Phosphoinositide Signaling
|
|
|
- Justin Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phosphoinositide Signaling Pietro De Camilli Department of Cell Biology Howard Hughes Medical Institute Program in Cellular Neuroscience, Neurodegeneration and Repair Yale University School of Medicine NIDA SAB meeting April 26, 2013
2 Phosphoinositides PtdIns PH domains Fyve domains PX domains etc.
3 Wendy Hill Membrane traffic in nerve terminals to cell body late endosomes synaptic vesicles endosomes
4 A cycle of PI(4,5)P2 synthesis and hydrolysis nested within the synaptic vesicle cycle PI 4-kinases PI4P 5-kinases (PIP kinase type 1γ) PI4P PI(4,5)P2 PI synaptojanin (PI(4,5)P2 phosphatase) PI(4,5)P2
5 A phosphoinositide code for cellular membranes PI4P PI(4,5)P 2 PI(3,5)P 2 PI3P PI(3,4)P 2 PI(3,4,5)P 3
6 Four PI 4-kinases in mammalian cells PI4-kinase IIIα (Stt4 in yeast) PI4-kinase IIIβ (Pik1 in yeast) PI4P PI(4,5)P 2 PI(3,5)P 2 PI3P PI(3,4)P 2 PI(3,4,5)P 3 PI4-kinase IIα & β (Lsb6 in yeast)
7 Stt4 is targeted to the plasma membrane in a complex with Efr3 and Ypp1 Yeast GFP-Stt4 PI4KIIIα Baird et al. (Emr lab), J Cell Biol 2008 Mammalian cell anti-pi4kiiiα Anti-PI4KIIIα immunoprecipitation Wong, (Cantley lab) J. Biol. Chem.1997
8 GFP-PI4KIIIα is cytosolic Based on the sequence reported in: Nakagawa, T., K. Goto, and H. Kondo Cloning, expression, and localization of 230-kDa phosphatidylinositol 4- kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 271 : Fubito Nakatsu
9 PI4KA (which encodes PI4KIIIα) had an incorrectly annotated translation start site M1 M1* likely the correct start site annotated start site recombinant endog. M1 M1* PI4KIIIα Fubito Nakatsu
10 ribosome Harringtonine mrna Ribosome footprinting after harringtonine treatment enabled determination of PI4KIIIα translational start sites Method in: Ingolia et al. (Weissman lab), Cell 2011 initiating ribosomes only Nuclease digestion M1 T* M1* Deep sequencing library collaboration with N. Ingolia s lab (Carnegie Institute)
11 EFR3B-Tomato GFP-PI4KIIIα TTC7B-GFP together alone A PI4KIIIα/EFR3/TTC7 complex as in yeast 2 µm 20 µm What is the function of this complex? Jeremy Baskin and Fubito Nakatsu
12 Conditional PI4KIIIα KO mice Germline gene disruption = embryonic lethality onditional KO crossed to CreER expressing mouse hen isolation of mouse embrynic fibroblasts (MEFs) + tamoxifen conditional PI4KIIIα MEFs Fubito Nakatsu
13 PI4KIIIα KO MEFs confirm central role of this kinasein plasma membrane PI4P synthesis No change in levels of other PI 4-kinases Decrease in total PI4P Decrease in PI4P at the plasma membrane but not at the Golgi apparatus Fubito Nakatsu
14 PI4KIIIα KO MEFs confirm central role of this kinasein plasma membrane PI4P synthesis Disruption of F-actin No change in levels of other PI 4-kinases Decrease in total PI4P Fubito Nakatsu
15 In PI4IIIα KO MEFs the drop of PI(4,5)P2 is much less robust than the loss of PI4P PI4P PI(4,5)P2 GFP-PH PLCγ Control compensatory increase of PI4P 5-kinases (Type 1 PIP kinases) 5 µm Fubito Nakatsu KO 20 µm PI(4,5)P2 decreases at plasma membrane but accumulates on cytoplasmic vesicles
16 In PI4IIIα KO cells PI4P 5-kinases are localized on internal vesicles rather than at the plasma membrane PI4P PI(4,5)P2 PI4P 5-kinase PI(4,5)P2 (PHPLCd) Wild type cell PI4IIIα KO cell Fubito Nakatsu
17 A phosphoinositide code for cellular membranes PI4P PI(4,5)P 2 PI(3,5)P 2 PI3P PI(3,4)P 2 PI(3,4,5)P 3 Can we by pass the problems intrinsic to genetic studies?long-term nature -> adaptive/compensatory changes
18 Light-induced protein heterodimerization
19 Optogenetic depletion of PI(4,5)P2 at the plasma membrane (blue light-mediated recruitment of a PI(4,5)P2 5-phosphatase) CAAX Idevall-Hagren et al. PNAS 2012
20 Optogenetic depletion of PI(4,5)P2 at the plasma membrane (blue light-mediated recruitment of a PI(4,5)P2 5-phosphatase) CAAX Movie Idevall-Hagren et al. PNAS 2012
