Supplementary Information
|
|
|
- Brenda Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Information Optial ontrolling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-orn dentate granule ells Yan Gu, Maithe Arruda-Carvalho 3,4, Jia Wang, Stephen Janoshka,, Sheena Josselyn 3-5, Paul Frankland 3-5,* and Shaoyu Ge,,* Department of Neuroiology and Behavior, SUNY at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, NY 794 Program in Neurosiene, SUNY at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, NY Program in Neurosienes and Mental Health, Hospital for Sik Children, 555 University Ave, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M5G X8 4 Institute of Medial Siene, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M5S A8 5 Department of Physiology, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, M5S A8 Contents: Supplementary Figures -9 Supplementary Tales
2 wpi M P D A L V wpi Injetion oordinates (in mm to Bregma) A/P M/L D/V. ± ±.6 3. wpi d d wpi e e 4 wpi d e Supplementary Figure. Retroviral infetion in the adult hippoampus. a, Shemati drawing in the upper panel shows the viral injetion sites in the dentate gyrus. The lower panel lists the injetion oordinates. A/P: anterior/posterior; M/L: medial/lateral; D/V: dorsal/ventral., Sample images showing the injetion traks at (upper) and (lower) wpi. Note that injetion traks (arrow) were hardly seen at wpi. Sale ar: µm. -e, Laeling speifiity of neworn Cs with high-titer retrovirus. Shown in the upper pannel in, d and e are sample images of neworn neurons at, and 4 wpi. Shown in the lower pannel in, d and e are enlarged view of these neworn neurons, respetively. Note that, morphologially, there are no mature C-like ells at and wpi. Sale ars: 5 µm.
3 Single episode: ursts at 5 Hz Ten 5 ms pulses at Hz TBS paradigm = 4 episodes repeated at. Hz 3 wpi 4 wpi 8 wpi V-Clamp I-Clamp d e V-Clamp I-Clamp Supplementary Figure. Response of ChIEF+ adult-orn Cs to optial TBS. a, Shemati diagram depiting theta urst stimulation (TBS). TBS is omposed of four stimulation episodes at. Hz. Eah episode is a urst of ten Hz, 5ms pulses delivered at the theta frequeny (5 Hz)., Wholeell reordings were made on ChIEF+ adult-orn Cs in aute slies. Shown is a sample image of a reorded adult-orn C filled with ioytin through the reording pipette. Sale ar: 5 µm., Optial TBS-indued urrents (upper traes) and ation potentials (lower traes) reorded from neworn neurons at 3, 4 and 8 wpi in response to optial TBS (lue ars). Sale ars: vertial 5 pa or mv; horizontal ms. In oxes are enlarged traes of one urst ( Hz, pulses). Sale ars: vertial 5 pa or mv; horizontal 5 ms. d, A representative image showing a mossy fier terminal of neworn neurons filled with ioytin through the reording pipette. Sale ar: µm. e, Optial-indued urrents (upper traes) and ation potentials (lower traes) reorded from neworn neurons at 3 wpi. Sale ars: vertial 5 pa or mv; horizontal ms. In oxes are enlarged traes of one urst. Sale ars: vertial 5 pa or mv; horizontal 5 ms.
4 Optial Stimulation Field Potential Reording 3 M P D A V L Supplementary Figure 3. Sites of stimulation and reording in the - fepsps examination in vivo. a, Shemati drawing shows the optial stimulation site in the and reording site in the. A/P: anterior/posterior; M/L: medial/lateral; D/V: dorsal/ventral., Sample DIC images showing the traks of optial stimulation site in the (left panel) and reording site in the (right panel). Sale ar: 5 µm., Two-photon images showing ChIEF-dTomato expressing adult-orn neurons in the (left panel) and (axonal terminals, right panel). Sale ar: 5 µm.
5 4 Young Old Normalized EPSCs Young Old d Potentiation 3 * Time (min) Young Old Supplementary Figure 4. Enhaned plastiity in output synapses of young adult-orn neurons using a tetani indution paradigm. a, Shemati drawing shows whole-ell reording from a pyramidal neuron while optial stimulation was delivered on ChIEF expressing adult-orn Cs. -d, Exitatory postsynapti responses were reorded from pyramidal neurons y optially stimulating young (~4 wpi) or old (~ 8 wpi) ChIEF expressing adult-orn Cs. LTP was indued y a tetani optial stimulation (5 Hz, s)., Shown are traes efore (lak traes) and after (red traes) LTP indution (lue arrow). Sale ars: vertial: pa; horizontal: 5 ms., LTP expression. d, Histogram showing the amplitudes of LTP measured etween 45 and 6 minutes. All values represent mean±sem (*: p<.5, t-test).
