MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Haired skin, dermis: Fibrosarcoma, breed unspecified, feline.
|
|
|
- Constance Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NEOPLASMS HISTORY: A rapidly growing cutaneous mass from a cat. MORPHOLOGIC DESCRIPTION: Within, expanding and replacing the dermis, elevating and compressing the overlying superficial dermis, and extending to the cut border is a multilobulated, partially encapsulated, poorly demarcated, moderately cellular infiltrative mass composed of poorly defined interlacing streams and bundles of tightly packed spindle cells. The neoplastic cells have indistinct cell borders and a moderate amount of eosinophilic fibrillar cytoplasm. Nuclei are irregularly round to elongate with lightly stippled chromatin, prominent nuclear borders, and a single, usually central magenta nucleolus. There is scattered anisokaryosis and karyomegaly. Mitoses average 1 per 10 HPF but in areas are up to 2 per HPF. Multifocally within the mass are areas of necrosis with hemorrhage, fibrin, edema, and infiltrates of few lymphocytes, plasma cells, and macrophages (often containing hemosiderin). Multifocally lymphatics are distended by clear space (edema). Multifocally within the stroma and adjacent dermis are nodular perivascular aggregates of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and lesser macrophages. Multifocally there is minimal orthokeratotic hyperkeratosis of the overlying epithelium. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Haired skin, dermis: Fibrosarcoma, breed unspecified, feline. HISTORY: Sclerotic mass in the intestine of a cow. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Small intestine. Multifocally expanding and infiltrating all layers of the intestinal wall is an unencapsulated, poorly demarcated, poorly cellular infiltrative mass composed of widely scattered tubules supported by an abundant dense fibrovascular stroma. Neoplastic cells are cuboidal to columnar, with variably distinct cell borders and small to moderate amounts of granular eosinophilic cytoplasm. Nuclei are basilar with coarsely stippled chromatin and one to two basophilic nucleoli. The mitotic rate averages 1-3 per HPF. There is multifocal vascular invasion. Tubules often contain variable amounts of eosinophilic and karyorrhectic cellular debris admixed with small numbers of degenerate neutrophils and macrophages. Multifocally, the stroma contains small to moderate numbers of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and fewer macrophages, scattered neutrophils and eosinophils, and often contains moderate amounts of a foamy, amphophilic material (mucin). Within the lamina propria and submucosa of the remaining preexisting tissue, there is a moderate increase in lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils. Lymphatics in the submucosa are dilated and connective tissue fibers are loosely arranged (edema). MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Small intestine: Adenocarcinoma, tubular, breed not specified, bovine.
2 INFLAMMATORY LESIONS HISTORY: Two cutaneous masses, one on the right distal tibia and one on the left forelimb digit were excised from a 2-1/2 year old female grey kangaroo (Macropus fuliginosus). MORPHOLOGIC DESCRIPTION: Haired skin: There is a focally extensive, verrucous proliferation of the epidermis, characterized by multiple, closely associated, elongate folds (up to 1/2 cm) which compress the interposed dermis and extend above and below the adjacent unaffected epidermis. Within this area, severe ballooning degeneration thickens the stratum spinosum and occasionally the stratum granulosum 4-5X normal thickness; affected cells frequently contain a large (15-20u), irregularly shaped, homogenous, eosinophilic to basophilic, intracytoplasmic inclusion body (Molluscum body) which displaces the nucleus. The epithelium of hair follicles is similarly affected. There is diffuse mild parakeratotic hyperkeratosis, often containing retained inclusion bodies admixed with necrotic cellular debris and hemorrhage; similar material often fills hair follicles. Mildly thickening the deep dermis are nodular aggregates of moderate numbers of lymphocytes and macrophages, admixed with occasional plasma cells and neutrophils. Scattered throughout, within the remaining dermis are similar inflammatory cells and occasional mildly dilated lymphatics (edema). MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Haired skin: Hyperplasia, epidermal and follicular, focally extensive, severe, with eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies and chronic dermatitis (molluscum contagiosum) HISTORY: Tissue from a Mangabey monkey that died shortly after arrival from the supplier. MORPHOLOGIC