gall bladder mucosa, granulation tissue and lymphoplasmocytic infiltrate with marked increase in number of eosinophils, suggesting eosinophilic cholecystitis. Picture 4. An image of Eosinophils in the airways of the Lungs. It has a plug of eosinophilrich inflammatory exudate and mucus in the airway of a patient with asthma, concentric rings of eosinophils appears in blue. Body Parts / Organs Human Blood Blood / Immature Gall Bladder Lungs (airways) polarizadorjym.wordpress.com/.../ Picture 1. In this image of human blood smear, the neutrophils are clearly shown, its cytoplasm is consist of light violet or pink granules and the nucleus consists of several lobes connected by a narrow chromatin strands. Picture 2. Another image of blood smear which shows a single band neutrophil. They are usually 9 to 15 µm in diameter.the nucleus forms a "U" or curled rod prior to segmentation. The chromatin pattern is coarse and Neutrophil clumped. Picture 3. This is an image of neutrophils found in the Bone Marrow, pointed by the arrow is an neutrophilic myelocyte, it is an immature neutrophil. The nuclear chromatin is more coarse and is starting to clump, most of the granules are still primary granules, most of the cytoplasm is still blue, and nucleoli are still visible. Picture 4. An image of brand and mature neutrophils in the Bone Marrow in the Femur of an infant The band Body Parts / Organs Blood Blood Bone Marrow / Immature Bone Marrow / Femur commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/image:segmented_ne Lymphocyte Picture 1. This is an image of Lymphocyte in the Blood and have a large nuclues and larger than red blood cells. Picture 2. This is an image of a large granular lymphocytes in Blood. You can see a clearer view of the nucleus on this image. Picture 3. This is a sample of Lymphatic tissue and as you can see the lymphocytes is in a more magnified view. Picture 4. This image is a young lymphocyte normally found in Blood, it is larger with more abundant basophilic cytoplasm. Body Parts / Organs Blood Blood smear Lymphatic Tissue Blood cellbio.utmb.edu/.../blood/blood_cells.htm Monocyte Picture 1. This is an image of monocytes in the blood. They are large mononuclear phagocytes of the peripheral blood and immature stage of macrophage. Their size is from 10 to 30 um. The nucleus looks like a horse shoe. Picture 2. Another image of monocyte in blood, notice the kidney shaped nucleus. Picture 3. In this image the monocyte found in blood has a nucleus in a shape of a fetal position inside the womb. Picture 4. This image of monocyte has a "brainy" folded nucleus, a fine "ground glass" appearance to the cytoplasm, and cytoplasmic vacuoles. Body Parts / Organs Blood Blood Peripheral Blood Blood faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/histolab3a.htm pathmicro.med.sc.edu/bowers/immune%20cells.htm Macrophage Picture 1. This is an image of alveolar macrophage found in the lungs, labeled and pointed by the arrow, you can see the nucleus and some dark spots that surrounds it and measures 10um. Picture 2. In this image of the inner region of the Lymph node (medulla) is filled connective tissue that contains a lot of macrophages labeled as M. The nucleus is visible. Picture 3. This is an image of two macrophages found in the Bone marrow. One has numerous presumptive iron particles and the other has ingested several erythrocytes and has a lot of iron particles. Picture 4. Another image of macrophages in the Lungs and as you can see the nucleus is visible. Body Parts / Organs Lungs Lymph node (Medulla) Bone Marrow Lungs cellbio.utmb.edu/.../specialized_cells.htm www1.imperial.ac.uk/medicine/news/heartlung/ Platelets Picture 1. This is an image of peripheral blood tissue where you can see the platelets circulating as small discs. It measures an average 1 to 4um in diameter. The cytoplasm stains light blue to purple, and is very granular and no nucleus present. Picture 2. Another image of blood and you see the arrows pointing at some platelets and they measures 10um. Picture 3. This image shows clumping of platelets with some red blood cells caught in between and around the platelets. Picture 4. This is an image of qualitative platelet abnormalities. First picture, two giant platelets one with no granules. Second picture, large platelets with no granules. Third picture, large platelet with abnormal central structure. Body Parts / Organs