21 PI(4,5)P2 hydrolysis upon blue light-induced inositol 5 -phosphatase recruitment Idevall-Hagren et al. PNAS 2012
22 Loss of K + currents upon blue light-induced inositol 5 -phosphatase recruitment KCNQ2/3 (Kv7.2/7.3) channels whole cell currents blue light (458 nm) 1s pulse of blue light (458 nm) > 95% current inhibition: t1/2 = 1.2 ± 0.3 s Recovery: t1/2 = 286 ± 33 s tsa-201 cells Eamonn Dickson, Bertil Hille Idevall-Hagren et al. PNAS 2012
23 Local blue light-illumination produces local effects and opposite effects at distant sites Focal PI(4,5)P2 depletion Movie PC12 cells Movie COS-7 cell Idevall-Hagren et al. PNAS 2012
24 Light-induced recruitment of PI 3-kinase to the plasma membrane and induction of ruffling mcherry-cry2-ish2 Movie COS-7 cells Idevall-Hagren et al. PNAS 2012
25 Using optogenetics to discover new biology
26 ER-plasma membrane contacts PDI PAG 10 m From Orci fibroblast PM neuron
27 The extended synaptotagmins: a family of proteins implicated in tethering the ER to the plasma membrane? E-Syt3 in neuron Giordano et al. Cell 2013
28 The extended synaptotagmins: a family of proteins implicated in tethering the ER to the plasma membrane? is PI(4,5)P2 needed to contact formation? Giordano et al. Cell 2013
29 Optogenetic depletion of PI(4,5)P2 dissociates E-Syt3 Movie irfp-ph-plcδ [PI(4,5)P2 biosensor] from the plasma membrane Movie E-Syt3-mCherry Loss of cortical ER induced by E-Syt3 overexpression as seen by EM Nucleus Nucleus PM PM Giordano et al. Cell 2013
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Golgi and plasma membrane pools of PI(4)P contribute to plasma membrane PI(4,5)P 2 and maintenance of KCNQ2/3 ion channel current
 and plasma membrane pools of PI(4)P contribute to plasma membrane PI(4,5)P 2 and maintenance of KCNQ2/3 ion channel current Eamonn J. Dickson, Jill B. Jensen, and Bertil Hille 1 Department of Physiology
and plasma membrane pools of PI(4)P contribute to plasma membrane PI(4,5)P 2 and maintenance of KCNQ2/3 ion channel current Eamonn J. Dickson, Jill B. Jensen, and Bertil Hille 1 Department of Physiology
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Biophysical Analysis of Membrane Functions by Laser Tweezers
 Biophysical Analysis of Membrane Functions by Laser Tweezers Plasma Membrane Functions (Control by PIP2 Levels in Plasma Membrane) Cell Motility Endocytosis (Cell Volume regulation) Membrane resealing
Biophysical Analysis of Membrane Functions by Laser Tweezers Plasma Membrane Functions (Control by PIP2 Levels in Plasma Membrane) Cell Motility Endocytosis (Cell Volume regulation) Membrane resealing
The machinery at endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites contributes to spatial regulation of multiple Legionella effector proteins
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 7-3-2014 The machinery at endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 7-3-2014 The machinery at endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites
PI(4,5)P 2 -Dependent and Ca 2+ -Regulated ER-PM Interactions Mediated by the Extended Synaptotagmins
 PI(4,5)P 2 -Dependent and Ca 2+ -Regulated ER-PM Interactions Mediated by the Extended Synaptotagmins Francesca Giordano, 1,3,4,7 Yasunori Saheki, 1,3,4,7 Olof Idevall-Hagren, 1,3,4 Sara Francesca Colombo,
PI(4,5)P 2 -Dependent and Ca 2+ -Regulated ER-PM Interactions Mediated by the Extended Synaptotagmins Francesca Giordano, 1,3,4,7 Yasunori Saheki, 1,3,4,7 Olof Idevall-Hagren, 1,3,4 Sara Francesca Colombo,
Molecular Trafficking
 SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling
 Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling Francesc R. Garcia-Gonzalo, Siew Cheng Phua, Elle C. Roberson, Galo Garcia
Developmental Cell Supplemental Information Phosphoinositides Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking to Modulate Hedgehog Signaling Francesc R. Garcia-Gonzalo, Siew Cheng Phua, Elle C. Roberson, Galo Garcia
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003