DESCRIPTION: Lung: Diffusely, alveoli and bronchioles are partially to completely filled with abundant RBCs, fibrin and edema admixed with variable combinations and concentrations of often degenerate macrophages, neutrophils, and rare lymphocytes. In some areas of the section, alveolar septa are thin, fragmented and discontinuous, and replaced by karyorrhectic debris (necrosis). In other areas, they are mildly thickened with similar inflammatory cells, fibrin and edema as described previously. Multifocally, there is mild hemorrhage in the bronchiolar mucosa and smooth muscle and mild peribronchiolar and perivascular hemorrhage and edema. Bronchiolar mucosa is segmentally lost and bronchioles are occasionally lined by flattened epithelium covered by scattered, small, surface colonies of 1um basophilic cocci. Multifocally, low numbers of neutrophils, often degenerate, transmigrate the walls of pulmonary veins disrupting and fragmenting smooth muscle (vasculitis). There is diffuse mild congestion. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Lung: Pneumonia, fibrinohemorrhagic, acute, diffuse, with vasculitis and colonies of cocci, Mangabey monkey, primate. ETIOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Pneumococcal pneumonia ETIOLOGY: Streptococcus pneumoniae (Diplococcus)
3 HISTORY: Tissue from a dog with a two-year history of progressive ataxia and posterior paresis with pain. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Cerebral cortex and diencephalon: Multifocally within and expanding the neuropil of both grey and white matter, more severely in the diencephalon, are multiple randomly scattered, often periventricular, nodular aggregates (up to 3 mm in diameter) of large numbers of macrophages, lymphocytes, and plasma cells, with fewer neutrophils and rare Mott cells. Similar individual or small clusters of these inflammatory cells extend into the surrounding fragmented neuropil. The periventricular inflammatory foci expand into the ventricle and elevate the overlying ependyma. Within these areas are multiple, small blood vessels lined by plump endothelium (neovascularization). Within the adjacent neuropil there is minimal to mild microgliosis, rounded astrocytes with eosinophilic cytoplasm (gemistocytes) and a few eosinophilic spheroids (swollen axons). Multifocally, blood vessels are surrounded by cuffs of low to moderate numbers of lymphocytes and fewer plasma cells, which occasionally extend into the adjacent neuropil. Low to moderate numbers of macrophages contain one to ten, 2-4 um, round to oval yeasts with a central 1 um basophilic dot surrounded by a clear space. Morphologic Diagnosis: Cerebral cortex and diencephalon: Encephalitis, granulomatous and lymphoplasmacytic, subacute to chronic, multifocal, moderate with intrahistiocytic yeasts, etiology--consistent with Histoplasma capsulatum, breed unspecified, canine. HISTORY: Esophageal lesion found in a dog. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: Within a focally extensive area, thickening the wall of the esophagus (2x), and elevating the overlying mucosa, there is a large (l x l.5cm), expansile nodule which replaces much of the submucosa and tunica muscularis. The nodule is composed of a thick, 1 to 3mm fibrous connective tissue capsule, containing numerous small blood vessels, with an inner rim of abundant plasma cells, and lesser lymphocytes and macrophages (many containing hemosiderin) enmeshed in strands of fibrous connective tissue, which in turn, surrounds a central cavity containing multiple sections of a large (1 mm dia.) metazoan parasite and abundant necrotic cellular debris. The parasite is characterized by a smooth cuticle, coelomyarian-polymyarian musculature, prominent lateral cords, a pseudocoelom containing small amounts of an eosinophilic granular material, a large digestive tract lined by columnar epithelium with long microvilli, and reproductive organs. Multifocally within the adjacent muscularis, there are swollen and condensed muscle fibers (degeneration) often separated by small amounts of fibrous connective tissue. Diffusely, there is a mild increase in fibrous connective tissue within the lamina propria and remaining submucosa and there are low numbers of lymphocytes and plasma cells scattered throughout the section. There is a nodular focus on the adventitia containing occasional macrophages, haphazardly arranged fibrous connective tissue, necrotic cellular debris and numerous basophilic coccoid bacteria (probably postmortem overgrowth). MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Esophagus, submucosa, tunica muscularis: Granuloma, focally extensive, severe, with nematode parasite consistent with Spirocerca lupi, breed unspecified, canine.