Peripheral Blood Blood smear Blood Smear Blood Plasma Picture 1. This image of Plasma cells found in Blood, more magnified view and you can see the nucleus very clear. Picture 2. Another image of plasma cells in Bone Marrow, indicated by the arrows the nucleus on the left has small rounded nucleus with granules, the nucleus on the right has no granules. Picture 3. This image of Lymphocytic Hypophysitis, an inflamed Pituitary Gland that reveals a diffuse inflammatory infiltrate composed mainly of lymphocytes and plasma cells forming occasional lymphoid follicles. Picture 4. Another image of Plasma cells in Blood but this one has binucleated plasma cell indicated by the arrow which is a plasma disorder. Body Parts / Organs Blood Bone Marrow Pituitary Gland Blood Lymph Picture 1. The white space pointed by the blue arrow is the lymph (extracellular fluid) in the lymphatic vessel of spermatic cord. Picture 2. This is an image of afferent lymphatic vessel, consist of lymp and the cell size is 200um. Picture 3. Image of Lymph node (cortex) and the clear space arround the nodes are lymph fluid. Picture 4. This is an image of lymphatic vessels in case of edema, the clear space in between the cells are the lymph. Body Parts / Organs Spermatic cord Lymphatic vessels Lymph node cortex Lymphatic vessel (edema) Page 3 of
4 Nervous Neurons Picture 1. This is an image of two neuron tissues found in the Brain, the top one is called a bipolar neuron, it has a clear view of the cell body and the axon. The developing neuron (bottom) is just the cell body is present, no axon and dendrites. Picture 2. This image of motor neurons found in the Spinal cord consist of a cell body and axon and measures 20um. Picture 3. This image of Pyramidal neuron found in the Cerebrum, in here the axon is pointed by the arrow, also it has a cell body and dendrites as well and measures 50um. Picture 4. This is a cross section of the human spinal cord lumbar region showing the nucleus, nucleolus, cell body, axon and oligodendrocytes (O) and astrocytes (A) as labeled and pointed by the arrows. Body Parts / Organs Brain Spinal Cord Cerebrum Spinal Cord Picture 1. This image of Satellite cells found in the Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG) shows the central nuclei, indicated by the yellow arrow, the white arrows are pointing to nuclei of cells that surrounds each sensory neuron called satellite cells. Picture 2. An image of Satellite cells in Trigeminal Neuroglia Peripheral 2 types Satellite cells Ganglion are pointed by the arrows. It surrounds the cell body of pseudounipolar neurons. Picture 3. This image of satellite cells indicated by the arrows are small rounded cells that surrounds the cell body of a neuron. Picture 4. Another image of satellite cells in Dorsal Root Ganglion from a person with HIV. The nagoette nodules are compact areas of multiplying satellite cells that accompany DRG neuronal loss, infiltration activated by macrophages (indicated by the arrow and line). Body Parts / Organs Dorsal Root Ganglion Trigeminal Ganglion Brain Dorsal Root Ganglion Schwann cells Picture 1. This is an image of the schwann cells in the Brain, non myelinated nerve fibers and visible elongated nuclei. Picture 2. This is a left superficial peroneal nerve biopsy in the lower one third of the leg performed on an old woman with progressive paresthesia, notice the presence of regenerative cluster pointed by the arrow. Picture 3. Image of schwann cells in the cranial nerves, their nuclei are the dark, cigar-shaped structures among the myelinated fibers.. Picture 4. This is an image of schwann cells in Dorsal Root Ganglion, labeled and indicated by the blue arrows. Body Parts / Organs Brain Human Leg (left) Cranial nerves Dorsal Root Ganglion picasaweb.google.com/.../xqhkoibcxt8pocrwikbjdg Central 4 types Ependymal cells Picture 1. This image of the ependymal cells found in between the Cerebellum and Medulla, arranged in a single layer labeled and pointed by the blue arrow. Picture 2. An image of ependymal cells in the Spinal Cord that shows the ependymal cells are all packed together pointed by the blue arrow and lies next to the cental canal. Picture 3. This image of the central canal in Spinal cord, the ependymal cells are lined up in a single pile. Picture 4. Image of the Spinal cord, central canal, here the ependymal cells are lined, often cilated and form a simple cuboidal or