Class : XI Phylum Porifera
|
|
|
- Maximilian Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Class : XI Phylum Porifera 1. Name Porifera is given by (a) Aristole (b) Robert Grant (c) Lamarck (d) None 2. Choanocyte cells are characteristics of (a) Jelly fishes (b) Sponges (c) Platyhelminthes (d) All the above 3. Canal system is found in (a) Coelenterata (b) Enchinodermata (c) Porifera (d) All the above 4. In Leucosolenia, asexual reproduction takes place by (a) Binary fission (b) Sporulation (c) External budding (germination) (d) Cyst formation 5. The gametes in sponges develop from (a) Amoebocytes (b) Archeocytes (c) Choanocytes (d) Myocytes 6. Phylogenetically, the sponges have evolved from: (a) Protozoans (b) Flagallates (c) Choanoflagellates (d) Ciliates 7. In sponges, the food is stored in : (a) Trophocytes (b) Thesocytes (c) Desmocytes (d) Archeocytes 8. Which of the cells are found in sponges only (a) Amoebocytes (b) Chromocytes (c) Choanocytes (d) Archeocytes 9. Which one of the sponge corresponds to the mouth of other animals (a) Osculum (b) Incurrent canal (c) Ostia (d) Excurrent canal 10. A chamber common to all types of canal system of sponges is called : (a) Paragastric cavity (b) Radial chamber (c) Excurrent canal (d) Incurrent canal 11. If a carmine particle is put on the osculum of a living sponge, it will (a) Be ingested (b) Be thrown away (c) Rotate (d) Adhere 12. Canal System in Leucosolenia is (a) Asconoid (b) Syconoid (c) Lecuconoid (d) Rhagon
2 (a) Mesoderm (b) Mesenchyme (c) Mesogloea (d) Mesentery 18. The spongocoel in Leucosolenia is lined by (a) Amoebocytes (b) Choancoytes (c) Scleroblasts (d) Pinacocytes 19. The larva of Leucosolenia is (a) Parenchymula (b) Planula (c) Amphiblastual (d) Archeoblastual 20. The larva of Sycon is (a) Parenchymula (b) Planula (c) Amphiblastual (d) Redia 21. Exogenous budding a type of asexual reproduction in sponges is known as (a) Gemmulation (b) Gemmation (c) Regeneration (d) Amphimixis 22. Endogenous buddings is (a) Gemmule formation (b) Gamets formation (c) Gemmation (d) Endomixis 23. Spongilla is (a) Marine sponge (b) Fresh water sponge (c) No sponge (d) Parasiticsponge 24. Spongacoel is also known as (a) Paragastric cavity (b) Gastro-vascular (c) Water vascular cavity (d) Coelenteron 25. The body wall of sponges has many (a) Pores (b) Gemmules (c) Osculla (d) Trophocytes 26. Venus flower Basket is (a) Euplectella (b) Chalina (c) Hyalonema (d) Hippospongia 27. Excretory waste of Leucosolenia & sycon is (a) Ammonia (b) Urea (c) Guianine (d) Uric Acide 28. Maximum power of regeneration is found in (a) Sponge (b) Hydra (c) Starfish (d) None 29. Spicules in sponges are made up of (a) CaCO 3 (b) silica (c) Both (d) None 30. Tissue grade is absent in one of the following (a) Sponges (b) Protozoans (c) Both (d) None 31. A sponge can be distinguished from other animals by the presence of
3 (a) Porifera (b) Desmospongia (c) Hexactinellida (d) Calcarea 36. Parazoa includes (a) Cnidaria (b) Acidaria (c) Porifera (d) None of these 37. Most common method of reproduction in sponges is (a) binary fission (b) budding (c) multiple fission (d) sexual reproduction 38. The only fresh water species of sponges is (a) Scypha (b) Euspongia (c) Spongilla (d) Oscarella 39. Venus s flower basket is a (a) Sea anemone resembling a flower basket (b) sponge resembling a flower basket (c) glass rope sponge (d) ornamental mollusc 40. Digestion in sponges is (a) intracellular (b) intercellular (c) both a & b (d) extracellular