6 Control Miefradil Normalized fepsps n.s...5 Control Miefradil Control SNX48 Miefradil 5 d Normalized fepsps 3 Control SNX48 Miefradil Time (min) e Potentiation Supplementary Figure 5. Miefradil aolished LTP at the axon terminals of young Cs. a-, Miefradil does not alter asal MF- synapti transmission in vivo. a, Traes of fepsps efore and after miefradil appliation. Sale ar: vertial.5 mv; horizontal ms., Histogram showing normalized fepsps slopes efore and after appliation of miefradil (n=6, n.s.:p>.5, t-test). -f, Field EPSPs were reorded in in vitro y stimulating young adult-orn Cs (~4 weeks) in ontrol ACSF (n=6), or in the presene of R-type alium hannel loker SNX48 (n=6) or T-type alium hannel loker mieradil (n=5). Optial TBS were used for LTP indution., Shown are traes efore (lak traes) and after (red traes) LTP indution. Sale ars: vertial:. mv; horizontal: 5 ms. d, LTP expression in ontrol ACSF, SNX48 (5 nm) and miefradil ( µm). Gray ar indiates the applation of SNX48 or miefradil y perfusion, and lue arrow indiates the optial TBS. e, Histogram showing the amplitudes of LTP measured etween 45 and 6 minutes. LTP were aolished y miefradil ut not SNX48. f, Neither SNX48 nor Miefradil hanged synapti transmission. All values represent mean±sem (*: p<.5; n.s.: p>.5; t-test). * Control SNX48 Miefradil f Normalized fepsps..5 Control SNX48 Miefradil
7 Implantation Orange laser eam 6 Hippoampus Dorsal Arh- Orange laser eam dorsal Ventral ventral Supplementary Figure 6. Site for optrode implantation in the dorsal hippoampus. a, Sample image of a sagittal setion from mouse rain showing the loation of optrode implantation. Arrowhead: trak of optrode implantation. Sale ar: mm., A sample two-photon image showing Arh- expressing adult-orn neurons after ehavioral tests. Sale ar: µm., Shown is a gloal view of infeted neurons in the hippoampus after viral injetion. Diagrammati drawing roughly illustrates illumination area with the implanted optrode. Sale ar: mm.
8 Arh Hidden WM training 7, 4 or 8 weeks Lateny (s) 4 3 wpi Lateney (s) wpi Lateny (s) wpi Training Sessions Training Sessions Training Sessions Supplementary Figure 7. Optial silening of neworn Cs does not influene aquisition of spatial memory. a, Shemati drawing shows, 4,or 8 weeks after injetion of Arh- retrovirus. Mie were trained in the hidden platform version of the water maze. Half of the animals were trained with light on in the dentate gyrus during training ( light group), while the other half were trained with no light ( no light group)., During training, lateny to find the platform delined normally oth in the no light and light groups at (Two-way ANOVA, signifiant effet of Training session only, F5,5=.8, p<.; n=6,6), 4 (Two-way ANOVA, signifiant effet of Training session only, F5,5=44.6, p<.; n=6,6) and 8 wpi (Two-way ANOVA, signifiant effet of Training session only, F5,5=34.54, p<.; n=6,6). All values represent mean±sem (n=6 in eah group at eah time point).
9 8 a 4 Hidden 5 * * Laterny (s) 3 Visile P3 P4 Perent searh 4 3 P P Training sessions NE NW SW SE NE NW SW SE Supplementary Figure 8. illumination of -laeled neworn ells does not interfere with hippoampal memory retrieval. a-, illumination of a ohort of 4 week-old adult orn neurons laeled with showed no effet on hippoampal memory retrieval. a, During training (no light), lateny to find the platform delined normally in oth groups., During proe tests in oth ontrol ( no light ) and light onditions, the animals searhed seletively (One-way repeated measures ANOVA : F3,=8.438, p=.7; : F3,=4.83, p<.; NE>NW, SW, SE y paired t-test planned omparison in oth groups; n=8) spending more time in the target quadrant (NE) ompared to the other quadrants, displaying roust spatial memory. Visile platform tests were also performed, showing no differene of lateny in finding the platform (data not shown). All values represent mean±sem (*: p<.5).