low columnar epithelium, cilia is visible. Body Parts / Organs Cerebellum and Medulla Spinal Cord Spinal Cord Spinal Cord Astrocytes Picture 1. This image of fibrous astrocytes in the Cerebrum (white matter), have many long unbranched processed and its cell size is 50um. Picture 2. This is an image of protoplasmic astrocytes found in the Cerebrum (gray matter), have many short branching processes and its cell size is 50um. Picture 3. Another image of fibrous astrocytes in the Cerebrum in a manified view, you can still see the long unbranched processes and the cell size is 20um. Picture 4. Another image of protoplasmic astrocyte in the human Brain, it still has that short branching processes. Body Parts / Organs Cerebrum Cerebrum Cerebrum Brain Oligodendrocytes Picture 1. This is an image of an oligodendrocytes cell of an adult Brain, it has fewer processes. Picture 2. This image of a normal adult oligodendrolial cells in the cortex. Picture 3. Another image of oligodendrocyte cells in the Brain, smaller than astrocytes and have fewer processes. Picture 4. This is image of oligodendrocyte cells in the Brain of a person who have a rare disease called progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). The blue arrow points toward an oligodendrocyte nucleus which has been enlarged with viral particles, giving it a magenta color. Body Parts / Organs Adult Brain Cortex Brain Brain missinglink.ucsf.edu/.../didactic/pml.htm Microglia Picture 1. This image of microglia in the human Brain is small cell with slender processes and numerous spinelike projections. Picture 2. This is an image of microglia in a normal human brain and have a rod-shaped nuclei. Picture 3. On this stained image of microglia in human brain, you can see the slender processes. Picture 4. This image of microglia came from a brain cerebral cortex section from a patient with Tay-Sachs disease. The Microglia are visible and stained (brown). Body Parts / Organs Brain Normal Human Brain Brain Brain cerebral cortex hmg.oxfordjournals.org/.../issue11/cover.dtl Page 4 of
5 Epithelial Simple Squamous Picture 1. This is an image of simple squamous epithelium in mesentry, the cells are flat and in single layered, also several nucleus are also visible, the cell size is 20um. Picture 2. Another image of simple squamous epithelium found in cheek (oral smear), cells are single layered and flat and the nuclues of each cells are visible. Picture 3. In this image of the sublingual gland blood vessels are lined by simple squamous epithelium indicated by the gray circle. Picture 4. This is an image of the stomach tissue, the cells are once again flat and single layered wih the nuclei in the center. Body Parts / Organs Mesentry Cheek (oral smear) Sublingual Gland Stomach washington.uwc.edu/.../tissuespage.htm Cuboidal Picture 1. This is an image of simple cuboidal epithelium in urinary tubules of the Kidney, it is a single layer of cube-shaped cells and centrally located nuclei, the cell size is 20um. Picture 2. Another image of simple cuboidal epithelium in the medulla of the Kidney, it has several nucleus in the center and cube like shape cells. The cell size is 20um. Picture 3. This image of simple cuboidal epithelium in Thyroid have single layer and cube like shape cells with nuclei in the center of the cells and surrounds the follicles. Picture 4. This is an image of Alveoli tissue in the Lungs, the cells are in circular elongated pattern, flat and single layered. Body Parts / Organs Kidney, urinary tubules Kidney, medulla Thyroid Lung (alveoli) washington.uwc.edu/.../tissuespage.htm capital2.capital.edu/.../histology/simple.htm Columnar Ciliated Picture 1. This is an image of simple columnar - ciliated found in the ampulla of oviduct. The cells are single layered, ciliated column-like and the nuclei is near the base, looks like it has some goblet cells present, cilia is visible and indicated by the arrows. Picture 2. An image of ciliated simple columnar found in the Fallopian tube, labeled and indicated by the arrows are the nucleus, cilia, lumen, and the cells. Picture 3. Blue arrows are pointing to the cilia on this image of simple columnar epithelium in the uterine tube. Picture 4. Another image of ciliated simple columnar found in the uterine tube. The cilia are clearly visible and the cells are column like shape. Body Parts / Organs Ampulla of Oviduct Fallopian tube Uterine Tube faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/histolab2.htm webanatomy.net/.../epithelial_index.htm w3.ouhsc.edu/.../female%20reprodcutive.html pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/pth225.html Non Ciliated Picture 1. This is an image of simple columnar non ciliated and found in the gastrointestinal tract, the cells are single layer non ciliated column-like cells with nuclei and the cell size is 20um. Picture 2. Another image of simple columnar non ciliated found in Ileum (note to see this picture on the website, click the picture itself and the Ileum pic. will show), the cells are labeled and indicated by the lines as wells as the brush border/microvilli. Picture 3. An image of non ciliated simple columnar epithelium found in Duodenum, some goblet cells are visible and also the microvilii pointed by the blue arrow. Picture 4. Non ciliated simple columnar found in the gallbladder, it has column-like cells with nuclei near base of cells and microvilli. Body Parts / Organs Gastrointestinal tract Ileum Duodenum Gallbladder w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html Page 5 of
6 Picture 1. An image of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium found in the skin pointed by the yellow arrow and it shows the thick cornified layer of the skin and the changes in cells as one moves toward the lifeless keratinized cells. Picture 2. Another image of keratinized stratrified squamous found in the skin, labeled and indicated by the arrows are the living stratified cells and the keratinzed or dead cells. Picture 3. The cells on Stratified Squamous Keratinized the surface of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium found in thee palmar skin are very flat and dead and no nucleus. The cells on the basal layer are cuboidal or columnar in shape and have nuclei. Picture 4. The blue line indicates the length of epithelium, yellow line indicates non nucleated keratinized cells and the green line indicates the non keratinized cells, nuclei present Body Parts / Organs Skin Skin Palmar skin Skin (epidermis) w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/histolab2.htm ml Picture 1. This is an image of stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium found in the mucous membranes of the Esophagus, the cells have several layers, cuboidal to columnar in shape in the deep layers and flat on the apical layer. Picture 2. Another image of non keratinized stratified squamous epithelium located in the Esophagus, in this magnified view you can clearly see the several layers of the cells, columnar shape in deep Non Keratinized layers but the squamous cells form the apical layer. Picture 3. Stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium found in the surface of the tongue, the blue line shows cells at the bottom start off round and as they migrate upwards they get more squamous (green line) Picture 4. Non keratinized cells found in the cornea of the eye, there are nuclei present on the flat surface(orange arrow) Body Parts / Organs Esophagus Esophagus Surface of Tongue Cornea w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html faculty.une.edu/com/abell/histo/histolab2.htm Picture 1. This is an image of stratified cuboidal epithelium found in the submaxillary gland, pointed by the yellow arrows are the cube-shaped cells. Picture 2. In this image of stratified columnar epithelium found in sweat gland ducts (thick skin/dermis), two or more layers of cells in which the cells in apical layer are cube-shaped. Picture 3. Another image of the sweat Cuboidal gland ducts epithelial tissue, an example of stratified cuboidal epithelium, there are two layers of cells and in the apical layer are cube-shaped cells. Picture 4. This is an image of stratified cuboidal epithelium found in the sweat glands of the Skin, pointed by the blue arrows are the two layers of cells and the cells in the apical layer are cube-shaped. The cells are formed in circles. Body Parts / Organs Submaxillary Gland Sweat Gland Ducts Sweat Gland Ducts Skin w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/integument.html Columnar Picture 1. This is an image of stratified columnar epithelium found in submaxillary gland, pointed by the yellow arrows are the apical layer that has the columnar cells, also you can see several layers of irregularly shaped cells. Picture 2. In this image of stratified columnar epithelium found in