4 HISTORY: Tissue from an adult rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Lung: Multifocally, bronchioles and bronchi have varying amounts of inflammatory and epithelial changes. Within the lumen and extending through the bronchiolar wall are moderate numbers of neutrophils and macrophages with fewer eosinophils, lymphocytes, and foreign body multinucleate giant cells. This inflammatory infiltrate often extends into adjacent alveoli. Mucosal epithelial cells vary from columnar to cuboidal to squamous and occasionally are denuded. Bronchiolar walls are also variably thickened by moderate to abundant amounts of increased fibrous connective tissue. Multifocally within bronchiolar walls and the pulmonary interstitium are numerous aggregates of large numbers of macrophages with intracytoplasmic golden-brown, globular to granular pigment containing refractile spicules. Also, there is a multifocal mild increase in peribronchiolar lymphoid aggregates (lymphoid hyperplasia) and there is a small focus of peribronchiolar hemorrhage. Three subpleural bronchioles contain round to oval sections of a metazoan parasite, u in diameter. These parasites have a body cavity, striated musculature, and jointed appendages with a lightly chitinized cuticle which lacks external segmentation. Other identifiable structures include the brain, gut segments, and uterus. Often surrounding the parasite is a concentrated infiltrate of neutrophils. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS - Lung: Bronchitis, bronchiolitis, and peribronchiolitis, pyogranulomatous, chronic, multifocal, moderate with peribronchiolar pigmentation and intraluminal acarine parasites, rhesus monkey, Macaca mulatta. ETIOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Pulmonary acariasis. ETIOLOGY: Pneumonyssus simicola HISTORY: Incidental finding in a squirrel monkey. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Multifocally within large bile ducts, distending and occluding the lumina, are cross-sections of a trematode parasite which is slightly flattened, measuring up to 700 x 400µ diameter, with a thin tegument overlying a narrow band of somatic muscle, and no discernible body cavity. Scant internal structures are suspended in a parenchymatous matrix, and consist of paired tubular organs lined by a ciliated epithelium (ceca), a few cells with small dense nuclei and globular, golden brown cytoplasm (vitellarian glands) and numerous yellow, thick shelled, rarely operculate eggs measuring up to 40 x 25µ, often containing deeply eosinophilic, basophilic, or black, multinucleate structures (morula). Diffusely, portal areas are infiltrated by moderate numbers of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and fewer macrophages of neutrophils. There is diffuse mild hepatocellular vacuolar change. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, lymphoplasmacytic, diffuse, periportal, mild, with intraductal trematodes, squirrel monkey, Saimiri sciureus, primate. ETIOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Biliary distomiasis.
5 ETIOLOGY: Most likely Athesmia foxi, but A. heterolecithodes, wehri have been reported. HISTORY - Tissue from a female rhesus monkey that had a poor appetite for several months. She had lost 4 kg of body weight prior to death, and on gross necropsy a firm palpable mass was found in the abdomen. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Colon, mesentery and mesenteric lymph nodes: Multifocally within the tunica muscularis, extending into and replacing glands of the mucosa, and present within the mesenteric fat are discreet foci of tortuous glandular tissue surrounded by abundant, densely cellular stroma. The glands are lined by a pseudostratified columnar epithelium with palisading, often anti-basilar nuclei and moderate amounts of a clear to lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm (uterine glands). The stroma is composed of stellate to spindled cells with scant eosinophilic, fibrillar cytoplasm and oval to elongate nuclei. Mitoses in these areas are 1/HPF (uterine stroma). There is within the mesenteric fat a single focus of glands and stroma, as described, which is undergoing lytic necrosis, with scattered pyknotic and karyorrhectic cellular debris and infiltration by moderate numbers of viable and degenerate neutrophils, occasional macrophages and moderate hemorrhage, which extends into the adjacent adipose tissue. The lymph node contains mildly increased numbers of erythrophagocytic macrophages within the paracortical and medullary sinuses. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Colon, mesentery: Endometriosis, transmural, moderate. HISTORY: Incidental finding in a Sprague-Dawley rat. MORPHOLOGIC DESCRIPTION: Small intestine and mesentery: Diffusely affecting up to 85% of mesenteric and mural arteries and arterioles, thickening the walls up to 20x normal are numerous plump fibroblasts which extend from the media to the adventitia and into the perivascular connective tissue. The intima and media of most vessels is disrupted, with segmental fragmentation of collagen bundles, loss of the internal elastic lamina, scattered karyorrhectic debris, and infiltration by moderate numbers of neutrophils, macrophages and fewer fibroblasts (necrotizing vasculitis). Occasionally the media is replaced by abundant, amorphous to flocculent, brightly eosinophilic material (fibrinoid necrosis). Within the media, adventitia and, less often, perivascular tissue there are moderate numbers of neutrophils, fewer lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages and eosinophils, with scattered minimal hemorrhage. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Small intestine and mesentery, arteries: Vasculitis, proliferative and necrotizing, chronic-active, diffuse, moderate. CONDITION: Polyarteritis nodosa