10 9 a /Arh- Training Proe 4 weeks 9 min Fixation -fos staining and analysis DI -fos Merge DI -fos Merge fos / (%) n.s. n.s. * Arh DI DI Arh -fos Merge -fos Merge Supplementary Figure 9. -fos staining showing the involvement of neworn Cs in spatial memory retrieval during the water maze test. a, Shemati drawing: 4 weeks after Arh- or -retrovirus injetion and optrode implantation, mie were trained in the water maze. After training, half of the mie were tested with light illumination, while the other half with no light. 9 minutes after the proe tests, mie were transardially perfused with PFA and rains were fixed. -fos expression was then stained, imaged and analyzed., Shown is -fos expression in the + or Arh+ 4-week-old neworn neurons. Arrows: -fos++ or -fos+arh+ neurons. Sale ar: µm., Histogram showing ativity-indued expression of -fos in +/Arh+ neworn neurons during water maze test. Optial illumination signifiantly redued the numer of -fos+arh+ neworn neurons. All values represent mean±sem (*: p<.5 and n.s.: p>.5, t-test).
11 wpi a. Intrinsi properties of adult-orn neurons expressing or optogenes at wpi. Memrane Capaitane (pf) Memrane Resistane (MΩ) Resting Potential Threshold Peak Amplitude Halfwidth (ms) 6.3± ± ± ±. 39.4± ±7..6±.4 ChR 6.± ± ±.6-3.9±. 33.± ±3.7.9±.6 ChIEF 5.±.3 78.± ± ±3. 4.±4.4 9.±.9.3±.5 Arh 6.4± ± ± ± ±6. 76.±5.3 3.±.7. Intrinsi properties of adult-orn neurons expressing or optogenes at 3 wpi. Memrane Memrane Resting 3 wpi Capaitane Resistane Potential Threshold Peak Amplitude Halfwidth (pf) (MΩ) (ms) 3.8± ± ± ±.7 6.±4.6.7±6.6.5±. ChR 8.5±4. 98.± ± ±.4 55.±4.3.8±4.9.7±. ChIEF 35.3± ± ± ± ±6.3.9±.8.7±. Arh 6.9± ± ±.3-3.3± ± ±6.5.6±.. Intrinsi properties of adult-orn neurons expressing or optogenes at 4 wpi. Memrane Memrane Resting 4 wpi Capaitane Resistane Potential Threshold Peak Amplitude Halfwidth (pf) (MΩ) (ms) 4.4± ± ± ±.4 73.± ±5..5±. ChR 38.± ± ± ±.3 74.± ±9.9.5±. ChIEF 35.5±5.3 4.± ± ±.7 7.± ±9.8.5±. Arh 4.6± ± ± ± ±.8 39.±7.6.5±. d. Intrinsi properties of adult-orn neurons expressing or optogenes at 8 wpi. 8 wpi Memrane Capaitane (pf) Memrane Resistane (MΩ) Resting Potential Threshold Peak Amplitude Halfwidth (ms) 5.8± ± ± ±.7 74.±.4 38.±3.9.±. ChR 48.8± ± ±.9-4.8± ± ±5.3.±. ChIEF 46.3±3.5 3.± ± ±3. 7.3± ±6..±. Arh 53.5± ±4.3-8.± ± ± ±4..±. Supplementary Tale. Expression of optogenes does not hange intrinsi properties of neworn neurons along time. Mie were injeted with retrovirus expressing, Channelrhodopsin (ChR), Channelrhodopsin variant ChIEF, or Arheorhodopsin (Arh), and aute rain slies were ut at, 3, 4 and 8 week post viral injetion (wpi). Fluoresent adult-orn neurons were whole-ell pathed and intrinsi properties were reorded. Shown are the Memrane Capaitane, Memrane Resistane, Resting Memrane Potential, Ation Potential () Threshold, Peak, Amplitude and Halfwidth of adult orn ells at wpi (a), 3 wpi (), 4 wpi () and 8 wpi (d). All values represent mean±sem, and there is no statistial differene etween groups at eah time stage (n=-5, p>.5 y t-test).
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Learned spatiotemporal sequence recognition and prediction in primary visual cortex
 Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustrating major conclusions of this study.
 ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
100 μm. Axon growth cones. Tubulin (red) + scr (green)
 Supplementary Figures mirorna-9 regulates axon extension an ranhing y targeting Map1 in mouse ortial neurons Dajas-Bailaor, F., Bonev, B., Garez, P., Stanley, P., Guillemot, F., Papalopulu, N. a 2 μm 1
Supplementary Figures mirorna-9 regulates axon extension an ranhing y targeting Map1 in mouse ortial neurons Dajas-Bailaor, F., Bonev, B., Garez, P., Stanley, P., Guillemot, F., Papalopulu, N. a 2 μm 1
Spontaneous persistent ac.vity in entorhinal cortex modulates cor.co- hippocampal
 Spontaneous persistent a.vity in entorhinal ortex moulates or.o- hippoampal intera.ons in vivo Thomas T. G. Hahn, James M. MFarlan, Sven Bererih, Bert Sakmann, Mayank R. Mehta Neoortial persistent Up states
Spontaneous persistent a.vity in entorhinal ortex moulates or.o- hippoampal intera.ons in vivo Thomas T. G. Hahn, James M. MFarlan, Sven Bererih, Bert Sakmann, Mayank R. Mehta Neoortial persistent Up states
Amplitude and time course of evoked and spontaneous synaptic currents in rat submandibular ganglion cells
 4372 Journal of Physiology (1996), 49.1, pp. 149-157 Amplitude and time ourse of evoked and spontaneous synapti urrents in rat submandibular ganglion ells Robert J. allister and Brue Walmsley * The Neurosiene
4372 Journal of Physiology (1996), 49.1, pp. 149-157 Amplitude and time ourse of evoked and spontaneous synapti urrents in rat submandibular ganglion ells Robert J. allister and Brue Walmsley * The Neurosiene
A toolbox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing
 A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
A toolox of Cre-dependent optogenetic transgenic mice for light-induced activation and silencing Linda Madisen 1, Tianyi Mao 2,7, Henner Koch 3, Jia-min Zhuo, Antal Berenyi 5, Shigeyoshi Fujisawa 5, Yun-Wei
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillance by human γδ T cell receptor binding to Endothelial Protein C Receptor
 Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
Cytomegalovirus and tumor stress-surveillane y human γδ T ell reeptor inding to Endothelial Protein C Reeptor Carrie R. Willox, Vinent Pitard, Sonia Netzer, Lionel Couzi, Mahoo Salim, Toias Silerzahn,
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment
 Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Rapid, experience-dependent expression of synaptic NMDA receptors in visual cortex in vivo
 artiles Rapid, experiene-dependent expression of synapti NMDA reeptors in visual ortex in vivo Elizaeth M. Quinlan 1, enjamin D. Philpot 1, Rihard L. Huganir 2 and Mark F. ear 1 1 Howard Hughes Medial
artiles Rapid, experiene-dependent expression of synapti NMDA reeptors in visual ortex in vivo Elizaeth M. Quinlan 1, enjamin D. Philpot 1, Rihard L. Huganir 2 and Mark F. ear 1 1 Howard Hughes Medial
Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus
 Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus Authors: Jeffrey Lopez-Rojas a1, Martin Heine b1 and Michael R. Kreutz ac1 a Research Group Neuroplasticity, b Research
Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus Authors: Jeffrey Lopez-Rojas a1, Martin Heine b1 and Michael R. Kreutz ac1 a Research Group Neuroplasticity, b Research
Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human embryoid body preparations contain non-cardiac structures. In early studies, infarcted hearts
 a Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human emryoid ody preparations ontain non-ardia strutures. In early studies, infarted hearts reeived ell preparations of low ardia purity (
a Supplementary Figure 1. Implants derived from human emryoid ody preparations ontain non-ardia strutures. In early studies, infarted hearts reeived ell preparations of low ardia purity (
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Closed-loop optogenetic control of thalamus as a new tool to interrupt seizures after cortical injury Jeanne T. Paz, Thomas J. Davidson, Eric S. Frechette, Bruno Delord, Isael Parada,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Closed-loop optogenetic control of thalamus as a new tool to interrupt seizures after cortical injury Jeanne T. Paz, Thomas J. Davidson, Eric S. Frechette, Bruno Delord, Isael Parada,
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT. Keywords: Medical, Optimization, Modelling, Oscillation, Noise characteristics.
 PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Neuroscience 201A (2016) - Problems in Synaptic Physiology
 Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
Question 1: The record below in A shows an EPSC recorded from a cerebellar granule cell following stimulation (at the gap in the record) of a mossy fiber input. These responses are, then, evoked by stimulation.
% of Nestin-EGFP (+) cells
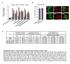 8 7 6 3 Nestin CD % of Nestin-EGFP (+) ells 8 6 Nestin-EGFP Marge Nestin-EGFP Marge Expression levels of Expression levels of Tumorigeniity y stemness markers ifferentiation markers limiting ilution assay
8 7 6 3 Nestin CD % of Nestin-EGFP (+) ells 8 6 Nestin-EGFP Marge Nestin-EGFP Marge Expression levels of Expression levels of Tumorigeniity y stemness markers ifferentiation markers limiting ilution assay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
1.0. FSL NMDAR-fEPSP 0.8. amplitude (mv) Intensity (µa) 2.0 SD FSL Time (ms)
 a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Regulation of spike timing in visual cortical circuits
 Regulation of spike timing in visual ortial iruits Paul Tiesinga*, Jean-Mar Fellous and Terrene J. Sejnowski Abstrat A train of ation potentials (a spike train) an arry information in both the average
Regulation of spike timing in visual ortial iruits Paul Tiesinga*, Jean-Mar Fellous and Terrene J. Sejnowski Abstrat A train of ation potentials (a spike train) an arry information in both the average
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
LETTER. Synaptic potentiation onto habenula neurons in the learned helplessness model of depression
 doi:.38/nature974 Synapti potentiation onto habenula neurons in the learned helplessness model of depression Bo Li,, Joaquin Piriz, Martine Mirrione,3, ChiHye Chung, Christophe D. Proulx, Daniela Shulz
doi:.38/nature974 Synapti potentiation onto habenula neurons in the learned helplessness model of depression Bo Li,, Joaquin Piriz, Martine Mirrione,3, ChiHye Chung, Christophe D. Proulx, Daniela Shulz
Mineral Oil Application Experiments: Reducing Current Season PVY
 Mineral Oil Appliation Experiments: Reduing Current Season PVY Prinipal Investigator(s). Russell L. Groves, Assistant Professor and Entomology Extension Speialist, Department of Entomology, 537 Russell
Mineral Oil Appliation Experiments: Reduing Current Season PVY Prinipal Investigator(s). Russell L. Groves, Assistant Professor and Entomology Extension Speialist, Department of Entomology, 537 Russell
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
Rho-kinase Regulates Energy Balance by Targeting Hypothalamic Leptin Receptor Signaling
 Rho-kinase Regulates Energy Balane y Targeting Hypothalami Leptin Reeptor Signaling Hu Huang 1, Dong Kong 1, Kyung Hee Byun 2, Chianping Ye 1, Shuihi Koda 1, Dae Ho Lee 1, Byung-Chul Oh 2, Sam W Lee 3,
Rho-kinase Regulates Energy Balane y Targeting Hypothalami Leptin Reeptor Signaling Hu Huang 1, Dong Kong 1, Kyung Hee Byun 2, Chianping Ye 1, Shuihi Koda 1, Dae Ho Lee 1, Byung-Chul Oh 2, Sam W Lee 3,
by corticosteroid receptor activation
 Psyhobiology 1994, 22 (2), 123-133 Modulation of hippoampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression by ortiosteroid reeptor ativation D. STEVEN KERR, ANN M. HUGGETT, and WICKLIFFE C. ABRAHAM University
Psyhobiology 1994, 22 (2), 123-133 Modulation of hippoampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression by ortiosteroid reeptor ativation D. STEVEN KERR, ANN M. HUGGETT, and WICKLIFFE C. ABRAHAM University
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information. Cofilin Regulates Nuclear Architecture through a Myosin-II Dependent Mechanotransduction Module
 Supplementary Information Cofilin Regulates Nuclear Architecture through a Myosin-II Dependent Mechanotransduction Module O Neil Wiggan, Bryce Schroder, Diego Krapf, James R. Bamurg and Jennifer G. DeLuca
Supplementary Information Cofilin Regulates Nuclear Architecture through a Myosin-II Dependent Mechanotransduction Module O Neil Wiggan, Bryce Schroder, Diego Krapf, James R. Bamurg and Jennifer G. DeLuca
Systematic Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Mercury Concentrations
 Systemati Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Merury Conentrations Tom Grieb 1, Roxanne Karimi 2, Niholas Fisher 2, Leonard Levin 3 (1) Tetra Teh, In., Lafayette, CA, USA; (2) State University of New York,