salivary gland, pointed by the needle of the microscope are the columnar cells and underneath it are some irregularly shaped cells. Picture 3. Another image of stratified columnar epithelium found in salivary gland ducts, the cells are columnar in the apical layer and irregularly shaped cells on top of the basement membrane. Picture 4. This image of stratified columnar in the urethra, the cells are columnar on apical layer only and below are several layers of irregularly shaped cells. Body Parts / Organs Submaxillary Gland Salivary Gland (large tubules) Salivary Gland Ducts Urethra w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html cwx.prenhall.com/.../custom1/deluxe-content.html Transitional Picture 1. An image of transitional epithelium found in the Ureter, pointed by the yellow arrows the cells in the apical layer are cuboidal and the middle layers are squamous in shape. Picture 2. This is an image of transitional epithelium found in the Urinary bladder, has several layers of cells some are cuboidal and squamous in shape. Picture 3. This is the transitional epithelium (1) of the prostatic part of the urethra and the tunica propria of the mucosa (2). Picture 4. Another image of transitional epithelium in the urethra (note: in the website under unrinary system/image 701), the shape of cells in apical layer is cuboidal. Body Parts / Organs Ureter Urinary Bladder prostatic part of the Urethra Urethra w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html pathology.mc.duke.edu/research/pth225.html Pseudostratified Picture 1. This is an image of ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium found in the Trachea, the cilia and cells are labeled and pointed by the blue arrows and attached to the basement membrane. Picture 2. Another image of ciliated pseudostratified found in the Trachea, you can see the cilia on the apical surface of the cells, goblet cell (G) and the nuclei are at different levels, cell size is 20um. Picture 3. In this image of the Epididymis (efferent ducts) epithelial tissue the cilia (blue arrow) are clearly shown and the nuclei are in different levels. Picture 4. This image is pseudostratified columnar epithelium that lines most of the penile urethra. The cell nuclei are still in differanet levels and in columnar shape. Body Parts / Organs Trachea Trachea Epididymis Male Urethra w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html w3.ouhsc.edu/.../text%20sections/epithelium.html Page 6 of
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology. Study of body tissues
 Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Chapter 5. Tissues. 4 Types of Body Tissues. Tissues
 Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
The Tissue Level of Organization
 Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review
 Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Anatomy and Physiology Tissue Review OVERVIEW Histology practicals can be rough, especially when access to slides is limited to the lab period. This resource provides an opportunity to learn or review
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Connective Tissue. Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix
 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the matrix (wandering) Macrophages:
What is a tissue? Points to ponder. Tissues Connective Tissue. 1. Connective tissue 2/23/2019. Organization and Regulation of Body Systems
 Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Chapter 04 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education.
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Bio& 241 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 Connective Tissue Consists of two basic elements: Cells and Extra-cellular matrix 1 True Connective Tissue Cells Fibroblasts: Secrete both fibers and ground substance of the
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as
 Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 5 Tissues Four major tissue types 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial Tissues General characteristics - cover organs and the body
Epithelial Tissue. Simple Cuboidal Function: secretion and absorption. Simple Squamous
 Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Histology= the study of tissues
 Unit 3-Histology Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Unit 3-Histology Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job).