 7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
GFP Assays
 GFP Assays 2009-07-03 GFP Assays Akt1 SMAD2 STAT3 NFAT-C1 MAPKAP-k2 Rac-1 PLCδ PH domain FYVE G2M CCPM Cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, insulin response pathways TGF-beta signalling, growth, differentiation,
GFP Assays 2009-07-03 GFP Assays Akt1 SMAD2 STAT3 NFAT-C1 MAPKAP-k2 Rac-1 PLCδ PH domain FYVE G2M CCPM Cell survival, proliferation, apoptosis, insulin response pathways TGF-beta signalling, growth, differentiation,
Chapter 20. Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors. Three general types of extracellular signaling. endocrine signaling. paracrine signaling
 Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Overview: The Cellular Internet
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication Overview: The Cellular Internet Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Biologists have discovered some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation
Chapter 11 Cell Communication Overview: The Cellular Internet Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Biologists have discovered some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure.
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. Animal cells have a lysosome (related to vacuole) and centrioles (function
Cell wall components:
 Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have: cell walls, a large central vacuole, plastids and turgor pressure. The Cell Wall The primary cell wall is capable of rapid expansion during
Cell Communication. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Supplementary Figure 1 Generation and validation of mtef4-knockout mice. (a) Alignment of EF4 (E. coli) with mouse, yeast and human EF4. (b) Domain structures of mouse mtef4 compared to those of EF4 (E.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Intrinsic Photosensitivity Enhances Motility of T Lymphocytes by Phan X. Thieu, Barbara Jaruga, Sandeep C. Pingle, Bidhan C. Bandyopadhyay, & Gerard P. Ahern Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Information Intrinsic Photosensitivity Enhances Motility of T Lymphocytes by Phan X. Thieu, Barbara Jaruga, Sandeep C. Pingle, Bidhan C. Bandyopadhyay, & Gerard P. Ahern Supplementary Figure
Materiale per uso didattico 1
 BCII - Perroteau - shuttling citoplasma nucleus 1 ERK regulation by scaffolds and anchors 2 Materiale per uso didattico 1 ERK Pathway regulation by feedback loops and phosphatases 3 ERK has more
BCII - Perroteau - shuttling citoplasma nucleus 1 ERK regulation by scaffolds and anchors 2 Materiale per uso didattico 1 ERK Pathway regulation by feedback loops and phosphatases 3 ERK has more
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
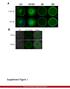 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental information
 Supplemental information PI(3)K p11δ controls the sucellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock Ezra Aksoy, Salma Taoui, David Torres, Sandrine Delauve, Aderrahman
Supplemental information PI(3)K p11δ controls the sucellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock Ezra Aksoy, Salma Taoui, David Torres, Sandrine Delauve, Aderrahman
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
04_polarity. The formation of synaptic vesicles
 Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Brefeldin prevents assembly of the coats required for budding Nocodazole disrupts microtubules Constitutive: coatomer-coated Selected: clathrin-coated The formation of synaptic vesicles Nerve cells (and
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Lectures by Chris Romero. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: The Cellular Internet Cell-to-cell communication Is absolutely
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: The Cellular Internet Cell-to-cell communication Is absolutely
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae.
 Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of folded membranes that form channels through the cytoplasm and sacs called cisternae. Cisternae serve as channels for the transport of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Cell Communication. Local and Long Distance Signaling
 Cell Communication Cell to cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation providing more evidence for the evolutionary relatedness of all life
Cell Communication Cell to cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Some universal mechanisms of cellular regulation providing more evidence for the evolutionary relatedness of all life
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Chapter 11. Cell Communication
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication Overview: The Cellular Internet Cell-to-cell communication Is absolutely essential for multicellular organisms Concept 11.1: External signals are converted into responses
Chapter 11 Cell Communication Overview: The Cellular Internet Cell-to-cell communication Is absolutely essential for multicellular organisms Concept 11.1: External signals are converted into responses
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Biology. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012
 Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion. Richard H. Scheller
 The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion Richard H. Scheller The human brain contains approximately 10 15 connections between nerve cells (Figure 2). The specific formation and modulation
The Molecular Mechanism of Intracellular Membrane Fusion Richard H. Scheller The human brain contains approximately 10 15 connections between nerve cells (Figure 2). The specific formation and modulation
PI3K class II α regulates δ-opioid receptor export from the trans-golgi network
 MBoC ARTICLE PI3K class II α regulates δ-opioid receptor export from the trans-golgi network Daniel J. Shiwarski a,b, Marlena Darr a, Cheryl A. Telmer a, Marcel P. Bruchez a,c,d, and Manojkumar A. Puthenveedu
MBoC ARTICLE PI3K class II α regulates δ-opioid receptor export from the trans-golgi network Daniel J. Shiwarski a,b, Marlena Darr a, Cheryl A. Telmer a, Marcel P. Bruchez a,c,d, and Manojkumar A. Puthenveedu
Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA
 Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Cellular Biochemistry
 Cellular Biochemistry Fall Semester 2013 Sept. 23 Benoit Kornmann Institute of Biochemistry Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry
Cellular Biochemistry Fall Semester 2013 Sept. 23 Benoit Kornmann Institute of Biochemistry Introduction to biological membranes General functions and properties Membrane lipids Physical properties Distribution/asymmetry
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
doi:10.1038/nature11700 Figure 1: RIP3 as a potential Sirt2 interacting protein. Transfected Flag-tagged Sirt2 was immunoprecipitated from cells and eluted from the Sepharose beads using Flag peptide.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C. N. Petrok, J.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Propagation of the Signal
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
General Principles of Endocrine Physiology
 General Principles of Endocrine Physiology By Dr. Isabel S.S. Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong The major human endocrine glands Endocrine glands and hormones
General Principles of Endocrine Physiology By Dr. Isabel S.S. Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong The major human endocrine glands Endocrine glands and hormones
Homeostatic Control Systems
 Homeostatic Control Systems In order to maintain homeostasis, control system must be able to Detect deviations from normal in the internal environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate
Homeostatic Control Systems In order to maintain homeostasis, control system must be able to Detect deviations from normal in the internal environment that need to be held within narrow limits Integrate
* Department of Biological Sciences, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA.
 PI3K Class II regulates δ-opioid Receptor Export from the trans-golgi Network Daniel J. Shiwarski*, Marlena Darr*, Cheryl A. Telmer*, Marcel P. Bruchez*, Manojkumar A. Puthenveedu* * Department of Biological
PI3K Class II regulates δ-opioid Receptor Export from the trans-golgi Network Daniel J. Shiwarski*, Marlena Darr*, Cheryl A. Telmer*, Marcel P. Bruchez*, Manojkumar A. Puthenveedu* * Department of Biological
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
THE SYNAPTIC VESICLE CYCLE
 Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004. 27:509 47 doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131412 Copyright c 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on March 12, 2004
Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2004. 27:509 47 doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131412 Copyright c 2004 by Annual Reviews. All rights reserved First published online as a Review in Advance on March 12, 2004
A Reciprocal Interdependence between Nck and PI(4,5)P 2 Promotes Localized N-WASp-Mediated Actin Polymerization in Living Cells
 Molecular Cell, Volume 36 Supplemental Data A Reciprocal Interdependence between Nck and PI(4,5)P 2 Promotes Localized N-WASp-Mediated Actin Polymerization in Living Cells Gonzalo M. Rivera, Dan Vasilescu,
Molecular Cell, Volume 36 Supplemental Data A Reciprocal Interdependence between Nck and PI(4,5)P 2 Promotes Localized N-WASp-Mediated Actin Polymerization in Living Cells Gonzalo M. Rivera, Dan Vasilescu,
Why chaperone vectors?