Systemati Review of Trends in Fish Tissue Merury Conentrations Tom Grieb 1, Roxanne Karimi 2, Niholas Fisher 2, Leonard Levin 3 (1) Tetra Teh, In., Lafayette, CA, USA; (2) State University of New York,
Funding: MPIC/Agrochemical Industry USDA/ARS
 Evaluation and omparison of iofungiides and fungiides for the ontrol of post harvest potato tuer diseases. E. Gahango, W. W. Kirk, P. S. Wharton, R. Shafer and P. Tumalam. Department of Plant Pathology,
Evaluation and omparison of iofungiides and fungiides for the ontrol of post harvest potato tuer diseases. E. Gahango, W. W. Kirk, P. S. Wharton, R. Shafer and P. Tumalam. Department of Plant Pathology,
Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson
 Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson Supplementary Tale 1: Genotypes The genotypes used y figure are as follows: Figure 1a Figure
Stereotyped connectivity and computations in higher order olfactory neurons Mehmet Fisek and Rachel I. Wilson Supplementary Tale 1: Genotypes The genotypes used y figure are as follows: Figure 1a Figure
Closed-loop optogenetic control of thalamus as a tool for interrupting seizures after cortical injury
 a r t i l e s Closed-loop optogeneti ontrol of thalamus as a tool for interrupting seizures after ortial injury Jeanne T Paz 1, Thomas J Davidson 2, Eri S Frehette 1, Bruno Delord 3, Isael Parada 1, Kathy
a r t i l e s Closed-loop optogeneti ontrol of thalamus as a tool for interrupting seizures after ortial injury Jeanne T Paz 1, Thomas J Davidson 2, Eri S Frehette 1, Bruno Delord 3, Isael Parada 1, Kathy
Acute transcriptional up-regulation specific to osteoblasts/osteoclasts in medaka fish
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Aute transriptional up-regulation speifi to osteoblasts/osteolasts in medaka fish immediately after exposure to mirogravity Masahiro Chatani, 1, Hiroya Morimoto,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Aute transriptional up-regulation speifi to osteoblasts/osteolasts in medaka fish immediately after exposure to mirogravity Masahiro Chatani, 1, Hiroya Morimoto,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
Supplemental Information. Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons. Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses
 Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
WT;ATTAC-5 ** ** SkM
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.3/nature a WT;ATTAC- H/H;ATTAC- WT;ATTAC- H/H;ATTAC- 3 weeks months GFP p Inka relative expression 3 SkM Skel. Mus. FKBP- relative expression SkM Skel. Mus. relative expression
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.3/nature a WT;ATTAC- H/H;ATTAC- WT;ATTAC- H/H;ATTAC- 3 weeks months GFP p Inka relative expression 3 SkM Skel. Mus. FKBP- relative expression SkM Skel. Mus. relative expression
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
doi: 10.1038/nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to
Presenilins regulate synaptic plasticity and mitochondrial calcium homeostasis in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway
 Presenilins regulate synaptic plasticity and mitochondrial calcium homeostasis in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
Presenilins regulate synaptic plasticity and mitochondrial calcium homeostasis in the hippocampal mossy fiber pathway The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BK channels affect glucose homeostasis and cell viability of murine pancreatic beta cells
 Diabetologia (211) 54:423 432 DOI 1.17/s125-1-1936- ARTICLE BK hannels affet gluose homeostasis and ell viability of murine panreati beta ells M. Düfer & Y. Neye & K. Hörth & P. Krippeit-Drews & A. Hennige
Diabetologia (211) 54:423 432 DOI 1.17/s125-1-1936- ARTICLE BK hannels affet gluose homeostasis and ell viability of murine panreati beta ells M. Düfer & Y. Neye & K. Hörth & P. Krippeit-Drews & A. Hennige
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam Ready for Pickup By the elevator on the 3 rd Floor of Pacific Hall (waiver) Exam Depot Window at the north entrance to Pacific Hall (no waiver) Mon-Fri, 10:00
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam Ready for Pickup By the elevator on the 3 rd Floor of Pacific Hall (waiver) Exam Depot Window at the north entrance to Pacific Hall (no waiver) Mon-Fri, 10:00
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Synaptic plasticity. Activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength. Changes in innervation patterns. New synapses or deterioration of synapses.