4 Class : XI Phylum Coelenterata 1. Nematocysts are the specialized cells found in the members of the phylum (a) Cnidaria (b) Prorifea (c) Annelida (d) Mollusca 2. Tentacles of Hydra help in (a) locomotion (b) food capturing (c) both a & b (d) None of these 3. Hydra is put under the phylum cnidaria because it has (a) cnidoblasts (b) tentacles (c) hypostome (d) interstitial cells 4. The posionous fluid present in the nematocysts of Hydra is (a) toxin (b) Hypnotoxin (c) venom (d) Haematin 5. Nematocysts are th organs of (a) sensation (b) reproduction (c) defence & offence (d) respiration 6. Hydra prevents self fertilization by being (a) Protogynous (b) hermaphrodite (c) protandrous (d) monoecious 7. The planula larva is found in the life history of (a) Hydrozoan (b) Anthozoan (c) Scyphozoan (d) All of the above 8. Polymorphic cnidarians are the members of the class (a) Hydrozoa (b) Scyphozoa (c) Actinozoa (d) None of these 9. Coral reef forming coelenterates belong to the class (a) Hydrozoa (b) Scyphozoa (c) Actinozoa (d) All of the above 10. Among coelenterates medusoid individuals are absent in members of the class (a) Anthozoa (b) Hydrozoa (c) Scyphozoa (d) None of these 11. Ephyra is the larval form of (a) Sea anemone (b) Aurelia (c) Obelia (d) Hydra 12. Six septa or six mesenteries are characteristic of (a) Aurelia (b) Hydra (c) Obelia (d) Sea anemone 13. Sea anemone is (a) diploblastic, radially symmetrical animal (b) diploblastic, bilaterally symmetrical animal
5 (a) Porifera (b) Coelenterata (c) Annelida (d) Vertebrata 18. Sexual dimorphism present in : (a) Porifera (b) Cnidarians (c) Sponges (d) None of these 19. In Hydra, nemato cysts are found in : (a) epidermis (b) gastro dernis (c) mesodermis (d) endodermis 20. Which of the following groups of animals is bilaterally symmetrical & diploblastics? (a) Sponges (b) Coelenterates (cnidarians) (c) Aschelminthes (d) Ctenophores 21. Primitive nervous system is formed in (a) Sponge (b) Coelenterata (c) Echin odermata (d) None of these 22. Third layer present between ectoderm & endoderm in coelenterata are : (a) Mesochyl (b) Mesoderm (c) Mesoglea (d) None of these 23. Digestion in cnidarians are : (a) Intracellular (b) Extracellular (c) Both (d) None of these 24. Stinging cells are : (a) Cnidoblast (Nematcyst) (b) Porifera (c) Annelide (d) None of these 25. The portuguese man of war is : (a) Hydra (b) Aurelia (c) Physalia (d) Obelia 26. Hydra is a : (a) Freswater polyp (b) Sea feather (c) Sea anemone (d) None of these 27. Medusae is present in : (a) Hydra (b) Aurelia (c) Both (d) Earthworm 28. Hypostome is present in : (a) Porifera (b) Cnidarian (c) Annelida (d) None of these 29. Skeleton in chidarian is composed of : (a) CaCO 3 (b) silica (c) Both (d) Chitin 30. Sea-fan is also known as (a) Meandrina (b) Gorgonia (c) Adamsia (d) Physalia
6 Class : XI Phylum Ctenophora 1. Ctenophora also known as : (a) Sea walnuts (b) Sea fan (c) Both (d) None of these 2. Statocyst is a : (a) Balance organ (b) Nerve cell (c) Nematocyst (d) None of these 3. Cydippid larva is present in : (a) Porifera (b) Coelenterata (c) Ctenophora (d) None of these 4. Digestion in ctenophora is : (a) Intracellular (b) Extra cellular (c) Both (d) None of these 5. Most distinctive feature of ctenophora is (a) Nematocyst (b) Bioluminscence (c) Hypostome (d) Both a & b 6. Fertilisation in ctenophora is : (a) External (b) Internal (c) Both (d) None of these 7. Eight rows of cilliated comb plates are feature of which phylum? (a) Porifera (b) Annelida (c) Ctenophora (d) Cnidarian 8. Comb plates helps in : (a) Reproduction (b) Feeding (c) Locomotion (d) Excretion 9. Member of ctenophora : (a) Pleurobrachia (b) Asterias (c) Earthworm (d) Sea anemone 10. Role of colloblasts cells : (a) Loco motion (b) Capturing the prey (c) Both (d) Respiration 11. Ctenophore known as comb jellies because of : (a) Colloblast (b) Comb like locomotory organs (c) Respiration (d) Bioluminescence 12. In ctenophora, members are : (a) Dioecious (b) Monoecious (c) Both (d) None of these 13. Which of the following phylum has no fresh water living?