 Why chaperone vectors? A protein folding initiative An open discussion with structural biologists Protein Structure Initiative: Pilot Phase Whether the pilot phase achieved its goal depends on how we measure
Why chaperone vectors? A protein folding initiative An open discussion with structural biologists Protein Structure Initiative: Pilot Phase Whether the pilot phase achieved its goal depends on how we measure
Optogenetics. how to use light to manipulate neuronal networks. Alexandra Götz
 Optogenetics how to use light to manipulate neuronal networks Alexandra Götz 1 http://www.stanford.edu/group/dlab/optogenetics/ 2 Outline Background Neuron and ion channels Action potential Light sensitive
Optogenetics how to use light to manipulate neuronal networks Alexandra Götz 1 http://www.stanford.edu/group/dlab/optogenetics/ 2 Outline Background Neuron and ion channels Action potential Light sensitive
Antibodies for Unfolded Protein Response
 Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Key Concepts in Chapter 11. Cellular Messaging. Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 11 1. External signals are converted to responses within the cell. 2. Reception: A signaling
Chapter 11 Cell Communication Dr. Wendy Sera Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 11 1. External signals are converted to responses within the cell. 2. Reception: A signaling
REVIEWS. Phosphoinositide Signaling: New Tools and Insights
 PHYSIOLOGY 24: 231 244, 2009; doi:10.1152/physiol.00014.2009 REVIEWS Phosphoinositide Signaling: New Tools and Insights Phosphoinositides constitute only a small fraction of cellular phospholipids, yet
PHYSIOLOGY 24: 231 244, 2009; doi:10.1152/physiol.00014.2009 REVIEWS Phosphoinositide Signaling: New Tools and Insights Phosphoinositides constitute only a small fraction of cellular phospholipids, yet
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Supplemental material JCB El Azzouzi et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510043 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Acquisition of -phluorin correlates negatively with podosome
Phosphoinositides: lipid regulators of membrane proteins
 J Physiol 588.17 (2010) pp 3179 3185 3179 SYMPOSIUM REVIEW Phosphoinositides: lipid regulators of membrane proteins Björn H. Falkenburger, Jill B. Jensen, Eamonn J. Dickson, Byung-Chang Suh and Bertil
J Physiol 588.17 (2010) pp 3179 3185 3179 SYMPOSIUM REVIEW Phosphoinositides: lipid regulators of membrane proteins Björn H. Falkenburger, Jill B. Jensen, Eamonn J. Dickson, Byung-Chang Suh and Bertil
Supplementary Figure S1 (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
Supplementary Figure S1: IC87114 does not affect basal Ca 2+ level nor nicotineinduced Ca 2+ influx. (a) Bovine chromaffin cells were loaded with Fluo-4AM (1 μm) in buffer A containing 0.02% of pluronic
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson
 Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Intracellular vesicular traffic. B. Balen
 Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Synaptic Plasticity and Memory
 Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Properties and synaptic mechanisms underlying the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) The role of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CamKII) in the induction,
Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Properties and synaptic mechanisms underlying the induction of long-term potentiation (LTP) The role of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CamKII) in the induction,
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
BIOLOGY. Cell Communication CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 11 Cell Communication Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Cellular Messaging Cells can signal to
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 11 Cell Communication Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Cellular Messaging Cells can signal to
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development
 Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Cell Communication. Chapter 11. Biology. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 11 Cell Communication PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
The Role of Sorting Nexins in Antigen Presentation
 The Role of Sorting Nexins in Antigen Presentation Chng X.R.J 1 and Wong S.H. 2 Department of Microbiology Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore Block MD4, 5 Science Drive 2,