 Synaptic plasticity Activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength. Changes in innervation patterns. New synapses or deterioration of synapses. Repair/changes in the nervous system after damage. MRC Centre
Synaptic plasticity Activity-dependent changes in synaptic strength. Changes in innervation patterns. New synapses or deterioration of synapses. Repair/changes in the nervous system after damage. MRC Centre
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Coupled feedback loops maintain synaptic long-term. potentiation: A computational model of PKMzeta
 1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
100 osimertinib. concentration of drugs (nm) Ba/F3 C797S/del19. concentration of drugs (nm) Ba/F3 C797S/T790M/L858R. relative cell vaibility (% of
 Ba/F3 del19 Ba/F3 L858R a afatini afatini EGF-816 EGF-816 ty (% of ontrol) relative ell vaiilit elative ell vaiility (% of ontrol) 5 1 1 5 ty (% of ontrol) relative ell vaiilit 5 1 1 Ba/F3 T79M/L858R Ba/F3
Ba/F3 del19 Ba/F3 L858R a afatini afatini EGF-816 EGF-816 ty (% of ontrol) relative ell vaiilit elative ell vaiility (% of ontrol) 5 1 1 5 ty (% of ontrol) relative ell vaiilit 5 1 1 Ba/F3 T79M/L858R Ba/F3
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development
 Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Disrupting GluA2-GAPDH Interaction Affects Axon and Dendrite Development 1 Frankie Hang Fung Lee, 1 Ping Su, 1 Yu Feng Xie, 1 Kyle Ethan Wang, 2 Qi Wan and 1,3 Fang Liu 1 Campbell Research Institute, Centre
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA3 output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity
 Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity David L. Hunt, Nagore Puente, Pedro Grandes, Pablo E. Castillo a NMDAR EPSC (pa) - - -8-6 -4 - st 5 nd 5 b NMDAR
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals
 Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of. parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala
 Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
Increased serotonin transporter expression reduces fear and recruitment of parvalbumin interneurons of the amygdala Marco Bocchio, Giulia Fucsina, Lydia Oikonomidis, Stephen B McHugh, David M Bannerman,
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
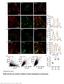 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
affecting conductance
 Pro. Nati. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 81, pp. 2929-2933, May 1984 Neurobiology Halothane shortens aetylholine reeptor hannel kinetis without affeting ondutane (general anesthetis/path lamp/myoytes/ell ulture) JAMES
Pro. Nati. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 81, pp. 2929-2933, May 1984 Neurobiology Halothane shortens aetylholine reeptor hannel kinetis without affeting ondutane (general anesthetis/path lamp/myoytes/ell ulture) JAMES
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/317/5841/183/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Astrocytes Potentiate Transmitter Release at Single Hippocampal Synapses Gertrudis Perea and Alfonso Araque* *To whom
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II)
 BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II) 1. Early v.s. Late LTP 2. Long-Term Depression 3. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression: NMDA-R dependent 4. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression:
BIPN140 Lecture 12: Synaptic Plasticity (II) 1. Early v.s. Late LTP 2. Long-Term Depression 3. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression: NMDA-R dependent 4. Molecular Mechanisms of Long-Term Depression:
b PolyA RNA-seq c RNA-seq read distribution FPKM
 a Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly+ RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.998 1-4 -4-2 1 1 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.996 1-4 1-4 1-2 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) RN-seq rea istriution Intron 12% 14% Intergeni
a Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly+ RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.998 1-4 -4-2 1 1 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) Repliate 2 (FPKM) Poly RN-seq 14 1-2 R2 =.996 1-4 1-4 1-2 14 Repliate 1 (FPKM) RN-seq rea istriution Intron 12% 14% Intergeni
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus. Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity. Outline. Synaptic plasticity hypothesis
 Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Synaptic plasticityhippocampus Neur 8790 Topics in Neuroscience: Neuroplasticity Outline Synaptic plasticity hypothesis Long term potentiation in the hippocampus How it s measured What it looks like Mechanisms