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Epithelial cells Epithelium
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous Epithelial cells Epithelium
A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure. B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space
 I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
I. tissue components A. cells that perform related functions and are similar in structure B. extracellular material - made by cells and secreted into interstitial space II. tissue types A. epithelium (e.)
Chapter 05. Review. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 05 Review 5.1: Introduction Similar cells with a common function are called tissues. The study of tissues is called histology. There are four (4) primary or major tissue types: 1. Epithelial Tissue
Chapter 05 Review 5.1: Introduction Similar cells with a common function are called tissues. The study of tissues is called histology. There are four (4) primary or major tissue types: 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues. Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering. 2. Connective support
 Histology Tissues Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering 2. Connective support 3. Muscle movement 4. Nervous control Epithelial
Histology Tissues Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: 1. Epithelial lining and covering 2. Connective support 3. Muscle movement 4. Nervous control Epithelial
Tissues. Tissues. Four basic tissues. A collection of cells with a common function. 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4.
 Tissues Tissues A collection of cells with a common function Four basic tissues 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4. Nervous Epithelia: cells in layers Types of epithelia 1) lining Layers of cells
Tissues Tissues A collection of cells with a common function Four basic tissues 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscular 4. Nervous Epithelia: cells in layers Types of epithelia 1) lining Layers of cells
8/30/2017. Tissue: The Living Fabric. 4.3 Connective Tissue
 Chapter 4 Part B Tissue: The Living Fabric Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 4.3 Connective Tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 4 Part B Tissue: The Living Fabric Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College 4.3 Connective Tissue Connective tissue
Epithelia of Coverings and Linings. Tissues. Tissue
 Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Tissue Tissues Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement Protection Support Production
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System
 Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Unit II: Tissues and Integumentary System 2.1 - Tissues Chapter 4 Written Response #1 1. What is a tissue? 2. What are four major types of tissues? Tissue Definition: a group or mass of similar cells working
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Tissues. How do cells form tissues?
 Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Tissues How do cells form tissues? Using cell junctions Tissues Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial Tissue Closely packed cells in continuous sheets connected by
Histology. The study of tissues.
 Histology The study of tissues. Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Histology The study of tissues. Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S
 UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
UNIT 4 T I S S U E S WHAT IS A TISSUE Group of cells that work together to do a function Cells are similar Extracellular fluid around them is similar Histology EPITHELIAL TISSUE Also called epithelium
Histology 101! !! Name:! Block: Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties!
 Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
 Cells Location Function Simple squamous epithelium Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and
Cells Location Function Simple squamous epithelium Air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and
Tissues Description Function(s) Locations Miscellaneous. avascular -thelium = covering
 Epithelial Tissue Simple Squamous flattened cells diffusion and Kidney glomeruli disc-shaped central filtration air sacs of lung Simple = Single layer nuclei secretes lubricating lining of heart, blood
Epithelial Tissue Simple Squamous flattened cells diffusion and Kidney glomeruli disc-shaped central filtration air sacs of lung Simple = Single layer nuclei secretes lubricating lining of heart, blood
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
The Tissue Level of Organization
 The Tissue Level of Organization 4.5-4.11 August 31, 2012 4.5 Connective Tissues Describe the general features of connective Describe the structure, location, and function of the various types of connective
The Tissue Level of Organization 4.5-4.11 August 31, 2012 4.5 Connective Tissues Describe the general features of connective Describe the structure, location, and function of the various types of connective
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types:
 Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
Tissue Outline (chapter 4) Tissues group of cells that perform structural and roles. List the 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. I. Epithelial Tissue covers all the surfaces, inside & out. Are the major tissues of,
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject:- Anatomy, Physiology and Health Education Class:- B.P. Ed. Semester- I Presented By:- Dr. Mahesh Singh Dhapola Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells.
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject:- Anatomy, Physiology and Health Education Class:- B.P. Ed. Semester- I Presented By:- Dr. Mahesh Singh Dhapola Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells.