The Role of Sorting Nexins in Antigen Presentation Chng X.R.J 1 and Wong S.H. 2 Department of Microbiology Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore Block MD4, 5 Science Drive 2,
Overview of clathrin-mediated endocytosis
 Overview of clathrin-mediated endocytosis Accessory and adaptor proteins promote clathrin nucleation on the plasma membrane and some help deform membrane. Clathrin assembly into lattices stabilize the
Overview of clathrin-mediated endocytosis Accessory and adaptor proteins promote clathrin nucleation on the plasma membrane and some help deform membrane. Clathrin assembly into lattices stabilize the
Significance of the MHC
 CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
CHAPTER 8 Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) What is is MHC? HLA H-2 Minor histocompatibility antigens Peter Gorer & George Sneell (1940) Significance of the MHC role in immune response role in organ
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
(Please activate your clickers)
 Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Organelles in prokaryotes and eukaryotes! Plasma membrane! Cell wall (in prokaryotes, plants, fungi, some protists)! Ribosomes! Nucleoid/nucleus! Mitochondria! Plastids (Please activate your clickers)
Regulation of subcellular localization of lipid phosphatase SAC1
 Oregon Health & Science University OHSU Digital Commons Scholar Archive May 2013 Regulation of subcellular localization of lipid phosphatase SAC1 Jinzhi Wang Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.ohsu.edu/etd
Oregon Health & Science University OHSU Digital Commons Scholar Archive May 2013 Regulation of subcellular localization of lipid phosphatase SAC1 Jinzhi Wang Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.ohsu.edu/etd
7.06 Spring of PROBLEM SET #6
 7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
7.6 Spring 23 1 of 6 7.6 PROBLEM SET #6 1. You are studying a mouse model of hypercholesterolemia, a disease characterized by high levels of cholesterol in the blood. In normal cells, LDL particles in
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental FIG. 1. Localization of myosin Vb in cultured neurons varies with maturation stage. A and B, localization of myosin Vb in cultured hippocampal neurons. A, in DIV
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: cholesterol manipulation alters the positioning of autophagosomes in cells, related to figure 1. (a) HeLa cells were treated for 24h under conditions reducing
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: cholesterol manipulation alters the positioning of autophagosomes in cells, related to figure 1. (a) HeLa cells were treated for 24h under conditions reducing
Phosphoinositide Phosphatases and Disease. Duke University Medical Center, Durham, North Carolina, 27710
 Phosphoinositide Phosphatases and Disease Philip W. Majerus 1 * and John D. York 2 * 1 Division of Hematology, Washington University School of Medicine, Box 8125, St. Louis MO, 63110; 2 Department of Pharmacology
Phosphoinositide Phosphatases and Disease Philip W. Majerus 1 * and John D. York 2 * 1 Division of Hematology, Washington University School of Medicine, Box 8125, St. Louis MO, 63110; 2 Department of Pharmacology
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN No Treatment. EZN-3920, 2 μm. Time, h
 Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
Figure S1 Time-dependent down-modulation of HER3 by EZN-392 HE ER3 mrna A, %Contr rol 12 No Treatment EZN-392, 2 μm 1 8 6 4 2 2 8 24 Time, h Figure S2. Specific target down-modulation by HER3 (EZN-392)
Biochem 503 Fall Protein Tyr Phosphatases
 Biochem 503 Fall 2005 Protein Tyr Phosphatases David Brautigan assigned reading: Stoker (2005) J. Endocrin. 185:19-33 History 1981-1982 First description of P-Tyr specific phosphohydrolyase activity in
Biochem 503 Fall 2005 Protein Tyr Phosphatases David Brautigan assigned reading: Stoker (2005) J. Endocrin. 185:19-33 History 1981-1982 First description of P-Tyr specific phosphohydrolyase activity in
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Plasma membranes. Plasmodesmata between plant cells. Gap junctions between animal cells Cell junctions. Cell-cell recognition
 Cell Communication Cell Signaling Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Communicate by chemical messengers Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect
Cell Communication Cell Signaling Cell-to-cell communication is essential for multicellular organisms Communicate by chemical messengers Animal and plant cells have cell junctions that directly connect