7
8 Kingdom : Monera 1. In Mycoplasma (PPLO) the plasmalemma is rich in : (a) Cellulose (b) Myosin (c) Mycosin (d) Glycogen (e) Cholesterol 2. Which cell inclusions are found in Mycoplasma, spirochaetes & rikettsiae? (a) RNA (b) DNA (c) Ribosomes (d) Sexual reproduction 3. Archaea differ from eubacteria in one of the following features : (a) They have 16S RNA (b) They are very ancient (c) They have a rigid wall (d) Their cell wall lacks peptidoglycan component 4. A peculiar odour that prevails in marshy areas & cowsheds is on account of a gas produced by : (a) Mycoplasma (b) Archaebacteria (c) Slime moulds (d) Cyanobacteria 5. The scientist to isolate sterptomycin for the first time is : (a) Pasteur (b) Fleming (c) Waksman (d) Burkholder 6. Which is not correct about antibiotics? (a) An antibiotic is effective against one specific pathogen (b) Fleming discovered the first commercial antibiotic (c) Waksman coined the term antibiotic in 1942 (d) Allergy may develop against an antibiotic 7. Antibiotics active against fungi are : (a) Polyenes (b) Neomycin (c) Terramycin (d) Streptomycin 8. The mode of action of novobiocin is : (a) induces abnormal protein synthesis (b) interferes with protein synthesis (c) inhibits DNA polymerization (d) inhibits cell wall synthesis 9. Which one does not have eukaryotic organisation? (a) Green algae (b) Blue-green algae (c) Red alage (d) Golden-brown algae 10. The cyanobacteria are also referred to as : (a) protists (b) golden algae (c) slime moulds (d) blue-green alage 11. Pigments phycocyanin & phycoerythrin occur in : (a) Bacillariophyceae (b) Archaebacteria
9 (c) Salvinia & Marsilea (d) Nostoc & legumes 14. Which one is nitrogen fixer blue-green alga? (a) Ulothrix (b) Anabaena (c) Ulva (d) Hydrodictyon 15. Sexual reproduction is absent in : (a) Xanthophyta (b) Cyanophyta (c) Chlorophyta (d) Rhodophyta 16. People recovering from long illness are often advised to take Spirulina because it : (a) restores intestinal microflora (b) makes food easily digestible (c) has antibiotic properties (d) is rich in proteins 17. Largest population of organisms of any type on Earth is of : (a) Insects (b) Algae (c) Bacteria (d) Fungi 18. Membrane bound organelles are absent in : (a) Streptococcus (b) Chlamydomonas (c) Plasmodium (d) Saccharomyces 19. The main difference in Gram (+) ve & Gram (-) ve bacteria resides in their (a) cell wall (b) flagella (c) cytoplasm (d) cell membrane 20. Gram negative bacteria detect & respond to chemicals by : (a) Porins (b) Muramic acid (c) Voutin granules (d) Lipopolysaccharide 21. What is correct about Escherichai coli & Rhizobium japonicum? (a) Both Gram (+) (b) Both Gram (-) (c) E. coli Gram (-) & R.japonicum Gram (+) (d) E. coli Gram (+) & R.japonicum Gram (-) 22. Which is not characteristic of Gram (=) bacteria? (a) Smooth cell wall (b) Outer membrane (c) Prominent mesosomes (d) 70-80% murien in cell wall (e) Two rings in basal body of flagellum 23. Which of the following is a gram negative bacterium? (a) Esherichia coli (b) Bascillus subtilis (c) Streptomyces coelicolor (d) Ampycolatopsis orientalis 24. Peptidoglycan is characteristic constituent of cell wall in : (a) Eudacteria & unicellular Eukaryotes (b) Archaebacteria & Eukaryotes (c) Bacteria & Cyanobacteria (d) Monera & Protista 25. Amino acid found only in bacteria & cyanobacteria is :
10 (d) Saccharomyces & Clostridum 29. Respiratory enzymes of aerobic bacteria are mainly located in : (a) Mitochondria (b) Chondrioids (c) Sphaerosomes (d) Phagosomes (e) Polysomes 30. Conversion of ammonia into nitrite & nitrate is : (a) Ammonification (b) Dentrification (c) Nitrification (d) All of these 31. Bacteria that uses chemical energy to fix CO 2 are : (a) Photoautotrophs (b) Heterotrophs (c) Chemoautotrophs (d) None of these 32. Streptococcus is used in preparation of : (a) Wine (b) Idli (c) Cheese (d) Bread 33. Bacteria connected with acetogenesis is : (a) Streptomonas (b) Clostridium (c) Bacillus (d) Citromonas 34. Azolla has symbiotic relationship with : (a) Chlorella (b) Anabaena (c) Nostoc (d) Tolypothrix 35. Which of the following is a commonest bacterial disease? (a) T.B. (b) Rabies (c) Small pox (d) Influenza 36. What is the disease tetanus also known as? (a) Gangrene (b) Shingles (c) Lockjaw (d) Whooping cough 37. Botulism is due to contamination of : (a) E. coli (b) Salmonella (c) Clostridium (d) Pseudomonas 38. Genetic recombination through transduction was first discovered in bacterium : (a) Escherichia coli (b) Salmonell typhimurium (c) Diplococcus pneumoniae (d) Agrobacterium tumefaciens 39. The common nitrogen fixer in paddy fields is : (a) Frankia (b) Oscillatoria (c) Rhizobium (d) Azospirillum 40. Nitrogen fixation by Rhizobium occurs inside : (a) Soil (b) Nodulated roots (c) Rhizosphere (d) Foliar association 41. Maximum modes of nutritiion are found in : (a) Monera (b) Protista
11 (c) Mesosomes (d) Holdfast
Downloaded from
 A.I.P.M.T. Foundation - XI Biology MCQs Time: 30 min MCQ#10 Full Marks: 40 Choose the most appropriate answer. 1. Which of the following is the asexual method of reproduction in Protozoa? 1. Isogamy 2.
A.I.P.M.T. Foundation - XI Biology MCQs Time: 30 min MCQ#10 Full Marks: 40 Choose the most appropriate answer. 1. Which of the following is the asexual method of reproduction in Protozoa? 1. Isogamy 2.
Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #8: The Radiate Animals, Phylum Cnidaria Lab Guide
 Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #8: The Radiate Animals, Phylum Cnidaria Lab Guide These animals are called radiates because all are radially (or biradially) symmetrical, a form of symmetry in which body
Zoology Name: Block: Exercise #8: The Radiate Animals, Phylum Cnidaria Lab Guide These animals are called radiates because all are radially (or biradially) symmetrical, a form of symmetry in which body
Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms
 Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms Section 1: What is an animal? Multicellular that feed on other organisms STRUCTURE- levels of organization of cells 1. Cells- basic unit of animal structure 2. Tissues- many
Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms Section 1: What is an animal? Multicellular that feed on other organisms STRUCTURE- levels of organization of cells 1. Cells- basic unit of animal structure 2. Tissues- many
Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms
 Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms Section 1: What is an animal? that feed on other organisms STRUCTURE- levels of organization of cells 1. Cells- basic unit of animal structure 2. Tissues- many cells make
Sponges, Cnidarians, and Worms Section 1: What is an animal? that feed on other organisms STRUCTURE- levels of organization of cells 1. Cells- basic unit of animal structure 2. Tissues- many cells make
Contribution of Animals. Many provide food for us and other animals. Clothing and shoes are sometimes made from animal products
 1 2 Contribution of Animals Many provide food for us and other animals Clothing and shoes are sometimes made from animal products Research shows that holding or petting a cat or dog slows the heartbeat
1 2 Contribution of Animals Many provide food for us and other animals Clothing and shoes are sometimes made from animal products Research shows that holding or petting a cat or dog slows the heartbeat
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE (NSC) GRADE 11 MID-YEAR EXAMINATION LIFE SCIENCES (NSC11-10) D DURATION: 2½ HOURS DATE: 14 JUNE 2013
 LIFHIG211 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE (NSC) GRADE 11 MID-YEAR EXAMINATION LIFE SCIENCES (NSC11-10) D10055614-5 TIME: 09H00 11H30 TOTAL: 150 MARKS DURATION: 2½ HOURS DATE: 14 JUNE 2013 This question paper
LIFHIG211 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE (NSC) GRADE 11 MID-YEAR EXAMINATION LIFE SCIENCES (NSC11-10) D10055614-5 TIME: 09H00 11H30 TOTAL: 150 MARKS DURATION: 2½ HOURS DATE: 14 JUNE 2013 This question paper
Notes - Platyhelminthes and Nematodes
 Notes - Platyhelminthes and Nematodes - These two phylum are composed of. However, the worms we are going to look at are not common. Both of these phyla are composed of unsegmented worms. That is, these
Notes - Platyhelminthes and Nematodes - These two phylum are composed of. However, the worms we are going to look at are not common. Both of these phyla are composed of unsegmented worms. That is, these
Academic Script. Symmetry. 1 st Year Undergraduate Model 1 UGC Syllabus. Animal Diversity - I. Topic No. & Title: Topic : A-3 Symmetry
 Academic Script Symmetry Course Name: Paper No. & Title: Zoology 1 st Year Undergraduate Model 1 UGC Syllabus Z 101 B Animal Diversity - I Topic No. & Title: Topic : A-3 Symmetry Academic Script: 1.Introduction
Academic Script Symmetry Course Name: Paper No. & Title: Zoology 1 st Year Undergraduate Model 1 UGC Syllabus Z 101 B Animal Diversity - I Topic No. & Title: Topic : A-3 Symmetry Academic Script: 1.Introduction
BIO3334 Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam February 24, Name: Student number:
 24 pts. 1. Briefly, using one or two sentences, describe what each of the following biological terms means. Use an example where possible. Trophosome Seminal vesicle Choanosyncytium Coeloblastula larva
24 pts. 1. Briefly, using one or two sentences, describe what each of the following biological terms means. Use an example where possible. Trophosome Seminal vesicle Choanosyncytium Coeloblastula larva
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers. EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3
 Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
1/29/2013. Viruses and Bacteria. Infectious Disease. Pathogens cause disease by: Chapters 16 and 17
 Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Viruses and Bacteria Chapters 16 and 17 Infectious Disease Caused by the invasion of a host by agents whose activities harm the host s tissues Can be transmitted to others Pathogen microorganisms that
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses
 Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Key underlined answers are the correct answers
 Key underlined answers are the correct answers 1) In the diagram above: a) fetal hemoglobin has a higher oxygen affinity than adult hemoglobin b) oxygen saturation is 0% when oxygen levels are high (above
Key underlined answers are the correct answers 1) In the diagram above: a) fetal hemoglobin has a higher oxygen affinity than adult hemoglobin b) oxygen saturation is 0% when oxygen levels are high (above