6 HISTORY: Tissue from a male German shepherd that developed an abnormal gait with a progressive loss of proprioceptive and motor nerve function. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Spinal cord (2 sagittal and 2 cross sections with dura and nerve roots): There is diffuse moderate degeneration of white matter affecting all funiculi and nerve roots with large variation in the diameter of axon sheaths, ranging up to 50 um. Swollen sheaths contain axons which are swollen and rounded up to 30 um diameter (spheroids). Sheaths also contain acidophilic fibrillar material, single or rarely multiple macrophages with abundant foamy cytoplasm (Gitter cells), or clear space (loss of axons, demyelination). On sagittal section, there are numerous linear 30 x 50 um clear spaces containing degenerative/necrotic axons and gitter cells (ellipsoids, digestion chambers). There is a mild gemistocytic gliosis within white matter. Scattered neurons contain an intracytoplasmic finely granular, yellow-brown pigment (lipofuscin). One cross section contains multifocal dural ossification with bone marrow. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: 1. Spinal cord and nerve roots: Degeneration, axonal, with swollen axon sheaths, and digestion chambers, diffuse, moderate 2. Spinal cord: Lipofuscin, intraneuronal, multifocal, mild. 3. Spinal cord, dura mater: Osseous metaplasia, multifocal, mild.
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with numerous trichomonads. (3 pt)
 Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #1 Key
 2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #1 Key Test 1, Slide 1. Tissue from a dog. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Prostate gland: Multifocally and extensively infiltrating the prostate gland (1 pt.), and
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #1 Key Test 1, Slide 1. Tissue from a dog. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Prostate gland: Multifocally and extensively infiltrating the prostate gland (1 pt.), and
WSC , Conference 9. Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque.
 Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals
 Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Tissues 10/21/2016. Epithelial Tissue
 Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Tissues This is a generalized cell diagram. It shows the anatomy of a cell, but most cells do not actually look like this. Cells can have a wide variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their function.
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Chapter 5. Tissues. 4 Types of Body Tissues. Tissues
 Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Chapter 5 Tissues Tissues Tissues - groups of cells that are similar in structure & function RBC, WBC, & platelets are a group of cells working together to form BLOOD tissue Histology Pathohistology study
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
川北医学院讲稿. Under low power note the testis is enclosed by a strong fibrous. layer of serous epithelium. These fibrous tissue
 川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory.
 Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
Normal endometrium: A, proliferative. B, secretory. Nội mạc tử cung Nội mạc tử cung Cyclic changes in endometrium.. Approximate relationship of useful microscopic changes. Arias-Stella reaction in endometrial
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul)
 TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul) ANATOMY BASICS I. Basic concepts of anatomy a. Spatial terminology 1. Anatomical position 2. Body regions 3. Directional terms 4. Planes b. Structural hierarchy
TOPIC OUTLINE IPHY 3410 sec. 1 (Leif Saul) ANATOMY BASICS I. Basic concepts of anatomy a. Spatial terminology 1. Anatomical position 2. Body regions 3. Directional terms 4. Planes b. Structural hierarchy
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER
 CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
(JPC ) Caprine lungs
 2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
2011-7-2 (JPC 3133973) Caprine lungs Bat Otgontugs Bovine Pathology Contributor: Natoinal Institute Animal Health, Tsukuba, Japan Signalment: 5-year 3-month old female Japanese native breed goat, (Capra
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of INFECTIOUS DISEASES MICROSCOPY Rengin Ahıskalı Macroscopy samples are shown in the macroscopy presentations of the first two courses.