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche
 Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
Ivy/Neurogliaform Interneurons Coordinate Activity in the Neurogenic Niche Sean J. Markwardt, Cristina V. Dieni, Jacques I. Wadiche & Linda Overstreet-Wadiche Supplementary Methods. Animals We used hemizygous
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay. Nucleotide sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay Name FoxO1 forward FoxO1 reverse GK forward GK reverse INS-1 forward INS-1 reverse INS-2 forward INS-2 reverse Glut2 forward Glut2
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Anatomy of the Hippocampus
 Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
clinical conditions using a tape recorder system
 Thorax (1964), 19, 125 Objetive assessment of ough suppressants under linial onditions using a tape reorder system C. R. WOOLF AND A. ROSENBERG From the Respiratory Unit, Sunnybrook Hospital (Department
Thorax (1964), 19, 125 Objetive assessment of ough suppressants under linial onditions using a tape reorder system C. R. WOOLF AND A. ROSENBERG From the Respiratory Unit, Sunnybrook Hospital (Department
Differential modulation of Ca v 2.1 channels by calmodulin and Ca 2+ -binding protein Nature Publishing Group
 Differential modulation of Ca v 2.1 hannels y almodulin and Ca 2+ -inding protein 1 Amy Lee 1, Ruth E. Westenroek 1, Françoise Haeseleer 2, Krzysztof Palzewski 1 3, Todd Sheuer 1 and William A. Catterall
Differential modulation of Ca v 2.1 hannels y almodulin and Ca 2+ -inding protein 1 Amy Lee 1, Ruth E. Westenroek 1, Françoise Haeseleer 2, Krzysztof Palzewski 1 3, Todd Sheuer 1 and William A. Catterall
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
More dendritic spines, changes in shapes of dendritic spines More NT released by presynaptic membrane
 LEARNING AND MEMORY (p.1) You are your learning and memory! (see movie Total Recall) L&M, two sides of the same coin learning refers more to the acquisition of new information & brain circuits (storage)
LEARNING AND MEMORY (p.1) You are your learning and memory! (see movie Total Recall) L&M, two sides of the same coin learning refers more to the acquisition of new information & brain circuits (storage)
Markscheme May 2016 Biology Higher level Paper 3
 M16/4/BIOLO/HP3/ENG/TZ0/XX/M Marksheme May 2016 Biology Higher level Paper 3 23 pages 2 M16/4/BIOLO/HP3/ENG/TZ0/XX/M Setion A 1. a a. negative orrelation/inverse relationship Do not aept negative alone..
M16/4/BIOLO/HP3/ENG/TZ0/XX/M Marksheme May 2016 Biology Higher level Paper 3 23 pages 2 M16/4/BIOLO/HP3/ENG/TZ0/XX/M Setion A 1. a a. negative orrelation/inverse relationship Do not aept negative alone..
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Data Retrieval Methods by Using Data Discovery and Query Builder and Life Sciences System
 Appendix E1 Data Retrieval Methods by Using Data Disovery and Query Builder and Life Sienes System All demographi and linial data were retrieved from our institutional eletroni medial reord databases by
Appendix E1 Data Retrieval Methods by Using Data Disovery and Query Builder and Life Sienes System All demographi and linial data were retrieved from our institutional eletroni medial reord databases by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
doi:1.138/nature9553 Supplementary Table 1. Overlap of neuronal marker and PKC- expression in CEl. Marker/PKC- PKC- Marker Gad65 87.4±4.7 5.3±12.6 CRH 1.2±1. 16.9±15.2 Dyn 1.9±1.2 4.5±2.9 Enk 42.8±7.4
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development
 Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Lecture: Introduction to nervous system development Prof. Ilan Davis, Department of Biochemistry. Wellcome Senior Research Fellow Senior Research Fellow, Jesus College ilan.davis@bioch.ox.ac.uk http://www.ilandavis.com
Lisa M. Giocomo & Michael E. Hasselmo
 Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependence of Radiation Induced Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1
 Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Figure 1 - Weiner
 Supplementary Figure - Weiner Figure : Bioinformatis pipeline. Sequening of samples was performed on oth the Rohe 454 GS FLX+ instrument and the Illumina MiSeq instrument. Raw reads from 454 sequening
Supplementary Figure - Weiner Figure : Bioinformatis pipeline. Sequening of samples was performed on oth the Rohe 454 GS FLX+ instrument and the Illumina MiSeq instrument. Raw reads from 454 sequening