 International E Publication www.isca.me, www.isca.co.in M.Sc. (Gold Medalist), Ph.D., F.I.S.C.A., F.S.L.Sc., F.J.O.Z.S., F.B.P.S., F.Z.S.I. A. Professor Department of Zoology Govt. Post Graduate College
International E Publication www.isca.me, www.isca.co.in M.Sc. (Gold Medalist), Ph.D., F.I.S.C.A., F.S.L.Sc., F.J.O.Z.S., F.B.P.S., F.Z.S.I. A. Professor Department of Zoology Govt. Post Graduate College
NOTES KEY. Chapter 19 Bacteria (Biotic) and Viruses (Abiotic)
 NOTES KEY Chapter 19 Bacteria (Biotic) and Viruses (Abiotic) BACTERIA - PROKARYOTES Page 471 Definition: Single celled organisms that lack a nucleus, the DNA is free floating in the cytoplasm Classifying
NOTES KEY Chapter 19 Bacteria (Biotic) and Viruses (Abiotic) BACTERIA - PROKARYOTES Page 471 Definition: Single celled organisms that lack a nucleus, the DNA is free floating in the cytoplasm Classifying
Organelles Defined. Class Copy CELL STUDY NOTES Class Copy
 Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Cell Theory States: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Organelles Defined Golgi
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Asexual Reproduction
 Asexual Reproduction Only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction. The offspring is genetically identical to the parent. The offspring inherits all of its traits from one parent. Therefore, the
Asexual Reproduction Only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction. The offspring is genetically identical to the parent. The offspring inherits all of its traits from one parent. Therefore, the
Bacteria and Viruses. Chapter 20 Biology II
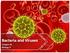 Bacteria and Viruses Chapter 20 Biology II 3 Domains of Living Organisms Section 1 - Bacteria Prokaryotes Oldest living things on Earth Date back 3.5 mya Single-celled organisms No membrane bound organelles
Bacteria and Viruses Chapter 20 Biology II 3 Domains of Living Organisms Section 1 - Bacteria Prokaryotes Oldest living things on Earth Date back 3.5 mya Single-celled organisms No membrane bound organelles
Pop Quiz 2. Give the dominant body form for each. List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Scyphozoa anthozoa
 Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Pop Quiz 2 Give the dominant body form for each Scyphozoa anthozoa List 2 causes of coral reef damage. What is the function of a colloblast? Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms - the Simplest Bilateral Animals
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
General Body Plan. Diploblastic. Tissue. Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes. epidermis gastrodermis
 General Body Plan Diploblastic Tissue epidermis gastrodermis Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes General Body Plan Dimorphism: 2 different body forms are usually present in the life cycle: oral aboral aboral
General Body Plan Diploblastic Tissue epidermis gastrodermis Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes General Body Plan Dimorphism: 2 different body forms are usually present in the life cycle: oral aboral aboral
Asexual & Sexual Reproduction
 Reproduction is the creation of a new individual or individuals from previously existing individuals. In animals, reproduction can occur in two primary ways: Asexual & Sexual Reproduction i. Asexual means
Reproduction is the creation of a new individual or individuals from previously existing individuals. In animals, reproduction can occur in two primary ways: Asexual & Sexual Reproduction i. Asexual means
Section. Clam Worm. 1. What are the two ways that starfish reproduce? a) Testes and Ovaries b) Fission and Autotomy c) Sexual and asexual
 Name Section Date Clam Worm 1. What are two examples of reproductive glands in the Clam Worm? a) Ovaries and Testes b) Ovaries and hormones c) Testes and hormones 2. Where does fertilization take place
Name Section Date Clam Worm 1. What are two examples of reproductive glands in the Clam Worm? a) Ovaries and Testes b) Ovaries and hormones c) Testes and hormones 2. Where does fertilization take place
WELCOME TO BIOLOGY 11. Mr. Gandha
 WELCOME TO BIOLOGY 11 Mr. Gandha TOPICS OF BIOLOGY 11 Chemicals of life Cells Evolution Taxonomy Microbio Plants Animals BIOLOGY THIS SEMESTER Review of Biology and Processes Adaptation and Evolution:
WELCOME TO BIOLOGY 11 Mr. Gandha TOPICS OF BIOLOGY 11 Chemicals of life Cells Evolution Taxonomy Microbio Plants Animals BIOLOGY THIS SEMESTER Review of Biology and Processes Adaptation and Evolution:
29-2 Form and Function in Invertebrates Slide 1 of 52
 29-2 Form and Function in 1 of 52 How do different invertebrate phyla carry out life functions? 2 of 52 Feeding and Digestion Feeding and Digestion The simplest animals break down food primarily through
29-2 Form and Function in 1 of 52 How do different invertebrate phyla carry out life functions? 2 of 52 Feeding and Digestion Feeding and Digestion The simplest animals break down food primarily through
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
2. Identify the 4 major trends in the evolution of animals. 3. Describe the differences between a protostome and a deuterostome.