Simple Squamous Epithelium
 Histology Simple Squamous Epithelium One layer of flattened cells. Protective characteristics are diminished because of this. Examples: Alveoli in the lungs Capillaries where diffusion of nutrients and
Histology Simple Squamous Epithelium One layer of flattened cells. Protective characteristics are diminished because of this. Examples: Alveoli in the lungs Capillaries where diffusion of nutrients and
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
BIOLOGY. Chapter 33 Animal Body: Histology Portion Pearson Education, Inc.
 BIOLOGY Chapter 33 Animal Body: Histology Portion Tissues: groups of cells with common function Tissue Category Epithelial (covers & lines) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Tissues to know:
BIOLOGY Chapter 33 Animal Body: Histology Portion Tissues: groups of cells with common function Tissue Category Epithelial (covers & lines) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Tissues to know:
CONNECTIVE TISSUE (Refer to pp for specific characteristics of each) VAN (**Be familiar with exceptions**)
 CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
CONNECTIVE TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS: *Most abundant tissue type; Composed of ECM (GS & Protein Fibers) + Cells (Refer to pp.129-131 for specific characteristics of each) *Highly equipped with VAN assists
Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion
 Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio211 Laboratory 2. Epithelial and Connective Tissues
 Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Bio211 Laboratory 2 Epithelial and Connective Tissues 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue (p. 79 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Connective Tissue (p. 93 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Muscle/Nervous
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Tissues, Glands, and Membranes. Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek
 Tissues, Glands, and Membranes Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek Objectives 1. Name the four main groups of tissues and give the location and general characteristics of each. 2. Differentiate between voluntary
Tissues, Glands, and Membranes Chapter Five Mrs. Hornacek Objectives 1. Name the four main groups of tissues and give the location and general characteristics of each. 2. Differentiate between voluntary
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
TISSUES. Objectives. Tissues
 TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE
 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION PART I: EPITHELIAL TISSUE 4 Main Tissue Types Epithelium Covers surfaces, lines cavities, forms glands Connective Tissue Support and protects body Muscular Tissue Movement
Lecture Overview. Connective Tissues. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10 Lecture Overview General composition and function of connective tissue Components of
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Connective Tissues Lecture 10 Lecture Overview General composition and function of connective tissue Components of
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical
 Ch. 3 - Cells and Tissues Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical Miss School, Miss Out! Simple squamous epithelium line and cover; site of diffusion Simple squamous epithelium apical surface
Ch. 3 - Cells and Tissues Tissues and Structures to Know for the Lab Practical Miss School, Miss Out! Simple squamous epithelium line and cover; site of diffusion Simple squamous epithelium apical surface
Tissues. Group of cells that are similar in structure and function. 4 primary types. Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control)
 Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Histology= the study of tissues
 Histology 2014 Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
Histology 2014 Histology= the study of tissues A tissue is a group of cells that have a similar shape and function. Different types of tissues can be found in different organs. In humans, there are four
They cells can not function death.
 Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
What is histology? HISTOLOGY
 Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Introduction to Histology What is histology? HISTOLOGY histo = tissue ogy = study So HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues! What is a TISSUE? Tissues are groups of cells with specialized structural and functional
Tissues organs system organism. pg151
 Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
Histology is the study of tissues A TISSUE is a group of cells, usually of one kind, & their intercellular substance (e.g. intercellular matrix in animal) which are linked together & perform a particular
B. Classification of epithelium: by number of cell layers present and by shape of the superficial cell layers.
 I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology: Epithelial and Connective Tissue The Histology lab involves study of the appropriate laboratory exercise, completing the Review Sheet for the exercise,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology: Epithelial and Connective Tissue The Histology lab involves study of the appropriate laboratory exercise, completing the Review Sheet for the exercise,
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
10/3/2012. Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B. Extracellular matrix Ground substance Fibers Collagen fiber Elastic fiber Reticular fiber.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Human anatomy Unit III. Tissue
 Human anatomy Unit III Tissue Definition of Tissues Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function within an organism. In other words, it is a group of cells
Human anatomy Unit III Tissue Definition of Tissues Biological tissue is a collection of interconnected cells that perform a similar function within an organism. In other words, it is a group of cells
Pick a cell that isn t yours!