Histology. Study of body tissues
 Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Histology Study of body tissues 2 Introduction to Body Tissues 1. Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function 2. Four major types (4 Cs) a. Epithelial - Cover b. Connective
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions
 Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Tissues Chapter 5...Tissue - a group or mass of similar cells working together to perform certain common functions There are 4 major types of tissue Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous 1. Epithelial Tissue
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Avian Pathology. QUIZ HISTOPATHOLOGY: Answers
 ECVP/ESVP Summer School 202 Avian Pathology QUIZ HISTOPATHOLOGY: Answers Jérôme ABADIE Frédérique NGUYEN Q Tissue from a Hen Q. Hen Lung. Infiltrating and effacing nearly 60% of the pulmonary parenchyma,
ECVP/ESVP Summer School 202 Avian Pathology QUIZ HISTOPATHOLOGY: Answers Jérôme ABADIE Frédérique NGUYEN Q Tissue from a Hen Q. Hen Lung. Infiltrating and effacing nearly 60% of the pulmonary parenchyma,
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System
 Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J TISSUE TYPES M. Spector, Ph.D. and I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. The
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s Hospital VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J TISSUE TYPES M. Spector, Ph.D. and I.V. Yannas, Ph.D. The
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
The Tissue Level of Organization
 Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Tissue The Tissue Level of Organization Chapter 3 Definition an aggregation of cells in which each cooperates with all others in the performance of a given function Examples of general functions Movement
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Urinary system. Urinary system
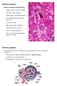 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as
 Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Connective tissue Most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the body Binds, support, and strengthen body tissues, protect and insulate internal organ, serve as major transport system, compartmentalizes
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Histology 101! !! Name:! Block: Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties!
 Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Histology 101 Identify and describe the functions of major tissue types including their subclasses and varieties Name: Block: "1 Introduction to Tissues Histology Notes Tissue (living fabric) : groups
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
They cells can not function death.
 Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel
 Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Small Intestine, Large Intestine and anal cannel 32409 Small intestine Large intestine Small intestine General Structure of the Digestive Tract rat 32409 Epithelium with goblet cells and absorptive cells
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
ECVP/ESVP Summer School in Veterinary Pathology Summer School 2015 Histology Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney.
 Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Case 5 DOG HD: Kidney. 100% of mid to deep renal cortex is characterized by coagulative necrosis/infarction, linear widespread haemorrhages and multifocal vasculitis with thrombosis. Throughout the section
Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion
 Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Chapter 4: TISSUES IX. Tissues Intro Epithelial Tissue lining, covering, glandular tissue > Function protect, absorption, filtration, secretion, excretion Connective Tissue most widespread tissue type
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 4 Outline Tissues and Membranes 1 Tissue group of cells with similar structure and function o 4 major groups epithelial, connective, muscle, nerve Epithelial tissue (Fig
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi
 Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Study of Tissues Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Tissues Tissues are composed of cells similar in structure and specialized to perform a specific function for the body. The human body is made of four general types
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
TISSUES. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs
 Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Tissues: Four classes Epithelium Connective Muscle Nervous Tissues are: group of similar or identical cells that share a common function. used to build organs Overview: Epithelial o Line body cavities
Body Tissues. Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure. and function Four primary tissue types:
 Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Chapter 3 Tissues Body Tissues Cells are specialized for particular functions Tissues - groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary tissue types: Epithelium Connective tissue Nervous
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues. Group of cells that are similar in structure and function. 4 primary types. Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control)
 Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Tissues Tissues Group of cells that are similar in structure and function 4 primary types Epithelium (covering) Connective (support) Nervous(control) Epithelial tissue (epithelium) Lining, covering, and
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
TISSUES. Objectives. Tissues
 TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
TISSUES Objectives Introduce the four major types of tissues Describe the general characteristics and functions of epithelial & connective tissue Name the major types of epithelial & connective tissues
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