 ANIMAL KINGDOM 1 EVOLUTIONARY TRENDS and PHYLUM PORIFERA 1. Describe the biological definition for an animal. 2. Identify the 4 major trends in the evolution of animals. 3. Describe the differences between
ANIMAL KINGDOM 1 EVOLUTIONARY TRENDS and PHYLUM PORIFERA 1. Describe the biological definition for an animal. 2. Identify the 4 major trends in the evolution of animals. 3. Describe the differences between
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
BIO3334 Invertebrate Zoology Midterm Exam February 14, Name: Student number:
 30 pts. 1) Briefly, using one or two sentences, describe what each of the following biological terms means. Use an example where possible. Colloblast cell Spirocyst Water expulsion vesicles Coeloblastula
30 pts. 1) Briefly, using one or two sentences, describe what each of the following biological terms means. Use an example where possible. Colloblast cell Spirocyst Water expulsion vesicles Coeloblastula
14. Which plant performs vegetative reproduction with the help of floral buds? (a) Agave (b) Bryophyllum (c) Ginger (d) Asparagus
 NEET Biology MCQ Chapter-1. Reproduction in Organisms 1. In which of the following mammal estrous cycle is absent: (a) cow (b) horse (c) monkey (d) rabbit 2. Identify the incorrect statement. a. In asexual
NEET Biology MCQ Chapter-1. Reproduction in Organisms 1. In which of the following mammal estrous cycle is absent: (a) cow (b) horse (c) monkey (d) rabbit 2. Identify the incorrect statement. a. In asexual
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic
 Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined the term cell (1839)Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden all living things are made
General Body Plan. Diploblastic. Tissue. Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes. epidermis gastrodermis
 General Body Plan Diploblastic Tissue epidermis gastrodermis Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes General Body Plan Dimorphism: 2 different body forms are usually present in the life cycle: oral aboral aboral
General Body Plan Diploblastic Tissue epidermis gastrodermis Radially symmetrical Cnidocytes General Body Plan Dimorphism: 2 different body forms are usually present in the life cycle: oral aboral aboral
The Immune System & Non- Infectious Disease. Ch. 18: Sections 1, 2, & 4
 The Immune System & Non- Infectious Disease Ch. 18: Sections 1, 2, & 4 What is the Immune System? The purpose of the immune system is to: keep infectious microorganisms, such as certain bacteria, viruses,
The Immune System & Non- Infectious Disease Ch. 18: Sections 1, 2, & 4 What is the Immune System? The purpose of the immune system is to: keep infectious microorganisms, such as certain bacteria, viruses,
Diversity. Echinodermata means spiny skin Echinoderms usually inhabit shallow coastal waters and ocean trenches organisms in this class include:
 Echinoderms Diversity Echinodermata means spiny skin Echinoderms usually inhabit shallow coastal waters and ocean trenches organisms in this class include: Sea stars Brittle stars Sand dollars Sea cucumbers
Echinoderms Diversity Echinodermata means spiny skin Echinoderms usually inhabit shallow coastal waters and ocean trenches organisms in this class include: Sea stars Brittle stars Sand dollars Sea cucumbers
Fig. LPS in Gram negative bacteria
 Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Chapter Guided Notes
 Chapter 34-35 Guided Notes 34.1 Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms Invertebrates w/ soft, symmetry 3 tissue layers organized into organs & systems Exhibit Planaria Freshwater -shaped anterior and a posterior
Chapter 34-35 Guided Notes 34.1 Phylum Platyhelminthes Flatworms Invertebrates w/ soft, symmetry 3 tissue layers organized into organs & systems Exhibit Planaria Freshwater -shaped anterior and a posterior
Biology. Chapter 19. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 19 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea 19.1 What Are Viruses? Viruses: noncellular infectious agents Consists of a protein coat around a core of
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 19 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea 19.1 What Are Viruses? Viruses: noncellular infectious agents Consists of a protein coat around a core of
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles
 Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
6) An animal with the cross section shown above has a: a) Gastrovascular cavity b) Pseudocoelom c) Coelom
 1) A 12 foot tall human: a) Would need a disproportionally larger and stronger skeleton than a 6 foot tall human b) Would need a disproportionally smaller and weaker skeleton than a 2 foot tall human c)
1) A 12 foot tall human: a) Would need a disproportionally larger and stronger skeleton than a 6 foot tall human b) Would need a disproportionally smaller and weaker skeleton than a 2 foot tall human c)
Platyhelminthes. Presentation by Brendan, John, and Kunio Period 6 3/12/10. Slide by Brendan
 Platyhelminthes Presentation by Brendan, John, and Kunio Period 6 3/12/10 http://www-tc.pbs.org/kcet/shapeoflife/imganim/platyhelminthes5.jpg Slide by Brendan Intro Phyla: Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) marine,
Platyhelminthes Presentation by Brendan, John, and Kunio Period 6 3/12/10 http://www-tc.pbs.org/kcet/shapeoflife/imganim/platyhelminthes5.jpg Slide by Brendan Intro Phyla: Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) marine,
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use Figure 20.1 to answer the following question. Figure 20.1 1) Which enzyme was used to produce
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Use Figure 20.1 to answer the following question. Figure 20.1 1) Which enzyme was used to produce
ILOs. 10/10/2016 Maha Fathy 2
 ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
Ch 3 Cell Structure 10/1/2008. Cells Under the Microscope. Natural laws limit cell size. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs.