 Pick a cell that isn t yours! Quiz 1: Introduction and Cells Module 2: Histology The study of tissues This module is very visual! Know these images! Introduction www.quizlet.com is a very useful tool for
Pick a cell that isn t yours! Quiz 1: Introduction and Cells Module 2: Histology The study of tissues This module is very visual! Know these images! Introduction www.quizlet.com is a very useful tool for
Biology 4B LABORATORY Histology A. EPITHELIAL TISSUE
 Biology 4B LABORATORY Histology Objectives To be able to identify the four major types of vertebrate tissues (epithelial, connective, nervous and muscle). To understand how each type of tissue is organized
Biology 4B LABORATORY Histology Objectives To be able to identify the four major types of vertebrate tissues (epithelial, connective, nervous and muscle). To understand how each type of tissue is organized
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet
 Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Anatomy &- Physiology Histology Worksheet 1. The four primary tissue types found in the human body are a) squamous, cuboidal, columnar, glandular b) adipose, elastic, reticular, cartilage c) skeletal,
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Tissues. groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types. epithelium connective muscle nervous
 Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Tissues groups of cells similar in structure and function 4 types epithelium connective muscle nervous Epithelial Tissue lining covering glandular Functions protection absorption filtration secretion Epithelium
Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together. Packet #12
 Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together Packet #12 Introduction Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelial tissue (epithelium)
Introduction to Types of Body Tissue Putting it All Together Packet #12 Introduction Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types Epithelial tissue (epithelium)
Connective Tissue. Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment.
 Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
Connective Tissue Found everywhere in the body. Most abundant and widely distributed. Never exposed to the outside environment. Connective Tissue Functions Binding and support Protection Insulation Transportation
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi
 Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types:
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types:
Lab Exercise 6a-2. Classification of connective tissues. Connective Tissue. Connective tissues. Areolar. Areolar tissue
 Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology
 NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
NOTES: CH 40 Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology THE HUMAN BODY Anatomy Physiology (= structures) (= functions or processes) Characteristics of LIFE: 1) Made up of 1 or more CELLS. 2) Obtain and
TISSUE. A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS
 TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
TISSUE A group of cells that perform a similar function within an organism. Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous CREDITS Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Epithelium Composed of a layer of cells. Lines
I. Introduction. Unit One. Tendons of the hand. The white glistening appearance results from the collagen of which tendons are composed.
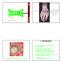 5 Tendons of the hand tendons The white glistening appearance results from the collagen of which tendons are composed. Chapter 5 Karen Webb Smith Unit One I. Introduction A. Cells are arranged in tissues
5 Tendons of the hand tendons The white glistening appearance results from the collagen of which tendons are composed. Chapter 5 Karen Webb Smith Unit One I. Introduction A. Cells are arranged in tissues
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems
 Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
Chapter 4 :Organization & Regulation of Body Systems 4.1 Types of tissues What is a tissue? A collection of cells of the same type that perform a common function There are 4 major tissue types in the body:
The Tissue Level of Organization
 4 The Tissue Level of Organization PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 4-1 Four Types of Tissue Tissue Are collections of cells and cell products that
4 The Tissue Level of Organization PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 4-1 Four Types of Tissue Tissue Are collections of cells and cell products that
Blood. Hematopoietic Tissue
 Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Blood Hematopoietic Tissue Is a type of connective tissue in which its cells are suspended in a circulating fluid. Erythrocytes+ leukocytes + platelets (thrombocytes) =formed elements of blood. These formed
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