 Ch 3 Cell Structure Cells Under the Microscope Electron microscopes have much higher magnifying and resolving powers than light microscopes. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs. Stolipher Cell size and shape
Ch 3 Cell Structure Cells Under the Microscope Electron microscopes have much higher magnifying and resolving powers than light microscopes. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs. Stolipher Cell size and shape
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
 Warm-up Introduction to the Animal Kingdom What characteristics are common to all animals? Eukaryotic cells NO cell wall Multicellular Cell specialization Heterotrophic Reproduction/Development Categories
Warm-up Introduction to the Animal Kingdom What characteristics are common to all animals? Eukaryotic cells NO cell wall Multicellular Cell specialization Heterotrophic Reproduction/Development Categories
Life Science Unit I. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells
 Name: ate: 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells. are much smaller. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. ell iagram. have permeable membranes.. have
Name: ate: 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells. are much smaller. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. ell iagram. have permeable membranes.. have
Bacterial Structures. Capsule or Glycocalyx TYPES OF FLAGELLA FLAGELLA. Average size: µm 2-8 µm Basic shapes:
 PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
Oceans 11 Practice Test #3 12/14/2014
 Practice test #3 1. The following is an advantage to living in a marine environment: (a) water s density is high (b) abundance of water available (c) salt content (d) all of these Name: 2. This includes
Practice test #3 1. The following is an advantage to living in a marine environment: (a) water s density is high (b) abundance of water available (c) salt content (d) all of these Name: 2. This includes
Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I
 Name: Period: Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I Assignments: Description Page(s) Due Date 1 Biology 4 th & 5 th Six Weeks MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY Feb 9 10 11 12 13 Review for Test Test - Classification
Name: Period: Biology 5-1: Animal Systems I Assignments: Description Page(s) Due Date 1 Biology 4 th & 5 th Six Weeks MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY Feb 9 10 11 12 13 Review for Test Test - Classification
Kingdom: PROTISTA PROTOZOANS 3/7/2006 1
 Kingdom: PROTISTA PROTOZOANS 3/7/2006 1 Kingdom: PROTISTA Single celled (unicellular), colonial or multicellular organisms Reproduce sexually or asexually Three major categories: Protozoans - first animals
Kingdom: PROTISTA PROTOZOANS 3/7/2006 1 Kingdom: PROTISTA Single celled (unicellular), colonial or multicellular organisms Reproduce sexually or asexually Three major categories: Protozoans - first animals
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3)
 Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Microbiology. Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism. Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi
 Microbiology Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi Microbiology: the study of organisms too small to be seen without magnification. Micro - too small to be seen
Microbiology Morphology & Ultra-Structure of Microorganism Prof. Dr. Batool Hassan Al-Ghurabi Microbiology: the study of organisms too small to be seen without magnification. Micro - too small to be seen
Overview: Life Without a Backbone. Invertebrates are animals that lack a backbone They account for 95% of known animal species
 Fig. 33-1 Overview: Life Without a Backbone Invertebrates are animals that lack a backbone They account for 95% of known animal species Fig. 33-2 Calcarea and Silicea ANCESTRAL PROTIST Cnidaria Common
Fig. 33-1 Overview: Life Without a Backbone Invertebrates are animals that lack a backbone They account for 95% of known animal species Fig. 33-2 Calcarea and Silicea ANCESTRAL PROTIST Cnidaria Common
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Position and Biological Contributions Phylum Platyhelminthes Simplest animals with primary bilateral symmetry Solid body without a coelom Organ-system
 Acoelomate Chapter 14 Bilateral Acoelomates No internal body space other than digestive tube. Spaces between organs filled with a loose connective tissue with more cells than mesoglea = parenchyma. Solid
Acoelomate Chapter 14 Bilateral Acoelomates No internal body space other than digestive tube. Spaces between organs filled with a loose connective tissue with more cells than mesoglea = parenchyma. Solid
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Overview of Cell Structures
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
Classification of Infectious Agents. Dr W. D. Colby
 Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
Classification of Infectious Agents Dr W. D. Colby Nonliving Infectious Agents PRIONS: abnormally configured self-replicating protein templates VIRUSES: nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) genes packaged in protein
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
XI CLASS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 12: MINERAL NUTRITION
 XI CLASS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 12: MINERAL NUTRITION Mineral nutrition is the study of source, mode of absorption, distribution and metabolism of various inorganic substances (minerals) by plants for their growth,
XI CLASS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 12: MINERAL NUTRITION Mineral nutrition is the study of source, mode of absorption, distribution and metabolism of various inorganic substances (minerals) by plants for their growth,
BIOL 110 Exam 1 Practice Test Solutions
 www.liontutors.com BIOL 110 Exam 1 Practice Test Solutions Problem #1: B. 1 Half Life = 30 yrs. After 90 yrs, 3 half lives must have occurred (90/30 = 3). Since you start with 80 mg, after the first half
www.liontutors.com BIOL 110 Exam 1 Practice Test Solutions Problem #1: B. 1 Half Life = 30 yrs. After 90 yrs, 3 half lives must have occurred (90/30 = 3). Since you start with 80 mg, after the first half
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s)
 Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Cell Structure Plants, Animals, Fungi and Protists have Eukaryotic Cell(s) Plant Cell Animal Cell straight edges curved edges Cell Organization cytoplasm cell membrane Eukaryotic cells have 3 major parts:
Easter School Life Sciences Grade 11. Viruses & Bacteria 29 March 2013
 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Viruses - Basic structure and general characteristics - Diseases - Medical biotechnology Bacteria - Basic structure
Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Viruses - Basic structure and general characteristics - Diseases - Medical biotechnology Bacteria - Basic structure
Flatworms. Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
Flatworms Phylum Platyhelminthes Characteristics of Flatworms Flatworms are acoelomates, which means they have no coelom. A coelom is a fluid-filled body cavity The digestive cavity is the only body cavity
KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27
 KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27 CHARACTERISTICS Eukaryotic Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Mostly unicellular ; some multicellular Asexual reproduction binary fission Sexual reproduction - conjugation Plant
KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27 CHARACTERISTICS Eukaryotic Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Mostly unicellular ; some multicellular Asexual reproduction binary fission Sexual reproduction - conjugation Plant
bacteria review 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Biology Structures in Cells. 1.3 Structures in Cells
 Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
Biology 2201 1.3 Structures in Cells Structures in Cells ALL cells start out as fully functional living things They must be able to create and maintain substances (compounds, ATP, ADP) and structures (membranes,
NUCLEOLUS CELL MEMBRANE MITOCHONDRIA CELL WALL CHLOROPLAST NUCLEAR MEMBRANE VACOULE NUCLEUS ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD ORGANELLE CARD
 CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
CELL MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CELL WALL MITOCHONDRIA NUCLEAR MEMBRANE CHLOROPLAST NUCLEUS VACOULE CENTRAL VACOULE LEUCOPLAST CHROMOPLAST LYSOSOME CYTOPLASM CYTOSKELETON CENTRIOLE RIBOSOME CHROMATIN ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 NOVEMBER 2014 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2:30
 1 GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 NOVEMBER 2014 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2:30 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Answer all questions. 2. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this
1 GRADE 11 LIFE SCIENCES PAPER 2 NOVEMBER 2014 MARKS: 150 TIME: 2:30 INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION 1. Answer all questions. 2. Number the answers correctly according to the numbering system used in this
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL
 STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL All Organisms are Made of Cells Principles of the Cell Theory Cell Diversity Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Internal Cell Structure
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
21.4 Prokaryotes Enduring, Abundant, and Diverse
 Chapter 21 21.4 Prokaryotes Enduring, Abundant, and Diverse Prokaryotes Structurally simple cells that lack a nucleus Evolved before eukaryotes Abundance and Metabolic Diversity Prokaryotes are Earth s
Chapter 21 21.4 Prokaryotes Enduring, Abundant, and Diverse Prokaryotes Structurally simple cells that lack a nucleus Evolved before eukaryotes Abundance and Metabolic Diversity Prokaryotes are Earth s
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Biology EOC Review. Saturday Session
 Biology EOC Review Saturday Session Cells DNA Ribosome Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryotic Bacteria Flagellum Cell Membrane (Plasma) Cell Wall Eukaryotic Animal Mitochondria Ribosome
Biology EOC Review Saturday Session Cells DNA Ribosome Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryotic Bacteria Flagellum Cell Membrane (Plasma) Cell Wall Eukaryotic Animal Mitochondria Ribosome
Phylum Echinodermata. by: Muhammad Arif Asadi
 Phylum Echinodermata by: Muhammad Arif Asadi Pentaradial symmetry no freshwater or terrestrial representatives Water vascular system: A complex series of fluid filled canals with numerous flexible feeding
Phylum Echinodermata by: Muhammad Arif Asadi Pentaradial symmetry no freshwater or terrestrial representatives Water vascular system: A complex series of fluid filled canals with numerous flexible feeding
Chapter 20. Table of Contents. Section 1 Viruses. Section 2 Bacteria. Viruses and Bacteria
 Viruses and Bacteria Table of Contents Section 1 Viruses Section 2 Bacteria Section 1 Viruses Objectives Describe why a virus is not considered a living organism. Describe the basic structure of a virus.
Viruses and Bacteria Table of Contents Section 1 Viruses Section 2 Bacteria Section 1 Viruses Objectives Describe why a virus is not considered a living organism. Describe the basic structure of a virus.
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Structure of Prokaryotes
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege There are many differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, all cells have four common structures: the plasma membrane, which functions as a barrier for the cell
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege There are many differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. However, all cells have four common structures: the plasma membrane, which functions as a barrier for the cell
Name Class Date. What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
Cell Structure and Function. Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells
 Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Cell Structure and Function Concept 1: Common Features of All Cells Common Features of All Cells All cells, whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, have some common features. Common Features of All
Chapter 4. Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryotic cells. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells. Comparing Prokaryotic and. Eukaryotic cells.
 Chapter 4 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No nucleus No organelles Cell walls composed of peptidoglycan Reproduce asexually via binary fission
Chapter 4 Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No nucleus No organelles Cell walls composed of peptidoglycan Reproduce asexually via binary fission
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths
 Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Lecture 4 Medical Parasitology Course (MLAB 362) Dr. Mohamed A. El-Sakhawy 1 Parasitic Helminths Eukaryotic, multicellular animals that usually have digestive, circulatory,
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Bacteria are all the organisms in the kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. Bacteria outnumber all the members of all the other kingdoms combined.
 Bacteria are all the organisms in the kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. Bacteria outnumber all the members of all the other kingdoms combined. Bacteria Facts: A bacteria cell on average is 1000x
Bacteria are all the organisms in the kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. Bacteria outnumber all the members of all the other kingdoms combined. Bacteria Facts: A bacteria cell on average is 1000x
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells eye 100 mm (10 cm) Chicken egg aid n 10 mm
 Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
